Cadmium as an Endocrine Disruptor That Hinders the Reproductive and Developmental Pathways in Freshwater Fish: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
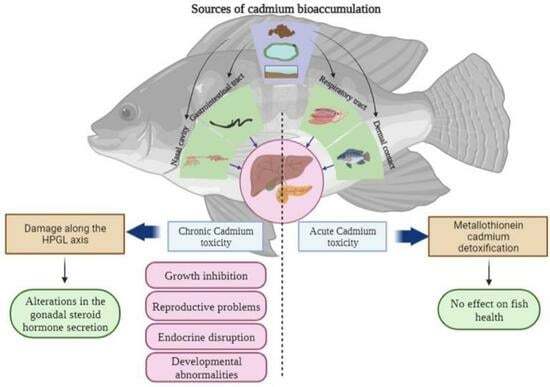
2. Sources of Cadmium Contamination in Aquatic Systems
3. Bioaccumulation of Cadmium in Freshwater Fish
4. Metallothionein as a Cadmium Detoxifier
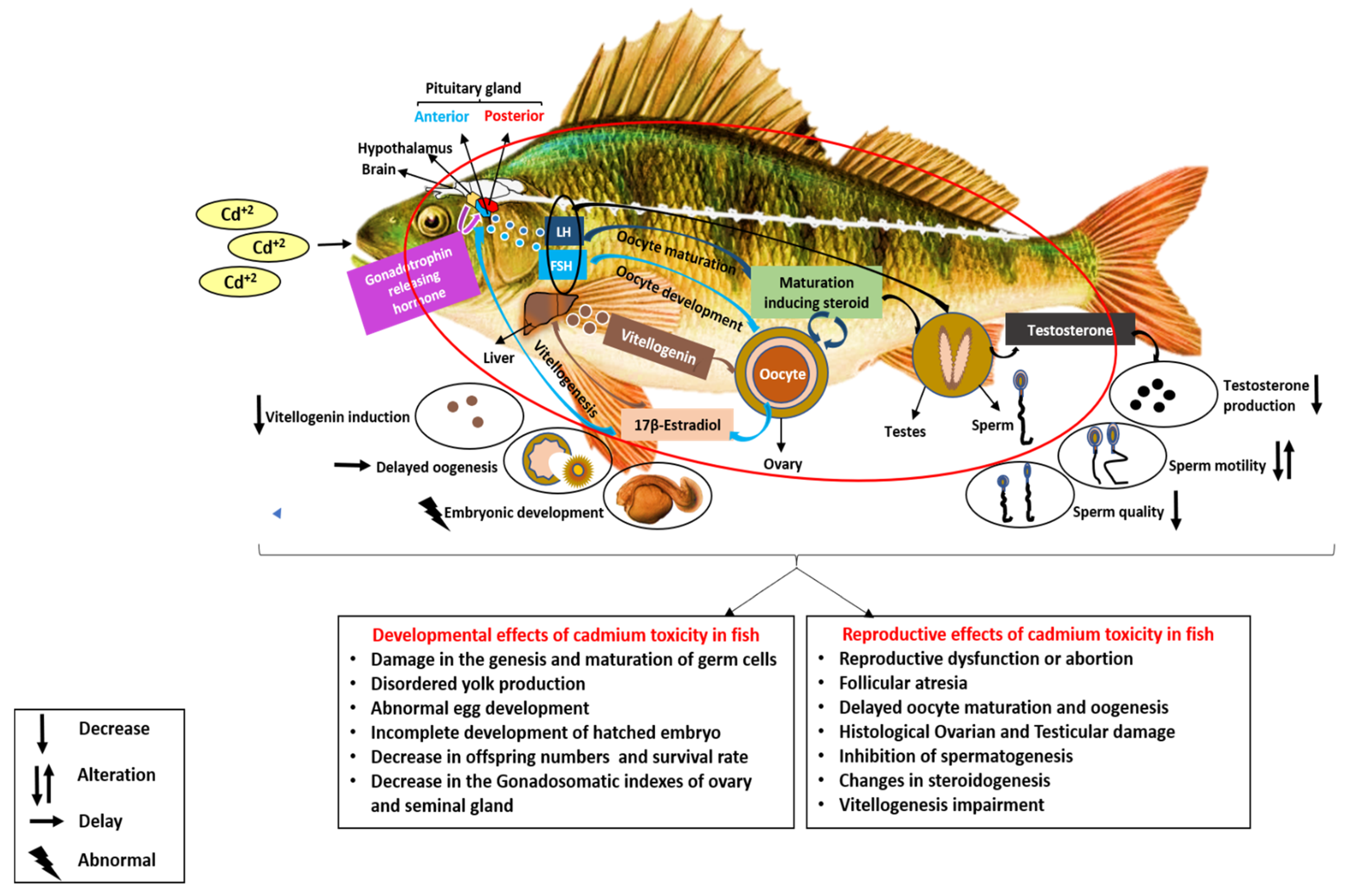
5. Cadmium as an Endocrine Disruptor in Freshwater Fish
- Enzymatic activity: Changes in the activity of certain enzymes can indicate the presence of toxic substances in the fish body. For example, Cd burden in fish can affect the activity of enzymes involved in steroid hormone synthesis or detoxification.
