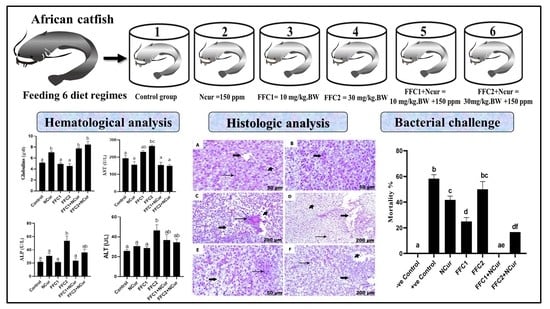
Dietary Nanocurcumin Impacts Blood Biochemical Parameters and Works Synergistically with Florfenicol in African Catfish Challenged with Aeromonas veronii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Florfenicol Medicated Feed
2.2. Preparation of Nanocurcumin
2.3. Fish Acclimation and Husbandry Conditions
2.4. Experiment I (Sampling Tanks)
2.4.1. Experimental Conditions
2.4.2. Analysis of Serum Biochemical Indices
2.4.3. Histopathological Examination
2.5. Experiment II (Bacterial Challenge)
2.5.1. Bacterial Strain, Suspension, and Counts
2.5.2. Bacterial Infection
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
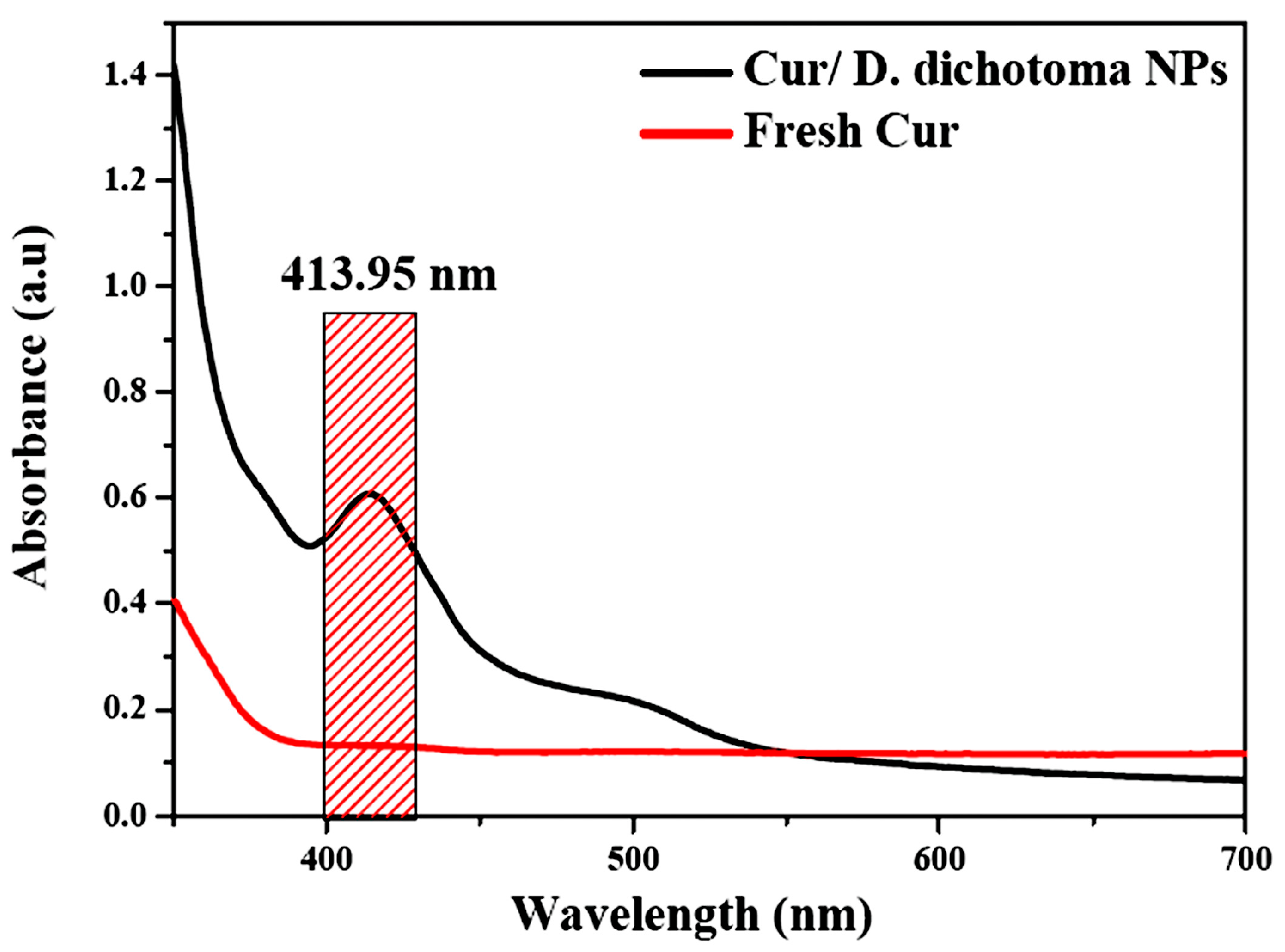
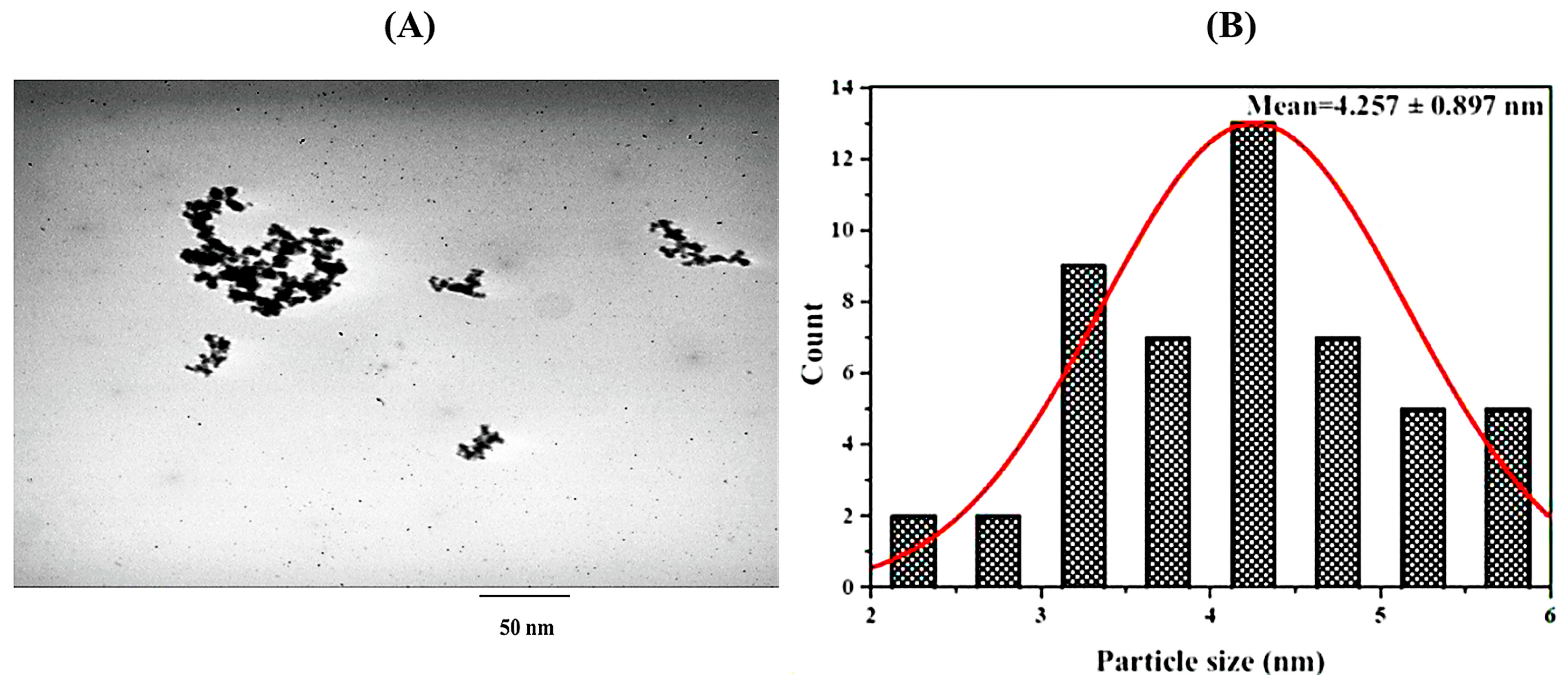
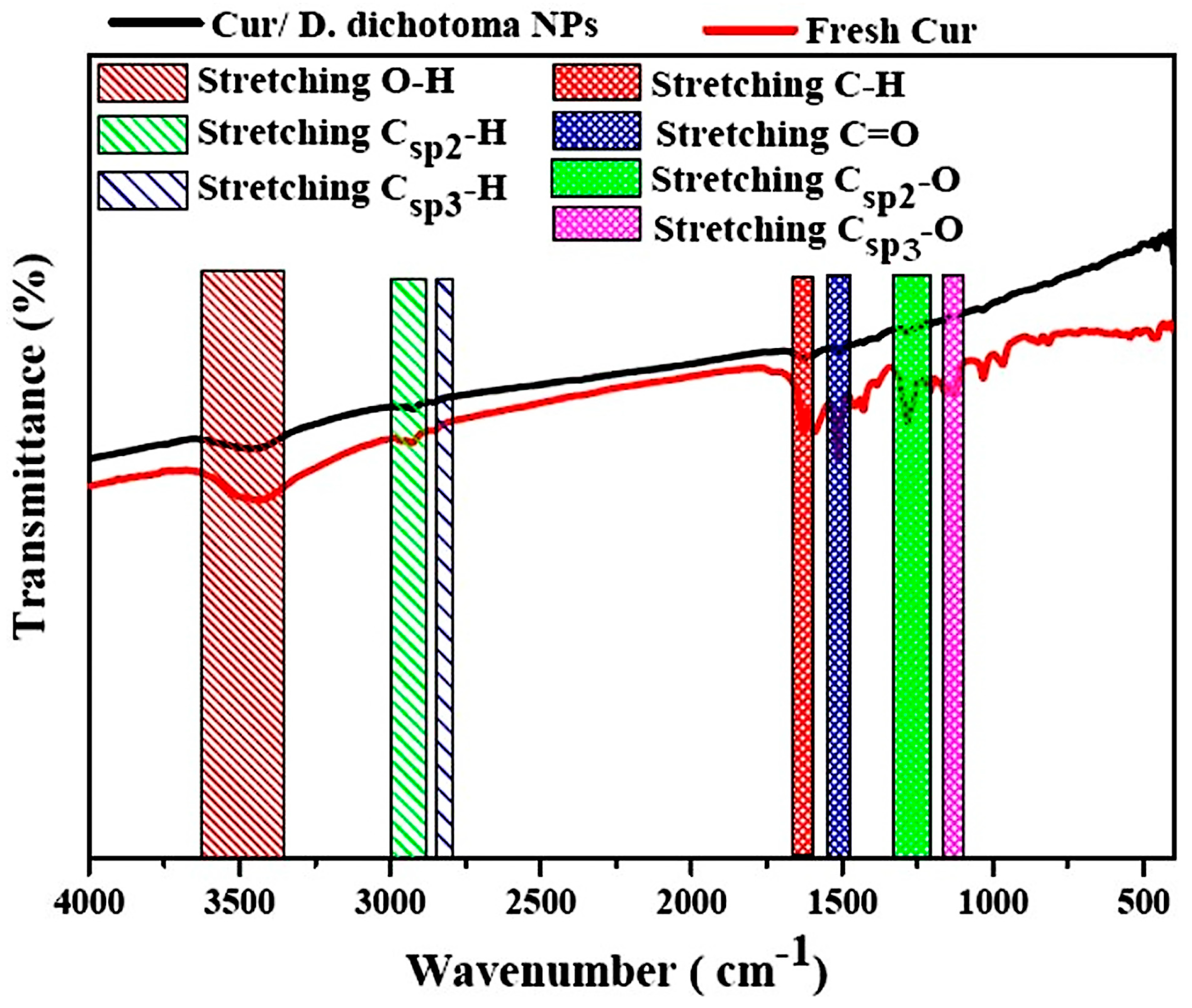
3.1. Characterization of Cur/D. dichotoma NPs
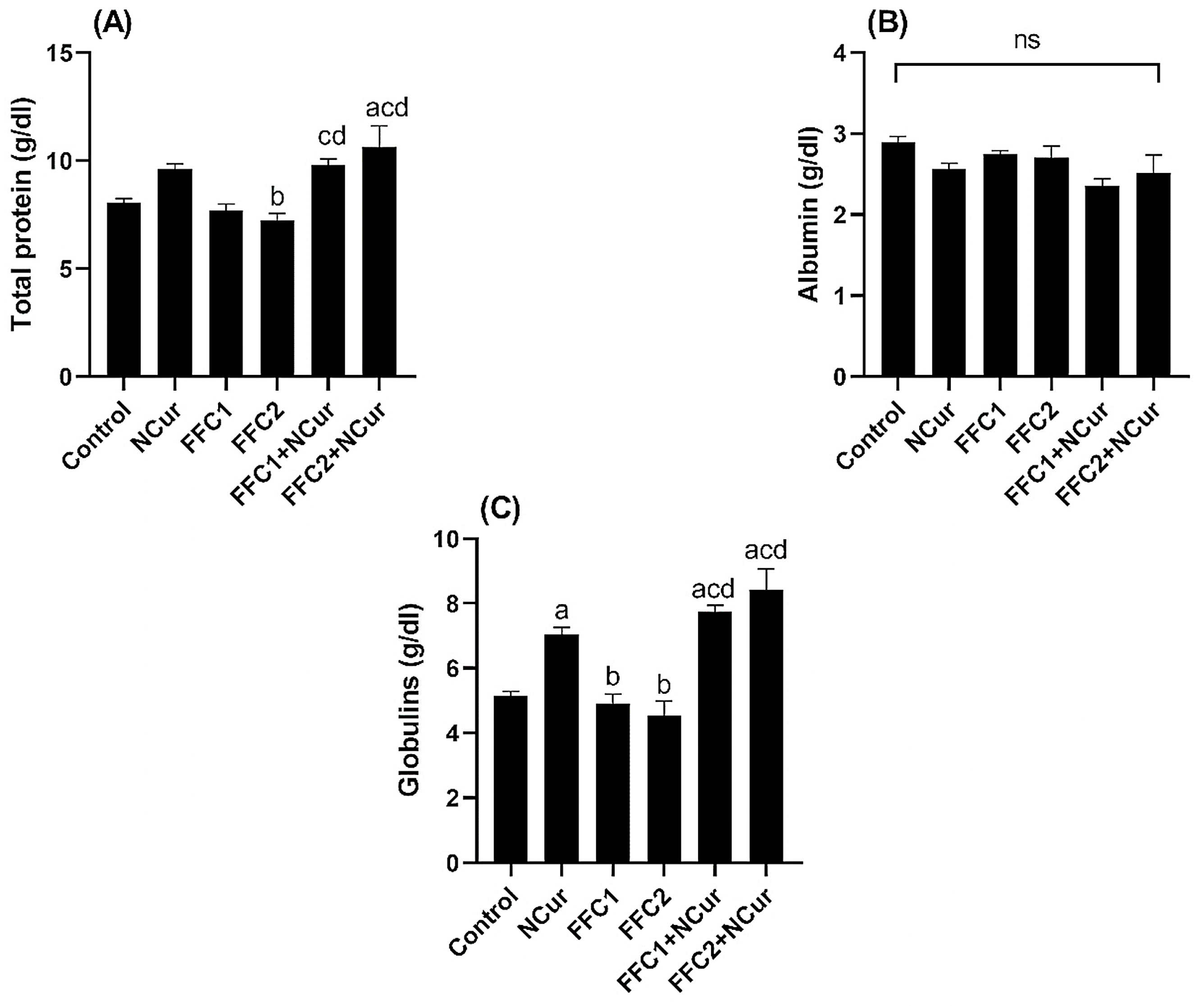
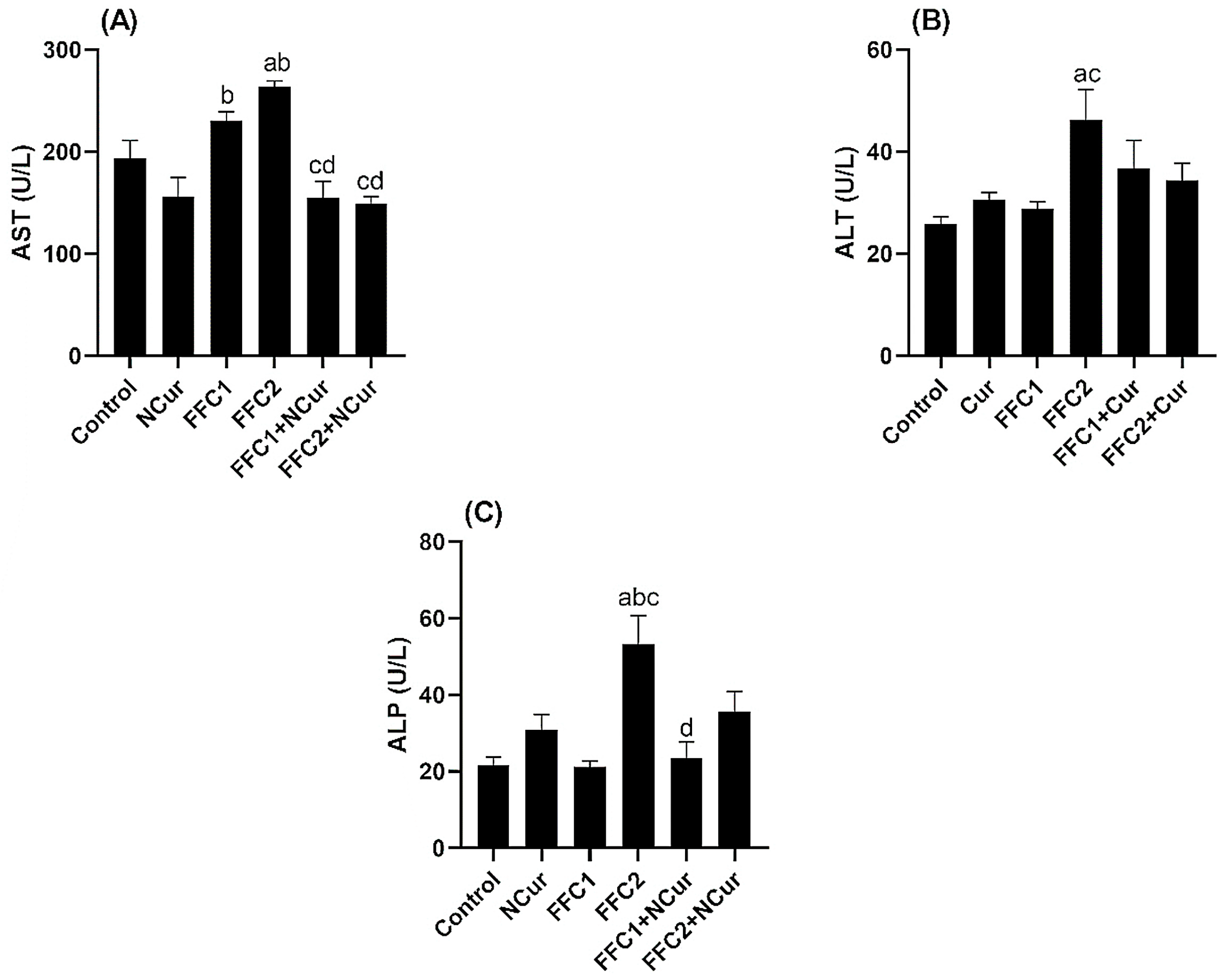
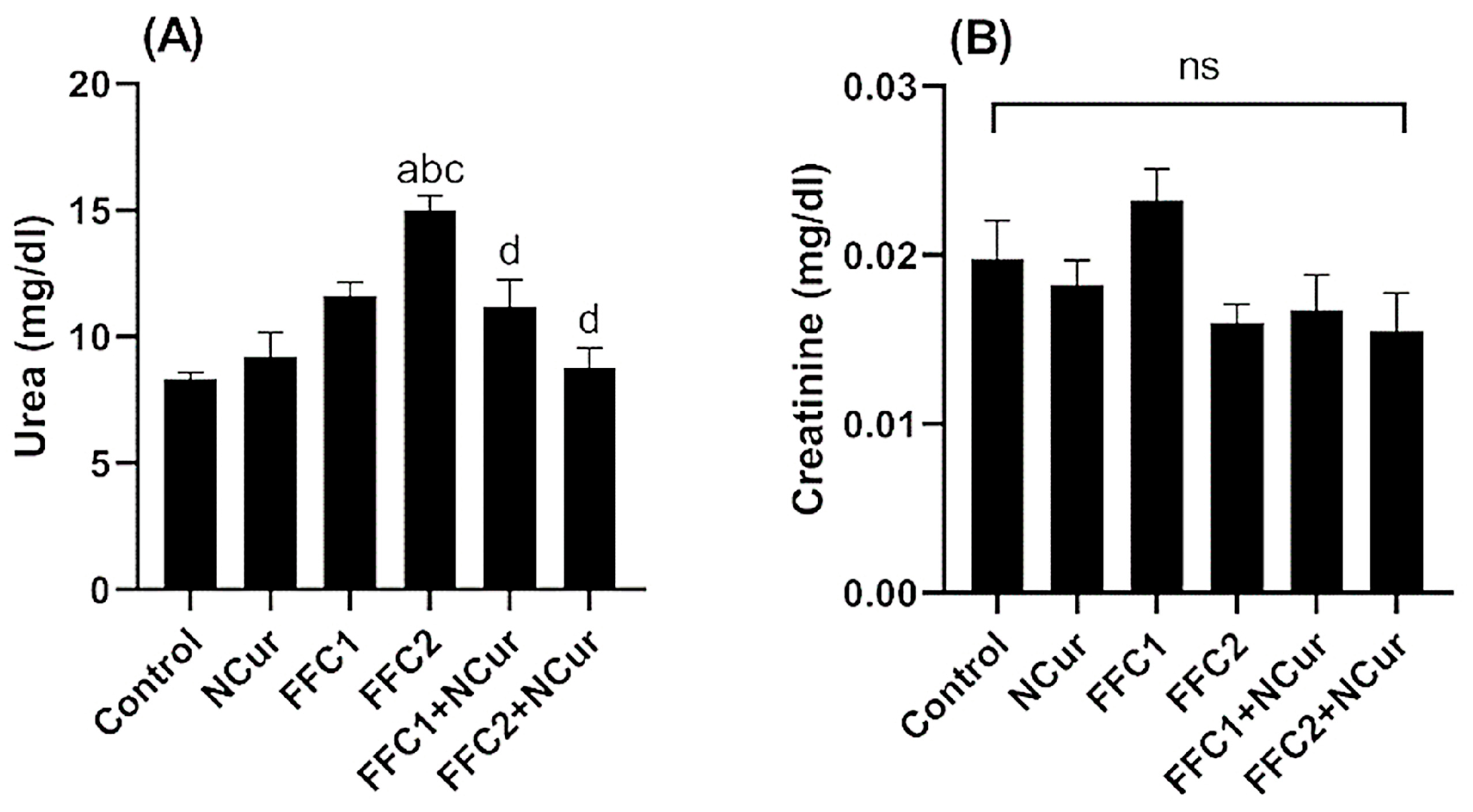
3.2. Biochemical Parameters
3.3. Histological Studies
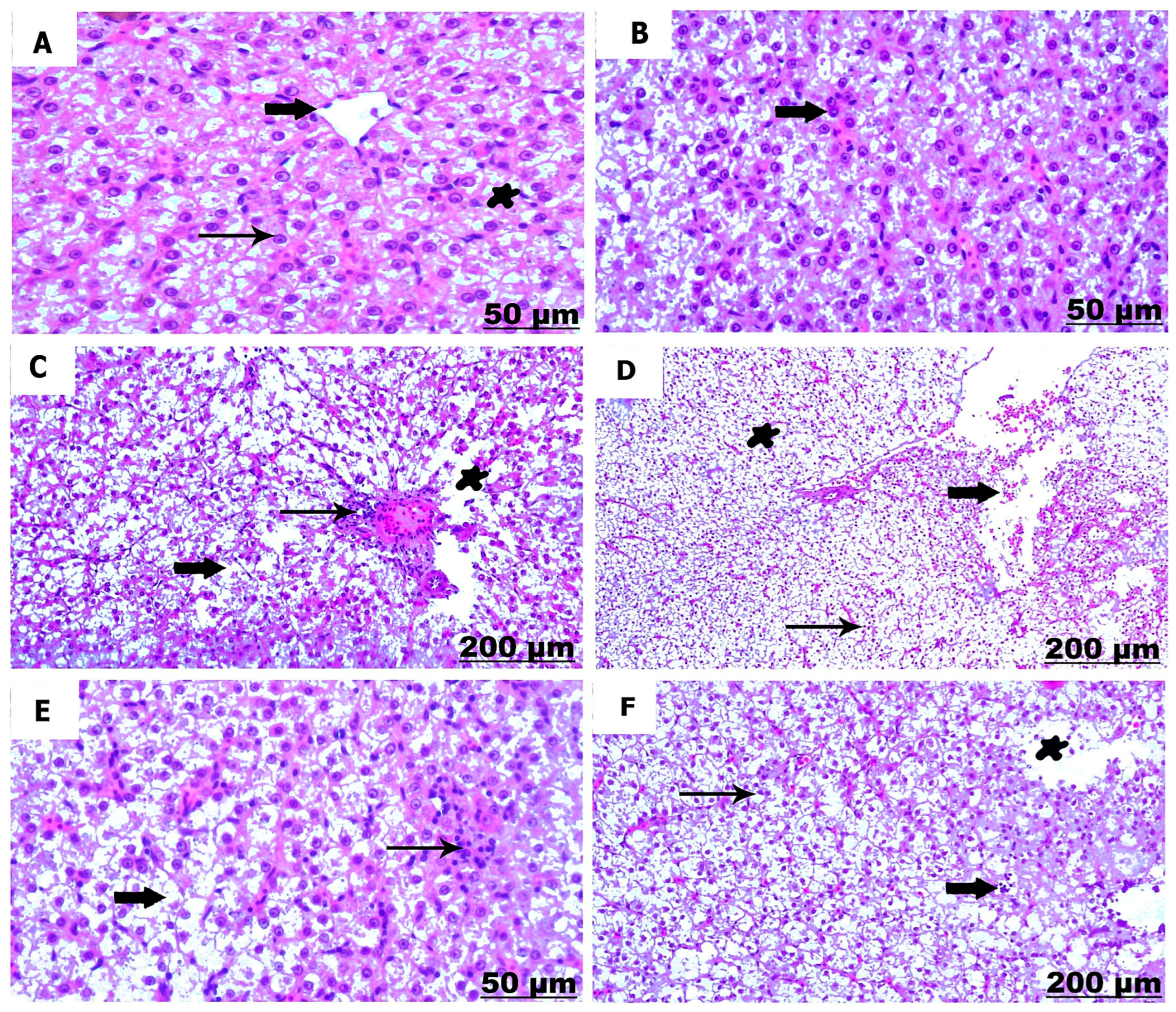
3.3.1. Histological Examination of the Liver
3.3.2. Histological Examination of the Kidney
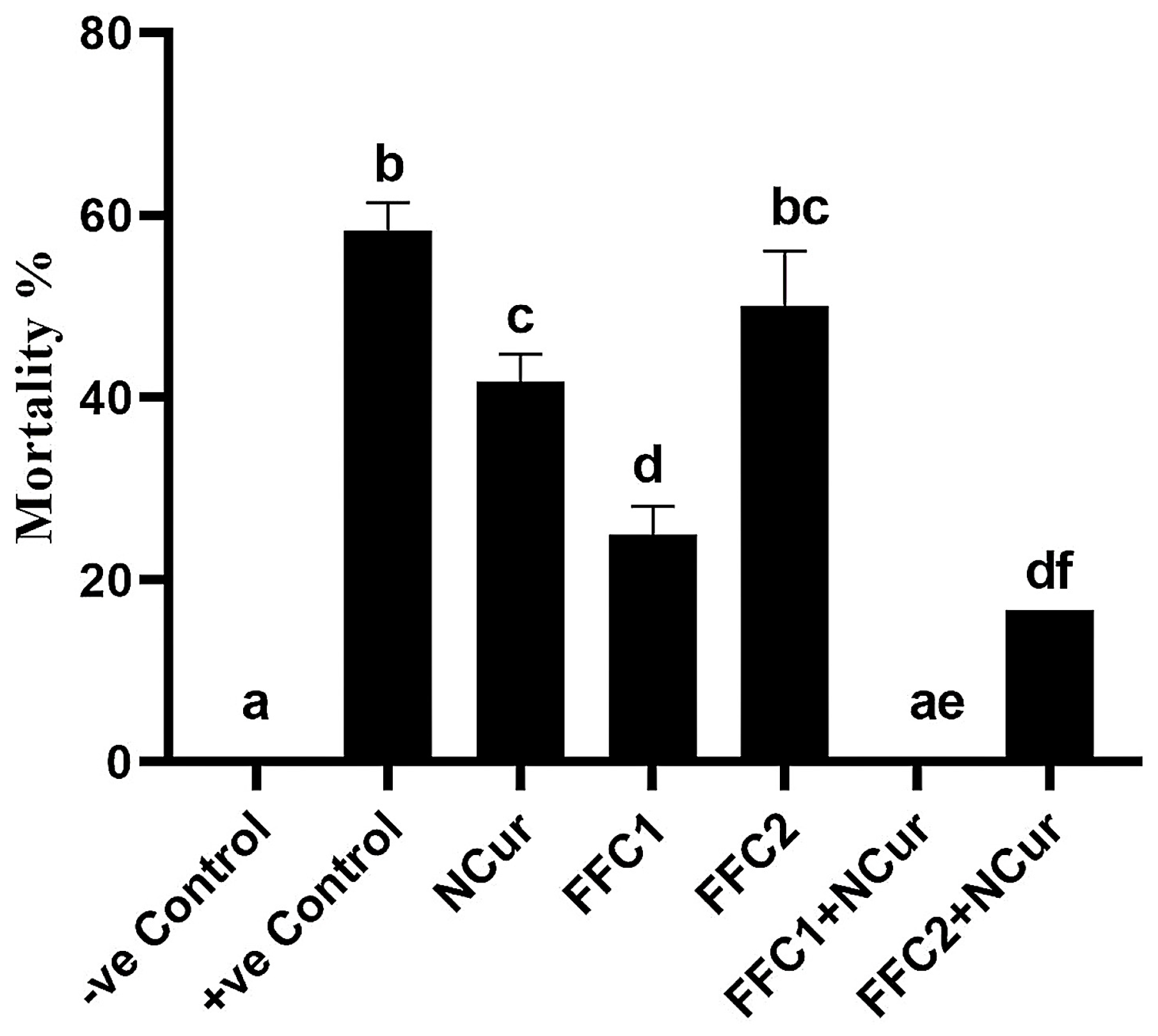
3.4. Bacterial Challenge Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020; Sustainability in Action: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pulkkinen, K.; Suomalainen, L.R.; Read, A.F.; Ebert, D.; Rintamäki, P.; Valtonen, E.T. Intensive fish farming and the evolution of pathogen virulence: The case of columnaris disease in Finland. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.J. Efficacy of orally administered florfenicol and oxolinic acid for the treatment of vibriosis in cod (Gadus morhua). Aquaculture 2001, 235, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Assane, I.M.; Gozi, K.S.; Valladao, G.M.R.; Pilarski, F. Combination of antimicrobials as an approach to reduce their application in aquaculture: Emphasis on the use of thiamphenicol/florfenicol against Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 2019, 507, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraschi, S.P.; Cruz, C.; Machado Neto, J.G.; Castro, M.P.; Bortoluzzi, N.L.; Gírio, A.C.F. Eficácia do florfenicol e da oxitetraciclina no controle de Aeromonas hydrophila em pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus). Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2011, 63, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, P.M. Chloramphenicol, Thiamphenicol, and Florfenicol. In Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary Medicine, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 269–278. [Google Scholar]
- Orlando, E.A.; Costa Roque, A.G.; Losekann, M.E.; Colnaghi Simionato, A.V. UPLC-MS/MS determination of florfenicol and florfenicol amine antimicrobial residues in tilapia muscle. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1035, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, H.; Fujihara, Y.; Kano, T. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of florfenicol, a new fluorinated analog of thiamphenicol, against fish pathogens. Fish Pathol. 1987, 22, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, L.K.; Elbæk, T.H. Simultaneous determination of trimethoprim sulfadiazine, florfenicol and oxolinic acid in surface water by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Chromatographia 2004, 60, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, L.; Giraud, E.; Ganière, J.