Abstract
The shell biosynthesis of oysters plays a critical role in protection against environmental stress, in which cartilage matrix proteins (CMPs) determine the mineralogical and crystallographic properties of the shell. In the present study, a cartilage matrix protein (designated as MgCMP1) was identified from the Pacific oyster Magallana gigas (Crassostrea gigas) with the objective of understanding its possible role in shell formation. The open reading frame (ORF) of MgCMP1 was 1815 bp, encoding a polypeptide of 605 amino acids with two von Willebrand factor (VWA) domains. The mRNA transcript of MgCMP1 was expressed constitutively in all examined tissues with a higher level in the mantle, especially highest in the middle fold (MF) of the three folds of the mantle. In addition, the interaction between recombinant protein MgCMP1 (rMgCMP1) and recombinant protein bone morphogenesis protein 7 (rMgBMP7) was identified in vitro. After injection of dsRNA to inhibit the expression of MgCMP1, the mRNA expression level of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X in the MF of the mantle significantly decreased. After pre-puncturing and acidification treatment (pH 7.8), the thickness and length of the new formation shells were lower than those in control group (pH 8.1), and the positive hybridization signals of the MgCMP1 mRNA transcript in the three mantle folds were obviously weakened, especially in the MF, whereas the mRNA expression level of MgCMP1, Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X in the MF of mantle decreased significantly. These results suggested that MgCMP1 was involved in regulating the expression of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X in the MF of the mantle in response to ocean acidification (OA).
Keywords:
ocean acidification; Magallana gigas (Crassostrea gigas); cartilage matrix protein; middle fold of the mantle; collagen Key Contribution:
The mRNA of MgCMP1 was highly expressed in the MF of the mantle. OA severely inhibited the growth of oyster calcified shell and the expression of MgCMP1, Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X. The activation of the CMP1-BMP7 pathway was inhibited under acidification, which further affected Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X synthesis as well as the shell growth of the oysters.
1. Introduction
OA is a global marine ecological disaster, which probably brings about reduction in biodiversity and a radical alteration in marine ecosystems [1,2]. Previous studies have shown that the ocean pH is expected to decrease from 8.1 to 7.8 by the end of 2100 [3,4]. Bivalve shells consist of more than 95% calcium carbonate minerals and a small amount of organic matrix [5,6,7]. OA can reduce the saturation state of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and affect the calcification rate of shells [8,9,10]. The calcification rates of Mytilus edulisand and M. gigas decrease by 25% and 10%, respectively, at CO2 concentrations of 740 ppm [9]. The mantle is the main tissue for shell formation [11]. Different regions and folds of the mantle are involved in the formation of different shells. The periosteum layer and prismatic layer are formed by secretions from the marginal zone [11,12,13], and the mantle marginal zone can be further divided into the inner fold (IF), MF and outer fold (OF) of the mantle [14]. OA inhibits the secretion of organic matrix in the MF of the mantle to inhibit the formation of shells [15,16,17]. With the deepening understanding of the mechanisms of shell formation affected by OA, studies have gradually extended from phenomenon observation to the molecular level. Recent studies have found that a new family of molecules, cartilage matrix protein (CMP), may play an important role in shell formation in shellfish [18].
CMP (also known as matrilin-1) belongs to the matrilin family and is a type of extracellular matrix protein that was first isolated and identified in 1992 [19]. There are four currently known matrix proteins in vertebrates: matrilin-1, matrilin-2, matrilin-3 and matrilin-4. Similar to other matrilins, CMPs share a structure consisting of two tandem von Willebrand factor domains (VWA domain), an epidermal growth factor-like domain (EGF domain) and a coiled coil α-helical module [20]. Analysis of the evolutionary relationships revealed that the VWA modules of matrilin-2, matrilin-3 and matrilin-4 were possible replicated from the second VWA module of matrilin-1 [21]. The matrix proteins interact with other extracellular matrix proteins via the metal ion-dependent adhesion site (MIDAS) of the VWA domain [22,23]. CMP is mainly expressed in the cartilage of vertebrates, and it plays important physiological roles in the development of the osteoarticular system and in maintaining the homeostasis of various connective tissue structures, mainly via interacting with bone morphogenesis protein (BMP) and modulating collagen [24]. CMP may serve as an “instructive matrix” component, binding to bone morphogenesis proteins 2 (BMP2), 4 (BMP4) and 7 (BMP7), to participate in the regulation of corresponding downstream signaling pathways [25,26]. CMPs act as modulators of collagen fibrillogenesis in cartilage, which may affect the organization and integrity of the human cartilage growth matrix [27,28,29,30]. Mice that lack CMP and collagen IX exhibit ultrastructural abnormalities in the shortened long bones [27,31]. The knockdown of CMP in zebrafish results in growth defects, disturbed craniofacial cartilage formation and decreased collagen II deposition [32].
In mollusks, an organic matrix provides the framework for the deposition of CaCO3 crystals [6,23,33]. CMPs and VWA domain-containing proteins have also been identified in mollusks and play an important role in shell formation. The CMPs in oyster Crassostrea virginica and conch Biomphalaria glabrata harbor the typical VWA domains, missing the EGF-like domain and the coiled coil α-helical module, which are different from the matrilin family members in vertebrates [34,35]. Currently, research on CMPs and VWA domain containing proteins in invertebrates is mainly focused on their expression pattern in tissues and their possible role in regulating the nacreous shell layer. For instance, in Pinctada fucata, CMP was found to be highly expressed in the mantle. Aragonite-binding protein (Pif 97) containing one VWA domain was mainly expressed in the nacreous layer of M. gigas [23]. Blue mussel shell protein (BMSP) with four VWA domains was involved in maintaining nacreous matrix formation in Mytilus galloprovincialis [36].
The Pacific oyster M. gigas is an important cultured species worldwide, and a model organism for investigation mechanisms of adaptation to the marine environment [37]. OA causes the dissolution of adult oyster shells, leading to significant ecological and economic losses. It has been demonstrated that OA could inhibit shell formation by affecting the secretion of chitin synthase (chitin) and carbonic anhydrase (CA) in M. gigas [38,39]. CMP may be involved in shell formation in oysters; however, whether OA affects shell formation by regulating CMP is unclear and needs to be further studied. In this study, the regulation mechanism of MgCMP1 in shell formation under acidification treatment will be explored; this could contribute to better understanding how OA affects marine calcifiers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oyster Treatment, and Sample Collection
2.1.1. Obtaining and Maintenance of Oysters
The animal experiments in this study are in accordance with the animal ethics guidelines approved by the Ethics Committee of Dalian Ocean University. The Pacific oyster M. gigas (2–3 years old) was purchased from a farm (Dalian, China). In this study, 20–30 oysters were acclimated in a tank, whose size was 200 cm × 100 cm × 50 cm, with filtered and aerated seawater at 15–20 °C for a week. During the experiment, the oysters were fed with spirulina algae powder, and 2/3 of the volume of seawater was changed daily.
