Population Genetic Differentiation of Walleye (Sander vitreus) across the Eastern Highlands of the United States
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Microsatellite Markers
2.3. Data Analysis
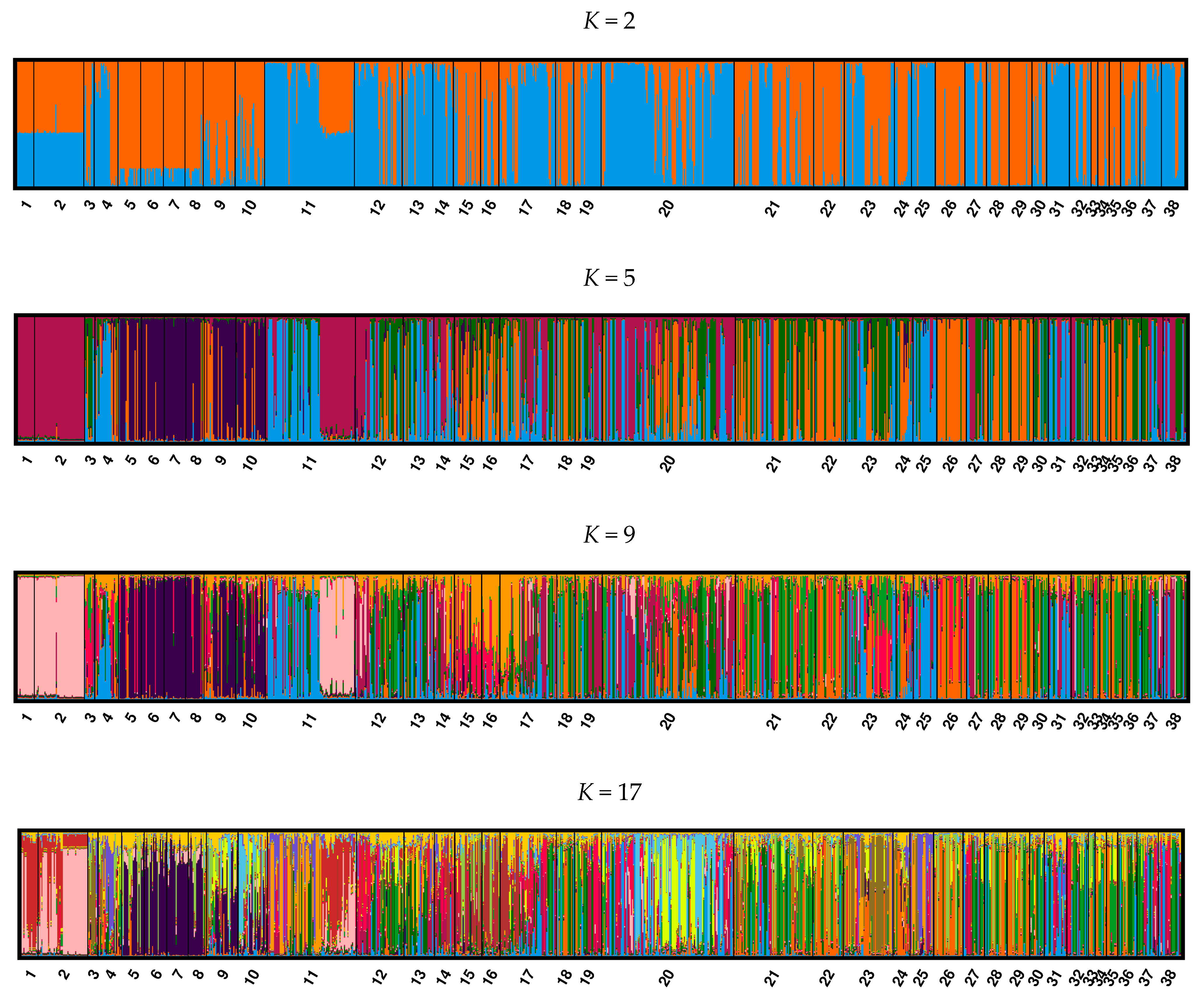
3. Results
3.1. Range-Wide Analysis of Individual Population Samples
3.2. Range-Wide Analysis of Population Assemblages within Watersheds
3.3. Mississippi-Tennessee-New-Ohio-Great Lakes Watersheds
3.4. Mississippi-Tennessee-New Watersheds
3.5. Mobile Bay—Tennessee Watersheds
4. Discussion
4.1. Population Genetic Processes within Walleye Populations
4.2. Genetic Differentiation of Walleye Populations
4.3. Inferences Regarding Natural History
4.4. Management Implications
4.5. Future Work
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Billington, N.; Hebert, P.D.N. Mitochondrial DNA variation in Great Lakes Walleye (Stizostedion vitreum) populations. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 45, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepien, C.A.; Faber, J.E. Population genetic structure, phylogeography and spawning philopatry in Walleye (Stizostedion. vitreum) from mitochondrial DNA control region sequences. Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 1757–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.R. Evidence for a genetically unique Walleye population in the upper Tombigbee River system of northeastern Mississippi. Southeast. Fishes Counc. Proc. 1990, 22, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Billington, N.; Maceina, M. Genetic and population characteristics of Walleyes in the Mobile drainage of Alabama. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1997, 126, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billington, N.; Strange, R.M. Mitochondrial DNA analysis confirms the existence of a divergent Walleye population in Northeastern Mississippi. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1995, 124, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Silliman, K.; Lewis, M.; Johnson, S.; Kratina, G.; Rider, S.J.; Stepien, C.A.; Hallerman, E.M.; Beck, B.; Fuller, A.; et al. SNP discovery and panel development for genetic identification and hybridization analysis in Walleye, Sander vitreus. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 77, 1366–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strange, R.M.; Stepien, C.A. Genetic divergence and connectivity among river and reef spawning groups of Walleye (Sander vitreus vitreus) in Lake Erie. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 64, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepien, C.A.; Banda, J.A.; Murphy, D.M.; Haponski, A.E. Temporal and spatial genetic consistency of Walleye spawning groups. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2012, 14, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haponski, A.E.; Stepien, C.A. Genetic connectivity and diversity of walleye (Sander vitreus) spawning groups in the Huron–Erie Corridor. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepien, C.A.; Murphy, D.J.; Lohner, R.N.; Sepulveda-Villet, O.J.; Haponski, A.E. Signatures of vicariance, postglacial dispersal and spawning philopatry: Population genetics of the Walleye Sander vitreus. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 3411–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepien, C.A.; Murphy, D.J.; Lohner, R.N.; Haponski, A.E.; Sepulveda-Villet, O.J. Status and delineation of Walleye (Sander vitreus) genetic stock structure across the Great Lakes. In Status of walleye in the Great Lakes: Proceedings of the 2006 symposium. Great Lakes Fish. Comm. Technol. Rep. 2010, 69, 189–223. [Google Scholar]
