Condition, Reproductive Fitness, and Fluctuating Asymmetry in Brook Stickleback: Responses to Anthropogenic Runoff
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Sites
3. Methods
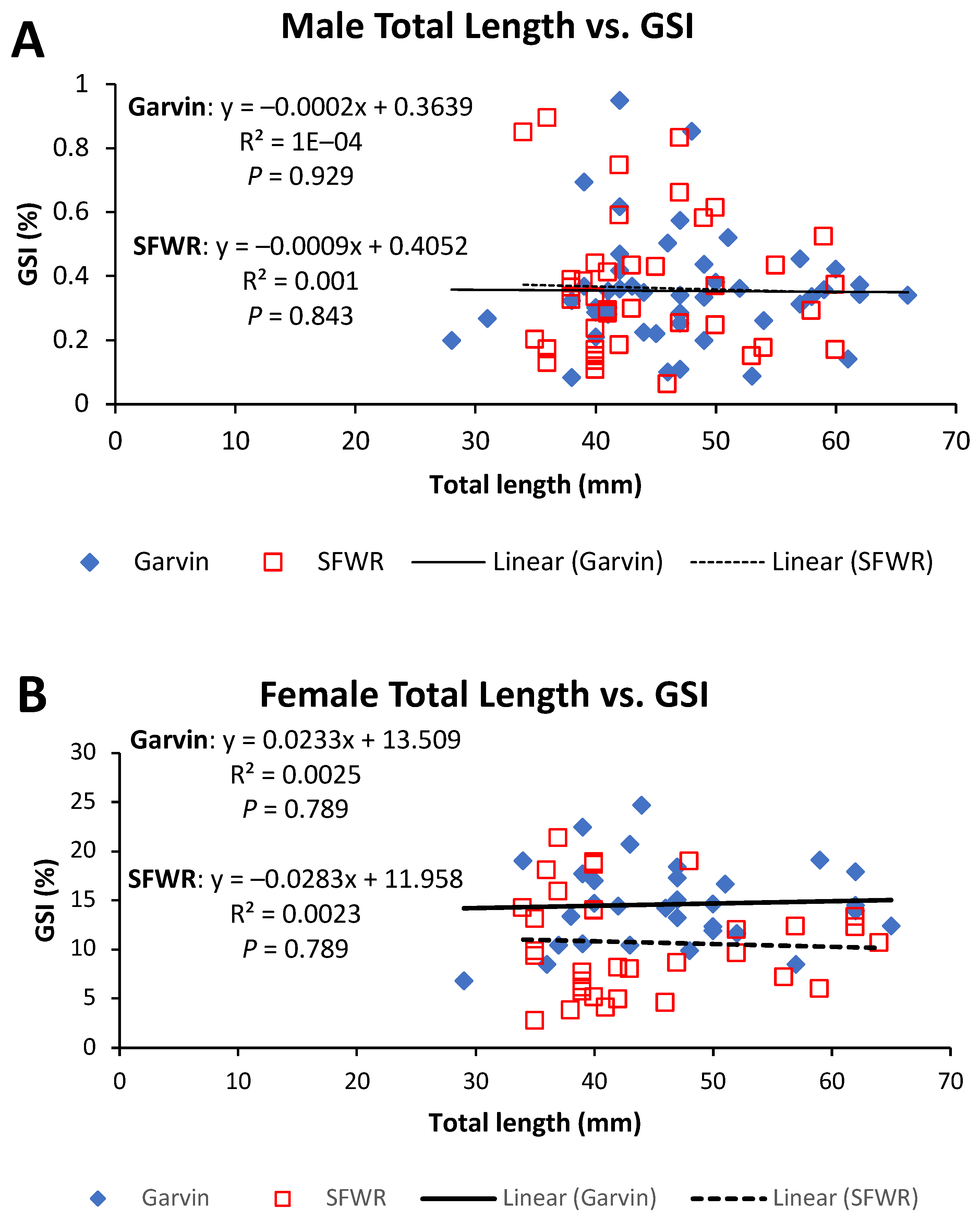
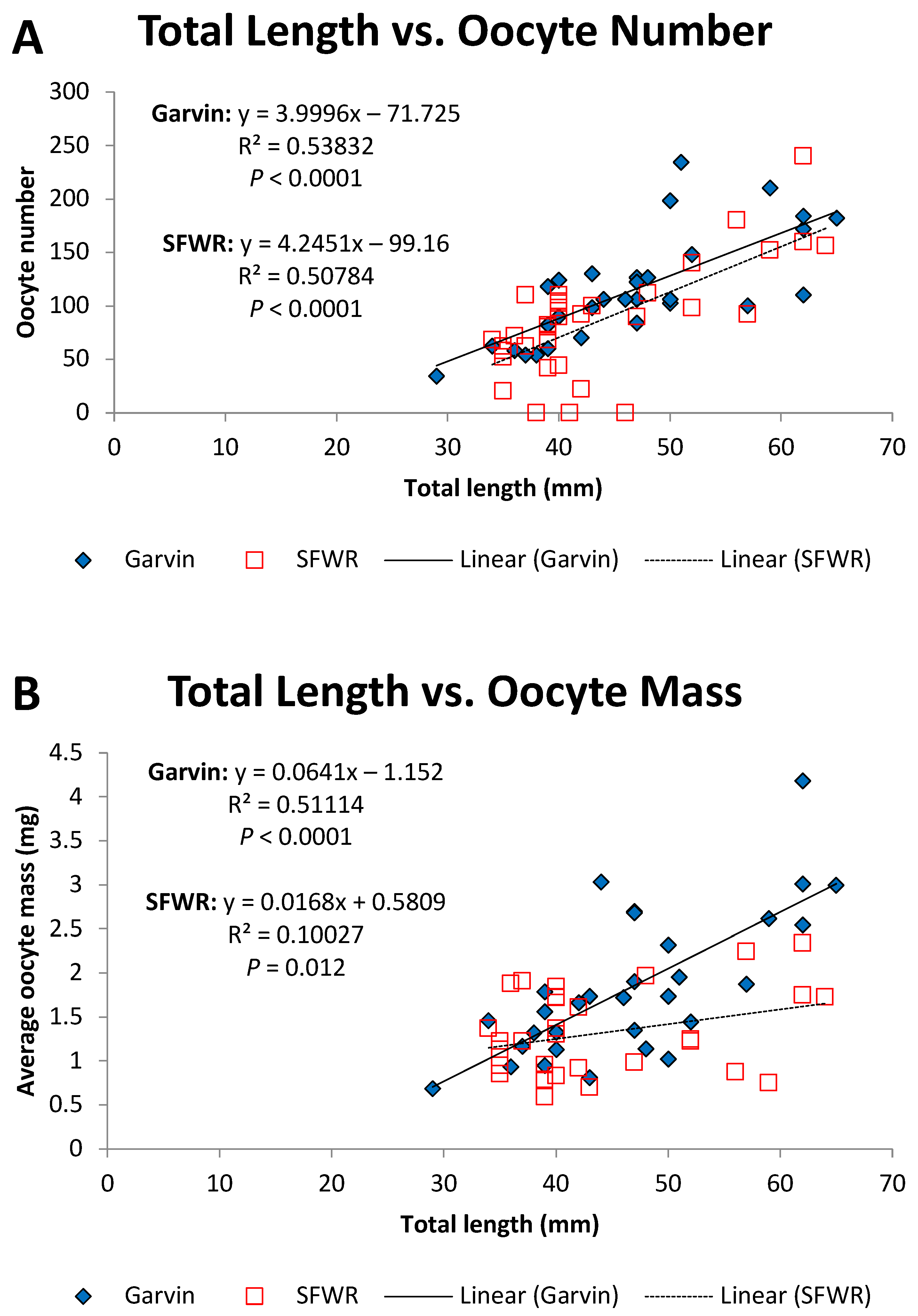
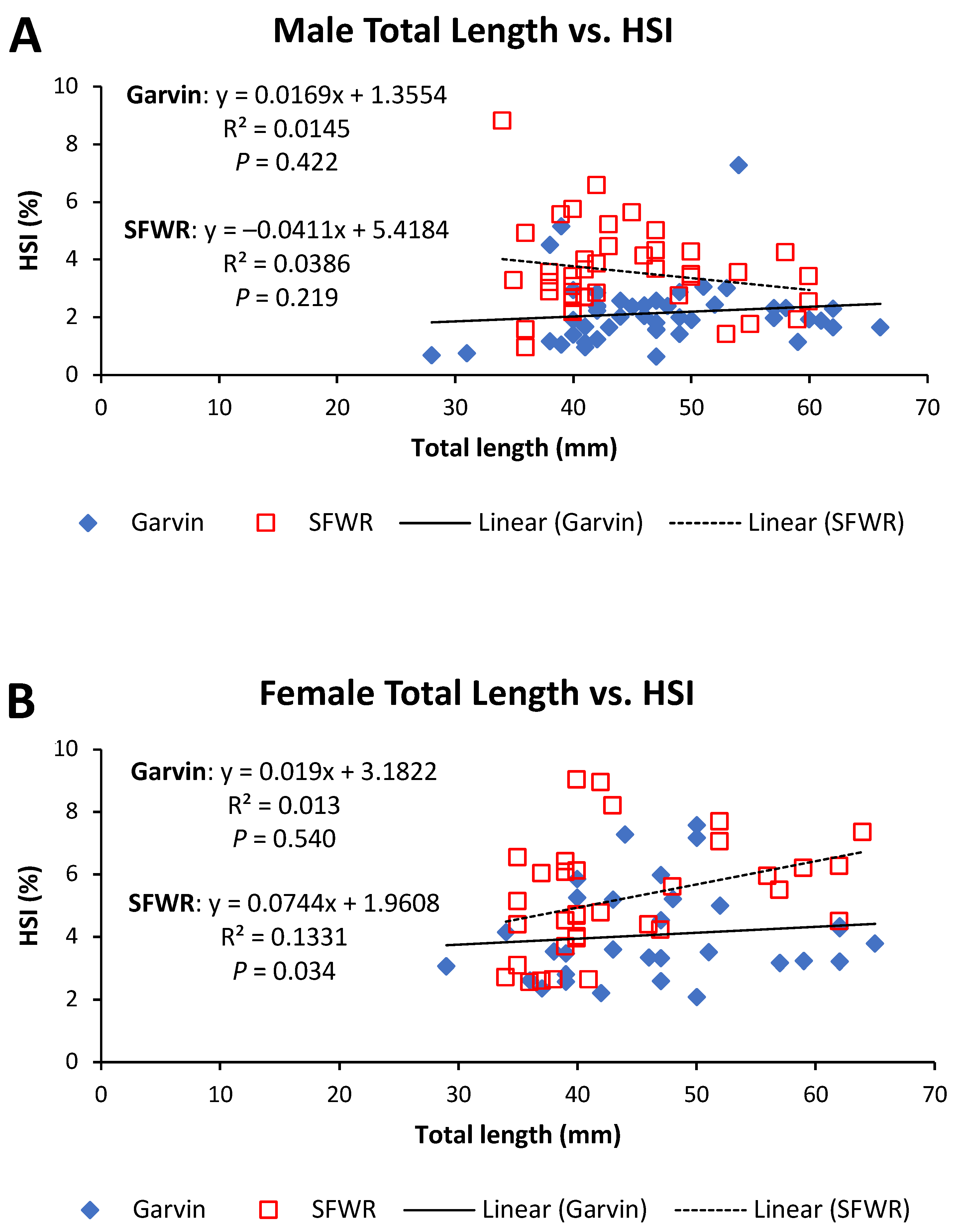
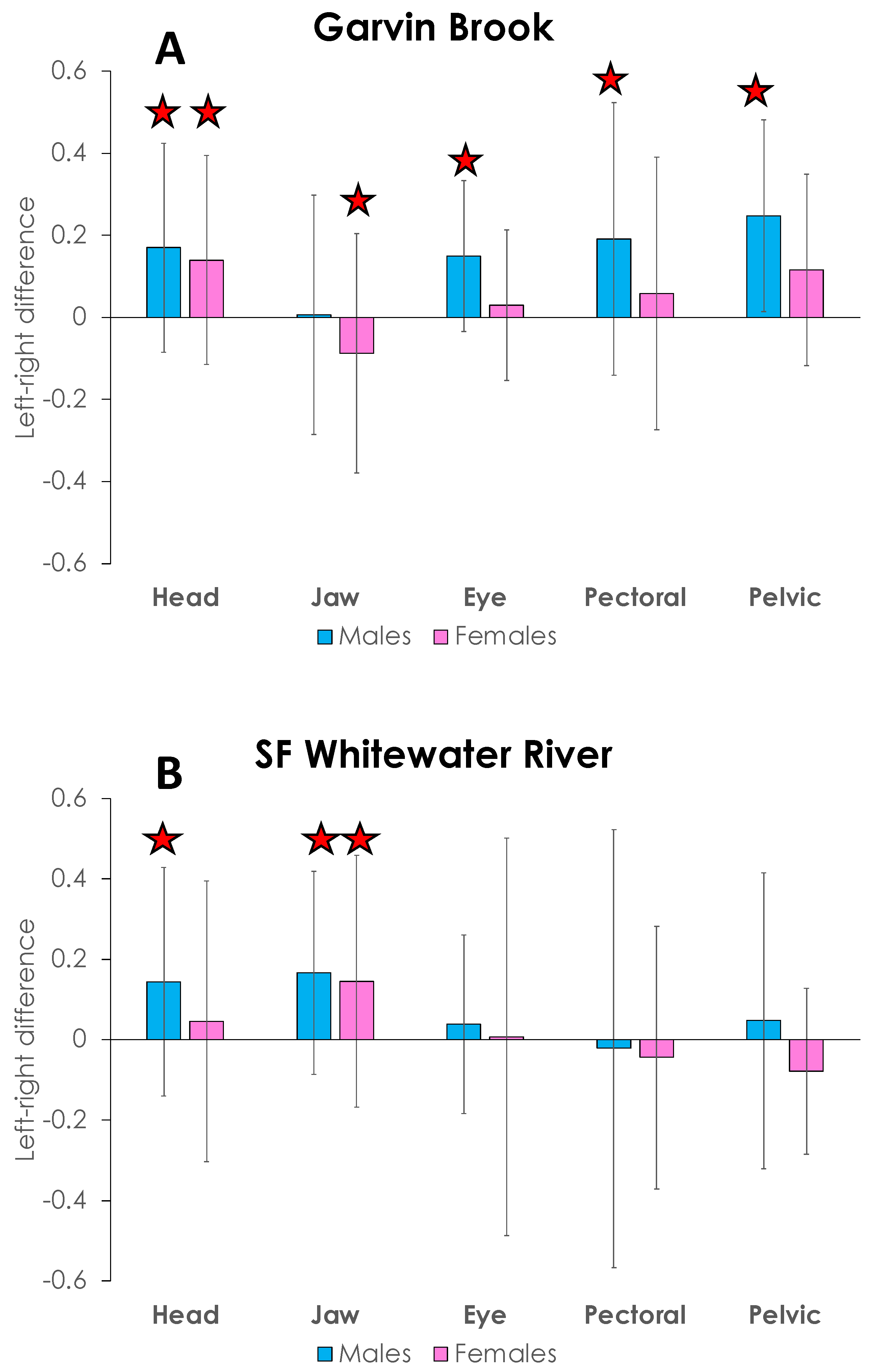
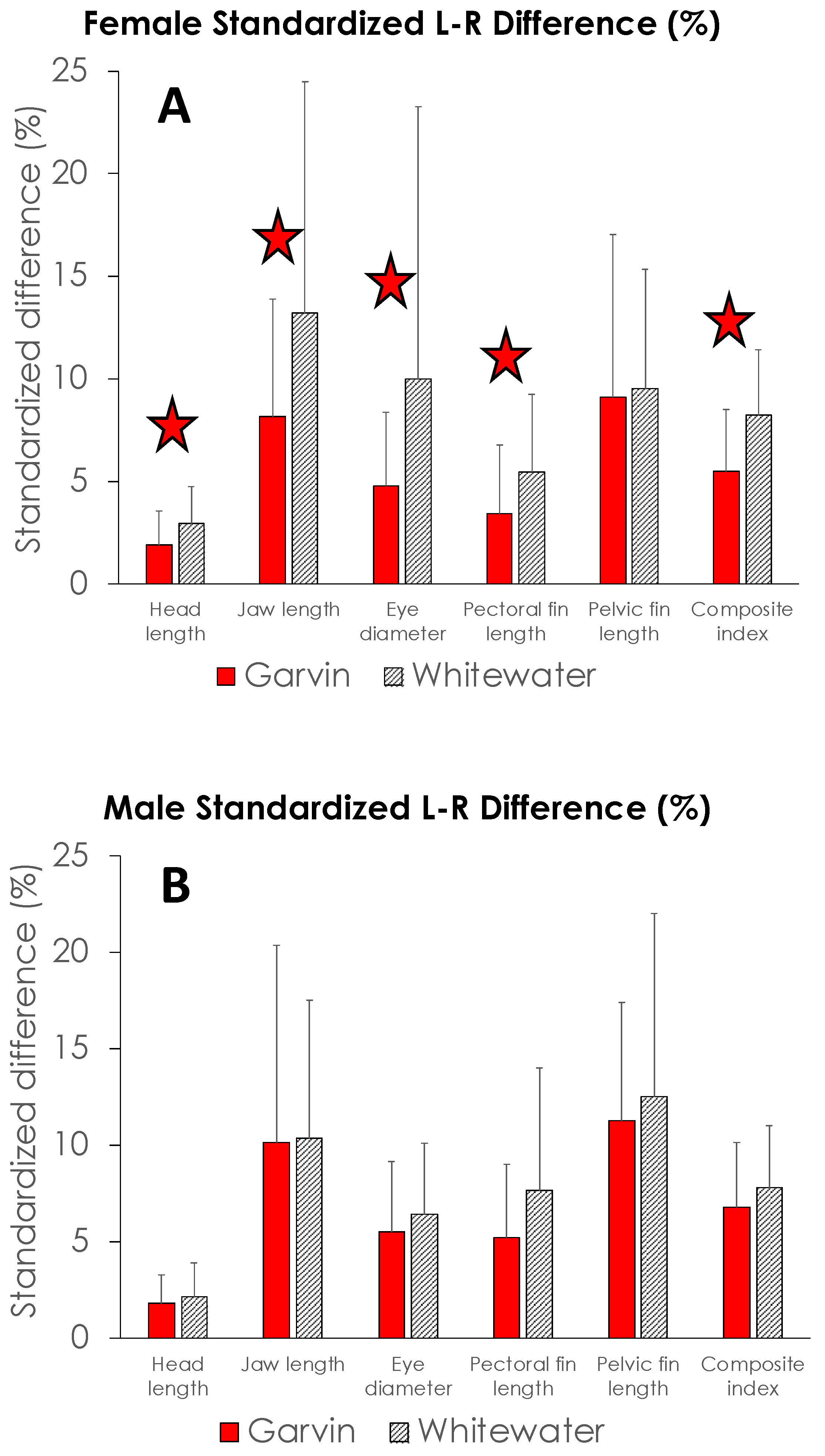
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thronson, A.; Quigg, A. Fifty-five years of fish kills in coastal Texas. Estuar. Coasts 2008, 31, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, N.B.D.; Bueno, I.; Poo-Muñoz, D.A.; Knowles, S.J.; Massarani, S.; Rettkowski, R.; Shen, L.; Rantala, H.; Phelps, P.L.F.; Escobar, L.E. Retrospective and predictive investigation of fish kill events. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2019, 31, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnaser, A.C.; Mundahl, N.D. Recovery of a headwater stream population of brown trout after a fish kill in southeastern Minnesota, USA. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2022, 105, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colborn, T.; vom Saal, F.S.; Soto, A.M. Developmental effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. Environ. Health Perspect. 1993, 101, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, J.R.; McCoy, K.A. A qualitative meta-analysis reveals consistent effects of atrazine on freshwater fish and amphibians. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, D.E.; Bonisoli-Alquati, A.; Mousseau, T.A. The use of fluctuating asymmetry as a measure of environmentally induced developmental instability: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 30, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.P.; Burskey, J.L. Deformity, erosion, lesion, and tumor occurrence, fluctuating asymmetry, and population parameters for bluntnose minnow (Pimephales notatus) as indicators of recovering water quality in a Great Lakes area of concern, USA. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 70, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, K.A.; Bortnick, L.J.; Campbell, C.M.; Hamlin, H.J.; Guillette, L.J., Jr.; St. Mary, C. Agriculture alters gonadal form and function in the toad Bufo marinus. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1526–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelsen, S.; Schaefer, J.; Peterson, M.S. Fluctuating asymmetry in Menidia beryllina before and after the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Minnesota Pollution Control Agency. Minnesota’s Impaired Waters List. 2023. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/air-water-land-climate/minnesotas-impaired-waters-list (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Muldoon, B.M.; Hogan, N.S. Biomarker responses to estrogen and androgen exposure in the brook stickleback (Culaea inconstans): A new bioindicator species for endocrine disrupting compounds. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 180, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, R.D.; Runnalls, T.; Russell, P.M. Histopathologic biomarkers in three-spined sticklebacks, Gasterosteus aculeatus, from several rivers in southern England that