Spatial Distribution of Major Fish Species Catches and Their Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
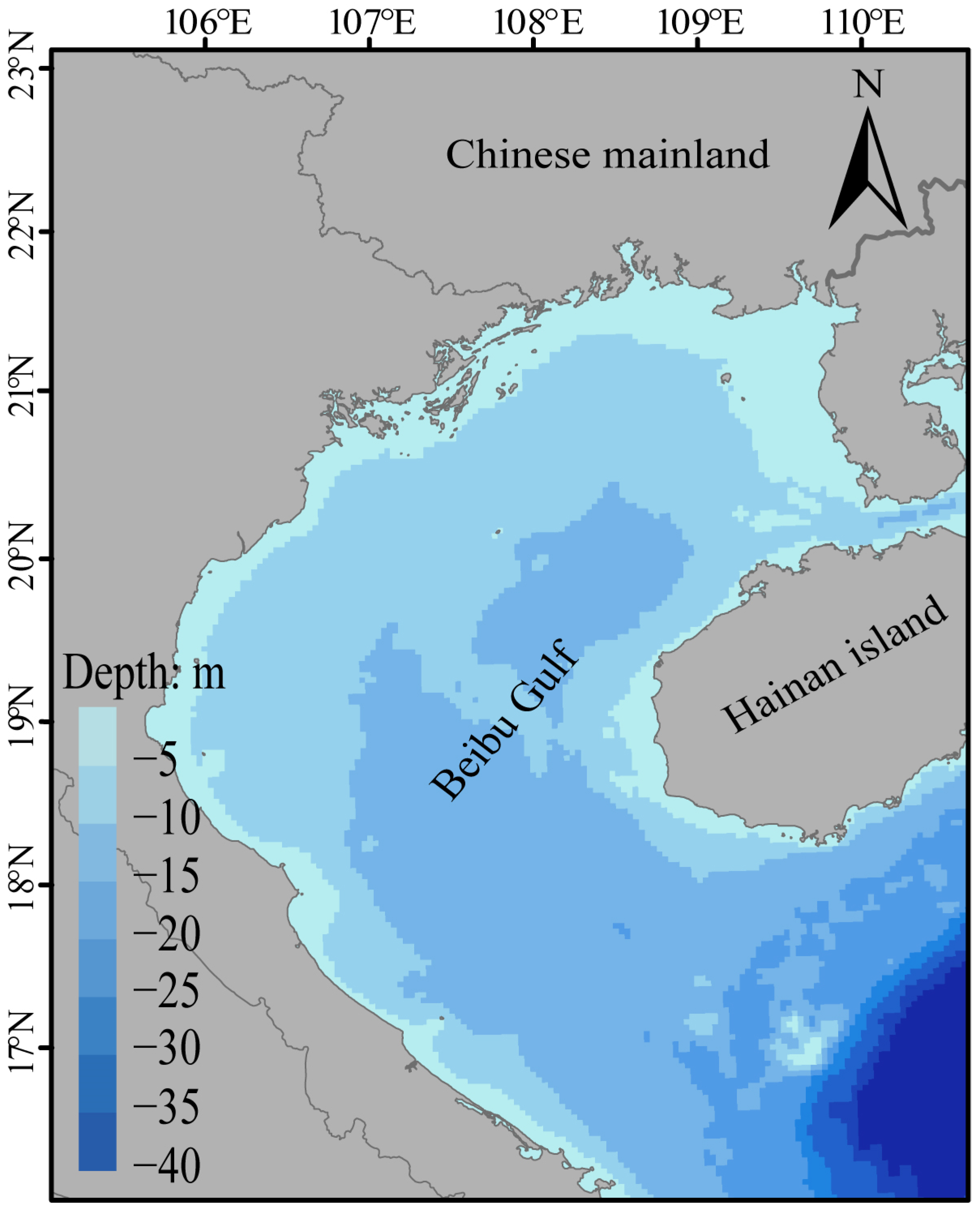
2.1. Data Collection and Collation
2.2. Acquisition and Processing of Environmental Data
2.3. Evaluation of the MaxEnt Model
2.4. Prediction of Potentially Suitable Areas and Analysis of Major Environmental Factors
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of the Model Performance
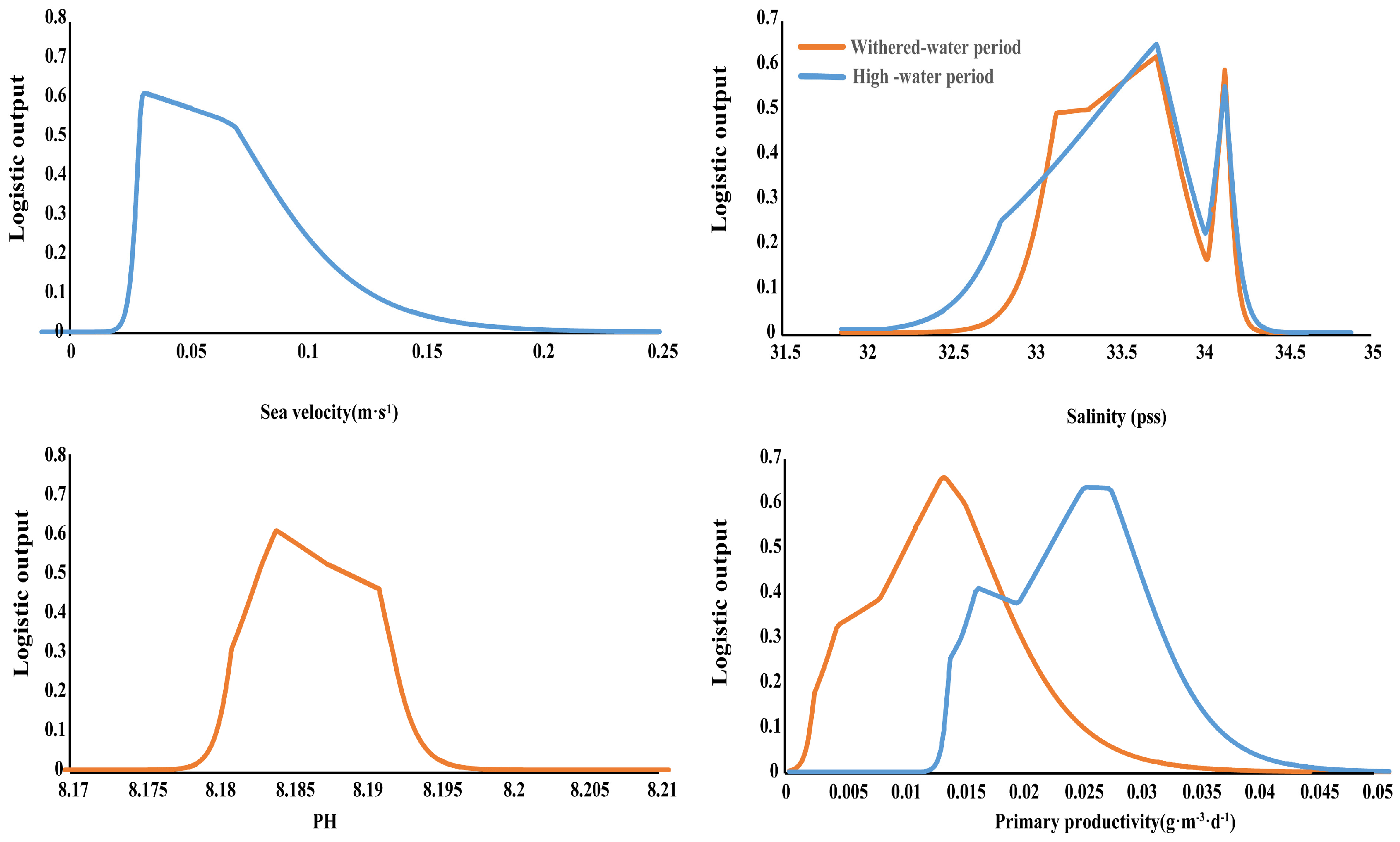
3.2. Dominant Environmental Factors
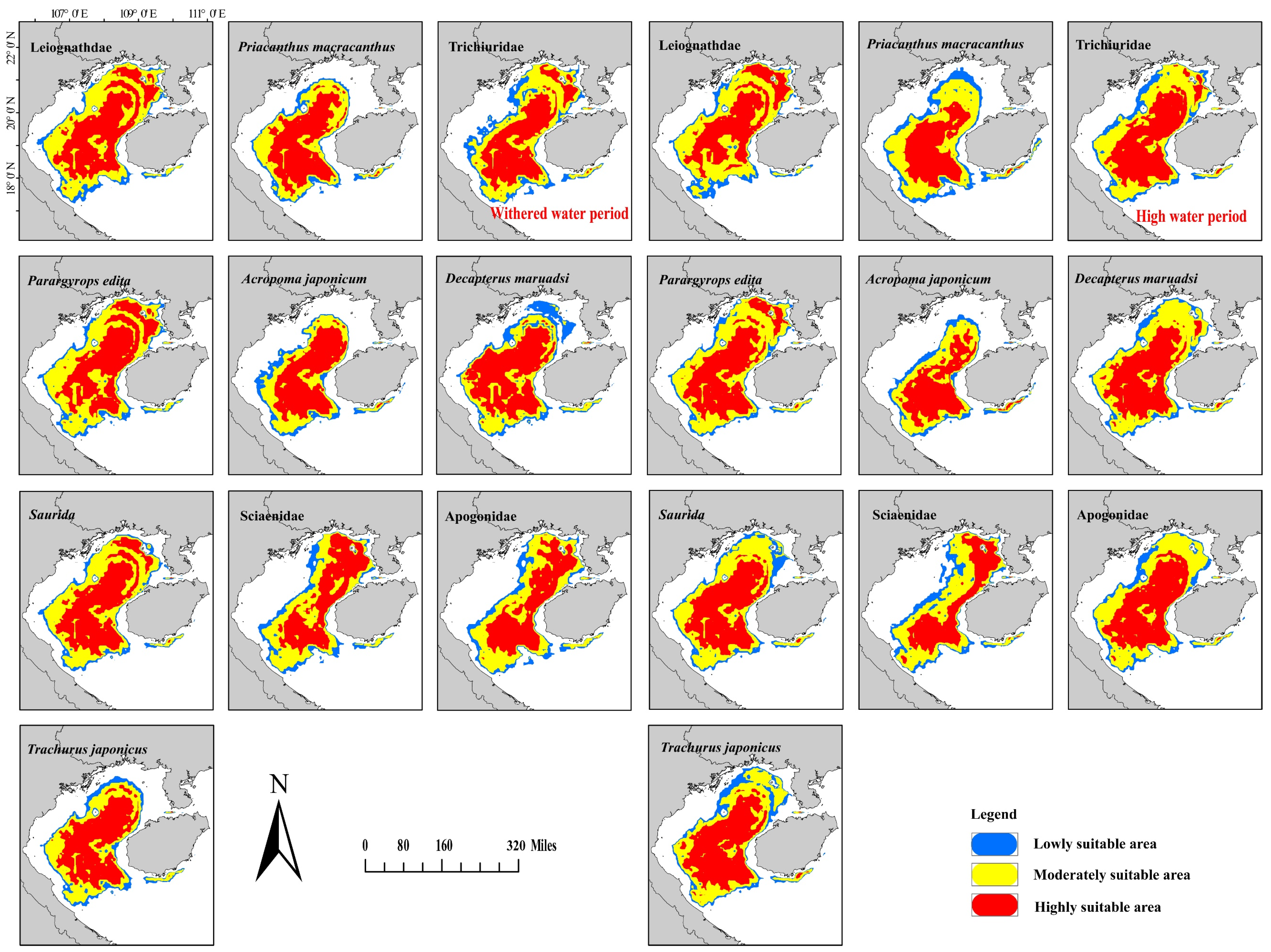
3.3. Distribution of Potentially Suitable Areas for Different Flood Seasons
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationships between the Major Fish Catches and Environmental Factors
4.2. Applicability of the Prediction of Potentially Suitable Areas
4.3. Outlook
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Bruno, J.F. The Impact of Climate Change on the World’s Marine Ecosystems. Science 2010, 328, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polansky, L.; Newman, K.B.; Nobriga, M.L.; Mitchell, L. Spatiotemporal Models of an Estuarine Fish Species to Identify Patterns and Factors Impacting Their Distribution and Abundance. Estuaries Coasts 2018, 41, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, S.A.; Barahona, M.; Weidberg, N.; Broitman, B.R. Climate change in the coastal ocean: Shifts in pelagic productivity and regionally diverging dynamics of coastal ecosystems. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2022, 289, 20212772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, L.; Peng, X.; Lin, L.; Kang, B. Redistribution of the Lizardfish Harpadon Nehereus in Coastal Waters of China Due to Climate Change. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 4919–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X. Evaluation of Biological Reference Points of Two Important Fishery Resources in the East China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Fu, S.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X. Distribution of Meiofaunal Abundance in Relation to Environmental Factors in Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 31, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvetat, J.; Bez, N.; Habasque, J.; Lebourges-Dhaussy, A.; Lopes, C.; Roudaut, G.; Simier, M.; Travassos, P.; Vargas, G.; Bertrand, A. Comprehensive Spatial Distribution of Tropical Fish Assemblages from Multifrequency Acoustics and Video Fulfils the Island Mass Effect Framework. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worm, B.; Hilborn, R.; Baum, J.K.; Branch, T.A.; Collie, J.S.; Costello, C.; Fogarty, M.J.; Fulton, E.A.; Hutchings, J.A.; Jennings, S.; et al. Rebuilding Global Fisheries. Science 2009, 325, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenford, J.H.; Liang, D.; Bailey, H.; Hoover, A.L.; Zarate, P.; Azócar, J.; Devia, D.; Alfaro-Shigueto, J.; Mangel, J.C.; de Paz, N.; et al. Using Fisheries Observation Data to Develop a Predictive Species Distribution Model for Endangered Sea Turtles. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2021, 3, e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, K. Climate and coastal habitat change: A recipe for a dirtier ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1079–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wei, H.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Q. Spatial and Seasonal Characteristics of Dissolved Heavy Metals in the Seawater of Beibu Gulf, the Northern South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 996202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Chen, P.; Yu, J.; Wu, Q. Environmental Influence on the Spatiotemporal Variability of Fishing Grounds in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Guo, J.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Fan, J.; Xu, S.; Chen, Z. Long-Term Variations in Fish Community Structure under Multiple Stressors in a Semi-Closed Marine Ecosystem in the South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Xie, B.; Huang, L. Climate-Induced Habitat Suitability Changes Intensify Fishing Impacts on the Life History of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, F.; Shannon, L.J.; Angelini, R.; Steenbeek, J.; Coll, M. Overfishing Species on the Move May Burden Seafood Provision in the Low-Latitude Atlantic Ocean. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.F.; Kyne, P.M.; Jabado, R.W.; Leeney, R.H.; Davidson, L.N.K.; Derrick, D.H.; Finucci, B.; Freckleton, R.P.; Fordham, S.V.; Dulvy, N.K. Overfishing and Habitat Loss Drive Range Contraction of Iconic Marine Fishes to near Extinction. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabb6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Graham, C.; Valavi, R.; Abegg, M.; Bruce, C.; Ford, A.; Guisan, A.; Hijmans, R.J.; Huettmann, F.; Lohmann, L.; et al. Presence-Only and Presence-Absence Data for Comparing Species Distribution Modeling Methods. Biodivers. Inform. 2020, 15, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, B.; Araújo, M.B. Sdm: A reproducible and extensible R platform for species distribution modelling. Ecography 2016, 39, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Wang, L.; Kiu, M.; Zhao, L.; Kang, B. Global prediction of spatial distribution and migratory corridors of green turtles based on species distribution modeling. J. Fish. Sci. China 2021, 28, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Kerr, L.A.; Record, N.R.; Bridger, E.; Tupper, B.; Mills, K.E.; Armstrong, E.M.; Pershing, A.J. Modeling Marine Pelagic Fish Species Spatiotemporal Distributions Utilizing a Maximum Entropy Approach. Fish. Oceanogr. 2018, 27, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Hu, W.; Chen, B.; Tan, H.; Su, S.; Ding, L.; Dong, P.; Yu, W.; Du, J. Impact of Climate Change on Potential Habitat Distribution of Sciaenidae in the Coastal Waters of China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Lai, J.; Pan, C.; Wang, S.; Fu, H.; Zhang, B.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, L. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Nitrogen Biogeochemical Processes in the Coastal Regions of Northern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Shi, H.; Hou, G.; Zhao, H.; Dong, C. Relationships between Environmental Variables and Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Jack Mackerel (Trachurus japonicus) in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhou, X.; Jin, G.; Huang, P.; Deng, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Quantification of the Seasonal Intrusion of Water Masses and Their Impact on Nutrients in the Beibu Gulf Using Dual Water Isotopes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2022, 127, e2021JC018065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xu, X.; Jefferson, T.A.; Olson, P.A.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, H.; He, L.; Yang, G. Conservation Status of the Indo-Pacific Humpback Dolphin (Sousa chinensis) in the Northern Beibu Gulf, China. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2016, 73, 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Pessanha, A.L.M.; Araújo, F.G. Spatial, Temporal and Diel Variations of Fish Assemblages at Two Sandy Beaches in the Sepetiba Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 57, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharitt, C.A.; González, M.J.; Williamson, T.J.; Vanni, M.J. Nutrient Excretion by Fish Supports a Variable but Significant Proportion of Lake Primary Productivity over 15 Years. Ecology 2021, 102, e03364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaureguizar, A.J.; Menni, R.; Guerrero, R.; Lasta, C. Environmental Factors Structuring Fish Communities of the Río de La Plata Estuary. Fish. Res. 2004, 66, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, M.; Masud, M.M.; Alam, L.; Mokhtar, M.B.; Amir, A.A. The Impact of Climate Variables on Marine Fish Production: An Empirical Evidence from Bangladesh Based on Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL) Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 87923–87937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sleen, P.; Zuidema, P.A.; Morrongiello, J.; Ong, J.L.J.; Rykaczewski, R.R.; Sydeman, W.J.; Di Lorenzo, E.; Black, B.A. Interannual Temperature Variability Is a Principal Driver of Low-Frequency Fluctuations in Marine Fish Populations. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombano, D.D.; Carlson, S.M.; Hobbs, J.A.; Ruhi, A. Four Decades of Climatic Fluctuations and Fish Recruitment Stability across a Marine-Freshwater Gradient. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 5104–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Jing, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Advances in the Use of Nighttime Light Data to Monitor and Assess Coastal Fisheries under the Impacts of Human Activities and Climate and Environmental Changes: A Case Study in the Beibu Gulf. Mar. Policy. 2022, 144, 105227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlotta, M.; Beare, D.; Hall-Spencer, J.M. Overfishing and the Replacement of Demersal Finfish by Shellfish: An Example from the English Channel. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101506. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Du, F.; Lin, Z.; Sun, D.; Huang, L. Spatio-temporal variability of fish diversity and dominant species in the Beibu Gulf. J. Fish. Sci. China 2011, 18, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H. Spatiotemporal distribution of threadfin porgy evynnis cardinalis in Beibu Gulf and its relationship with environmental factors. J. Guangdong Ocean Univ. 2021, 41, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, R.; Fan, J.; Chen, Z.