Abstract
Biofloc technology (BFT) as an efficient aquaculture alternative is attracting attention for boosting biosecurity with minimal water exchange and reduced feed intake. BFT relies on applying organic carbon to maintain a high C/N ratio above 10, which allows heterotrophs to assimilate toxic nitrogen. A high percentage of carbon loss is thus generated from BFT. For this review, a thorough search of the relevant literature was conducted to gather valuable information on the optimization of carbon utilization. The keywords searched included ‘BFT’, ‘carbon use efficiency’, ‘carbon conversion’, ‘carbon retention’, ‘carbon emission’, ‘carbon loss’, and ‘carbon release’. The current review discusses the possible effects of various C/N ratios, carbon types, addition strategies, and technology integration with respect to the optimized carbon utilization in BFT. Given the extreme lack of accessible research, it was concluded that the carbon utilization in BFT is still in its initial research stage. Anyhow, this review sheds light on plausible approaches for boosted carbon utilization by adopting slow-release carbon, reducing carbon input, integrating with other technologies, and enhancing interactions between functional microbes within BFT, thereby contributing to sustainable aquaculture.
Key Contribution:
This paper focuses on carbon loss in biofloc systems. At present, this issue has not received enough attention from the academic community, but it is of great value for building a green, low-carbon, and sustainable aquaculture industry.
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
The conflict between the growing demand for fish protein and limited environmental resources constitutes a great threat to aquaculture production [1]. With the reinforcement of environmental awareness, more attention has been paid to sustainable intensive production at the cost of using the least water and land resources, resulting in the gradual replacement of traditional aquaculture production [2]. Thus, one key issue of current aquaculture is the commitment to advance toward sustainability [3].
Among intensive production, the active use of biofloc technology (BFT) offers the possibility of minimal water exchange along with reduced feed intake for cost-effective and sustainable aquaculture development [4,5,6,7]. It was calculated that the water consumption/kg tilapia in a flow-through system (water flow of 0.6 L/day) was 42 times higher than that in BFT under zero water exchange [8]. Basically, zero water exchange entitles a BFT system to a higher degree of biosecurity and better environmental control. BFT has positive impacts on enhanced resistance against infectious viruses [9], Vibrio [10], and environmental stress [11]. Also, BFT systems could improve net productivity by 8–43% compared to conventional and recirculating aquaculture systems [12]. In addition, BFT can not only decompose aquaculture residues, excreta, and other wastes, but also convert harmful nitrogen in water into its own bacterial protein, providing cheap food protein sources for aquaculture animals [13], thereby reducing feed coefficients [14] and improving breeding efficiency [15]. For example, through isotope labeling experiments, Daniel and Bayer [16] and Burford et al. [17] found that proteins taken up and transformed by bacteria in bioflocs were taken up and assimilated by aquaculture animals. As a result, BFT is widely used in the intensive culture of Carassius auratus [18], Cyprinus carpio [19], tilapia [20], Clarias gariepinus [21], Jade perch [22], Pelteobagrus vachelli [23], and Pacific white shrimp [24,25].
1.2. Components of a BFT System
BFT is a microbial-based culture system that works by adding organic carbon sources to water or increasing the carbon content in the feed to increase the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. BFT systems support nutrient cycling and are therefore more environmentally friendly [26,27,28]. Hargreaves [29] defined it as suspended biological systems that rely on active phytoplankton, flocculants, protozoa, microalgae, etc., to regulate ammonia nitrogen and maintain nutrient levels in water bodies. Thus, BFT is essentially a water quality management technology that minimizes water exchange by converting nitrogen-containing toxic wastes such as ammonia and nitrite into less toxic nitrates through microorganisms [30,31,32]. The key of BFT is the formation of internal flocculation structures, containing bacteria, protozoa, algae, and other zooplankton, possibly up to 1000–2000 different species [33]. Bacteria exist in free form in water. Due to the heterogeneity of water concentration, nitrogen molecules diffuse, making it difficult for free bacteria to capture them, and the BFT system can solve this problem well [34,35]. The internal structure of the bioflocs is porous and the gaps are large enough to allow bacteria to fully absorb the nutrients in the aquaculture water flowing from the pores and gaps. In addition, bacteria can use bioflocs as safeguards to provide shelter for their own reproduction. Another important factor influencing the formation of bioflocs is the flocculation mechanism. Bacteria are coagulated together by extracellular polymeric substances consisting of multiple enzymes, polysaccharides, and other organic substances, resulting in flocculent structures [36,37].
BFT has a probiotic effect and is therefore able to inhibit pathogenic bacteria [26]. It contains active compounds such as bromophenol, carotenoids, chlorophyll, poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB), and phytosterol [38,39,40], some of which have antibacterial properties [41]. For example, BFT is known to contain polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) and PHB that can synthesize PHA particles [26]. PHB is an important polymer produced by various microorganisms in response to physiological stress and as an energy store, which can account for 16–18% of dry weight depending on the carbon source [42]. PHB can also positively affect the host by stimulating the growth of beneficial microbial cells in the gut and altering the composition of the gut flora [40]. Disruption of quorum sensing is a mechanism by which BFT inhibits pathogenic organisms. Quorum sensing is cell-to-cell communication between bacteria. Therefore, infectious bacteria in aquaculture can be controlled by destroying quorum sensing [30,41].
For a BFT system, the prosperity of heterotrophic bacteria plays a great role in assimilating inorganic nitrogen [43]. The nitrogen uptake rate by heterotrophic bacteria is higher than that by denitrifying bacteria, resulting in a growth rate and production of microbial biomass per unit substrate 10 times higher than those of the latter. Thus, immobilization of ammonia by heterotrophic bacteria usually occurs rapidly in BFT over a period of hours or days with appropriate C/N ratios [44,45]. BFT largely depends on organic carbon sources for the maintenance of heterotrophic bacteria. The major driver of floc formation is the growth of heterotrophic bacteria dependent on supplied carbon [46,47]. Thus, additional carbon sources are introduced to the BFT tank, offering a suitable C/N ratio (Figure 1).
