Dynamic Distribution of Mesanophrys sp. and Tissue Enzyme Activities in Experimentally Infected Mud Crab Scylla paramamosain
Abstract
1. Introduction
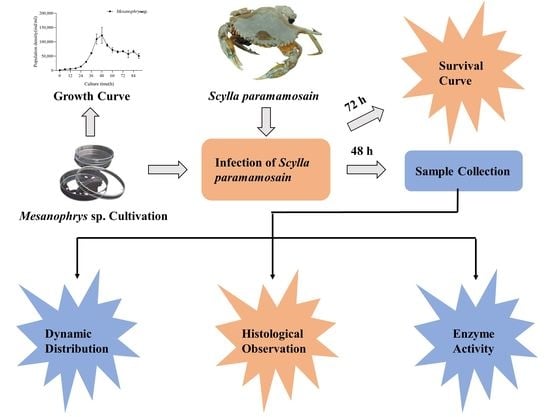
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Conditions
2.2. Mesanophrys sp. Cultivation
2.3. Infection of Experimental Animals
2.4. Detection and Quantification of Mesanophrys sp. in Tissues
2.5. Histology Observation
2.6. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Curve of Mesanophrys sp. and Establishment of the Standard Curve for qPCR Detection
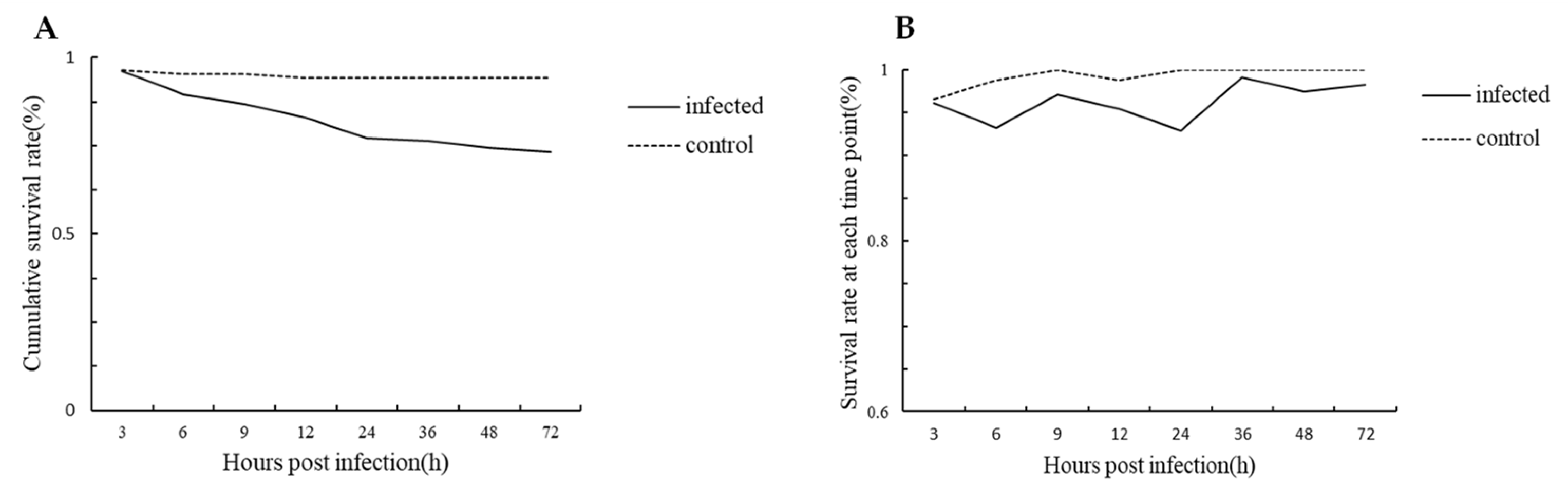
3.2. Survival Curve of Crabs in Infected and Control Group
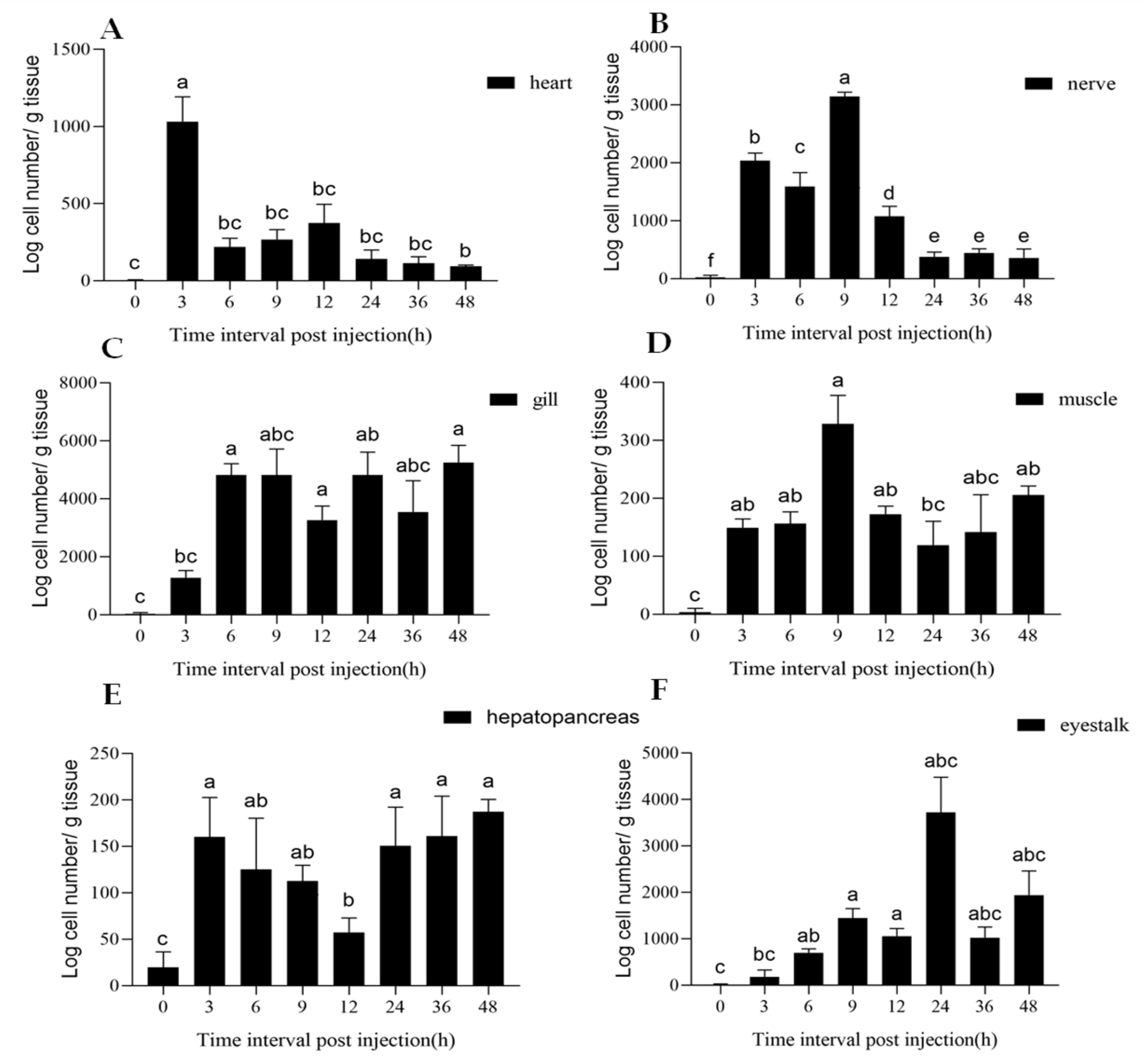
3.3. Tissue Distribution of Mesanophrys sp.
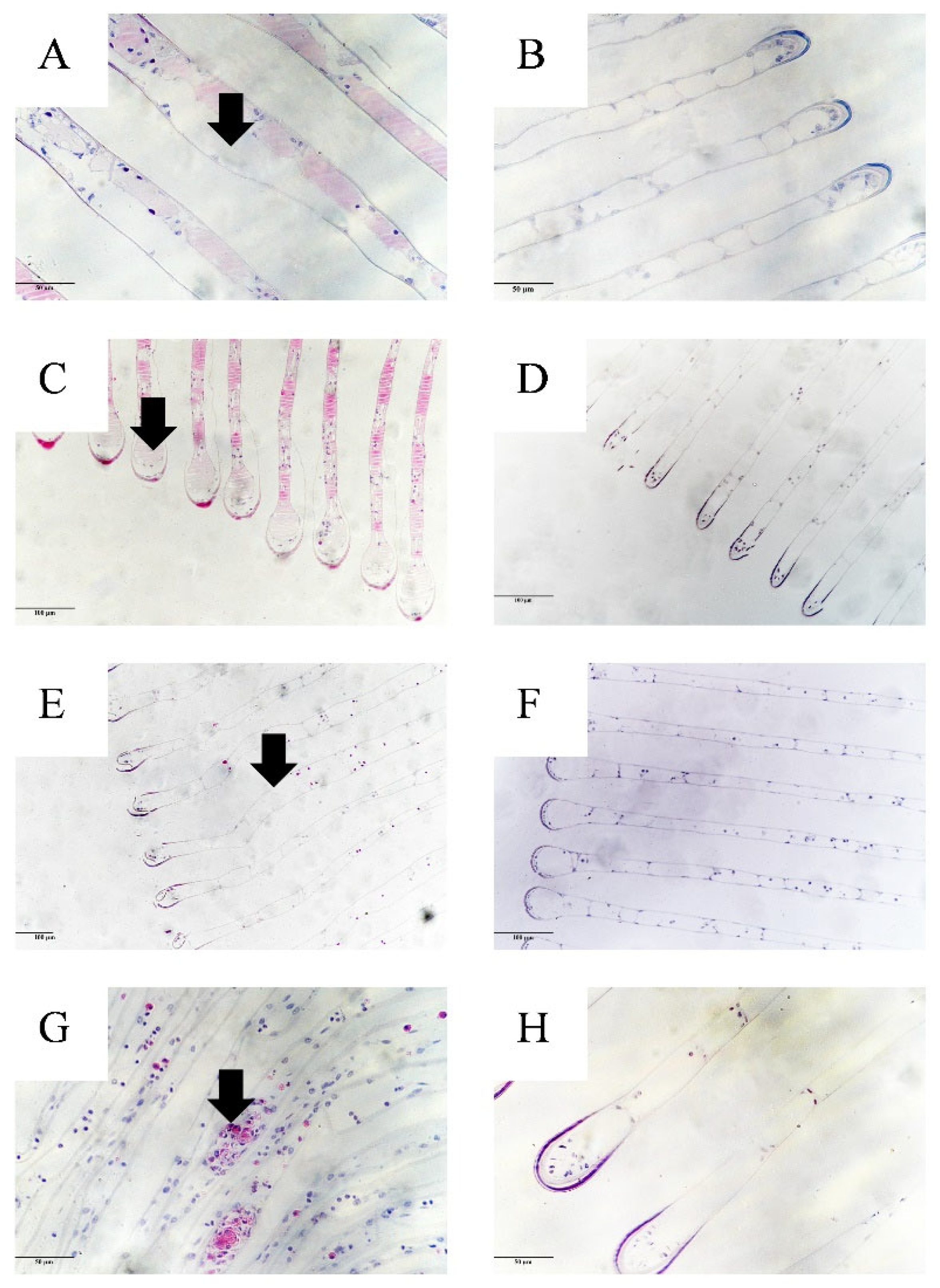
3.4. Histopathology
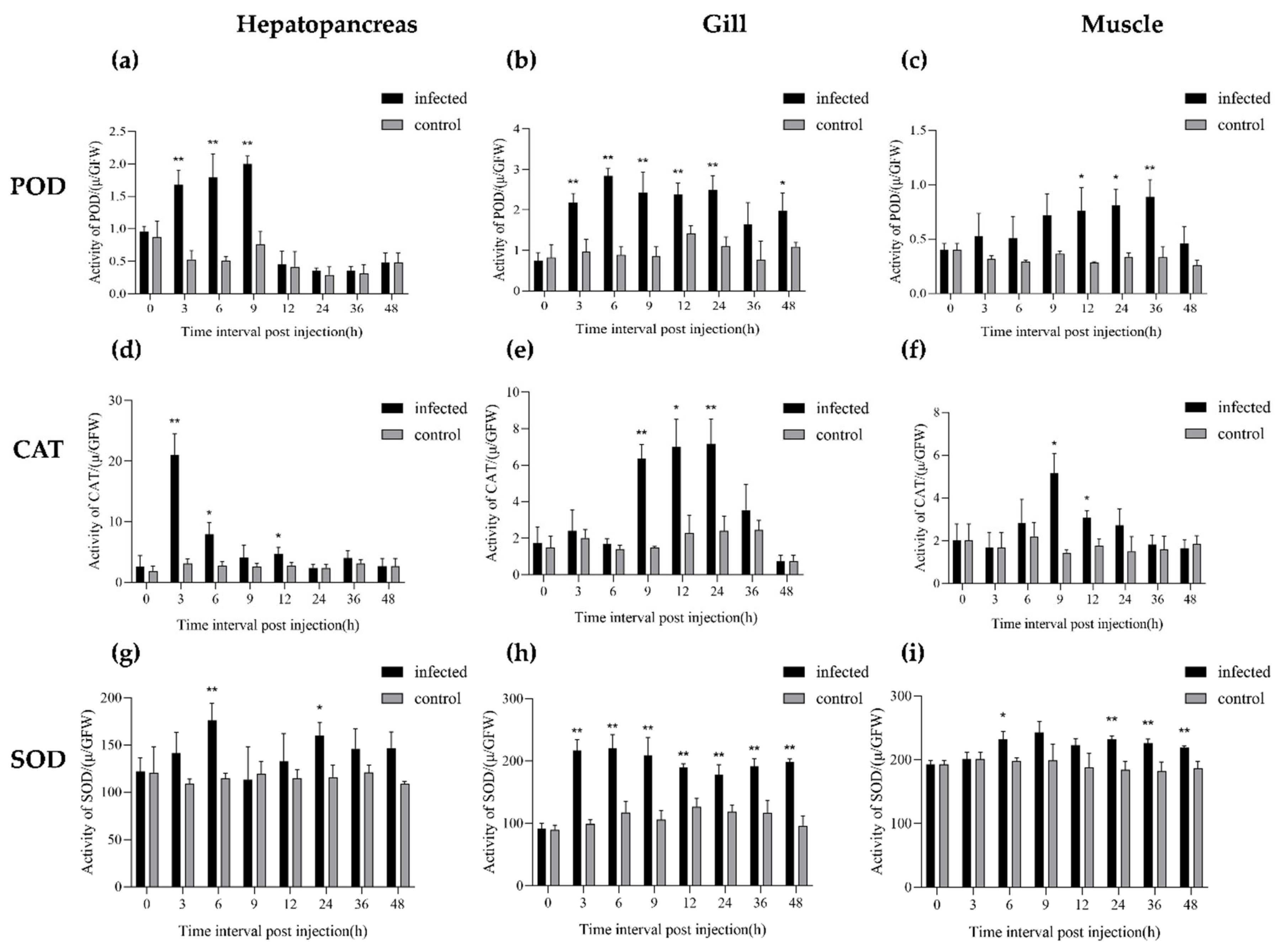
3.5. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waiho, K.; Fazhan, H.; Quinitio, E.T.; Baylon, J.C.; Fujaya, Y.; Azmie, G.; Wu, Q.; Shi, X.; Ikhwanuddin, M.; Ma, H. Larval rearing of mud crab (Scylla): What lies ahead. Aquaculture 2018, 493, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiadhas, R.; Najmudeen, T. Economic evaluation of mud crab farming under different production systems in India. Aquac. Econ. Manag. 2004, 8, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazhan, H.; Waiho, K.; Norfaizza, W.I.W.; Megat, F.H.; Ikhwantddin, M. Inter-species mating among mud crab genus Scylla in captivity. Aquaculture 2017, 471, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafaat, M.N.; Azra, M.N.; Waiho, K.; Fazhan, H.; Abol-Munafi, A.B.; Ishak, S.D.; Syahnon, M.; Ghazali, A.; Ma, H.; Ikhwanuddin, M. A Review of the Nursery Culture of Mud Crabs, Genus Scylla: Current Progress and Future Directions. Animals 2021, 11, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, T.; Ren, X.; Lin, S.; Li, S.; Gong, Y. Elucidation of metabolic responses in mud crab Scylla paramamosain challenged to WSSV infection by integration of metabolomics and transcriptomics. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 113, 103799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hong, W.J.; Zhu, F. The role of astakine in Scylla paramamosain against Vibrio Alginolyticus and white spot syndrome virus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.B.; Zhu, M.Z.; Chen, Z.G.; Wang, M. Diagnostic assessment of some common pathogenic genera within the order Scuticociliatida: Members inhabiting mariculture biotopes. J. Qingdao Ocean Univ. 2000, 30, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Kong, J.; Perveen, S.; Lei, Y.; Feng, B.; Yang, L.; Yin, F. Anti-parasitic effects of quinine sulfate on the swimming crab parasite Mesanophrys sp. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, S.; Lei, Y.H.; Yin, F.; Wang, C.L. Effect of environmental factors on survival and population growth of ciliated parasite, Mesanophrys sp. (Ciliophora: Scuticociliatia) infecting Portunus trituberculatus. Parasitology 2021, 148, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.H.; Perveen, S.; Xie, X.; Yang, L.J.; Gao, Q.X.; Wang, C.L.; Yin, F. Host-parasite interactions: A study on the pathogenicity of Mesanophrys sp. and hemocytes-mediated parasitic resistance of swimming crabs (Portunus trituberculatus) at different temperatures. Aquaculture 2022, 551, 737920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lei, Y.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, S.; Qian, D.; Yu, Y.; Yin, F.; Wang, C. Isolation, characterization and virulence of Mesanophrys sp. (Ciliophora: Orchitophryidae) in farmed swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) in eastern China. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, S.; Jin, S.; Qian, D.; Xie, X.; Yin, F.; Wang, C. Anti-parasitic effects and toxicity of formalin on the parasite Mesanophrys sp. of the swimming crab Portnus trituberculatus. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 212, 107886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, M.; Xiao, J.; Xu, W.J.; Li, C.W. Hematodinium spp. infections in wild and cultured populations of marine crustaceans along the coast of China. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2017, 124, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, C.J.; Rowley, A.F. Emerging diseases and epizootics in crabs under cultivation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, e809759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midorikawa, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Sanda, T.; Hamasaki, K.; Dan, S.; Lal, M.T.B.M.; Kato, G.; Sano, M. Characterization of Aquimarina hainanensis isolated from diseased mud crab Scylla serrata larvae in a hatchery. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groben, G.; Clarke, B.B.; Murphy, J.A.; Koch, P.L.; Crouch, J.A.; Lee, S.; Zhang, N. Real-time PCR detection of Clarireedia spp., the causal agents of dollar spot in turfgrasses. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 3118–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lv, Q.; He, Y.; Gu, R.; Zhou, B.; Chen, J.; Fan, X.; Pan, G.; Long, M.; Zhou, Z. Integrated qPCR and staining methods for detection and quantification of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei in Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, T.A.; Morado, J.F. Changes in total hemocyte and differential counts in Dungeness crabs infected with Mesanophrys pugettensis, a marine facultative parasitic ciliate. Aquat. Anim. Health. 2001, 13, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parama, A.; Iglesias, R.; Alvarez, M.F.; Leiro, J.; Aja, C.; Sanmartin, M.L. Philasterides dicentrarchi (Ciliophora, Scuticociliatida): Experimental infection and possible routes of entry in farmed turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquaculture 2003, 217, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Shields, J.D. A review of the parasitic dinoagellates Hematodinium species and Hematodinium-like infections in marine crustaceans. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005, 66, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, S.; Yang, L.; Xie, X.; Han, X.; Gao, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Yin, F. Vitamin C elicits the activation of immunological responses in swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) hemocytes against Mesanophrys sp. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.F.; Fu, Y.W.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Guo, S.Q.; Yan, Y.L.; Tu, Y.F.; Guo, T.G.; Zhang, Q.Z. Establishment and application of a TaqMan probe–based qPCR for the detection of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 2263–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.M.; Qiu, L.; Sheng, A.Z.; Wan, X.Y.; Cheng, D.Y.; Huang, J. Quantitative detection method of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei using TaqMan probe real-time PCR. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 151, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correya, M.S.; Vijayagopal, P.; Sanil, N.K. Morphological and molecular description of a new species of Myxobolus (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) infecting Planiliza macrolepis (Smith, 1846) from India. J. Parasit Dis. 2021, 45, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frischer, M.E.; Landers, S.C.; Walker, A.N.; Powell, S.A.; Lee, R.F. Black gill in marine decapod crustaceans: A review. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2022, 30, 498–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morado, J.F.; Small, E.B. Ciliate parasites and related diseases of crustacea: A review. Fish Res. 1995, 3, 275–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.H.; Ma, H.L.; Liu, G.X.; Deng, Y.Q.; Jiang, J.J.; Feng, J.; Guo, Z.X. Biochemical, metabolic, and immune responses of mud crab (Scylla paramamosain) after mud crab reovirus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 127, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roma, E.H.; Macedo, J.P.; Goes, G.R.