- Euclide, P.T.; Larson, W.A.; Bootsma, M.; Miller, L.M.; Scribner, K.T.; Stott, W.; Wilson, C.C.; Latch, E.K. A new GTSeq resource to facilitate multijurisdictional research and management of Walleye Sander vitreus. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, C.B.; Hilling, C.D.; Orth, D.J. Egg Size Variation among Walleye in Virginia. Unpublished manuscript, 2023.
- Billington, N.; Sloss, B.L. Mitochondrial DNA and allozyme analysis of Walleyes from the Rockcastle River and the Cumberland River (Big South Fork), Kentucky. In Report of Cooperative Fisheries Research Laboratory; Southern Illinois University to Kentucky Department of Fish and Wildlife Resources: Frankfort, KY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- White, M.M.; Faber, J.E.; Zipfel, K.J. Genetic identity of Walleye in the Cumberland River. Am. Midl. Nat. 2012, 167, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.M.; Kassler, T.W.; Philipp, D.P.; Schell, S.A. A genetic assessment of Ohio River Walleyes. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2005, 134, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, G.C.; Culver, M.; Dutton, D.; Murphy, B.R.; Hallerman, E.M.; Billington, N.; Williams, J. Genetically distinct Walleye stocked in Claytor Lake and the Upper New River, Virginia. Proc. Southeast Assoc. Fish. Wildl. Agencies 2006, 60, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Billington, N.; Barrette, R.J.; Hebert, P.D.N. Management implications of mitochondrial DNA variation in Walleye stocks. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1992, 12, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haponski, A.E.; Sloss, B.L. Distribution and population genetics of Walleye and Sauger. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 133. [Google Scholar]
- Borer, S.; Miller, L.M.; Kapuscinski, A.R. Microsatellites in Walleye Stizostedion vitreum. Mol. Ecol. 1999, 8, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wirth, T.; Saint-Laurent, R.; Bernatchez, L. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci in the Walleye (Stizostedion vitreum), and cross-species amplification within the family Percidae. Mol. Ecol. 1999, 8, 1960–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, W.E.; Bacigalupi, M.D.; Adelman, I.R.; Miller, L.M.; Kapuscinski, A.R. Determination of relative survival of two stocked Walleye populations and resident natural-origin fish by microsatellite DNA parentage assignment. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cena, C.J.; Morgan, G.E.; Malette, M.D.; Heath, D.D. Inbreeding, outbreeding and environmental effects on genetic diversity in 46 Walleye (Sander vitreus) populations. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite, version 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 10, 310–322. [Google Scholar]
- Van Oosterhout, C.; Hutchinson, W.F.; Willis, D.P.M.; Shipley, P. MICRO-CHECKER: Software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, M.H.; Williamson, E.G. Detection of reduction in population size using data from microsatellite loci. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 10, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopelman, N.M.; Mayzel, J.; Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A.; Mayrose, I. CLUMPAK: A program for identifying clustering modes and packaging population structure inferences across K. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 5, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earl, D.A.; von Holdt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, C.; Waples, R.S.; Peel, D.; Macbeth, G.M.; Tillett, B.J.; Ovenden, J.R. NeEstimator v2: Re-implementation of software for the estimation of contemporary effective population size (Ne) from genetic data. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, S.T.; Wagner, A.P.; Taper, M.L. ML-Relate: A computer Program for maximum likelihood estimation of relatedness and relationship. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, J. A simple sequentially rejective Bonferroni test procedure. Scand. J. Stat. 1979, 6, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, G.C.; Williams, J.; Scott, M.; Finne, K.; Johnson, N.; Dutton, D.; Murphy, B.R.; Hallerman, E.M. Genetic marker-assisted restoration of the presumptive native Walleye fishery in the New River, Virginia and West Virginia. Proc. Annu. Conf. Southeast. Assoc. Fish Wildl. Agencies 2007, 61, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, G.I. The course of the Tennessee River and the physiography of the southern Appalachian region. J. Geol. 1928, 36, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haponski, A.E.; Dean, H.; Blake, B.; Stepien, C.A. Genetic history of walleye (Sander vitreus) spawning in Lake Erie’s Cattaraugus Creek: A comparison of pre- and post-stocking. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2014, 143, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.J.; Bozek, M.A.; Newby, J.R.; Newman, S.P.; Staggs, M.D. Factors affecting recruitment of walleyes in Escanaba Lake, Wisconsin, 1958–1996. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1998, 18, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozek, M.A.; Baccante, D.A.; Lester, N.P. Walleye and sauger life history. In Biology, Management, and Culture of Walleye and Sauger; Barton, B.A., Ed.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2011; pp. 233–301. [Google Scholar]
- Crowe, W.R. Homing behavior in walleyes. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1962, 91, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, M.J.; Claussen, J.E.; Philipp, D.P. Evidence for heritable preferences for spawning habitat between two Walleye populations. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1996, 125, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, T.T.; Binder, T.R.; Holbrook, C.M.; Vandergoot, C.S.; Fielder, D.G.; Cooke, S.J.; Dettmers, J.M.; Krueger, C.C. Spawning site fidelity and apparent annual survival of Walleye (Sander vitreus) differ between a Lake Huron and Lake Erie tributary. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2018, 27, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryman, N.; Laikre, L. Effects of supportive breeding on the genetically effective population size. Conserv. Biol. 1991, 5, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franckowiak, R.P.; Sloss, B.L.; Bozek, M.A.; Newman, S.P. Temporal effective size estimates of a managed Walleye Sander vitreus population and implication for genetic-based management. J. Fish Biol. 2009, 74, 1086–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, M.D.; Sloss, B.L.; Isermann, D.A. Relationships among Walleye population characteristics and genetic diversity in northern Wisconsin lakes. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2014, 143, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayden, R.L. Vicariance biogeography, parsimony, and evolution in North American freshwater fishes. Syst. Biol. 1988, 37, 329–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingo, W.M. Characteristics of Walleye in the Tombigbee River and Tributaries. Master’s Thesis, Mississippi State University, Starkville, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Stepien, C.A.; Sepulveda-Villet, O.J.; Haponski, A.E. Comparative genetic diversity, population structure, and adaptations of Walleye and Yellow Perch across North America. In Biology and Culture of Percid Fishes: Principles and Practices; Kestemont, P., Dabrowski, K., Summerfelt, R.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 643–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda-Villet, O.J.; Stepien, C.A. Waterscape genetics of the Yellow Perch (Perca flavescens): Patterns across large connected ecosystems and isolated relict populations. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 5795–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.C.; Hebert, P.D.N. Phylogeographic origins of Lake Trout (Salvelinus nemaycush) in eastern North America. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1996, 53, 2764–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatchez, L.; Wilson, C.C. Comparative phylogeography of Nearctic and Palearctic fishes. Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazyak, D.C.; Lubinski, B.A.; Kulp, M.A.; Pregler, K.C.; Whiteley, A.R.; Hallerman, E.; Coombs, J.A.; Kanno, Y.; Rash, J.M.; Morgan, R.P.; et al. Population genetics of Brook Trout in the southern Appalachian Mountains. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2022, 151, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatchez, L.; Dodson, J.J. Phylogenetic relationships among Palearctic and Nearctic whitefish (Coregonus sp.) populations as revealed by mitochondrial DNA variation. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1994, 51 (Suppl. 1), 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Allendorf, F.W.; Luikart, G. Conservation and the Genetics of Populations; Blackwell Publishing: Malden, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Ryder, O. Species conservation and systematics: The dilemma of subspecies. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1986, 1, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizon, A.E.; Lockyear, C.; Perrin, W.F.; Demaster, D.P.; Sisson, J. Rethinking the stock concept—A phylogeographic approach. Conserv. Biol. 1992, 6, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waples, R.S. Pacific salmon, Oncorhynchus spp., and the definition of “species” under the Endangered Species Act. Mar. Fish. Rev. 1991, 53, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Avise, J.C. Phylogeography: The History and Formation of Species; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hohenlohe, P.A.; Bassham, S.; Etter, P.D.; Stiffler, N.; Johnson, E.A.; Cresko, W.A. Population genomics of parallel adaptation in Threespine Stickleback using sequenced RAD tags. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFaveri, J.; Shikano, T.; Shimada, Y.; Goto, A.; Merila, J. Global analysis of genes involved in freshwater adaptation in Threespine Sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Evolution 2011, 65, 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, W.A.; Seeb, L.W.; Everett, M.V.; Waples, R.K.; Templin, W.D.; Seeb, J.E. Genotyping by sequencing resolves shallow population structure to inform conservation of Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.S.; Bourret, V.; Dionne, M.; Bradbury, I.; O’Reilly, P.; Kent, M.; Chaput, G.; Bernatchez, L. Conservation genomics of anadromous Atlantic salmon across its North American range: Outlier loci identify the same patterns of population structure as neutral loci. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 5680–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackiss, A.S.; Larson, W.A.; Stott, W. Genotyping-by-sequencing illuminates high levels of divergence among sympatric forms of coregonines in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 1037–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Nie, H.; Huo, Z.; Ding, J.; Li, Z.; Yan, L.; Jiang, L.; Mu, Z.; Wang, H.; Meng, X.; et al. Clam genome sequence clarifies the molecular basis of its benthic adaptation and extraordinary shell color diversity. Iscience 2019, 19, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, A.B.; Wolf, J.B.; Alves, P.C.; Bergström, L.; Bruford, M.W.; Brännström, I.; Colling, G.; Dalén, L.; De Meester, L.; Ekblom, R.; et al. Genomics and the challenging translation into conservation practice. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benestan, L.M.; Ferchaud, A.L.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Garner, B.A.; Naylor, G.J.; Baums, I.B.; Schwartz, M.K.; Kelley, J.L.; Luikart, G. Conservation genomics of natural and managed populations: Building a conceptual and practical framework. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 2967–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenlohe, P.A.; Funk, W.C.; Rajora, O.P. Population genomics for wildlife conservation and management. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 62–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Major Drainage | River | Location | Number (Year) | Provided by |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New | New River, VA | Foster Falls, VA, USA | 23 (2015–2016) | Virginia Department of Wildlife Resources |
| Ivanhoe, VA, USA | 23 (2015–2016) | |||
| Native New River-spawning individuals | 320 (2008, 2017–2018) | |||
| Ohio | Barren River | Barren River, KY, USA | 69 (2017) | Kentucky Dept. of Fisheries and Wildlife Resources |
| Rockcastle River | Rockcastle River, KY, USA | 43 (2017–2018) | ||
| Big Sandy River | Levisa Fork, KY, USA | 8 (2017–2018) | ||
| Russell Fork, KY, USA | 7 (2017–2018) | |||
| Goose Creek, KY, USA | 26 (2018) | |||
| Allegheny River | Allegheny River, PA, USA | 20 | ||
| Tennessee | Clinch River | Ft. Blackmore, VA, USA | 20 (2016–2017) | Virginia Department of Wildlife Resources |
| Clinchport, VA, USA | 20 (2015–2017) | |||
| Dungannon, VA, USA | 10 (2015–2017) | |||
| Burton’s Ford, VA, USA | 13 (2015–2017) | |||
| Carterton, VA, USA | 12 (2015–2017) | |||
| Powell River, TN | 4 (2018) | North Carolina Wildlife Resources Commission | ||
| Little Tennessee River | Lake Fontana, NC, USA | 41 | ||
| Hiwassee River | Lake Hiwassee, NC, USA | 15 | ||
| Tuckasegee River | Lake Glenville, NC, USA | 23 | ||
| Little Tennessee River | Nantahala Lake, NC, USA | 26 | ||
| Cheoah River | Lake Santeelah, NC, USA | 17 | ||
| Tuckasegee River | Bear Lake, NC, USA | 24 | ||
| Wolf Lake, NC, USA | 15 | |||
| Lake James, NC, USA | 49 | |||
| Mississippi | White River Basin | Fellows Lake, MO, USA | 9 | Missouri Department of Conservation |
| Stockton Lake, MO, USA | 21 | |||
| Beaver tailwater/Table Rock Lake, AK/MO, USA | 20 | |||
| James River/Table Rock Lake, MO, USA | 20 | |||
| Mozingo Lake, MO, USA | 19 | |||
| Smithville Lake, MO, USA Current River, MO, USA Black River, AK, USA | 16 28 26 | |||
| Mississippi | Upper Mississippi R. | Mille Lacs, MN, USA | 19 (2004). | Nick Milroy, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service |
| Great Lakes | Lake Ontario | Oneida Lake, NY, USA | 10 (2005) | Lars Rudstam, Cornell University |
| Bay of Quinte, Lake Ontario | 18 (2005) | Timothy Johnson, Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources | ||
| Lake Michigan | Grand River, MI, USA | 12 (1998) | Michael Thomas, Michigan Department of Natural Resources | |
| Lake Superior | THUNDER BAY, ON, Canada | 6 (2000) | Henry Quinlan, USFWS | |
| Lake Michigan | Muskegon River, Lake Michigan | 19 (1998) | Michael Thomas, Michigan Department of Natural Resources | |
| Lake Huron | Flint River, MI, USA | 19 (1998) | Michael Thomas, Michigan Department of Natural Resources | |
| Tittabawassee River, Saginaw Bay, MI, USA | 10 (2012) | William Wellenkamp, Michigan Department of National Resources | ||
| St. Mary’s River | Munuscong Bay MI, Lake Huron | 18 (2002) | Barbara Evans, Lake Superior State University | |
| Lake Winnipeg | Lake Manitoba, MB, Canada | 17 (2006) | Wolfgang Jansen, North/South Consultants, Winnipeg, MN, USA | |
| Lake Winnipeg, MB, Canada | 18 (2012) | Christopher Wilson, Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry | ||
