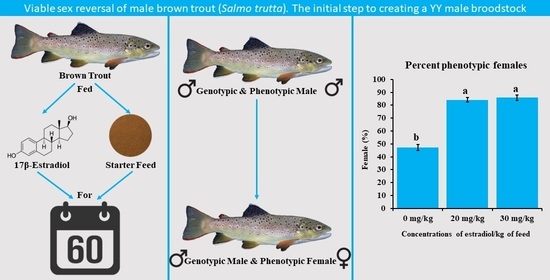
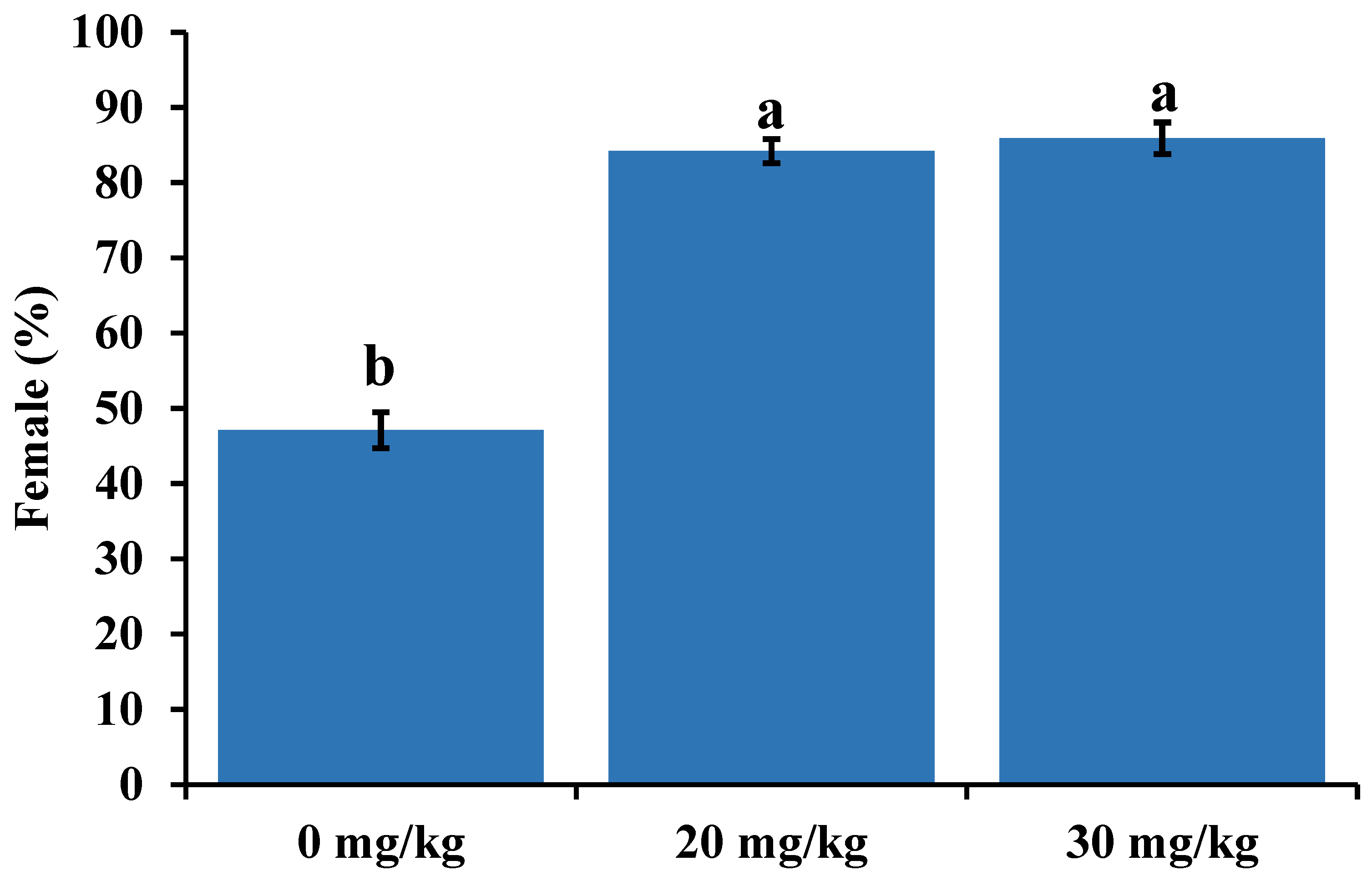
17β-Estradiol Can Induce Sex Reversal in Brown Trout
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piferrer, F. Endocrine sex control strategies for the feminization of teleost fish. Aquaculture 2001, 197, 229–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, T.J.; Sheela, S.G. Hormonal induction of sex reversal in fish. Aquaculture 1995, 138, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.B.; Teem, J.L. A model describing the effect of sex-reversed YY fish in an established wild population: The use of the Trojan Y chromosome to cause extinction of an introduced exotic species. J. Theor. Biol. 2006, 241, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teem, J.L.; Gutierrez, J.B. A Theoretical Strategy for Eradication of Asian Carps using a Trojan Y Chromosome to Shift the Sex Ratio of the Population. In Proceedings of the Invasive Asian Carps in North America: A Forum to Understand the Biology and Manage the Problem, Peoria, IL, USA, 22–23 August 2006; Chapman, D.C., Hoff, M.H., Eds.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2011; pp. 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Schill, D.J.; Meyer, K.A.; Hansen, M.J. Simulated effects of YY-male stocking and manual suppression for eradicating nonnative brook trout populations. N. Am. J. Fish Manag. 2017, 37, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, S.; Wedekind, C. Control of introduced species using trojan sex chromosomes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schill, D.J.; Heindel, J.A.; Campbell, M.R.; Meyer, K.A.; Mamer, E.R.J.M. Production of a YY male brook trout broodstock for potential eradication of undesired brook trout populations. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2016, 78, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teem, J.; Alphey, L.; Descamps, S.; Edgington, M.; Edwards, O.; Gemmell, N.; Harvey-Samuel, T.; Melnick, R.; Oh, K.; Piaggio, A.; et al. Genetic biocontrol for invasive species. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, T.J.; Kirankumar, S. Recent advances in hormonal injection of sex-reversal in fish. J. Appl. Aquac. 2003, 13, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.; Macintosh, D.J.; Wright, R.S. Elimination of orally administered 17α-methyltestosterone by Oreochromis mossambicus (tilapia) and Salmo gairdneri (rainbow trout) juveniles. Aquaculture 1983, 3, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M. Effects of estradiol-17β on gonadal sex differentiation in two species of salmonids, the masu salmon, Oncorhynchus masou and the chum salmon, O. keta. Aquaculture 1984, 48, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, G.A.; Solar, I.I.; Baker, I.J.; Donaldson, E.M. Feminization of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) and Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) by immersion of alevins in a solution of estradiol-11β. Aquaculture 1986, 53, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piferrer, F.; Donaldson, E.M. The comparative effectiveness of the natural and a synthetic estrogen for the direct feminization of Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Aquaculture 1992, 106, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.; Simpson, T.H.; Youngson, A.F. Sex reversal in salmonid culture. Aquaculture 1978, 13, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.; Simpson, T.H.; Walker, A.F. Sex reversal in salmonid culture. Part III. The production and performance of all female populations of brook trout. Aquaculture 1979, 18, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, E.M.; Hunter, G.A. Sex control in fish with particular reference to salmonids. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1982, 39, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, G.A.; Donaldson, E.M.; Stoss, J.; Baker, I. Production of monosex female groups of Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) by the fertilization of normal ova with sperm from sex-reversed females. Aquaculture 1983, 33, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feist, G.; Yeoh, C.G.; Fitzpatrick, M.S.; Schreck, C.B. The production of functional sex reversed rainbow trout with 17α-methyltestosteron and 11β-hydroxyanderostenedione. Aquaculture 1995, 131, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feist, G.; Schreck, C.B.; Gharrett, A.J. Controlling the Sex of Salmonids. Oregon Sea Grant, Ploidy/Sex Manipulation Work Group, 1996, ORESU-H-96-001:26. Available online: https://seagrant.oregonstate.edu/sites/seagrant.oregonstate.edu/files/sgpubs/onlinepubs/h96001.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- Ashby, K.R. The effect of steroid hormones on the brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) during the period of gonadal differentiation. Development 1957, 5, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; De Poorter, M. 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species: A Selection from the Global Invasive Species Database; Invasive Species Specialist Group: Auckland, New Zealand, 2004; Volume 12, Available online: https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/2000-126.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- Simberloff, D. Invasive species. In Conservation Biology for All; Sodhi, N.S., Ehrlich, P.R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rypel, A.L. Do invasive freshwater fish species grow better when they are invasive? Okios 2014, 123, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, W.C.; Budy, P.; Thiede, G.P. Demographic changes following mechanical removal of exotic brown trout in an intermountain West (USA), high-elevation stream. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 2015, 24, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.A.; Meyer, K.A.; Schill, D.J.; Campbell, M.R.; Vu, N.V. Survival and reproductive success of hatchery YY male brook trout stocked in Idaho streams. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 2018, 147, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buterbaugh, G.L.; Willoughby, H. A feeding guide to brook, brown, and rainbow trout. Progr. Fish.