Hermetia illucens for Replacing Fishmeal in Aquafeeds: Effects on Fish Growth Performance, Intestinal Morphology, and Gene Expression in the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Breeding System
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Data Collection
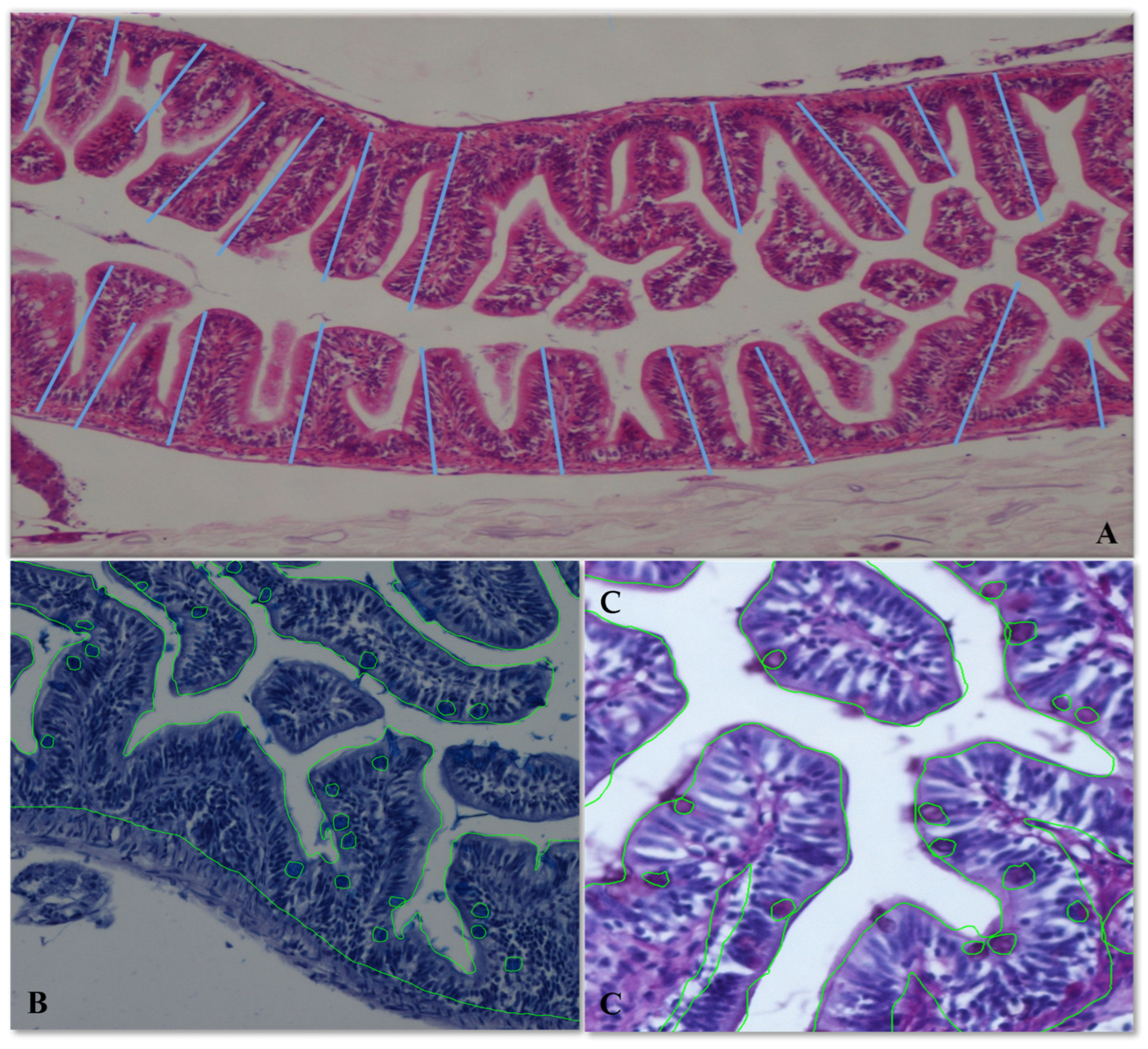
2.4. Tissue Sampling and Intestinal Morphometry Measurement
2.5. RNA Extraction from Tissues
2.6. Primer Design
2.7. Reverse Transcription and qPCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Survival Rate and Growth Performances
3.2. Intestinal Morphometry
3.3. Pept1, gata4 and nfkb1b mRNAs Expression in Intestine Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barroso, F.G.; de Haro, C.; Sánchez-Muros, M.-J.; Venegas, E.; Martínez-Sánchez, A.; Pérez-Bañón, C. The potential of various insect species for use as food for fish. Aquaculture 2014, 422–423, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, H.P.; Tran, G.; Heuzé, V.; Ankers, P. State-of-the-art on use of insects as animal feed. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2014, 197, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Gasco, L.; Piccolo, G.; Fountoulaki, E. Review on the use of insects in the diet of farmed fish: Past and future. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2015, 203, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronte, B.; Licitra, R.; Bibbiani, C.; Casini, L.; De Zoysa, M.; Miragliotta, V.; Sagona, S.; Coppola, F.; Brogi, L.; Abramo, F. Fishmeal Replacement with Hermetia illucens Meal in Aquafeeds: Effects on Zebrafish Growth Performances, Intestinal Morphometry, and Enzymology. Fishes 2021, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huis, A.; Oonincx, D.G.A.B. The environmental sustainability of insects as food and feed. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpold, B.A.; Schlüter, O.K. Nutritional composition and safety aspects of edible insects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collavo, A.; Huang, Y.-S.; Paoletti, M.G. Housekricket Smallscale Farming BioBio Project View Project BIOBIO: Indicators for Biodiversity in Organic and Low Input Farming (FP7 Project) View Project. In Ecological Implications of Minilivestock: Potential of Insects, Rodents, Frogs and Snails; Paoletti, M.G., Ed.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Van Huis, A.; Van Itterbeeck, J.; Klunder, H.; Mertens, E.; Halloran, A.; Muir, G.; Vantomme, P. Edible Insects: Future Prospects for Food and Food; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Muros, M.-J.; Barroso, F.G.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Insect meal as renewable source of food for animal feeding: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogari, G.; Amato, M.; Biasato, I.; Chiesa, S.; Gasco, L. The Potential Role of Insects as Feed: A Multi-Perspective Review. Animals 2019, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Shelomi, M. Review of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Animal Feed and Human Food. Foods 2017, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Jin, P.; Zheng, L.; Cai, M.; Yu, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J. Effects of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal protein as a fishmeal replacement on the growth and immune index of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, G.L.; Booram, C.V.; Barker, R.W.; Hale, O.M. Dried Hermetia illucens Larvae Meal as a Supplement for Swine. J. Anim. Sci. 1977, 44, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, L.; Sheppard, C.; Watson, D.W.; Burtle, G.; Dove, R. Using the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens, as a Value-Added Tool for the Management of Swine Manure; North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2005; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bondari, K.; Sheppard, D.C. Soldier fly, Hermetia illucens L., larvae as feed for channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque), and blue tilapia, Oreochromis aureus (Steindachner). Aquac. Res. 1987, 18, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sealey, W.M.; Gaylord, T.G.; Barrows, F.T.; Tomberlin, J.K.; McGuire, M.A.; Ross, C.; St-Hilaire, S. Sensory Analysis of Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, Fed Enriched Black Soldier Fly Prepupae, Hermetia illucens. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2011, 42, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeckel, S.; Harjes, A.-G.E.; Roth, I.; Katz, H.; Wuertz, S.; Susenbeth, A.; Schulz, C. When a turbot catches a fly: Evaluation of a pre-pupae meal of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as fish meal substitute—Growth performance and chitin degradation in juvenile turbot (Psetta maxima). Aquaculture 2012, 364–365, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lock, E.; Arsiwalla, T.; Waagbø, R. Insect larvae meal as an alternative source of nutrients in the diet of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) postsmolt. Aquac. Nutr. 2015, 22, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, R.; Sánchez-López, A.; Leal, R.S.; Martínez-Llorens, S.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Peres, H. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) pre-pupae meal as a fish meal replacement in diets for European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 2017, 476, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.; Romano, N.; Renukdas, N.; Kumar, V.; Sinha, A.K. Comparing black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae versus prepupae in the diets of largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides: Effects on their growth, biochemical composition, histopathology, and gene expression. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecillas, S.; Makol, A.; Caballero, M.; Montero, D.; Ginés, R.; Sweetman, J.; Izquierdo, M. Improved feed utilization, intestinal mucus production and immune parameters in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fed mannan oligosaccharides (MOS). Aquac. Nutr. 2011, 17, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ji, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J.; Yu, H. Defatted black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal in diets for juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian): Growth performance, antioxidant enzyme activities, digestive enzyme activities, intestine and hepatopancreas histological structure. Aquaculture 2017, 477, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, A.; Raggi, T.; Barkhouse, J.; Lewis, E.; Weltzien, E. The oil fraction and partially defatted meal of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) affect differently growth performance, feed efficiency, nutrient deposition, blood glucose and lipid digestibility of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2018, 492, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renna, M.; Schiavone, A.; Gai, F.; Dabbou, S.; Lussiana, C.; Malfatto, V.; Prearo, M.; Capucchio, M.T.; Biasato, I.; Biasibetti, E.; et al. Evaluation of the suitability of a partially defatted black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) larvae meal as ingredient for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) diets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randazzo, B.; Zarantoniello, M.; Cardinaletti, G.; Cerri, R.; Giorgini, E.; Belloni, A.; Contò, M.; Tibaldi, E.; Olivotto, I. Hermetia illucens and Poultry by-Product Meals as Alternatives to Plant Protein Sources in Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Diet: A Multidisciplinary Study on Fish Gut Status. Animals 2021, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naya-Català, F.; Pereira, G.D.V.; Piazzon, M.C.; Fernandes, A.M.