Trace Metals Distribution in Tissues of 10 Different Shark Species from the Eastern Mediterranean Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
2.2. Trace Metals Determination
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
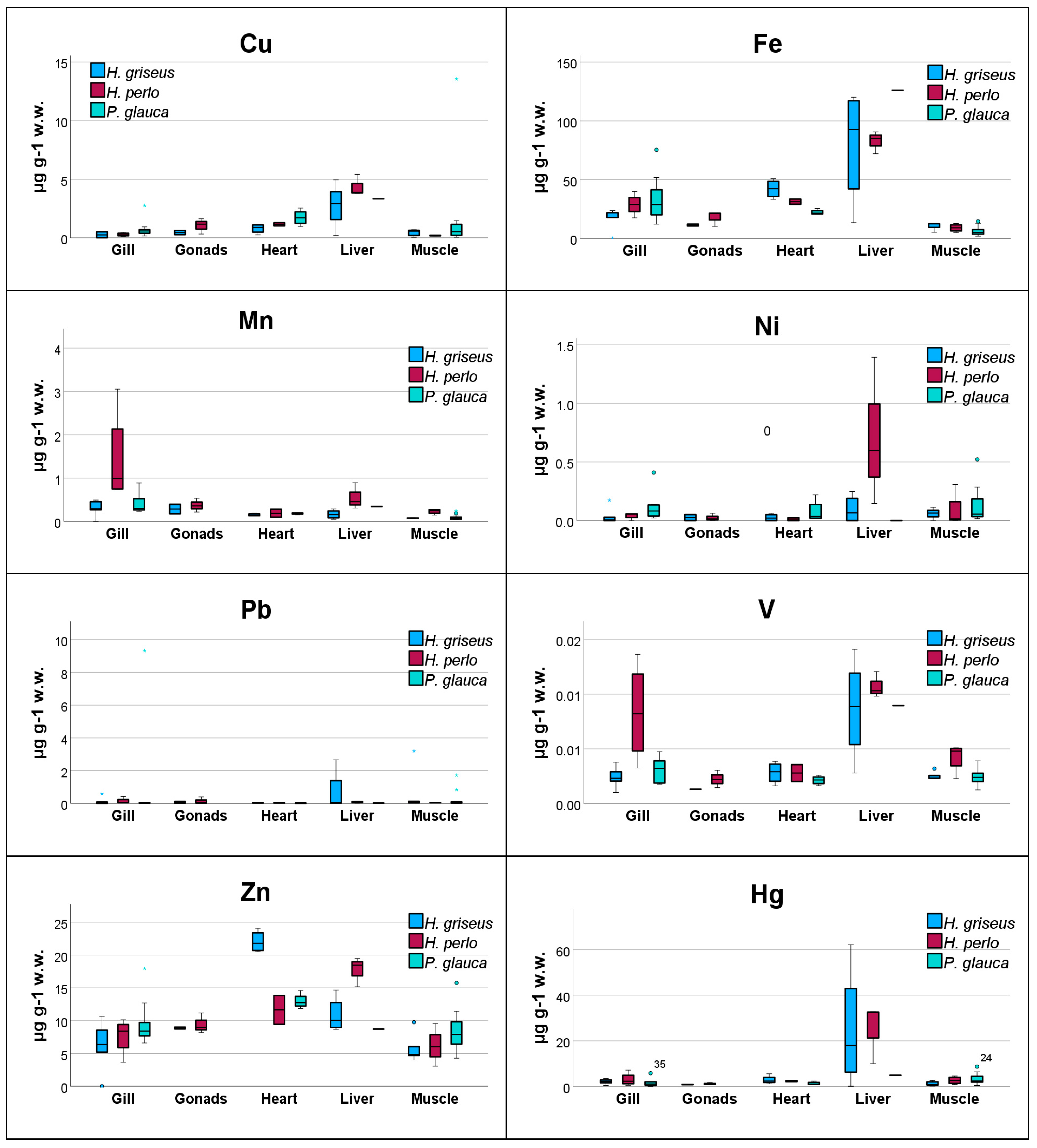
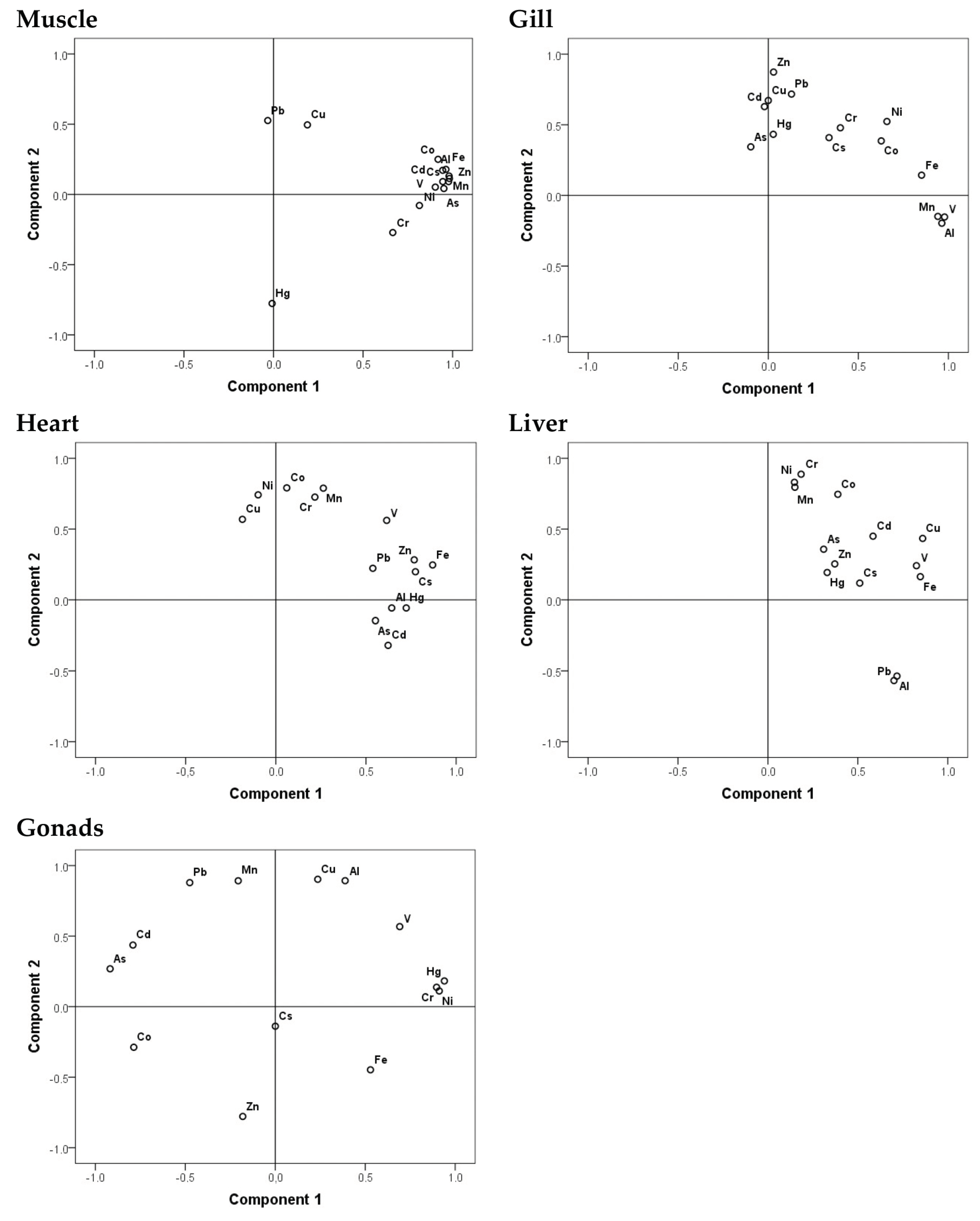
3.1. Trace Metals Concentrations
3.2. Correlation with Gender
3.3. Correlation with Size
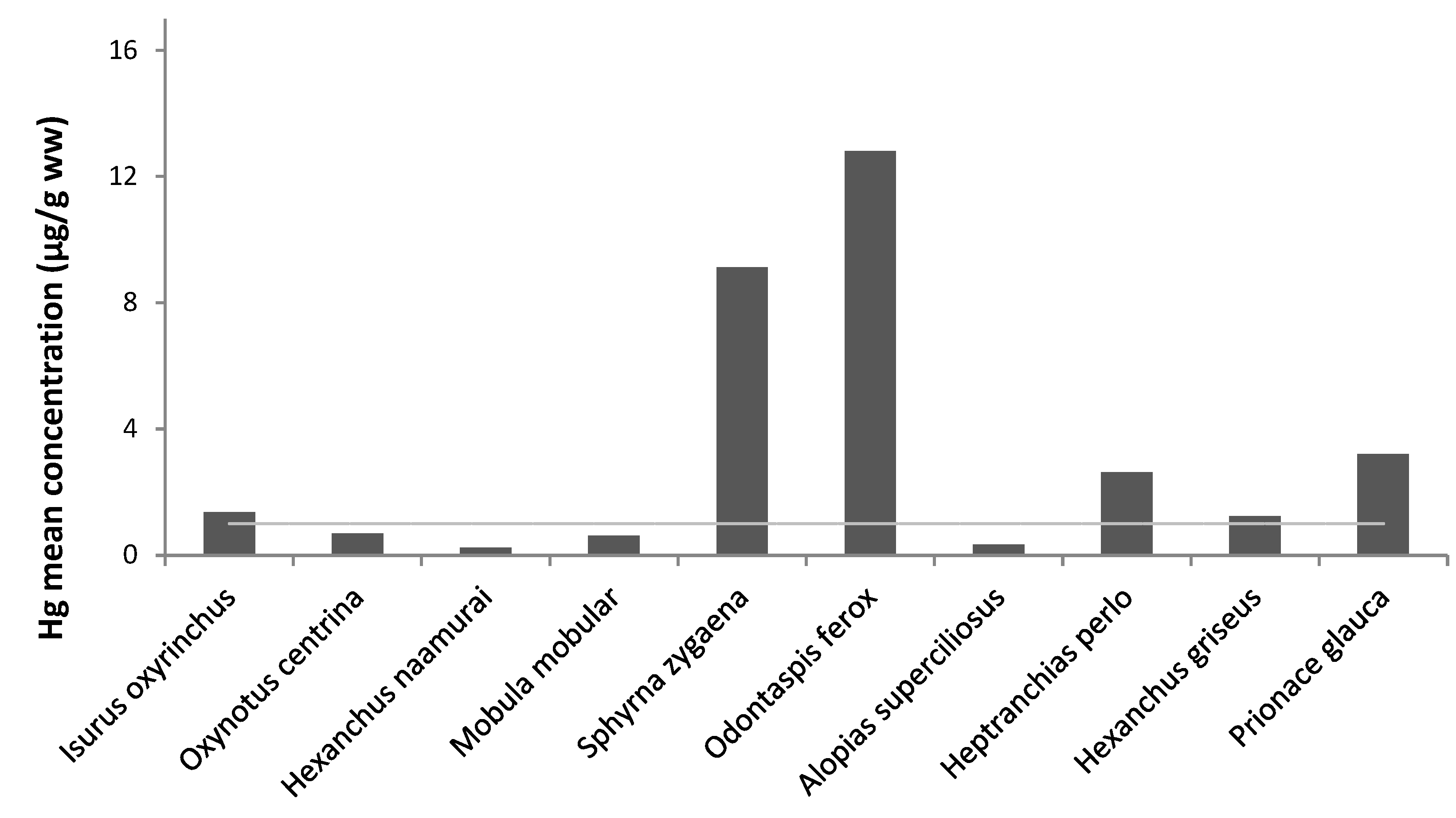
3.4. Comparison with Literature
3.5. Legislation Limits
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Souvermezoglou, E.; Krasakopoulou, E.; Pavlidou, A. Temporal variability in oxygen and nutrient concentrations in the southern Aegean Sea and the Straits of the Cretan Arc. Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 573–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, F.; Myers, R.A.; Serena, F.; Lotze, H.K. Loss of large predatory sharks from the Mediterranean Sea. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradai, M.N.; Said, B.; Enajjar, S. Elasmobranchs of the Mediterranean and Black Sea: Status, Ecology and Biology: A Bibiliographic Analysis; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bendall, V.A.; Barber, J.L.; Papachlimitzou, A.; Bolam, T.; Warford, L.; Hetherington, S.J.; Silva, J.F.; McCully, S.R.; Losada, S.; Maes, T.; et al. Organohalogen contaminants and trace metals in North-East Atlantic porbeagle shark (Lamnanasus). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.B.M.; Bolam, T.; Lyons, B.P.; Ellis, J.R. Concentrations of trace elements in a rare and threatened coastal shark from the Arabian Gulf (smoothtooth blacktip Carcharhinus leiodon). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, M.M.; Giacominelli Stuffler, R.; Marcotrigiano, G.O. Total mercury and methylmercury in tuna fish and sharks from the south Adriatic Sea. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2001, 13, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Vignatti, G.; Schneider, V.E.; Poletto, M. Biological assessment and metals concentration in blue shark (Prionace glauca) caught in the southeast-south coast of Brazil. Sci. Cum Ind. 2018, 6, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Han, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Jun, J.W.; Giri, S.S.; Chi, C.; Yun, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.G.; Kang, J.W.; et al. Heavy metal accumulation in and food safety of shark meat from Jeju island, Republic of Korea. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiszka, J.J.; Aubail, A.; Hussey, N.E.; Heithaus, M.R.; Caurant, F.; Bustamante, P. Plasticity of trophic interactions among sharks from the oceanic south-western Indian Ocean revealed by stable isotope and mercury analyses. Deep Sea Res 2015, 96, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, M.A.; Dean, K.; Hussey, N.E.; Cliff, G.; Wintner, S.P.; Dudley, S.F.; Zungu, M.P.; Fisk, A.T. Global versus local causes and health implications of high mercury concentrations in sharks from the east coast of South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.M.; Nunes, M.; Marchand, P.; Le Bizec, B.; Mendes, S.; Correia, J.P.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Novais, S.C. Blue sharks (Prionace glauca) as bioindicators of pollution and health in the Atlantic Ocean: Contamination levels and biochemical stress responses. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.; da Cunha, R.T.; dos Santos Rodrigues, A. Mid-Atlantic elasmobranchs: Suitable metal scouts? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, M.M.; Giacominelli-Stuffler, R.; Marcotrigiano, G.O. Mercury accumulation and speciation in muscle tissue of different species of sharks from Mediterranean Sea, Italy. B Environ. Contam. Tox. 2002, 68, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, M.M.; Ceci, E.; Storelli, A.; Marcotrigiano, G.O. Polychlorinated biphenyl, heavy metal and methylmercury residues in hammerhead sharks: Contaminant status and assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, M.M.; Marcotrigiano, G.O. Interspecific variation in total arsenic body concentrations in elasmobranch fish from the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 1145–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, M.M.; Cuttone, G.; Marcotrigiano, G.O. Distribution of trace elements in the tissues of smooth hound Mustelus mustelus (Linnaeus, 1758) from the southern–eastern waters of Mediterranean Sea (Italy). