Abstract
The study evaluated the effect of a commercial polyphenol (ELIFE®) on the growth performance and antioxidant defense system of Penaeus vannamei juveniles. The study was completely randomized with three experimental groups and eight repetitions, divided into two 28-day phases. The experimental groups consisted of different dietary inclusion levels of ELIFE® (0.0, 0.5, and 1.0 g kg−1). Five shrimps were stocked in each experimental unit. Growth performance, oxidative stress, and enzymatic activity in shrimp hepatopancreas were assessed. In Phase 1, shrimp fed ELIFE®, regardless of inclusion level, displayed higher specific growth rate, final weight, and final length than the control group. In Phase 2, shrimp fed 1.0 g kg−1 ELIFE® showed higher final biomass and SGR than all other experimental groups; they also displayed increased reduced glutathione and glutathione-S-transferase activities. In both test phases, shrimp fed 1.0 g kg−1 ELIFE® presented increased glutathione reductase activity compared to all other experimental groups. In both test phases, shrimp fed ELIFE®, regardless of inclusion level, exhibited increased glutathione peroxidase activity compared to control groups. Thus, ELIFE® enhanced the antioxidant defense system of P. vannamei and led to better shrimp performance and survival. This study recommends dietary supplementation with 1.0 g kg−1 ELIFE® for P. vannamei juveniles.
Keywords:
feed supplement; enzymatic defense; innate immunity; Pacific white shrimp; oxidative stress Key Contribution:
Dietary polyphenols from ELIFE® improve Penaeus vannamei juveniles’ performance and survival. P. vannamei juveniles fed ELIFE® display an enhanced antioxidant defence system.
1. Introduction
Shrimp farming plays an important role among aquaculture products since 46% of the shrimp consumed worldwide are from shrimp farming [1,2]. Among the species used, the Penaeus vannamei shrimp, popularly known as the Pacific white shrimp, stands out due to its rusticity, adaptation to varied salinities, good feed conversion, growth, and survival [2,3]. Nevertheless, its production has challenges due to the environmental impacts caused by releasing nitrogenous compounds and organic matter in the culture water. It potentially contaminates the ecosystems with pathogens and toxic compounds, decreasing the water quality [4], thus leading to animals in a state of oxidative stress [5].
Oxidative stress may result from the imbalance between the levels of pro-oxidant agents and the antioxidant defense system of shrimp. During the process, the formation of subcomponents harmful to animals also occurs. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) refer to the molecular species involved, which may or may not be free radicals, capable of oxidizing and damaging biomolecules such as lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ROS may appear in different tissues as a product resulting from the incomplete reduction of oxygen molecules or as a by-product of energy metabolism [6,7,8].
To avoid the damage caused by the excess of reactive species, aerobic organisms have developed complex antioxidant defense mechanisms that can be divided into enzymatic and non-enzymatic ones [9]. The enzymatic defense system is composed of enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GR), and glutathione S-transferase (GST). The enzymatic system converts oxidative products (e.g., superoxide anion O2−) into harmless molecules. The non-enzymatic defense system is composed of endogenous molecules such as reduced glutathione (GSH) and other exogenous components from the diet such as vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, carotenoid, selenium, and polyphenols. The non-enzymatic system prevents the formation of new ROS. GSH is among the most relevant non-enzymatic physiological antioxidant responses among the different species. It acts by scavenging free radicals [10,11,12,13,14].
Given these conditions, there is an increasing interest in adopting natural compounds with antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory activities as alternatives to improve the production of aquatic organisms, rather than using antibiotics or synthetic compounds [15,16]. An alternative are natural polyphenol compounds, which are organic compounds with one or more phenolic hydroxyl groups and are generally found in vegetables (e.g., herbs, fruits, and legumes). They have several bioactive functions such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial actions [17,18,19].
In addition, several studies also emphasize the inhibitory potential of pathogenic agents through the use of polyphenols, promoting the improvement of enzymatic activity and nutrient absorption, and enhancing the development of aquatic organisms [20,21,22,23]. These biological effects make polyphenols extremely advantageous for promoting shrimp health. Some studies demonstrate the use of polyphenols in the performance of farmed shrimp [24], which resulted in an increase in immunostimulant and immunomodulating capacities in the fight against oxidative stress, improvement in growth, and an increase in the survival of P. vannamei [12,25].