-P.; Armand, F.; Bouju-Albert, A.; De La Cotte, N.; Mangion, C.; Le Bris, H. Antimicrobial resistance survey in a river receiving effluents from freshwater fish farms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USFWS. Approved Drugs for Use in Aquaculture, 2nd ed.; U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service’s Aquatic Animal Drug Approval Partnership Program, American Fisheries Society’s Fish Culture and Fish Health Sections; Association of Fish and Wildlife Agencies and Fisheries and Water Resources Policy Committee’s Drug Approval Working Group: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, S.; Bueno, G.W.; Lorenz, E.K.; Diemer, O.; Feiden, A.; Boscolo, W.R. Additives in the water during transportation of Piaractus mesopotamicus: Effects of survival rates after stocking in cages. Zootec. Trop. 2013, 31, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, A.M. Laboratory efficacy of florfenicol against Streptococcus iniae infection in Sunshine Bass. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2007, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglam, N.; Yonar, M.E. Effects of sulfamerazine on selected haematological and immunological parameters in rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum, 1792). Aquacult. Res. 2009, 40, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, V.N.; Dang, N.; Anh, N.T.K.; Ky, L.X.; Thai, P.K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment of Vietnam: Sources, concentrations, risk and control strategy. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, A.P.J.G.; Rico, M.; Troell, D.H.; Klinger, A.H.; Buschmann, S.; Saksida, M.V.; Chadag, W.Z. Unpacking factors influencing antimicrobial use in global aquaculture and their implication for management: A review from a systems perspective. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 13, 1105–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossou, S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Zaineldin, A.I.; Abouelsaad, I.A.; Mzengereza, K.; Shadrack, R.S.; Zhang, Y.; El-Sharnouby, M.; Ahmed, H.A.; El Basuini, M.F. Dynamical hybrid system for optimizing and controlling efficacy of plantbased protein in aquafeeds. Complexity 2021, 2021, 9957723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Hao, H.; Xie, S.; Wang, X.; Dai, M.; Huang, L.; Yuan, Z. Antibiotic alternatives: The substitution of antibiotics in animal husbandry. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarsini, K.I. The chemistry of curcumin: From extraction to therapeutic agent. Molecules 2014, 19, 20091–20112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagawany, M.; Farag, M.R.; Abdelnour, S.A.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Elnesr, S.S.; Dhama, K. Curcumin and its different forms: A review on fish nutrition. Aquaculture 2021, 532, 736030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlings, S.; Kalman, D. Curcumin: A review of its effects on human health. Foods 2017, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadifar, E.; Yousefi, M.; Karimi, M.; Fadaei Raieni, R.; Dadar, M.; Yilmaz, S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R. Benefits of dietary polyphenols and polyphenol-rich additives to aquatic animal health: An overview. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 29, 478–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashry, A.