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 174, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagno, L.J.V. Sharks of the World: An Annotated and Illustrated Catalogue of the Shark Species Known to Date; Bullhead, mackerel and carpet sharks (Heterodontiformes, Lamniformes and Orectolobiformes); FAO Species Catalogue for Fisheries Purposes No. 1; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sperone, E.; Parise, G.; Leone, A.; Milazzo, C.; Circosta, V.; Santoro, G.; Paolillo, G.; Micarelli, P.; Tripepi, S. Spatiotemporal patterns of distribution of large predatory sharks in Calabria (central Mediterranean, southern Italy). Acta Adriat. 2012, 53, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Megalofonou, P.; Damalas, D.; Yannopoulos, C. Composition and abundance of pelagic shark by-catch in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Cybium 2005, 29, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Megalofonou, P.; Damalas, D. Morphological and biological characteristics of a gravid angular rough shark (Oxynotus centrina) and its embryos from the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Cybium 2004, 28, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kousteni, V.; Megalofonou, P. Observations on the biological traits of the rare shark Oxynotus centrina (Chondrichthyes: Oxynotidae) in the Hellenic Seas. J. Fish Biol. 2017, 89, 1880–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başusta, N. New records of neonate and juvenile sharks (Heptranchias perlo, Squatina aculeata, Etmopterus spinax) from the North-eastern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biodivers. 2016, 46, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Macêdo, G.R.; Tarantino, T.B.; Barbosa, I.S.; Pires, T.T.; Rostan, G.; Goldberg, D.W.; Pinto, L.F.B.; Korn, M.G.A.; Franke, C.R. Trace elements distribution in hawksbill turtle (Eretmochelys imbricata) and green turtle (Chelonia mydas) tissues on the northern coast of Bahia, Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 94, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, J.P.; Ernest, D.W.; Kagley, A.N. A comparison of the non-essential elements cadmium, mercury and lead found in fish and sediment from Alaska and California. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 339, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA, US Environmental Protection Agency. Guidelines Establishing Test Procedures for the Analysis of Pollutants (App. B, Part 136, Definition and Procedures for the Determination of the Method Detection Limit): US Code of Federal Regulations; Title 40; National Archives; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 265–267. [Google Scholar]
- Barrera-García, A.; O’Hara, T.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.C.; Castellini, J.M.; Zenteno-Savín, T. Trace elements and oxidative stress indicators in the liver and kidney of the blue shark (Prionace glauca). Comp. Biochem. Phys. A 2013, 165, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.F.; Lacerda, L.D.; Lai, C.T. Trace metals and persistent organic pollutants contamination in batoids (Chondrichthyes: Batoidea): A systematic review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenk, D.; Li-Schlenk, R. Characterization of liver flavin-containing monooxygenase of the dogfish shark (Squalus acanthias) and partial purification of liver flavin-containing monooxygenase of the silky shark (Carcharhinus falciformis). Comp. Biochem. Phys. B 1994, 109, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Rocha, R.C.C.; Saint’Pierre, T.D.; Adams, D.H. Metal concentrations and metallothionein metal detoxification in blue sharks, Prionace glauca L. from the Western North Atlantic Ocean. J. Tr. Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 68, 126813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Puig, P.; Colmenero, A.I.; Ruiz-García, D.; Molera- Arribas, A.J.; Hernandez-Martínez, A.M.; Raga, J.A.; Barría, C. Heavy metal concentrations in sharks, rays and chimaeras from the western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 115942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiftçi, N.; Cicik, B.; Ayas, D. First Report on the Elemental Composition of the Bigeye Thresher Shark Alopias superciliosus Lowe, 1841 from the Mediterranean Sea. Nat. Eng. Sci. 2023, 8, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordbar, L.; Strogyloudi, E.; Hatzianestis, I.; Paraskevopoulou, V.; Chatzispyrou, A. First evidence of trace metals and persistent organic contaminants from an endangered marine species, Mobula mobular (Bonattere, 1788) caught in Hellenic waters (Saronikos Gulf). Mar. Biol. Res. 2023, 19, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Amorim-Lopes, C.; Araujo, N.L.F.; Reboucas, M.; Gomes, R.I.; Rocha, R.C.C.; Saint’Pierre, T.D.; dos Santos, L.N. On mobulid rays and metals: Metal content for the first Mobula mobular record for the state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil and a review on metal ecotoxicology assessments for the Manta and Mobula genera. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Company, R.; Felícia, H.; Serafim, A.; Almeida, A.J.; Biscoito, M.; Bebianno, M.J. Metal concentrations and metallothionein-like protein levels in deep-sea fishes captured near hydrothermal vents in the Mid-Atlantic Ridge off Azores. Deep Sea Res. 2010, 57, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-García, A.; O’Hara, T.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.C.; Castellini, J.M.; Zenteno-Savín, T. Oxidative stress indicators and trace elements in the blue shark (Prionace glauca) off the east coast of the Mexican Pacific Ocean. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2012, 156, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fergusson, I.K.; Graham, K.J.; Compagno, L.J. Distribution, abundance and biology of the small tooths and tiger shark Odontaspis ferox (Risso, 1810) (Lamniformes: Odontaspididae). Environ. Biol. Fish. 2007, 81, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagno, L.J.V. FAO Species Catalogue. In Sharks of the World. An Annotated and Illustrated Catalogue of Shark Species Known to Date. Parts 1 and 2; FAO Fisheries Synopsis 125; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1984; Volume 4, pp. 1–655. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, F.; Lemos, L.S.; de Moura, J.F.; Rocha, R.C.C.; Moreira, I.; Di Beneditto, A.P.; Kehrig, H.A.; Bordon, I.C.A.C.; Siciliano, S.; Saint’Pierre, T.D.; et al. Subcellular metal distributions and metallothionein associations in rough-toothed dolphins (Steno bredanensis) from Southeastern Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 216, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boush, G.M.; Thieleke, J.R. Mercury content in sharks. B Environ. Contam. Tox. 1983, 30, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNeil, M.A.; Skomal, G.B.; Fisk, A.T. Stable isotopes from multiple tissues reveal diet switching in sharks. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 302, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, A.C.; O’Neill, B.; Sigge, G.O.; Kerwath, S.E.; Hoffman, L.C. Heavy metal accumulation and toxicity in smooth hound (Mustelus mustelus) shark from Langebaan Lagoon, South Africa. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atli, G.; Canli, M. Responses of metallothionein and reduced glutathione in a freshwater fish Oreochromis niloticus following metal exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Phar. 2008, 25, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethbridge, H.; Cossa, D.; Butler, E.C.V. Mercury in 16 demersal sharks from southeast Australia: Biotic and abiotic sources of variation and consumer health implications. Mar. Environ. Res. 2010, 69, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, V.; Vale, C.; Canário, J.; dos Santos, M.N. Mercury and selenium in blue shark (Prionace glauca, L. 1758) and swordfish (Xiphias gladius, L. 1758) from two areas of the Atlantic Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barghigiani, G.; Pellegrini, D.; D’ulivo, A.; De Ranieri, S. Mercury assessment and its relation to selenium levels in edible species of the Northern Tyrrhenian Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1991, 22, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.M.F.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Moutinho, A.B.; Ceia, F.R.; Munoz-Arnanz, J.; Jimenez, B.; Cabral, H.; Novais, S.C. Assessment of contaminants in blue sharks from the Northeast Atlantic: Profiles, accumulation dynamics, and risks for human consumers. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazama, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Harada, Y.; Kaneko, N.; Mizushima, H.; Tsuchiya, K.; Nemoto, M.; Takaku, Y.; Sahoo, Y.V.; Tanaka, M. Mercury concentrations in the tissues of blue shark (Prionace glauca) from Sagami Bay and cephalopods from East China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turoczy, N.J.; Laurenson, L.J.B.; Allinson, G.; Nishikawa, M.; Lambert, D.F.; Smith, C.; Cottier, P.E.; Irvine, S.B.; Stagnitti, F. Observations on metal concentrations in three species of shark (Deania calcea, Centroscymnus crepidater and Centroscymnus owstoni) from Southeastern Australian Waters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4357–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMeans, B.C.; Borgå, K.; Bechtol, W.R.; Higginbotham, D.; Fisk, A.T. Essential and non-essential element concentrations in two sleeper shark species collected in arctic waters. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 148, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núnez-Nogueira, G. Concentration of essential and non-essential metals in two shark species commonly caught in Mexican (Gulf of Mexico) coastline. In Golfo de México, Contaminación e Impacto Ambiental: Diagnóstico y Tendencias, 2nd ed.; Botello, A.V., Rendón von Osten, J., Gold-Bouchot, G., Agraz-Hernández, C., Eds.; Universidad Autónoma de Campeche, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Instituto Nacional de Ecología: Centro EPOMEX, Universidad Autónoma de Campeche:: Campeche, Mexico, 2005; pp. 451–474. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.B.; Kang, M.R.; Kim, J.W. Specific accumulation of heavy metals in squid collected from offshore Korean waters: Preliminary results for offshore biomonitoring and food safety assessment. Fish. Sci. 2008, 74, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, M.; Copat, C.; Asl, M.R.S.; Conti, G.O.; Babazadeh, M.; Ferrante, M. Bioaccumulation of trace metals in banded Persian bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium arabicum) from the Persian Gulf: A food safety issue. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, T.; Fisher, N.S. Dominance of dietary intake of metals in marine elasmobranch and teleost fish. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2009, 407, 5156–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, T.; Fisher, N.S.; Jeffree, R.A.; Teyssié, J.L. Assimilation and retention of metals in teleost and elasmobranch fishes following dietary exposure. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 360, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentreath, R.J. The accumulation from seawater of 65 Zn, 54Mn, 58Co, and 59Fe by the thornback ray, Raja clavata, L. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1973, 12, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.D.; Miller, J.A.; Heppell, S.S. Elemental markers in elasmobranchs: Effects of environmental and growth on vertebral chemistry. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boeck, G.; Eyckmans, M.; Lardon, I.; Bobbaers, R.; Sinha, A.K.; Blust, R. Metal accumulation and metallothionein induction in the spotted dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula. Comp. Biochem. Phys. A 2010, 155, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrim, A.I. Physiological, biochemical and histometric responses of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) by dietary organic chromium (chromium picolinate) supplementation. J. Adv. Res. 2014, 5, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.; da Cunha, R.T.; Maia, R.; dos Santos Rodrigues, A. Trophic ecology and bioindicator potential of the North Atlantic tope shark. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, K.; Carlisle, A.; Preti, A.; Mull, C.; Blasius, M.; O’Sullivan, J.; Winkler, C.; Lowe, C.G. Effects of trophic ecology and habitat use on maternal transfer of contaminants in four species of young of the year lamniform sharks. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 90, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesgo, L.; Sanpera, C.; García-Barcelona, S.; Sanchez-Fortún, M.; Coll, M.; Navarro, J. Understanding the role of ecological factors affecting mercury concentrations in the blue shark (Prionace glauca). Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.L.; Kutil, N.J.; Malek, A.J.; Collie, J.S. Mercury bioaccumulation in cartilaginous fishes from Southern New England coastal waters: Contamination from a trophic ecology and human health perspective. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 99, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Pinho, A.P.; Guimarães, J.R.D.; Martins, A.S.; Costa, P.A.S.; Olavo, G.; Valentin, J. Total mercury in muscle tissue of five shark species from Brazilian offshore waters: Effects of feeding habit, sex, and length. Environ. Res. 2002, 89, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajc, Z.; Jenčič, V.; Gačnik, K.Š. The heavy metal contents (Cd, Pb, Cu, Zn, Fe and Mn) and its relationships with the size of the rudd (Scardinius erythrophthalmus) from lake Cerknica, Slovenia. Slov. Vet. Res. 2016, 53, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Monperrus, M.; Tessier, E.; Amouroux, D.; Leynaert, A.; Huonnic, P.; Donard, O.F.X. Mercury methylation, demethylation and reduction rates in coastal and marine surface waters of the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Chem. 2007, 107, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvaro-Berlanga, S.; Calatayud-Pavía, C.E.; Cruz-Ramírez, A.; Soto-Jiménez, M.F.; Liñán-Cabello, M.A. Trace elements in muscle tissue of three commercial shark species: Prionace glauca, Carcharhinus falciformis, and Alopias pelagicus off the Manzanillo, Colima coast, Mexico. