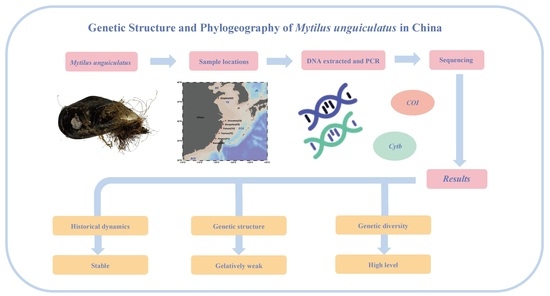
Genetic Structure and Phylogeography of Commercial Mytilus unguiculatus in China Based on Mitochondrial COI and Cytb Sequences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification
2.3. Genetic Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity among Samples
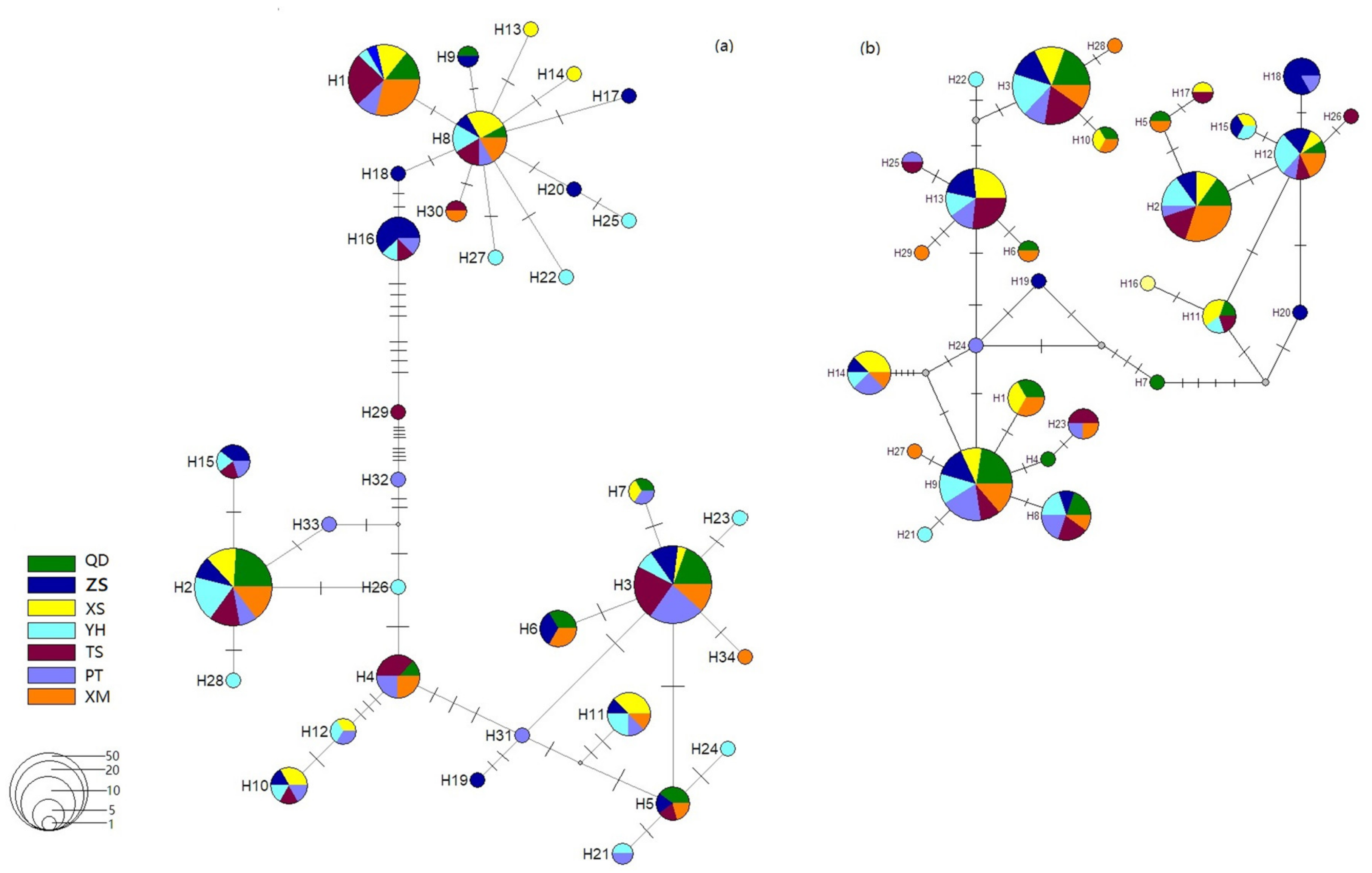
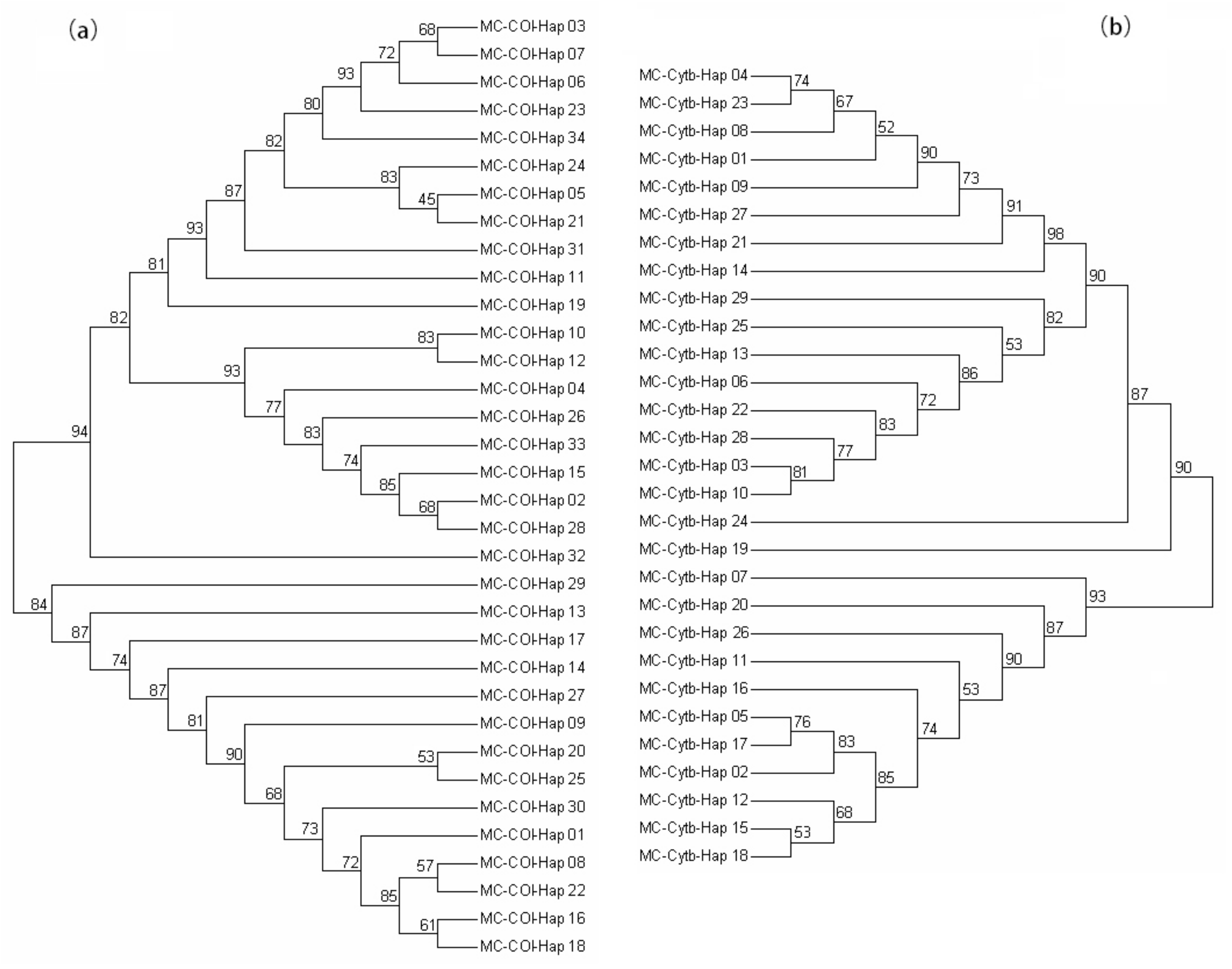
3.2. Genetic Divergence among Samples
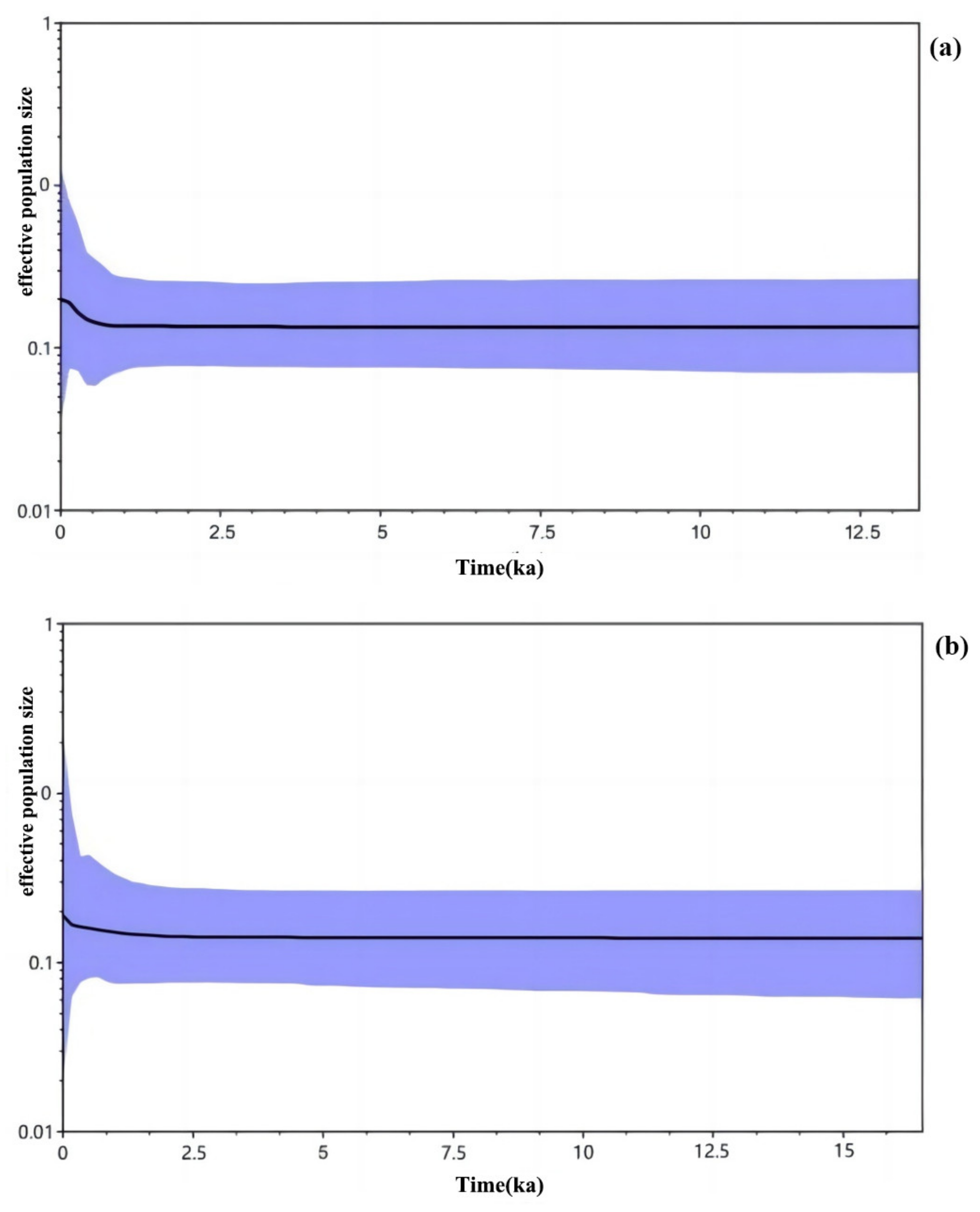
3.3. Historical Dynamics
4. Discussion
4.1. Genetic Diversity of M. unguiculatus
4.2. Genetic Structure of M. unguiculatus
4.3. Protection and Breeding Strategies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Fisheries and Aquaculture. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/home (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Chang, K.M.; Wu, J.F. Study on artificial propagation of mussel Mytilus coruscus. China Fish. 2007, 4, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.; Wang, X.C.; Liu, H.H.; Fan, M.H.; Sun, J.J.; Shen, W. Molecular characterization of a novel antimicrobial peptide from Mytilus coruscus. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2013, 34, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, L.M.; Salen, P.; Monjaud, I.; Delaye, J. The ‘diet heart’ hypothesis in secondary prevention of coronary heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 