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Cross-Talk between Intestinal Microbiota and Host Gene Expression in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Juveniles: Insights in Fish Feeds for Increased Circularity and Resource Utilization. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basto, A.; Calduch-Giner, J.; Oliveira, B.; Petit, L.; Sá, T.; Maia, M.R.G.; Fonseca, S.C.; Matos, E.; Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Valente, L.M.P. The Use of Defatted Tenebrio molitor Larvae Meal as a Main Protein Source Is Supported in European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) by Data on Growth Performance, Lipid Metabolism, and Flesh Quality. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Rodriguez, L.; Cardinaletti, G.; Secci, G.; Randazzo, B.; Bruni, L.; Cerri, R.; Olivotto, I.; Tibaldi, E.; Parisi, G. Appetite Regulation, Growth Performances and Fish Quality Are Modulated by Alternative Dietary Protein Ingredients in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Culture. Animals 2021, 11, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio), 4th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2000; Available online: http://zfin.org/zf_info/zfbook/zfbk.html (accessed on 8 January 2019).
- National Research Council (NRC). Nutrient Requirements of Fish and Shrimp; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Available online: https://books.google.it/books?hl=it&lr=&id=H8tABAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT24&dq=Nutrient+Requirements+of+Fish+and+Shrimp&ots=a8cfkd9cUn&sig=eIQf-nw21Lj5uYwH_OktiNd8pbA&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=Nutrient%20Requirements%20of%20Fish%20and%20Shrimp&f=false (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- Lawrence, C. The husbandry of zebrafish (Danio rerio): A review. Aquaculture 2007, 269, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronte, B.; Kim, C.; Bagliacca, M.; Casini, L.; De Zoysa, M. 1,3-1-6 ß-glucans enhance tissue regeneration in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Potential advantages for aquaculture applications. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 3163–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stejskal, V.; Tran, H.Q.; Prokesová, M.; Zare, M.; Gebauer, T.; Policar, T.; Caimi, C.; Gai, F.; Gasco, L. Defatted black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) in pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) diets: Effects on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, fillet quality, economic and environmental sustainability. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 12, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yossa, R.; Sarker, P.K.; Karanth, S.; Ekker, M.; Vandenberg, G.W. Effects of dietary biotin and avidin on growth, survival, feed conversion, biotin status and gene expression of zebrafish Danio rerio. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 160, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Hilaire, S.; Sheppard, C.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Irving, S.; Newton, L.; McGuire, M.A.; Mosley, E.E.; Hardy, R.W.; Sealey, W. Fly Prepupae as a Feedstuff for Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2007, 38, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Metian, M. Global overview on the use of fish meal and fish oil in industrially compounded aquafeeds: Trends and future prospects. Aquaculture 2008, 285, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtlander, T.; Stamer, A.; Buser, A.