meet the Freshwater Fisheries Directive. Ecotoxicology 2002, 11, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, G.C. Fishes of Wisconsin; University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1983; pp. 777–781. Available online: https://search.library.wisc.edu/digital/AWFIWUVZSK4EFH9B (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Hecter, R.P.; Moodie, P.F.; Moodie, G.E.E. Pectoral fin asymmetry, dimorphism and fecundity in the brook stickleback, Culaea inconstans. Behaviour 2000, 137, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajus, D.L.; Golovin, P.V.; Yurtseva, A.O.; Ivanova, T.S.; Dorgham, A.S.; Ivanov, M.V. Fluctuating asymmetry as an indicator of stress and fitness in stickleback: A review of the literature and examination of cranial structures. Evol. Ecol. Res. 2019, 20, 83–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrey, M.; Martinovic, D.; Backe, W.; Andrews, A. Pharmaceuticals and Chemicals of Concern in Rivers: Occurrence and Biological Effects. 2017. Minnesota Pollution Control Agency, Document Number tdr-g1-20, Saint Paul, Minnesota, USA. Available online: www.pca.state.mn.us/sites/default/files/tdr-g1-20.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Mundahl, N.D.; Hunt, A.M. Recovery of stream invertebrates after catastrophic flooding in southeastern Minnesota, USA. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2011, 26, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundahl, N.D. Analysis of a catch-and-harvest fishing contest for brown trout spanning 50+ years: Long-term trends influenced by fisheries management actions and angler behavior. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2022, 42, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundahl, N.D.; Mundahl, E.D. Aquatic community structure and stream habitat in a karst agricultural landscape. Ecol. Process. 2022, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundahl, N.D.; Schnaser, A.C. Abundance, cover use, and clustering of brown trout spawning redds during stream habitat rehabilitation. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2023, 32, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundahl, N.D.; Varela, W.L.; Weaver, C.; Mundahl, E.D.; Cochran-Biederman, J.L. Stream habitats and aquatic communities in an agricultural watershed: Changes related to a mandatory riparian buffer law. Environ. Manag. 2023, 72, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, W.L.; Mundahl, N.D.; Bergen, S.; Staples, D.F.; Cochran-Biederman, J.; Weaver, C.R. Physical and biological stream health in an agricultural watershed after 30+ years of targeted conservation practices. Water 2023, 15, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ney, J.J. Practical use of biological statistics. In Inland Fisheries Management in North America, 2nd ed.; Kohler, C.C., Hubert, W.A., Eds.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1999; pp. 167–191. [Google Scholar]
- Crim, L.W.; Glebe, B.D. Reproduction. In Methods for Fish Biology; Schreck, C.B., Moyle, P.B., Eds.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1990; pp. 529–553. [Google Scholar]
- Popović, N.T.; Čižmek, L.; Babic, S.; Strunjak-Perović, I.; Čož-Rakovac, R. Fish liver damage related to the wastewater treatment plant effluents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 48739–48768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rand, G.M.; Petrocelli, S.R. Fundamentals of Aquatic Toxicology: Methods and Applications; FMC Corporation: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, M.A.; Curry, R.A.; Arciszewski, T.J.; Munkittrick, K.R.; Brasfield, S.M. The biology and ecology of slimy sculpin: A recipe for effective environmental monitoring. FACETS 2018, 3, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.R.; Owen, S.F.; Peters, J.; Zhang, Y.; Soffker, M.; Paull, G.C.; Hosken, D.J.; Wahab, M.A.; Tyler, C.R. Climate change and pollution speed declines in zebrafish populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1237–E1246. Available online: https://www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1416269112 (accessed on 10 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Affandi, F.A.; Ishak, M.Y. Impacts of suspended sediment and metal pollution from mining activities oon riverine fish population—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16939–16951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deane, E.E.; and Woo, N.Y.S. Modulation of fish growth hormone levels by salinity, temperature, pollutants and aquaculture related stress: A review. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2009, 19, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruitwagen, G.; Hecht, T.; Pratap, H.B.; Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. Changes in morphology and growth of the mudskipper (Periophthalmus argentilineatus) associated with coastal pollution. Mar. Biol. 2006, 149, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authman, M.M.N.; Zaki, M.S.; Khallaf, E.A.; Abbas, H.H. Use of fish as bio-indicator of the effects of heavy metals pollution. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2015, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, J.B. Aquatic toxicology. In Methods for Fish Biology; Schreck, C.B., Moyle, P.B., Eds.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1990; pp. 491–528. [Google Scholar]
- Diana, J.S. Biology and Ecology of Fishes, 2nd ed.; Biological Sciences Press; Cooper Publishing Group: Traverse City, MI, USA, 2004; 498p. [Google Scholar]
- Slooff, W.; Van Kreijl, C.F.; Baars, A.J. Relative liver weights and xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes of fish from polluted surface waters in the Netherlands. Aquat. Toxicol. 1983, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabacher, D.L.; Baumann, P.C. Enlarged livers and hepatic microsomal mixed-function oxidase components in tumor-bearing brown bullheads from a chemically contaminated river. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1985, 4, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghais, S.M. Acetylcholinesterase, glutathione and hepatosomatic index as potential biomarkers of sewage pollution and depuration in fish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 74, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.M.; Tull, D.L.; De Souza, D.P.; Kouremenos, K.A.; Dayalan, S.; McConville, M.J.; Hassel, K.; Pettigrove, K.J.; Gagnon, M.M. Metabolomics provide sensitive insights into the impacts of low level environmental contamination on fish health—A pilot study. Metabolites 2020, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, R.M.; Sadauskas-Henrique, H.; de Almeida-Val, V.M.F.; Val, A.L.; Nice, H.E.; Gagnon, M.M. Biomarker responses and PAH ratios in fish inhabiting an estuarine urban waterway. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyle, P.; Cech, J., Jr. Fishes: An Introduction to Ichthyology, 5th ed.; Pearson/Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, D.; Burton, M. Essential Fish Biology: Diversity, Structure and Function; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hermita, Z.M.; Gorospe, J.G.; Torres, M.A.J.; Lumasag, G.J.; Demayo, C.G. Fluctuating asymmetry in the body shape of the mottled spinefoot fish, Siganus fuscescens (Houttuyn, 1782) collected from different bays in Mindanao Island, Philippines. Sci. Int. 2013, 25, 857–861. [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg, C.P.; McIntyre, G.S. Geometric morphometrics of developmental instability: Analyzing patterns of fluctuating asymmetry with Procrustes methods. Evolution 1998, 52, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

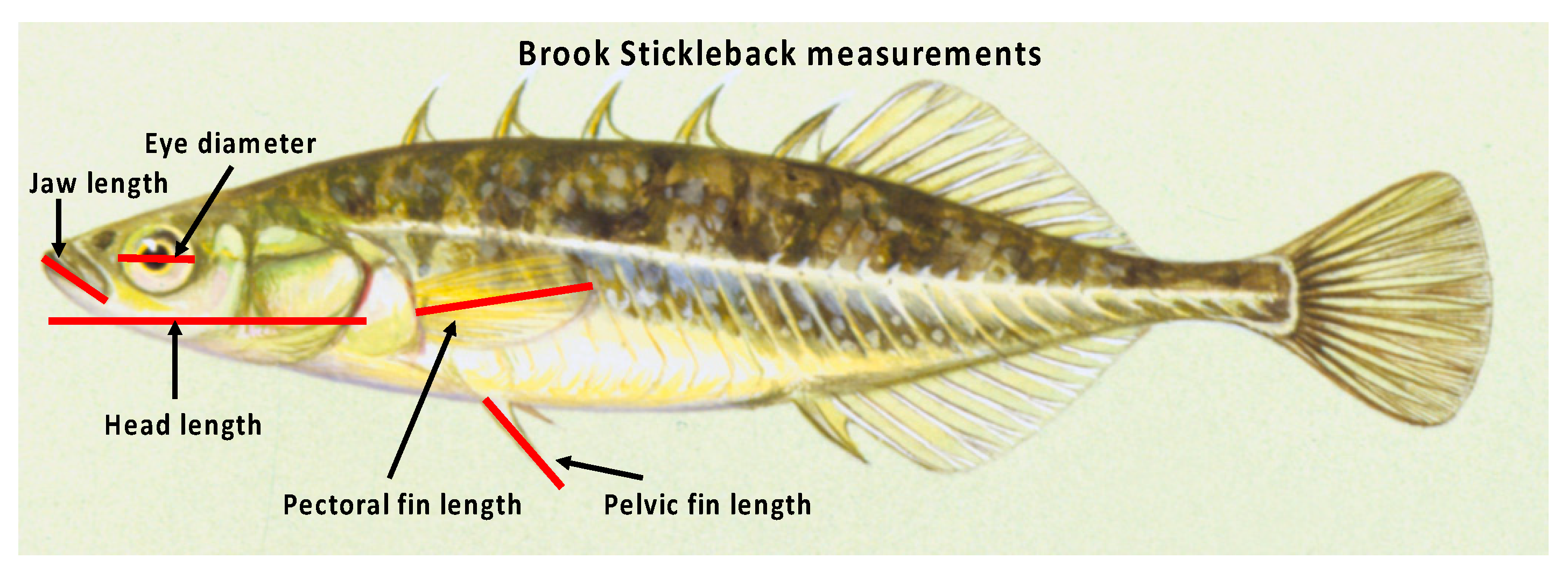
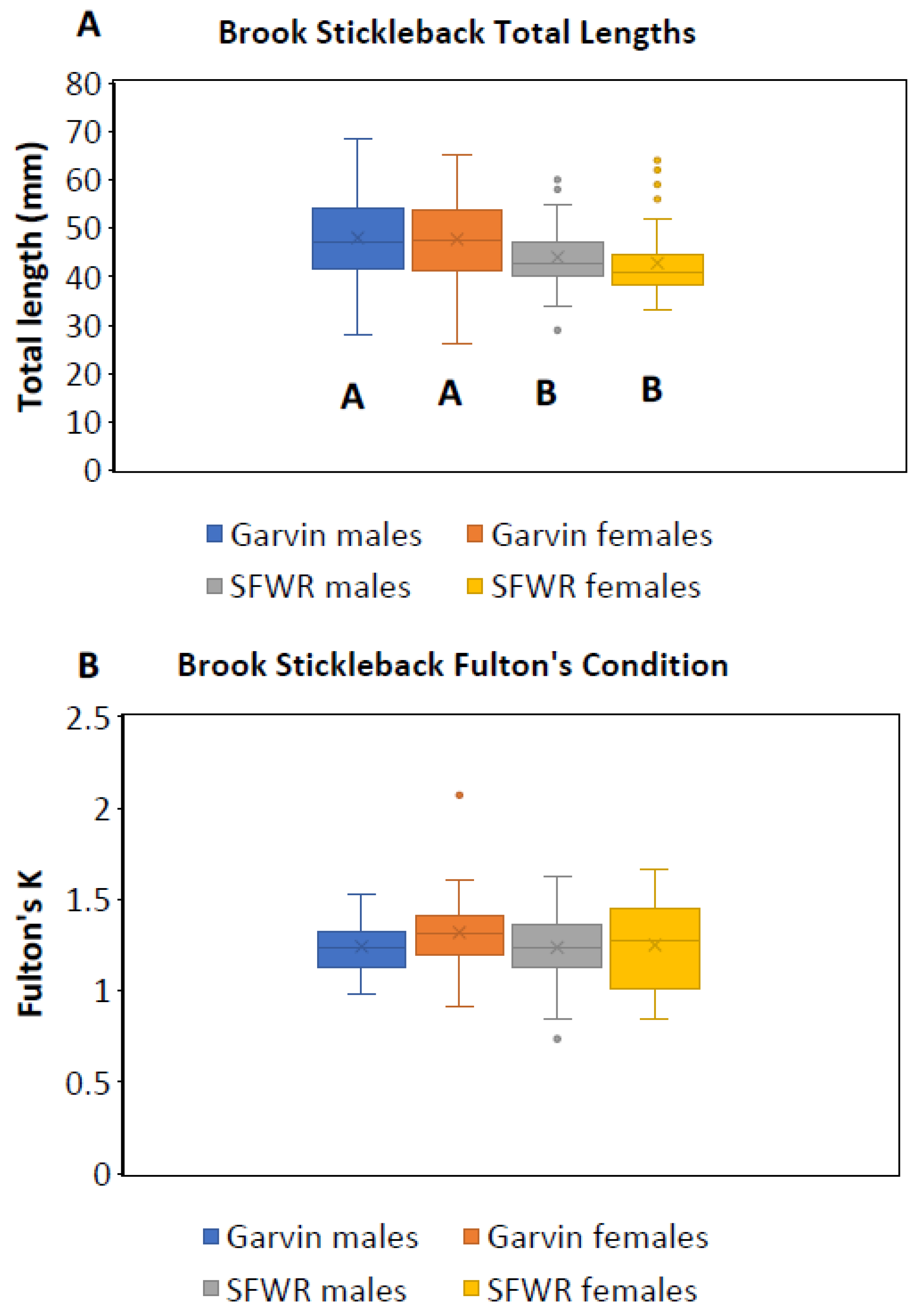
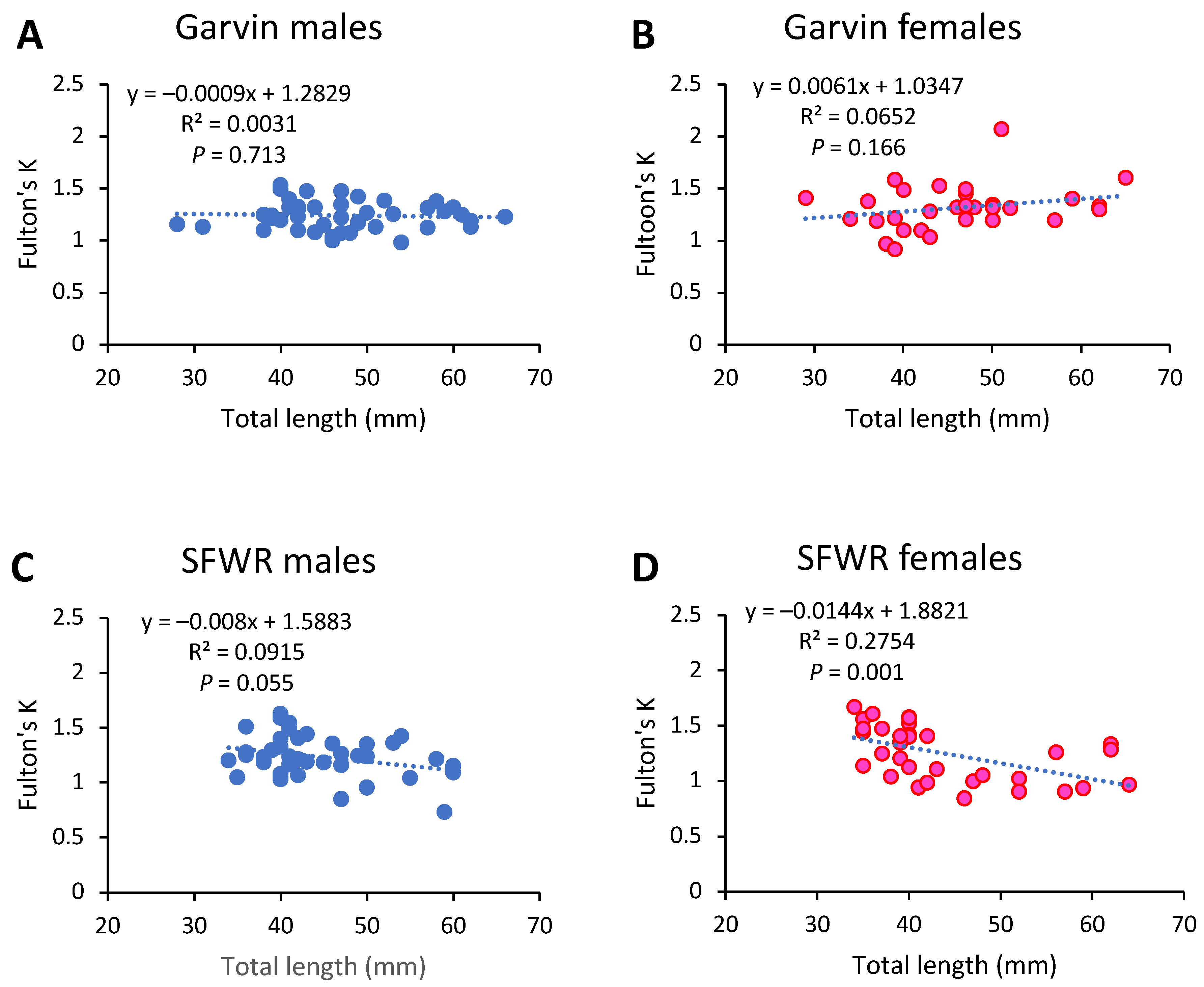
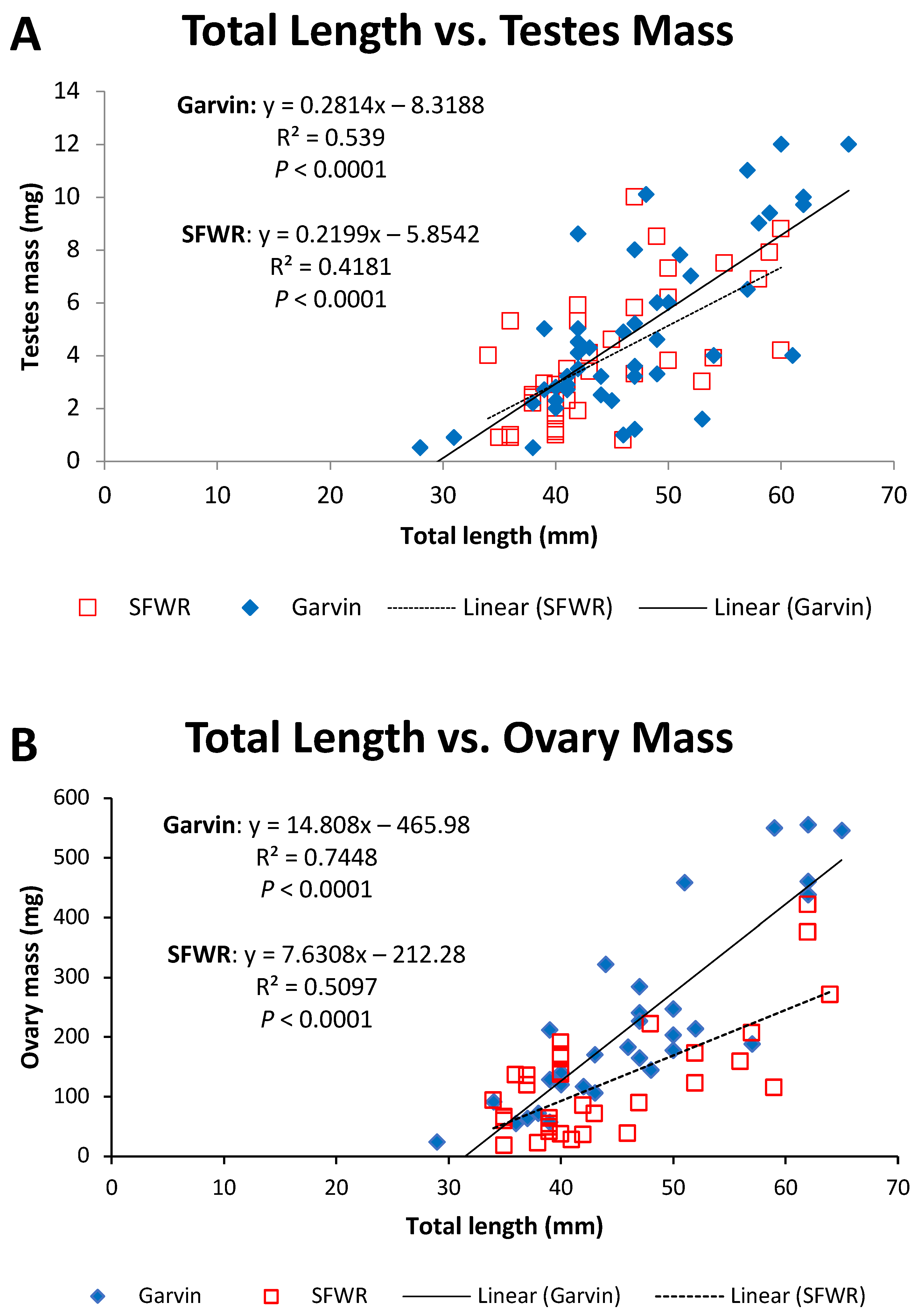
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stream | Sex | N | TL range | N | TL range | N | TL range | Total N |
| Garvin | M | 31 | 28–66 | 15 | 31–49 | 20 | 35–69 | 66 |
| F | 16 | 29–65 | 15 | 34–52 | 29 | 26–61 | 60 | |