1997, 18, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.X.; Liu, M.; Liao, Z.; Lu, T.; Wu, M.; He, G.Y. Purification and identification of Mytilins from Mytilus coruscus. J. Fish. China 2010, 34, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H.; Zhang, W.J.; Lu, J.K.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Mu, C.K.; Song, W.W.; Migaud, H.; Wang, C.L.; Bekaert, M. The whole-genome sequencing and hybrid assembly of Mytilus coruscus. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.L.; Feng, D.D.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.K.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.F.; Zhu, Y.T.; Liang, X.; Lu, Y. Chromosome-level genome assembly of the hard-shelled mussel Mytilus coruscus, a widely distributed species from the temperate areas of East Asia. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, V.L.; Tan, T.K.; Lim, P.E.; Domingues, L.N.; Tay, S.T.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Goh, T.G.; Panchadcharam, C.; Bathmanaban, P.; Sofian-Azirun, M. Use of COI, CytB and ND5 genes for intra- and inter-specific differentiation of Haematobia irritans and Haematobia exigua. Vet. Parasitol 2014, 204, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, J.D.; Duque, M.C.; Guhl, F. Phylogenetic reconstruction based on Cytochrome b (Cytb) gene sequences reveals distinct genotypes within Colombian Trypanosoma cruzi I populations. Acta Trop. 2011, 119, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laopichienpong, N.; Muangmai, N.; Supikamolseni, A.; Twilprawat, P.; Chanhome, L.; Suntrarachun, S.; Peyachoknagul, S.; Srikulnath, K. Assessment of snake DNA barcodes based on mitochondrial COI and Cytb genes revealed multiple putative cryptic species in Thailand. Gene 2016, 594, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibb, M.J.; Van Etten, R.A.; Wright, C.T.; Walberg, M.W.; Clayton, D.A. Sequence and gene organization of mouse mitochondrial DNA. Cell 1981, 26, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyllensten, U.; Wharton, D.; Wilson, A.C. Maternal inheritance of mitochondrial DNA during backcrossing of two species of mice. J. Hered. 1985, 76, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cann, R.L.; Stoneking, M.; Wilson, A.C. Mitochondrial DNA and human evolution. Nature 1987, 325, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vawter, L.; Brown, W.M. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA comparisons reveal extreme rate variation in the molecular clock. Science 1986, 234, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. Evolutionary rate at the molecular level. Nature 1968, 217, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljanabi, S.M.; Martinez, I. Universal and rapid salt-extraction of high quality genomic DNA for PCR-based techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4692–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Mangalam, A.K.; Dwivedi, S.; Naik, S. Primer premier: Program for design of degenerate primers from a protein sequence. Biotechniques 1998, 24, 318–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Swindell, S.R.; Plasterer, T.N. SEQMAN: Contig assembly. Methods Mol. Biol. 1997, 70, 75–89. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; Mcgettigan, P.A.; Mcwilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julio, R.; Albert, F.M.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Sara, G.R.; Pablo, L.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. Dnasp 6: Dna sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 12, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, W.R. Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 1989, 43, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. PHYLIP-Phylogeny Inference Package (Ver. 3.2). Cladistics 1989, 5, 164–166. [Google Scholar]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.K.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T.Y. ggtree: An R package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Röhl, A. Network: A Program Package for Calculating Phylogenetic Networks, Version 4.1.0.9; Fluxus Technology Ltd.: Hamburg, Germany, 2004.