- Pituitary gonadotropins: alterations in gonadotropin levels can indicate a disruption of the HPG axis, leading to downstream effects on reproductive development and function.
- Steroid hormones: changes in hormone levels can lead to developmental abnormalities, reproductive dysfunction, or other adverse effects.
- Gonadal structures: an examination of gonadal tissues can reveal abnormalities such as atrophy, hypertrophy, or intersex characteristics, indicating possible exposure to endocrine-disrupting compounds.
5.1. Reproductive Effects of Cadmium in Freshwater Fish
| Fish Species | Features of Fish | Cadmium Concentration | Time of Exposure | Effects | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage | Length | Weight | |||||
| Carassius auratus | Sperm and egg | NA | NA | 10 mg/g | NS | Discontinuation of ovulation | [29] |
| Danio rerio | Reproductive phase | NS | NS | 10 min | Sperm motility affected and disintegration of the plasma membrane | [89] | |
| Gymnotus carapo | Sexually matured | NS | NS | 5–40 M | 24–96 | Reduced germ cells | [96] |
| Oreochromis niloticus | 2-month-old | 12.38 ± 0.92 cm | 58.80 ± 13.84 g | 70.32–143.78 µg/L | 30 and 60 days | Altered effects on sex-related gene expression and deformed follicle | [86] |
| Pimephales promelas | Sexually matured | NS | NS | 50 mg/L | 21 days | Reduced fertility and spawning | [95] |
| Oreochromis sp. (Red tilapia) | Sexually matured | 8.2 ± 2.5 cm | 38.3 ± 2.5 g | 1 mg/g | NS | Decreased sperm motility and deformed ova | [73] |
| Rhamdia quelen | Adult | 20.0 ± 4.4 cm | 70.5 ± 38.0 g | >100 µg/L | NS | Increased hepatic vitellogenin expression | [84] |
| Carassius auratus | fingerlings | NS | 6 ± 1.2 g | 0.5 g | 14 days | Pronounced release of AST, ALT, Cortisol, and glucose concentrations | [17] |
| Danio rerio | 7 weeks old | NS | NS | 20 μg/L | 48 days | Reduced gonadosomatic index and 17 β-estradiol and vitellogenin concentrations in plasma | [18] |
| Siganus rivulatus | 8–14 months | 19.8 ± 1.9 cm | NS | NS | NS | Alterations in the levels of testosterone, β-estradiol, and progesterone hormones | [83] |
| Colossoma macropomum | NS | NS | NS | 0.6, 1.2 and 1.8 mg/L | NS | Increased SOD enzyme activity and LPO levels in sperm cells. Impairment of fertilization and hatching rate of the oocytes. | [50] |
| Odontesthes bonariensis | Adult | 14.82 ± 0.56 cm | 41.17 ± 6.51 g | 0.25 μg/L | 14 days | Decreased follicle-stimulating hormone transcript levels and showed structural damages in spermatic lobules, fibrosis, testis, and ova | [87] |
| Tilapia zilli | Adult | 11.5–22.8 cm | 32–235.4 g | 0.57 ± 0.11 µg/g wet wt. | Annual | Increased atresia, degenerative and necrotic changes in the oocytes, and conversion of ovarian to testicular cells. | [97] |
| Carassius gibelio B. | Adult | 23.25 ± 0.49 cm | 204.65 ± 12.58 g | 0.4 or 4.0 mg/L | 3–5 months | Decreased GSI, impaired LH secretion during exposure, and stimulation of spawning | [98] |
| Danio rerio | Embryo | NS | NS | NS | 72 h | Inhibition of Estradiol induction of Aromatase-B in radial glial cells | [99] |
| Pimephales promelas | 12 months old | NS | NS | 5 μg/L | 21 days | Impaired gametogenesis, reduced steroid levels and vitellogenesis, and delayed oogenesis. | [100] |
| Fish Species | Features of Fish | Cadmium Concentration | Time of Exposure | Effects | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage | Length | Weight | |||||
| Danio rerio | 6 days post-fertilization larvae | NS | NS | 10 µg/L | 3 days | Deformed larvae | [101] |
| Danio rerio | Embryo | NA | NA | Environmentally relevant concentration | 24 to 72 h post fertilization | Alterations in optomotor responses in the treated larvae of all ages | [8] |
| Gymnotus carapo | Sexually matured | 36.8 ± 6.0 cm | 205.8 ± 59.9 g | 5–40 M | 24–96 h | Damaged germ cell genesis | [96] |
| Odontesthes bonariensis | Sexually matured | NS | NS | 0.25–2.5 µg/L | NS | Reduced hatching, embryo, and larvae survival | [90] |
| Oreochromis niloticus | 2-month-old | 12.38 ± 0.92 cm | 58.80 ± 13.84 g | 143.78–161.15 g/L | 30 and 60 days | Premature spermatid | [86] |
| Prochilodus magdalenae | Two-year-old | NS | 282.3 ± 40.8 g | 0.0025–2.5 ppm | NS | Low fertility and decreased egg production | [63] |
| Oplegnathus fasciatus | Fingerlings | NS | 5.5 ± 0.06 g | 162 mg/kg | NS | Reduced growth rate | [14] |
| Carassius auratus | Fingerlings | NS | 6 ± 1.2 g | 0.5 g | 14 days | Dilation in sinusoids and unusual Kupffer cells occurs | [17] |
| Ictalurus punctatus | Fertilization to 6-month-old fingerlings | NS | NS | NS | 3 months | Increased metallothionein gene expression in heat-shock proteins in the liver | [30] |