Thus, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of a commercial polyphenol compound (ELIFE®) on the performance and antioxidant status of P. vannamei, and its potential antimicrobial activity.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Diets
Three experimental groups were evaluated with eight replicates each (n = 8). The experimental groups corresponded to the diets used in the feeding trials, with the inclusion levels of 0.0, 0.5, and 1.0 g kg−1 of ELIFE®. ELIFE®, used in test diets (treatments), is a commercial blend of plant extracts (grape) consisting of synergistic natural polyphenols, mainly flavonoids (e.g., single flavonols, proanthocyanidins, anthocyanins, and flavonols), phenolic acids (e.g., gallic acid), and stilbenes (e.g., resveratrol). It was designed to reduce oxidative stress in animals. Before our study, there was no recommended inclusion level of ELIFE® for decapod crustaceans by the manufacturer. The supplemental doses of ELIFE® tested were selected based on previous research on dietary supplementation for decapods [26,27].
The diets were based on a commercial feed formulation named Guabitech Active® (Table 1; Supplementary Material Table S1). The company Guabi®—Nutrição e Saúde Animal (Sao Paulo, Brazil) provided the mixture, thus allowing the preparation of test diets, with or without the addition of ELIFE® (Supplementary Material Table S2). The exact composition of the mixture was kept confidential by the company. According to the experimental group, the mixture was homogenized and sieved, then 24% hot water at 55 °C was added, and the resulting mixture was again mixed and sieved for homogenization. The mixture obtained was processed using an EXTEEC® extruder (Exteec Máquinas, Ribeirão Preto, São Paulo state, Brazil), with a 2 mm pellet size. After production, the feed was dried in an oven with forced air circulation at 45 °C for 24 h.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of the diet used on Penaeus vannamei feeding trial.
2.2. Experimental Design
The study consisted of two 28-day phases. In the first phase (Phase 1), the use of ELIFE® was assessed during a growth of approximately 2 g to 6 g, while in the second phase (Phase 2), a growth of approximately 6 g to 10 g was assessed. Different groups of animals were used for each test phase. The animals used in the experiment came from the SpeedLine® strain (Aquatec®, Canguaretama, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil).
The study design was a completely randomized design, with 24 tanks (experimental units) with 40 L capacity arranged in a recirculating system containing a mechanical Perlon® wool filter (AquaUra, Uberaba, Minas Gerais, Brazil) and biological filter (AquaUra, Uberaba, Minas Gerais, Brazil), and each one had constant individual aeration. The trial environment was fully controlled, with a photoperiod of 12:12 h (light/dark) in artificial light and temperature maintained at the range of 27 to 30 °C. The water used in the system was obtained from the public water system, dechlorinated, and artificially salinized using RED SEA® (Red Sea, Houston, TX, USA) salt, for a salinity of 15 g L−1. There was no water renewal during the trial period; it was only replaced (5%) to compensate for losses due to evaporation or the syphoning of residues.
In each trial phase, five shrimp were stocked in each experimental unit, totaling 120 P. vannamei juveniles. In the first phase, the initial shrimp weight (mean ± SD) was 1.76 ± 0.16 g; in the second phase, the initial shrimp weight (mean ± SD) was 5.58 ± 0.41 g. The animals underwent a 24 h acclimation period to the test environment, and then the test diets were offered.
The amount of feed offered was calculated based on the expected growth of one gram per week and a feed conversion ratio of 1.5:1 (grammes of feed/shrimp live weight addition) [28,29]. Then, the feed ratio was monitored daily and adjusted in case of death and/or decrease or increase in food consumption [29]. The test diet was supplied five times daily [30], at 5:00 a.m., 9:30 a.m., 1:30 p.m., 5:00 p.m., and 00:00 a.m., by hand and promoting greater food availability. For greater control of food consumption, each tank was visually inspected once a day, to identify the consumption of each unit; for this purpose, the syphoning of excreta and surplus pellets was carried out in the morning of each day and the leftovers were counted.
