Assessing the Attractive Effects of Floating Artificial Reefs and Combination Reefs on Six Local Marine Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
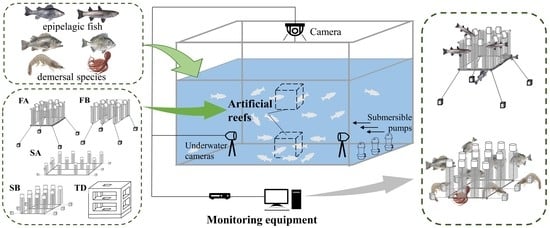
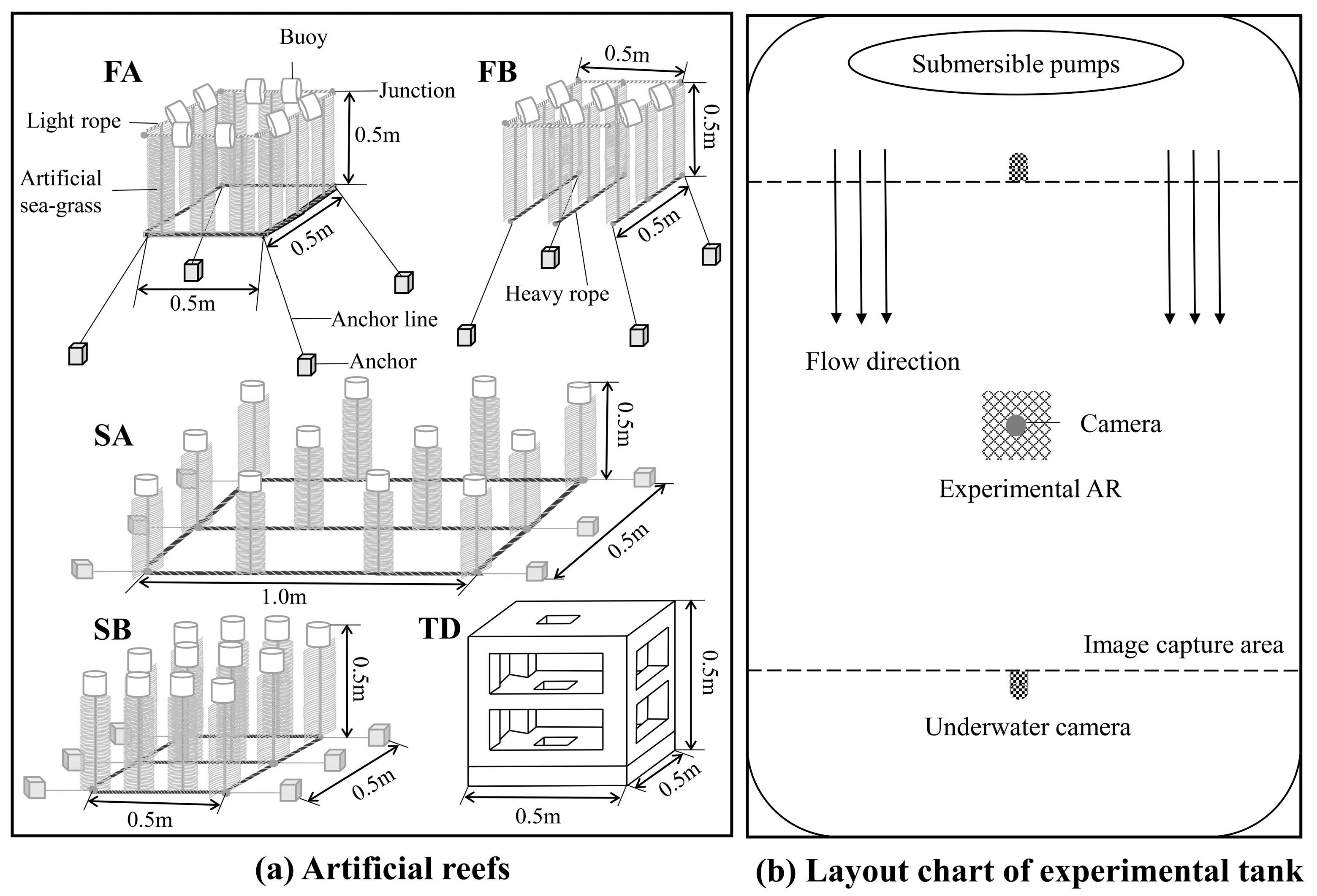
2. Materials and Methods
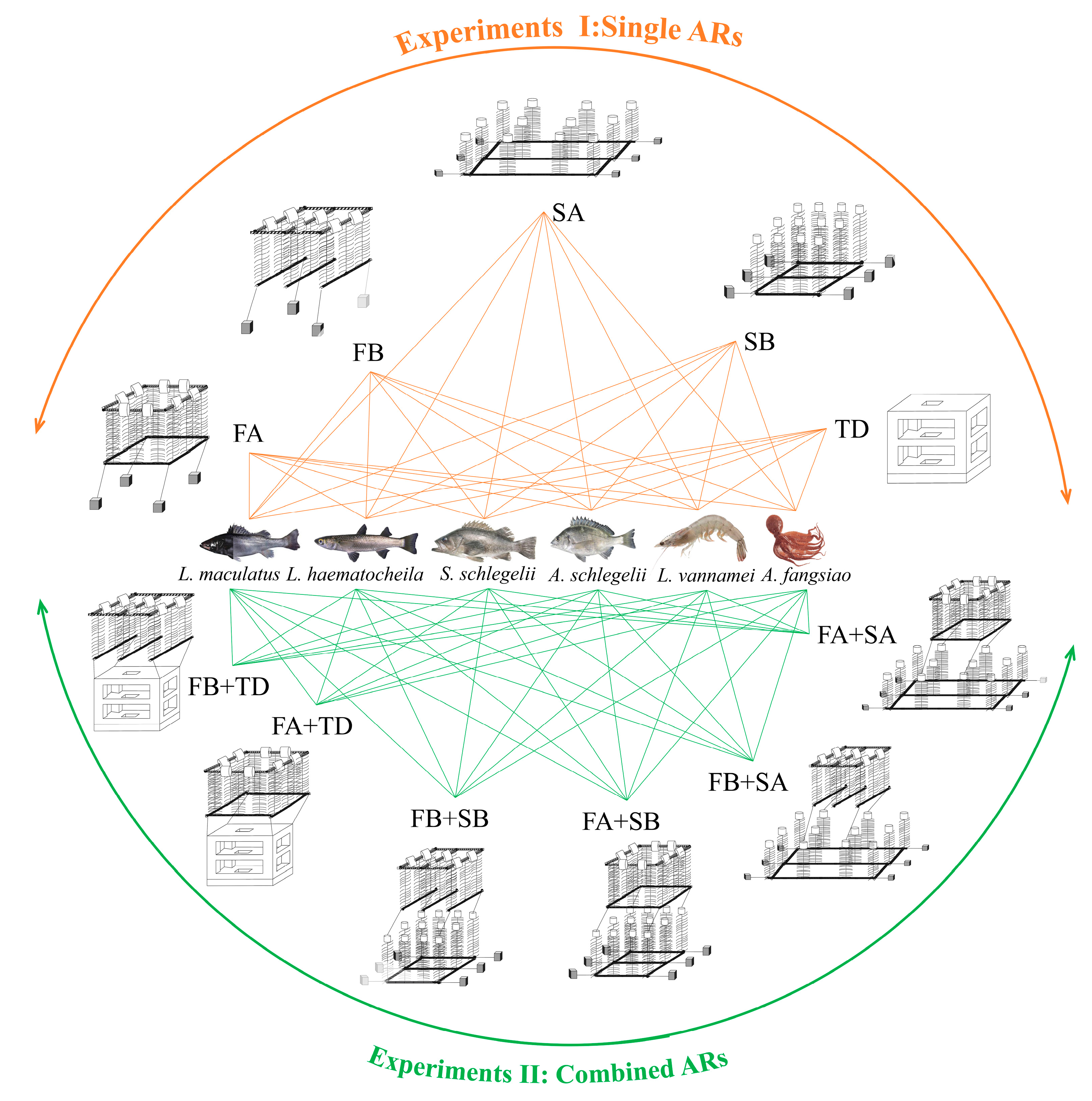
2.1. Experiments
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
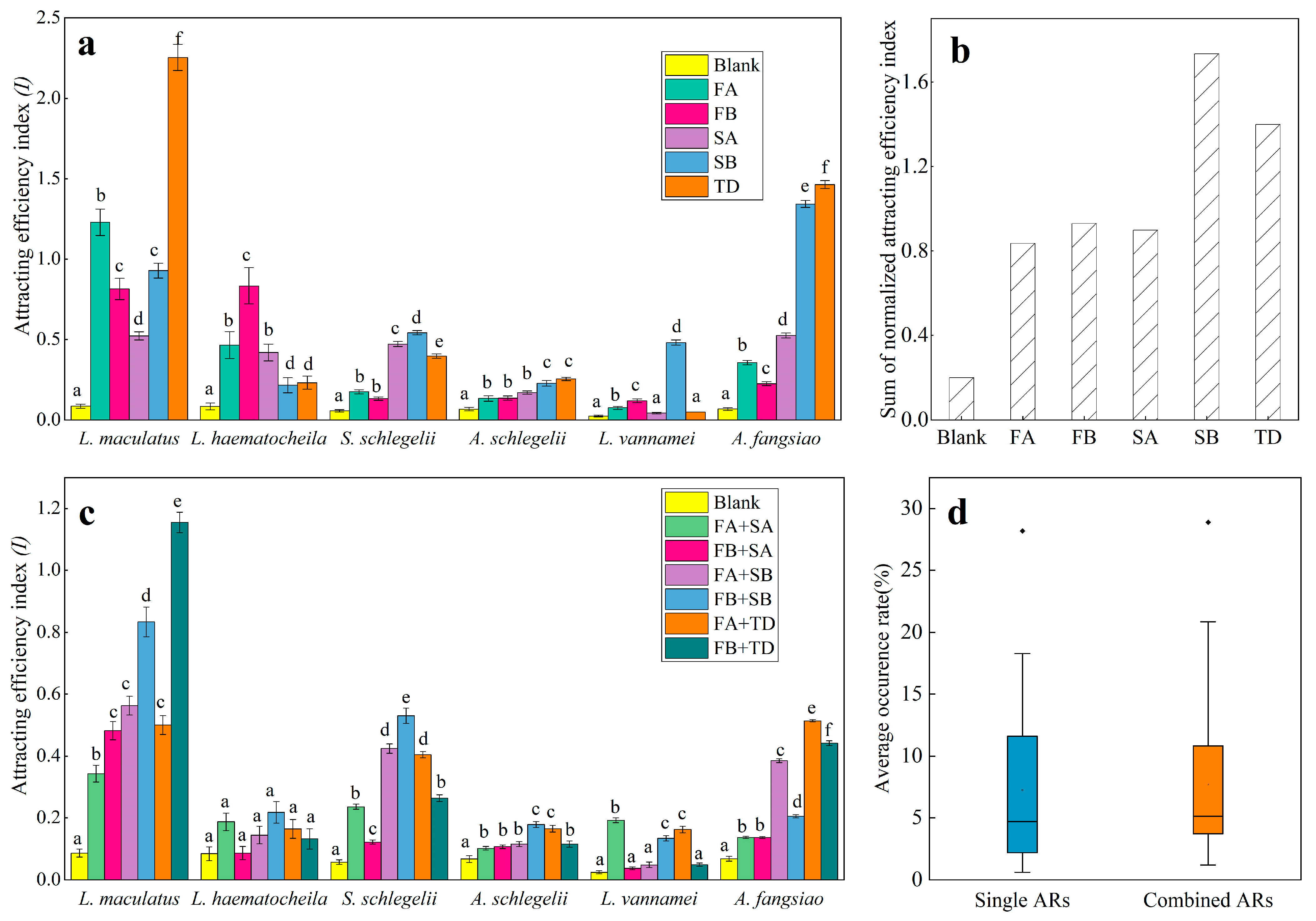
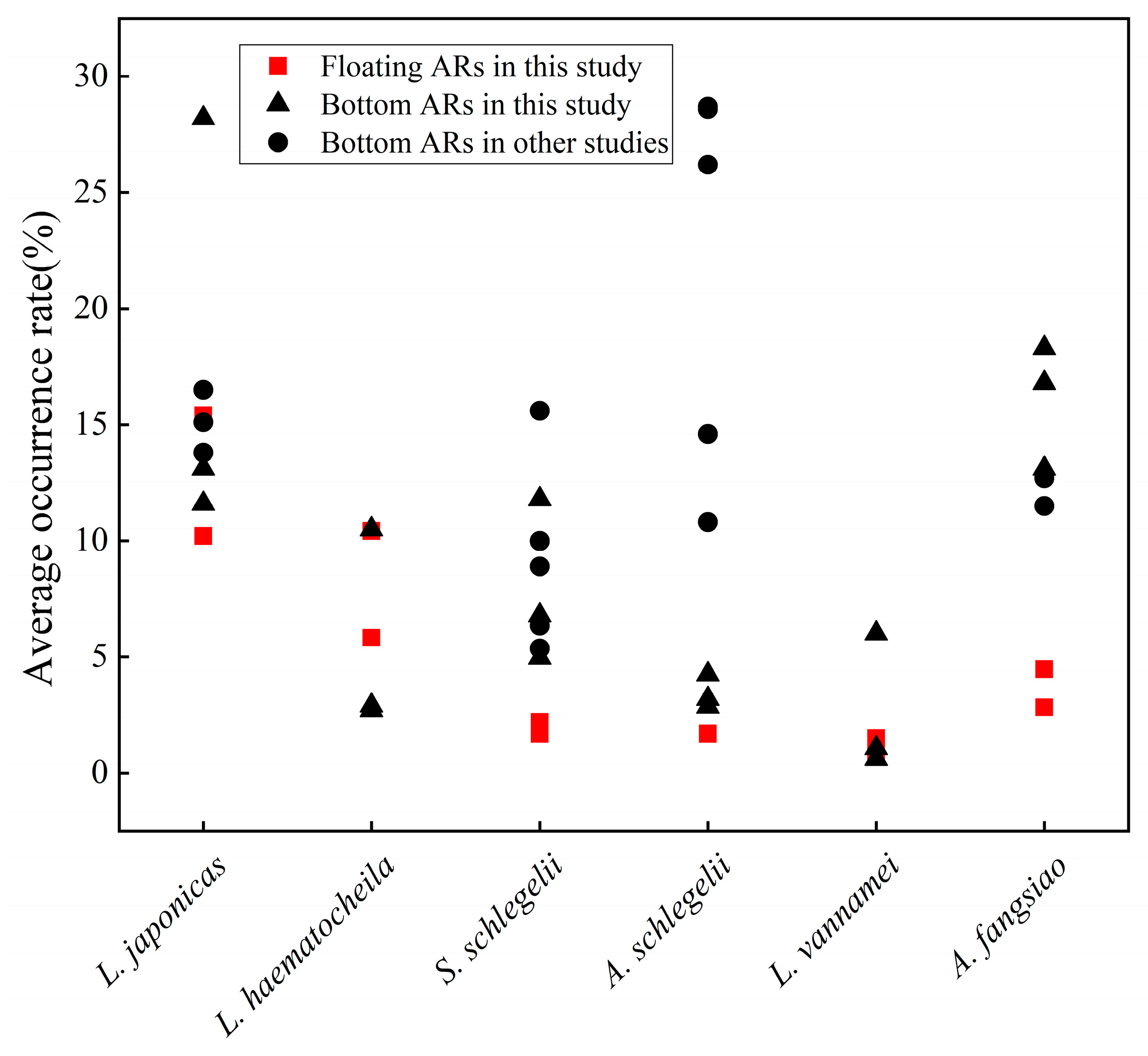
3.1. Attracting Effect of Single ARs
3.2. Attracting Effect of Combined ARs
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Species Ecology
4.2. Influence of ARs’ Configuration
4.3. Would the Combined ARs Be Better?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Species | L. maculatus | L. haematocheila | S. schlegelii | A. schlegelii | L. vannamei | A. fangsiao |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARs | ||||||
| Blank | 0.086 ± 0.013 | 0.084 ± 0.022 | 0.057 ± 0.007 | 0.067 ± 0.011 | 0.024 ± 0.005 | 0.068 ± 0.008 |
| FA | 1.229 ± 0.082 | 0.466 ± 0.084 | 0.176 ± 0.012 | 0.134 ± 0.017 | 0.076 ± 0.010 | 0.357 ± 0.014 |
| FB | 0.815 ± 0.066 | 0.834 ± 0.110 | 0.133 ± 0.010 | 0.136 ± 0.012 | 0.120 ± 0.012 | 0.226 ± 0.012 |
| SA | 0.523 ± 0.026 | 0.420 ± 0.052 | 0.472 ± 0.016 | 0.170 ± 0.010 | 0.043 ± 0.005 | 0.526 ± 0.015 |
| SB | 0.928 ± 0.046 | 0.216 ± 0.047 | 0.542 ± 0.013 | 0.228 ± 0.018 | 0.481 ± 0.016 | 1.343 ± 0.021 |
| TD | 2.254 ± 0.081 | 0.232 ± 0.041 | 0.397 ± 0.014 | 0.256 ± 0.010 | 0.049 ± 0.007 | 1.464 ± 0.025 |
| FA + SA | 0.342± 0.027 | 0.187 ± 0.028 | 0.238 ± 0.008 | 0.103 ± 0.006 | 0.189 ± 0.007 | 0.138 ± 0.003 |
| FB + SA | 0.478 ± 0.029 | 0.086 ± 0.021 | 0.120 ± 0.007 | 0.108 ± 0.006 | 0.037 ± 0.005 | 0.140 ± 0.003 |
| FA + SB | 0.558 ± 0.026 | 0.137 ± 0.028 | 0.417 ± 0.015 | 0.110 ± 0.008 | 0.048 ± 0.009 | 0.376 ± 0.006 |
| FB + SB | 0.827 ± 0.047 | 0.220 ± 0.035 | 0.528 ± 0.025 | 0.180 ± 0.010 | 0.129 ± 0.008 | 0.211 ± 0.005 |
| FA + TD | 0.500 ± 0.031 | 0.157 ± 0.030 | 0.398 ± 0.010 | 0.160 ± 0.011 | 0.157 ± 0.010 | 0.512 ± 0.003 |