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xu, Y.; Xu, S. The probability distribution of the jack mackerel (Trachurus japonicus) density in the offshore of the northern South China Sea. J. Fish. Sci. China 2019, 26, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pape, O.; Bonhommeau, S.; Nieblas, A.-E.; Fromentin, J.-M. Overfishing Causes Frequent Fish Population Collapses but Rare Extinctions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooper, C.N.; Ortiz, I.; Hermann, A.J.; Laman, N.; Cheng, W.; Kearney, K.; Aydin, K. Predicted Shifts of Groundfish Distribution in the Eastern Bering Sea under Climate Change, with Implications for Fish Populations and Fisheries Management. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, X.; Xing, W.; Li, X.; Yan, M.; Yuan, Y. Impacts of Changing Climate on the Distribution of Migratory Birds in China: Habitat Change and Population Centroid Shift. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Yuan, S.; Wang, H.; Zhong, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, C.; Chang, Q. Species distribution models for predicting the habitat suitability of Chinese fire-bellied newt Cynops orientalis under climate change. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 10147–10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, L.J.; Hughes, L.; Pitman, A.J. Why Is the Choice of Future Climate Scenarios for Species Distribution Modelling Important? Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, F.; Huang, X. Spatial and Seasonal Characteristics of Dissolved Heavy Metals in the East and West Guangdong Coastal Waters, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Taxa | Index | Available Data | |
|---|---|---|---|
| January (Withered-Water Period) | July (High-Water Period) | ||
| Leiognathidae | bottom | 514 | 462 |
| Priacanthus macracanthus | bottom | 281 | 136 |
| Trichiuridae | bottom | 389 | 408 |
| Parargyrops edita | bottom | 479 | 528 |
| Acropoma japonicum | bottom | 403 | 328 |
| Decapterus maruadsi | pelagic | 325 | 479 |
| Saurida | bottom | 492 | 505 |
| Sciaenidae | bottom | 447 | 300 |
| Apogonidae | bottom | 380 | 388 |
| Trachurus japonicus | pelagic | 388 | 500 |