The water quality parameters, including temperature, dissolved oxygen, pH, and salinity were daily assessed using a GM 380® infrared laser thermometer (Gama, Tatuapé, São Paulo state, Brazil), HANNA® HI 9146 oximeter (Hanna Instruments, Bogotá, Colombia), LUCADEMA® 210 (Lucadema Soluções para Laboratório, São José do Rio Preto, Brazil), and RHB0—90® analogue refractometer (Akso Instrumentos de Medição, São Leopolodo, Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil), respectively. The concentrations of nitrogen compounds were analyzed weekly. The nitrite concentration was evaluated by applying the Griess reaction colorimetric method, and the total ammonia concentration by the indophenol colorimetric method. Alkalinity was monitored on the 1st, 14th, and 28th day of each trial phase by titration [31].
The observed water quality parameters for Phase 1 were as follows (mean ± SD): temperature (28.72 ± 0.55 °C), pH (7.54 ± 0.02), dissolved oxygen (5.48 ± 0.24 mg L−1), total alkalinity (131.50 ± 23.28 mg L−1 of CaCO3), total ammonia (0.06 ± 0.02 mg L−1), nitrite (0.12 ± 0.01 mg L−1), and salinity (13.99 ± 1.23 g L−1).
In Phase 2, the observed water parameters were as follows (mean ± SD): temperature (28.14 ± 0.74 °C), pH (7.74 ± 0.03), dissolved oxygen (5.51 ± 0.42 mg L−1), total alkalinity (124.16 ± 16.19 mg L−1 of CaCO3), total ammonia (0.08 ± 0.07 mg L−1), nitrite (0.02 ± 0.002 mg L−1), and salinity (13.87 ± 0.77 g L−1).
2.3. Growth Parameters
After assay completion, all animals were counted, weighed, and measured individually, and the following were determined [32,33]:
2.4. Shrimp Hepatopancreas Collection and Processing
At the end of each trial phase, 15 animals (n = 15) per experimental group were randomly collected and euthanized by thermal shock (iced water, 5 min). The shrimp body surface was then sterilized with ethanol (70%, v/v) and their hepatopancreas were collected to analyze the activity of enzymes related to shrimp’s antioxidant defense system. The hepatopancreas samples were homogenized using a tissue homogenizer in a solution containing PBS, pH 7.2, and then centrifuged at 2800× g for 10 min at 4 °C. The supernatants were separated for further measurements.
2.5. Biochemical Analysis
Protein content on shrimp hepatopancreas was determined by the method of Bradford [34], using bovine albumin as reference and absorbance reading at 595 nm. Results were expressed in mg mL−1.
Glutathione reductase (GR) activity was determined using the methodology of Carlberg and Mannervik [35], and the results were expressed in µmol of NADPH/min/mg protein. Glutathione S-transferase (GST) activity was determined through spectrophotometry according to Habig et al. [36] and the values expressed as nmol of thioether/min/mg protein. Catalase (CAT) activity was determined according to the method described by Aebi [37] and the values expressed in µmol of H2O2/min/mg protein. Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity was determined by the methodology of Wendel [38], and the values were expressed as µmol of NADPH/min/mg protein. Reduced glutathione (GSH) levels were measured by the non-protein thiols method according to the methodology proposed by Sedlak and Lindsay [39] using a GSH standard curve, and the values were expressed in µM/mg protein.
The levels of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (lipid peroxidation—TBARS) were measured in the supernatant of hepatopancreas homogenates. For sample preparation, the medium containing an aliquot of 0.33 mg mL−1 of sample protein and 6.7% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) in a final volume of 180 μL was vortexed, left in an ice bath for five minutes, and then centrifuged for five minutes at 13,200× g at 4 °C. Afterwards, 40 μL of the supernatant was incubated with reaction medium containing butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) 0.007 mg mL−1 in 95% ethanol, thiobarbituric acid (TBA) 3.1 mg mL−1 in 0.3% NaOH, and 7.9% TCA in PBS, in a total volume of 315 μL, for 60 min at 60 °C. After that, the material was cooled, and the pink chromophore was measured through spectrophotometry at 535 nm. The values were expressed in µM MDA mg−1 protein, from a calibration curve prepared with malondialdehyde (MDA) under the same analysis conditions [40].
2.6. Statistical Analyses
All the results of the variables analyzed were submitted for the verification of normality and homoscedasticity assumptions. The results related to zootechnical performance and enzymatic activity were statistically evaluated by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). When significant differences were detected, data were submitted to Tukey’s mean comparison test. For all statistical tests, α = 5% was applied.