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22679–22692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, A.; Galvan-Magana, F.; Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R.; Marmolejo-Rodríguez, A.J.; Gonzalez-Armas, R.; Arreola-Mendoza, L.; Sujitha, S.B.; Jonathan, M.P.; Pantoja-Echevarría, L.M. Mercury, selenium and cadmium in juvenile blue (Prionace glauca) and smooth hammerhead (Sphyrna zygaena) sharks from the Northwest Mexican Pacific coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornung, H.; Krom, M.D.; Cohen, Y.; Bernhard, M. Trace metal content in deep-water sharks from the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biol. 1993, 115, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, K.A.; Agusa, T.; Mochizuki, H.; Ramu, K.; Inoue, S.; Kubodera, T.; Takahashi, S.; Subramanian, A.; Tanabe, S. Trace elements and stable isotopes (δ13 C and δ15 N) in shallow and deep-water organisms from the East China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 156, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmedo, P.; Hernández, A.F.; Pla, A.; Femia, P.; Navas-Acien, A.; Gil, F. Determination of essential elements (copper, manganese, selenium and zinc) in fish and shellfish samples. Risk and nutritional assessment and mercury–selenium balance. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, P.J.; Jackson, A.L. Arsenic in marine fish and invertebrates. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1973, 4, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovos, I.; Brundo, M.V.; Doumpas, N.; Kazlari, Z.; Loukovitis, D.; Moutopoulos, D.K.; Naasan, R.; Spyridopoulou, A.; Papadopoulou, A.; Papapetrou, M.; et al. Trace elements in edible tissues of elasmobranchs from the North Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean) and potential risks from consumption. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 184, 114129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.I. Mercury concentrations in edible tissues of elasmobranchs, teleosts, crustaceans and molluscs from south-eastern Australian waters. Mar. Freshwater Res. 1988, 39, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mársico, E.T.; Machado, M.E.S.; Knoff, M.; São Clemente, S.C. Total mercury in sharks along the southern Brazilian Coast. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zoo. 2007, 59, 1593–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vas, P. Trace metal levels in sharks from British and Atlantic waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1991, 22, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.K.; Badejo, A.C.; Lee, W.C.; Moon, H.B. Species-specific accumulation of methyl and total mercury in sharks from offshore and coastal waters of Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hernández, J.; Cadena-Cárdenas, L.; Betancourt-Lozano, M.; García-De-La-Parra, L.M.; García-Rico, L.; Márquez-Farías, F. Total mercury content found in edible tissues of top predator fish from the Gulf of California, Mexico. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2007, 89, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Sánchez, O.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Rosíles-Martínez, R. Biomagnification of mercury and selenium in blue shark Prionace glauca from the Pacific Ocean off Mexico. Biol. Τrace Εlem. Res. 2011, 144, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, S.A.; Abarca, N.L.; Meléndez, R.C. Heavy metal concentrations of two highly migratory sharks (Prionace glauca and Isurus oxyrinchus) in the southeastern Pacific waters: Comments on public health and conservation. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2013, 6, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maz-Courrau, A.; López-Vera, C.; Galvan-Magaña, F.; Escobar-Sánchez, O.; Rosíles-Martínez, R.; Sanjuán-Muñoz, A. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification of total mercury in four exploited shark species in the Baja California Peninsula, Mexico. B Environ. Contam. Tox. 2012, 88, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, V.; Canario, J.; Vale, C.; Raimundo, J.; Reis, C. Total and organic mercury concentrations in muscle tissue of the blue shark (Prionace glauca L. 1758) from the Northeast Atlantic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.D.; Brown, B.E. Occurrence of heavy metals in the blue shark Prionace glauca and selected pelagic in the NE Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Biol. 1974, 26, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, P.; Pla, A.; Hernández, A.F.; Barbier, F.; Ayouni, L.; Gil, F. Determination of toxic elements (mercury, cadmium, lead, tin and arsenic) in fish and shellfish samples. Risk assessment for the consumers. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, G.G.A.; Degaspari, I.A.M.; Branco, V.; Canário, J.; de Amorim, A.F.; Kennedy, V.H.; Ferreira, J.R. Assessment of total and organic mercury levels in blue sharks (Prionace glauca) from the south and southeastern Brazilian coast. Biol. Τrace Εlem. Res. 2014, 159, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Biton-Porsmoguer, S.; Bǎnaru, D.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Dekeyser, I.; Bouchoucha, M.; Marco-Miralles, F.; Lebreton, B.; Guillou, G.; Harmelin-Vivien, M. Mercury in blue shark (Prionace glauca) and short fin mako (Isurus oxyrinchus) from north-eastern Atlantic: Implication for fishery management. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero-Maldonado, C.; Espinoza, P. Cadmium and lead levels in muscle tissue of blue shark (Prionace glauca) in the Southeastern Pacific Waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 177, 113523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Regulation (EC) Number 1881/2006; Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs. L 364/5, 2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2006:364:0005:0024:EN:PDF (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Papp, A.; Pecze, L.; Szabó, A.; Vezér, T. Effects on the central and peripheral nervous activity in rats elicited by acute administration of lead, mercury and manganese, and their combinations. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2006, 26, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chien, L.C.; Hung, T.C.; Choang, K.Y.; Yeh, C.Y.; Meng, P.J.; Shieh, M.J.; Ha, B.C. Daily intake of TBT, Cu, Zn, Cd and As for fishermen in Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 285, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, J.; Lourenço, H.M.; Brito, P.; Maulvault, A.L.; Martins, L.L.; Afonso, C. Influence of bioaccessibility of total mercury, methyl-mercury and selenium on the risk/benefit associated to the consumption of raw and cooked blue shark (Prionace glauca). Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, N.; Karavoltsos, S.; Sakellari, A.; Avramidou, S.; Dassenakis, M.; Scoullos, M. Heavy metals in raw, fried and grilled Mediterranean finfish and shellfish. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3702–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Family/Species | Sex 1 | Length (cm) | Sampling Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobulidae | |||
| Mobula mobular | F | 203WD 2 | Ionian Sea |
| Mobula mobular | M | 285WD | Ionian Sea |
| Oxynotidae | |||
| Oxynotus centrina | F | 58 | Aegean Sea |
| Hexanchidae | |||
| Heptranchias perlo | F | 108 | Aegean Sea |
| Heptranchias perlo | F | 100 | Aegean Sea |
| Heptranchias perlo | F | 111 | Aegean Sea |
| Heptranchias perlo | M | 66.5 | Aegean Sea |
| Hexanchus griseus | F | 247 | Aegean Sea |
| Hexanchus griseus | M | 256 | Aegean Sea |
| Hexanchus griseus | F | 380 | Aegean Sea |
| Hexanchus griseus | M | 238 | Aegean Sea |
| Hexanchus griseus | F | 266 | Aegean Sea |
| Hexanchus nakamurai | M | 72 | Aegean Sea |
| Alopias superciliosus | M | 171 | Libyan Sea |
| Alopias superciliosus | F | 321 | Ionian Sea |
| Odontaspidae | |||
| Odontaspis ferox | F | 377 | Aegean Sea |
| Odontaspis ferox | F | 285 | Aegean Sea |
| Lamnidae | |||
| Isurus oxyrinchus | M | 97 | Aegean Sea |
| Sphyrinidae | |||
| Sphyrna zygaena | M | 326 | Libyan Sea |
| Carcharhinidae | |||
| Prionace glauca | U | 300 | Aegean Sea |
| Prionace glauca | U | 240 | Aegean Sea |
| Prionace glauca | U | 250 | Aegean Sea |
| Prionace glauca | F | 270 | Aegean Sea |
| Prionace glauca | M | 190 | Ionian Sea |
| Prionace glauca | M | 214 | Ionian Sea |
| Prionace glauca | F | 281 | Ionian Sea |
| Prionace glauca | F | 266 | Ionian Sea |
| Prionace glauca | M | 129 | Ionian Sea |
| Prionace glauca | M | 130 | Aegean Sea |
| Prionace glauca | M | 219 | Aegean Sea |
| Prionace glauca | F | 204 | Aegean Sea |
| Prionace glauca | F | 172 | Aegean Sea |
| Prionace glauca | F | 390 | Gulf of Corinth |
| Area | Tissue | Species | Al | As | Cd | Co | Cr | Cs | Cu | Fe | Hg | Mn | Ni | Pb | V | Zn | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern Mediterranean | muscle | H. griseus | 0.04 | 0.58 | 4.10 | 0.41–4.55 | 0.18 | 4.28 | [68] | ||||||||
| liver | 1.06 | 2.58 | 79.3 | 0.42–13.3 | 1.21 | 15.0 | |||||||||||
| Pacific coast of Canada | muscle | 2.2–37.8 | [71] | ||||||||||||||
| Mediterranean (north Aegean) | muscle | 10.85 ± 3.19 | 0.007 ± 0.004 | 0.006 ± 0.003 | 0.357 ± 0.077 | 1.98 ± 0.59 | 0.231 ± 0.052 | 0.040 ± 0.017 | 0.192 ± 0.082 | 0.029 ± 0.010 | 5.92 ± 0.98 | [72] | |||||