| FB + TD | 1.154 ± 0.034 | 0.133 ± 0.033 | 0.264 ± 0.011 | 0.116 ± 0.010 | 0.049 ± 0.005 | 0.442 ± 0.007 |
References
- Hilborn, R.; Amoroso, R.O.; Anderson, C.M.; Baum, J.K.; Ye, Y. Effective fisheries management instrumental in improving fish stock status. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2218–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeremy, B.C.J.; Michael, X.K.; Wolfgang, H.B.; Karen, A.B. Historical overfishing and the recent collapse of coastal ecosystems. Science 2001, 293, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, C.; Hédouin, L.; Lacorne, M.C.; Dalle, J.; Lapinski, M.; Blanc, P.; Nugues, M.M. Performance of innovative materials as attracting substrates for coral restoration. Restor. Ecol. 2022, 30, e13625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, D.J.; Pinsky, M.L.; Palumbi, S.R.; Estes, A. Marine defaunation: Animal loss in the global ocean. Science 2015, 347, 1255641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafforn, K.A.; Mayer-Pinto, M.; Morris, R.L.; Waltham, N.J. Application of management tools to integrate ecological principles with the design of marine infrastructure. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 158, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon tanks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, A.; Ferrari, M.C.O.; Harris, D.J. Evolution and behavioural responses to human-induced rapid environmental change. Evol. Appl. 2011, 4, 367–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Agusti, S.; Barbier, E.; Britten, G.L.; Castilla, J.C. Rebuilding marine life. Nature 2020, 580, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komyakova, V.; Chamberlain, D.; Jones, G.P.; Swearer, E.S. Assessing the performance of artificial reefs as substitute habitat for temperate reef fishes: Implications for reef design and placement. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folpp, H.R.; Schilling, H.T.; Clark, G.F.; Lowry, M.B.; Maslen, B. Artificial reefs increase fish abundance in habitat-limited estuaries. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komyakova, V.; Swearer, S.E. Contrasting patterns in habitat selection and attracting of temperate reef fishes among natural and artificial reefs. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 143, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, C.A.; Allgeier, J.E.; Montaña, C.G. Mechanistic evidence of enhanced production on artificial reefs: A case study in a Bahamian seagrass ecosystem. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanovski, R.; Abelson, A. Structural complexity enhancement as a potential coral-reef restoration tool. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 132, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Reimer, J.D. Reconsideration of the surface structure of settlement plates used in coral attracting studies. Zool. Stud. 2011, 50, 53–60. Available online: http://zoolstud.sinica.edu.tw/Journals/50.1/53.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Ramm, L.A.W.; Florisson, J.H.; Watts, S.L.; Becker, A.; Tweedley, J.R. Artificial reefs in the Anthropocene: A review of geographical and historical trends in their design; purpose; and monitoring. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2021, 97, 699–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, B.; Linden, P.; Pinto, I.S.; Almada, E.; Borges, M.T. Artificial reefs in the North-East Atlantic area: Present situation, knowledge gaps and future perspectives. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 213, 105854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Lin, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y. Structural and Functional Improvements of Coastal Ecosystem Based on Artificial Oyster Reef Construction in the Bohai Sea, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 829557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Qi, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y. Ecosystem attributes of trophic models before and after construction of artificial oyster reefs using Ecopath. Aquacult. Environ. Interac. 