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
Regarding the zootechnical performance at the end of Phase 1, significant differences were observed between the treatments with ELIFE® supplementation and the control group for final average weight, final average length, and SGR. The SGR, final weight, and final average length of P. vannamei were higher in both treatments with ELIFE® supplementation. For the final biomass and FCR variables, the treatment with the addition of 1.0 g kg−1 of ELIFE® was better than the control group (0.0 g kg−1 of ELIFE®) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Results of zootechnical performance parameters of P. vannamei juveniles fed with and without supplementation of a commercial polyphenol compound, ELIFE®, at the end of Phase 1.
At the end of Phase 2, significant differences were observed in treatments with ELIFE® supplementation for survival, final biomass, SGR, and FCR. The treatment with the addition of 1.0 g kg−1 of ELIFE® presented a survival significantly higher than the treatment with 0.5 g kg−1 of ELIFE®, and both treatments were significantly higher than survival in the control group (0.0 g kg−1 of ELIFE®). The final biomass and SGR were significantly higher in the treatment with the addition of 1.0 g kg−1 of ELIFE® than in the treatment with 0.5 g kg−1 of ELIFE® and the control group (0.0 g kg−1 of ELIFE®). For FCR, both treatments with ELIFE® supplementation were significantly higher than the control group and similar to each other (Table 3).

Table 3.
Results of zootechnical performance parameters of P. vannamei juveniles fed with and without supplementation of a commercial polyphenol compound, ELIFE®, at the end of Phase 2.
3.2. Antioxidant Defense System
Among the parameters of oxidative stress, the CAT enzyme activity in the hepatopancreas of P. vannamei juveniles did not change significantly in both test phases, i.e., Phases 1 and 2 (Figure 1A,B), whereas there was a significant increase (p < 0.05) in GR enzyme activity at the highest level of addition of ELIFE® to the shrimp diet (1.0 g kg−1), in both trial phases (Figure 1C,D).
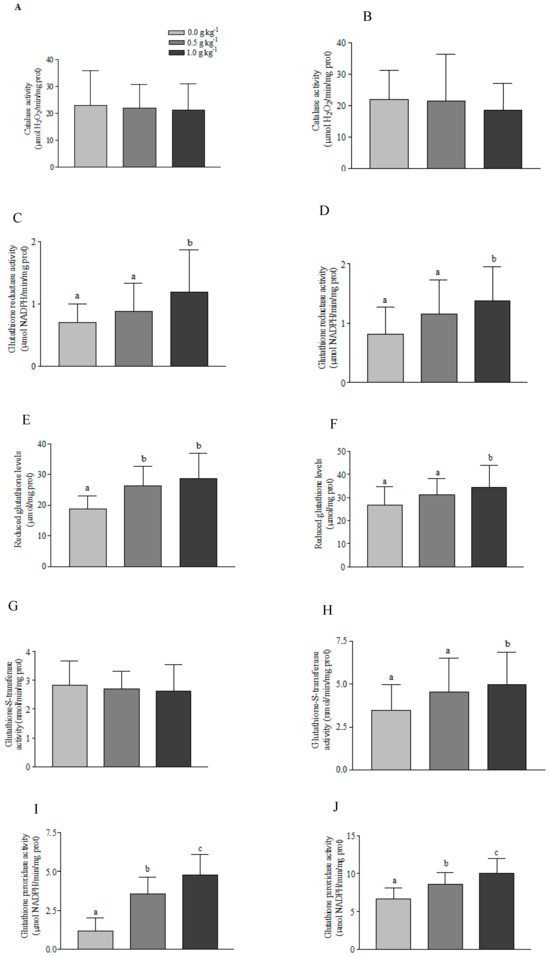
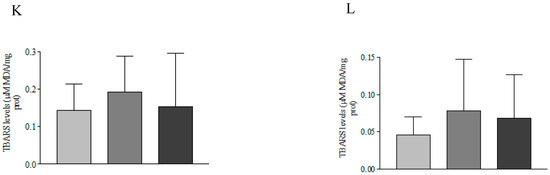
Figure 1.