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Rohl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PloS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. Tracer v1.4. Encycl. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 141, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar]
- Hellberg, M.E.; Vacquier, V.D. Rapid evolution of fertilization selectivity and lysin cDNA sequences in teguline gastropods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, A.R.; Apte, S.; MacAvoy, E.S.; Gardner, J.P. A molecular phylogeny of the marine mussel genus Perna (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) based on nuclear (ITS1&2) and mitochondrial (COI) DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 44, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; He, S.P. The Pattern of Upper and Middle Yangtze Drainages Shapes the Genetic Structure and Diversity of Hemiculter Leucisculus Reveales by Mitochondrial DNA Locus. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2014, 38, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.J.; Li, G.H.; Jin, F.P.; Zhao, J.X.; Lei, C.Y.; Gao, H.T.; Fu, S.Y.; Zhou, R.; Luo, Y.X.; Xue, S.W.; et al. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Mitochondrial D-Loop Region of Anabarilius graham in Fuxian Lake. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2022, 46, 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, C.L.; Li, J.J.; Guo, B.Y. Genetic Diversity Evaluation by the Comparative Analysis on Mitochondrial COI Gene between Wild and Cultured Populations of Mytilus coruscus. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2014, 40, 7660–7662. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.Y.; Xu, M.Y.; Guo, B.Y.; Wu, C.W. Genetic Structure and Sequence Analysis of Four Populations of Mytilus Coruscus in the Coastal Waters of Southeast China Sea Using 16S rRNA. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2012, 43, 376–381. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.X.; Mao, Y.L.; Song, N.; Gao, T.X.; Cai, H.C.; Zhang, Z.H. Sequence Analysis of Mitochondrial COI Gene of Mytilus Coruscus along Chinese Coast Waters. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2014, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, L.; Song, W.; Wei, H.Q.; Liang, S.Z.; Jiang, K.J.; Huang, H.L.; Ma, C.Y.; Zhang, F.Y.; Chen, X.Z.; Ma, L.B. Population genetic analysis of Trachurus murphyi based on the mitochondrial cytbchrome oxidase subunit I gene in the high seas off Chile. Mar. Fish. 2020, 42, 641–649. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, S.; Maxson, L. Evolution and the Genetics of Populations. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 1968, 8, 1191–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Slatkin, M. Gene Flow and the Geographic Structure of Natural Populations. Science 1987, 236, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.G.; Xu, G.P.; Yan, B.L.; Yang, J.X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xu, J.R.; Xu, P. Biochemical genetic structure and variation in different populations of Ruditapes philippinarum. Mar. Sci. 2009, 33, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.P.; Geng, R.Q.; Feng, J.; You, L.H.; Zhang, H.B.; Hong, J.; Yuan, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.Q. Analysis on the Genetic Structure of Different Geographical Populations of Cyclina sinensis. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 11846–11850. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.J.; Yu, Z.N.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.S.; Kong, X.Y.; Song, L.S. Sequence Polymorphism of Mitochondrial 16S rRNA Gene Fragment in Scallop Chlamys Farreri. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2002, 33, 477–483. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.Y.; Wu, C.W.; Li, J.J. Genetic population structure of Macridiscus multifarius (Mollusca: Bivalvia) on the basis of mitochondrial markers: Strong population structure in a species with a short planktonic larval stage. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0146260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, A.L.; Grantham, B.A.; Carr, M.H. Propagule dispersal distance and the size and spacing of marine reserves. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.Q.; Ni, M.L.; Fan, W.M. Observation on Embryonic Development of Mytilus Coruscus. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 18213–18215. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, G.; Li, Q.; Ni, L.; Kong, L.; Yu, H. Population subdivision of the surf clam Mactra chinensis in the East China Sea: Changjiang River outflow is not the sole driver. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.L. Overview of the South China Sea circulation and its influence on the coastal physical oceanography outside the Pearl River Estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 1745–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Ye, M.; Wang, R.X.; Shi, G.; Zhao, S.J. Natural distribution and ecological impacts of the aline species Mytilus galbprovincialis in the Zhoushan Waters. J. Oceanogra. Taiwan Straits 2011, 30, 250–256. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Bao-Cun, Y.U.; Yuan-Xin, B.I.; Wang, W.D. The biological characteristics and growth patterns of Mytilus Coruscus in the waters of zhongjieshan islands. Chin. J. Ecol. 2015, 34, 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Li, C.; Jiao, H.; Lin, Z.; Bao, Y. Genetic resources assessment of mussel Mytilus coruscus based on COI gene in Yushan Island. Mar. Sci. 2017, 41, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.B.; Li, J.L.; Feng, B.B. Genetic analysis of cultured and wild populations of Mytilus coruscus based on mitochondrial DNA. Zool. Res. 2009, 30, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.B.; Li, J.L.; Mou, Y.J. Molecular identification of introgression between the native Mytilus coruscus and the introduced Mytilus edulis using inter-simple sequence repeat marker (ISSR). Mar. Fish. 2006, 3, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.Y. The Population Genetics of Mytilus galloprovincialis and Hybridization between Mytilus galloprovincialis and Mytilus coruscus. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.R.; Li, T.W.; Ding, M.J. Studies on the Nutritive Contents of the Mussel Mytilus edulis and Mytilus coruscus. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 1998, 2, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.L.; Yang, L.; Zhao, D.B.; Ren, Y.S. Resources investigation and evaluation of Mytilus coruscus around Taishan Islands, Fujian. Mar. Sci. 2015, 39, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Jin, L.; Chen, S.; Guo, Y.M.; Zhu, J.P. Hygienic Monitoring and Health Risk Assessment of Cultured Mytilus coruscus in Shengsi. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. 2020, 39, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.L.; Dong, Y.Y.; Huang, L.Y.; Tian, X.L.; Han, L.M.; Li, D.H.; Cao, L. Toward offshore aquaculture in China: Opportunities, challenges and development strategies. J. Fish. China 2022. accepted. [Google Scholar]

| Sampling Site | Abbreviation | Coordinate | Sampling Date | Sample Size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COI | Cytb | ||||
| Qingdao | QD | 35°55′ N, 120°30′ E | September 2016 | 29 | 31 |
| Zhoushan | ZS | 30°12′ N, 122°42′ E | January 2017 | 27 | 26 |
| Xiangshan | XS | 29°14′ N, 121°58′ E | December 2016 | 23 | 30 |