| Mediterranean (Aegean) | muscle | 0.68 ± 0.54 | 29 ± 21 | 0.011 ± 0.003 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 0.21 ± 0.13 | 0.048 ± 0.024 | 0.43 ± 0.29 | 11 ± 3 | 1.2 ± 1.0 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.69 ± 1.4 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 5.9 ± 2.3 | Present study | |
| gills | 0.52 ± 0.61 | 7.0 ± 5.6 | 0.047 ± 0.048 | 0.009 ± 0.007 | 0.04 ± 0.05 | 0.021 ± 0.009 | 0.20 ± 0.25 | 15 ± 10 | 1.7 ± 1.0 | 0.31 ± 0.22 | 0.009 ± 0.013 | 0.17 ± 0.28 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 5.0 ± 3.6 | |||
| heart | 2.0 ± 1.8 | 9.5 ± 4.7 | 0.17 ± 0.08 | 0.006 ± 0.003 | 0.10 ± 0.09 | 0.041 ± 0.010 | 0.79 ± 0.40 | 42 ± 8 | 2.8 ± 1.9 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 22 ± 2 | |||
| liver | 3.8 ± 5.2 | 4.1 ± 1.8 | 0.62 ± 0.41 | 0.020 ± 0.011 | 0.36 ± 0.30 | 0.065 ± 0.024 | 2.8 ± 2.0 | 80 ± 49 | 25 ± 27 | 0.16 ± 0.10 | 0.10 ± 0.12 | 0.70 ± 1.3 | 0.009 ± 0.005 | 11 ± 3 | |||
| gonads | 0.33 ± 0.07 | 20 ± 1 | 0.031 ± 0.026 | 0.016 ± 0.004 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.035 ± 0.003 | 0.45 ± 0.25 | 11 ± 1 | 0.80 ± 0.10 | 0.28 ± 0.15 | 0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.07 ± 0.08 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 8.9 ± 0.2 | |||
| Ionian Sea | muscle | H. perlo | 10.88 ± 2.52 | [15] | |||||||||||||
| Ionian Sea | liver | 6.22 ± 1.73 | |||||||||||||||
| Ionian Sea | muscle | 1.27 ± 1.70 | [13] | ||||||||||||||
| SE Australia | muscle | 1.33 ± 0.38 | [73] | ||||||||||||||
| East China Sea | muscle | 44 | 5.52 | 0.06 | 1.2 | 0.03 | 6.16 | 0.30 | 2.85 | 0.152 | 0.057 | 32.6 | [69] | ||||
| Mediterranean (Aegean) | muscle | 1.9 ± 0.6 | 26 ± 25 | 0.029 ± 0.009 | 0.013 ± 0.003 | 0.06 ± 0.06 | 0.031 ± 0.013 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 9.0 ± 3.3 | 2.6 ± 1.6 | 0.23 ± 0.06 | 0.08 ± 0.15 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.004 ± 0.001 | 6.2 ± 2.6 | Present study | |
| gills | 5.5 ± 3.4 | 8.0 ± 4.6 | 0.060 ± 0.023 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.05 | 0.020 ± 0.005 | 0.28 ± 0.15 | 29 ± 9 | 3.0 ± 2.9 | 1.4 ± 1.1 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.14 ± 0.19 | 0.008 ± 0.004 | 7.6 ± 2.8 | |||
| heart | 0.57 ± 0.47 | 11 ± 7 | 0.078 ± 0.045 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 0.024 ± 0.004 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 31 ± 3 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 0.19 ± 0.13 | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 12 ± 3 | |||
| liver | 2.0 ± 0.9 | 21 ± 8 | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 1.6 ± 0.9 | 0.060 ± 0.009 | 4.4 ± 0.9 | 83 ± 10 | 25 ± 13 | 0.55 ± 0.30 | 0.71 ± 0.63 | 0.08 ± 0.07 | 0.011 ± 0.001 | 18 ± 2 | |||
| gonads | 0.54 ± 0.28 | 19 ± 11 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.12 | 0.023 ± 0.003 | 1.0 ± 0.7 | 18 ± 6 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 0.37 ± 0.16 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.14 ± 0.22 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 9.4 ± 1.5 | |||
| Atlantic (Santa Catarina, Brasil) | muscle | P. glauca | 0.40 ± 0.29 | [74] | |||||||||||||
| English channel (between Atlantic and North Sea) | muscle | 0.45 | 0.24 | 6.34 | 1.55 | 2.58 | <0.02 | [75] | |||||||||
| liver | 0.25 | 0.65 | 4.02 | 0.65 | 3.23 | 1.14 | |||||||||||
| gills | 0.99 | 0.55 | 21.71 | 0.55 | 1.91 | 0.36 | |||||||||||
| S. Atlantic | muscle | 1.70 | 0.14 | 0.98 | 5.38 | [7] | |||||||||||
| Ionian Sea | muscle | 7.20 ± 3.05 | [15] | ||||||||||||||
| liver | 5.95 ± 2.67 | ||||||||||||||||
| Baja California | muscle | 6.66 ± 0.55 | 0.2 ± 0.12 | 1.64 ± 0.13 | 27.4 ± 3.57 | 1.03 ± 0.08 | n.d. | 6.10 ± 0.37 | [35] | ||||||||
| Baja California | liver | 10.62 ± 4.76 | 34.7 ± 29.6 | 9.28 ± 8.39 | 196 ± 96 | 0.22 ± 0.35 | 0.37 ± 0.37 | 49.9 ± 27.1 | [26] | ||||||||
| Pacific | muscle | 0.55–7.0 | [76] | ||||||||||||||
| South Adriatic | muscle | 0.38 | [6] | ||||||||||||||
| Atlantic, Azores | muscle | 0.22–1.3 | [44] | ||||||||||||||
| liver | 0.032–0.96 | ||||||||||||||||
| Atlantic, Equator | muscle | 0.68–2.5 | |||||||||||||||
| liver | 0.15–2.2 | ||||||||||||||||
| Pacific, Mexico | muscle | 0.27 | [77] | ||||||||||||||
| Pacific, Mexico | muscle | 1.39 ± 1.58 | [78] | ||||||||||||||
| SE Pacific | muscle | 0.014 ± 0.1 | 2.24 ± 0.81 | [79] | |||||||||||||
| liver | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 1.60 ± 0.3 | |||||||||||||||
| SW Indian | muscle | [9] | |||||||||||||||
| SE Australia | muscle | 0.41 | [75] | ||||||||||||||