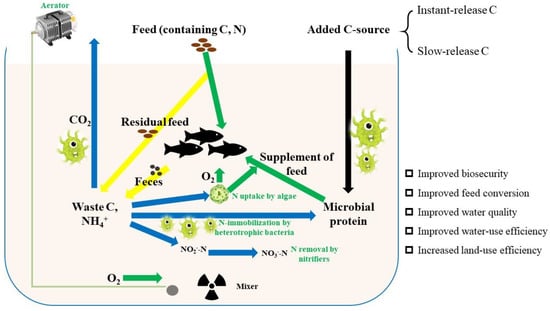
Figure 1.
Schematic carbon and nitrogen cycle within BFT.
1.3. Current Status of Carbon Loss in BFT Systems
Carbon source is one key factor for the management of BFT, and extensive studies have investigated the carbon types [8,11,48], addition amounts (i.e., C/N ratios) [49,50,51], and addition strategies [52,53] in an attempt to enhance BFT performance. Many helpful recommendations have been made when selecting and using carbon substrates according to specific cultured animals for desired performance. The nutrient composition of the bioflocs formed is related to the type of carbon source added and ultimately affects the growth of aquaculture animals (Table 1).

Table 1.
Nutrient composition of bioflocs corresponding to different carbon source types.
Regarding the consumption amount of carbon substrates, Avnimelech [14] proposed a calculation method based on feed N content and assumed that 20 g of carbon was required to convert 1 g of ammonia, which was the most commonly used method. Additionally, it can be calculated that 7.2 g of carbon is required to assimilate nitrogen from waste feed and fish excretion per kg feed per day when the desired C/N ratio is set at 10. The schematic calculation is presented in Figure 2. Then, the amount of carbon substrate applied is determined using its own carbon content. In the case of glucose, glycerol, and acetate (all containing 0.4 g C per g), up to 18 g of carbon sources are required per kg fish per day. The premise of this calculation method is that C and N exist in the form available for heterotrophs to assimilate. However, both C and N have various forms in practice, including the unavailable ones. In addition, this method only considers the C/N ratio of the input, rather than the C/N ratio of the BFT system where the bacteria live. Thus, it is difficult to ensure that the C/N ratio in BFT is suitable for the assimilation of ammonia by heterotrophic bacteria [14].

Figure 2.
Calculation of the daily carbon for removing nitrogen from wasted feed and fish excretion in BFT. The hypothesis of 75% of the feed-N ending up in water is based on Avimelech [14].
It should be noted that the unexpected carbon loss is often a reality to face in practice. The ratio of carbon assimilated to carbon metabolized is defined as the microbial conversion efficiency, usually in the range of 40–60% [14]. Carbon use efficiency is the ratio between the carbon retained in cultured species and the carbon input from feed and carbohydrates [53]. And carbon loss is defined as the difference between the total carbon input (feed + additional carbohydrates) and the carbon retained in all components of the whole BFT system (cultured species + biofloc + sediment + water + periphyton) [53]. For a BFT system, the carbon use depends on factors such as cultured species, farming density, aeration, input composition, and microbial community structures. Tinh et al. [53] documented that the feed-input-alone BFT retained 62% of the total carbon input, yet only 26–31% of total carbon was retained for the carbon-added BFT. The authors also stated that the carbon retention in corn starch and molasses BFT systems was as low as 15% and 17% of the total carbon input [63], which corresponds to an economic cost of 0.002 and 0.016 USD/m3/day due to the carbon loss, respectively (calculated by market unit price of 0.5 and 2 USD/kg, respectively). A similar doubling of C-loss was revealed for a tilapia BFT system when increasing the C/N ratio to 16 compared to feed input alone [64]. Using life cycle analysis, it was calculated that a ton of live weight shrimp production in BFT did generate 4657.2 kg CO2 eq, higher than that in RAS (4424.2 kg CO2 eq) [65]. Water exchange occurs when the total suspended solids in BFT exceed the limit of 500 mg/L [66], through which carbon loss is thus generated. The dissolved organic carbon (DOC) discharge from BFT would result in possible secondary pollution, especially for liquid-carbon-added BFT systems [67]. This puts an additional burden on the wastewater treatment system and operating costs, which conflicts with the sustainable development of aquaculture.
Thus, optimizing carbon utilization is of great significance to control operating costs and reduce the risk of secondary pollution. However, given the high carbon loss, the issue of carbon loss from biofloc systems has not received the attention it deserves. In this regard, the current review presents information on the possible state-of-the-art utilization strategies of the carbon source applied in BFT systems. This review regards the practice of BFT technology, achieving the goal of a greener and more sustainable production of aquaculture.
2. C/N Ratio Manipulation
Manipulating the C/N ratio is an ideal applied method when running a BFT system. Extensive research has evaluated the C/N ratio in an attempt to enhance the whole BFT system performance. Specific C/N ratio ranges have accordingly been recommended for different culturing animals. Azhar et al. [49] addressed that an increase in C/N ratio from 10 to 15 has positive effects on the feed utilization efficiency and water quality in the tilapia-redclaw crayfish co-culture BFT system. Azimi et al. [68] stated that increasing the C/N ratio from 10 to 20 enhanced the innate immunity of carp (Cyprinus carpio) reared in BFT. Similarly, positive effects of the increase in C/N ratio from 10 to 20 were also reported on immunological parameters and stress indicators of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) [50]. Yet, Chakrapani et al. [69] stated that the BFT water quality and growth performance of Litopenaeus vannamei were better at C/N ratios of 10 and 15 compared to 20.
It seems plausible that an increased C/N ratio leads to a high possibility of C-loss from BFT systems. Nevertheless, the aspect of C-loss is rarely mentioned when selecting C/N ratios in BFT. One study investigated the influence of C/N (0, 10, 15, and 20) on the input/output ratio and found that the input/output ratio increased with increasing C/N ratios [70]. Liu et al. [22] concluded that as the real-time nitrate was controlled at extremely low levels in BFT, less carbon could be applied to convert the heterotrophic denitrifying BFT biofilters into nitrifying ones, through which carbohydrates were saved. Also, Ferreira et al. [71] stated that the supply of carbohydrates to BFT tanks is necessary only in emergency situations, when occasional ammonia spikes need to be controlled. Thus, from the view of system sustainability, a reduced C supply to BFT might be a plausible method without adversely affecting the whole system performance except for emergency scenarios, through which C emission into the environment could be controlled to a certain degree (Table 2).