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Leiber, F.; Sandrock, C. Hermetia illucens meal as fish meal replacement for rainbow trout on farm. J. Insects Food Feed. 2017, 3, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinaletti, G.; Randazzo, B.; Messina, M.; Zarantoniello, M.; Giorgini, E.; Zimbelli, A.; Bruni, L.; Parisi, G.; Olivotto, I.; Tulli, F. Effects of Graded Dietary Inclusion Level of Full-Fat Hermetia illucens Prepupae Meal in Practical Diets for Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Animals 2019, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muin, H.; Taufek, N.; Kamarudin, M.; Razak, S. Growth performance, feed Utilization and body composition of nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) fed with different levels of black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (Linnaeus, 1758) maggot meal diet. Iran J. Fish Sci. 2017, 16, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belforti, M.; Gai, F.; Lussiana, C.; Renna, M.; Malfatto, V.; Rotolo, L.; De Marco, M.; Dabbou, S.; Schiavone, A.; Zoccarato, I.; et al. Tenebrio molitor Meal in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Diets: Effects on Animal Performance, Nutrient Digestibility and Chemical Composition of Fillets. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 14, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaconisi, V.; Marono, S.; Parisi, G.; Gasco, L.; Genovese, L.; Maricchiolo, G.; Bovera, F.; Piccolo, G. Dietary inclusion of Tenebrio molitor larvae meal: Effects on growth performance and final quality treats of blackspot sea bream (Pagellus bogaraveo). Aquaculture 2017, 476, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarantoniello, M.; Bruni, L.; Randazzo, B.; Vargas, A.; Gioacchini, G.; Truzzi, C.; Annibaldi, A.; Riolo, P.; Parisi, G.; Cardinaletti, G.; et al. Partial dietary inclusion of Hermetia illucens (black soldier fly) full-fat prepupae in zebrafish feed: Biometric, histological, biochemical, and molecular implications. Zebrafish 2018, 15, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarantoniello, M.; Randazzo, B.; Gioacchini, G.; Truzzi, C.; Giorgini, E.; Riolo, P.; Gioia, G.; Bertolucci, C.; Osimani, A.; Cardinaletti, G.; et al. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) physiological and behavioural responses to insect-based diets: A multidisciplinary approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.A.; Randazzo, B.; Riolo, P.; Truzzi, C.; Gioacchini, G.; Giorgini, E.; Loreto, N.; Ruschioni, S.; Zarantoniello, M.; Antonucci, M.; et al. Rearing zebrafish on black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens): Biometric, histological, spectroscopic, biochemical, and molecular implications. Zebrafish 2018, 15, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Peng, K.; Hu, J.; Yi, C.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Huang, Y. Evaluation of defatted black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) larvae meal as an alternative protein ingredient for juvenile Japanese seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus) diets. Aquaculture 2019, 507, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, M.; Mettraux, C.; Moennoz, D.; Godin, J.-P.; Vuichoud, J.; Rochat, F.; Breuillé, D.; Obled, C.; Corthésy-Theulaz, I. Specific Amino Acids Increase Mucin Synthesis and Microbiota in Dextran Sulfate Sodium–Treated Rats. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Khan, W.I. Goblet Cells and Mucins: Role in Innate Defense in Enteric Infections. Pathogens 2013, 2, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.E.V.; Sjövall, H.; Hansson, G.C. The gastrointestinal mucus system in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzi, C.; Pirone, A.; Baglini, A.; Mazzanti, E.; Fronte, B.; Franchi, G.; de Wolf, T. Histological Study of the Digestive Tract of Sparus Aurata Larvae Fed with Different Feeding Regimes. In Book of Abstract Aqua 2012—Global Aquaculture; European Aquaculture Society, 2012; p. 264. Available online: https://arpi.unipi.it/handle/11568/155233# (accessed on 8 January 2019).