| Taxa | Withered-Water Period | High-Water Period | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area under the Curve (AUC) Value | Standard Deviation | AUC Value | Standard Deviation | |
| Leiognathidae | 0.914 | 0.006 | 0.921 | 0.006 |
| Priacanthus macracanthus | 0.942 | 0.005 | 0.944 | 0.009 |
| Trichiuridae | 0.929 | 0.007 | 0.924 | 0.006 |
| Parargyrops edita | 0.924 | 0.005 | 0.922 | 0.005 |
| Acropoma japonicum | 0.933 | 0.005 | 0.942 | 0.005 |
| Decapterus maruadsi | 0.926 | 0.006 | 0.912 | 0.006 |
| Saurida | 0.919 | 0.005 | 0.924 | 0.005 |
| Sciaenidae | 0.925 | 0.005 | 0.95 | 0.006 |
| Apogonidae | 0.926 | 0.007 | 0.917 | 0.006 |
| Trachurus japonicus | 0.934 | 0.005 | 0.917 | 0.005 |
| Taxa | Withered-Water Period | High-Water Period |
|---|---|---|
| Dominant Environmental Factors | ||
| Leiognathidae | Bottom salinity, primary productivity, water current velocity | Bottom salinity, primary productivity, water current velocity |
| Priacanthus macracanthus | Bottom salinity, pH, water current velocity | Primary productivity, bottom salinity, pH |
| Trichiuridae | Bottom salinity, primary productivity, pH | Bottom salinity, pH, primary productivity |
| Parargyrops edita | Bottom salinity, primary productivity, water current velocity | Bottom salinity, pH, primary productivity |
| Acropoma japonicum | Bottom salinity, pH, primary productivity | pH, bottom salinity, primary productivity |
| Decapterus maruadsi | Bottom salinity, primary productivity, water current velocity | Bottom salinity, primary productivity, pH |
| Saurida | Bottom salinity, primary productivity, water current velocity | Bottom salinity, Primary productivity, Water current velocity |
| Sciaenidae | Bottom salinity, pH, primary productivity | pH, bottom salinity, primary productivity |
| Apogonidae | Bottom salinity, pH, Primary productivity | Primary productivity, bottom salinity, pH |
| Trachurus japonicus | Bottom salinity, primary productivity, water current velocity | Bottom salinity, primary productivity, pH |
| Taxa | Area Comparison | Withered-Water Period | High-Water Period | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate of Change (%) | Total Area/km2 | Less Suitable Area/km2 | Moderately Suitable Area/km2 | Highly Suitable Area/km2 | Total Area/km2 | Less Suitable Area/km2 | Moderately Suitable Area/km2 | Highly Suitable Area/km2 | |
| Leiognathidae | −4.78% | 81,023.28 | 8998.28 | 34,484.21 | 37,540.79 | 77,148.9 | 10,028.06 | 34,719.46 | 32,401.38 |
