Application of Organic Acid Salts as Feed Additives in Some Aquatic Organisms: Potassium Diformate
Abstract
1. Introduction
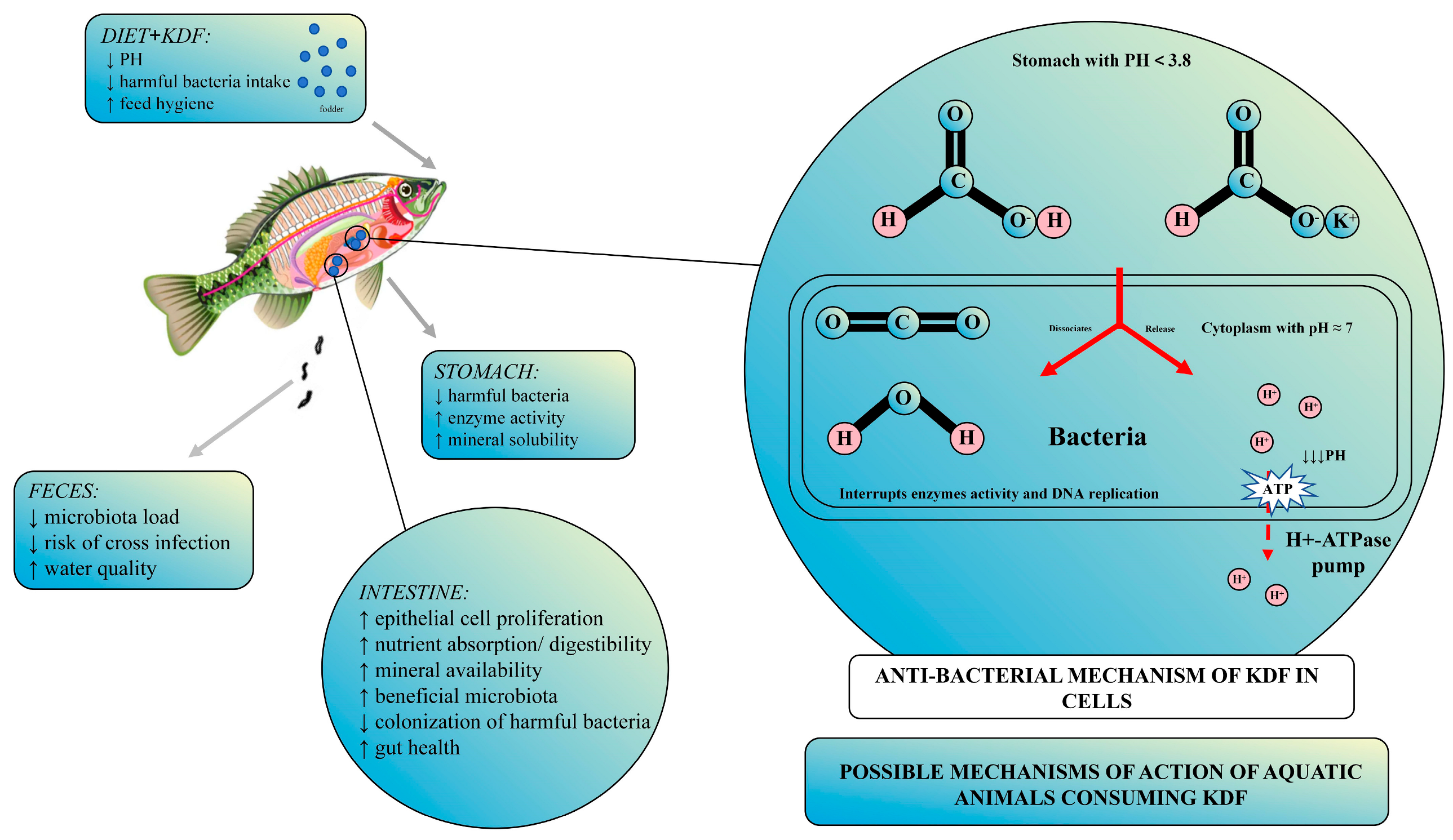
2. Chemical Properties and Mechanisms of Action
3. Production and Market Conditions
4. The Application of KDF in Aquaculture
4.1. Enhancing Growth Performance and Feed Efficiency
4.2. Improving Disease Resistance
4.3. Modulation of the Gut Microbiota
4.4. Reducing Intestinal pH Levels
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Metian, M. Fish matters: Importance of aquatic foods in human nutrition and global food supply. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2013, 21, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, S.P.; Dumas, A. Nutritional requirements of cultured fish: Formulating nutritionally adequate feeds. In Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 65–132. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zou, L. Review on global fisheries. In Brief Introduction to Fisheries; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 19–96. [Google Scholar]
- Yasin, I.S.M.; Mohamad, A.; Azzam-Sayuti, M. Control of fish diseases using antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents. In Recent Advances in Aquaculture Microbial Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 127–152. [Google Scholar]
- Sanches-Fernandes, G.M.M.; Sá-Correia, I.; Costa, R. Vibriosis outbreaks in aquaculture: Addressing environmental and public health concerns and preventive therapies using gilthead seabream farming as a model system. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 904815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; MacKinnon, B.; Karunasagar, I.; Fridman, S.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Brun, E.; Le Groumellec, M.; Li, A.; Surachetpong, W.; Karunasagar, I.; et al. Review of alternatives to antibiotic use in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1421–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanon, J.I.R. History of the use of antibiotic as growth promoters in european poultry feeds. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 2466–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaram, S.; Sun, Y.-Z.; Zuorro, A.; Ghafarifarsani, H.; Van Doan, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H. Bioactive immunostimulants as health-promoting feed additives in aquaculture: A review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 130, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlin, B.V.; Muthuvel, S.; Govidasamy, P.; Villavan, M.; Alagawany, M.; Farag, M.R.; Dhama, K.; Gopi, M. Role of acidifiers in livestock nutrition and health: A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajati, H. Application of organic acids in poultry nutrition. Int. Int. J. Avian Wildl. Biol. 2018, 3, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindl, U.; Paik, I. Enzymes and Potassium diformate in animal nutrition. Proc. Korea Feed Ingred. Assoc. Conf. 2004, 5, 99–161. [Google Scholar]