- Schroers, V.; Van Der Marel, M.; Steinhagen, D. Influence of carp intestinal mucus molecular size and glycosylation on bacterial adhesion. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 81, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroers, V.; van der Marel, M.; Neuhaus, H.; Steinhagen, D. Changes of intestinal mucus glycoproteins after peroral application of Aeromonas hydrophila to common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 2009, 288, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønnestad, I.; Murashita, K.; Kottra, G.; Jordal, A.-E.; Narawane, S.; Jolly, C.; Daniel, H.; Verri, T. Molecular Cloning and Functional Expression of Atlantic Salmon Peptide Transporter 1 in Xenopus Oocytes Reveals Efficient Intestinal Uptake of Lysine-Containing and Other Bioactive Di- and Tripeptides in Teleost Fish. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostaszewska, T.; Szatkowska, I.; Verri, T.; Dabrowski, K.; Romano, A.; Barca, A.; Muszyńska, M.; Dybus, A.; Grochowski, P.; Kamaszewski, M. Cloning Two PepT1 cDNA Fragments of Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio (Actinopterygii: Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae). Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2009, 39, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, T.; Kottra, G.; Romano, A.; Tiso, N.; Peric, M.; Maffia, M.; Boll, M.; Argenton, F.; Daniel, H.; Storelli, C. Molecular and functional characterisation of the zebrafish (Danio rerio) PEPT1-type peptide transporter. FEBS Lett. 2003, 549, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, T.; Barca, A.; Pisani, P.; Piccinni, B.; Storelli, C.; Romano, A. Di- and tripeptide transport in vertebrates: The contribution of teleost fish models. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2016, 187, 395–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, D.C. Intestinal morphogenesis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 23, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepage, D.; Bélanger, É.; Jones, C.; Tremblay, S.; Allaire, J.M.; Bruneau, J.; Asselin, C.; Perreault, N.; Menendez, A.; Gendron, F.-P.; et al. Gata4 is critical to maintain gut barrier function and mucosal integrity following epithelial injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortner, T.M.; Skugor, S.; Penn, M.H.; Mydland, L.T.; Djordjevic, B.; Hillestad, M.; Krasnov, A.; Krogdahl, Å. Dietary soyasaponin supplementation to pea protein concentrate reveals nutrigenomic interactions underlying enteropathy in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarbide, U.; Iturria, I.; Rainieri, S.; Pardo, M.A. Use of Gnotobiotic Zebrafish to Study Vibrio anguillarum Pathogenicity. Zebrafish 2015, 12, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spykman, R.; Hossaini, S.M.; Peguero, D.A.; Green, A.; Heinz, V.; Smetana, S. A modular environmental and economic assessment applied to the production of Hermetia illucens larvae as a protein source for food and feed. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 1959–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredient | IM0 | IM17 | IM33 | IM50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | % | % | % | |
| Fishmeal 1 | 50.00 | 33.00 | 17.00 | - |
| Black soldier fly larvae meal 2 | - | 17.00 | 33.00 | 50.00 |
| Squid meal | 7.00 | 7.00 | 8.00 | 9.00 |
| Wheat meal | 7.00 | 6.00 | 5.00 | 3.50 |
| Corn meal | 5.00 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 2.00 |
| Barley | 4.00 | 4.00 | 2.00 | 1.00 |