-Cult. 1967, 29, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warton, D.I.; Hui, F.K.C. Arcsine is asinine: The analysis of proportions in ecology. Ecology 2011, 92, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudie, C.A.; Redner, B.D.; Simco, B.A.; Davis, K.B. Feminization of channel catfish by oral administration of steroid sex hormones. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1983, 112, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, T.; Pandian, T.J. Hormonal induction of sex reversal and progeny testing in the zebra cichlid Cichlasoma nigrofasciatum. J. Exp. Zool. 1996, 275, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strüssmann, C.A.; Takashima, F.; Toda, K. Sex differentiation and hormonal feminization in pejerrey Odonthesthes bonariensis. Aquaculture 1996, 139, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Gao, Z.; Beres, B.; Ottobre, J.; Wallat, G.; Tiu, L.; Rapp, D.; O’Bryant, P.; Yao, H. Effects of estradiol-17β on survival, growth performance, sex reversal and gonadal structure of bluegill sunfish Lepomis macrochirus. Aquaculture 2008, 285, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malison, I.A.; Kayes, T.B.; Wentworth, B.C.; Amundson, C.H. Growth and feeding responses of male versus female yellow perch (Perca flavescens) treated with estradiol-17β. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1988, 45, 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, H.; Nimura, Y. Growth promotion in Japanese eel by the oral administration of an estrogen (diethylstilbestrol). Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 1991, 57, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.E.; Wintersteen, K.; Krebs, E.; Nero, P.; Tycz, J.; Reichert, S.; Zimmerman, S. 2010 McNenny State Fish Hatchery Annual Production Report. Annual Report No. 11-03; South Dakota Department of Game, Fish and Parks: Pierre, SD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kissil, G.W.; Lupatsch, I.; Higgs, D.A.; Hardy, R.W. Dietary substitution of soy and rapeseed protein concentrations for fish meal, and their effects on growth and nutrient utilization in gilthead seabream Sparus aurata L. Aquac. Res. 2000, 31, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, T.J.; Sindelar, S.C.; Voorhees, J.M.; Brown, M.L.; Barnes, M.E. Performance and immunological responses of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed bioprocessed plant-based proteins. Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regost, C.; Arzel, J.; Cardinal, M.; Laroche, M.; Kaushik, S.J. Fat deposition and flesh quality in seawater reared, triploid brown trout (Salmo trutta) as affected by dietary fat levels and starvation. Aquaculture 2001, 193, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.E.; Miller, J.; Durben, D.J. Partial overhead tank cover use during feral brown trout rearing. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2005, 67, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhees, J.M.; Barnes, M.E.; Chipps, S.R.; Brown, M.L. Rearing performance of juvenile brown trout (Salmo trutta) subjected to exercise and dietary bioprocessed soybean meal. Open. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 8, 303–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhees, J.M.; Barnes, M.E.; Chipps, S.R.; Brown, M.L. Direct substitution of fishmeal with bioprocessed soybean meal in brown trout diets. J. Fish. Aquac. Dev. 2018, JFAD-143, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, R.L.; Kincaid, H.L. Pathological effects of orally administered estradiol to rainbow trout. Aquaculture 1988, 72, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sower, S.A.; Dickhoff, W.W.; Flagg, T.A.; Mighell, J.L.; Mahnken, C.V.W. Effects of estradiol and diethylstilbesterol on sex reversal and mortality in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 1984, 43, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schill, D.J.; Coykendall, D.K.; Campbell, M.R.; Mamer, E.R.J.M. Development of YY male technology for eradicating invasive fish populations in Arizona streams—genetic sex marker development and field testing. IIAPM Funding Window Criterion: Development of YY male technology for salmonid species. Herit. Grant Proj. 2020, I18007, 39. [Google Scholar]
| Rearing Day | Estradiol (mg/kg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 30 | p-Value | ||
| 60 | Gain (kg) | 0.59 ± 0.02 z | 0.44 ± 0.02 y | 0.42 ±0.02 y | <0.001 |
| Gain (%) | 1465 ± 42 z | 1103 ± 54 y | 1053 ± 55 y | <0.001 | |
| FCR | 1.43 ± 0.04 z | 1.91 ± 0.09 y | 2.01 ± 0.10 y | <0.001 | |
| Mortality (%) | 1.0 ± 0.6 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 2.4 ± 0.7 | 0.08 | |
| 105 | Gain (kg) | 0.53 ± 0.02 | 0.49 ± 0.04 | 0.44 ± 0.02 | 0.25 |
| Gain (%) | 84 ± 5 | 101 ± 9 | 97 ± 7 | 0.27 | |
| FCR | 2.65 ± 0.11 | 2.94 ± 0.31 | 3.15 ± 0.17 | 0.31 | |
| Rearing Day | Estradiol (mg/kg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 30 | p-Value | ||
| 60 | Length (mm) | 52.28 ± 0.20 z | 46.12 ± 0.31 y | 43.53 ± 0.62 x | <0.001 |
| Weight (g) | 1.46 ± 0.01 z | 1.07 ± 0.02 y | 0.96 ± 0.05 y | <0.001 | |
| 105 | Length (mm) | 65.86 ± 1.22 | 61.99 ± 2.36 | 60.98 ± 0.79 | 0.13 |
| Weight (g) | 2.86 ± 0.12 | 2.29 ± 0.25 | 2.42 ± 0.12 | 0.10 | |
| 170 | Length (mm) | 95 ± 1 z | 92 ± 0 y | 89 ± 1 x | <0.001 |
| Weight (g) | 9.7 ± 0.2 z | 9.1 ± 0.1 y | 8.2 ± 0.2 x | <0.001 | |
| 456 | Length (mm) | 188 ± 1 y | 201 ± 8 z | 191 ± 1 zy | 0.03 |
| Weight (g) | 69.8 ± 1.3 y | 79.7 ± 3.5 z | 72.2 ± 1.3 zy | 0.03 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voorhees, J.M.; Mamer, E.R.J.M.; Schill, D.J.; Adams, M.; Martinez, C.; Barnes, M.E. 17β-Estradiol Can Induce Sex Reversal in Brown Trout. Fishes 2023, 8, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020103
Voorhees JM, Mamer ERJM, Schill DJ, Adams M, Martinez C, Barnes ME. 17β-Estradiol Can Induce Sex Reversal in Brown Trout. Fishes. 2023; 8(2):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020103
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoorhees, Jill M., Elizabeth R. J. M. Mamer, Daniel J. Schill, Mitchel Adams, Carlos Martinez, and Michael E. Barnes. 2023. "17β-Estradiol Can Induce Sex Reversal in Brown Trout" Fishes 8, no. 2: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020103
APA StyleVoorhees, J. M., Mamer, E. R. J. M., Schill, D. J., Adams, M., Martinez, C., & Barnes, M. E. (2023). 17β-Estradiol Can Induce Sex Reversal in Brown Trout. Fishes, 8(2), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8020103