| Mid Atlantic, Azores | muscle | 10.02 ± 0.69 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 0.70 ± 0.21 | 0.33 ± 0.02 | 3.95 ± 0.15 | [12] | ||||||||||
| Pacific, California | muscle | 1.96 ± 1.48 | [80] | ||||||||||||||
| NE Atlantic | muscle | 0.60–4.04 | [81] | ||||||||||||||
| NE Atlantic | muscle | <0.05 | 4.4 | <0.2 | 35 | [82] | |||||||||||
| liver | <0.05 | 5.7 | <0.2 | 35 | |||||||||||||
| gonads | <0.05 | 5.6 | <0.2 | 88 | |||||||||||||
| Basque, Spain | muscle | 0.142 | 0.033 | 1.952 | [70] | ||||||||||||
| Basque, Spain | muscle | 0.144 | 0.003 | 0.350 | 0.004 | [83] | |||||||||||
| Brazil | muscle | 0.46–2.40 | [84] | ||||||||||||||
| Atlantic | muscle | 23.8 ± 47.0 | 78.2 ± 22.0 | 0.006 ± 0.028 | 2.58 ± 3.27 | 1.15 ± 0.55 | 28.2 ± 26.2 | 1.36 ± 0.83 | 0.633 ± 0.579 | 0.341 ± 0.573 | 0.125 ± 0.109 | 24.6 ± 15.5 | [11] | ||||
| liver | 24.4 ± 40.1 | 40.0 ± 27.8 | 4.52 ± 3.60 | 1.61 ± 0.12 | 6.81 ± 3.89 | 99.8 ± 55.8 | 0.28 ± 0.35 | 2.46 ± 1.14 | 0.041 ± 0.152 | 1.30 ± 4.35 | 44.0 ± 39.6 | ||||||
| NE Atlantic, Azores | muscle | 0.14–1.71 | [85] | ||||||||||||||
| Pacific, Peru | muscle | 0.009 ± 0.002 | 0.009 ± 0.007 | [86] | |||||||||||||
| Western North Atlantic Ocean | muscle | 1.49 ± 0.60 | 60.40 ± 34.04 | 0.19 ± 0.15 | 0.005 ± 0.002 | 0.49 ± 0.27 | 0.077 ± 0.047 | 0.60 ± 0.74 | 3.86 ± 2.69 | 1.27 ± 0.53 | 0.057 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.13 | 0.052 ± 0.027 | 0.03 ± 0.017 | 7.84 ± 4.73 | [29] | |
| liver | 0.24 ± 0.15 | 23.46 ± 13.14 | 1.83 ± 1.34 | 0.025 ± 0.020 | 0.152 ± 0.125 | 0.007 ± 0.002 | 1.05 ± 1.08 | 38.6 ± 33.6 | 0.27 ± 0.22 | 0.46 ± 0.25 | <0.0007 | 0.035 ± 0.005 | 0.020 ± 0.022 | 6.54 ± 3.85 | |||
| Mexican Pacific Coast | muscle | 0.25 ± 0.20 | 0.44 ± 0.35 | [67] | |||||||||||||
| liver | 1.50 ± 0.72 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | |||||||||||||||
| Colima Coast, Mexico | muscle | 114.9 ± 83.26 | 0.76 ± 0.3 | 0.26 ± 0.07 | 2.1 ± 4.78 | 22.7 ± 15.95 | 445.3 ± 673 | 0.36 ± 0.1 | 7.35 ± 11.31 | 2.14 ± 2.91 | 2.89 ± 2.8 | 1.08 ± 0.78 | 169.2 ± 82 | [66] | |||
| Mediterranean (Ionian) | muscle | 0.65 ± 0.47 | 14 ± 5 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 0.013 ± 0.012 | 0.051 ± 0.040 | 0.014 ± 0.003 | 2.9 ± 6.0 | 3.4 ± 1.2 | 3.4 ± 2.5 | 0.07 ± 0.07 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.046 ± 0.047 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 8.2 ± 4.6 | Present study | |
| gills | 0.65 ± 0.24 | 8.6 ± 3.6 | 0.070 ± 0.062 | 0.041 ± 0.016 | 0.090 ± 0.077 | 0.015 ± 0.007 | 1.0 ± 1.0 | 26 ± 13 | 2.0 ± 2.2 | 0.46 ± 0.26 | 0.12 ± 0.16 | 1.90 ± 4.15 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 9.7 ± 4.7 | |||
| Mediterranean (Aegean) | muscle | 2.3 ± 3.1 | 17 ± 6 | 0.008 ± 0.003 | 0.015 ± 0.004 | 0.31 ± 0.35 | 0.022 ± 0.007 | 0.85 ± 0.52 | 8.3 ± 3.9 | 2.4 ± 1.2 | 0.11 ± 0.06 | 0.17 ± 0.17 | 0.35 ± 0.62 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 7.7 ± 1.7 | ||
| gills | 0.78 ± 0.35 | 7.3 ± 2.7 | 0.107 ± 0.040 | 0.055 ± 0.032 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 0.018 ± 0.005 | 0.51 ± 0.29 | 43 ± 19 | 1.0 ± 0.8 | 0.36 ± 0.19 | 0.098 ± 0.040 | 0.024 ± 0.019 | 0.004 ± 0.001 | 9.4 ± 2.0 | |||
| heart | 0.57 ± 0.33 | 6.3 ± 2.1 | 0.040 ± 0.013 | 0.013 ± 0.003 | 0.099 ± 0.132 | 0.017 ± 0.002 | 1.7 ± 0.7 | 22 ± 2 | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 0.078 ± 0.095 | 0.015 ± 0.016 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 13 ± 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roubie, E.; Karavoltsos, S.; Sakellari, A.; Katsikatsos, N.; Dassenakis, M.; Megalofonou, P. Trace Metals Distribution in Tissues of 10 Different Shark Species from the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Fishes 2024, 9, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9020077
Roubie E, Karavoltsos S, Sakellari A, Katsikatsos N, Dassenakis M, Megalofonou P. Trace Metals Distribution in Tissues of 10 Different Shark Species from the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Fishes. 2024; 9(2):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9020077
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoubie, Eleni, Sotirios Karavoltsos, Aikaterini Sakellari, Nikolaos Katsikatsos, Manos Dassenakis, and Persefoni Megalofonou. 2024. "Trace Metals Distribution in Tissues of 10 Different Shark Species from the Eastern Mediterranean Sea" Fishes 9, no. 2: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9020077
APA StyleRoubie, E., Karavoltsos, S., Sakellari, A., Katsikatsos, N., Dassenakis, M., & Megalofonou, P. (2024). Trace Metals Distribution in Tissues of 10 Different Shark Species from the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Fishes, 9(2), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9020077