- Ricke, S.C.; Dittoe, D.K.; Richardson, K.E. Formic acid as an antimicrobial for poultry production: A review. Front. Veter. Sci. 2020, 7, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mroz, Z.; Reese, D.E.; Øverland, M.; van Diepen, J.T.M.; Kogut, J. The effects of potassium diformate and its molecular constituents on the apparent ileal and fecal digestibility and retention of nutrients in growing-finishing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Wen, A.; Dong, Z.; Desta, S.T.; Shao, T. Effects of formic acid and potassium diformate on the fermentation quality, chemical composition and aerobic stability of alfalfa silage. Grass Forage Sci. 2017, 72, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, J.; Sun, D.; He, N.; Wang, Y. Optimization of green synthesis of potassium diformate and its potential as a mold inhibitor for animal feed. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 5981–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W.; Bossier, P. Short-chain fatty acids and poly-β-hydroxyalkanoates: (New) Biocontrol agents for a sustainable animal production. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yustiati, A.; Aminah, S.; Lili, W.; Andriani, Y.; Bioshina, I.B. Effect of using potassium diformate as a feed additive to growth rate and feed efficiency of Nirwana tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. GSD 2019, 7, 738–750. [Google Scholar]
- Maroccolo, S. Inclusion of a Species-Specific Probiotic or Calcium Diformate in Young Calves Diets: Effects on Gut Microbial Balance, Health Status and Growth Performance. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Milan, Milano, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Siqwepu, O.; Salie, K.; Goosen, N. Evaluation of potassium diformate and potassium chloride in the diet of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus in a recirculating aquaculture system. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lückstädt, C.; Mellor, S. The use of organic acids in animal nutrition, with special focus on dietary potassium diformate under European and Austral-Asian conditions. Recent Adv. Anim. Nutr. Aust. 2011, 18, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gatlin, D.M., III; Yamamoto, F.Y. Nutritional supplements and fish health. In Fish Nutrition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 745–773. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.; Zhou, X.-Q.; Wu, P.; Jiang, W.-D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.-N.; Feng, L. New perspective into possible mechanism in growth promotion of potassium diformate (KDF) on the juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquaculture 2023, 576, 739850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elala, N.M.A.; Ragaa, N.M. Eubiotic effect of a dietary acidifier (potassium diformate) on the health status of cultured Oreochromis niloticus. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, P.; Zhou, C.; Huang, X.; Huang, Z.; Yu, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, T.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Lin, H. Effects of dietary potassium diformate on growth performance, fillet quality, plasma indices, intestinal morphology and liver health of juvenile golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi Farsani, M.; Bahrami Gorji, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Rashidian, G.; Van Doan, H. Combined and singular effects of dietary PrimaLac® and potassium diformate (KDF) on growth performance and some physiological parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakavand, M.; Hosseini Shekarabi, S.P.; Shamsaie Mehrgan, M.; Islami, H.R. Potassium diformate in the diet of sterlet sturgeon (Acipenser ruthenus): Zootechnical performance, humoral and skin mucosal immune responses, growth-related gene expression and intestine morphology. Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 2392–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, S.; Shi, P.; Gao, X.; Yao, B.; Ringø, E. Effects of dietary potassium diformate (KDF) on growth performance, feed conversion and intestinal bacterial community of hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus♀× O. aureus♂). Aquaculture 2009, 291, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lückstädt, C. Effect of dietary potassium diformate on the growth and digestibility of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar. In Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Fish Nutrition & Feeding, Florianopolis, Brazil, 1–5 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yustiati, A.; Nadiyah, N.A.; Suryadi, I.B.B.; Rosidah, R. Immune performances of sangkuriang catfish (Clarias gariepinus) with addition of potassium diformate on feed. World News Nat. Sci. 2019, 25, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Yustiati, A.; Kundari, D.F.; Suryana, A.H.; Suryadi, I.B.B. Effectiveness of potassium diformate addition to feed to improve immune system of Pangasius (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) that challenged by Aeromonas hydrophila. World Sci. News 2019, 134, 86–100. [Google Scholar]
- Nugraha, A.A.; Yustiati, A.; Bangkit, I.; Andriani, Y. Growth performance and survival rate of giant gourami fingerlings (Osphronemus goramy Lacepede, 1801) with potassium diformate addition. World Sci. News 2020, 143, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sayah, A.B.; Mohammadian, T.; Mesbah, M.; Jalali, S.M.; Tabandeh, M.R. The effects of different levels of potassium diformate and calcium diformate on growth, digestion, antioxidant capacity, intestinal flora, stress markers, and some serum biochemical analytes in juvenile Bluga Huso huso. Res. Sq. 2023. preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, E.E.; Ashry, A.M.; Habiba, M.M. Effects of dietary potassium diformate (KDF) on growth performance and immunity of the sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax, reared in hapas. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantu, S. Osmoregulasi pada hewan akuatik. J. Perikan. Dan Kelaut. Trop. 2010, 6, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sivakumar, M.; Amirtharaj, K.V.; Chrisolite, B.; Sivasankar, P.; Subash, P. Dietary organic acids on growth, immune response, hepatopancreatic histopathology and disease resistance in Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei against Vibrio harveyi. Res. Sq. 2022. preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.Z.H.; Afzal, M.; Khan, S.Y.; Hussain, S.M.; Habib, R.Z. Prospects of using citric acid as fish feed supplement. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2015, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Safari, O.; Sarkheil, M.; Shahsavani, D.; Paolucci, M. Effects of single or combined administration of dietary synbiotic and sodium propionate on humoral immunity and oxidative defense, digestive enzymes and growth performances of African cichlid (Labidochromis lividus) challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila. Fishes 2021, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.; Rosales, M.; Pohlenz, C.; Gatlin, D.M. Effects of organic acids on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities of juvenile red drum Sciaenops ocellatus. Aquaculture 2014, 433, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demas, G.E.; Zysling, D.A.; Beechler, B.R.; Muehlenbein, M.P.; French, S.S. Beyond phytohaemagglutinin: Assessing vertebrate immune function across ecological contexts. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 710–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monalisa, S.S.; Rozik, M.; Pratasik, S.B. Effectivity of Arcangelisia flava as immunostimulant to prevent streptococcosis on Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2018, 11, 1834–1843. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, N.F.; Stafford, J.L.; Barreda, D.; Ainsworth, A.; Belosevic, M. Antimicrobial mechanisms of fish phagocytes and their role in host defense. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadstein, O. The use of immunostimulation in marine larviculture: Possibilities and challenges. Aquaculture 1997, 155, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryadi, I.B.B.; Ulfa, D.N.; Yustiati, A.; Rosidah, R. The Effect of Potassium Diformate as Feed Additive on Immune Performances of Nilem (Osteochilus hasselti Valenciennes, 1842) Under Infection of Aeromonas hydrophila. Omni-Akuatika 2020, 16, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassef, E.A.; Saleh, N.E.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. Beneficial effects of some selected feed additives for European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.): A review. Int. Aquat. Res. 2023, 15, 271–288. [Google Scholar]
- Awan, F.; Dong, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, J.; Ma, K.; Liu, Y. The fight for invincibility: Environmental stress response mechanisms and Aeromonas hydrophila. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 116, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, M.K.; Easa, M.E.S.; Faisal, M.; Abou-Elazm, I.M.; Hetrick, F.M. Motile aeromonas infection of striped (grey) mullet Mugil cephalus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1989, 56, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamphues, J.; Visscher, C.; Mößeler, A.; Häbich, A.; Wolf, P. 16.1 EFFORTS TO REDUCE THE AMOUNTS OF ANTIBIOTICS USED IN LIVESTOCK, FOCUSED ON YOUNG FOOD PRODUCING ANIMALS (PIGS/POULTRY). In Production Diseases in Farm Animals; Zentrum GmbH: Leipzig, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, J.R.; Friendship, R.M. Digestive system. In Diseases of Swine; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 234–263. [Google Scholar]
- Mangunwardoyo, W.; Ratih, I.; Etty, R. Pathogenicity and virulency of Aeromonas hydrophila stainer on nila fish (Oreochromis niloticus Lin.) using koch postulate. J. Ris. Akuakultur 2010, 5, 245–255. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A. Screening, Detection and Characterization of Bacterial Fish Pathogens in Coastal Region of Goa. Doctoral Dissertation, Goa University, Panaji, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Pande, V.; Singh, L.; Sharma, L.; Saxena, N.; Thakuria, D.; Singh, A.K.; Sahoo, P.K. Pathological findings of experimental Aeromonas hydrophila infection in golden mahseer (Tor putitora). Fish. Aquac. J. 2016, 7, 2150–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Deen, A.N.; Dorgham-Sohad, M.; Hassan-Azza, H.M.; Hakim, A.S. Studies on Aeromonas hydrophila in cultured Oreochromis niloticus at Kafr El Sheikh Governorate, Egypt with reference to histopathological alterations in some vital organs. World J. Fish Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, B.C.; do Nascimento Vieira, F.