2019, 11, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, J.C. Artificial Reef Evaluation with Application to Natural Marine Habitats. Fish Res. 2003, 63, 297–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Tong, H.H.; Wei, D.; Xiao, W.; Xue, D. Review of Structure Types and New Development Prospects of Artificial Reefs in China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 853452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, B.; Dauvin, J.C.; Navon, M.; Rusig, A.M.; Claquin, P. Marine artificial reefs; a meta-analysis of their design; objectives and effectiveness. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 27, e01538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Li, W.; Chen, P.M.; Zhang, H.Y.; Lin, J.X. The Corrosion Resistance Properties and Precipitate of Common Artificial Reef Materials. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 197–198, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.X.; Tweedley, J.; Loneragan, N.R. Artificial reefs can mimic natural habitats for fish and macroinvertebrates in temperate coastal waters of the Yellow Sea. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 139, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo-Garzón, O.; García, C.B.; Correa, J. Temporal dynamics of fishes assemblages on two artificial reefs in Morrosquillo Gulf; Colombian Caribbean. Actual. Biol. Medellin. 2004, 26, 219–230. [Google Scholar]
- Mallela, J.; Milne, B.C.; Martinez-Escobar, D. A comparison of epibenthic reef communities settling on commonly used experimental substrates: PVC versus ceramic tiles. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2017, 486, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Tong, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, C.; Xue, D. Numerical Simulation Study on Environment-Friendly Floating Reef in Offshore Ecological Belt under Wave Action. Water 2021, 13, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almany, G.R. Does increased habitat complexity reduce predation and competition in coral reef fish assemblages? Oikos 2004, 106, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrents, K.C. The influence of shelter availability on attracting and early juvenile survivorship of Lythrypnus dalli Gilbert Pisces: Gobiidae. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1987, 107, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.R.; Swearer, S.E. Two’s company; three’s a crowd: Food and shelter limitation outweigh the benefits of group living in a shoaling fish. Ecology 2013, 94, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hixon, M.A.; Menge, B.A. Species diversity: Prey refuges modify the interactive effects of predation and competition. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1991, 39, 178–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackradt, C.W.; Félix-Hackradt, F.C.; García-Charton, J.A. Influence of habitat structure on fish assemblage of an artificial reef in southern Brazil. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 72, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hixon, M.A.; Beets, J.P. Shelter characteristics and Caribbean fish assemblages: Experiments with artificial reefs. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1989, 44, 666–680. [Google Scholar]
- Kellison, T.G.; Sedberry, G.R. The effects of artificial reef vertical profile and hole diameter on fishes off South Carolina. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1998, 62, 763–780. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsson, D.; Yahya, S.A.S.; Öhman, M.C. Effects of high-relief structures on cold temperate fish assemblages: A field experiment. Mar. Biol. Res. 2006, 2, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baine, M. Artificial reefs: A review of their design; application; management and performance. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2001, 44, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.B.; Cai, W.G.; Chen, H.G.; Jia, X.P. The mechanism and research progress on fish attraction technique for artificial reefs. Mar. Fish. 2010, 32, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Shen, Y.; Su, M.; Yu, C.X. Numerical simulation of hydrodynamic and water quality effects of shoreline changes in Bohai Bay. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 12, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.B.; Luan, K.; Liu, K.F.; Chen, W. Effectiveness of four kinds of square reef in attracting Sebastes schlegelii and Hexagrammos otakii. J. Hebei Fish. China 2019, 308, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, J.E.; Binder, T.R.; Johnson, J.; He, J.; Dingledine, N. Five-year evaluation of habitat remediation in Thunder Bay; Lake Huron: Comparison of constructed reef characteristics that attract spawning lake trout. Fish. Res. 2016, 183, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.J.; Tang, J.H.; Liu, P.T.; Zhong, J.S.; Wu, L. Surface distribution and movement trend of Liza haematocheila larvae and juveniles along the southern yellow Sea. J. Shanghai Fish. Univ. 2007, 4, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Han, T.; Wang, J.T.; Liu, T.; Bian, P. Effects of replacing fish meal with soybean meal on growth performance; feed utilization and physiological status of juvenile redlip mullet Liza haematocheila. Aquacult. Rep. 2021, 20, 2352–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.J. Habitat selection and shelter use by Octopus tetricus. Mar. Ecol.-Prog. Ser. 1997, 150, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Fahrudin, A.; Boer, M.; Kamal, M.M.; Wardiatno, Y. The distribution of reef fish in Ternate Island, North Maluku, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth. Environ. Sci. 2020, 584, 012070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclean, M.; Roseman, E.F.; Pritt, J.J.; Kennedy, G.; Manny, B.A. Artificial reefs and reef restoration in the Laurentian Great Lakes. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overholtzer-McLeod, K.L. Variance in reef spatial structure masks density dependence in coral-reef fish populations on natural versus artificial reefs. Mar. Ecol.-Prog. Ser. 2004, 276, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granneman, J.E.; Steele, M.A. Effects of reef attributes on fish assemblage similarity between artificial and natural reefs. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 72, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, M.J. Resource limitation and attracting patterns in a coral reef fish assemblage. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1984, 74, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, C.; Suthers, I.M.; Smith, J.A. Zooplanktivory is a key process for fish production on a coastal artificial reef. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 541, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, E.K.; Auer, N.A.; Roseman, E.F.; Boase, J. Verifying success of artificial spawning reefs in the St. Clair–Detroit River System for lake sturgeon Acipenser fulvescens Rafinesque, 1817. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2014, 30, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, N.P.; Stephen, T.S. Fine-Scale Movements and Home Ranges of Red Snapper around Artificial Reefs in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2014, 143, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, S.; Carlo, C.; Franco, A.; Gianluca, S.; Christopher, M.B.; Michele, G. Influence of fish aggregating devices (FADs) on anti-predator behaviour within experimental mesocosms. Mar. Ecol. Res. 2015, 112, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashi, T. Fish ecology of reef fisheries IV. Survey of fish stocks in the vicinity of reef fisheries. Aquat. Civil. 1985, 21, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Moriguchi, T.; Takagi, Y. A proposal for new techniques related to the fish reef effect modulation scenarios for fish swarm detectors. Tech. J. Aquat. Eng. Res. Inst. 2003, 25, 7–19. Available online: https://agriknowledge.affrc.go.jp/RN/2030671615.pdf (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- Fischer, J.L.; Pritt, J.J.; Roseman, E.F.; Prichard, C.G.; Craig, J.M. Lake Sturgeon, Lake Whitefish, and Walleye Egg Deposition Patterns with Response to Fish Spawning Substrate Restoration in the St. Clair–Detroit River System. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2018, 147, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Age | Length (cm) | Weight (g) | Source | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lateolabrax maculatus | Juvenile | 12.56 ± 0.78 | 94.45 ± 5.35 | Breed aquatics | Epipelagic fishes |