Antioxidant activity in the hepatopancreas of Penaeus vannamei juveniles fed without and with two inclusion levels of a commercial polyphenol compound, ELIFE®, in two trial phases. (A): Catalase (Phase 1). (B): Catalase (Phase 2). (C): Glutathione reductase (Phase 1). (D): Glutathione reductase (Phase 2). (E): Reduced glutathione (Phase 1). (F): Reduced glutathione (Phase 2). (G): Glutathione S-transferase (Phase 1). (H): Glutathione S-transferase (Phase 2). (I): Glutathione peroxidase (Phase 1). (J): Glutathione peroxidase (Phase 2). (K): Lipid peroxidation (phase 1). (L): Lipid peroxidation (Phase 2). Different letters above bars indicate significant difference between experimental groups (p < 0.05).
In Phase 1, a significant increase (p < 0.05) was observed in the levels of GSH in the hepatopancreas of P. vannamei juveniles in both treatments with ELIFE® supplementation compared to the control group (Figure 1E). However, in Phase 2, only the treatment with 1.0 g kg−1 of ELIFE® presented a GSH concentration in the hepatopancreas of shrimp juveniles significantly higher than the control group (Figure 1F), whereas in Phase 1, the addition of ELIFE® did not impact the activity of the hepatopancreatic GST enzyme in P. vannamei juveniles. In Phase 2, there was a significant increase in the activity of the hepatopancreatic GST enzyme of shrimp juveniles when submitted to the highest concentration tested (1.0 g kg−1 of ELIFE®) compared to the control group (Figure 1G,H).
The hepatopancreatic GPx enzyme activity in P. vannamei juveniles displayed a significant increase (p < 0.05) in both trial phases. Both ELIFE® concentrations tested (0.5 and 1.0 g kg−1) caused an increase in activity when compared to the respective controls and between treatment groups (Figure 1I,J), whereas lipid peroxidation, assessed through a TBARS assay, did not show significant change (p > 0.05) in any of the experimental groups (Figure 1K,L).
4. Discussion
Polyphenols are plant-derived compounds with beneficial biological activities, promoting improvement in growth performance parameters, body composition, and digestive enzyme activities. Polyphenols also mitigate oxidative stress, increase the antioxidant status of fish, improve immune responses, and increase resistance against infectious diseases. In recent years, a growing number of studies have explored the use of polyphenols and polyphenol-rich additives in aquaculture as functional feed additives [41]. However, the use of commercially available polyphenols, such as ELIFE®, is more advantageous, since commercially available extracts are standardized according to polyphenol concentration, allowing a precise assessment of the inclusion level and allowing reproducible results to be obtained [42].
The positive results of the use of products that contain polyphenols in the zootechnical performance of shrimp in this study, where the growth parameters were higher in the treatments with ELIFE® supplementation in both phases, corroborate those reported by Niyamosatha et al. [43] and Niti Chuchird [44]. This indicates the potential use of natural compounds such as polyphenolics in the feeding of farmed aquatic organisms. Likewise, during Phase 2, supplementation with ELIFE® promoted a significant increase in survival, FCR, SGR, and final biomass results. These variables where supplementation promoted benefits are directly listed as the performance indicators that most influence profitability in all stages of shrimp farming [45]. One may note worse FCR in shrimp fed the control diet than shrimp fed 0.5 g kg−1 of ELIFE®, even if the first group displayed a larger final average weight, although non-significant, in Phase 2. This may have happened due to the significantly higher survival rate in shrimp fed ELIFE® than in the control group. Likewise, as FCR accumulates the error of feed intake and weight gain, the largest standard deviation observed on shrimp from the control group may have contributed to those results.
These results are directly related to the properties of phytogenic compounds that can benefit the activity of digestive enzymes and the absorption of nutrients, improving FCR and contributing to shrimp growth performance and activity profitability. Considering that ELIFE® is a product based on polyphenolic compounds, the growth performance results observed in this study may be due to the influence of these compounds on the digestive process, increasing the activity of digestive enzymes and improving nutrient absorption.