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Ferreira, G.S.; Seiffert, W.Q. Salts of organic acids selection by multiple characteristics for marine shrimp nutrition. Aquaculture 2013, 384, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajingi, Y.S.; Ruengvisesh, S.; Khunrae, P.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Jongruja, N. The combined effect of formic acid and Nisin on potato spoilage. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 24, 101523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariño, J.; Ramos, J.; Sychrova, H. Monovalent cation transporters at the plasma membrane in yeasts. Yeast 2018, 36, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, M.F. Serum protein changes associated with ulcerative dermal necrosis (UDN) in the trout Salmo trutta L. J. Fish Biol. 1971, 3, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, S.A.; Altalbawy, F.M.; Alameri, A.A.; Ramírez-Coronel, A.A.; Obaid, R.F.; Al-Hamdani, M.M.; Kadhim, A.J.; Zabibah, R.S.; Alzahrani, H.A.; Farsani, S.G.; et al. Effects of dietary Lactobacillus helveticus ATC 15009 on growth performance, hematology parameters, innate immune responses, and the antioxidant status of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under high rearing density. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2023, 23, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.C.; Vieira, F.D.N.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Bolivar, N.; Seiffert, W.Q. Butyrate and propionate improve the growth performance of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Boopathy, R. Use of formic acid to control vibriosis in shrimp aquaculture. Biologia 2013, 68, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.K.; Koh, C.B.; Sudesh, K.; Siti-Zahrah, A. Effects of dietary organic acids on growth, nutrient digestibility and gut microflora of red hybrid tilapia, Oreochromis sp., and subsequent survival during a challenge test with Streptococcus agalactiae. Aquac. Res. 2009, 40, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine, S.; Boopathy, R. Effect of organic acids on shrimp pathogen, Vibrio harveyi. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 63, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yu, P.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Gao, T.; Zhou, R.; Li, L. The feed additive potassium diformate prevents Salmonella enterica Serovar Pullorum infection and affects intestinal flora in chickens. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lückstädt, C. Use of organic acids as feed additives—Sustainable aquaculture production the non-antibiotic way. Int Aquafeed 2006, 9, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, C.; Lückstädt, C.; Webster, C.D.; Kesius, P. Organic acids and their salts. In Dietary Nutrients, Additives, and Fish Health; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 305–319. [Google Scholar]
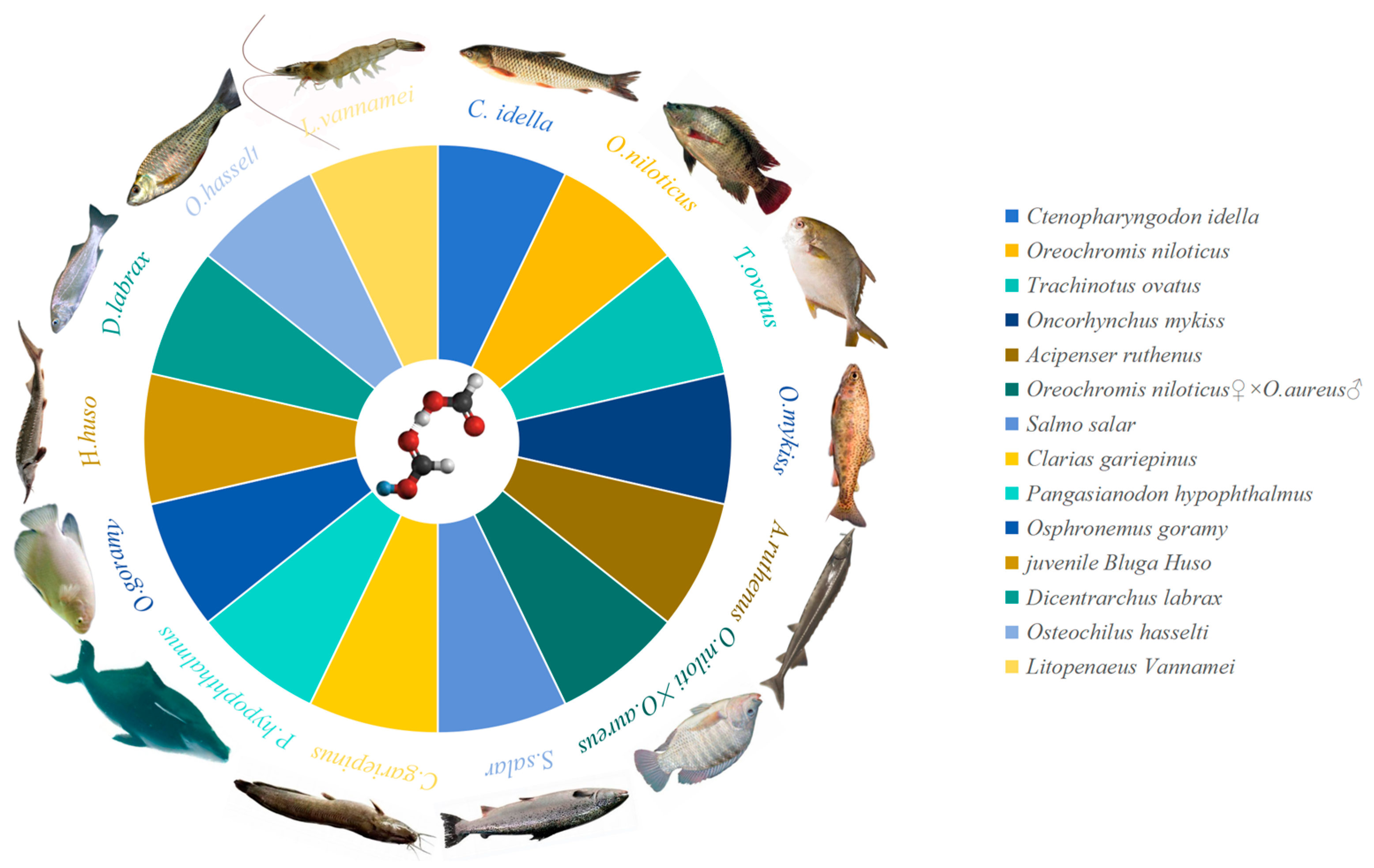