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Habiba, M.M.; El-Zayat, A.; El-Sharnouby, M.E.; Sewilam, H.; Dawood, M.A.O. The impact of dietary curcumin on the growth performance, intestinal antibacterial capacity, and haemato-biochemical parameters of gilthead seabream (sparus aurata). Animals 2021, 11, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, G.M.; Da Silva, A.S.; Biazus, A.H.; Reis, J.H.; Boiago, M.M.; Topazio, J.P.; Migliorini, M.J.; Guarda, N.S.; Moresco, R.N.; Ourique, A.F.; et al. Feed addition of curcumin to laying hens showed anticoccidial effect, and improved egg quality and animal health. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 118, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, G.M.; Gerbet, R.R.; Griss, L.G.; Fortuoso, B.F.; Petrolli, T.G.; Boiago, M.M.; Souza, C.F.; Baldissera, M.D.; Mesadri, J.; Wagner, R.; et al. Combination of herbal components (curcumin carvacrol, thymol, cinnamaldehyde) in broiler chicken feed: Impacts on response parameters, performance, fatty acid profiles, meat quality and control of coccidian and bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 139, 103916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, M.; da Rocha, B.A.; Francisco, C.R.L.; Miranda, C.G.; Santos, P.D.F.; de Araújo, P.H.H.; Sayer, C.; Leimann, F.V.; Gonçalves, O.H.; Bersani-Amado, C.A. Evaluation of the in vivo acute anti-inflammatory response of curcumin loaded nanoparticles. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reda, F.M.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Elnesr, S.S.; Alagawany, M.; Tufarelli, V. Effect of dietary supplementation of biological curcumin nanoparticles on growth and carcass traits, antioxidant status, immunity and caecal microbiota of Japanese quails. Animals 2020, 10, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwani, C.D.; Mkpadobi, B.N.; Onyishi, G.; Echi, P.C.; Chukwuka, C.O.; Oluah, S.N.; Ivoke, N. Changes in behavior and hematological parameters of freshwater African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell 1822) following sublethal exposure to chloramphenicol. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, A.; Abraham, T.J.; Singha, J.; Sar, T.K.; Rajisha, R.; Krishna, E.K.N.; Kumar, K.A.; Patil, P.K. Histopathological aberrations and oxidative stress responses in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus as influenced by dietary florfenicol and its metabolites. Aquaculture 2022, 559, 738447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, S.K.; Shahi, N.; Pathak, R.; Kala, K.; Patil, P.K.; Singh, B.; Ravindran, R.; Krishna, N.; Pandey, P.K. Pharmacokinetics and biosafety evaluation of a veterinary drug florfenicol in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum 1792) as a model cultivable fish species in temperate water. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1033170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.V.; Vinoth, S.; Baskar, V.; Arun, M.; Gurusaravanan, P. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles mediated by Dictyota dichotoma endophytic fungi and its photocatalytic degradation of fast green dye and antibacterial applications. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 151, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.M.; Takeuchi, K.P.; Geraldine, R.M.; Moura, C.J.d.; Torres, M.C.L. Production, Solubility and Antioxidant Activity of Curcumin Nanosuspension. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 35, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, R.S.; Gaikwad, S.C.; Agarkar, G.A.; Gade, A.K.; Rai, M. Curcumin Nanoparticles: Physico-Chemical Fabrication and Its in Vitro Efficacy against Human Pathogens. 3 Biotech. 2015, 5, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busher, J. Serum albumins and globulin. In Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations, 3rd ed.; Walker, H.K., Hall, W.D., Hurst, J.W., Eds.; Butterworths: Boston, UK, 1990; Chapter 101. [Google Scholar]
- Bacha, W.J.J.; Bacha, L.M. Color Atlas of Veterinary Histology, 2nd ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A. Aeromonadaceae representatives (Motile Aeromonads). In Bacterial Fish Pathogens. Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish, 6th ed.; Springer Nature Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 161–214. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, E.; Green, L.H. (Eds.) Practical Handbook of Microbiology, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yanez, M.; Catalán, V.; Apráiz, D.; Figueras, M.; Martínez-Murcia, A. Phylogenetic analysis of members of the genus Aeromonas based on gyrB gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, H.A.; Gavasane, A.J.; Choudhary, P.D. A Novel and Simple Approach for Extraction and Isolation of Curcuminoids from Turmeric Rhizomes. Adv. Recycl. Waste Manag. 2018, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Kumar, N. Nanonization of Curcumin by Antisolvent Precipitation: Process Development, Characterization, Freeze Drying and Stability Performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, D.H.; Saad, G.R. Nanocurcumin: Preparation, Characterization and Cytotoxic Effects towards Human Laryngeal Cancer Cells. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 20724–20737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siregar, C.E.; Martono, S.; Rohman, A. Application of Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Coupled with Multivariate Calibration for Quantitative Analysis of Curcuminoid in Tablet Dosage Form. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 8, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, W.; Ma, Y.; Ai, C.; Yu, W.; Gao, X.; Liu, S.; Luo, X.; You, W.; Ke, C. Dietary curcumin influence on growth, antioxidant status, immunity, gut flora and resistance to Vibrio harveyi AP37 in Haliotis discus hannai. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 26, 101336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, A.; Abraham, T.J.; Singha, J.; Rajisha, R.; Krishna, E.K.N.; Panda, S.K.; Patil, P.K. Impacts of Oral Florfenicol Medication and Residues on the Kidney and Liver of Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, E.H.; Ezzo, O.H.; Khalil, H.S.; Tawfik, W.A.; El-Badaw, A.A.; Abd Elghany, N.A.; Mossa, M.I.; Hassan, M.M.; Hassan, M.M.; Eissa, M.E.H.; et al. The effect of dietary nanocurcumin on the growth performance, body composition, haemato-biochemical parameters and histopathological scores of the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) challenged with Aspergillus flavus. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 6098–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, W.T.; El Ibrahim, T.B.; Elgendy, M.Y.; Abdel Zaher, M.F. Effect of Curcumin on Iron Toxicity and Bacterial Infection in Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 22, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgendy, M.Y.; Hakim, A.S.; Ibrahim, T.B.; Soliman, W.S.; Ali, S.E. Immunomodulatory effects of curcumin on Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus and its antimicrobial properties against Vibrio alginolyticus. J. Fish Aquatic. Sci. 2016, 11, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.R.; El-Houseiny, W.; EL-Murr, A.E.; Ebraheim, L.L.M.; Ahmed, A.I.; ElHakim, Y.M.A. Effect of hexavalent chromium exposure on the liver and kidney tissues related to the expression of CYP450 and GST genes of Oreochromis niloticus fish: Role of curcumin supplemented diet. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Mukherjee, S.C. Effect of dietary $-1,3 glucan on immune responses and disease resistance of healthy and aflatoxin B1-induced immunocompromised rohu (Labeo rohita Hamilton). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2001, 11, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, C.K.; Das, B.K.; Mukherjee, S.C.; Pattnaik, P. Effect of long-term administration of dietary $-glucan on immunity growth and survival of Labeo rohita fingerlings. Aquaculture 2006, 255, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrazek, H.M.A.; Tag, H.M.; Kilany, O.E.; Reddy, P.G.; Hassan, A.M. Immuomodulatory effect of dietary turmeric supplementation on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, I.A.M.; Ismail, T.; Yousseff, F.; Mansour, S. Trials for control of pseudomonas septicemia in tilapia Zillii using turmeric powder as a medicated feed. Suez Canal Vet. Med. J. 2019, 24, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kord, M.I.; Maulu, S.; Srour, T.M.; Omar, E.A.; Farag, A.A.; Nour, A.A.M.; Hasimuna, O.J.; Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Khalil, H.S. Impacts of water additives on water quality, production efficiency, intestinal morphology, gut microbiota, and immunological responses of Nile tilapia fingerlings under a zero-water-exchange system. Aquaculture 2021, 547, 737503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julinta, R.B.; Abraham, T.J.; Roy, A.; Singha, J.; Boda, S.; Patil, P.K. Dietary influences of oxytetracycline on the growth and serum biomarkers of Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarski, B.; Kot, B.; Witeska, M. Antibacterials in aquatic environment and their toxicity to fish. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Schiano, T.D. Review article: Drug hepatotoxicity. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 1135–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memik, F. Opinions on drugs and liver. Eurasian J. Med. 1975, 4, 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Gaikowski, M.P.; Wolf, J.C.; Endris, R.G.; Gingerich, W.H. Safety of Aquaflor1 (Florfenicol, 50% type A medicated article), administered in feed to channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Toxicol. Pathol. 2003, 31, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Qu, Y.K.; Wang, A.M.; Yu, Y.B.; Yang, W.P.; Lv, F.; Nie, Q. Effects of carotenoids on the growth performance, biochemical parameters, immune responses, and disease resistance of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) under hightemperature stress. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.D.; Li, M.; Chu, G.S.; Liu, H.J.; Shan, X.F.; Wang, G.Q.; Han, G.H. The positive effects of single or conjoint administration of lactic acid bacteria on Channa argus: Digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant capacity, intestinal microbiota, and morphology. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, A.; Abraham, T.J.; Singha, J.; Saha, S.; Sarker, S.; Patil, P.K. The effects of extended feeding of florfenicol coated medicated diets on the safety, serum biomarkers and blood cells morphology of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 39914–39927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltan, M.A.; Agouz, H.M.; Mohamed, M.G. Effect of oxytetracycline and florfenicol drugs on the physiological activities and its residues of Oreochromis niloticus. Egypt J. Aquat. Biol. Fish 2013, 17, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Reda, R.M.; Ibrahim, R.; Ahmed, E.N.G.; El-Bouhy, Z. Effect of oxytetracycline and florfenicol as growth promoters on the health status of cultured Oreochromis niloticus. Egypt J. Aquat. Res. 2013, 39, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, A.; Dik, B. The effects of florfenicol on the values of serum tumor necrosis factor- and other biochemical markers in lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia in brown trout. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Rabbi, M.H.; Guo, R.; Shi, S.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y. Effects of dietary florfenicol contained feeds on growth and immunity of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) in flow-through and recirculating aquaculture system. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, R.B. A division of J. B. Lippincott Company Philadelphia. In Drug, Facts and Comparisons, 1985th ed.; J. B. Lippincott Company: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1985; pp. 1296–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Barraze, M.I.; Coppock, C.E.; Brooks, K.N.; Wilks, D.L.; Saunders, R.G.; Latimer, J.R. Iron sulfate and feed pelleting to detoxify free gossypol in cotton seed diets for dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3457–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.S.; El-Sayed, M.G.; Abd El-Fatah, R.A. Pharmacological studies on some antibacterial drugs in fish. J. Vet. Med. Mansoura Univ. 2009, 9, 165–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbel, I.; Elwej, A.; Fendri, N.; Mnif, H.; Jamoussi, K.; Boudawara, T.; Grati Kamoun, N.; Zeghal, N. Olive oil abrogates acrylamide induced nephrotoxicity by modulating biochemical and histological changes in rats. Ren. Fail. 2017, 39, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Houseiny, W.; Khalil, A.A.; Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Badr, H.A. The potential role of turmeric and black pepper powder diet supplements in reversing cadmium-induced growth retardation, ATP depletion, hepatorenal damage, and testicular toxicity in Clarias gariepinus. Aquaculture 2019, 510, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, R.D.; Von Der Kammer, F.; Lead, J.R.; Hassellöv, M.; Owen, R.; Crane, M. The ecotoxicology and chemistry of manufactured nanoparticles. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaee, M.; Sureda, A.; Shahaf, S.; Fazilat, N. Protective effects of silymarin extract on malthion-induced zebra cichlid (Cichlasoma nigrofasciatum) hepatotoxicity. Iran. J. Toxicol. 