2.1.2. Aperture and Acidification Treatment
Eighty-one oysters were averagely and randomly divided into three groups, blank group, control group and OA group. Twenty-seven oysters in the blank group (pH 8.1 ± 0.05) were cultured for 6 weeks in aerated seawater. Twenty-seven oysters in the control group (pH 8.1 ± 0.05) underwent lateral pre-puncture in the closed side of the oyster shell adjacent to the adductor muscle (aperture treatment), and were cultured for 6 weeks in aerated seawater. Twenty-seven oysters in the OA group (pH 7.8 ± 0.05) under aperture treatment, were cultured for 6 weeks in aerated seawater with an air–CO2 mixture (acidification treatment). The pH value was automatically controlled using an acidometer and pH probe (AiKB, Qingdao, China), and the pH value parameter was set to 7.8 ± 0.05 [39].
2.1.3. Measurement of Length and Thickness of New-Formation Shells
Nine oysters from the control and OA groups were numbered. At the 2nd, 4th and 6th weeks, the length and thickness of newly formed shells of the same oysters in the control and OA groups were measured using vernier calipers (Syntek, Huzhou, China) (Figure S1).
2.1.4. Sample Collection
The mantle marginal zone, separated into inner/middle/outer fold (IF/MF/OF), was collected from each group at 2, 4 and 6 weeks. Samples from the edge area of the mantle were added to in situ hybridization fixative (Servicebio, Wuhan, China) for subsequent in situ hybridization (ISH) experiments. To detect the distribution pattern of MgCMP1 in normal oyster tissues, the gill, hepatopancreas, mantle marginal zone, adductor muscle, haemocytes and labial palp of nine oysters were collected without any treatment after culturing for a week. Tissues from three oysters were pooled together as one sample, and there were three replicates for each tissue (N = 3). Each sample was added into 1 mL TRIzol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) reagent for RNA extraction.
2.2. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
A 1 mL volume of TRIzol and 0.2 mL of RNA Extraction Agent (Trans Gen Biotech, Beijing, China) were added into every 50–100 mg tissue for homogenization. After centrifugation at 10,000× g at 4 °C for 15 min, the colorless upper aqueous phase was taken for total RNA extraction [40,41]. The first chain cDNA was synthesized using total RNA as template and oligo dT-adaptor as primers. The synthesis reaction was performed at 42 °C for 30 min and terminated by heating at 84 °C for 30 s. The synthesized cDNA products were diluted to 1:20 for gene cloning and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis, and stored at −80 °C.
2.3. Gene Cloning and Sequence Analysis
By screening the genome of the oyster M. gigas, a gene encoding CMP was identified from National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI accession no LOC 105349064). The ORF of MgCMP1 was cloned from the cDNA library of the mantle by using specific primers (MgCMP1-KL-F and MgCMP1-KL-R, Table 1) and Pro Taq DNA Polymerase kit (Accurate Biology, China). The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) system consisted of Pro Taq DNA polymerase 0.25 μL, 10 × Pro Taq PCR buffer Ver 5 μL, MgCl2 Solution 2 μL, dNTP Mix 1 μL, Template (1 μg/μL) 1 μL, MgCMP1-KL-F Primer 5 μL, MgCMP1-KL-R Primer 5 μL and DEPC water up to 50 μL.

Table 1.
Sequences of the primers used in this study.
The BLAST algorithm was used for amino acid sequence analysis. The theoretical isoelectric point (PI) and molecular weight of MgCMP1 were predicted using ExPasy’s pI/Mw tool. The domain of MgCMP1 was predicted by Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool (SMART). Based on the CMP amino acid sequences of different species, a phylogenetic NJ tree was constructed using MEGA 7.0 software (version no 1.0.0.0) to analyze the evolutionary relationships of MgCMP1. Multiple sequence alignment analysis of MgCMP1 was performed by the DNAMAN 9.0 program [42,43].
2.4. qRT-PCR Analysis of mRNA Expression
The qRT-PCR were performed using the Trans-Start Top Green qPCR Super Mix (Trans Gen Biotech, Beijing, China) reagent system (SYBR Green Master Mix 5 μL, ROX 0.2 μL, Forward primer 0.2 μL, Reverse primer 0.2 μL, cDNA template (1μg/μL) 2μL, DEPC water 2.4 μL, total volume 10 μL.) and on Quan Studio 6 Flex (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) reaction procedure (95 °C for 30 s. 95 °C, 5 s; 60 °C, 31 s, 40 cycles) [44]. Using the elongation factor gene (LOC105338957, MgEF) from M. gigas in Table 1 as internal control, the relative expression level of MgCMP1, Mgcollagen I (LOC105326709) and Mgcollagen X (LOC105346696) in Table 1 were analyzed using the comparative Ct method (2−ΔΔCt method) [45].
2.5. Recombinant Expression and Purification of MgCMP1
The sequence of the VWA domain in MgCMP1 was amplified using primers MgCMP1-M-F and MgCMP1-M-R (Table 1). The MgCMP1 PCR products with EcoR I and Xho I sites were cloned into expression vector pET-30a (+) and transferred into (DE3) Escherichia coli (E. coli) competent cells [46]. Positive transformants were screened with the primers MgCMP1-M-F and MgCMP1-M-R (Table 1), and incubated in LB liquid medium at 37 °C. The expression of rMgCMP1 was induced by adding isopropyl-β-dthiogalactoside (IPTG, final concentration 0.5 mM).
The denatured rMgCMP1 was purified using an Ni-NTA Sepharose column and pooled by elution with 400 mmol/L imidazole. The protein activity of rMgCMP1 was restored by dialysis using urea with concentration gradients (6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and 0 M) and PBS buffer (three times) at pH 8.0, 4 °C, 12 h apart. RMgCMP1 protein was detected and quantified using 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and BCA methods and stored at −80 °C [46].