| Trematomus hansoni | Adult | 21.2–24.6 cm | 130–159 g | 0.89 µM | 5 days | Increased metallothionein gene transcription | [52] |
| Ide Leuciscus idus | 21 days post-hatching | NS | NS | 100 μg/L | NS | Reduced embryonic survival | [75] |
| Oncorhynchus mykiss | Embryos and larvae | NA | NS | 0.5–8.0 μg/L | 96 h | Induced geno–cytotoxicity disturbs cardio-respiratory system activity and negatively impacts fish development at early life stages. | [77] |
| Danio rerio | Embryo | NA | NA | 30 µM | 1–3 days post fertilization | Increased mortality rate and delayed hatching | [102] |
| Gasterosteus aculeatus | Adult | 40.40 ± 0.49 mm | 955.80 ± 55.13 mg | 1 ppb | 15, 60, and 120 days | Reduced germ cell quality, decreased hatching rate, and increased mortality rate. | [103] |
| Oryzias javanicus | Newly spawned eggs | NS | NS | 0.01–0.10 ppm | NS | Failure in embryo development | [104] |
| Cyprinus carpio L. | Adult | NS | 768.50 g | 0.5 mg/L | NS | Reduced body weight gain | [64] |
| Danio rerio | Adult (120 days post fertilization) | NS | NS | 1 µmol/L | NS | Malformations in the produced offspring | [105] |
| Channa marulius and Hepteroneustes fossillis | Juveniles and smaller adults | NS | NS | 0–10 mg/L | 96 h | Respiratory strategy and adaptation to low-ionic-strength environments | [82] |
5.2. Developmental Effects of Cadmium on Freshwater Fish
6. Research Gaps and Future Research Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masindi, V.; Muedi, K.L. Environmental contamination by heavy metals. Heavy Met. 2018, 10, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Mahiya, S.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Contamination of Heavy Metals in Aquatic Media: Transport, Toxicity and Technologies for Remediation. In Heavy Metals in Water: Presence, Removal and Safety; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duruibe, J.O.; Ogwuegbu, M.O.C.; Egwurugwu, J.N. Heavy metal pollution and human biotoxic effects. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2007, 2, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- LeFauve, M.K.; Connaughton, V.P. Developmental exposure to heavy metals alters visually-guided behaviors in zebrafish. Curr. Zool. 2017, 63, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejna, M.; Gottardo, D.; Baldi, A.; Dell’Orto, V.; Cheli, F.; Zaninelli, M.; Rossi, L. Review: Nutritional ecology of heavy metals. Animal 2018, 12, 2156–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waalkes, M.P.; Misra, R.R.; Chang, L.W. Toxicology of Metals; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; pp. 1003–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Exp. Suppl. 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garai, P.; Banerjee, P.; Mondal, P.; Saha, N.C. Effect of heavy metals on fishes: Toxicity and bioaccumulation. J. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 11, 1–10. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Pradip-Mondal/publication/353848075 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, N.; Xin, M.; Geng, S.; Jia, J.; Meng, Q. Heavy metals in aquatic organisms of different trophic levels and their potential human health risk in Bohai Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17801–17810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, B.; Georgescu, C.; Dărăban, S.; Bouaru, A.; Paşcalău, S. Heavy metals acting as endocrine disrupters. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 44, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Feng, C.; Quan, W.; Chen, X.; Niu, J.; Shen, Z. Role of living environments in the accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in fishes and crabs in the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, P.A.C.T.; Kodithuwakku, S.P.; Sundarabarathy, T.V.; Edirisinghe, U. Bioaccumulation of Cadmium in freshwater fish. An environmental perspective. Insight Ecol. 2015, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, R.; Thilsted, S.H.; Hossain, N.; Ishihara, H.; Yagi, N. Fish is the preferred animal-source food in the rural community of Southern Bangladesh. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okorie, O.E.; Bae, J.Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, S.; Park, G.-H.; Mohseni, M.; Bai, S.C. Effects of Different Dietary Cadmium Levels on Growth and Tissue Cadmium Content in Juvenile Parrotfish, Oplegnathus fasciatus. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baatrup, E. Structural and functional effects of heavy metals on the nervous system, including sense organs, of fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. Pharmacol. 