Table 2.
Possible strategies for the purpose of improved carbon utilization in BFT.
3. Optimization of Carbon Types
Multiple organic carbon substrates have been applied to adjust C/N ratios in BFT aquaculture systems [77]. These C-substrates can be divided into two categories on the basis of the speed that they release dissolved organic carbon (DOC) into the water, i.e., instant-release ones and slow-release ones. In general, instant-release carbon could increase DOC instantly, while complex dose control puts a burden on BFT operation. By contrast, slow-release carbon shows advantages of ease of management, long service life, and low tendency for secondary pollution.
3.1. Instant-Release Carbon
Acetate, glucose, and glycerol are three simple and directly soluble carbohydrates that have been extensively applied in BFT [78,79,80]. These soluble carbohydrates decompose quickly, providing a high level of DOC for heterotrophic bacteria. Molasses and starch, as more complex carbohydrates, should first be decomposed into simple sugars, resulting in a slower increase in DOC level. The addition of water-soluble carbohydrates occurs a few times a day or every several days with careful calculation and constant supervision to avoid overdosing or starvation [77]. Undoubtedly, the complexity of dose control greatly increases BFT practice costs.
The completely instant release of DOC would cause a sudden spike in carbon concentration within a BFT system. Unexpectedly, it was found that the carbon retention ratio in corn starch and molasses BFT systems was only 15% and 17% of the total carbon input, respectively, and the rest was in loss [63]. As for the carbon distribution retained within the BFT, the authors stated that most carbon in the corn starch system was accumulated in shrimp and sediment, whereas retained carbon was more equally distributed in all compartments of molasses-added BFT [63].
3.2. Slow-Release Carbon
Compared to soluble carbohydrates, the slow-release ones are much less studied in BFT systems. Slow-release carbon usually includes synthetic high-molecular polymers and plant-based materials. As high-molecular polymers, PHB, PCL, and PHBV have been frequently supplemented in BFT-based systems, and they have exhibited desirable performance results [81,82]. Meanwhile, corn straw, rice straw, yam, rice bran, and sugarcane bagasse are the common plant-based materials adopted in BFT [83,84,85]. The slow-release carbon has gradually gained attention due to its ease of management, long service life, and low tendency for secondary pollution [72,86]. Notably, slow-release carbohydrates applied in aquaculture are mainly synthetic and novel ones, as aquaculture systems are sensitive to water quality and require carbon sources that can provide steady C-release rates, less DOC accumulation, and lower color intensity [87].
The supplementation of DOC by adding slow-release carbon requires the biodegradation of the carbonaceous substrates first. Zhang et al. [88] proposed that enzymes secreted from the bacteria on a solid-phase carbon surface are responsible for decomposing the carbon into small, water-soluble monomers. The insoluble carbon exhibited a more stable ability to release DOC for the maintenance of water parameters within an extended duration. Also, insoluble carbohydrates could better control the overdosing of carbon into water in comparison with soluble ones.
C-loss is closely related to the C-release characteristics of slow-release carbohydrates. Basically, the carbon release from slow-release carbohydrates follows first-order kinetics, among which raw slow-release carbohydrates can release a greater amount of DOC, and synthetic ones have obvious advantages in release sustainability [87]. One study investigated the addition amounts of PHB and showed that with the increase in PHB addition, the higher the degradation loss and the lower the degree of surface degradation and damage [72]. It is noted that most existing studies with respect to slow-release carbon focus on DOC supplementation for the denitrification process. In contrast, little research has focused on the carbon release kinetics of slow-release carbon applied in BFT. In this way, the attempt to reveal the C-loss parameters seems to be in vain in light of the limited available information. On the other hand, C-loss from BFT also directly correlates to bio-assimilation by microbes and microalgae within the system, which makes the C-loss characteristics more complicated to describe.
4. Optimization of Carbon Addition Strategy
Current research on carbon addition strategies in BFT mainly attempts to improve water quality and biofloc quality, ultimately ensuring a desirable welfare for cultured animals [8,89,90]. However, the corresponding C-loss under certain carbon addition strategies is rarely mentioned (Table 2). One study investigated the potential to combine a carbon source (corn starch) and feed in one pellet at a C/N ratio of 14.6 for BFT shrimp farming [53]. The results showed that compared to the commercial diet at a C/N ratio of 7.6, applying additional carbon reduced the carbon utilization efficiency regardless of the addition methods (added separately at 12%, with feed in one pellet at 10% and commercial diet at 21%). Also, the energy efficiency was the highest when additional carbon was not applied regardless of addition method.
Additionally, few studies have investigated the carbon addition frequency for the optimization of addition strategy. As reported, splitting the daily dosage of the carbon source from 1 to 3 and 6 times per day had no significant effect on Pacific white shrimp performance, and carbon and nitrogen retentions in BFT [73]. The low carbon addition dose could also help to avoid sudden drops in oxygen concentrations caused by bacterial consumption, thereby maintaining a stable environment for the animals reared in the system and improving survival rates [91]. Importantly, the conventional commercial-feed treatment retained 62% of the total carbon input, while in carbon-added treatment, this was 26–31%. In other words, regardless of the carbon addition frequencies, biofloc reared with Pacific white shrimp showed double carbon loss compared to conventional cultivation [73]. Similarly, Hu et al. [64] clarified that the employment of soluble starch to a tilapia-based BFT system increased the daily CO2 emission by 91.1% compared to the feed only.
Overall, neither changes in carbon addition method nor increases in frequency have been effective in improving carbon utilization of BFT (Table 2). Thus, further research on developing carbon addition strategies is needed, facilitating the carbon retention efficiency within BFT.
5. Integration with Other Technologies
BFT focuses on maximizing the efficiency of the use of resources, complying with several criteria that bring them closer to sustainability. However, BFT faces one key challenge in the biological compatibility between different cultivated organisms. Notably, evidence suggests that integrated multitrophic systems could be a viable pathway to replace traditional monoculture systems that are polluting and inefficient [92].