2015, 9, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Chen, X.C.; Chen, Z.Z.; Zeng, Y.Q.; Shi, G.B.; Su, Y.H.; Peng, X. Curcumin protects mitochondria from oxidative damage and attenuates apoptosis in cortical neurons. Acta. Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 1606–1612. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nkwuda, P.J.; Awoke, J.S.; Nwakpa, J.N. Histological Changes in Liver and Kidney of Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) Juvenile Exposed to Sub-lethal Doses of Chloramphenicol (CAP). Aquac. Stud. 2019, 20, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaikowski, M.P.; Wolf, J.C.; Schleis, S.M.; Tuomari, D.; Endris, R.G. Safety of florfenicol administered in feed to tilapia (Oreochromis sp.). Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 41, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravpreet, K.; Kuldeep, S.K.; Jasjit, K.K. Heavy metal induced histopathological alterations in liver, muscle and kidney of freshwater cyprinid, Labeo rohita (Hamilton). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 2137–2144. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, F.A.Z.; Abdel-Maksoud, F.M.; Abd Elaziz, H.O.; Al-Brakati, A.; Elmahallawy, E.K. Descriptive histopathological and ultrastructural study of hepatocellular alterations induced by aflatoxin B1 in rats. Animals 2021, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorshidi, Z.; Moghanlou, K.S.; Imani, A.; Behrouzi, S.; Policar, T.; Rahimnejad, S. Interactive Effects of Curcumin and Silver Nanoparticles on Growth, Hemato-Biochemical Parameters, Digestive Enzymes Activity and Histology of Common Carp (Cyprinus Carpio). Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manju, M.; Akbarsha, M.A.; Oommen, O.V. In vivo protective effect of dietary curcumin in fish Anabas testudineus (Bloch). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, Y.; Ratn, A.; Prasad, R.; Kumar, M.; Abha Trivedi, A.; Shukla, J.P.; Trivedi, S.P. A protective study of curcumin associated with Cr6+ induced oxidative stress, genetic damage, transcription of genes related to apoptosis and histopathology of fish, Channa punctatus (Bloch, 1793). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 103209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouz, M.E. Ameliorative Effect of Curcumin on Aflatoxin B1 Induced Changes in Liver Gene Expression of Oreochromis niloticus. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 49, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seely, J.C.; Francke, S.; Mog, S.R.; Frazier, K.S.; Hard, G.C. Renal papillary rarefaction: An artifact mimicking papillary necrosis. Toxicol. Pathol. 2019, 47, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Luo, L.; Jiang, L.; Chang, O.; Ju, J.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, F. Blood concentration and histological toxicology of different dosages of florfenicol in GIFT Nile tilapia. J. Ocean Univ. 2014, 23, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Junior, G.B.; de Souza, C.F.; da Silva, H.N.; Bianchini, A.E.; Rodrigues, P.; da Costa, S.T.; Heinzmann, B.M.; Cargnelutti, J.F.; Baldisserotto, B. Combined effect of florfenicol with linalool via bath in combating Aeromonas hydrophila infection in silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen). Aquaculture 2021, 545, 737247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, A.; Bhuvaneshwar, D.; Charles, P.M.; Seetha, K.S. Antibacterial synergy of curcumin with antibiotics against biofilm producing clinical bacterial isolates. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, V.; Richards, R.H.; Varma, K.J.; Sutherland, I.H.; Brokken, E.S. Florfenicol in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., parr: Tolerance and assessment of efficacy against furunculosis. J. Fish Dis. 1991, 14, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaunt, P.S.; Endris, R.G.; Khoo, L.; Howard, R.; McGinnis, A.L.; Santucci, T.D.; Katz, T. Determination of dose rate of florfenicol in feed for control of mortality in channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque) infected with Edwardsiella ictaluri, etiological agent of enteric septicemia. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2004, 35, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
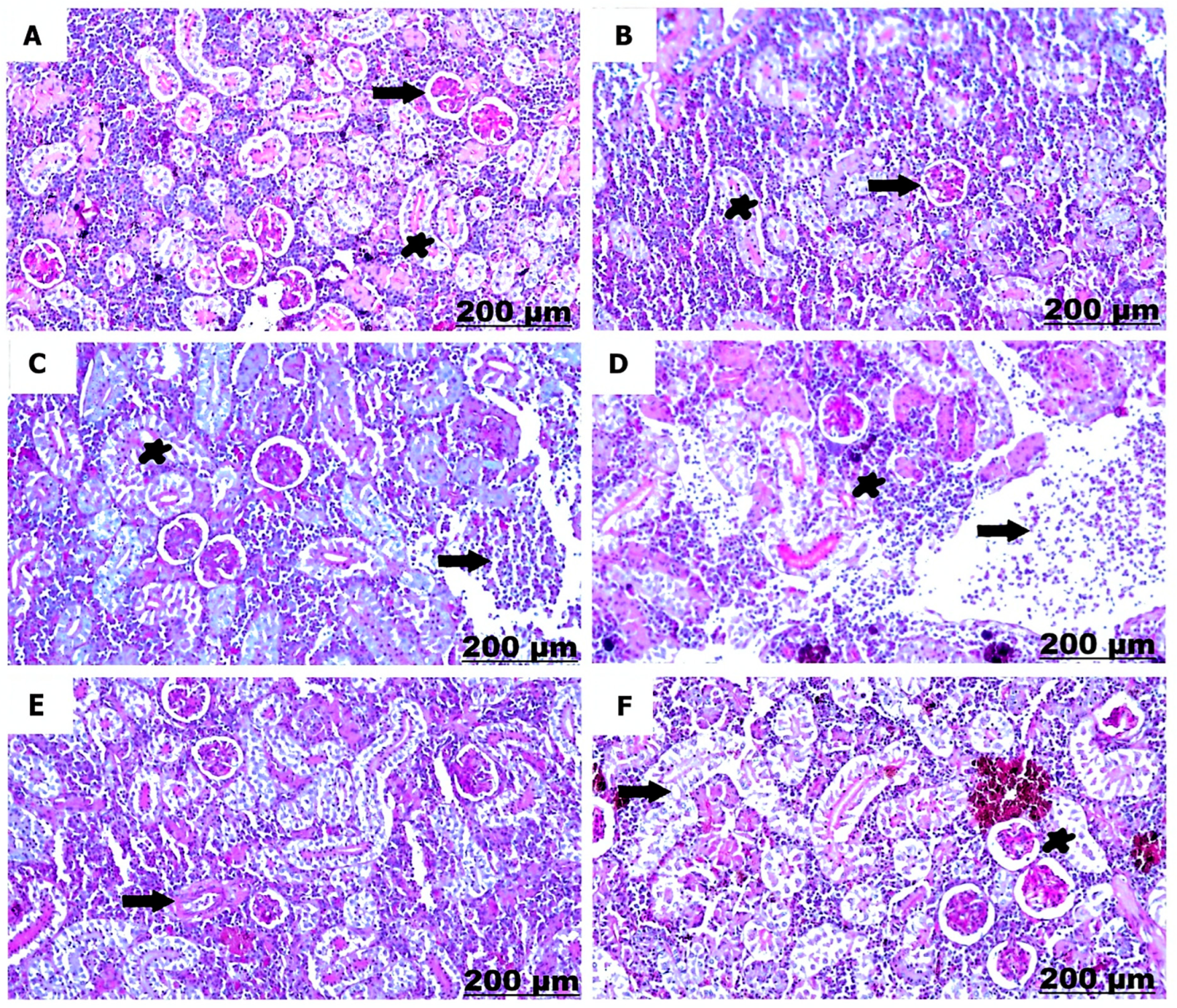
| Control | NCur | FFC1 | FFC2 | FFC1+ NCur | FFC2 + NCur | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | ||||||
| Dilation and congestion of blood vessels | − | + | + | +++ | + | ++ |
| Infiltrations of inflammatory cell | − | + | ++ | +++ | + | ++ |
| Melanomacrophage aggregation | − | + | ++ | +++ | + | ++ |
| Hepatic necrosis and degeneration | − | − | + | ++ | + | + |
| Dilation of blood vessel | − | − | + | ++ | + | + |
| Hemorrhage | − | − | + | ++ | + | + |
| Kidney | ||||||
| Necrosis of renal tubules | − | − | ++ | +++ | + | ++ |
| Degenerative changes of renal tubules | − | − | ++ | +++ | + | ++ |
| Hemorrhage with erythrocytic infiltration | − | − | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| Thickening of the renal capsule | − | − | + | ++ | + | + |
| Focal aggregation of mononuclear cells | − | − | + | +++ | + | ++ |
| Dilation and congestion of blood vessel | − | − | + | ++ | + | + |
| Thickening of blood vessel | − | − | ++ | +++ | + | ++ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mansour, S.; Bakry, K.A.; Alwaleed, E.A.; Ahmed, H.; Al-Amgad, Z.; Mohammed, H.H.; Emeish, W.F.A. Dietary Nanocurcumin Impacts Blood Biochemical Parameters and Works Synergistically with Florfenicol in African Catfish Challenged with Aeromonas veronii. Fishes 2023, 8, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060298
Mansour S, Bakry KA, Alwaleed EA, Ahmed H, Al-Amgad Z, Mohammed HH, Emeish WFA. Dietary Nanocurcumin Impacts Blood Biochemical Parameters and Works Synergistically with Florfenicol in African Catfish Challenged with Aeromonas veronii. Fishes. 2023; 8(6):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060298
Chicago/Turabian StyleMansour, Salwa, Karima A. Bakry, Eman A. Alwaleed, Hassan Ahmed, Zeinab Al-Amgad, Haitham H. Mohammed, and Walaa F. A. Emeish. 2023. "Dietary Nanocurcumin Impacts Blood Biochemical Parameters and Works Synergistically with Florfenicol in African Catfish Challenged with Aeromonas veronii" Fishes 8, no. 6: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060298
APA StyleMansour, S., Bakry, K. A., Alwaleed, E. A., Ahmed, H., Al-Amgad, Z., Mohammed, H. H., & Emeish, W. F. A. (2023). Dietary Nanocurcumin Impacts Blood Biochemical Parameters and Works Synergistically with Florfenicol in African Catfish Challenged with Aeromonas veronii. Fishes, 8(6), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060298