2.6. The Molecular Interaction between rMgCMP1 and rMgBMP7
The rMgCMP1 was prepared at different concentrations (2.22 μM, 1.66 μM, 1.25 μM, 0.94 μM and 0.71 μM), and rMgBMP7 was biotinylated with a Biotinylation Kit (GENEMORE, Shanghai, China). Based on previous studies, the in vitro interaction of rMgCMP1 and rMgBMP7 was detected using Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI) and Octet K2 (ForteBio, Silicon Valley, CA, USA). The Octet K2 program was running according to Baseline, Loading, Association, and Dissociation [46]. The binding constant (Kon) and dissociation constant (Koff) were analyzed by ForteBio software, and the affinity (KD) was obtained by fitting calculation [47].
2.7. In Vivo RNA Interference (RNAi) Treatment of Oysters
The cDNA fragments of MgCMP1 and EGFP were amplified as templates to synthesize dsRNA using the primers MgCMP1-Fi, MgCMP1-Ri, EGFP-Fi and EGFP-Ri (Table 1). The dsRNAs were synthesized using Transcription T7 Kit (NEB, Ipswich, MA, USA).
Thirty-six oysters were randomly divided into four groups: blank group (without any treatment), seawater group (SW group, injections SW), EGFP-RNAi group (injections dsEGFP) and CMP1-RNAi group (injections dsMgCMP1), with nine individuals in each group. To enhance the effect of RNAi, dsEGFP and dsMgCMP1 (100 μL, 1 μg μL-1) were injected twice, 12 h apart. Twenty-four hours after the second injection, the MF of the mantle (N = 3) of each group was collected for total RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis. MgCMP1-RT-Fi and MgCMP1-RT-Ri primers (Table 1) and qRT-PCR were used to detect and evaluate the effect of RNAi.
2.8. In Situ Hybridization
2.8.1. RNA Probe Preparation
The fragments were cloned from the mantle cDNA library using primers MgCMP1-WEISH-F and MgCMP1-WEISH-R (Table 1). The fragments were purified and connected to the pGEM-T vector (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), then transferred into (DE3) E. coli competent cells [46]. Positive transformants were screened with the primers MgCMP1-WEISH-F and MgCMP1-WEISH-R (Table 1), and incubated in LB liquid medium at 37 °C. The recombinant plasmid MgCMP1-pGEM-T was digested using Nco I or Nde I endonuclease The probe was synthesized using T7/SP6 RNA polymerase and DIG RNA labeling kit (Roche, Mannheim, Germany), and tested using a nucleic acid detection kit (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) [48].
2.8.2. ISH Techniques
Tissue sections were obtained from the edge area of the M. gigas mantle according to previous reports [49]. Firstly, the paraffin wax in the mantle tissue sections was replaced with 50% ethanol (xylene, 100%–90%–70%–50% ethanol), then fixed with 4% PFA, and digested with protease K solution. Secondly, the mantle tissue sections were hybridized with digoxin-labeled RNA probes at 53 °C. Finally, the water in the mantle tissue sections was replaced with xylene (50%–70%–90%–100% ethanol, xylene) to facilitate color observation. ISH techniques are detailed in the previous report [50,51].
2.9. Statistical Analysis
All data are given as means ± S.D. Significant difference was determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test, or by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan multiple comparisons. Different letters indicated statistically significant difference at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. The Sequence Characteristics and Phylogenetic Relationship of MgCMP1
The ORF of MgCMP1 was of 1815 bp encoding a polypeptide of 605 amino acids (Figure S2A) with a predicted molecular mass of 67.28 kDa. There were two VWA domains (Figure S2B) in the amino acid sequence of MgCMP1, which were located at residues 26–208 and residues 239–420. The theoretical isoelectric point (PI) of MgCMP1 was predicted to be 4.71 using the computational pI/Mw tool of ExPasy.
The phylogenetic tree showed that these CMPs from vertebrates and invertebrates were separated into two major branches. MgCMP1 was closely clustered with the CMP of C. virginica. (Figure S2C).
The amino acid sequences of CMPs were compared and analyzed, and it was found that there was high identity between MgCMP1 and CMPs form other species, such as 31% identity with that of Homo sapiens, 32.98% identity with that of Mus musculus, 29.62% identity with that of Danio Rerio, 21.3% identity with that of Fulmarus glacialis, 31.6% identity with that of Patella vulgate and 74.79% identity with that of C. virginica (Figure S2D).
3.2. The Distribution of MgCMP1 mRNA in Different Tissues
The mRNA expression levels of MgCMP1 in different tissues (hepatopancreas, labial palp, mantle, gills, adductor muscle and hemocytes.) of oyster were detected by qRT-PCR. The transcripts of MgCMP1 were expressed in all tissues, and the expression level in mantle was the highest, being 8.67-fold (p < 0.01) higher than that in labial palp. MgCMP1 mRNA was also highly expressed in hemocytes and gill, being 4.84-fold (p < 0.01) and 3.63-fold (p < 0.01) of that in labial palp, respectively (Figure 1A). There were no significant differences among adductor muscle, labial palp and hepatopancreas. Expression levels of MgCMP1 mRNA in different folds of oyster mantles, including IF, MF and OF, were also detected. The expression level of MgCMP1 in MF was the highest, being 1.43-fold and 2.98-fold higher than that in IF and OF (p < 0.05, Figure 1B).
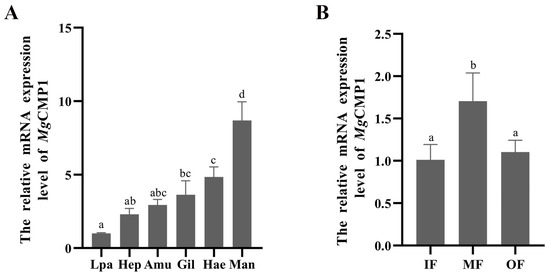
Figure 1.
The expression level of MgCMP1 mRNA in different tissues. (A) Gil, gill; Man, mantle marginal zone; Hep, hepatopancreas; Amu, adductor muscle; Lpa, labial palp; Hae, haemocytes. (B) IF, inner fold of the mantle; MF, middle fold of the mantle; OF, outer fold of the mantle. The different letters (a, b, c, and d) indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). Each value is shown as mean ± S.D. (N = 3).
3.3. Recombinant Protein of rMgCMP1 and Its Interaction with rMgBMP7 In Vitro
After IPTG induction, the purified rMgCMP1 was analyzed with 12% SDS-PAGE. A distinct band consistent with the predicted molecular mass of rMgCMP1 was observed, at about 73.9 kDa (Figure 2A).