A study found that integrating L. vannamei and Sarcocornia ambigua at different salinities (16 and 24 psu) facilitated the removal of N and P without negative effects on shrimp growth [93]. In addition, promoted water quality and shrimp growth were observed through the incorporation of seaweed to a BFT system rearing L. vannamei [94]. Also, it was reported that an integrated BFT system of L. vannamei and Ulva fasciata promoted the N and P recovery by 5.5% and 7.6%, respectively, compared to the BFT with L. vannamei alone [95]. However, it is noted that the current research paid little attention to the carbon utilization within the BFT integration systems.
In an attempt to seek the potential of promoted carbon utilization through BFT integration, Li et al. [67] established a newly Combined Denitrification and Biofloc Technology (CDBFT) system, which applied the waste effluent DOC from solid-phase denitrification as the carbon source for biofloc growth. This method has great potential in solving both the troublesome issues of the denitrification effluent pollution and the biofloc carbon source addition (see Table 2).
Additionally, to utilize BFT effluents in light of the sufficient nutrient content, existing feasible alternatives include reusing the water over multiple culture cycles [74] or recycling the nutrients in an aquaponics system for vegetable production to achieve sustainable development and a circular economy. The latter system, i.e., FLOCponics, integrates the production of both aquaculture animals and plants, and thus, in theory, enhances the overall utilization efficiency of nutrients within the system. For instance, Pinheiro et al. [75] proposed an aquaponic system with BFT, which could produce 2 kg of halophyte Sarcocornia ambigua for each kg of Pacific white shrimp. In a similar study, Pinho et al. [76] noted that nutrients from tilapia BFT effluent contributed to enhancing lettuce yield in an aquaponics production system. Also, Pinho et al. [96] observed a better Nile tilapia productive performance in FLOCponics, with a mean final weight of 36.7 g compared to 34.9 g for conventional aquaponics.
The level of integration increases in the following order: polyculture > aquaponics > BFT > FLOCponics [97]. Nevertheless, one of the challenges is the compatibility between the components of the integrated system, such as the compatibility between the resources excreted by one species for use by another. Thus, FLOCponics would be technically feasible if efficient and smooth management is developed to improve compatibility within the system (e.g., solids accumulation and nutrient imbalance in plant roots).
6. Challenges and Perspectives
Undoubtedly, carbohydrates play a crucial role in BFT practice, and the benefits of applying carbohydrates were intensively demonstrated on water quality, biofloc quality, and cultured animal performance [68,98]. Nevertheless, excessive carbon emission from BFT is an undeniable fact, exhibiting a great threat to the receiving system [63]. For the purpose of access to reduced resource waste and aquaculture sustainability, practical and effective strategies aimed at optimizing carbon utilization are urgently needed for BFT operations. Therefore, this review discusses the selection of carbon source types, the optimization of carbon addition strategies, and the synergy with other technologies, and proposes practical methods to improve carbon use efficiency, contributing to green and sustainable aquaculture.
Applying low-cost carbohydrates is thus recommended since it is an obvious alternative that entitles BFT to economic sustainability [99]. It is worth noting that carbohydrates applied in aquaculture are mainly synthetic and novel ones, as cultured species require carbon sources with steady C-release rates, less DOC accumulation, and lower color intensity [87]. Additionally, although the economic impact of part of C-loss can be solved by applying cheap by-product carbohydrates, this undesired high C-loss will undoubtedly raise concerns about the environmental impacts of BFT practice.
The application of less carbon to BFT [22], or only even in the case of occasional ammonia spikes [71], has been previously reported as a plausible approach, through which carbon was saved and C-loss was accordingly reduced. Remarkably, the premise of the above approaches is that it does not cause any adverse effect on overall BFT performance; otherwise, the approaches are not worth the benefits and are meaningless. Therefore, the practical scenarios for achieving an overall satisfactory performance of BFT at the cost of a certain amount of C-loss are currently within reach.
The implication of most current studies emphasized the role of carbon in determining BFT running performance, usually from the aspect of carbon types and C/N ratios [8,11,49]. Yet, related sustainability issues including resources waste and environmental pollution induced by a high percentage of C-loss have not received the attention they deserve. One consequence of this ignorance is the extreme lack of relevant studies (Table 2), which brings great difficulties in overviewing the current optimized utilization strategies of carbon sources of this paper. Thus, the authors are looking forward to bringing attention to this review for the purpose of further filling the gap in C-loss control of BFT. BFT itself is an excellent alternative for obtaining sustainable aquaculture, as it could reduce feed intake along with minimal water exchange and a high degree of biosecurity. If nutrient loss, especially C-loss, is not well addressed, the green sustainability of BFT will be reduced.
It is evident that carbon addition reduced the carbon retention efficiency of the total carbon input compared to the commercial feed alone (Table 2). Nevertheless, the manipulation of the addition method or frequency failed in elevating the carbon utilization as expected [53,73]. By contrast, the integration of BFT with denitrification and aquaponics recycling nutrients for multiple uses seems plausible to reduce carbon emission for sustainable aquaculture production [67,76], and further research is thereby warranted.
Further research is needed on optimizing the carbon utilization efficiency and reducing carbon emission, either directly by farmed animals or indirectly by capturing nutrients for other purposes. The standardization of methods, techniques, and equipment is critical to the application of carbon to BFT aquaculture systems. In the near future, it is anticipated that BFT will become a more competitive alternative to aquaculture, adopting upgraded approaches to maximize the utilization of resources while reducing the impact on the external environment.
In addition, research on the diversity and dynamics of biofloc microorganisms is still scarce, and the possible mechanisms of their interaction with farmed species, mass balance, and receiving environment remain unclear. The interactions between biofloc microbes are complicated; one example is that heterotrophic bacteria could utilize the organic carbon secreted by algae [100]. This carbon availability due to algal constituents can be considered when evaluating carbon cycling within BFT systems. In this regard, the enhancement in mass transfer between functional microbes might be another feasible method for the purpose of improved carbon utilization in BFT systems. Thus, exploring the interaction mechanism between biofloc microbes is of great significance, which deserves further study.