| Liza haematocheila | Juvenile | 4.26 ± 0.77 | 1.56 ± 1.47 | ||
| Sebastes schlegelii | Juvenile | 6.26 ± 0.84 | 14.18 ± 3.26 | Demersal species | |
| Acanthopagrus schlegelii | Juvenile | 5.37 ± 0.32 | 8.54 ± 0.85 | ||
| Litopenaeus vannamei | Juvenile | 12.88 ± 2.24 | 11.49 ± 1.58 | ||
| Amphioctopus fangsiao | Juvenile | 18.38 ± 4.26 | 157.36 ± 32.70 | Netted |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, C.; Liu, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Guo, B.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yamashita, O.; Zheng, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Assessing the Attractive Effects of Floating Artificial Reefs and Combination Reefs on Six Local Marine Species. Fishes 2023, 8, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050248
Han C, Liu K, Kinoshita T, Guo B, Zhao Y, Ye Y, Liu Y, Yamashita O, Zheng D, Wang W, et al. Assessing the Attractive Effects of Floating Artificial Reefs and Combination Reefs on Six Local Marine Species. Fishes. 2023; 8(5):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050248
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Chenglong, Kefeng Liu, Toshihisa Kinoshita, Biao Guo, Yifan Zhao, Yuhang Ye, Yufei Liu, Osamu Yamashita, Debin Zheng, Wenhui Wang, and et al. 2023. "Assessing the Attractive Effects of Floating Artificial Reefs and Combination Reefs on Six Local Marine Species" Fishes 8, no. 5: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050248
APA StyleHan, C., Liu, K., Kinoshita, T., Guo, B., Zhao, Y., Ye, Y., Liu, Y., Yamashita, O., Zheng, D., Wang, W., & Lu, X. (2023). Assessing the Attractive Effects of Floating Artificial Reefs and Combination Reefs on Six Local Marine Species. Fishes, 8(5), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8050248