| Lac Mistassini | Lac Mistassini, QC, Canada | 19 | Christopher Wilson, Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry | |
| Lake Erie | Fairport, OH, USA | 25 (1996) | Ohio Department of Wildlife | |
| Alabama | Coosa River | Hatchet Creek, AL, USA | 15 (2005–2014) | Eric Peatman, Auburn University |
| Tombigbee River | John Allen Fish Hatchery, AL, USA | 44 (2018) |
| Locus | Multiplex, Master Mix | PCR Protocol | Size Range (bp) | Number of Alleles | (°C) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Svi5 | 1 | 1 | 130–192 | 32 | 50/59 | [24] |
| Svi6 | 1 | 1 | 126–164 | 14 | 50/59 | [24] |
| Svi16 | 1 | 1 | 175–299 | 42 | 50/59 | [24] |
| Svi17 | 2 | 2 | 99–113 | 7 | 57 | [22] |
| Svi18 | 1 | 1 | 110–142 | 17 | 50/59 | [22] |
| Svi33 | 2 | 2 | 73–95 | 12 | 57 | [22] |
| SviL1 | 3 | 3 | 151–209 | 29 | 53 | [23] |
| SviL7 | 3 | 4 | 135–269 | 39 | 48 | [23] |
| Population Sample | N | A | HO | HE | Allele Size Range | M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coosa drainage, AL, USA | 4 | 3.00 (1.41) | 0.32 (0.44) | 0.51 (0.18) | 7.00 (6.22) | 0.45 (0.20) |
| Tombigbee drainage, AL, USA | 6 | 3.83 (1.33) | 0.23 (0.41) | 0.55 (0.08) | 70.83 (66.17) | 0.21 (0.23) |
| Fellows Lake, MO, USA | 7 | 6.43 (2.64) | 0.65 (0.24) | 0.82 (0.10) | 63.57 (62.69) | 0.26 (0.23) |
| Stockton Lake, MO, USA | 8 | 8.38 (3.33) | 0.44 (0.26) | 0.75 (0.14) | 158.88 (52.64) | 0.05 (0.01) |
| Beaver/Table Rock Lake, AK/MO, USA | 7 | 8.29 (3.00) | 0.49 (0.36) | 0.82 (0.08) | 65.00 (72.17) | 0.33 (0.25) |
| James/Table Rock Lake, MO, USA | 7 | 7.57 (1.51) | 0.39 (0.25) | 0.78 (0.09) | 111.71 (82.17) | 0.17 (0.19) |
| Mozingo Lake, MO, USA | 8 | 6.75 (2.82) | 0.40 (0.31) | 0.71 (0.25) | 77.38 (77.00) | 0.29 (0.26) |
| Smithville Lake, MO, USA | 7 | 8.29 (3.50) | 0.51 (0.31) | 0.82 (0.07) | 41.14 (41.06) | 0.38 (0.22) |
| Current River, MO, USA | 7 | 6.00 (3.65) | 0.23 (0.32) | 0.59 (0.27) | 112.86 (87.28) | 0.19 (0.25) |
| Black River, AK, USA | 7 | 7.29 (4.07) | 0.32 (0.38) | 0.61 (0.23) | 101.86 (98.28) | 0.27 (0.27) |
| Clinch and Powell Rivers, VA, USA | 8 | 12.25 (4.59) | 0.34 (0.17) | 0.76 (0.13) | 155.75 (78.43) | 0.14 (0.18) |
| Lake Fontana, NC, USA | 8 | 10.75 (3.92) | 0.33 (0.26) | 0.75 (0.20) | 119.75 (66.04) | 0.17 (0.20) |
| Nantahala Lake, NC, USA | 6 | 8.33 (3.45) | 0.30 (0.29) | 0.74 (0.15) | 67.00 (48.55) | 0.25 (0.22) |
| Lake Santeetlah, NC, USA | 6 | 8.33 (3.67) | 0.43 (0.22) | 0.82 (0.12) | 129.83 (81.64) | 0.12 (0.17) |
| Bear Lake, NC, USA | 6 | 7.83 (3.76) | 0.37 (0.20) | 0.79 (0.07) | 28.83 (33.59) | 0.43 (0.18) |
| Wolf Lake, NC, USA | 7 | 6.29 (2.50) | 0.48 (0.31) | 0.72 (0.18) | 112.43 (111.03) | 0.24 (0.25) |
| Lake James, NC, USA | 7 | 10.57 (4.43) | 0.55 (0.27) | 0.83 (0.08) | 80.71 (93.36) | 0.31 (0.24) |
| Lake Hiwassee, NC, USA | 6 | 6.33 (1.97) | 0.49 (0.32) | 0.76 (0.11) | 61.67 (49.89) | 0.24 (0.23) |
| Lake Glenville, NC, USA | 7 | 7.86 (2.91) | 0.51 (0.30) | 0.75 (0.24) | 96.14 (116.61) | 0.32 (0.26) |
| New River, VA, USA | 7 | 11.57 (6.88) | 0.66 (0.37) | 0.73 (0.33) | 90.29 (125.17) | 0.37 (0.23) |
| Barren River, KY, USA | 8 | 11.75 (4.65) | 0.44 (0.30) | 0.78 (0.13) | 126.00 (76.99) | 0.16 (0.18) |
| Goose Creek, KY, USA | 7 | 8.00 (3.46) | 0.50 (0.40) | 0.73 (0.14) | 108.57 (109.14) | 0.23 (0.24) |
| Rockcastle River, KY, USA | 8 | 8.50 (4.04) | 0.38 (0.30) | 0.68 (0.28) | 88.00 (67.33) | 0.21 (0.19) |
| Levisa and Russell Forks, KY, USA | 7 | 8.29 (3.10) | 0.55 (0.24) | 0.80 (0.10) | 64.43 (76.82) | 0.33 (0.22) |
| Allegheny River, PA, USA | 8 | 7.63 (3.34) | 0.49 (0.31) | 0.77 (0.18) | 32.00 (46.13) | 0.44 (0.18) |
| Lake Erie | 7 | 5.57 (1.90) | 0.53 (0.38) | 0.67 (0.28) | 12.29 (7.52) | 0.48 (0.13) |
| Lake Ontario | 7 | 8.29 (3.04) | 0.55 (0.27) | 0.83 (0.07) | 76.71 (93.96) | 0.30 (0.25) |