1991, 100, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielcarek, K.; Nowakowski, P.; Puścion-Jakubik, A.; Gromkowska-Kępka, K.J.; Soroczyńska, J.; Markiewicz-Żukowska, R.; Naliwajko, S.K.; Grabia, M.; Bielecka, J.; Żmudzińska, A.; et al. Arsenic, cadmium, lead and mercury content and health risk assessment of consuming freshwater fish with elements of chemometric analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 379, 132167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, Z.; Khan, S.A.; Noor, M. Assessment of cadmium toxicity and its possible effects on goldfish (Carassius auratus), employing microscopy and biochemical techniques. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2020, 83, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Peng, L.; Xia, L.; Li, J.; Zhu, Q. Effects of continuous and intermittent cadmium exposure on HPGL axis, GH/IGF axis and circadian rhythm signaling and their consequences on reproduction in female zebrafish: Biomarkers independent of exposure regimes. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 130879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faroon, O.; Ashizawa, A.; Wright, S.; Tucker, P.; Jenkins, K.; Ingerman, L.; Rudisill, C. Toxicological Profile for Cadmium; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (US): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012; pp. 11–15.
- Morrow, H. Cadmium and cadmium alloys. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 5th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, K.; Ghosh, S.; Haque, S. A review on contamination, bioaccumulation and toxic effect of cadmium, mercury and lead on freshwater fishes. Int. J. Zool. Stud. 2018, 3, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Muntau, H.; Baudo, R. Sources of cadmium, its distribution and turnover in the freshwater environment. IARC Sci. Publ. 1992, 118, 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Baharom, Z.S.; Ishak, M.Y. Determination of heavy metal accumulation in fish species in Galas River, Kelantan and Beranang mining pool, Selangor. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 30, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamari, A.; Yusof, N.; Abdullah, H.; Haraguchi, A.; Abas, M.F. Assessment of heavy metals in water, sediment, Anabas testudineus and Eichhornia crassipes in a former mining pond in Perak, Malaysia. Chem. Ecol. 2017, 33, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namieśnik, J.; Rabajczyk, A. The speciation and physicochemical forms of metals in surface waters and sediments. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2010, 22, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubier, A.; Wilkin, R.T.; Pichler, T. Cadmium in soils and groundwater: A review. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 108, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimzadeh, M.R.; Rahimzadeh, M.R.; Kazemi, S.; Moghadamnia, A.A. Cadmium toxicity and treatment: An update. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 8, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, A.; Verma, A.; Jaiswal, P. Detrimental effects of heavy metals in soil, plants, and aquatic ecosystems and in humans. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2018, 37, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczerbik, P.; Mikołajczyk, T.; Sokołowska-Mikołajczyk, M.; Socha, M.; Chyb, J.; Epler, P. Influence of long-term exposure to dietary cadmium on growth, maturation and reproduction of goldfish (subspecies: Prussian carp Carassius auratus gibelio B.). Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 77, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, J.S.; Small, B.C. Chronic exposure to environmental cadmium affects growth and survival, cellular stress, and glucose metabolism in juvenile channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 230, 105705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbost, P.M.; Van Rooij, J.; Flik, G.; Lock, R.A.C.; Bonga, S.W. The movement of cadmium through freshwater trout branchial epithelium and its interference with calcium transport. J. Exp. Biol. 1989, 145, 185–197. Available online: https://repository.ubn.ru.nl/bitstream/handle/2066/16645/10833, (accessed on 15 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Irwin, R.; Van Mouwerik, M.; Stevens, L.; Seese, M.D.; Basham, W. Environmental Contaminants Encyclopedia, Copper Entry; Water Resources Division: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1997.