| Soy lecithin | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 |
| Fish gelatine | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.50 |
| Potato concentrate | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Fish oil | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Brewer’s yeast | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Linseed meal | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 |
| Soy protein concentrate | 2.17 | 2.17 | 3.17 | 3.17 |
| Pre-digested fishmeal | 2.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Pea protein concentrate | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 3.00 |
| Wheat gluten | 1.00 | 2.00 | 4.00 | 5.00 |
| Vitamin and mineral premix 3 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Antioxidant | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Sodium propionate | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Vitamin E | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0,03 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Proximate composition (on DM basis) | ||||
| Crude protein (%) | 58.84 | 58.36 | 58.53 | 58.42 |
| Crude lipid (%) | 13.61 | 14.77 | 15.73 | 16.75 |
| Fibre (%) | 0.99 | 3.04 | 4.91 | 6.92 |
| Starch (%) | 11.01 | 9.72 | 7.35 | 5.25 |
| Ash (%) | 8.07 | 7.09 | 6.15 | 5.13 |
| Gross energy (MJ/kg) | 20.91 | 20.91 | 20.77 | 20.62 |
| Amino Acids (g/kg) | ||||
| Arginine | 3.74 | 7.32 | 10.7 | 14.34 |
| Histidine | 1.05 | 4.22 | 7.23 | 10.41 |
| Isoleucine | 2.03 | 5.85 | 9.47 | 13.30 |
| Leucine | 4.11 | 10.18 | 15.95 | 22.04 |
| Lysine | 3.88 | 8.75 | 13.32 | 18.22 |
| Threonine | 2.10 | 5.54 | 8.79 | 12.24 |
| Tryptophan | 0.59 | 2.10 | 3.53 | 5.03 |
| Valine | 2.18 | 8.23 | 13.96 | 20.02 |
| Methionine + Cysteine | 2.12 | 4.06 | 5.90 | 7.82 |
| Phenylalanine + Tyrosine | 4.42 | 5.26 | 6.12 | 6.97 |
| Minerals and vitamins | ||||
| Total p (%) | 1.27 | 1.08 | 0.90 | 0.72 |
| Ca (%) | 1.82 | 1.53 | 1.26 | 0.96 |
| Na (%) | 0.76 | 0.50 | 0.26 | 0.01 |
| K (g/kg) | 5.90 | 3.89 | 2.01 | - |
| Vit C (mg/kg) | 1020.40 | 1020.41 | 1020.41 | 1020.41 |
| Vit E (mg/kg) | 255.10 | 255.10 | 255.10 | 255.10 |
| Vit D (IU/kg) | 2638.50 | 2456.12 | 2284.44 | 2102.04 |
| Fatty Acids | ||||
| DHA/EPA | 1.23 | 1.18 | 1.09 | 0.93 |
| DHA + EPA (%) | 1.64 | 1.30 | 0.97 | 0.63 |
| zf Genes | RefSeq mRNA | Sense Primer 5′–3′ (Tm) | Antisense Primer 5′–3′ (Tm) | PCR Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| slc15a1/pept1 | NM_198064.1 | TGTGACCATCTCTGCTGGAG (56 °C) | CCGCGTGCACATTATCAGAC (56 °C) | 206 |
| gata4 | NM_131236.2 | TCAAACCACAGAGACGACT (52 °C) | GTTGCAGACTGGCTCTCCTT (56 °C) | 116 |
| nfkb1b | XM_021481269.1 | CACAGACAGTTTGCCATCGT (55 °C) | ATCTGTGGATGGTAGGTGAA (52 °C) | 143 |
| 28S rRNA | EF417169.1 | GGTCTAAGTCCTTCTGATGG (55 °C) | GGCTGCATTCCCAAACAAC (55 °C) | 112 |
| Parameters | IM0 | IM17 | IM33 | IM50 | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feed intake (mg) | ||||||
| Day 0–7 | 21.0 | 23.0 | 22.0 | 23.0 | 0.001 | 0.916 |
| Day 8–14 | 47.0 | 47.0 | 38.0 | 43.0 | 0.0028 | 0.619 |
| Day 15–28 | 110.0 | 131.0 | 123.0 | 129.0 | 0.0063 | 0.664 |
| Day 29–42 | 152.0 | 120.0 | 119.0 | 121.0 | 0.0057 | 0.170 |
| Cumulative FI (day 0–42) | 331.0 | 321.0 | 301.0 | 318.0 | 0.0066 | 0.490 |
| Feed conversion rate | ||||||
| Day 0–7 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.071 | 0.883 |
| Day 8–14 | 2.2 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 0.141 | 0.592 |
| Day 15–28 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 0.085 | 0.943 |
| Day 29–42 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 1.9 | 0.127 | 0.129 |