| Mille Lacs, MN, USA | 6 | 6.33 (1.34) | 0.42 (0.36) | 0.78 (0.07) | 41.00 (45.84) | 0.37 (0.24) |
| Lake Michigan | 7 | 6.14 (0.68) | 0.44 (0.34) | 0.68 (0.15) | 71.57 (92.27) | 0.31 (0.26) |
| Grand River, MI, USA | 7 | 5.57 (1.27) | 0.27 (0.20) | 0.71 (0.15) | 124.00 (101.50) | 0.19 (0.25) |
| Flints River, MI, USA | 7 | 7.71 (2.29) | 0.62 (0.32) | 0.83 (0.04) | 76.14 (94.43) | 0.30 (0.24) |
| St. Mary’s River, MI, USA | 7 | 8.00 (2.31) | 0.47 (0.33) | 0.79 (0.10) | 76.71 (94.48) | 0.30 (0.24) |
| Thunder Bay, ON, Canada | 6 | 5.00 (1.79) | 0.50 (0.45) | 0.76 (0.15) | 76.17 (86.18) | 0.24 (0.24) |
| Saginaw Bay, MI, USA | 7 | 5.29 (1.38) | 0.53 (0.39) | 0.69 (0.15) | 71.29 (94.07) | 0.28 (0.24) |
| Oneida Lake, NY, USA | 6 | 4.00 (0.89) | 0.50 (0.37) | 0.67 (0.13) | 38.33 (44.40) | 0.27 (0.19) |
| Lake Manitoba, MB, Canada | 7 | 6.57 (2.30) | 0.47 (0.35) | 0.77 (0.10) | 73.57 (92.76) | 0.30 (0.25) |
| Lake Winnipeg, MB, Canada | 7 | 8.71 (3.95) | 0.51 (0.38) | 0.77 (0.14) | 77.86 (90.34) | 0.29 (0.23) |
| Lac Mistassini, QC, Canada | 7 | 7.71 (3.77) | 0.51 (0.37) | 0.80 (0.10) | 109.71 (107.70) | 0.23 (0.24) |
| Population Sample | FIS |
|---|---|
| Hatchet Creek, AL, USA | 0.39 |
| J. Allen Fish Hatchery, AL, USA | 0.58 |
| Fellows Lake, MO, USA | 0.21 |
| Stockton Lake, MO, USA | 0.42 |
| Beaver/Table Rock Lake, AK/MO, USA | 0.41 |
| James/Table Rock Lake, MO, USA | 0.50 |
| Mozingo Lake, MO, USA | 0.44 |
| Smithville Lake, MO, USA | 0.39 |
| Current River, MO, USA | 0.62 |
| Black River, AK, USA | 0.48 |
| Clinch and Powell Rivers, VA, USA | 0.56 |
| Lake Fontana, NC, USA | 0.56 |
| Nantahala Lake, NC, USA | 0.60 |
| Lake Santeetlah, NC, USA | 0.49 |
| Bear Lake, NC, USA | 0.54 |
| Wolf Lake, NC, USA | 0.34 |
| Lake James, NC, USA | 0.34 |
| Lake Hiwassee, NC, USA | 0.37 |
| Lake Glenville, NC, USA | 0.33 |
| New River, VA, USA | 0.10 |
| Barren River, KY, USA | 0.43 |
| Goose Creek, KY, USA | 0.32 |
| Rockcastle River, KY, USA | 0.44 |
| Levisa and Russell Forks, KY, USA | 0.31 |
| Allegheny River, PA, USA | 0.37 |
| Lake Erie | 0.21 |
| Lake Ontario | 0.35 |
| Mille Lacs, MN, USA | 0.47 |
| Lake Michigan | 0.36 |
| Grand River, MI, USA | 0.62 |
| Flint River, MI, USA | 0.26 |
| St. Mary’s River, MI, USA | 0.42 |
| Thunder Bay, ON, Canada | 0.36 |
| Saginaw Bay, MI, USA | 0.25 |
| Oneida Lake, NY, USA | 0.27 |
| Lake Manitoba, MB, Canada | 0.40 |
| Lake Winnipeg, MB, Canada | 0.34 |
| Lac Mistassini, QC, Canada | 0.36 |
| Population Sample | N | Estimated Ne | 95% C.I. | Jackknife Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hatchet Creek, AL, USA | 15 | 63.1 | 1.6–Undefined | 0.7–Undefined |
| J. Allen Fish Hatchery, AL, USA | 44 | 8.9 | 3.0–23.5 | 2.0–48.8 |
| Fellows Lake, MO, USA | 9 | 68.7 | 7.6–Undefined | 3.1–Undefined |
| Stockton Lake, MO, USA | 21 | 8.6 | 4.5–16.2 | 2.5–47.9 |
| Beaver/Table Rock Lake, AK/MO, USA | 20 | 10.7 | 6.8–17.7 | 4.1–31.5 |
| James/Table Rock Lake, MO, USA | 20 | 5.3 | 2.7–10.5 | 2.0–21.5 |
| Mozingo Lake, MO, USA | 19 | 8.0 | 4.0–14.5 | 2.7–27.4 |
| Smithville Lake, MO, USA | 16 | 10.6 | 5.9–20.8 | 4.0–32.6 |
| Current River, MO, USA | 28 | 4.4 | 2.2–11.9 | 1.4–66.3 |
| Black River, AK, USA | 26 | 11.6 | 5.3–31.5 | 3.1–81.0 |
| Clinch and Powell Rivers, VA, USA | 79 | 8.9 | 6.6–11.6 | 5.1–13.4 |
| Lake Fontana, NC, USA | 42 | 17.0 | 11.8–26.2 | 8.2–48.6 |
| Nantahala Lake, NC, USA | 27 | 4.5 | 2.6–8.5 | 1.8–15.3 |
| Lake Santeetlah, NC, USA | 18 | 87.9 | 19.0–Undefined | 18.4–Undefined |
| Bear Lake, NC, USA | 24 | 16.8 | 8.7–41.9 | 6.1–118.1 |
| Wolf Lake, NC, USA | 16 | 19.9 | 7.3–Undefined | 2.9–Undefined |
| Lake James, NC, USA | 50 | 14.4 | 10.9–19.8 | 8.2–26.3 |
| Lake Hiwassee, NC, USA | 16 | 1.8 | 1.3–2.7 | 1.0–5.1 |