| Yuhuan | YH | 28°14′ N, 121°24′ E | March 2017 | 29 | 29 |
| Taishan | TS | 26°57′ N, 120°47′ E | November 2016 | 25 | 22 |
| Pingtan | PT | 25°34′ N, 119°47′ E | February 2017 | 29 | 29 |
| Xiamen | XM | 24°35′ N, 118°23′ E | November 2016 | 27 | 28 |
| Total | 189 | 195 | |||
| Sample | COI | Cytb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | n | h | π | N | n | h | π | |
| QD | 29 | 9 | 0.77 ± 0.06 | 0.0044 ± 0.0007 | 31 | 12 | 0.83 ± 0.06 | 0.0052 ± 0.0006 |
| ZS | 27 | 15 | 0.88 ± 0.05 | 0.0059 ± 0.0004 | 26 | 11 | 0.88 ± 0.05 | 0.0063 ± 0.0006 |
| XS | 23 | 10 | 0.93 ± 0.03 | 0.0064 ± 0.0003 | 30 | 12 | 0.89 ± 0.04 | 0.0063 ± 0.0003 |
| YH | 29 | 17 | 0.88 ± 0.06 | 0.0054 ± 0.0007 | 29 | 11 | 0.84 ± 0.06 | 0.0058 ± 0.0006 |
| PT | 25 | 15 | 0.88 ± 0.03 | 0.0058 ± 0.0005 | 22 | 11 | 0.84 ± 0.06 | 0.0055 ± 0.0007 |
| TS | 29 | 11 | 0.92 ± 0.04 | 0.0047 ± 0.0007 | 29 | 11 | 0.90 ± 0.04 | 0.0049 ± 0.0008 |
| XM | 27 | 10 | 0.86 ± 0.04 | 0.0055 ± 0.0004 | 28 | 14 | 0.91 ± 0.03 | 0.0066 ± 0.0006 |
| Total | 189 | 34 | 0.88 ± 0.02 | 0.0054 ± 0.0002 | 195 | 29 | 0.86 ± 0.02 | 0.0058 ± 0.0002 |
| Sample | QD | ZS | XS | YH | PT | TS | XM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QD | - | 0.022 | 0.005 | −0.020 | −0.016 | −0.024 | −0.004 |
| ZS | 0.036 | - | −0.012 | −0.010 | 0.039 | 0.011 | −0.020 |
| XS | 0.080 | −0.001 | - | −0.027 | 0.013 | −0.015 | −0.016 |
| YH | −0.015 | −0.013 | 0.034 | - | 0.003 | −0.028 | −0.018 |
| PT | −0.021 | 0.016 | 0.053 | −0.016 | - | −0.007 | 0.017 |
| TS | 0.014 | −0.026 | −0.013 | −0.014 | −0.003 | - | −0.005 |
| XM | 0.017 | −0.024 | −0.006 | −0.004 | 0.010 | −0.031 | - |
| Marker | Source of Variation | Degrees of Freedom | Sum of Squares | Φ Statistic | Percentage of Variation | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COI | Among samples | 6 | 21.7 | ΦSC = 0.001 | 0.1 | 0.032 |
| Within samples | 182 | 809.4 | ΦST = 0.016 | 98.2 | 0.031 | |
| Cytb | Among samples | 6 | 15.3 | ΦSC = 0.001 | 0.6 | 0.050 |
| Within samples | 188 | 684.8 | ΦST = 0.006 | 99.3 | 0.023 |
| Sample | COI | Cytb | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tajima’s D | Fu’s Fs | Tajima’s D | Fu’s Fs | |
| QD | 1.42 (0.91) | 2.63 (0.91) | 0.93 (0.81) | 0.26 (0.60) |
| ZS | 2.13 (0.96) | 2.01 (0.90) | 1.32 (0.90) | 0.86 (0.72) |
| XS | 2.04 (0.93) | −0.64 (0.55) | 1.34 (0.88) | 1.07 (0.74) |
| YH | 1.02 (0.79) | −2.33 (0.24) | 1.25 (0.89) | 1.08 (0.74) |
| PT | 0.56 (0.66) | −2.25 (0.20) | −0.36 (0.43) | −0.66 (0.41) |
| TS | 1.74 (0.92) | 2.23 (0.92) | 0.82 (0.80) | 0.99 (0.71) |
| XM | 2.62 (0.92) | 2.51 (0.93) | 0.83 (0.77) | −0.68 (0.46) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Fu, Z.; Li, J.; Guo, B.; Ye, Y. Genetic Structure and Phylogeography of Commercial Mytilus unguiculatus in China Based on Mitochondrial COI and Cytb Sequences. Fishes 2023, 8, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020089
Wei X, Fu Z, Li J, Guo B, Ye Y. Genetic Structure and Phylogeography of Commercial Mytilus unguiculatus in China Based on Mitochondrial COI and Cytb Sequences. Fishes. 2023; 8(2):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020089
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xuelian, Zeqin Fu, Jiji Li, Baoying Guo, and Yingying Ye. 2023. "Genetic Structure and Phylogeography of Commercial Mytilus unguiculatus in China Based on Mitochondrial COI and Cytb Sequences" Fishes 8, no. 2: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020089
APA StyleWei, X., Fu, Z., Li, J., Guo, B., & Ye, Y. (2023). Genetic Structure and Phylogeography of Commercial Mytilus unguiculatus in China Based on Mitochondrial COI and Cytb Sequences. Fishes, 8(2), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020089