Habitat Use of Two Coral-Associated Cryptobenthic Gobiid Fishes (Family: Gobiidae) in the Southern Caribbean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
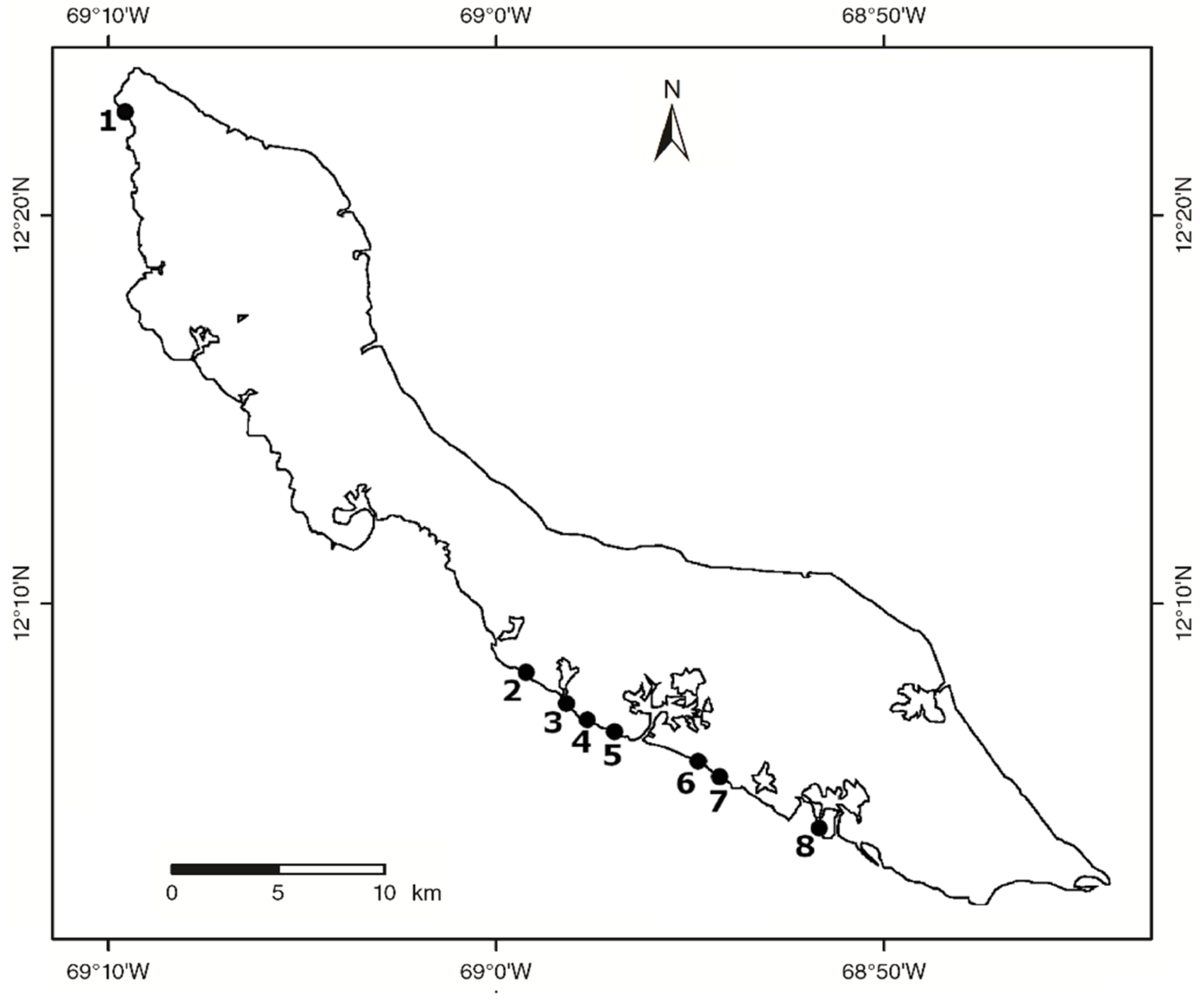
2.1. Study Locations
2.2. Data Collecting
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
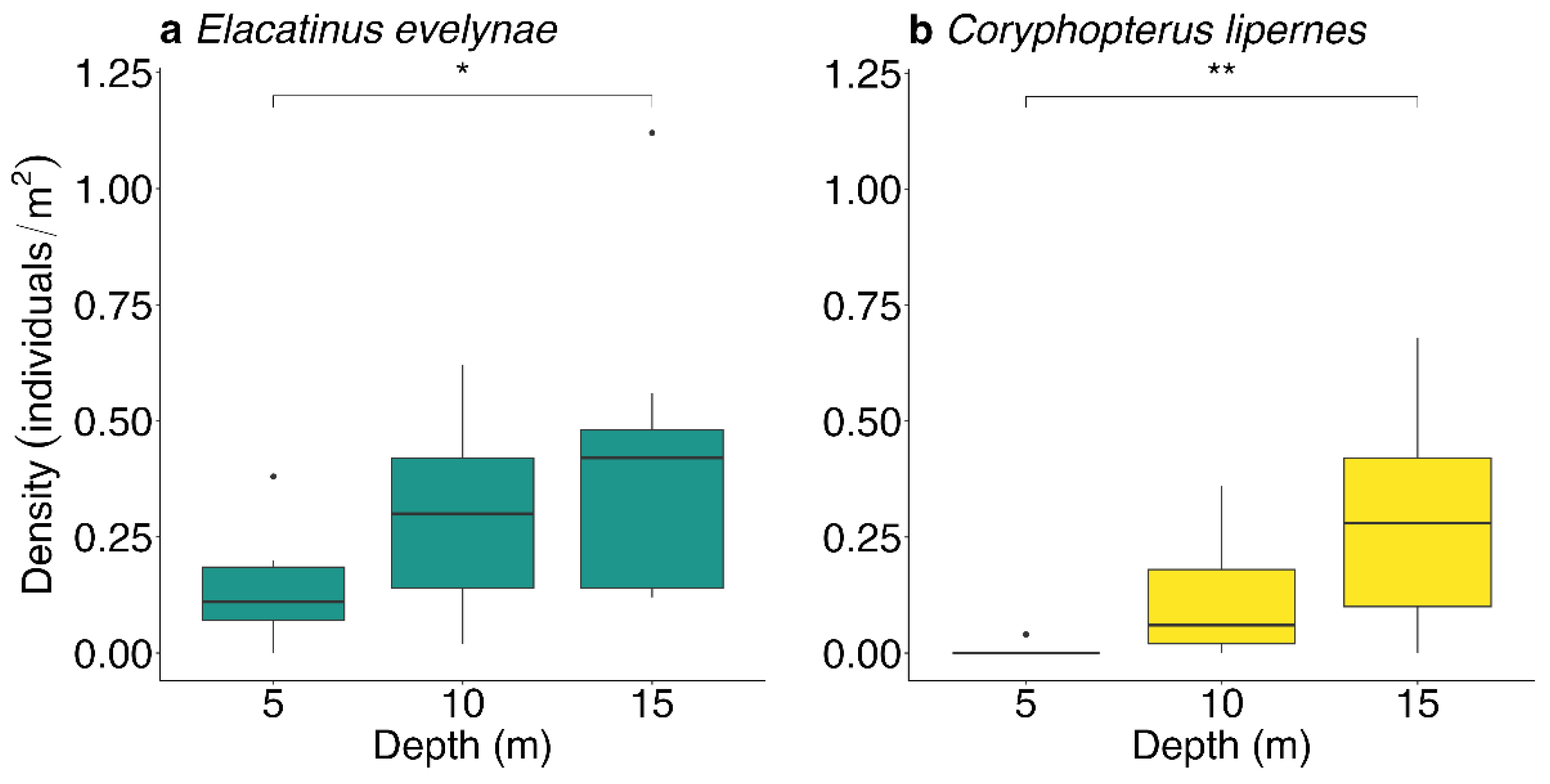
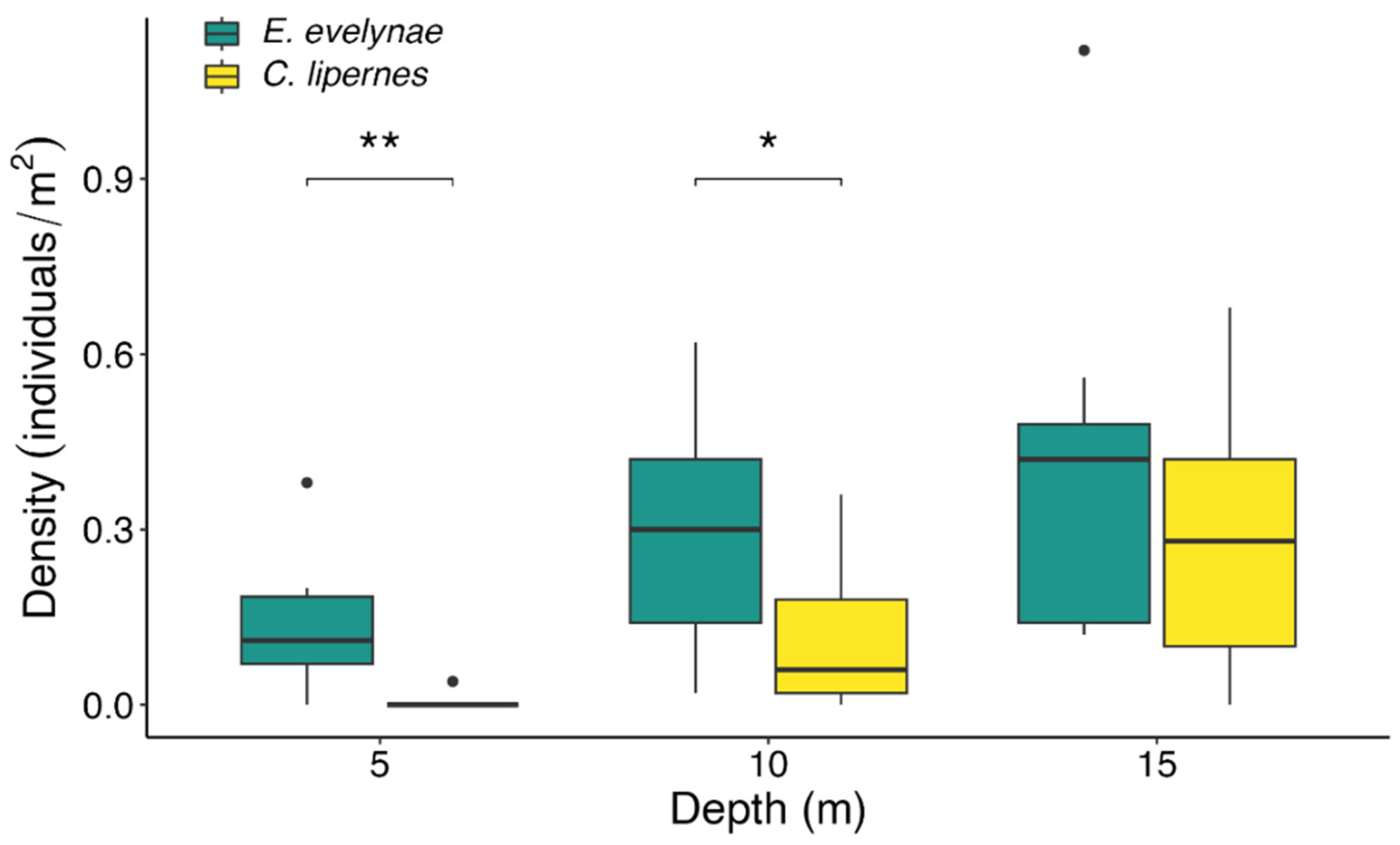
3.1. Depth Distributions
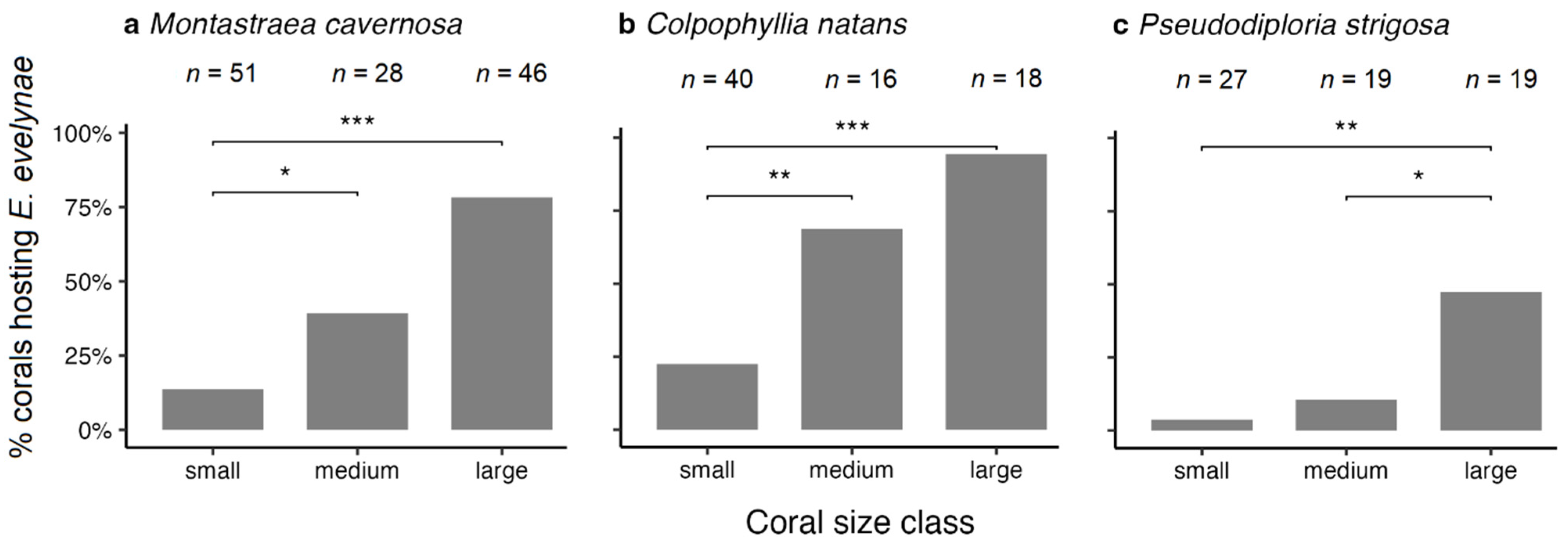
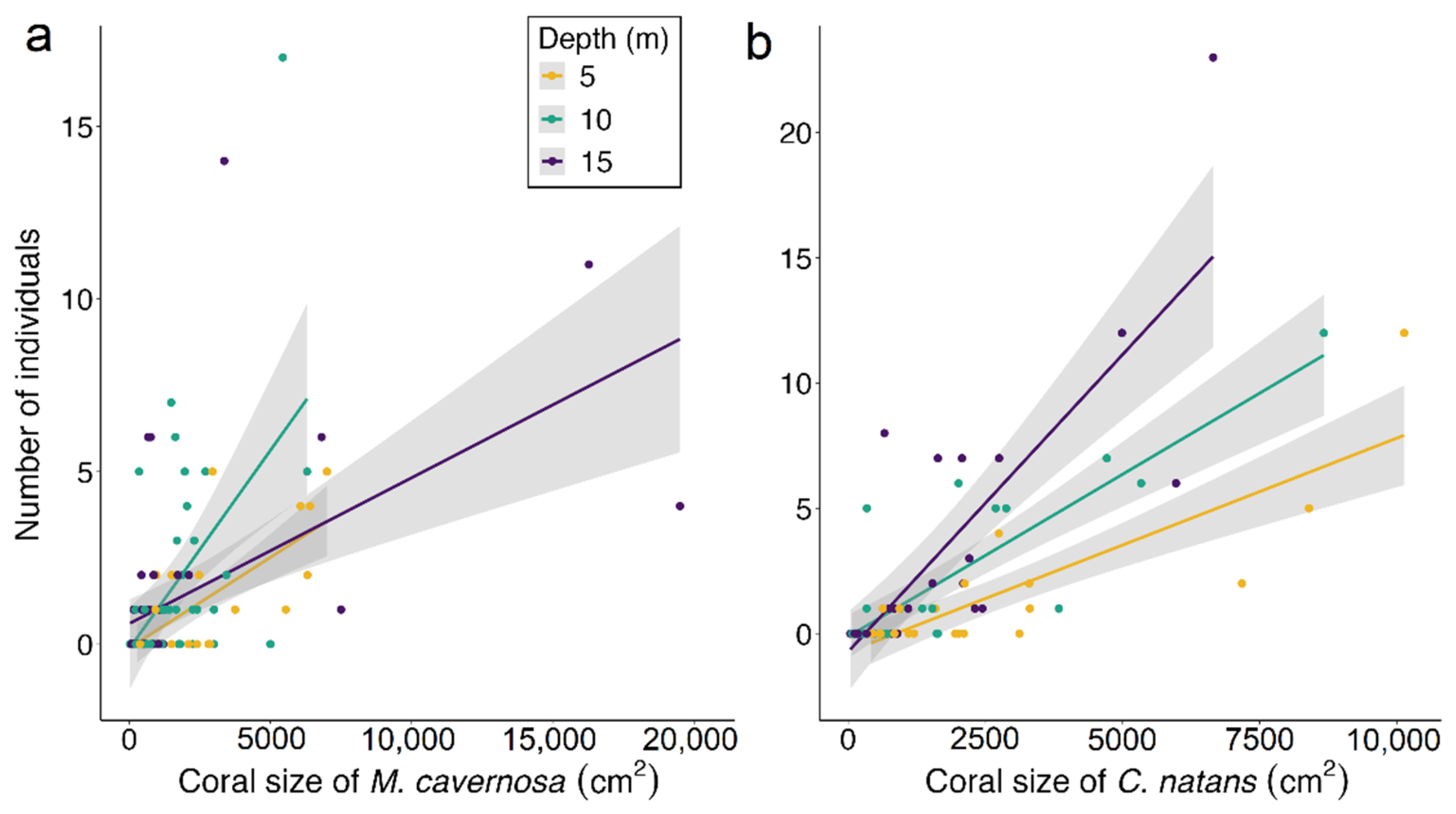
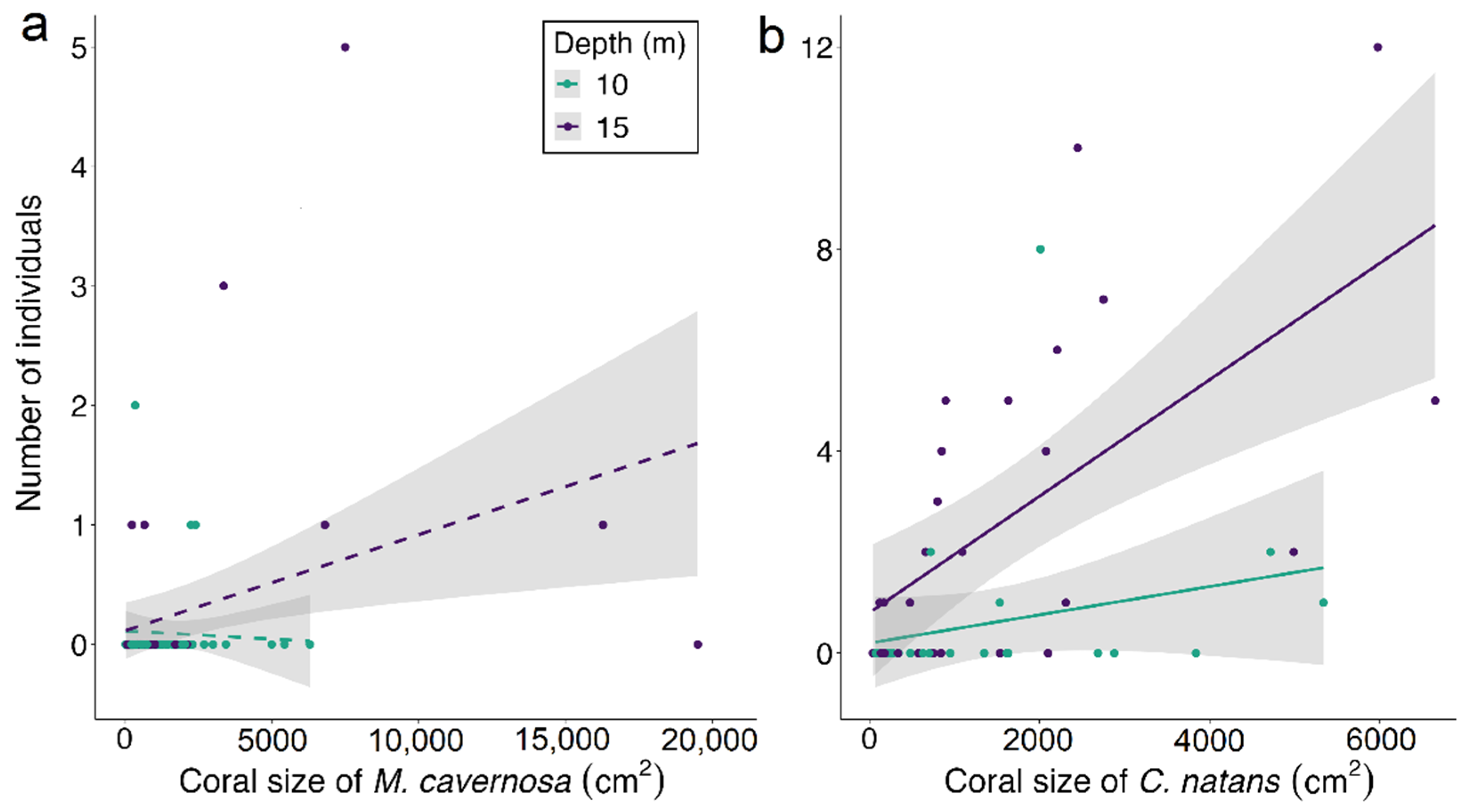
3.2. Influence of Body Size on Depth Distribution
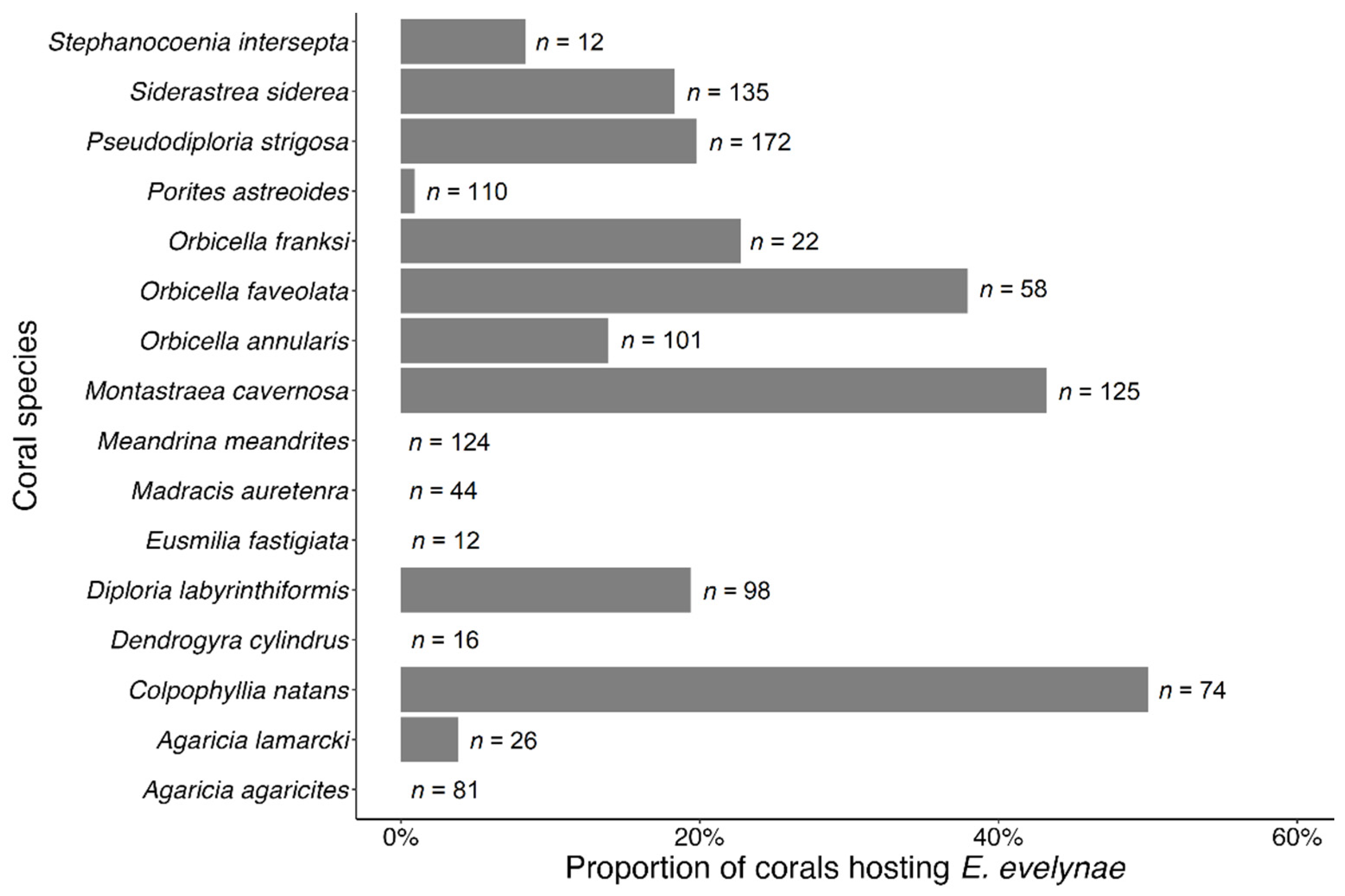
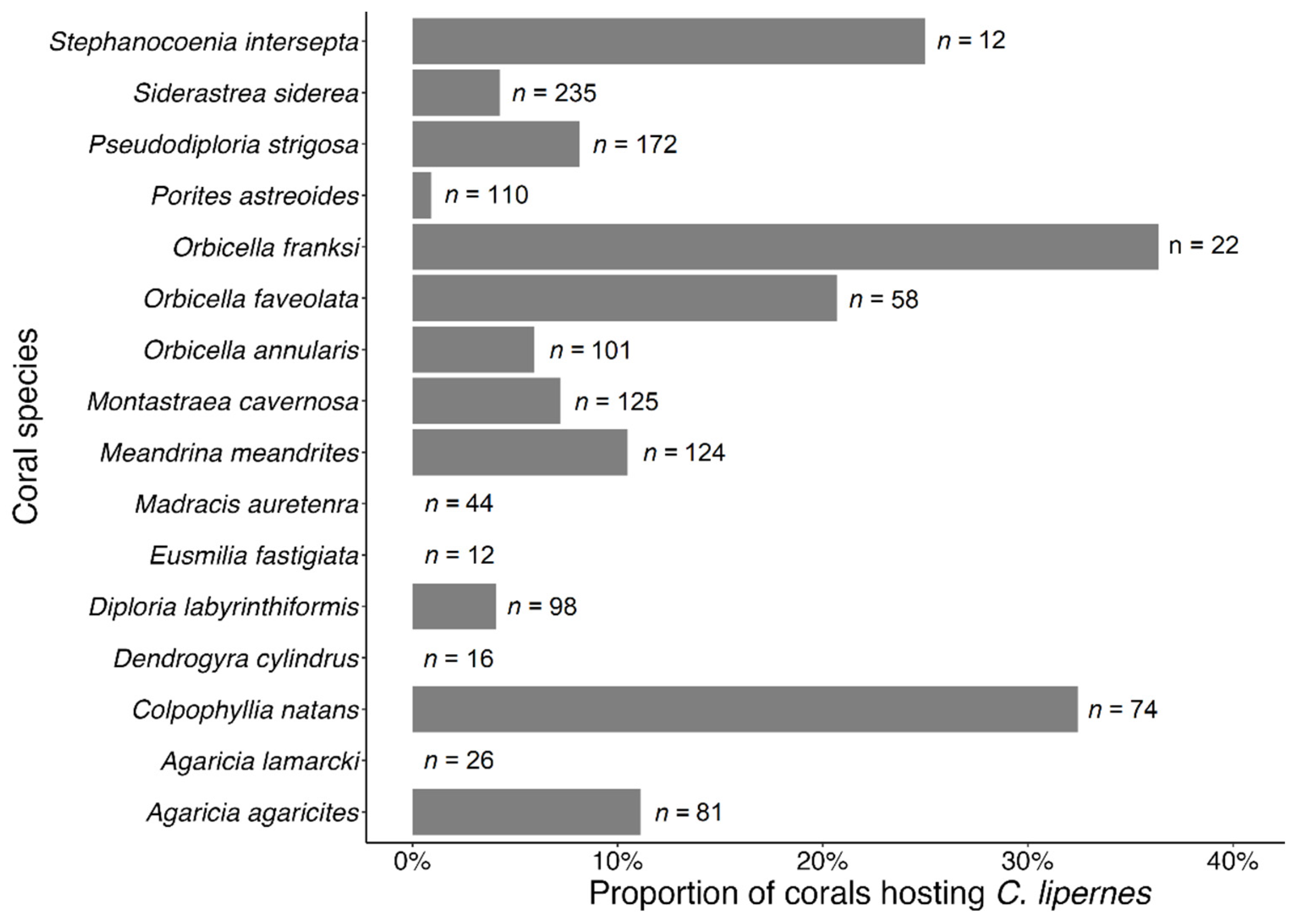
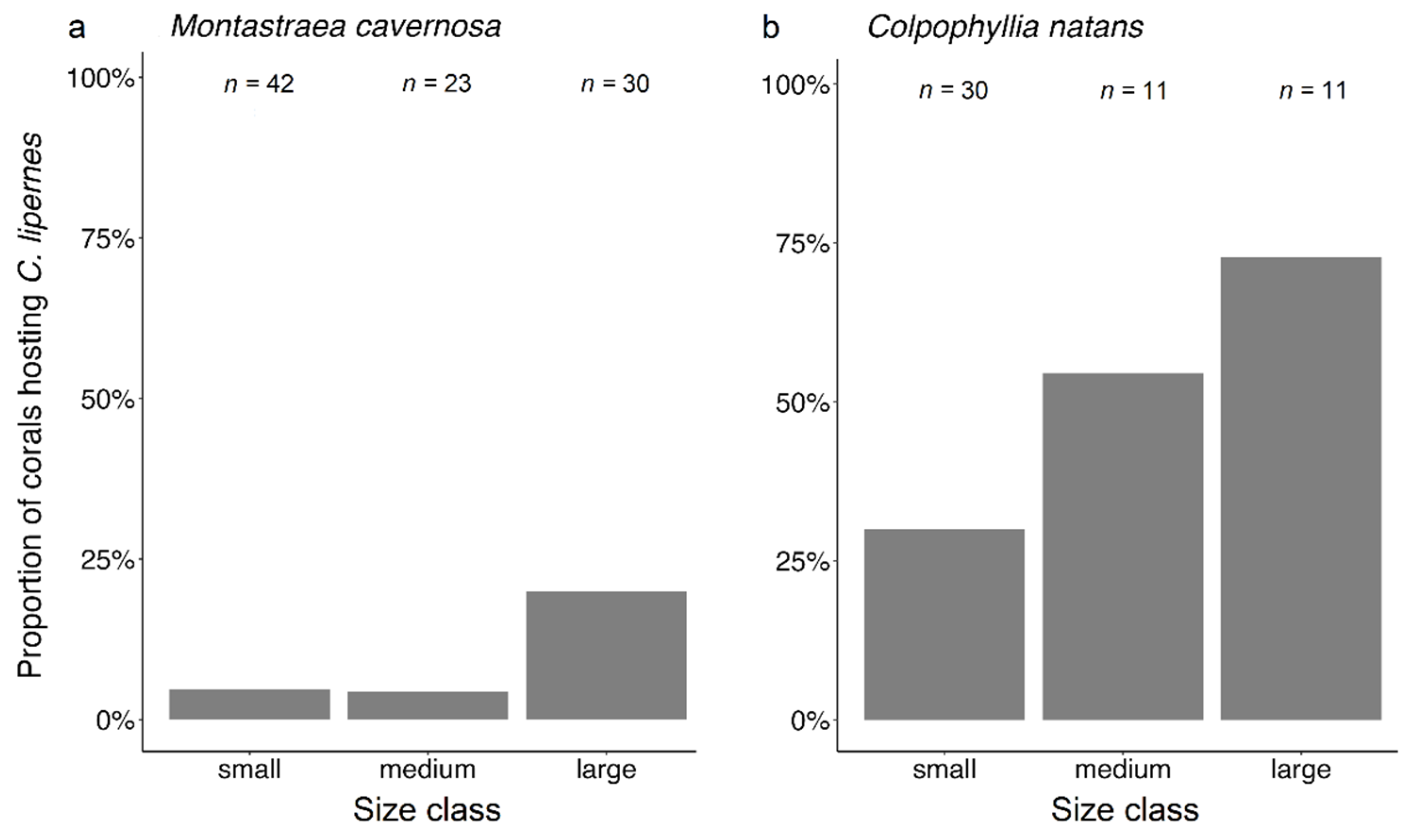
3.3. Coral Habitat
4. Discussion
4.1. Depth Distribution
4.2. Relation between Goby Body Size and Depth Distribution
4.3. Coral Habitat
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scott, P.J.B. Associations between corals and macro-infaunal invertebrates in Jamaica, with a list of Caribbean and Atlantic coral associates. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1987, 40, 271–286. [Google Scholar]
- Zann, L.P. A review of macrosymbiosis in the coral reef ecosystem. Int. J. Parasitol. 1987, 17, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, W.K. Distribution and ecology of animals associated with branching corals (Acropora spp.) from the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1994, 55, 193–211. [Google Scholar]
- Stella, J.S.; Pratchett, M.S.; Hutchings, P.A.; Jones, G.P. Coral-associated invertebrates: Diversity, ecological importance and vulnerability to disturbance. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2011, 49, 43–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; van der Meij, S.E.T.; Fransen, C.H.J.M. The mushroom coral as a habitat. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2012, 92, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; van Beusekom, M.; ten Hove, H.A.; Ivanenko, V.N.; van der Meij, S.E.T.; van Moorsel, G.W.N.M. Helioseris cucullata as a host coral at St. Eustatius. Dutch Caribbean. Mar. Biodivers. 