| Lake Glenville, NC, USA | 24 | 6.8 | 4.0–10.3 | 3.0–12.7 |
| New River, VA, USA | 117 | 15.3 | 12.8–18.1 | 12.0–19.2 |
| Barren River, KY, USA | 70 | 8.6 | 6.6–10.8 | 4.3–13.2 |
| Goose Creek, KY, USA | 27 | 2.7 | 2.1–4.6 | 1.8–6.4 |
| Rockcastle River, KY | 44 | 7.2 | 4.9–10.0 | 3.2–12.6 |
| Levisa and Russell Forks, KY, USA | 15 | 16.4 | 7.8–61.1 | 3.1–Undefined |
| Allegheny River, PA, USA | 21 | 6.4 | 3.4–9.6 | 2.7–14.0 |
| Lake Erie | 26 | 1.9 | 1.5–2.4 | 0.9–5.6 |
| Lake Ontario | 19 | 4.1 | 2.7–7.2 | 2.1–11.0 |
| Mille Lacs, MN, USA | 20 | 2.3 | 1.7–3.1 | 1.5–4.3 |
| Lake Michigan | 20 | 2.7 | 1.9–5.3 | 1.1–18.7 |
| Grand River, MI, USA | 13 | 8.5 | 2.1–Undefined | 1.4–Undefined |
| Flint River, MI, USA | 20 | 7.6 | 4.4–12.4 | 4.0–13.2 |
| St. Mary’s River, MI, USA | 19 | 6.8 | 3.2–12.1 | 2.6–19.1 |
| Thunder Bay, ON, Canada | 6 | 8.3 | 1.3–Undefined | 0.8–Undefined |
| Saginaw Bay, MI, USA | 10 | 3.0 | 1.5–25.9 | 1.1–Undefined |
| Oneida Lake, NY, USA | 10 | 1.1 | 0.6–2.2 | 0.6–2.4 |
| Lake Manitoba, MB, Canada | 17 | 7.0 | 2.9–15.4 | 2.9–16.1 |
| Lake Winnipeg, MB, Canada | 19 | 4.7 | 2.7–8.6 | 2.4–10.9 |
| Lac Mistassini, QC, Canada | 20 | 2.5 | 1.9–3.3 | 1.2–10.8 |
| A. Within and among Individual Populations. | ||||
| Source of Variation | d.f. | Sum of Squares | Variance Components | Percentage of Variation |
| Among population samples | 5 | 668.38 | 0.32 | 9.5 |
| Among individuals within population samples | 1273 | 5583.44 | 1.37 | 41.0 |
| Within individuals | 1279 | 2114.50 | 1.65 | 49.5 |
| Total | 2557 | 8366.23 | 3.34 | |
| B. Within and among Populations and Groups of Populations (Mississippi, Tennessee, New, and Ohio River Drainages, and Great Lakes). | ||||
| Source of Variation | d.f. | Sum of Squares | Variance Components | Percentage of Variation |
| Among groups of populations | 5 | 537.11 | 0.19 | 5.9 |
| Among population samples within groups | 32 | 748.75 | 0.42 | 13.0 |
| Among individuals within population samples | 989 | 3642.52 | 1.04 | 32.0 |
| Within individuals | 1027 | 1640.50 | 1.60 | 49.1 |
| Total | 2053 | 6568.88 | 3.23 | |
| Population | Number of Polymorphic Loci | Number of Gene Copies | Number of Alleles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile Bay drainage | 6 | 118 | 4.00 (1.67) |
| Mississippi River | 8 | 318 | 14.75 (5.70) |
| Tennessee River | 8 | 592 | 17.63 (7.25) |
| New River | 8 | 738 | 23.25 (16.04) |
| Ohio River | 8 | 354 | 16.88 (8.54) |
| Great Lakes | 7 | 438 | 13.29 (0.77) |
| MB | MR | TR | NR | OR | GL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MB | - | |||||
| MR | 0.233 | - | ||||
| TR | 0.233 | 0.043 | - | |||
| NR | 0.274 | 0.102 | 0.094 | - | ||
| OR | 0.244 | 0.072 | 0.050 | 0.030 | - | |
| GL | 0.305 | 0.074 | 0.027 | 0.115 | 0.067 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harris, S.C.; Palmer, G.; Stepien, C.A.; Hallerman, E.M. Population Genetic Differentiation of Walleye (Sander vitreus) across the Eastern Highlands of the United States. Fishes 2024, 9, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010015
Harris SC, Palmer G, Stepien CA, Hallerman EM. Population Genetic Differentiation of Walleye (Sander vitreus) across the Eastern Highlands of the United States. Fishes. 2024; 9(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarris, Sheila C., George Palmer, Carol A. Stepien, and Eric M. Hallerman. 2024. "Population Genetic Differentiation of Walleye (Sander vitreus) across the Eastern Highlands of the United States" Fishes 9, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010015
APA StyleHarris, S. C., Palmer, G., Stepien, C. A., & Hallerman, E. M. (2024). Population Genetic Differentiation of Walleye (Sander vitreus) across the Eastern Highlands of the United States. Fishes, 9(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010015