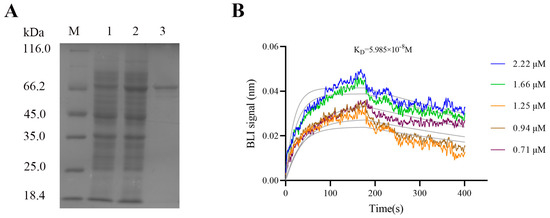
Figure 2.
The recombinant protein of rMgCMP1 and its interaction with rMgBMP7 in vitro. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of the recombinant protein rMgCMP1. Lane M, standard protein molecular weight marker; Lane 1, negative control (without IPTG induction); Lane 2, induced recombinant protein rMgCMP1; Lane 3, purified recombinant protein rMgCMP1. (B) The binding capability of rMgCMP1 with rMgBMP7 measured by BLI assay.
The interaction between rMgCMP1 and rMgBMP7 in vitro was detected by BLI. At lower concentrations, no valid response of MgBMP7 was detected. With an increase in rMgCMP1concentration (from 0.71 μM to 2.22 μM), the binding affinity of rMgCMP1 to rMgBMP7 was enhanced, and the affinity KD was 5985 × 10−8 mol·L−1 (Figure 2B). This indicated that rMgCMP1 and rMgBMP7 had specific binding activity.
3.4. The mRNA Transcripts of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X in MgCMP1-RNAi Oysters
In order to explore the relationship between CMP and collagen, the expression levels of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X in the MF of mantle were examined after MgCMP1 had been inhibited by MgCMP1-dsRNA. The expression level of MgCMP1 decreased significantly (0.49-fold of that in EGFP-RNAi oysters, p < 0.01) at 24 h after the injection of MgCMP1 dsRNA (Figure 3A). Meanwhile, the expression levels of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X were also significantly decreased, being 0.21-fold (p < 0.001) and 0.35-fold (p < 0.05) of those of EGFP-RNAi oysters (Figure 3B,C) at 24 h after the injection of MgCMP1 dsRNA.
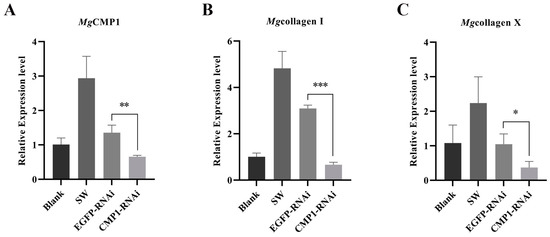
Figure 3.
The mRNA expression levels of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X in the MF of mantle of MgCMP1-RNAi oysters. (A) The mRNA expression of MgCMP1 in MF of mantle after the injection of dsMgCMP1. (B,C) The mRNA expression levels of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X in MgCMP1-RNAi oysters. EGFP-RNAi oysters were used as control. Vertical bars represent the mean ± S.D. (N = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences (*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01 and ***: p < 0.001).
3.5. Morphologic Characteristics of New-Formed Shell in Punctured Oysters under Acidification Treatment
After 2, 4 and 6 weeks of acidification treatment, the lengths of the new-formed shells were, respectively, 0.79, 0.83 and 0.84-fold shorter than those of the control group (pH 8.1 ± 0.05) (Figure 4A). The thicknesses of the new shells in the acidification treatment group (OA group, pH 7.8 ± 0.05) were 0.44, 0.37 and 0.45-fold lower than those of the control group (pH 8.1 ± 0.05), respectively (Figure 4B). These results indicated that shell formation was delayed in the acidification treatment group (OA group, pH 7.8 ± 0.05) compared to the control group (pH 8.1 ± 0.05).
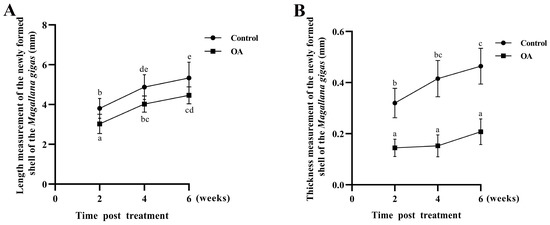
Figure 4.
The length and thickness of new-formation oyster shells. (A) Length of newly formed oyster shells after perforation stimulation (control) and acidification (OA) treatment. (B) Thickness of newly formed oyster shells after perforation stimulation (control) and acidification (OA) treatment. Vertical bars represent the mean ± S.D. (N = 3) and the different letters (a, b, c, d and e) indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.6. The mRNA Expression Levels of MgCMP1 in IF, MF and OF of Mantle of Punctured Oysters under Acidification Treatment
The expression levels of MgCMP1 mRNA in the IF, MF and OF in the mantle of oysters after aperture and acidification treatment were investigated by qRT-PCR. Significant changes in MgCMP1 mRNA expression were detected in MF. When the oysters were cultured at pH 8.1 for 2, 4 and 6 weeks, the expression level of MgCMP1 mRNA in the MF of oysters with the aperture treatment (control group, pH 8.1 ± 0.05) was significantly increased compared to that of the oysters that had received no treatment (blank group, pH 8.10 ± 0.05) (Figure 5A–C, p < 0.05). After these punctured oysters were exposed to acidification treatment (OA group, pH 7.8 ± 0.05) for 2, 4 and 6 weeks, the expression level of MgCMP1 mRNA in MF of was significantly decreased, 0.26-fold (Figure 5A, p < 0.05), 0.16-fold (Figure 5B, p < 0.05) and 0.19-fold (Figure 5C, p < 0.05), compared to those in the control group (pH 8.1 ± 0.05). No significant changes were observed in IF and OF between the control group and OA group.
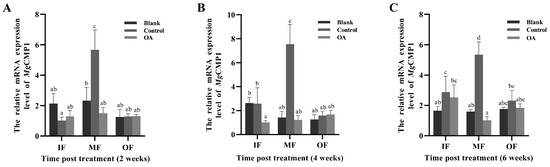
Figure 5.
