Molecular Characterization and Antibacterial Potential of Goose-Type Lysozyme from Japanese Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Analysis
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Healthy Tissue Collection
2.4. Bacterial Infection and Sample Collection
2.5. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.6. Expression Analysis via qRT-PCR
2.7. Expression and Purification of rTrLysG
2.8. Effect of pH and Temperature on Dissociate Activity of rTrLysG
2.9. Antibacterial Activity of rTrLysG by Minimal Inhibitory Concentration
3. Results
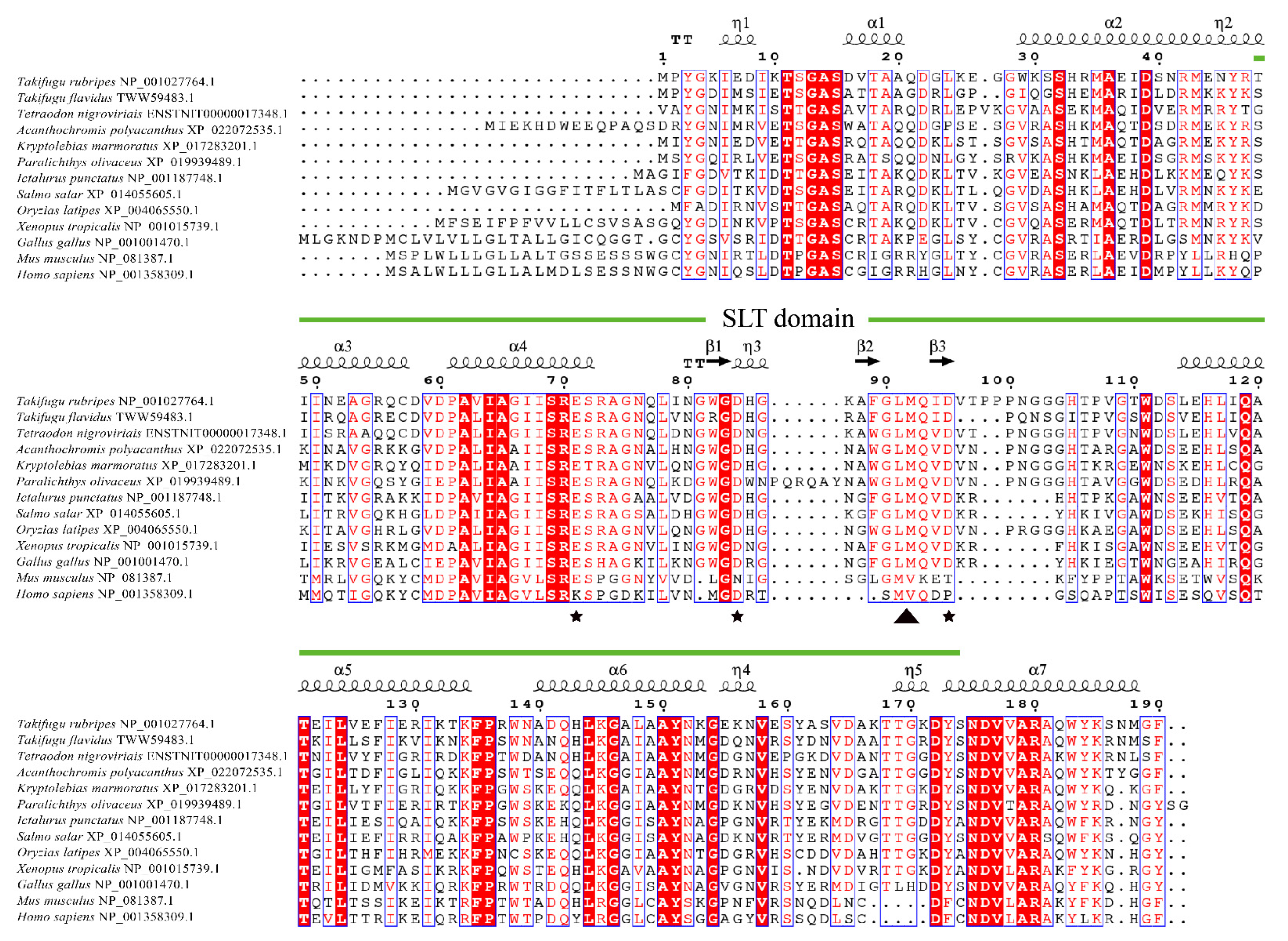
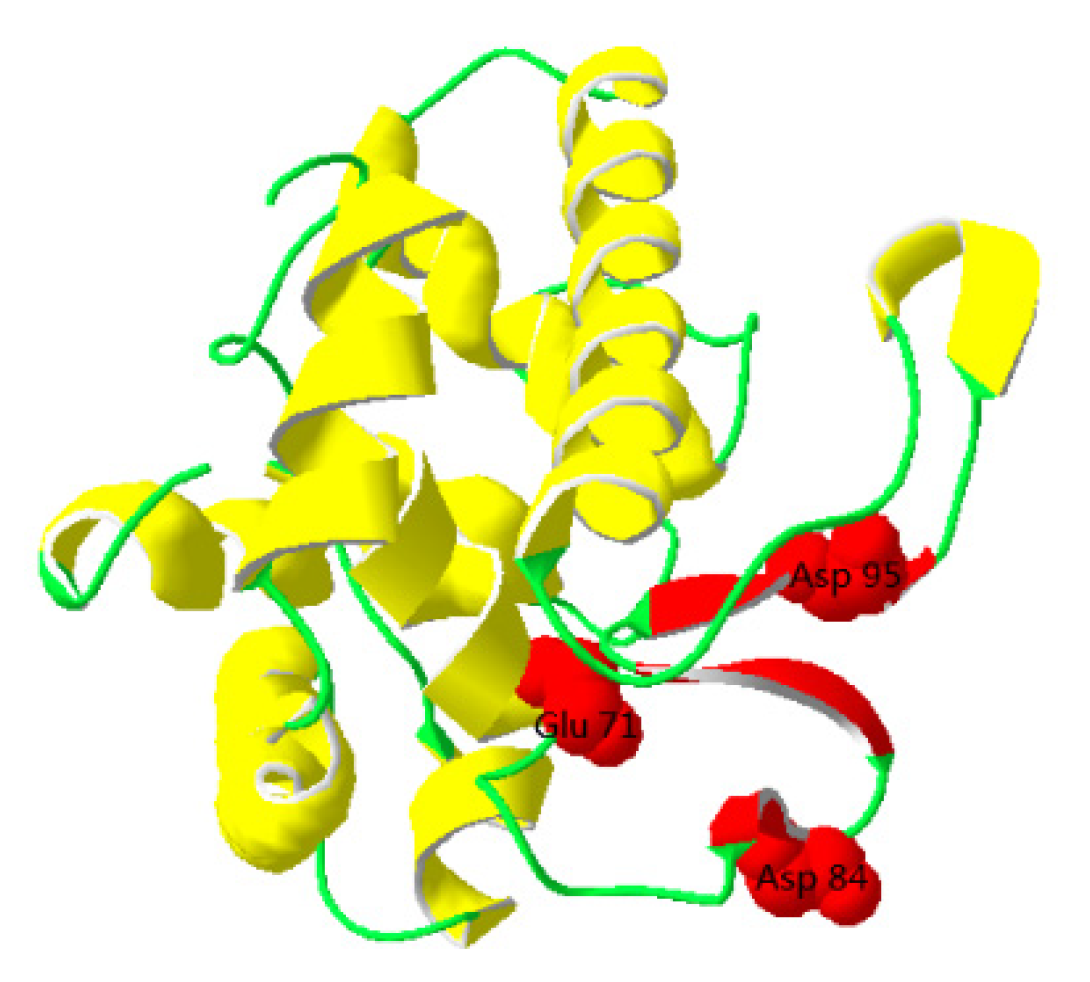
3.1. Sequence Analysis of TrLysG
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
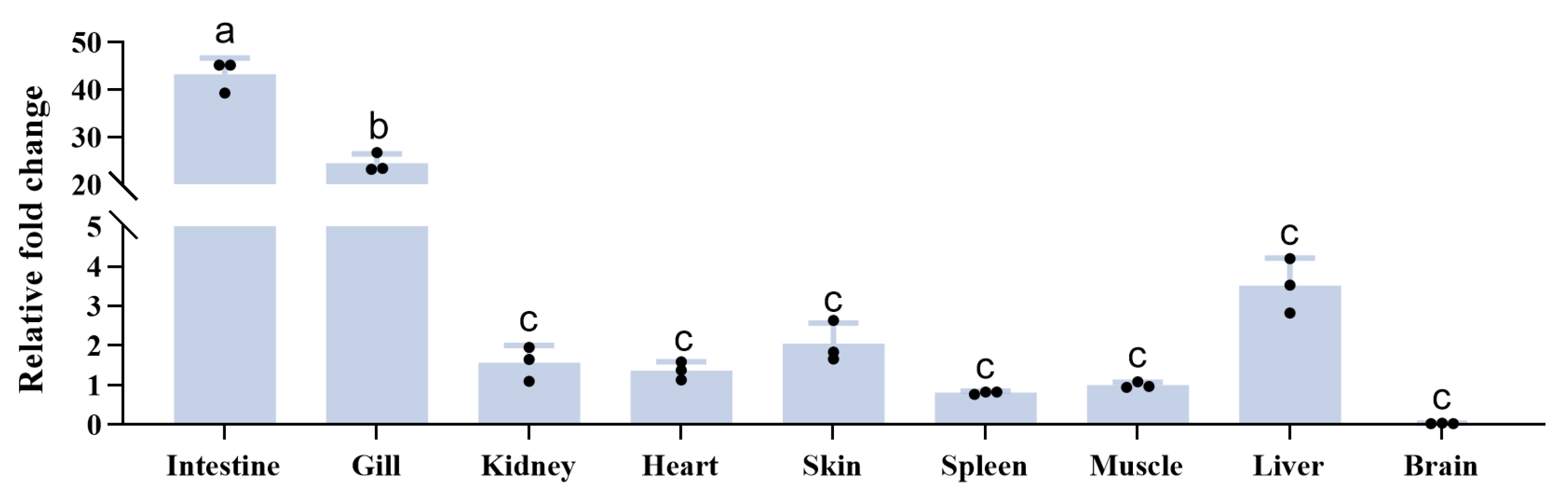
3.3. Expression Analysis of TrLysG in Healthy Tissues
3.4. Temporal Expression Profiles of TrLysG post V. harveyi Injection
3.5. Expression and Purification of rTrLysG
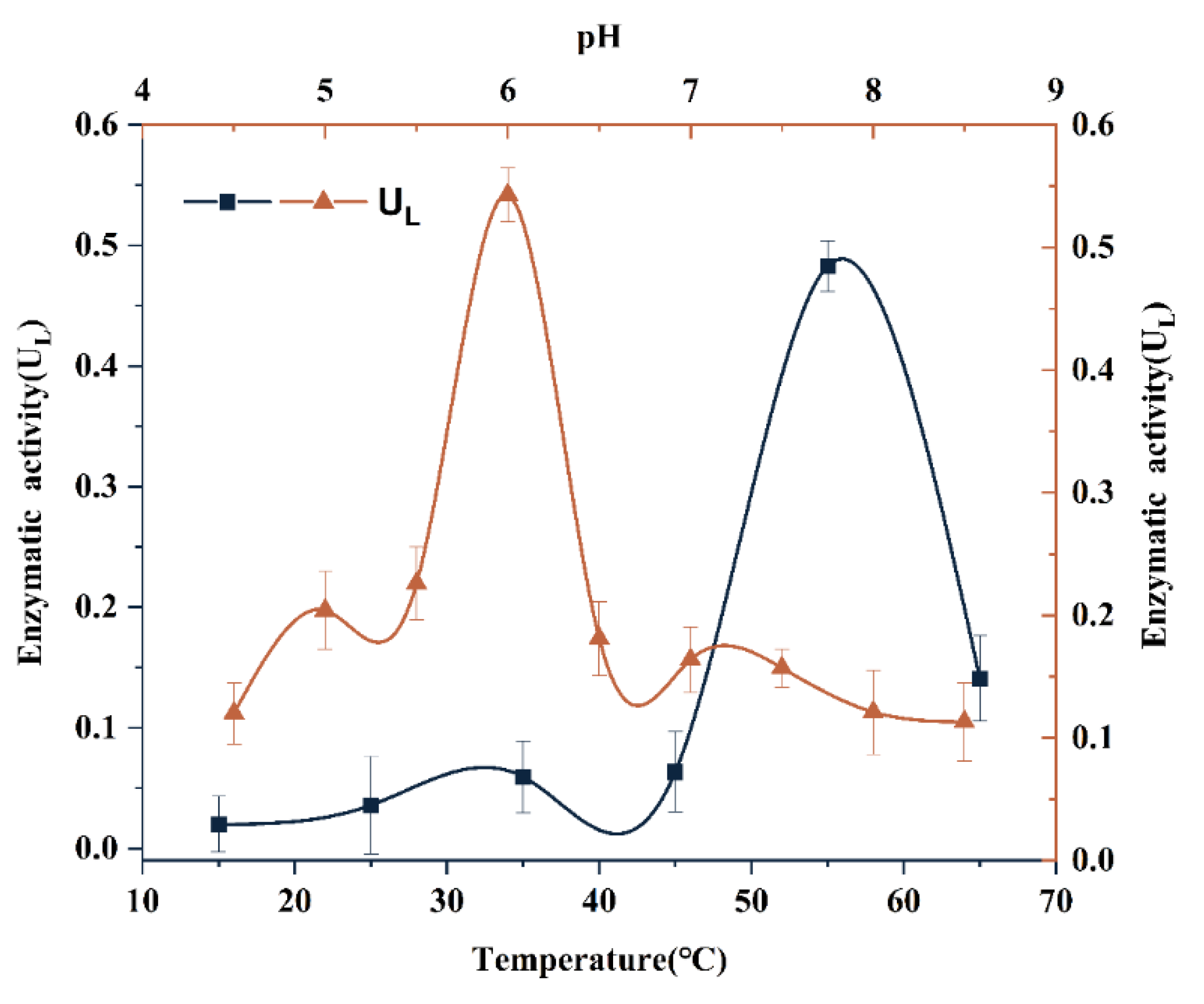
3.6. Lytic Activity of rTrLysG at Different pH and Temperature
3.7. Antibacterial Activity of Recombinant Protein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, C.; Yu, H.; Liu, W.; Su, H.; Shan, Z.; Bao, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, L.; Gao, X. A goose-type lysozyme gene in Japanese scallop (Mizuhopecten yessoensis): cDNA cloning, mRNA expression and promoter sequence analysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 162, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnadóttir, B. Innate immunity of fish (overview). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2006, 20, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jollès, P.; Jollès, J. What’s new in lysozyme research? Always a model system, today as yesterday. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1984, 63, 165–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saurabh, S.; Sahoo, P.K. Lysozyme: An important defence molecule of fish innate immune system. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Ku, S.-K.; Na, D.H.; Bae, J.-S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Lysozyme Against HMGB1 in Human Endothelial Cells and in Mice. Inflammation 2015, 38, 1911–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.-D.; He, J.-G.; Qiu, W.; Tang, J.; Liu, T.-T. Microbial community related to lysozyme digestion process for boosting waste activated sludge biodegradability. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callewaert, L.; Michiels, C.W. Lysozymes in the animal kingdom. J. Biosci. 2010, 35, 127–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfield, R.E.; McMurry, S. Purification and characterization of a lysozyme from goose egg white. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1967, 26, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.M. Evolution of the vertebrate goose-type lysozyme gene family. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Gao, J.; Lu, Y.; Guang, H.; Cai, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Molecular cloning, sequence analysis and phylogeny of first caudata g-type lysozyme in axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum). Zool. Sci. 2013, 30, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savan, R.; Aman, A.; Sakai, M. Molecular cloning of G type lysozyme cDNA in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2003, 15, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathige, S.D.N.K.; Umasuthan, N.; Whang, I.; Lim, B.-S.; Jung, H.-B.; Lee, J. Evidences for the involvement of an invertebrate goose-type lysozyme in disk abalone immunity: Cloning, expression analysis and antimicrobial activity. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 35, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikima, J.-i.; Minagawa, S.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T. Molecular cloning, expression and evolution of the Japanese flounder goose-type lysozyme gene, and the lytic activity of its recombinant protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gene Struct. Expr. 2001, 1520, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Ding, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, B. Molecular cloning, expression analyses and functional characterization of a goose-type lysozyme gene from Bostrychus sinensis (family: Eleotridae). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 96, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zha, H.; Yu, S.; Zhong, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Zhu, Q. Molecular characterization and antibacterial activities of a goose-type lysozyme gene from roughskin sculpin (Trachidermus fasciatus). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 127, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Huang, M. Molecular cloning, expression and antibacterial activity of goose-type lysozyme gene in Microptenus salmoides. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 82, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Huang, Y.; Huang, X.; Cai, J.; Wei, J.; Li, P.; Ouyang, Z.; Qin, Q. Molecular cloning and characterization of a new G-type lysozyme gene (Ec-lysG) in orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 46, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Song, W.; Cui, D.; Wang, L. Identification and characterization of a novel goose-type and chicken-type lysozyme genes in Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) with potent antimicrobial activity. Genes Genom. 2018, 40, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, A.; Parida, S.; Mohanty, J.; Sahoo, P.K. Identification and functional characterization of a g-type lysozyme gene of Labeo rohita, an Indian major carp species. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 92, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Y.; Tan, A.; Bai, J.; Li, S. Identification and expression analysis of the g-type and c-type lysozymes in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, I.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Oh, M.-J.; Jung, S.-J.; Choi, C.Y.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, J. Characterization and expression analysis of a goose-type lysozyme from the rock bream Oplegnathus fasciatus, and antimicrobial activity of its recombinant protein. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2011, 30, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, J.-s.; Sun, L. The g-type lysozyme of Scophthalmus maximus has a broad substrate spectrum and is involved in the immune response against bacterial infection. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2011, 30, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Feng, J.; Li, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Four lysozymes (one c-type and three g-type) in catfish are drastically but differentially induced after bacterial infection. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 35, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, Y.; Yamaguchi, A. Reduced lifetime fitness (growth, body condition and survivability) of hatchery-reared tiger pufferfish Takifugu rubripes compared to wild counterparts. J. Fish Biol. 2022, 101, 1270–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, F.; Meng, X.; Cui, X.; Ma, Q.; Wei, Y.; Liang, M.; Xu, H. Recovery of Fatty Acid and Volatile Flavor Compound Composition in Farmed Tiger Puffer (Takifugu rubripes) with a Fish Oil-Finishing Strategy. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Su, P.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Life cycle assessment of tiger puffer (Takifugu rubripes) farming: A case study in Dalian, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Ying, L.; Yan, H. Retinal development and the expression profiles of opsin genes during larval development in Takifugu rubripes. J. Fish Biol. 2023, 102, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yan, H.; Hu, P.; Liu, W.; Shen, X.; Cui, X.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Growth and survival of Takifugu rubripes larvae cultured under different light conditions. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 45, 1533–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Shen, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y. Gene Expression of Takifugu rubripes Gonads During AI- or MT-induced Masculinization and E2-induced Feminization. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Yan, H.; Jiang, J.; Li, W.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y. Profile of gene expression changes during estrodiol-17β-induced feminization in the Takifugu rubripes brain. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Shang, F.; Liu, F.; Hu, Z.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, C.; Jiang, J.; et al. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of the brain in Takifugu rubripes shows its tolerance to acute hypoxia. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 1669–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, F.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, B.; Wei, R.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Key Metabolic Changes in the Brain of Takifugu rubripes in Response to Chronic Hypoxia. Genes 2022, 13, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.-Q.; Fei, F.; Huang, B.; Meng, X.S.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, K.-F.; Chen, H.-B.; Xing, R.; Liu, B.-L. Alterations in hematological and biochemical parameters, oxidative stress, and immune response in Takifugu rubripes under acute ammonia exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 243, 108978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, P.; Wu, B.; Hou, J.; Ren, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Si, F.; Sun, Z.; Liu, X. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the genes involved in tetrodotoxin (TTX) accumulation, translocation, and detoxification in the pufferfish Takifugu rubripes. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, Z.; Li, Q.; Kong, N.; Wang, L.; Song, L. The variation of intestinal autochthonous bacteria in cultured tiger pufferfish Takifugu rubripes. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1062512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.-X.; Lu, W.-J.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, H.-y.; Wang, Y.-h.; Tu, H.-q.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Gui, J.-F.; Zhao, Z. Transcriptome profiling revealed the growth superiority of hybrid pufferfish derived from Takifugu obscurus ♀ × Takifugu rubripes ♂. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 40, 100912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, S.; Chapman, J.; Stupka, E.; Putnam, N.; Chia, J.-m.; Dehal, P.; Christoffels, A.; Rash, S.; Hoon, S.; Smit, A.; et al. Whole-Genome Shotgun Assembly and Analysis of the Genome of Fugu rubripes. Science 2002, 297, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroyanagi, M.; Katayama, T.; Imai, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Chisada, S.-i.; Yoshiura, Y.; Ushijima, T.; Matsushita, T.; Fujita, M.; Nozawa, A.; et al. New approach for fish breeding by chemical mutagenesis: Establishment of TILLING method in fugu (Takifugu rubripes) with ENU mutagenesis. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhang, H.; Tan, E.; Watabe, S.; Asakawa, S. Characterization of the torafugu (Takifugu rubripes) immunoglobulin heavy chain gene locus. Immunogenetics 2015, 67, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zhao, R.; Peng, H.; Cao, X.; Gao, M.; Wang, S.; Jiang, C. Genome-wide characterization of caspase genes in Japanese pufferfish, Takifugu rubripes, and expression profiles in response to Vibrio harveyi infection. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2022, 53, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Peng, H.; Li, B.; Cai, Z.; Jiang, C. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of galectins in Japanese pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) in response to Vibrio harveyi infection. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 86, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Jiao, C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y. A live attenuated Vibrio anguillarum vaccine induces efficient immunoprotection in Tiger puffer (Takifugu rubripes). Vaccine 2018, 36, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, T.; Ida, T.; Kawahara, N.; Watanabe, F.; Biswas, G.; Sato, T.; Mori, K.; Miyazato, M. Identification and immunoregulatory function of neuromedin U (Nmu) in the Japanese pufferfish Takifugu rubripes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 73, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, S.; Zou, J.; Kono, T.; Sakai, M.; Dijkstra, J.M.; Secombes, C. Characterisation and expression analysis of interleukin 2 (IL-2) and IL-21 homologues in the Japanese pufferfish, Fugu rubripes, following their discovery by synteny. Immunogenetics 2005, 56, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Gan, L.; Kunisada, T.; Lee, I.; Yamagishi, H.; Hood, L. Characterization of the Japanese pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) T-cell receptor α locus reveals a unique genomic organization. Immunogenetics 2001, 53, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombel, I.T.; Sykes, K.F.; Rayner, S.; Johnston, S.A. ORF-FINDER: A vector for high-throughput gene identification. Gene 2002, 282, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; de Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E.; et al. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W597–W603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Doerks, T.; Bork, P. SMART 6: Recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D229–D232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Geng, H.; Tariq Javed, M.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Xu, Y. Passive protection of Japanese pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) against Vibrio harveyi infection using chicken egg yolk immunoglobulins (IgY). Aquaculture 2021, 532, 736009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultmark, D. Insect lysozymes. Exs 1996, 75, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Yu, K.; Yang, F.; Xiang, J. Recombinant Expression of a Modified Shrimp Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor Gene in Pichia pastoris GS115 and Its Characteristic Analysis. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, J.M. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 48 (Suppl. S1), 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonocore, F.; Randelli, E.; Trisolino, P.; Facchiano, A.; de Pascale, D.; Scapigliati, G. Molecular characterization, gene structure and antibacterial activity of a g-type lysozyme from the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Mol. Immunol. 2014, 62, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilojan, J.; Bathige, S.D.N.K.; Kugapreethan, R.; Thulasitha, W.S.; Nam, B.-H.; Lee, J. Molecular, transcriptional and functional insights into duplicated goose-type lysozymes from Sebastes schlegelii and their potential immunological role. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 67, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaresan, V.; Bhatt, P.; Ganesh, M.-R.; Harikrishnan, R.; Arasu, M.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Pasupuleti, M.; Marimuthu, K.; Arockiaraj, J. A novel antimicrobial peptide derived from fish goose type lysozyme disrupts the membrane of Salmonella enterica. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 68, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höppner, C.; Carle, A.; Sivanesan, D.; Hoeppner, S.; Baron, C. The putative lytic transglycosylase VirB1 from Brucella suis interacts with the type IV secretion system core components VirB8, VirB9 and VirB11. Microbiology 2005, 151, 3469–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.M.; Gong, Z.M. Molecular Evolution of Vertebrate Goose-Type Lysozyme Genes. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 56, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulaj, G. Formation of disulfide bonds in proteins and peptides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2005, 23, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, S.; Ohkuma, M.; Chijiiwa, Y.; Kohno, D.; Nakagawa, H.; Hirakawa, H.; Kuhara, S.; Torikata, T. Role of disulfide bonds in goose-type lysozyme. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 2818–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, X.; Kong, X.; Wang, L.; Jiao, D.; Zhang, H. Molecular characterization and expressing analysis of the c-type and g-type lysozymes in Qihe crucian carp Carassius auratus. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 52, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myrnes, B.; Seppola, M.; Johansen, A.; Øverbø, K.; Callewaert, L.; Vanderkelen, L.; Michiels, C.W.; Nilsen, I.W. Enzyme characterisation and gene expression profiling of Atlantic salmon chicken- and goose-type lysozymes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 40, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe, C.; Folch, H.; Enriquez, R.; Moran, G. Innate and adaptive immunity in teleost fish: A review. Vet. Med. 2011, 56, 486–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Trede, N.S. Fish immunology. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.H.; Bai, Z.Y.; Xia, J.H.; Liu, F.; Liu, P.; Yue, G.H. Analysis of two lysozyme genes and antimicrobial functions of their recombinant proteins in Asian seabass. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.-N.; Xin, Z.-Z.; Zhang, D.-Z.; Jiang, S.-H.; Chai, X.-Y.; Li, C.-F.; Zhou, C.-L.; Tang, B.-P. Molecular identification and expression analysis of a goose-type lysozyme (LysG) gene in yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 58, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; He, X.; Austin, B. Vibrio harveyi: A serious pathogen of fish and invertebrates in mariculture. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, Q.; Boscari, E.; Du, H.; Qi, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Di, J.; Yue, H.; Li, C.; et al. Characterization and expression analysis of g- and c-type lysozymes in Dabry’s sturgeon (Acipenser dabryanus). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 76, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.; Wan, Q.; Bathige, S.D.N.K.; Lee, J. Molecular characterization, transcriptional profiling, and antibacterial potential of G-type lysozyme from seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 58, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, Z.-X.; Wang, Q.-L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.-L. Identification and expression analysis of goose-type lysozyme in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2012, 32, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chipman, D.M.; Sharon, N. Mechanism of lysozyme action. Science 1969, 165, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, W.-j.; Wang, W.-n. Protection of blue shrimp (Litopenaeus stylirostris) against the White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) when injected with shrimp lysozyme. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2010, 28, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, W.-j.; Hu, C.-q. Molecular cloning, characterization, expression and antibacterial analysis of a lysozyme homologue from Fenneropenaeus merguiensis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 36, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyomuhendo, P.; Myrnes, B.; Nilsen, I.W. A cold-active salmon goose-type lysozyme with high heat tolerance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2841–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Ma, M. The antimicrobial spectrum of lysozyme broadened by reductive modification. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3992–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine, Y.; Ma, F.; Lauriau, S. Antimicrobial peptides released by enzymatic hydrolysis of hen egg white lysozyme. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, A.V.; Karyagina, A.S.; Vasina, D.V.; Vasina, I.V.; Gushchin, V.A.; Lunin, V.G. Resistance to peptidoglycan-degrading enzymes. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 46, 703–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraboschi, P.; Ciceri, S.; Grisenti, P. Applications of Lysozyme, an Innate Immune Defense Factor, as an Alternative Antibiotic. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, A.A.; Magouz, F.I.; Mahmoud, S.A.; Abdel-Rahim, M.M. The effects of some commercial probiotics as water additive on water quality, fish performance, blood biochemical parameters, expression of growth and immune-related genes, and histology of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primers | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| TrLysG-F | ATCCTGGTTGAGTTTATC |
| TrLysG-R | AGTAGTCCTTCCCTGTTG |
| β-actin-F | ATCCGTAAGGACCTGTATGC |
| β-actin-R | AGTATTTACGCTCAGGTGGG |
| Bacteria | Types | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Streptococcus parauberis | Gram-positive | 100 |
| Staphylococcus pasteuri | Gram-positive | 50 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | Gram-positive | 200 |
| Shewanella | Gram-negative | 200 |
| Aeromonas hydrophila | Gram-negative | 200 |
| Escherichia coli | Gram-negative | 200 |
| Vibrio Parahaemolyticus | Gram-negative | 200 |
| Vibrio harveyi | Gram-negative | 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, X.; Yang, Z.; Gao, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, R.; Chen, L.; Jiang, C.; Wang, H. Molecular Characterization and Antibacterial Potential of Goose-Type Lysozyme from Japanese Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes). Fishes 2023, 8, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120577
Cao X, Yang Z, Gao M, Yang X, Wang S, Zhao R, Chen L, Jiang C, Wang H. Molecular Characterization and Antibacterial Potential of Goose-Type Lysozyme from Japanese Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes). Fishes. 2023; 8(12):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120577
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Xinyu, Zhen Yang, Minghong Gao, Xu Yang, Shuhui Wang, Ruihu Zhao, Lei Chen, Chen Jiang, and He Wang. 2023. "Molecular Characterization and Antibacterial Potential of Goose-Type Lysozyme from Japanese Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes)" Fishes 8, no. 12: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120577
APA StyleCao, X., Yang, Z., Gao, M., Yang, X., Wang, S., Zhao, R., Chen, L., Jiang, C., & Wang, H. (2023). Molecular Characterization and Antibacterial Potential of Goose-Type Lysozyme from Japanese Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes). Fishes, 8(12), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120577