7. Conclusions
High carbon loss from BFT has not received the attention it deserves. This review discussed the possible impacts of C/N ratios, carbon types, addition strategies, and technology integration on the optimization of BFT carbon utilization. For this purpose, the application of less carbon to BFT, or only even in the case of occasional ammonia spikes, could be served as a plausible approach. Notably, the manipulation of the addition method or frequency failed in elevating the carbon utilization as expected. By contrast, the integration of BFT with denitrification and aquaponics recycling nutrients for multiple uses seems plausible to reduce carbon emission for sustainable aquaculture production.
A cursory look at the literature reveals that research on optimized carbon utilization in BFT has just emerged. A large gap exists in practical BFT operation in terms of efficient carbon cycles. Future research should focus on revealing interactions between BFT microbial components, which is helpful for the standardization of carbon application in a more sustainable and economic manner.
Author Contributions
C.L.: conceptualization, writing, investigation. X.Z.: investigation, visualization. Y.C. (Yu Chen): investigation. S.Z.: review. L.D.: review. W.Z.: review. Y.C. (Yuan Chen): review, conceptualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32202999), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20220521), the Jiangsu Province Agricultural Science and Technology Independent Innovation Fund Project (No. CX(21)3061), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (No. PAPD-2018-87), and the Jiangsu University Senior Talent Fund Project (No. 5501200006).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yan, W.; Zhong, C. The coordination of aquaculture development with environment and resources: Based on measurement of provincial eco-efficiency in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; D’Abramo, L.R.; Glencross, B.D.; Huyben, D.C.; Juarez, L.M.; Lockwood, G.S.; McNevin, A.A.; Tacon, A.G.J.; Teletchea, F.; Tomasso, J.R.; et al. Achieving sustainable aquaculture: Historical and current perspectives and future needs and challenges. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 578–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthman, O.; Jonell, M.; Rönnbäck, P.; Troell, M. Strong and weak sustainability in Nordic aquaculture policies. Aquaculture 2022, 550, 737841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-B.; Choi, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Jo, A.H.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, J.-H. Biofloc technology in fish aquaculture: A review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, S.; Yogev, U.; Kpordzaxor, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Gur, N.; Gross, A.; Zilberg, D. From fish excretions to high-protein dietary ingredient: Feeding intensively cultured barramundi (Lates calcarifer) a diet containing microbial biomass (biofloc) from effluent of an aquaculture system. Aquaculture 2023, 562, 738780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.M.; de Lima, J.P.; Tarigan, N.B.; David, L.H.; Portella, M.C.; Keesman, K.J. Modelling FLOCponics systems: Towards improved water and nitrogen use efficiency in biofloc-based fish culture. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 229, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, S.S.; Singh, S.K.; Biswas, P.; Debbarma, R.; Parhi, J.; Ngasotter, S.; Waikhom, G.; Meena, D.K.; Devi, A.G.; Mahanand, S.S.; et al. Effect of stocking density on growth, water quality changes and cost efficiency of butter catfish (Ompok bimaculatus) during seed rearing in a biofloc system. Fishes 2023, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridha, M.T.; Hossain, M.A.; Azad, I.S.; Saburova, M. Effects of three carbohydrate sources on water quality, water consumption, bacterial count, growth and muscle quality of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in a biofloc system. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 4225–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Zhang, M.M.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Xu, D.H.; Zhao, Z.G.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, Q. Biofloc technology (BFT): An alternative aquaculture system for prevention of Cyprinid herpesvirus 2 infection in gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 83, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, S.M.; Liu, D.Z.; Guo, X.S.; Ye, Z.Y. Effects of stocking density of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) on immunities, antioxidant status, and resistance against Vibrio harveyi in a biofloc system. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Hu, J.; Wan, W.; Han, B.; Zhou, Y.; Xin, Z.; Sun, L. Biofloc technology with addition of different carbon sources altered the antibacterial and antioxidant response in Macrobrachium rosenbergii to acute stress. Aquac. Int. 2020, 525, 735280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekasari, J. Biofloc Technology as an Integral Approach to Enhance Production and Ecological Performance of Aquaculture. Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Gent, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, H.; Shahkar, E.; Katya, K.; Jang, I.-K.; Kim, S.K.; Bai, S.C. Effects of bioflocs on dietary protein requirement in juvenile whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 3203–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Carbon/nitrogen ratio as a control element in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 1999, 176, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, C.; Bemani, A.; Alizadeh, M.; Siyahati, G.; Ardakani, T. Environmental sustainability assessment of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) breeding in biofloc system. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2022, 21, 1508–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, P.C.; Bayer, R.C. Fish byproducts as chemo-attractant substrates for the American lobster (Homarus americanus): Concentration, quality and release characteristics. Fish. Res. 1989, 7, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Thompson, P.J.; McIntosh, R.P.; Bauman, R.H.; Pearson, D.C. The contribution of flocculated material to shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) nutrition in a high-intensity, zero-exchange system. Aquaculture 2004, 232, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besen, K.P.; da Cunha, L.; de Oliveira, N.S.; Cipriani, L.A.; Bender, M.; Gomes, R.; Skoronski, E.; Fabregat, T.E.H.P. Biofloc technology (BFT) system improves survival and intestinal health of Carassius auratus larvae subjected to different food management. Aquac. Int. 2023, 31, 1979–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajamhasani, E.; Akrami, R.; Najdegerami, E.H.; Chitsaz, H.; Shamloofar, M. Different carbon sources and probiotics in biofloc based common carp (Cyprinus carpio) culture: Effects on water quality, growth performance, fish welfare and liver histopathology. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Kiessling, A.; Zhang, J. The future of intensive tilapia production and the circular bioeconomy without effluents: Biofloc technology, recirculation aquaculture systems, bio-RAS, partitioned aquaculture systems and integrated multitrophic aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15 (Suppl. S1), 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.W.; Utomo, N.B.P.; Yuhana, M.; Widanarni. Growth performance of catfish (Clarias gariepinus) in biofloc-based super intensive culture added with Bacillus sp. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, W.C.; Du, X.Z.; Tan, H.X.; Xie, J.; Luo, G.Z.; Sun, D.C. Performance of a recirculating aquaculture system using biofloc biofilters with convertible water-treatment efficiencies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Chen, J.; Gou, J.; Hou, J.; Li, D.; He, X. The effect of different carbon sources on water quality, microbial community and structure of biofloc systems. Aquaculture 2018, 482, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.F.; Pereira, S.A.; Martins, M.A.; Rezende, P.C.; Owatari, M.S.; Martins, M.L.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Vieira, F.d.N. Hemato-immunological parameters can be influenced by microalgae addition and fish feed supplementation in the integrated rearing of Pacific white shrimp and juvenile Nile tilapia using biofloc technology. Aquaculture 2023, 574, 739622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Costa, L.C.d.O.; Holanda, M.; Poersch, L.H.; Turan, G. Influence of total suspended solids on the growth of the sea lettuce ulva lactuca integrated with the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in a biofloc system. Fishes 2023, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerenciano, M.; Cuzon, G.; Goguenheim, J.; Gaxiola, G. Floc contribution on spawning performance of blue shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris. Aquac. Res. 2012, 44, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossier, P.; Ekasari, J. Biofloc technology application in aquaculture to support sustainable development goals. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.-B.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, J.-H.; Kang, J.-C.; Kim, J.-H. Comparative analysis of morphological characteristics, hematological parameters, body composition and sensory evaluation in olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus raised in biofloc and seawater to evaluate marketability. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 30, 101616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Photosynthetic suspended-growth systems in aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 344–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crab, R.; Defoirdt, T.; Bossier, P.; Verstraete, W. Biofloc technology in aquaculture: Beneficial effects and future challenges. Aquaculture 2012, 356–357, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.F.M. Use of biofloc technology in shrimp aquaculture: A comprehensive review, with emphasis on the last decade. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 13, 676–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, J.; Luo, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R.; Xu, W.; Huang, X. Combined effects of eco-substrate and carbon addition on water quality, fish performance and nutrient budgets in the pond polyculture system. Fishes 2022, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Biofloc technology: Fifteen years of progress. Hatch. Int. 2015, 16, 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, M.; Grossart, H.P.; Schweitzer, B.; Ploug, H. Microbial ecology of organic aggregates in aquatic ecosystems. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 28, 175–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshedi, V.; Kochanian, P.; Bahmani, M.; Yazdani-Sadati, M.A.; Pourali, H.R.; Ashouri, G.; Pasha-Zanoosi, H.; Azodi, M. Compensatory growth in sub-yearling Siberian sturgeon, Acipenser baerii Brandt, 1869: Effects of starvation and refeeding on growth, feed utilization and body composition. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2013, 29, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, P.; Zheng, D.; Deng, L.; Wang, W. N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL)-mediated microalgal–bacterial communication driving Chlorella-activated sludge bacterial biofloc formation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 12645–12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Bourven, I.; Guibaud, G.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Panico, A.; Pirozzi, F.; Esposito, G. Role of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) production in bioaggregation: Application to wastewater treatment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 9883–9905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Pan, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, C. Effect of using sodium bicarbonate to adjust the pH to different levels on water quality, the growth and the immune response of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei reared in zero-water exchange biofloc-based culture tanks. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 1194–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.Y.; Forster, I.; Conquest, L.; Dominy, W.; Kuo, W.C.; David Horgen, F. Determination of microbial community structures of shrimp floc cultures by biomarkers and analysis of floc amino acid profiles. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Rani, A.M.B.; Verma, A.K.; Maqsood, M. Biofloc technology: An emerging avenue in aquatic animal healthcare and nutrition. Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W.; Bossier, P. Quorum sensing and quorum quenching in Vibrio harveyi: Lessons learned from in vivo work. ISME J. 2007, 2, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schryver, P.; Verstraete, W. Nitrogen removal from aquaculture pond water by heterotrophic nitrogen assimilation in lab-scale sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, O.A.L.F.; Amado, A.M.; They, N.H. Biofloc colors as an assessment tool for water quality in shrimp farming with BFT systems. Aquac. Eng. 2023, 101, 102321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Biofloc Production Systems for Aquaculture; Southern Regional Aquaculture Center: Stoneville, MS, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, G.S.; Santos, D.; Schmachtl, F.; Machado, C.; Fernandes, V.; Bögner, M.; Schleder, D.D.; Seiffert, W.Q.; Vieira, F.N. Heterotrophic, chemoautotrophic and mature approaches in biofloc system for Pacific white shrimp. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Jiayang, L.; Jinxiang, X.; Liu, W.; Tan, H. Effects of dissolved organic carbon and total ammonia nitrogen concentrations with the same DOC/TAN on biofloc performance. Aquaculture 2023, 574, 739713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, H.; Tan, H.; Liu, W. Rapid production bioflocs by inoculation and fertilized with different nitrogen and carbon sources. Aquac. Eng. 2022, 98, 102262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Akrami, R.; Najdegerami, E.H.; Ghiasvand, Z.; Koohsari, H. Effects of different protein levels and carbon sources on water quality, antioxidant status and performance of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) juveniles raised in biofloc based system. Aquac. Int. 2020, 516, 734639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, M.H.; Suciyono, S.; Budi, D.S.; Ulkhaq, M.F.; Anugrahwati, M.; Ekasari, J. Biofloc-based co-culture systems of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and redclaw crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus) with different carbon-nitrogen ratios. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghparast, M.M.; Alishahi, M.; Ghorbanpour, M.; Shahriari, A. Evaluation of hemato-immunological parameters and stress indicators of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) in different C/N ratio of biofloc system. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 2191–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minabi, K.; Sourinejad, I.; Alizadeh, M.; Ghatrami, E.R.; Khanjani, M.H. Effects of different carbon to nitrogen ratios in the biofloc system on water quality, growth, and body composition of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) fingerlings. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 1883–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luo, G.; Tan, J.; Tan, H.; Yao, M. Effects of carbohydrate supply strategies and biofloc concentrations on the growth performance of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) cultured in biofloc systems. Aquac. Int. 2020, 517, 734808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinh, T.H.; Momoh, T.A.; Kokou, F.; Hai, T.N.; Schrama, J.W.; Verreth, J.A.J.; Verdegem, M.C.J. Effects of carbohydrate addition methods on Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2021, 543, 736890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasielesky, W.; Atwood, H.; Stokes, A.; Browdy, C.L. Effect of natural production in a zero exchange suspended microbial floc based super-intensive culture system for white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerenciano, M.; Cuzon, G.; Arévalo, M.; Miquelajauregui, M.M.; Gaxiola, G. Effect of short-term fresh food supplementation on reproductive performance, biochemical composition, and fatty acid profile of Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) reared under biofloc conditions. Aquac. Int. 2012, 21, 987–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crab, R.; Chielens, B.; Wille, M.; Bossier, P.; Verstraete, W. The effect of different carbon sources on the nutritional value of bioflocs, a feed for Macrobrachium rosenbergii postlarvae. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liao, S.-A.; Wang, A.-l. The effect of different carbon sources on the nutritional composition, microbial community and structure of bioflocs. Aquaculture 2016, 465, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugimura, M.M.S.; dos Reis Flor, H.; de Melo, E.P.; da Costa, T.V.; Wasielesky, W.; Oshiro, L.M.Y. Brewery residues as a source of organic carbon in Litopenaeus schmitti white shrimp farms with BFT systems. Aquac. Int. 2014, 23, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, M.; Rajabi Islami, H.; Nafisi Bahabadi, M.; Hosseini Shekarabi, S.P. Production of Pacific white shrimp under different stocking density in a zero-water exchange biofloc system: Effects on water quality, zootechnical performance, and body composition. Aquac. Eng. 2023, 100, 102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Alizadeh, M.; Sharifinia, M. Effects of different carbon sources on water quality, biofloc quality, and growth performance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fingerlings in a heterotrophic culture system. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, M.; Pandey, P.K.; Aravind, R.; Vennila, A.; Bharti, V.; Purushothaman, C.S. Effect of different biofloc system on water quality, biofloc composition and growth performance in Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931). Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 3432–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, S.; Meshram, S.J.; Dhamagaye, H.B.; Naik, S.D.; Shingare, P.E.; Yadav, B.M.; Ghafarifarsani, H. Effect of C/N ratio levels and stocking density of Catla spawn (Gibelion catla) on water quality, growth performance, and biofloc nutritional composition in an indoor biofloc system. Aquac. Res. 2023, 2023, 2501653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinh, T.H.; Koppenol, T.; Ngoc, H.T.; Verreth, J.A.J.; Verdegem, M.C.J. Effects of carbohydrate sources on a biofloc nursery system for whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lee, J.W.; Chandran, K.; Kim, S.; Sharma, K.; Khanal, S.K. Influence of carbohydrate addition on nitrogen transformations and greenhouse gas emissions of intensive aquaculture system. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hou, H.; Dong, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Song, X. Comparative life cycle assessment of whiteleg shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) cultured in recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS), biofloc technology (BFT) and higher-place ponds (HPP) farming systems in China. Aquaculture 2023, 574, 739625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaona, C.A.P.; Poersch, L.H.; Krummenauer, D.; Foes, G.K.; Wasielesky, W.J. The effect of solids removal on water quality, growth and survival of Litopenaeus vannamei in a biofloc technology culture system. Int. J. Recirc. Aquac. 2011, 12, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Li, J.W.; Liu, G.; Deng, Y.L.; Zhu, S.M.; Ye, Z.Y.; Shao, Y.F.; Liu, D.Z. Performance and microbial community analysis of Combined Denitrification and Biofloc Technology (CDBFT) system treating nitrogen-rich aquaculture wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, A.; Shekarabi, S.P.H.; Paknejad, H.; Harsij, M.; Khorshidi, Z.; Zolfaghari, M.; Hatami, A.S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Mazloumi, N.; Zakariaee, H. Various carbon/nitrogen ratios in a biofloc-based rearing system of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fingerlings: Effect on growth performance, immune response, and serum biochemistry. Aquaculture 2022, 548, 737622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrapani, S.; Panigrahi, A.; Sundaresan, J.; Sivakumar, M.R.; Palanisamy, R.; Kumar, V. Three different C: N ratios for Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei under practical conditions: Evaluation of growth performance, immune and metabolic pathways. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauda, A.B.; Romano, N.; Ebrahimi, M.; Teh, J.C.; Ajadi, A.; Chong, C.M.; Karim, M.; Natrah, I.; Kamarudin, M.S. Influence of carbon/nitrogen ratios on biofloc production and biochemical composition and subsequent effects on the growth, physiological status and disease resistance of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) cultured in glycerol-based biofloc systems. Aquaculture 2018, 483, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.S.; Silva, V.F.; Martins, M.A.; Chede Pereira da Silva, A.C.; Machado, C.; Seiffert, W.Q.; Vieira, F.d.N. Strategies for ammonium and nitrite control in Litopenaeus vannamei nursery systems with bioflocs. Aquac. Eng. 2020, 88, 102040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, G.; Luo, G.; Tan, H. The effect of different addition amounts of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate acid(PHB) as a slow-release carbon source in biological flocculation. Fish. Mod. 2021, 48, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tinh, T.H.; Hai, T.N.; Verreth, J.A.J.; Verdegem, M.C.J. Effects of carbohydrate addition frequencies on biofloc culture of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2021, 534, 736271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krummenauer, D.; Samocha, T.; Poersch, L.; Lara, G.; Wasielesky, W. The reuse of water on the culture of Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, in BFT system. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2014, 45, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, I.; Arantes, R.; Santo, C.M.D.; Vieira, F.D.; Lapa, K.R.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Fett, R.; Barcelos-Oliveira, J.L.; Seiffert, W.Q. Production of the halophyte Sarcocornia ambigua and Pacific white shrimp in an aquaponic system with biofloc technology. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 100, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.M.; Molinari, D.; de Mello, G.L.; Fitzsimmons, K.M.; Emerenciano, M.G.C. Effluent from a biofloc technology (BFT) tilapia culture on the aquaponics production of different lettuce varieties. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 103, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abakari, G.; Luo, G.Z.; Kombat, E.O.; Alhassan, E.H. Supplemental carbon sources applied in biofloc technology aquaculture systems: Types, effects and future research. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1193–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, D.D.; Lawrence, A.L.; Crockett, J. Dietary toxicity of manganese to shrimp and its accumulation in bioflocs. Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkuar, N.; Li, L.; Srisapoome, P.; Dong, S.; Tian, X. Application of biodegradable polymers as carbon sources in ex situ biofloc systems: Water quality and shift of microbial community. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 3570–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, A.-Z.; Li, M.-Y. Bioflocs attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation, immunosuppression and oxidative stress in Channa argus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 114, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.Z.; Zhang, N.; Cai, S.L.; Tan, H.X.; Liu, Z.F. Nitrogen dynamics, bacterial community composition and biofloc quality in biofloc-based systems cultured Oreochromis niloticus with poly-beta-hydroxybutyric and polycaprolactone as external carbohydrates. Aquaculture 2017, 479, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Liu, G.; Li, C.W.; Deng, Y.L.; Tadda, M.A.; Lan, L.H.; Zhu, S.M.; Liu, D.Z. Effects of different solid carbon sources on water quality, biofloc quality and gut microbiota of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) larvae. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abakari, G.; Luo, G.; Meng, H.; Yang, Z.; Owusu-Afriyie, G.; Kombat, E.O.; Alhassan, E.H. The use of biochar in the production of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in a biofloc technology system-BFT. Aquac. Eng. 2020, 91, 102123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontakke, R.; Tiwari, V.K.; Kurcheti, P.; Asanaru Majeedkutty, B.R.; Ande, M.P.; Haridas, H. Yam-based biofloc system improves the growth, digestive enzyme activity, bacterial community structure and nutritional content in milkfish (Chanos chanos). Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 3460–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.A.H.; Sharawy, Z.Z.; El Nahas, A.F.; Hemeda, S.A.; El-Haroun, E.; Abbas, E.M. Modulatory effects of various carbon sources on growth indices, digestive enzymes activity and expression of growth-related genes in Whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei reared under an outdoor zero-exchange system. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 5594–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaorui, L.; Xiefa, S.; Guangjun, Z.; Dengpan, D. Study on biofloc of mariculture using PLA and PHBV as carbon sources. Fish. Mod. 2022, 49, 1110. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.F.; Ma, C.J.; Huang, X.F.; Liu, J.; Lu, L.J.; Peng, K.M.; Li, S.Y. Research progress in solid carbon source-based denitrification technologies for different target water bodies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Luo, G.Z.; Tan, H.X.; Liu, W.C.; Hou, Z.W. Growth, digestive enzyme activity and welfare of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) reared in a biofloc-based system with poly-beta-hydroxybutyric as a carbon source. Aquaculture 2016, 464, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Cai, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Xia, L. Effects of different carbon sources and carbon-nitrogen ratios on the survival, growth, intestinal biochemical parameters, and water quality of seahorse juveniles cultured under zero-water exchange conditions. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 2095–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Li, L.; Dong, S.; Gao, Q.; Tian, X. The Effects of different carbon sources on the production environment and breeding parameters of Litopenaeus vannamei. Water 2021, 13, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Biofloc Technology-A Practical Guide Book; The World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Zahedi, S.; Mohammadi, A. Integrated multitrophic aquaculture (IMTA) as an environmentally friendly system for sustainable aquaculture: Functionality, species, and application of biofloc technology (BFT). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 67513–67531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, I.; Carneiro, R.F.S.; Vieira, F.D.N.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Fett, R.; Costa, A.C.D.O.; Magallón-Barajas, F.J.; Seiffert, W.Q. Aquaponic production of Sarcocornia ambigua and Pacific white shrimp in biofloc system at different salinities. Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Rekha, P.N.; Panigrahi, A.; Das, R.R.; Rajamanickam, S.; Balasubramanian, C.P. Integrated brackishwater farming of red seaweed Agarophyton tenuistipitatum and Pacific white leg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) in biofloc system: A production and bioremediation way out. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 2145–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legarda, E.C.; da Silva, D.; Miranda, C.S.; Pereira, P.K.M.; Martins, M.A.; Machado, C.; de Lorenzo, M.A.; Hayashi, L.; do Nascimento Vieira, F. Sea lettuce integrated with Pacific white shrimp and mullet cultivation in biofloc impact system performance and the sea lettuce nutritional composition. Aquaculture 2021, 534, 736265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.M.; David, L.H.C.; Goddek, S.; Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Portella, M.C. Integrated production of Nile tilapia juveniles and lettuce using biofloc technology. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Cordova, L.R.; Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Miranda-Baeza, A.; Pinho, S.M.; Garibay-Valdez, E.; Martinez-Porchas, M. Advancing toward a more integrated aquaculture with polyculture > aquaponics > biofloc technology > FLOCponics. Aquac. Int. 2022, 31, 1057–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharawy, Z.Z.; Abbas, E.M.; Abdelkhalek, N.K.; Ashry, O.A.; Abd El-Fattah, L.S.; El-Sawy, M.A.; Helal, M.F.; El-Haroun, E. Effect of organic carbon source and stocking densities on growth indices, water microflora, and immune-related genes expression of Litopenaeus vannamei Larvae in intensive culture. Aquac. Int. 2022, 546, 737397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaduzzaman, M.; Wahab, M.A.; Verdegem, M.C.J.; Adhikary, R.K.; Rahman, S.M.S.; Azim, M.E.; Verreth, J.A.J. Effects of carbohydrate source for maintaining a high C:N ratio and fish driven re-suspension on pond ecology and production in periphyton-based freshwater prawn culture systems. Aquaculture 2010, 301, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogello, E.O.; Outa, N.O.; Obiero, K.O.; Kyule, D.N.; Munguti, J.M. The prospects of biofloc technology (BFT) for sustainable aquaculture development. Sci. Afr. 2021, 14, e01053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).