The mRNA expression level of MgCMP1 under acidification treatment. (A) Acidification treatment 2 weeks; (B) acidification treatment 4 weeks; (C) acidification treatment 6 weeks. IF: inner fold of the mantle; MF: middle fold of the mantle; OF: outer fold of the mantle. Blank: without any treatment (blank group, pH 8.1 ± 0.05); Control: aperture treatment (control group, pH 8.1 ± 0.05); OA: acidification treatment (OA group, pH 7.8 ± 0.05). Vertical bars represent the mean ± S.D. (N = 3) and the different letters (a, b, c, and d) indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.7. The Distribution of MgCMP1 mRNA Transcripts in IF, MF and OF in Mantle of Punctured Oysters under Acidification Treatment
After acidification treatment for 4 weeks, precise localization of MgCMP1 mRNA transcripts in IF, MF and OF in mantle was investigated via ISH. No signals were detected in all negative groups (Figure 6A–C), and bluish-violet positive hybridization signals were distributed in the three mantle folds of the oyster (Figure 6D–F). When the oysters were cultured at pH 8.1 for 4 weeks after being punctured (control group, pH 8.1 ± 0.05), the positive hybridization signals of MgCMP1 in the three mantle folds were obviously strengthened, especially in MF (Figure 6E). After these punctured oysters were exposed to acidification treatment (OA group, pH 7.8 ± 0.05), the positive hybridization signals of MgCMP1 in the three mantle folds were all weakened (black arrows), especially in MF (Figure 6F).
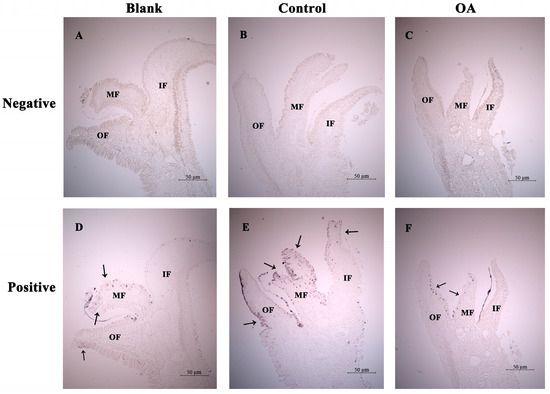
Figure 6.
The distribution of MgCMP1 mRNA transcripts in the mantle of punctured oysters under acidification treatment via ISH. (A–C) Righteous RNA probe hybridization (negative control); (D–F) antisense RNA probe hybridization (positive group). IF: inner fold of the mantle; MF: middle fold of the mantle; OF: outer fold of the mantle. Blank: without any treatment (blank group, pH 8.1 ± 0.05); Control: aperture treatment (control group, pH 8.1 ± 0.05); OA: acidification treatment (OA group, pH 7.8 ± 0.05). The positive bluish-violet signals are labeled with arrows.
3.8. The mRNA Expression Levels of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X in IF, MF and OF in Mantle of Punctured Oysters under Acidification Treatment
The expression levels of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X mRNA in IF, MF and OF in mantle of punctured oysters under acidification treatment for 4 weeks were investigated by qRT-PCR. Significant changes in Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X transcripts were detected in MF. The expression levels of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X mRNA in MF of the punctured oysters in the control group (pH 8.1 ± 0.05) were significantly higher than those of the unpunctured oysters in the blank group (pH 8.1 ± 0.05) (Figure 7A,B, p < 0.01). After these punctured oysters were exposed to acidification treatment (OA group, pH 7.8 ± 0.05) the mRNA expression levels of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X in MF were all significantly decreased, 0.07-fold (Figure 7A, p < 0.01) and 0.14-fold (Figure 7B, p < 0.01), compared to the control group (pH 8.1 ± 0.05).
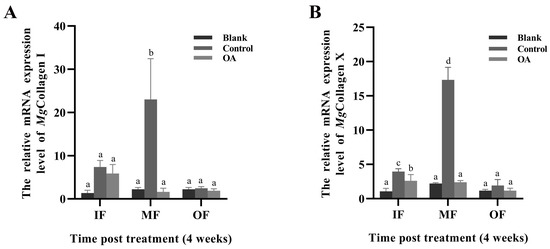
Figure 7.
The mRNA expression levels of Mgcollagen I (A) and Mgcollagen X (B) under acidification treatment for 4 weeks. IF: inner fold of the mantle; MF: middle fold of the mantle; OF: outer fold of the mantle. Blank: without any treatment (blank group, pH 8.1 ± 0.05); Control: aperture treatment (control group, pH 8.1 ± 0.05); OA: acidification treatment (OA group, pH 7.8 ± 0.05). Vertical bars represent the mean ± S.D. (N = 3), and the different letters (a, b, c, and d) indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
Marine bivalves evolved shells to maintain their soft bodies, store inorganic ions, and protect themselves from predators and dehydration [52]. In recent years, OA has become a threat to many marine organisms and it inhibits shell synthesis [53]. Previous studies have demonstrated that shell organic matrix is responsible for nucleation, polymorphism, orientation, morphology and texture of calcium carbonate crystallites in the shell [54,55]. In the present study, a cartilage matrix protein (MgCMP1) was identified from M. gigas. The response of MgCMP1 secreted by the middle membrane of the mantle to acidification treatment was studied; this may help to better understand the regulatory effect of MgCMP1 on oyster shell formation under acidification conditions.
During shell formation, matrix proteins are associated with the mineral phase and influence calcite CaCO3 crystal growth [56,57,58]. In the present study, a cartilage matrix protein gene was identified from M. gigas. Compared with CMPs in vertebrates, MgCMP1 contains only two VWA domains, which is similar to the structure of CMPs in other invertebrates [34,59]. The VWA domain is a common domain in the protein family and can interact with other extracellular substrates [22,23]. The phylogenetic tree suggested that MgCMP1 was more similar to CMPs from invertebrates, especially bivalves (P. vulgata and C. virginica). These results suggest that MgCMP1 is a member of the cartilage matrix protein family with a relatively conserved evolutionary position and might have similar functions in other invertebrates and vertebrates.
In vertebrates, CMP plays an important physiological role in the development of the osteoarticular system and in maintaining the homeostasis of connective tissue structures [24]. In invertebrates, CMP and VWA domain-containing proteins have been associated with shell formation in P. fucata and Mytilus coruscus. CMP may be involved in regulating the formation of prodissoconch II [18]. The VWA domain-containing protein (VDCP) in M. coruscus was found to be highly expressed in the mantle and associated with shell mineralization and shell attachment [60]. Oyster fasciclin-like protein (Flp), which contains a VWA domain, is also highly expressed in the mantle and involved in shell matrix maintenance [61,62]. In this study, the mRNA transcript of MgCMP1 was expressed in all the examined tissues of oyster, with the highest expression level in the mantle. It is speculated that MgCMP1 might be related to shell formation in oysters. The mantle is an important tissue involved in the formation of mollusk shells, and different shell layers are related to different zones and folds of the mantle. In P. fucata, the nacreous layer is formed by submarginal zone and central zone secretions [14,63]. Periostracum protein (PPP-10) secreted form the OF of the mantle is involved in periostracum formation in P. fucata [13]. BMP3 secreted from MF might participate in calcium ion metabolism regulation in P. fucata [64]. In M. gigas, previous research proved that genes secreted by the MF of the mantle are involved in shell formation. Calmodulin (CaM) and engrailed, which are involved in the regulation of calcium homeostasis and the biosynthesis of periostracum, are highly expressed in the MF of mantle [17,48]. In this study, MgCMP1 was highly expressed in MF of the mantle, and the expression level of MgCMP1 in the MF of mantle was significantly increased after aperture treatment. This indicates that MgCMP1 secreted in the MF of mantle might be involved in oyster shell formation.