2017, 47, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counsell, C.W.W.; Donahue, M.J.; Edwards, K.F.; Franklin, E.C.; Hixon, M.A. Variation in coral-associated cryptofaunal communities across spatial scales and environmental gradients. Coral Reefs 2018, 37, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperaki, M.M.; Hill, C.E.; Hoeksema, B.W. The effects of wave exposure and host cover on coral-associated fauna of a centuries-old artificial reef in the Caribbean. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 176, 106536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Schoot, R.J.; Hoeksema, B.W. Abundance of coral-associated fauna in relation to depth and eutrophication along the leeward side of Curaçao, southern Caribbean. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 181, 105738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, A.C.; Muruga, P.; Bellwood, D.R. On the evolution of fish–coral interactions. Ecol. Lett. 2023, 26, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.K.K.; Wong, K.J.H.; Cheng, Y.R. Biogeography and host usage of coral-associated crustaceans: Barnacles, copepods, and gall crabs as model organisms. In The Natural History of the Crustacea: Evolution and Biogeography of the Crustacea; Thiel, M., Poore, G.C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; Volume 8, pp. 183–215. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanenko, V.N.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Mudrova, S.V.; Nikitin, M.A.; Martínez, A.; Rimskaya-Korsakova, N.N.; Berumen, M.L.; Fontaneto, D. Lack of host specificity of copepod crustaceans associated with mushroom corals in the Red Sea. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 127, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korzhavina, O.A.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Ivanenko, V.N. A review of Caribbean Copepoda associated with reef-dwelling cnidarians, echinoderms and sponges. Contrib. Zool. 2019, 88, 297–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; García-Hernández, J.E. Host-related morphological variation of dwellings inhabited by the crab Domecia acanthophora in the corals Acropora palmata and Millepora complanata (Southern Caribbean). Diversity 2020, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Fransen, C.H.J.M. Space partitioning by symbiotic shrimp species cohabitating in the mushroom coral Heliofungia actiniformis at Semporna, eastern Sabah. Coral Reefs 2011, 30, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rauch, C.