| Cumulative FCR | 2.1 a | 1.8 b | 1.8 b | 1.8 b | 0.032 | 0.013 * |
| Body weight gain (mg) | ||||||
| Day 0–7 | 21.5 b | 25.9 a | 26.2 ab | 25.4 a | 0.508 | 0.004 * |
| Day 8–14 | 21.2 b | 23.7 ab | 22.2 ab | 24.9 a | 0.454 | 0.029 * |
| Day 15–28 | 61.1 b | 71.2 a | 67.7 ab | 67.7 ab | 1.277 | 0.045 * |
| Day 29–42 | 52.6 b | 55.6 ab | 51.7 b | 61.6 a | 1.085 | 0.007 * |
| Cumulative BWg | 156.5 b | 176.8 a | 168.0 ab | 180.1 a | 2.708 | 0.012 * |
| Body weight (mg) | ||||||
| Day 0 | 43.4 | 45.1 | 42.8 | 43.1 | 1.30 | 0.922 |
| Day 7 | 65.0 | 71.0 | 68.7 | 68.6 | 1.61 | 0.626 |
| Day 14 | 86.3 | 94.6 | 90.8 | 95.8 | 1.88 | 0.282 |
| Day 28 | 147.6 | 165.8 | 158.5 | 164.3 | 3.06 | 0.144 |
| Day 42 | 200.2 | 221.2 | 210.3 | 226.3 | 3.74 | 0.068 |
| Parameter | IM0 | IM17 | IM33 | IM50 | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Villus length | 165 | 160.5 | 171.0 | 161.0 | 0.51 | 0.813 |
| Upper | 170.3 | 173.5 | 178.5 | 171.5 | 0.51 | 0.737 |
| Lower | 164.4 | 145.8 | 161.7 | 152.9 |
| Parameter | Upper | Lower | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Villus length | 173.7 a | 156.5 b | 0.51 | 0.016 |
| Parameter | IM0 | IM17 | IM33 | IM50 | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC-AB density | 486.2 SD 351.74 (n = 10) | 711.5 SD 365.5 (n = 5) | 333.4 SD 99 (n = 3) | 499.5 SD 361.14 (n = 10) | 3.61 | 0.307 |
| GC-AB area | 54.2 SD 16.84 (n = 10) | 70.1 SD 19.5 (n = 5) | 62.5 SD 0.84 (n = 3) | 51.8 SD 9.51 (n = 10) | 4.64 | 0.200 |
| GC-PAS density | 598 SD 280.86 (n = 9) | 514.4 SD 136.4 (n = 4) | 236.5 SD 147.94 (n = 4) | 603.9 SD 291.87 (n = 9) | 6.25 | 0.100 |
| GC-PAS area | 41.3 SD 8.51 b (n = 9) | 53.6 SD 16.8 ab (n = 4) | 63.3 SD 6.19 a (n = 4) | 36.8 SD 10.58 b (n = 9) | 11.29 | 0.010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barca, A.; Abramo, F.; Nazerian, S.; Coppola, F.; Sangiacomo, C.; Bibbiani, C.; Licitra, R.; Susini, F.; Verri, T.; Fronte, B. Hermetia illucens for Replacing Fishmeal in Aquafeeds: Effects on Fish Growth Performance, Intestinal Morphology, and Gene Expression in the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model. Fishes 2023, 8, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030127
Barca A, Abramo F, Nazerian S, Coppola F, Sangiacomo C, Bibbiani C, Licitra R, Susini F, Verri T, Fronte B. Hermetia illucens for Replacing Fishmeal in Aquafeeds: Effects on Fish Growth Performance, Intestinal Morphology, and Gene Expression in the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model. Fishes. 2023; 8(3):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030127
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarca, Amilcare, Francesca Abramo, Sareh Nazerian, Francesca Coppola, Chiara Sangiacomo, Carlo Bibbiani, Rosario Licitra, Francesca Susini, Tiziano Verri, and Baldassare Fronte. 2023. "Hermetia illucens for Replacing Fishmeal in Aquafeeds: Effects on Fish Growth Performance, Intestinal Morphology, and Gene Expression in the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model" Fishes 8, no. 3: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030127
APA StyleBarca, A., Abramo, F., Nazerian, S., Coppola, F., Sangiacomo, C., Bibbiani, C., Licitra, R., Susini, F., Verri, T., & Fronte, B. (2023). Hermetia illucens for Replacing Fishmeal in Aquafeeds: Effects on Fish Growth Performance, Intestinal Morphology, and Gene Expression in the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model. Fishes, 8(3), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030127