In addition to the potential effect of phenolic compounds as metabolism modulators, another great advantage of their application in aquafeeds is the potential antioxidant effect of this group of compounds. The antioxidant properties of polyphenols are related to the presence and number of phenolic rings, which neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), including peroxy radicals, superoxide anions, and hydroxyl radicals, absorbing electrons and neutralizing them [42]. In this study, the supplementation of ELIFE® polyphenols in the shrimp diet improved the antioxidant status of the animals, observed by the increases in the GSH content and the activities of GR and GPx, without change in the activity of CAT and lipid peroxidation levels (TBARS) in the two trial phases.
GR and GPx are key enzymes in the glutathione cycle and in the defense and neutralization of reactive species. GSH is one of the endogenous molecules with antioxidant action that acts in neutralization reactions by transferring electrons or directly binding to various types of reactive species. Through the action of GPx, GSH provides electrons to hydrogen peroxide, transforming it into water and assuming the form of oxidized glutathione. Oxidized glutathione is further reduced by the action of GR using electrons originating from NADPH, closing the glutathione cycle. The increase in GPx activity observed in this study allows the cell to be prepared for the neutralization of reactive species, especially the hydrogen peroxide that may be formed. This way, there is a CAT activity complement that was not influenced by the addition of ELIFE® polyphenols in the shrimp diet. Also, increases in GSH content and GR activity in the recycling of oxidized glutathione ensure the necessary reducing power (source of electrons) for ROS neutralization reactions under stressful conditions for the animals. In addition, the absence of changes in the levels of lipid peroxidation (TBARS) in the hepatopancreas of shrimp reinforces the modulating role of the antioxidant defense system of the polyphenols present in ELIFE®.
In addition to the redox cycle, glutathione also participates in the biotransformation reactions of chemical compounds, specifically in the conjugation reactions catalyzed by GST, forming substances of low toxicity/high solubility [5]. The increase in GST activity and the greater availability of GSH suggest that the phenolic compounds present in ELIFE® can improve the biotransformation capacity of cells. Phenolic compounds can abduct or even inhibit ROS, enabling animals to metabolize xenobiotics more efficiently, reducing the potential damage of these chemical substances, and favoring detoxification. They are of great importance since ROS are highly toxic and with the potential to damage proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, resulting in cellular lesions such as mutations and lipid peroxidation [46,47].
The supplementation of ELIFE®, which contains polyphenols, in the diet of P. vannamei benefited the activity of enzymes that act to improve the antioxidant status of the animals. The use of the product provided a better absorption of nutrients and, consequently, better FCR, resulting in greater production of final biomass, generating more profitability for the activity.
5. Conclusions
Supplementation with grape polyphenols from the commercial compound ELIFE® in the Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) diet played a modulating role in the antioxidant defense system, promoting an improvement in the antioxidant status of the animals, and resulting in better FCR and SGR, and increased survival and final biomass, thus recommending the supplementation of 1.0 g kg−1 ELIFE®. Further studies can assess the potential wider pharmacodynamic effects of ELIFE®, such as antiviral and antimicrobial effects and the promotion of gut microbiota health. Likewise, the key mechanisms of ELIFE®’s bioactivity and its bioavailability along the shrimp’s liver and intestinal tract can be further investigated.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fishes9100410/s1, Table S1:Ingredients of the diet (Guabitech Active®, Guabi®—Nutrição e Saúde Animal, Sao Paulo, Brazil) used in Penaeus vannamei feeding trial, based on the technical report made available by the company. Table S2: Guaranteed levels of ingredients on diet Guabitech Active®, Guabi®—Nutrição e Saúde Animal, Sao Paulo, Brazil) used in Penaeus vannamei feeding trial, based on the company’s technical reportGuaranteed levels of ingredients on diet Guabitech Active®, Guabi®—Nutrição e Saúde Animal, Sao Paulo, Brazil) used in Penaeus vannamei feeding trial, based on the company’s technical report.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: E.L.C.B. and L.R.; Resources and funding acquisition: E.L.C.B.; Methodology: H.D.F.C. and C.H.d.N.F.; Formal analysis: C.H.d.N.F., M.C.R. and L.H.C.; Writing—original draft preparation: H.D.F.C. and L.R.; Writing—review and editing: I.V.Z., C.d.S.V. and E.L.C.B.; Supervision: E.L.C.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Council of Technological and Scientific Development (CNPq), Brazil, under grant № PQ 311456/2020-0, to Prof. Eduardo Luis Cupertino Ballester.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to the current absence of animal protective legislation that includes decapod crustaceans in Brazil (Law № 11.794, 2008, Brazil). This study did not involve humans or vertebrates.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
This study was part of Hallypher Deyrrikson Ferreira Colares’s Master’s dissertation. Impextraco® Latin American donated the commercial product analysed in this study. This did not affect, alter, or influence this research’s development, including the experimental design, data analysis and interpretation, and decision for publication. No patent or market product under development is related to this study. The authors declare no other conflicts of interest.