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Hermanto, B.; Fransen, C.H.J.M. Shrimps of the genus Periclimenes (Crustacea, Decapoda, Palaemonidae) associated with mushroom corals (Scleractinia, Fungiidae): Linking DNA barcodes to morphology. Contrib. Zool. 2019, 88, 201–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransen, C.H.J.M.; van der Veer, E.; Ďuriš, Z. A new species of Palaemonella (Decapoda, Caridea, Palaemonidae) associated with scleractinian corals of the genus Euphyllia Dana. Crustaceana 2023, 96, 345–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittenberger, A.; Gittenberger, E. Cryptic, adaptive radiation of endoparasitic snails: Sibling species of Leptoconchus (Gastropoda: Coralliophilidae) in corals. Org. Divers. Evol. 2011, 11, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittenberger, A.; Hoeksema, B.W. Habitat preferences of coral-associated wentletrap snails (Gastropoda: Epitoniidae). Contrib. Zool. 2013, 82, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potkamp, G.; Vermeij, M.J.A.; Hoeksema, B.W. Genetic and morphological variation in corallivorous snails (Coralliophila spp.) living on different host corals at Curaçao, southern Caribbean. Contrib. Zool. 2017, 86, 111–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Harper, C.E.; Langdon-Down, S.J.; van der Schoot, R.J.; Smith-Moorhouse, A.; Spaargaren, R.; Timmerman, R.F. Host range of the coral-associated worm snail Petaloconchus sp. (Gastropoda: Vermetidae), a newly discovered cryptogenic pest species in the southern Caribbean. Diversity 2022, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, S.K.F.; Qiu, J.W. Distribution, dietary preference and larval settlement preference of three scleractinian-coral-eating nudibranchs Phestilla spp. (Nudibranchia: Trinchesiidae) from Hong Kong waters. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 61, 102858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, K. Boring and growth in chemically boring bivalves from the Caribbean, Eastern Pacific and Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. Senckenb. Marit. 1990, 22, 101–154. [Google Scholar]