- Hossain, M.B.; Tanjin, F.; Rahman, M.S.; Yu, J.; Akhter, S.; Noman, M.A.; Sun, J. Metals Bioaccumulation in 15 commonly consumed fishes from the lower Meghna River and adjacent areas of Bangladesh and associated human health hazards. Toxics 2022, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, G.; Patel, D.A. Drug bioavailability. In StatPearls [Internet]; Statpearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Drexler, J.; Fisher, N.; Henningsen, G.; Lanno, R.; McGeer, J.; Sappington, K.; Beringer, M. Issue Paper on the Bioavailability and Bioaccumulation of Metals; US Environmental Protection Agency Risk Assessment Forum: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- Lall, S.P.; Kaushik, S.J. Nutrition and metabolism of minerals in fish. Animals 2021, 11, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.M.; Farrell, A.P.; Brauner, C.J. (Eds.) Homeostasis and Toxicology of Essential Metals; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, S.M.; Ikenaka, Y.; Muzandu, K.; Choongo, K.; Oroszlany, B.; Teraoka, H.; Mizuno, N.; Ishizuka, M. Heavymetal accumulation in lake sediments, fish (Oreochromis niloticus and Serranochromis thumbergi) and crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus) in LakeItezhi-tezhi and Lake Kariba, Zambia. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol 2010, 59, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, C.M. Toxic responses of the gill. In Target Organ Toxicity in Marine and Freshwater Teleosts; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- Smet, H.D.; Blust, R. Stress responses and changes in protein metabolism in carp Cyprinus carpio during cadmium exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environm. Saf. 2001, 48, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, P.; Kling, P.; Hogstrand, C. Mechanism of Heavy Metal Accumulation and Toxicity in Fish. In Metal Metabolism in Aquatic Environments; Langston, W.J., Bebianno, M.J., Eds.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1998; pp. 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mai, K.; Ai, Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L. Effects of dietary squid viscera meal on growth and cadmium accumulation in tissues of large yellow croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea R. Front. Agric. China 2009, 3, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, J.J.V.; Pacini, A.; Gulisano, M.; Taddei, N.; Fiorillo, C.; Becatti, M. Cadmium-induced cytotoxicity: Effects on mitochondrial electron transport chain. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 604377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedeji, O.B.; Okocha, R.C. Constraint to aquaculture development in Nigeria and way forward. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 7, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg, M.; Nordberg, G.F. Metallothionein and Cadmium Toxicology-Historical Review and Commentary. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradl, H. Heavy Metals in the Environment: Origin, Interaction and Remediation, 1st ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, D.A.; Welbourn, P. Environmental Toxicology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Puvaneswari, S.; Karuppasamy, R. Accumulation of cadmium and its effects on the survival and growth of larvae of Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch, 1794). J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 2, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pinto, G.L.; da Silva Castro, J.; Val, A.L. Copper and cadmium impair sperm performance, fertilization and hatching of oocytes from Amazonian fish Colossoma macropomum. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 128957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amutha, C.; Subramanian, P. Cadmium alters the reproductive endocrine disruption and enhancement of growth in the early and adult stages of Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 39, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakiu, R.; Pacchini, S.; Piva, E.; Schumann, S.; Tolomeo, A.M.; Ferro, D.; Irato, P.; Santovito, G. Metallothionein expression as a physiological response against metal toxicity in the striped rockcod Trematomus hansoni. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.U.M.I.T.; Vincent, S.; Meena, B.; Suresh, A.; Mani, R. Metallothionein induction in fresh water catfish Clarias gariepinus on exposure to cadmium. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 377–383. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284819201 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Chowdhury, M.J.; Baldisserotto, B.; Wood, C.M. Tissue-specific cadmium and metallothionein levels in rainbow trout chronically acclimated to waterborne or dietary cadmium. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 48, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichert, W.L.; Federighi, D.A.; Malins, D.C. Uptake and metabolism of lead and cadmium in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. Pharmacol. 1979, 63, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordberg, M.; Nordberg, G.F. Toxicological aspects of metallothionein. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2000, 46, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Annabi, A.; Messaoudi, I.; Kerkeni, A.; Said, K. Cadmium accumulation and histological lesion in mosquito fish (Gambusia affinis) tissues following acute and chronic exposure. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2011, 5, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollis, L.; Hogstrand, C.; Wood, C.M. Tissue-specific cadmium accumulation, metallothionein induction, and tissue zinc and copper levels during chronic sublethal cadmium exposure in juvenile rainbow trout. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, S.; Sangem, P.; Anusha, N.; Senthilkumaran, B. Endocrine disruptors in teleosts: Evaluating environmental risks and biomarkers. Aquac. Fish. 2021, 6, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezierska, B.; Ługowska, K.; Witeska, M. The effects of heavy metals on embryonic development of fish (a review). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfakianakis, D.G.; Renieri, E.; Kentouri, M.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Effect of heavy metals on fish larvae deformities: A review. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetillard, A.; Bailhache, T. Cadmium: An endocrine disrupter that affects gene expression in the liver and brain of juvenile rainbow trout. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 72, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Marquez, L.; Espinosa-Araujo, J.; Atencio-Garcia, V.; Olivero-Verbel, J. Effects of cadmium exposure on sperm and larvae of the neotropical fish Prochilodus magdalenae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2019, 225, 108577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.B. Non-Essential Heavy Metals as Endocrine Disruptors: Evaluating Impact on Reproduction in Teleosts. In Proceedings of the Zoological Society; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2021; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Chen, Y.; Feng, J.; Huang, M.; Zhang, J. Amelioration of Cd-induced bioaccumulation, oxidative stress and immune damage by probiotic Bacillus coagulans in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevcikova, M.; Modra, H.; Slaninova, A.; Svobodova, Z. Metals as a cause of oxidative stress in fish: A review. Vet. Med. 2011, 56, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemmiche, S. Oxidative signaling response to cadmium exposure. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 156, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, P.N.; Pillai, A.; Gupta, S. Effect of Simultaneous Exposure to Lead and Cadmium on Gonadotropin Binding and Steroidogenesis on Granulosa Cells: An In Vitro Study; NISCAIR-CSIR: New Delhi, India, 2014.