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Castro, W.D.; Cisalpino, D.; Vieira, L.Q. Impact of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on the control of parasite loads and inflammation in Leishmania amazonensis infection. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, D.D.; Zhou, Y.L.; Gu, W.B.; Zhu, Q.H.; Xu, B.P.; Zhou, Z.K.; Liu, Z.P.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Shu, M.A. Identification and characterization of six peroxiredoxin transcripts from mud crab Scylla paramamosain: The first evidence of peroxiredoxin genefamily in in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 93, 223–235. [Google Scholar]
- Cecerska-Heryc, E.; Surowska, O.; Heryc, R.; Serwin, N.; Napiontek-Balinska, S.; Dołegowska, B. Are antioxidant enzymes essential markers in the diagnosis and monitoring of cancer patients—A review. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewska-Ziob, M.; Adamek, B.; Kasperczyk, J.; Romuk, E.; Hudziec, E.; Chwalinska, E.; Dobija-Kubica, K.; Rogozinski, P.; Brulinski, K. Activity of antioxidant enzymes in the tumor and adjacent noncancerous tissues of non-small-cell lung cancer. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 31, 2901840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittle, R.; Vanderauwera, S.; Gollery, M.; Van Breusegem, F. Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant. Sci. 2004, 9, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.H.; Huang, Y.; Yan, G.W.; Pan, C.; Zhang, J.L. Antioxidative status, immunological responses, and heat shock protein expression in hepatopancreas of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis under the exposure of glyphosate. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, O.M.; Akinloye, O.A. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.X.; Cao, C.Y.; Sun, Y.C.; Wang, L.L.; Li, N.; Xu, S.W.; Li, J.L. Effects on liver hydrogen peroxide metabolism induced by dietary selenium deficiency or excess in chickens. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 159, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.L.; Zuo, D.; Wang, L.M.; Sun, T.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.L. Effects of white spot syndrome virus infection on immuno-enzyme activities and ultrastructure in gills of Cherax quadricarinatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) | PCR Objective |
|---|---|---|
| ITS1-5.8s-ITS2F | GTAGGTGAACCTGCGGAAGGATCATTA | qPCR |
| ITS1-5.8s-ITS2R | TACTGATATGCTTAAGTTCAGCGG | qPCR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Zhang, W.; Li, R.; Lu, J.; Chen, Q.; Hu, H.; Yin, F.; Mu, C.; Song, W.; Wang, C. Dynamic Distribution of Mesanophrys sp. and Tissue Enzyme Activities in Experimentally Infected Mud Crab Scylla paramamosain. Fishes 2023, 8, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050249
Zhang K, Zhang W, Li R, Lu J, Chen Q, Hu H, Yin F, Mu C, Song W, Wang C. Dynamic Distribution of Mesanophrys sp. and Tissue Enzyme Activities in Experimentally Infected Mud Crab Scylla paramamosain. Fishes. 2023; 8(5):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050249
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kexin, Weiren Zhang, Ronghua Li, Junkai Lu, Qingwei Chen, Haojie Hu, Fei Yin, Changkao Mu, Weiwei Song, and Chunlin Wang. 2023. "Dynamic Distribution of Mesanophrys sp. and Tissue Enzyme Activities in Experimentally Infected Mud Crab Scylla paramamosain" Fishes 8, no. 5: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050249
APA StyleZhang, K., Zhang, W., Li, R., Lu, J., Chen, Q., Hu, H., Yin, F., Mu, C., Song, W., & Wang, C. (2023). Dynamic Distribution of Mesanophrys sp. and Tissue Enzyme Activities in Experimentally Infected Mud Crab Scylla paramamosain. Fishes, 8(5), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050249