| SFWR | M | 26 | 34–60 | 15 | 35–59 | 34 | 29–61 | 75 |
| F | 26 | 34–62 | 15 | 35–64 | 28 | 34–62 | 62 | |
| Total N | 92 | 60 | 111 | 263 | ||||
| ANCOVA Test | Homogeneity of Slopes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | F Value | p Value | F Value | p Value |
| Testes masses | 0.54 | 0.464 | 1.11 | 0.295 |
| Ovary masses | 12.63 | <0.001 | 12.02 | 0.001 |
| Male GSI | 0.04 | 0.842 | 0.01 | 0.921 |
| Female GSI | 10.39 | 0.002 | 0.14 | 0.710 |
| Oocyte numbers | 4.02 | 0.049 | 0.00 | 1.000 |
| Oocyte masses | 11.85 | 0.001 | 5.87 | 0.018 |
| Male HSI | 23.82 | <0.001 | 2.35 | 0.129 |
| Female HSI | 9.87 | 0.003 | 1.46 | 0.232 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mundahl, N.D.; Hoffmann, K.A. Condition, Reproductive Fitness, and Fluctuating Asymmetry in Brook Stickleback: Responses to Anthropogenic Runoff. Fishes 2023, 8, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110557
Mundahl ND, Hoffmann KA. Condition, Reproductive Fitness, and Fluctuating Asymmetry in Brook Stickleback: Responses to Anthropogenic Runoff. Fishes. 2023; 8(11):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110557
Chicago/Turabian StyleMundahl, Neal D., and Kelsey A. Hoffmann. 2023. "Condition, Reproductive Fitness, and Fluctuating Asymmetry in Brook Stickleback: Responses to Anthropogenic Runoff" Fishes 8, no. 11: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110557
APA StyleMundahl, N. D., & Hoffmann, K. A. (2023). Condition, Reproductive Fitness, and Fluctuating Asymmetry in Brook Stickleback: Responses to Anthropogenic Runoff. Fishes, 8(11), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110557