| Species | Dosage | Route of Administration | Influence | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctenopharyngodon idella | 3 g/kg | Feed for 70 days | Enhancing growth performance, pancreatic protease and lipase activities, lowering intestinal pH, and modulating gut microbiota. | [22] |
| Oreochromis niloticus | 2–3 g/kg | Feed for 60 days | Enhancing growth performance and feed efficiency, reducing intestinal pH, and enhancing immune response. | [23] |
| Trachinotus ovatus | 6.58 g/kg | Feed for 56 days | Enhancing growth performance, muscle elasticity, antioxidant enzyme activities, and improving intestinal morphology. | [24] |
| Oncorhynchus mykiss | 12 g/kg | Feed for 56 days | Enhancing growth performance, lipase, protease, and amylase activities, and reducing glucose and cortisol levels. | [25] |
| Acipenser ruthenus | 8.48–8.83 g/kg | Feed for 70 days | Enhancing growth performance, protein content, immunity, intestinal villus length, and width. | [26] |
| Oreochromis niloticus ♀ × O. aureus ♂ | 3 g/kg | Feed for 56 days | Enhancing growth performance and feed conversion efficiency, and modulating gut microbiota. | [27] |
| Salmo salar | 13.5 g/kg | Feed for 80 days | Enhancing growth performance and digestibility | [28] |
| Clarias gariepinus | 5 g/kg | Feed for 40 days | Increasing survival rate and immunity. | [29] |
| Pangasianodon hypophthalmus | 5 g/kg | Feed for 14 days | Enhancing immune response and disease resistance. | [30] |
| Osphronemus goramy | 3–5 g/kg | Feed for 40 days | Enhancing growth performance, feed efficiency, survival rate, and reducing intestinal pH. | [31] |
| Bluga huso | 1.5–2 g/kg | Feed for 60 days | Enhancing growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, gene expression levels, antioxidant activity, and gut microbiota modulation. | [32] |
| Dicentrarchus labrax | 2–3 g/kg | Feed for 90 days | Enhancing growth performance, hemoglobin levels, and immunity. | [33] |
| Osteochilus hasselti | 1–5 g/kg | Feed for 56 days | Enhancing disease resistance. | [34] |
| Litopenaeus vannamei | 2 g/kg | Feed for 70 days | Enhancing growth performance, disease resistance, immunity, and gut microbiota modulation. | [35] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; He, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Zheng, P.; Xian, J.; Lu, Y. Application of Organic Acid Salts as Feed Additives in Some Aquatic Organisms: Potassium Diformate. Fishes 2024, 9, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030085
Chen J, He S, Zhang Z, Li J, Zhang X, Li J, Xu J, Zheng P, Xian J, Lu Y. Application of Organic Acid Salts as Feed Additives in Some Aquatic Organisms: Potassium Diformate. Fishes. 2024; 9(3):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030085
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Junxiang, Shilong He, Zelong Zhang, Jiajun Li, Xiuxia Zhang, Juntao Li, Jiarui Xu, Peihua Zheng, Jianan Xian, and Yaopeng Lu. 2024. "Application of Organic Acid Salts as Feed Additives in Some Aquatic Organisms: Potassium Diformate" Fishes 9, no. 3: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030085
APA StyleChen, J., He, S., Zhang, Z., Li, J., Zhang, X., Li, J., Xu, J., Zheng, P., Xian, J., & Lu, Y. (2024). Application of Organic Acid Salts as Feed Additives in Some Aquatic Organisms: Potassium Diformate. Fishes, 9(3), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030085