References
- Mălina Petrescu-Mag, R.; Păsărin, B.; Gigi Şonea, C.; Petrscu-Mag, I.V. Customer preferences and trends for aquarium fish in Transylvania (Romania). North-West. J. Zool. 2013, 9, 166. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2020. In Sustainability in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ravichndran, P.; Panigrahi, A.; Kumaran, M. Biology and culture of Litopenaeus vannamei vis-Ã-vis Penaeus monodon. In Handbook on Seed Production and Farming of Litopenaeus vannamei; Central Institute of Brackishwater Aquaculture (CIBA), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR): New Delhi, India, 2009; Volume 46, p. 70. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalheiro, T.B.; Carvajal, J.C.L.; de Lucena, R.F.P.; do Nascimento, C.V.C.; Ribeiro, T.T.B.C. Water parameters correlated with the zootechnical performance of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei grown in oligohaline waters. Acta Scientiarum. Anim. Sci. 2022, 45, e57700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: A concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhao, D.; Wang, L.; Sun, M.; Wang, M.; Song, L. Ammonia exposure induces oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in hepatopancreas of pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banh, S.; Wiens, L.; Sotiri, E.; Treberg, J.R. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production by fish muscle mitochondria: Potential role in acute heat-induced oxidative stress. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 191, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comporti, M. Free radicals, oxidative stress and antioxidants. J. Siena Acad. Sci. 2010, 2, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kütter, M.; Romano, L.; Ventura-Lima, J.; Tesser, M.; Monserrat, J. Antioxidant and toxicological effects elicited by alpha-lipoic acid in aquatic organisms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 162, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K. Reduced glutathione supplementation in practical diet improves the growth, anti-oxidative capacity, disease resistance and gut morphology of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 73, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.M.; Liu, J.-H.; Shu, L.-H.; Chen, C.H. Anti-oxidative responses of zebrafish (Danio rerio) gill, liver and brain tissues upon acute cold shock. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 187, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, S.C.; Klein, R.D.; Costa, P.G.; Crivellaro, M.S.; Santos, S.; de Siqueira Bueno, S.L.; Bianchini, A. Phylogenetic and environmental components of inter-specific variability in the antioxidant defense system in freshwater anomurans Aegla (Crustacea, Decapoda). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, S.R. Medicinal uses of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) improves growth and enhances immunity in aquaculture. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2015, 3, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, E.; Awaad, A. Role of medicinal plants on growth performance and immune status in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, F.F.; de Paulo Farias, D.; Neri-Numa, I.A.; Pastore, G.M. Polyphenols and their applications: An approach in food chemistry and innovation potential. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Ishiyama, K.; Sheng, H.; Ikai, H.; Kanno, T.; Niwano, Y. Bactericidal activity and mechanism of photoirradiated polyphenols against gram-positive and-negative bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7707–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasingha, W.; Wijendra, W.; Karunaratne, D.; Liyanapathirana, V.; Ekanayake, E.M.; Jayasinghe, S.; Karunaratne, V. Antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, brine shrimp lethality and polyphenolic content of Holarrhena mitis (Vahl) R. Br. ex Roem. & Schult. Ceylon J. Sci. 2018, 47, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Wink, M.; Schimmer, O. Modes of action of defensive secondary metabolites. In Annual Plant Reviews Online; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 18–137. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, E.-Q.; Deng, G.-F.; Guo, Y.-J.; Li, H.-B. Biological activities of polyphenols from grapes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 622–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landete, J. Updated knowledge about polyphenols: Functions, bioavailability, metabolism, and health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D Archivio, M.; Filesi, C.; Di Benedetto, R.; Gargiulo, R.; Giovannini, C.; Masella, R. Polyphenols, dietary sources and bioavailability. Ann.-Ist. Super. Sanita 2007, 43, 348. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Martins, Á.C.; Artigas Flores, J.; Porto, C.; Romano, L.A.; Wasielesky Junior, W.; Caldas, S.S.; Primel, E.G.; Külkamp-Guerreiro, I.; Monserrat, J.M. Antioxidant effects of nanoencapsulated lipoic acid in tissues and on the immune condition in haemolymph of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931). Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh Asadi, M.; Gharaei, A.; Mirdar Harijani, J.; Arshadi, A. A Comparison between dietary effects of Cuminum cyminum essential oil and Cuminum cyminum essential oil, loaded with iron nanoparticles, on growth performance, immunity and antioxidant indicators of white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesselring, J.; Gruber, C.; Standen, B.; Wein, S. Effect of a phytogenic feed additive on the growth performance and immunity of Pacific white leg shrimp, fed a low fishmeal diet. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2021, 52, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.M.; Kien, N.T.; Thanh Thuy, N.T. Effects of dietary mannan oligosaccharide on growth, survival, physiological, immunological and gut morphological conditions of black tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon Fabricius 1798). Aquac. Nutr. 2014, 20, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.; McNevin, A.A. Overview of aquaculture feeds: Global impacts of ingredient production, manufacturing, and use. In Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, G.; Hostins, B.; Bezerra, A.; Poersch, L.; Wasielesky, W. The effects of different feeding rates and re-feeding of Litopenaeus vannamei in a biofloc culture system. Aquac. Eng. 2017, 77, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Aquaculture Feed and Fertilizer Resources Information System. In Species Profile; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Servin Arce, K.; de Souza Valente, C.; do Vale Pereira, G.; Shapira, B.; Davies, S.J. Modulation of the gut microbiota of Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei Boone, 1931) by dietary inclusion of a functional yeast cell wall-based additive. Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 1114–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.-C.; Li, C.-C.; Liu, C.-W.; Chi, S.-Y.; Yang, Q.-H. Effects of dietary lipid sources on growth and fatty acid composition of juvenile shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Nutr. 2007, 13, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, I.; Mannervik, B. [59] Glutathione reductase. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985; pp. 484–490. [Google Scholar]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Fleischner, G.; Gatmaitan, Z.; Arias, I.M.; Jakoby, W.B. The Identity of Glutathione -S-Transferase B with Ligandin, a Major Binding Protein of Liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 3879–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. [13] Catalase in vitro. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1984; pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wendel, A. [44] Glutathione peroxidase. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1981; pp. 325–333. [Google Scholar]
- Sedlak, J.; Lindsay, R.H. Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal. Biochem. 1968, 25, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, G.; Shaw, B.J.; Handy, R.D. Toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Gill injury, oxidative stress, and other physiological effects. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 84, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadifar, E.; Yousefi, M.; Karimi, M.; Fadaei Raieni, R.; Dadar, M.; Yilmaz, S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R. Benefits of Dietary Polyphenols and Polyphenol-Rich Additives to Aquatic Animal Health: An Overview. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 29, 478–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Bagheri, D.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Morshedi, V.; Paolucci, M. Beneficial role of polyphenols as feed additives on growth performances, immune response and antioxidant status of Lates Calcarifer (Bloch, 1790) juveniles. Aquaculture 2022, 552, 737955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyamosatha, H.; Chuchird, N.; Rairat, T. Effect of Dietary Polyphenol-Rich Feed Additive from Grape Pomace on Growth, Survival and Tolerance to Vibrio Infection in Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). J. Fish. Environ. 2015, 39, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Niti Chuchird, H.N. Tirawat Rairat and Arunothai Keetanon. Effect of Dietary Phytobiotics Products on Growth, Immune Responses and Vibriosis Resistance in Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 12, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Velazco, J.M.J.; González-Romero, M.A.; Estrada-Perez, N.; Hernandez-Llamas, A. Evaluating partial harvesting strategies for whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus (Penaeus) vannamei semi-intensive commercial production: Profitability, uncertainty, and economic risk. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, D.K.; Ringseis, R.; Eder, K. Potential of plant polyphenols to combat oxidative stress and inflammatory processes in farm animals. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 101, 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, T.; Farrar, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, X. Antioxidants Maintain Cellular Redox Homeostasis by Elimination of Reactive Oxygen Species. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 532–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).