- Prucha, M.S.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Doperalski, N.J.; Kroll, K.J.; Barber, D.S.; Denslow, N.D. Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein transcription is regulated by estrogen receptor signaling in largemouth bass ovary. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 286, 113300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; Li, Y. The environment and female reproduction: Potential mechanism of cadmium poisoning to the growth and development of ovarian follicle. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 244, 114029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benninghoff, A.D.; Williams, D.E. Identification of a transcriptional fingerprint of estrogen exposure in rainbow trout liver. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 101, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, J.M.; Segner, H. Estrogen-mediated suppression of cytochrome P4501A (CYP1A) expression in rainbow trout hepatocytes: Role of estrogen receptor. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2001, 138, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ebiary, E.; Wahbi, O.; El-Greisy, Z. Influence of dietary Cadmium on sexual maturity and reproduction of Red Tilapia. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2013, 39, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaduce, A.P.S.; Kochhann, D.; Flores, E.M.; Dressler, V.L.; Baldisserotto, B. Toxicity of cadmium for silver catfish Rhamdia quelen (Heptapteridae) embryos and larvae at different alkalinities. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 54, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witeska, M.; Sarnowski, P.; Ługowska, K.; Kowal, E. The effects of cadmium and copper on embryonic and larval development of ide Leuciscus idus L. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 40, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizardo-Daudt, H.M.; Kennedy, C. Effects of cadmium chloride on the development of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss early life stages. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 702–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgelėnė, Ž.; Stankevičiūtė, M.; Kazlauskienė, N.; Baršienė, J.; Jokšas, K.; Markuckas, A. Toxicological potential of cadmium impact on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in early development. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foran, C.M.; Peterson, B.N.; Benson, W.H. Influence of parental and developmental cadmium exposure on endocrine and reproductive function in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 133, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilton, S.C.; Foran, C.M.; Benson, W.H. Effects of cadmium on the reproductive axis of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 136, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattink, J.; De Boeck, G.; Blust, R. The toxicokinetics of cadmium in carp under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 75, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Attar, A.M. Biochemical effects of short-term cadmium exposure on the freshwater fish, Oreochromis niloticus. J. Biol. Sci. 2005, 5, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ferro, J.P.; Ferrari, L.; Eissa, B.L. Acute toxicity of cadmium to freshwater fishes and its relationship with body size and respiratory strategy. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 248, 109109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hasawi, Z.M. Adverse Impacts of Toxic Metal Pollutants on Sex Sterosid Hormones of Siganus rivulatus (Teleostei: Siganidae) from the Red Sea. Fishes 2022, 7, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, M.; Fernandes, L.D.; Marques, A.E.; Osório, F.H.; Baika, L.M.; Risso, W.E.; dos Reis Martinez, C.B.; Grassi, M.T.; Fávaro, L.F.; Mela, M.; et al. Effects of cadmium on the female reproductive axis of a Neotropical fish. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevel, R. Inhibition of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Estrogen Receptor Activity by Cadmium. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 63, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Shan, D.; Zhong, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Cao, J.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, J.; He, F.; Huang, Y.; et al. Subchronic effects of cadmium on the gonads, expressions of steroid hormones and sex-related genes in tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gárriz, Á.; Del Fresno, P.S.; Carriquiriborde, P.; Miranda, L.A. Effects of heavy metals identified in Chascomu´s shallow lake on the endocrine-reproductive axis of pejerrey fish (Odontesthes bonariensis). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 273, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abascal, F.J.; Cosson, J.; Fauvel, C. Characterization of sperm motility in sea bass: The effect of heavy metals and physicochemical variables on sperm motility. J. Fish. Biol 2007, 70, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, I.B.; Junior, A.S.V.; e Silva, E.F.; Cardoso, T.F.; Caldas, J.S.; Jardim, R.D.; Corcini, C.D. Effects of exposure to cadmium in sperm cells of zebrafish, Danio rerio. Toxicol. Rep. 2016, 3, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gárriz, A.; Miranda, L. Effects of metals on sperm quality, fertilization and hatching rates, and embryo and larval survival of pejerrey fish (Odontesthes bonariensis). Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Taherianfard, M. The effects of heavy metals exposure on reproductive systems of cyprinid fish from Kor River. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2011, 10, 13–24. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1834/11305 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Lizardo-Daudt, H.M.; Bains, O.S.; Singh, C.R.; Kennedy, C.J. Cadmium chloride-induced disruption of testicular steroidogenesis in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 55, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, A. The hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis is target of cadmium toxicity. An update of recent studies and potential therapeutic approaches. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Dutt, N. Cadmium-induced histomorphological changes in the testis and pituitary gonadotrophic hormone secreting cells of the cyprinid Puntius sarana. Ital. J. Zool. 1991, 58, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellin, M.; Kolok, A. Cd exposures in fathead minnows: Effects on adult spawning success and reproductive physiology. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 51, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vergilio, C.; Moreira, R.; Carvalho, C.; Melo, E. Evolution of cadmium effects in the testis and sperm of the tropical fish Gymnotus carapo. Tissue Cell 2015, 47, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azab, A.; Aly-Eldeen, M.; Khalaf Allah, H.; El-Battal, M. Effect of heavy metals on the ovary of Tilapia zillii in some canals of Nile Delta area, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2019, 23, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Drąg-Kozak, E.; Socha, M.; Gosiewski, G.; Łuszczek-Trojnar, E.; Chyb, J.; Popek, W. Protective effect of melatonin on cadmium-induced changes in some maturation and reproductive parameters of female Prussian carp (Carassius gibelio B.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 9915–9927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouchene, L.; Pellegrini, E.; Gueguen, M.M.; Hinfray, N.; Brion, F.; Piccini, B.; Kah, O.; Saïd, K.; Messaoudi, I.; Pakdel, F. Inhibitory effect of cadmium on estrogen signaling in zebrafish brain and protection by zinc. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driessnack, M.; Matthews, A.; Raine, J.; Niyogi, S. Interactive effects of chronic waterborne copper and cadmium exposure on tissue-specific metal accumulation and reproduction in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2016, 179, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarasco, M.; Cardeira, J.; Viegas, M.N.; Caria, J.; Martins, G.; Gavaia, P.J.; Cancela, M.L.; Laizé, V. Anti-Osteogenic Activity of Cadmium in Zebrafish. Fishes 2019, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risnawati; Diestika, Y.; Khotimah, H.; Ali, M.M.; Widodo, M.A.; Nurdiana; Kalsum, U. Development of cadmium-induced zebrafish larvae improved by Centella asiatica. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2108, p. 020032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hani, Y.M.; Turies, C.; Palluel, O.; Delahaut, L.; Bado-Nilles, A.; Geffard, A.; Dedourge-Geffard, O.; Porcher, J.M. Effects of a chronic exposure to different water temperatures and/or to an environmental cadmium concentration on the reproduction of the threespine stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Yusof, S. Effect of mercury and cadmium on early life stages of Java medaka (Oryzias javanicus): A potential tropical test fish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Hu, J.; He, W.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Y. Parental exposure to cadmium chloride causes developmental toxicity and thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish offspring. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2020, 234, 108782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, H.; Meng, Y.; Jin, G.; Zhu, M. The toxicity of cadmium (Cd2+) towards embryos and pro-larva of soldatov’s catfish (Silurus soldatovi). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flament, S.; Kuntz, S.; Chesnel, A.; Grillier-Vuissor, I.; Tankozic, C.; Penrad-Mobayed, M.; Chardard, D. Effect of cadmium on gonadogenesis and metamorphosis in Pleurodeles waltl (urodele amphibian). Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 64, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, T.; Kumar, S.; Devi, M.; Kumar, V.; Behera, B.; Das, B. Effect of heavy metals in fish reproduction: A review. J. Environ. Biol. 2022, 43, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blechinger, S.; Kusch, R.; Haugo, K.; Matz, C.; Chivers, D.; Krone, P. Brief embryonic cadmium exposure induces a stress response and cell death in the developing olfactory system followed by long-term olfactory deficits in juvenile zebrafish. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 224, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.; Hui, M.; Lin, C.; Cheng, S. Cadmium inhibits neurogenesis in zebrafish embryonic brain development. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 87, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.C. Cadmium toxicity to gonads in a freshwater fish, Labeo bata (Hamilton). Arch. Für Hydrobiol. 1988, 112, 467–474. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/etdeweb/biblio/6704198 (accessed on 23 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Tsai, P.; Chou, M.; Wang, W. Effects of maternal cadmium exposure on female reproductive functions, gamete quality, and offspring development in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 65, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Huang, W.; Shan, X.