Acute Effects of Fluoxetine on Stress Responses and Feeding Motivation in Nile Tilapia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Fish and Holding Conditions
2.2.1. Stock Population
2.2.2. Experimental Aquaria
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Measured Variables
2.4.1. Ventilation Rate (VR)
2.4.2. Feeding Behavior
2.4.3. Blood Collection, Sample Processing and Plasma Cortisol Analysis
2.5. Data Analyses
3. Results
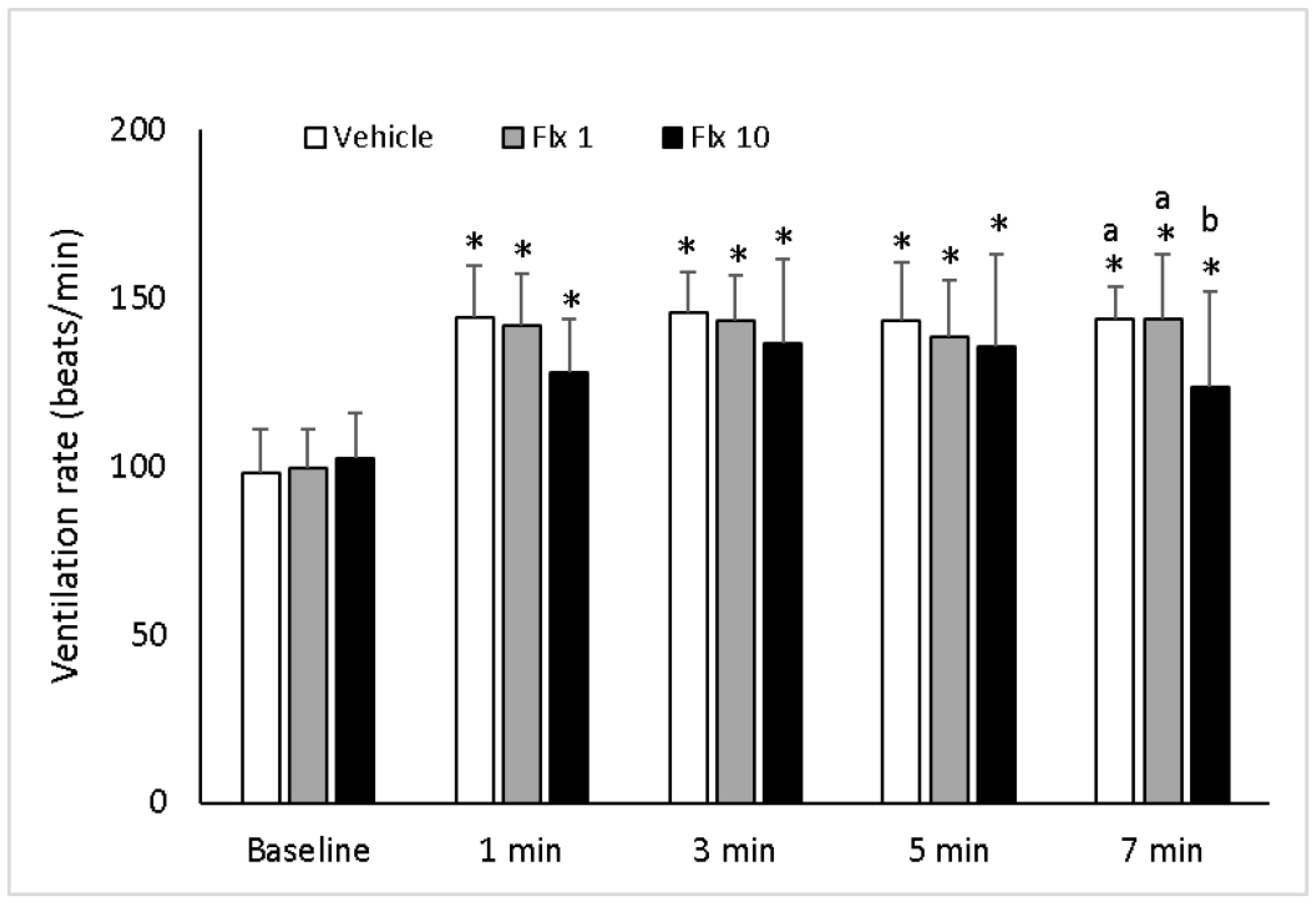
3.1. Ventilation Rate (VR)
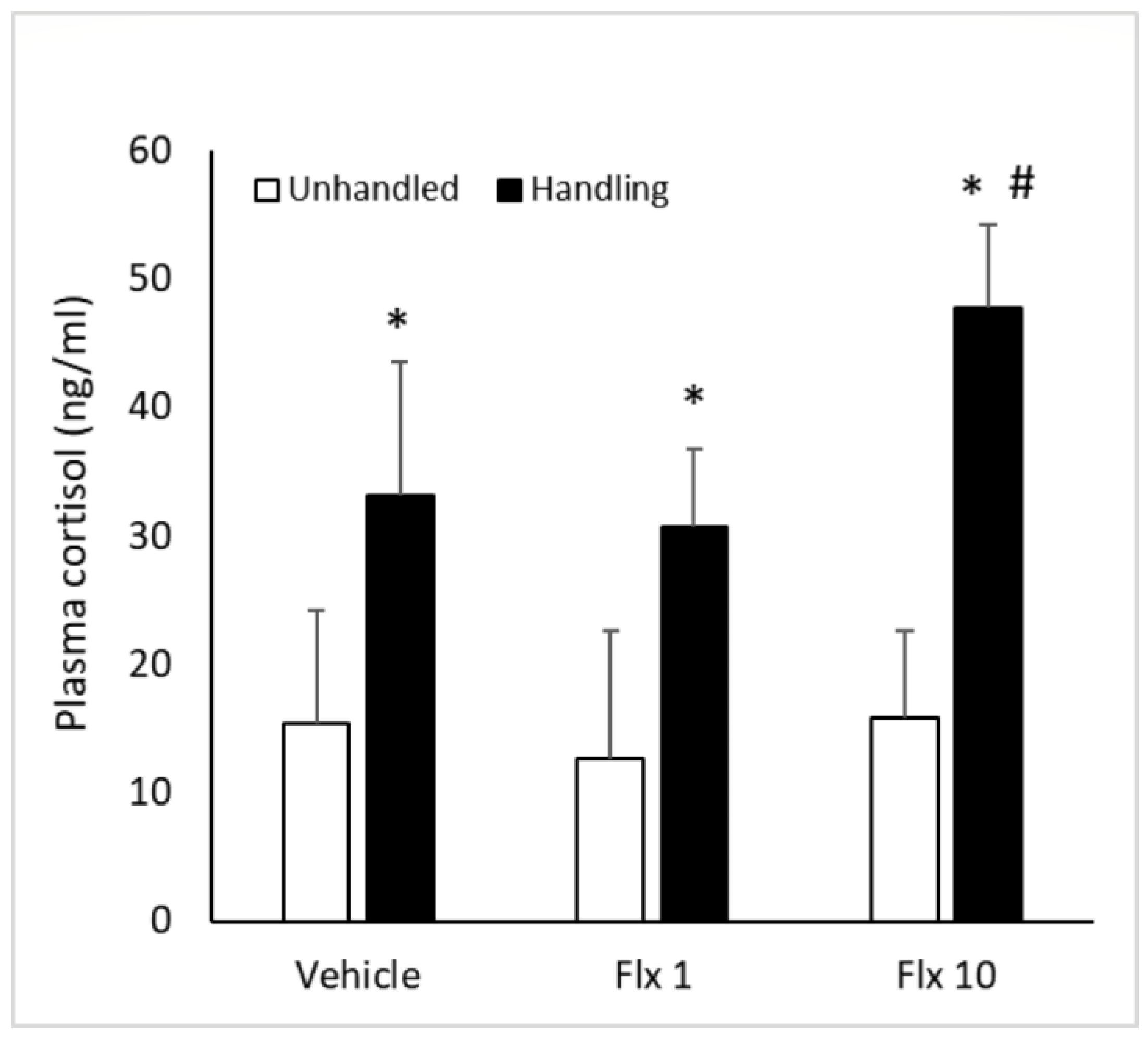
3.2. Plasma Cortisol
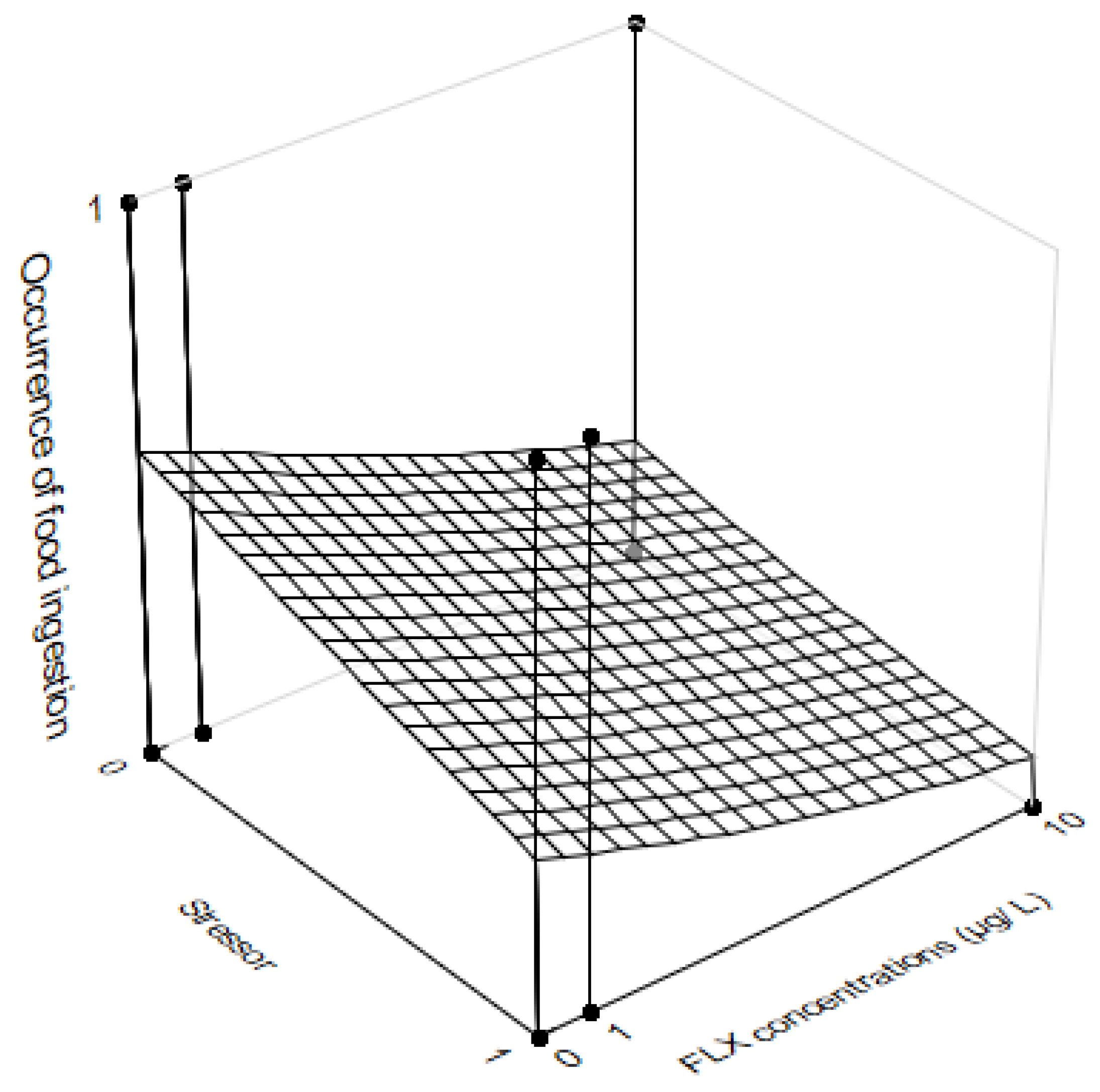
3.3. Feeding Behavior
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reid, S.G.; Bernier, N.J.; Perry, S.F. The adrenergic stress response in fish: Control of catecholamine storage and release. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C—Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1998, 120, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, S.F.; Bernier, N.J. The acute humoral adrenergic stress response in fish: Facts and fiction. Aquaculture 1999, 177, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altimiras, J.; Larsen, E. Non-invasive recording of heart rate and ventilation rate in rainbow trout during rest and swimming. Fish go wireless! J. Fish Biol. 2000, 57, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, R.E.; Volpato, G.L. Caution for using ventilatory frequency as an indicator of stress in fish. Behav. Proc. 2004, 66, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, R.E.; Volpato, G.L. Ventilatory frequency of Nile tilapia subjected to different stressors. J. Exp. Anim. Sci. 2006, 43, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, R.E.; Volpato, G.L. Ventilation rates indicate stress-coping styles in Nile tilapia. J. Biosci. 2011, 36, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, C.M.; Volpato, G.L. Environmental light color affects the stress response of Nile tilapia. Zoology 2013, 116, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, B.A.; Iwama, G.K. Physiological changes in fish from stress in aquaculture with emphasis on the response and effects of corticosteroids. Ann. Rev. Fish Dis. 1991, 1, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendelaar-Bonga, S.E. The stress response in fish. Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 591–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, B.A. Stress in fishes: A diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integrat. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommsen, T.P.; Vijayan, M.M.; Moon, T.W. Cortisol in teleosts: Dynamics, mechanisms of action, and metabolic regulation. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1999, 9, 211–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calogero, A.E.; Bagdy, G.; Szemeredi, K.; Tartaglia, M.E.; Gold, P.W.; Chrousos, G.P. Mechanisms of serotonin receptor agonist-induced activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary- adrenal axis in the rat. Endocrinology 1990, 126, 1888–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, C.A. Functional subsets of serotonergic neurones: Implications for control of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2002, 14, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiradentes, R.V.; Pires, J.G.P.; Silva, N.F.; Ramage, A.G.; Santuzzi, C.H.; Futuro Neto, H.A. Effects of acute administration of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on sympathetic nerve activity. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herculano, A.M.; Maximino, C. Serotonergic modulation of zebrafish behavior: Towards a paradox. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psych. 2014, 55, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahinejad, A.; Attaran, A.; Meuthen, D.; Chivers, D.P.; Niyogi, S. Proximate causes and ultimate effects of common antidepressants, fluoxetine and venlafaxine, on fish behavior. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, B.B.; Schoonheim, P.J.; Ziv, L.; Voelker, L.; Baier, H.; Gahtan, E. A zebrafish model of glucocorticoid resistance shows serotonergic modulation of the stress response. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winberg, S.; Nilsson, A.; Hylland, P.; Soderstom, V.; Nilsson, G.E. Serotonin as a regulator of hypothalamic-pituitary-interrenal activity in teleost fish. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 230, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolpin, D.W.; Furlong, E.T.; Meyer, M.T.; Thurman, E.M.; Zaugg, S.D.; Barber, L.B.; Buxton, H.T. Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in streams, 1999–2000: A national reconnaissance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, C.D.; Miao, X.S.; Koenig, B.G.; Struger, J. Distribution of acidic and neutral drugs in surface waters near sewage treatment plants in the lower Great Lakes, Canada. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 2881–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, C.D.; Chu, S.; Judt, C.; Li, H.; Oakes, K.D.; Servos, M.R.; Andrews, D.M. Antidepressants and their metabolites in municipal wastewater, and downstream exposure in an urban watershed. Environ. Sci. Chem. 2010, 29, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.M.; Markussen, B.; Baun, A.; Halling-Sørensen, B. Probabilistic environmental risk characterization of pharmaceuticals in sewage treatment plant discharges. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farré, M.; Pérez, S.; Kantiani, L.; Barceló, D. Fate and toxicity of emerging pollutants, their metabolites and transformation products in the aquatic environment. TrAC—Trends Analyt. Chem. 2008, 27, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.M.; Furlong, E.T.; Kolpin, D.W.; Werner, S.L.; Schoenfuss, H.L.; Barber, L.B.; Blazer, V.S.; Norris, D.O.; Vajda, A.M. Antidepressant pharmaceuticals in two effluent-impacted U.S. streams: Occurrence and fate in water and sediment and selective uptake in fish neural tissue. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, B.W. Fish on Prozac (and Zoloft): Ten years later. Aquat. Toxciol. 2014, 151, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, P.; Cunha, V.; Ferreira, M.; Reis-Henriques, M.A.; Oliva-Teles, L.; Guimarães, L.; Carvalho, A.P. Differential Molecular Responses of Zebrafish Larvae to Fluoxetine and Norfluoxetine. Water 2022, 14, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, N.O.; Oliveira, R.; Moretti, P.N.S.; Mona e Pinto, J.; Oliveira, A.C.; Santos, V.L.; Rocha, P.S.; Andrade, T.S.; Grisolia, C.K. Fluoxetine chronic exposure affects growth, behavior and tissue structure of zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 237, 108836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morando, M.B.; Medeiros, L.R.; McDonald, M.D. Fluoxetine treatment affects nitrogen waste excretion and osmoregulation in a marine teleost fish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 95, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, M.D.; Gonzalez, A.; Sloman, K.A. Higher levels of aggression are observed in socially dominant toadfish treated with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, fluoxetine. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 153C, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, D.; Domingues, I.; Faria, M.; Oliveira, M. Effects of fluoxetine on fish: What do we know and where should we focus our efforts in the future? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857 Pt 2, 159486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennigen, J.A.; Stroud, P.; Zamora, J.M.; Moon, T.W.; Trudeau, V.L. Pharmaceuticals as Neuroendocrine Disruptors: Lessons Learned from Fish on Prozac. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health—Part B 2011, 14, 387–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, M.S.D.; Giacomini, A.C.V.; Koakoski, G.; Piato, A.L.; Barcellos, L.J.G. Divergent effect of fluoxetine on the response to physical or chemical stressors in zebrafish. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, M.S.D.; Koakoski, G.; Ferreira, D.; Oliveira, T.A.; Rosa, J.G.S.D.; Gusso, D.; Giacomini, A.C.V.; Piato, A.L.; Barcellos, L.J.G. Diazepam and fluoxetine decrease the stress response in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera-Chang, M.N.; St-Jacques, A.D.; Lu, C.; Moon, T.W.; Trudeau, V.L. Fluoxetine exposure during sexual development disrupts the stress axis and results in sex-and time-dependent effects on the exploratory behavior in adult zebrafish Danio rerio. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebire, M.; Davis, J.E.; Hatfield, R.; Winberg, S.; Katsiadaki, I. Prozac affects stickleback nest quality without altering androgen, spiggin or aggression levels during a 21-day breeding test. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 168, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridi, A.; Tsalafouta, A.; Pavlidis, M. Acute Exposure to Fluoxetine Alters Aggressive Behavior of Zebrafish and Expression of Genes Involved in Serotonergic System Regulation. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valassi, E.; Scacchi, M.; Cavagnini, F. Neuroendocrine control of food intake. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 18, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpato, G.L.; Bovi, T.S.; de Freitas, R.H.A.; da Silva, D.F.; Delicio, H.C.; Giaquinto, P.C.; Barreto, R.E. Red Light Stimulates Feeding Motivation in Fish but Does Not Improve Growth. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.J.; Cerdá-Reverter, J.M.; Soengas, J.L. Hypothalamic integration of metabolic, endocrine and circadian signals in fish: Involvement in cortisol of food intake. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennigen, J.A.; Harris, E.A.; Chang, J.P.; Moon, T.W.; Trudeau, V.L. Fluoxetine affects weight gain and expression of feeding peptides in the female goldfish brain. Regul. Pept. 2009, 155, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennigen, J.A.; Sassine, J.; Trudeau, V.L.; Moon, T.W. Waterborne fluoxetine disrupts feeding and energy metabolism in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, V.P.; Gaydou, R.C.; Schiöth, H.B.; de Barioglio, S.R. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (fluoxetine) decreases the effects of ghrelin on memory retention and food intake. Regul. Pept. 2007, 140, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pedro, N.; Pinillos, M.L.; Valenciano, A.I.; Alonso-Bedate, M.; Delgado, M.J. Inhibitory effect of serotonin on feeding behavior in goldfish: Involvement of CRH. Peptides 1998, 19, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-Sieira, M.; Chivite, M.; Míguez, J.M.; Soengas, J.L. Stress effects on the mechanisms regulating appetite in teleost fish. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijitkul, P.; Kongsema, M.; Toommakorn, T.; Bullangpoti, V. Investigation of genotoxicity, mutagenicity, and cytotoxicity in erythrocytes of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) after fluoxetine exposure. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, W.C.; Barros, H.P.; Moraes-Valenti, P.; Bueno, G.W.; Cavalli, R.O. Aquaculture in Brazil: Past, present and future. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves-de-Freitas, E.; Bolognesi, M.C.; Gauy, A.C.d.S.; Brandão, M.L.; Giaquinto, P.C.; Fernandes-Castilho, M. Social Behavior and Welfare in Nile Tilapia. Fishes 2019, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.R.; Arvigo, A.L.; Giaquinto, P.C.; Delicio, H.C.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Barreto, R.E. Effects of clove oil on behavioral reactivity and motivation in Nile tilapia. Aquaculture 2021, 532, 736045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, V.C.L.; Delicio, H.C.; Barreto, R.E. Effects of stress-associated odor on ventilation rate and feeding performance in Nile tilapia. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.C.C. A Presença de Fármacos e Cafeína em Água Superficial e Destinada ao Consumo Humano (The Presence of Pharmaceuticals and Caffeine in Surface and Treated Water). Ph.D. Thesis, University of São Paulo (USP), São Paulo, SP, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedner, M.; MacCrehan, W.A. Reactions of the amine-containing drugs fluoxetine and metoprolol during chlorination and dechlorination processes used in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, J.; Klaper, R. Environmental concentrations of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor fluoxetine impact specific behaviors involved in reproduction, feeding and predator avoidance in the fish Pimephales promelas (fathead minnow). Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 151, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, A.K.; Mathis, A. Opercular beat rate for rainbow darters Etheostoma caeruleam exposed to chemical stimuli from conspecific and heterospecific. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 69, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, E.; Brownscombe, J.W.; Cooke, S.J. Behavioural and reflex responses of mottled mojarra Eucinostomus lefroyi (Gerreidae) to cold shock exposure. Aquat. Biol. 2014, 23, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freret-Meurer, N.V.; Carmo, T.F.; Cabiró, G. Opercular beat: A non-invasive and rapid method to detect stress in seahorses. J. Appl. Aquac. 2021, 33, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roza-e-Silva, M.L.; Pereira, R.T.; Arvigo, A.L.; Zanuzzo, F.S.; Barreto, R.E. Effects of water flow on ventilation rate and plasma cortisol in Nile tilapia introduced into novel environment. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, C.M.D.; Volpato, G.L. Agonistic profile and metabolism in alevins of the Nile tilapia. Physiol. Behav. 1995, 57, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilderhus, P.A.; Marking, L.L. Comparative efficacy of 16 anaesthetic chemicals on rainbow trout. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1987, 7, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoskopf, M. Anaesthesia. In Aquaculture for Veterinarians; Brown, L., Ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1993; pp. 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Sink, T.D.; Lochmann, R.T.; Fecteau, K.A. Validation, use, and disadvantages of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits for detection of cortisol in channel catfish, largemouth bass, red pacu and golden shiners. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 75, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice-Hall/Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, S.K.; Kim, J.H. Statistical data preparation: Management of missing values and outliers. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2017, 70, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, R.J.; Bergner, C.L.; Hart, P.C.; Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elegante, M.F.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Tien, A.K.; Tien, D.H.; et al. Understanding behavioural and physiological phenotypes of stress and anxiety in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, A.C.V.V.; Abreu, M.S.; Giacomini, L.V.; Siebel, A.M.; Zimerman, F.F.; Rambo, C.L.; Mocelin, R.; Bonan, C.D.; Piato, A.L.; Barcellos, L.J.G. Fluoxetine and diazepam acutely modulate stress induced-behavior. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 296, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, M.S.D.; Giacomini, A.C.V.V.; Kalueff, A.V.; Barcellos, L.J.G. The smell of “anxiety”: Behavioral modulation by experimental anosmia in zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 157, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.B.; Jessop, D.S.; Harbuz, M.S.; Mørk, A.; Sánchez, C.; Mikkelsen, J.D. Acute and long-term treatments with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram modulate the HPA axis activity at different levels in male rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 1999, 11, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.T.; Leutz, J.A.C.M.; Valença-Silva, G.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Barreto, R.E. Ventilation responses to predator odors and conspecific chemical alarm cues in the frillfin goby. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 179, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanuzzo, F.S.; Bovolato, A.L.C.; Pereira, R.T.; Valença-Silva, G.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Barreto, R.E. Innate response based on visual cues of sympatric and allopatric predators in Nile tilapia. Behav. Proc. 2019, 164, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panlilio, J.; Marin, S.; Lobl, M.M.; McDonald, D. Treatment with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, fluoxetine, attenuates the fish hypoxia response. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.F.; Reid, S.G.; Gilmour, K.M.; Boijink, C.L.; Lopes, J.M.; Milsom, W.K.; Rantin, F.T. A comparison of adrenergic stress responses in three tropical teleosts exposed to acute hypoxia Amer. J. Physiol.—Regul. Integrat. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 287, R188–R197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.N.; Rantin, F.T. Relationships between oxygen availability and metabolic cost of breathing in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Aquacultural consequences. Aquaculture 1994, 127, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruibal, C.; Soengas, J.; Aldegunde, M. Brain serotonina and the control of food intake in rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss): Effects of changes in plasma glucose levels. J. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 188, 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, J.J.M.; Mancebo, M.J.; Aldegunde, M. The involvement of HT-like receptors in the regulation of food intake in rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2014, 161, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Varela, A.C.C.; Soares, S.M.; Fortuna, M.; Costa, V.C.; Piasson, Í.B.; Mozatto, M.T.; Siqueira, L.; Barcellos, H.H.A.; Barreto, R.E.; Barcellos, L.J.G. A single exposure to sub-lethal concentrations of a glyphosate-based herbicide or fluoxetine-based agent on growth performance in Nile tilapia. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2023, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miranda, J.P.G.A.; Isaac, A.B.J.; Silva, R.B.; Toledo, L.C.S.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Delicio, H.C.; Barreto, R.E. Acute Effects of Fluoxetine on Stress Responses and Feeding Motivation in Nile Tilapia. Fishes 2023, 8, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070348
Miranda JPGA, Isaac ABJ, Silva RB, Toledo LCS, Barcellos LJG, Delicio HC, Barreto RE. Acute Effects of Fluoxetine on Stress Responses and Feeding Motivation in Nile Tilapia. Fishes. 2023; 8(7):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070348
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiranda, Julia P. G. A., Ana Beatriz J. Isaac, Rebeca B. Silva, Leandro C. S. Toledo, Leonardo J. G. Barcellos, Helton Carlos Delicio, and Rodrigo Egydio Barreto. 2023. "Acute Effects of Fluoxetine on Stress Responses and Feeding Motivation in Nile Tilapia" Fishes 8, no. 7: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070348
APA StyleMiranda, J. P. G. A., Isaac, A. B. J., Silva, R. B., Toledo, L. C. S., Barcellos, L. J. G., Delicio, H. C., & Barreto, R. E. (2023). Acute Effects of Fluoxetine on Stress Responses and Feeding Motivation in Nile Tilapia. Fishes, 8(7), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8070348