It has been found that the VWA domain in CMP has a function in exercising protein–protein interactions. In vertebrates, CMPs can bind to BMP to participate in the regulation of corresponding downstream signaling pathways, affecting collagen gene expression and the integrity of the cartilage growth matrix [65,66]. In this study, interaction was identified between rMgCMP1 and rMgBMP7, indicating the possible presence of a CMP1-BMP7 signaling pathway in oysters. In addition, after inhibition of the MgCMP1 gene, the mRNA expression levels of downstream Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X decreased significantly, which is similar to the results in zebrafish [32]. These results suggest that the CMP1-BMP7 pathway could regulate collagen genes, which may affect shell formation in oysters.
There are two main hypotheses for how OA affects shell formation in shellfish. On the one hand, OA reduces the saturation state of calcium carbonate minerals and affects the integrity of shell deposits [9,67,68,69]. On the other hand, the secretion of shell matrix proteins is inhibited by OA. In P. fucata, the nacreous layer formation protein (n16) and nacrein are suppressed under acidification, and then shell formation is delayed [70]. Acidification could also inhibit the expression of CaM and engrailed in the MF of mantle, affecting calcium homeostasis and shell periostracum formation in M. gigas [17,48]. In the present study, the growth rate of the new-formation oyster shell after acidification treatment (pH 7.8 ± 0.05) was slower than those in the control group (pH 8.1 ± 0.05), which indicates that acidification inhibited shell formation. After acidification treatment (pH 7.8 ± 0.05), the mRNA expression level of MgCMP1 in the MF the of mantle was significantly reduced. The ISH result also showed that the positive MgCMP1 signals in the MF of mantle were weakened. In addition, after acidification (pH 7.8 ± 0.05), the mRNA expression levels of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X in the MF of mantle were significantly reduced. These results indicate that the activation of the CMP1-BMP7 pathway might be inhibited under acidification, which further affects collagen synthesis as well as the shell growth of oysters.
5. Conclusions
In summary, a homolog of CMP, MgCMP1 was identified from M. gigas. The mRNA of MgCMP1 was highly expressed in the mantle, especially in the MF of the mantle. rMgCMP1 can interact with rMgBMP7 in vitro. The mRNA expression level of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X in the MF significantly decreased after the expression of MgCMP1 was inhibited. When oysters were subjected to CO2-induced acidification stress, calcified shell growth was severely inhibited, and the expression of MgCMP1, Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X was significantly suppressed. The above results indicate that the CMP1-BMP7 pathway is involved in regulating the expression of Mgcollagen I and Mgcollagen X in the MF of the mantle in response to OA.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fishes8060290/s1, Figure S1: The length and thickness of new formation oyster shells. (A) Length (labeled with red arrows) of Newly formed oyster shells after perforation stimulation and acidification treatment; (B) Thickness (labeled with yellow arrows) of Newly formed oyster shells after perforation stimulation and acidification treatment. Figure S2: The sequence characteristics of MgCMP1. (A) The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of MgCMP1. The VWA domains are marked with a red font. (B) The structure of MgCMP1 predicted by SMART. (C) Phylogenetic analysis of MgCMP1 with other CMPs from different species. The MgCMP1 is marked with a triangle. (D) Multiple sequence alignment of MgCMP1 with CMPs from other species, including Homo sapiens (NP_002370.1), Mus musculus (NP_034899.2), Danio rerio (NP_001093210.1), Cyanistes caeruleus (XP_023796800.1), Fulmarus glacialis (XP_009573578.1), Patella vulgata (XP_050403925.1), Mercenaria mercenaria (XP_045215666.1), Magallana gigas (XP_011457035.2), Gigantopelta aegis (XP_041375252.1), Crassostrea virginica (XP_022329001.1). MgCMP1 is marked with a red font.
Author Contributions
T.Z., C.L. and Z.L. conceived and designed the experiments; T.Z., Y.G. and X.X. performed the experiments; T.Z. and C.L. analyzed the data; T.Z. wrote the original manuscript; C.L., L.W. and L.S. revised and approved the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We are grateful to all the laboratory members for their technical advice and helpful discussions. This research was supported by NSFC grant (41961124009, 32072946), National Key R & D Program (2018YFD0900606), the Distinguished Professor of Liaoning (XLYC1902012) fund from Liaoning Department of Education (LJKMZ20221123), the innovation team of Aquaculture Environment Safety from Liaoning Province (LT202009) and Dalian High Level Talent Innovation Support Program (2022RG14).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUS) of Shanghai Ocean University (approval number SHOU-23-014) in February, 2023.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all the laboratory members for their technical advice and helpful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Michaelidis, B.; Ouzounis, C.; Paleras, A.; Pörtner, H.-O. Effects of long-term moderate hypercapnia on acid-base balance and growth rate in marine mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 293, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, J.A.; Bjerkeng, B.; Pettersen, O.; Schaanning, M.T.; Øxnevad, S. Effects of increased sea water concentrations of CO2 on growth of the bivalve Mytilus edulis L. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldeira, K.; Wickett, M.E. Oceanography: Anthropogenic carbon and ocean pH. Nature 2003, 425, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzer, S.C.; Phoenix, V.R.; Cusack, M.; Kamenos, N.A. Ocean acidification impacts mussel control on biomineralisation. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freer, A.; Bridgett, S.; Jiang, J.; Cusack, M. Biomineral Proteins from Mytilus edulis Mantle Tissue Transcriptome. Mar. Biotechnol. 2014, 16, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, F.; Luquet, G. Molluscan shell proteins. Comptes Rendus Palevol 2004, 3, 469–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, F.; Luquet, G.; Marie, B.; Medakovic, D. Molluscan Shell Proteins: Primary Structure, Origin, and Evolution. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2007, 80, 209–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeau, S.; Edmunds, P.; Spindel, N.; Carpenter, R. The responses of eight coral reef calcifiers to increasing partial pressure of CO2 do not exhibit a tipping point. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazeau, F.P.H.; Quiblier, C.M.L.; Jansen, J.M.; Gattuso, J.P.; Middelburg, J.J.; Heip, C.H.R. Impact of elevated CO2 on shellfish calcification. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 34, L07603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, J.C. Recent and Future Changes in Ocean Carbonate Chemistry. In Ocean Acidification; Gattuso, J.-P., Hansson, L., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xie, L.; Zhang, R. Hemocytes in the extrapallial space of Pinctada fucata are involved in immunity and biomineralization. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubel, A. An electron-microscope study of periostracum formation in some marine bivalves. II. The cells lining the periostracal groove. Mar. Biol. 1973, 20, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, S.; Suzuki, M.; Endo, H.; Iimura, K.; Kinoshita, S.; Watabe, S.; Kogure, T.; Nagasawa, H. Identification and characterization of a matrix protein (PPP-10) in the periostracum of the pearl oyster, Pinctada fucata. FEBS Open Bio 2013, 3, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Chi, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhang, R. Investigation of cell proliferation and differentiation in the mantle of Pinctada fucata (Bivalve, Mollusca). Mar. Biol. 2008, 153, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.X.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, X.B.; Song, J.; Yin, D.H.; Tian, Y.; Hao, Z.L.; Han, B.; Chang, Y.Q. Histological and Expression Differences Among Different Mantle Regions of the Yesso Scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) Provide Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of Biomineralization and Pigmentation. Mar. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kádár, E. Haemocyte response associated with induction of shell regeneration in the deep-sea vent mussel Bathymodiolus azoricus (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 362, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zong, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Wang, L.; Song, L. The Increased Expression of an Engrailed to Sustain Shell Formation in Response to Ocean Acidification. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 530435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, G.; Fan, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, B.; Su, J.; Yu, D. Molecular cloning and expression profiles of matrilin-1 inpearl oyster (Pinctada fucata). S. China Fish. Sci. 2017, 13, 76–84. Available online: https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/welcome/?target=%2fcabdirect%2fabstract%2f20173126376 (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Mörgelin, M.; Heinegård, D.; Engel, J.; Paulsson, M. Electron microscopy of native cartilage oligomeric matrix protein purified from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma reveals a five-armed structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 6137–6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deák, F.; Wagener, R.; Kiss, I.; Paulsson, M. The matrilins: A novel family of oligomeric extracellular matrix proteins. Matrix Biol. 1999, 18, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatt, A.R.; Becker, A.-K.A.; Neacsu, C.D.; Paulsson, M.; Wagener, R. The matrilins: Modulators of extracellular matrix assembly. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.-K.A.; Mikolajek, H.; Werner, J.M.; Paulsson, M.; Wagener, R. Characterization of recombinantly expressed matrilin VWA domains. Protein Expr. Purif. 2015, 107, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Song, X.; Wang, T.; Zhu, Q.; Miao, G.; Chen, Y.; Fang, X.; Que, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, G. Evolution and functional analysis of the Pif97 gene of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Curr. Zool. 2013, 59, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posey, K.L.; Coustry, F.; Hecht, J.T. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein: COMP opathies and beyond. Matrix Biol. 2018, 71–72, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Acharya, C.; Christiansen, B.A.; Yik, J.H.N.; DiCesare, P.E.; Haudenschild, D.R. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein enhances osteogenesis by directly binding and activating bone morphogenetic protein-2. Bone 2013, 55, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, V.; Karsai, A.; Fong, M.C.; Cai, W.; Yik, J.H.N.; Klineberg, E.; Haudenschild, D.R.; Liu, G.Y. Label-Free and Direct Visualization of Multivalent Binding of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 with Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolae, C.; Ko, Y.P.; Miosge, N.; Niehoff, A.; Studer, D.; Enggist, L.; Hunziker, E.B.; Paulsson, M.; Wagener, R.; Aszodi, A. Abnormal Collagen Fibrils in Cartilage of Matrilin-1/Matrilin-3-deficient Mice*. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 22163–22175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaucke, F.; Grässel, S. Genetic mouse models for the functional analysis of the perifibrillar components collagen IX, COMP and matrilin-3: Implications for growth cartilage differentiation and endochondral ossification. Histol. Histopathol. 2009, 24, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasuriya, C.T.; Goldring, M.B.; Terek, R.; Chen, Q. Matrilin-3 induction of IL-1 receptor antagonist is required for up-regulating collagen II and aggrecan and down-regulating ADAMTS-5 gene expression. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttigi, M.S.; Kim, B.J.; Choi, B.; Yoshie, A.; Kumar, H.; Han, I.; Park, H.; Lee, S.H. Matrilin-3 codelivery with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes articular cartilage regeneration in a rat osteochondral defect model. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumbach, K.; Niehoff, A.; Paulsson, M.; Zaucke, F. Ablation of collagen IX and COMP disrupts epiphyseal cartilage architecture. Matrix Biol. 2008, 27, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neacsu, C.D.; Ko, Y.P.; Tagariello, A.; Karlsen, R.K.; Neiss, W.F.; Paulsson, M.; Wagener, R. Matrilin-1 is essential for zebrafish development by facilitating collagen II secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Song, L. Recent Advances of Shell Matrix Proteins and Cellular Orchestration in Marine Molluscan Shell Biomineralization. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchut, A.; Roger, E.; Coustau, C.; Gourbal, B.; Mitta, G. Compatibility in the Biomphalaria glabrata/Echinostoma caproni model: Potential involvement of adhesion genes. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.F.; Fang, X.D.; Guo, X.M.; Li, L.; Luo, R.B.; Xu, F.; Yang, P.C.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, X.T.; Qi, H.G.; et al. The oyster genome reveals stress adaptation and complexity of shell formation. Nature 2012, 490, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Iwashima, A.; Tsutsui, N.; Ohira, T.; Kogure, T.; Nagasawa, H. Identification and characterisation of a calcium carbonate-binding protein, blue mussel shell protein (BMSP), from the nacreous layer. Chembiochem 2011, 12, 2478–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocot, K.M.; Cannon, J.T.; Todt, C.; Citarella, M.R.; Kohn, A.B.; Meyer, A.; Santos, S.R.; Schander, C.; Moroz, L.L.; Lieb, B.; et al. Phylogenomics reveals deep molluscan relationships. Nature 2011, 477, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Wang, M.Q.; Jia, Z.H.; Song, X.R.; Wang, L.L.; Song, L.S. A shell-formation related carbonic anhydrase in Crassostrea gigas modulates intracellular calcium against CO2 exposure: Implication for impacts of ocean acidification on mollusk calcification. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 189, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Song, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Song, L. The Inhibition of Ocean Acidification on the Formation of Oyster Calcified Shell by Regulating the Expression of Cgchs1 and Cgchit4. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, A.; Qiu, L.; Song, L. A new non-phagocytic TLR6 with broad recognition ligands from Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 65, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W.; Dong, M.; Wang, M.; Gong, C.; Jia, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, A.; Wang, L.; et al. A DM9-containing protein from oyster Crassostrea gigas (CgDM9CP-2) serves as a multipotent pattern recognition receptor. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 84, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Tao, Z.; Jiang, S.; Wang, M.; Cheng, Q.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.; Song, L. An integrin from oyster Crassostrea gigas mediates the phagocytosis toward Vibrio splendidus through LPS binding activity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 53, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, W.L.; Wu, S.S.; Li, J.L.; Dong, M.R.; Wang, L.L.; Song, L.S. CgBlimp-1 inhibits granulocytes proliferation and interleukin production in the immune response of oyster Crassostrea gigas. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 142, 104652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.L.; Lv, X.J.; Liu, Z.Q.; Song, X.R.; Yi, Q.L.; Wang, L.L.; Song, L.S. The sensing pattern and antitoxic response of Crassostrea gigas against extracellular products of Vibrio splendidus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 102, 103467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.Q.; Wang, W.L.; Fan, S.Q.; Li, J.L.; Li, Q.; Wu, S.S.; Wang, L.L.; Song, L.S. The receptor CgIL-17R1 expressed in granulocytes mediates the CgIL-17 induced haemocytes proliferation in Crassostrea gigas. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 131, 104376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.B.; Duncan, T.M. Bio-layer interferometry for measuring kinetics of protein-protein interactions and allosteric ligand effects. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 84, e51383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, T.; Wang, L.; Song, L. Calmodulin regulates the calcium homeostasis in mantle of Crassostrea gigas under ocean acidification. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1050022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L.; Zhen, D.K.; Bianchi, D.W. The use of fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) on paraffin-embedded tissue sections for the study of microchimerism. Biotechniques 2000, 29, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thisse, C.; Thisse, B. High-resolution in situ hybridization to whole-mount zebrafish embryos. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yao, B.; Sun, L.; Pu, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R. Immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization studies of gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) and its receptor in rat digestive tract. Life Sci. 2001, 68, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, I.; Duarte, C.; Olsen, Y.; Steckbauer, A.; Ramajo, L.; Moore, T.; Trotter, J.; McCulloch, M. Biological mechanisms supporting adaptation to ocean acidification in coastal ecosystems. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 152, A1–A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldbusser, G.G.; Salisbury, J.E. Ocean acidification in the coastal zone from an organism′s perspective: Multiple system parameters, frequency domains, and habitats. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mount, A.S.; Wheeler, A.P.; Paradkar, R.P.; Snider, D. Hemocyte-mediated shell mineralization in the eastern oyster. Science 2004, 304, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Liang, J.; Sun, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, S.r.; Liu, Y.j.; Xie, L.p.; Zhang, R.q. Influence of the Extrapallial Fluid of Pinctada fucata on the Crystallization of Calcium Carbonate and Shell Biomineralization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addadi, L.; Joester, D.; Nudelman, F.; Weiner, S. Mollusk shell formation: A source of new concepts for understanding biomineralization processes. Chemistry 2006, 12, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, T.; Schwarzinger, C.; Miksik, I.; Smrz, M.; Beran, A. Molluscan shell evolution with review of shell calcification hypothesis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 154, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, N. Studies on shell formation: XI. Crystal—Matrix relationships in the inner layers of mollusk shells. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1965, 12, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Faisal, M. Matrilin-like molecules produced by circulating hemocytes of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) upon stimulation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2007, 31, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Liao, Z. Characterization of a novel shell matrix protein with vWA domain from Mytilus coruscus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2020, 84, 1629–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjärnmark, N.A.; Yarra, T.; Churcher, A.M.; Felix, R.C.; Clark, M.S.; Power, D.M. Transcriptomics provides insight into Mytilus galloprovincialis (Mollusca: Bivalvia) mantle function and its role in biomineralisation. Mar. Genom. 2016, 27, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarra, T.; Gharbi, K.; Blaxter, M.; Peck, L.S.; Clark, M.S. Characterization of the mantle transcriptome in bivalves: Pecten maximus, Mytilus edulis and Crassostrea gigas. Mar. Genom. 2016, 27, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, L.D.; Mills, D.; Wiegand, A.; Leavesley, D.; Elizur, A. Spatial analysis of biomineralization associated gene expression from the mantle organ of the pearl oyster Pinctada maxima. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Zhou, D.; Xu, Y.; Yu, D. Cloning and functional analysis of BMP3 in the pearl oyster (Pinctada fucata). J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2019, 47, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, K.; Olsson, H.; Mörgelin, M.; Heinegård, D. Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein Shows High Affinity Zinc-dependent Interaction with Triple Helical Collagen*. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20397–20403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Trehan, S.K.; Guan, Y.j.; Sun, C.q.; Moore, D.C.; Jayasuriya, C.T.; Chen, Q. Matrilin-3 Inhibits Chondrocyte Hypertrophy as a Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Antagonist*. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 34768–34779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doney, S.C.; Fabry, V.J.; Feely, R.A.; Kleypas, J.A. Ocean acidification: The other CO2 problem. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 169–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emma, T.-S.; Coffey, W.D.; Hua, W.; Nunn, B.L.; Dickinson, G.H.; Roberts, S.B. Shotgun proteomics reveals physiological response to ocean acidification in Crassostrea gigas. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, G.E.; Barry, J.P.; Edmunds, P.J.; Gates, R.D.; Hutchins, D.A.; Klinger, T.; Sewell, M.A. The Effect of Ocean Acidification on Calcifying Organisms in Marine Ecosystems: An Organism to Ecosystem Perspective. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2010, 41, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yu, Z.; Huang, X.; Shi, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, H.; Yi, X.; He, M. Effect of ocean acidification on growth, calcification, and gene expression in the pearl oyster, Pinctada fucata. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 130, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).