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Q.; Dou, S. Cadmium toxicity to embryonic-larval development and survival in red sea bream Pagrus major. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1966–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metin, C. Effects of aqueous cadmium on embryos and larvae of mirror carp. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 71, 885–888. Available online: https://epubs.icar.org.in/index.php/IJAnS/article/view/37010 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Fraysse, B.; Mons, R.; Garric, J. Development of a zebrafish 4-day embryo-larval bioassay to assess toxicity of chemicals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 63, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fausch, K.D.; Torgersen, C.E.; Baxter, C.V.; Li, H.W. Landscapes to riverscapes: Bridging the gap between research and conservation of stream fishes: A continuous view of the river is needed to understand how processes interacting among scales set the context for stream fishes and their habitat. BioScience 2002, 52, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanigaivel, S.; Vickram, S.; Dey, N.; Jeyanthi, P.; Subbaiya, R.; Kim, W.; Govarthanan, M.; Karmegam, N. Ecological disturbances and abundance of anthropogenic pollutants in the aquatic ecosystem: Critical review of impact assessment on the aquatic animals. Chemosphere 2022, 313, 137475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asagba, S.O.; Eriyamremu, G.E.; Igberaese, M.E. Bioaccumulation of cadmium and its biochemical effect on selected tissues of the catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 34, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Wang, L. Metal accumulation and antioxidant defenses in the freshwater fish Carassius auratus in response to single and combined exposure to cadmium and hydroxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 275, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, K.; Khare, A.; Dange, S. The applicability of oxidative stress biomarkers in assessing chromium induced toxicity in the fish Labeo rohita. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 782493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, M.; Usmani, N.; Firdaus, F.; Zafeer, M.F.; Ahmad, S.; Akhtar, K.; Hossain, M.M. In vivo induction of antioxidant response and oxidative stress associated with genotoxicity and histopathological alteration in two commercial fish species due to heavy metals exposure in northern India (Kali) river. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 176, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, P.; Shu, H.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y. Amelioration of Cd-induced bioaccumulation, oxidative stress and intestinal microbiota by Bacillus cereus in Carassius auratus gibelio. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, P.; Vattapparumbil, I.P. Patterns of cadmium accumulation in selected tissues of the catfish Clarias batrachus (Linn.) exposed to sublethal concentration of cadmium chloride. Vet. Arh. 2006, 76, 167–177. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/5077 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Wu, N.; Gao, M.; Tan, Y. Combined toxicity of pyrethroid insecticides and heavy metals: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1693–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Muzammal, M.; Rehman, A.; Rustam, S.A.; Shehzadi, Z.; Mehmood, A.; Waqar, M. Water pollution on heavy metals and its effects on fishes. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2020, 8, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Moiseenko, T.I.; Gashkina, N.A. Distribution and bioaccumulation of heavy metals (Hg, Cd and Pb) in fish: Influence of the aquatic environment and climate. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 115013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vinanthi Rajalakshmi, K.S.; Liu, W.-C.; Balamuralikrishnan, B.; Meyyazhagan, A.; Sattanathan, G.; Pappuswamy, M.; Joseph, K.S.; Paari, K.A.; Lee, J.-W. Cadmium as an Endocrine Disruptor That Hinders the Reproductive and Developmental Pathways in Freshwater Fish: A Review. Fishes 2023, 8, 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120589
Vinanthi Rajalakshmi KS, Liu W-C, Balamuralikrishnan B, Meyyazhagan A, Sattanathan G, Pappuswamy M, Joseph KS, Paari KA, Lee J-W. Cadmium as an Endocrine Disruptor That Hinders the Reproductive and Developmental Pathways in Freshwater Fish: A Review. Fishes. 2023; 8(12):589. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120589
Chicago/Turabian StyleVinanthi Rajalakshmi, Kaakarlu Shivakumar, Wen-Chao Liu, Balasubramanian Balamuralikrishnan, Arun Meyyazhagan, Govindharajan Sattanathan, Manikantan Pappuswamy, Kadanthottu Sebastian Joseph, Kuppusamy Alagesan Paari, and Jang-Won Lee. 2023. "Cadmium as an Endocrine Disruptor That Hinders the Reproductive and Developmental Pathways in Freshwater Fish: A Review" Fishes 8, no. 12: 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120589
APA StyleVinanthi Rajalakshmi, K. S., Liu, W.-C., Balamuralikrishnan, B., Meyyazhagan, A., Sattanathan, G., Pappuswamy, M., Joseph, K. S., Paari, K. A., & Lee, J.-W. (2023). Cadmium as an Endocrine Disruptor That Hinders the Reproductive and Developmental Pathways in Freshwater Fish: A Review. Fishes, 8(12), 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120589