| Priacanthus macracanthus | 9.56% | 65,981.63 | 8389.03 | 24,586.27 | 33,006.32 | 72,291.28 | 14,682.31 | 30,835.6 | 26,773.37 |
| Trichiuridae | 3.57% | 75,997.62 | 13,423.31 | 29,439.59 | 33,134.72 | 78,712.96 | 10,995.79 | 31,172.54 | 36,544.62 |
| Parargyrops edita | 0.81% | 80,887.12 | 8882.8 | 34,299.79 | 37,704.52 | 81,542.05 | 9405.02 | 35,709.6 | 36,427.43 |
| Acropoma japonicum | 10.23% | 55,406.37 | 9101.69 | 20,864.42 | 25,440.26 | 61,076.61 | 9864.33 | 20,560.23 | 30,652.05 |
| Decapterusmaruadsi | 6.26% | 73,117.69 | 13,783.51 | 22,459.5 | 36,874.67 | 78,002.88 | 9735.06 | 32,591.83 | 35,675.99 |
| Saurida | −0.88% | 77,737.47 | 8409.71 | 31,575.84 | 37,751.92 | 77,055.83 | 10,632.1 | 30,527.96 | 35,894.87 |
| Sciaenidae | −6.22% | 68,149.76 | 11,121.6 | 27,264.56 | 29,763.6 | 63,909.14 | 12,194.47 | 27,502.4 | 24,212.28 |
| Apogonidae | 10.61% | 69,620.75 | 11,191.4 | 28,421.87 | 30,007.47 | 77,004.13 | 10,746.75 | 30,160 | 36,097.38 |
| Trachurus japonicus | 10.92% | 68,919.29 | 9704.9 | 24,924.94 | 34,289.45 | 76,448.31 | 11,843.74 | 27,580.82 | 37,023.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Wang, X.; Du, F.; Peng, S.; Wang, L.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Qiu, Y. Spatial Distribution of Major Fish Species Catches and Their Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Fishes 2023, 8, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110559
Li M, Wang X, Du F, Peng S, Wang L, Sun D, Wang Y, Chen P, Qiu Y. Spatial Distribution of Major Fish Species Catches and Their Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Fishes. 2023; 8(11):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110559
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Menghui, Xuehui Wang, Feiyan Du, Shuai Peng, Lianggen Wang, Dianrong Sun, Yuezhong Wang, Pimao Chen, and Yongsong Qiu. 2023. "Spatial Distribution of Major Fish Species Catches and Their Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea" Fishes 8, no. 11: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110559
APA StyleLi, M., Wang, X., Du, F., Peng, S., Wang, L., Sun, D., Wang, Y., Chen, P., & Qiu, Y. (2023). Spatial Distribution of Major Fish Species Catches and Their Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Fishes, 8(11), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110559