- Maggioni, D.; Arrigoni, R.; Seveso, D.; Galli, G.; Berumen, M.L.; Denis, V.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Huang, D.; Manca, F.; Pica, D.; et al. Evolution and biogeography of the Zanclea-Scleractinia symbiosis. Coral Reefs 2022, 41, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunihiro, S.; Farenzena, Z.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Groenenberg, D.S.; Hermanto, B.; Reimer, J.D. Morphological and phylogenetic diversity of Waminoa and similar flatworms (Acoelomorpha) in the western Pacific Ocean. Zoology 2019, 136, 125692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molodtsova, T.N.; Britayev, T.A.; Martin, D. Cnidarians and their polychaete symbionts. In The Cnidaria, Past, Present and Future; Goffredo, S., Dubinsky, Z., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 387–413. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; ten Hove, H.A. The invasive sun coral Tubastraea coccinea hosting a native Christmas tree worm at Curaçao, Dutch Caribbean. Mar. Biodivers. 2017, 47, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Timmerman, R.F.; Spaargaren, R.; Smith-Moorhouse, A.; van der Schoot, R.J.; Langdon-Down, S.J.; Harper, C.E. Morphological modifications and injuries of corals caused by symbiotic feather duster worms (Sabellidae) in the Caribbean. Diversity 2022, 14, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S. Multiscale habitat associations of detrivorous blennies (Blenniidae: Salariini). Coral Reefs 2001, 20, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, T.; Hoeksema, B.W. Habitat selection of the coral-dwelling spinyhead blenny, Acanthemblemaria spinosa, at Curaçao, Dutch Caribbean. Mar. Biodivers. 2017, 47, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gardiner, N.M.; Jones, G.P. Habitat specialisation and overlap in a guild of coral reef cardinalfishes (Apogonidae). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 305, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratchett, M.S.; Coker, D.J.; Jones, G.P.; Munday, P.L. Specialization in habitat use by coral reef damselfishes and their susceptibility to habitat loss. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2, 2168–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonan, S.H.C.; Jones, G.P.; Pratchett, M.S. Coral size, health and structural complexity: Effects on the ecology of a coral reef damselfish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 456, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, D.W.; Johnson, R.K. Assemblage structure and habitat associations of Western Caribbean gobies (Teleostei: Gobiidae). Copeia 1999, 2, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, A.R.; Hoeksema, B.W. Mushroom corals (Fungiidae) in the Davao Gulf, Philippines, with records of associated fish and other cryptofauna. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2017, 65, 198–206. [Google Scholar]
- Doll, P.C.; Munday, P.L.; Bonin, M.C.; Jones, G.P. Habitat specialisation and overlap in coral reef gobies of the genus Eviota (Teleostei: Gobiidae). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 677, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahara, N. Cryptic diversity of Eviota (Teleostei: Gobiidae) and their habitat use in the shallow waters of Okinawa Island. Mar. Biodivers. 2023, 53, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, A.R.; Hoeksema, B.W. Cryptobenthic fishes and co-inhabiting shrimps associated with the mushroom coral Heliofungia actiniformis (Fungiidae) in the Davao Gulf, Philippines. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2015, 98, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keita, K.; Takuma, F. Records of the Pughead pipefsh, Bulbonaricus brauni (Gasterosteiformes: Syngnathidae), from Amami-oshima Island, Central Ryukyu Archipelago, Southern Japan. S. Pac. Stud. 2015, 36, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeksema, B.W. The hidden biodiversity of tropical coral reefs. Biodiversity 2017, 18, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depczynski, M.; Bellwood, D.R. The role of cryptobenthic reef fishes in coral reef trophodynamics. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 256, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depczynski, M.; Bellwood, D.R. Microhabitat utilisation patterns in cryptobenthic coral reef fish communities. Mar. Biol. 2004, 145, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadia, G.N.; Pezold, F.L.; Smith, D.J. Cryptobenthic fish biodiversity and microhabitat use in healthy and degraded coral reefs in SE Sulawesi, Indonesia. Mar. Biodivers. 2012, 42, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernaman, V.; Munday, P.L. Life-history characteristics of coral reef gobies. I. Growth and life-span. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 290, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernaman, V.; Munday, P.L. Life-history characteristics of coral reef gobies. II. Mortality rate, mating system and timing of maturation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 290, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeken, N.S.; Selwyn, J.D.; Hogan, J.D. Determining the life history strategy of the cryptobenthic reef gobies Coryphopterus hyalinus and C. personatus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 659, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalitsis, M.; Morais, R.A.; Bellwood, D.R. Small predators dominate fish predation in coral reef communities. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depczynski, M.; Fulton, C.J.; Marnane, M.J.; Bellwood, D.R. Life history patterns shape energy allocation among fishes on coral reefs. Oecologia 2007, 153, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, M.; Meyer, C.P.; Mills, S.C. Metabarcoding dietary analysis of coral dwelling predatory fish demonstrates the minor contribution of coral mutualists to their highly partitioned, generalist diet. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, S.J.; Casey, J.M.; Meyer, C.P. Dietary and habitat niche partitioning in congeneric cryptobenthic reef fish species. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvuloni, A.; Armoza-Zvuloni, R.; Loya, Y. Structural deformation of branching corals associated with the vermetid gastropod Dendropoma maxima. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 363, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, S.J.; Tornabene, L.; Goatley, C.H.R.; Casey, J.M.; Morais, R.A.; Côté, I.M.; Baldwin, C.C.; Parravicini, V.; Schiettekatte, N.M.; Bellwood, D.R. Demographic dynamics of the smallest marine vertebrates fuel coral-reef ecosystem functioning. Science 2019, 364, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, R.E. A critique of the visual census method for assessing coral reef fish populations. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1982, 32, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Willis, T.J. Visual census methods underestimate density and diversity of cryptic reef fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 59, 1408–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, S.J.; Goatley, C.H.R.; Bellwood, D.R.; Tornabene, L. The hidden half: Ecology and evolution of cryptobenthic fishes on coral reefs. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2018, 93, 1846–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Vaniz, W.; Jelks, H.; Rocha, L. Relevance of cryptic fishes in biodiversity assessments: A case study at Buck Island Reef National Monument, St. Croix. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2006, 79, 17–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman, J.L.; Bellwood, D.R. Reef fish assemblages: A re-evaluation using enclosed rotenone stations. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 206, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessey, C.; Depczynski, M.; Goetze, J.S.; Moore, G.; Fulton, C.J.; Snell, M.; Parsons, S.K.; Berry, O.; Wilson, S. Cryptic biodiversity: A portfolio-approach to coral reef fish surveys. Limnol. Oceanogr. Meth. 2023, 21, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, C.Y.M.; Klanten, O.S.; Hing, M.L.; Dowton, M.; Wong, M.Y.L. Uneven declines between corals and cryptobenthic fish symbionts from multiple disturbances. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.L. Habitat loss, resource specialization, and extinction on coral reefs. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2004, 10, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.S.; Grande, T.; Wilson, M. Fishes of the World, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase. Gobiiformes. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1517500 (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Sale, P.F.; Douglas, W.A.; Doherty, P.J. Choice of microhabitats by coral reef fishes at settlement. Coral Reefs 1984, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.S.; van Tassell, J.L. Observations on microhabitat utilization by three widely distributed neotropical gobies of the genus Elacatinus. Copeia 2002, 2002, 1134–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirnwöber, M.; Herler, J. Microhabitat specialisation and ecological consequences for coral gobies of the genus Gobiodon in the Gulf of Aqaba, northern Red Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 342, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.L.; Jones, G.P.; Caley, M.J. Habitat specialisation and the distribution and abundance of coral-dwelling gobies. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 152, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwamura, T.; Yogo, Y.; Nakashima, Y. Population dynamics of goby Paragobiodon echinocephalus and host coral Stylophora pistillata. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 103, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, J.P.; Munday, P.L. Intraspecific competition controls spatial distribution and social organisation of the coral-dwelling goby Gobiodon histrio. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 278, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.L.; Pierce, S.J.; Jones, G.P.; Larson, H.K. Habitat use, social organization and reproductive biology of the seawhip goby, Bryaninops yongei. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 53, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiemer, L.; Niedermüller, S.; Herler, J. The influence of colony size and coral health on the occupation of coral-associated gobies (Pisces: Gobiidae). Coral Reefs 2009, 28, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhlke, J.E.; Robins, C.R. Western Atlantic seven-spined gobies, with descriptions of ten new species and a new genus, and comments on Pacific relatives. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila. 1968, 120, 45–174. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase. Elacatinus evelynae. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=280601 (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Böhlke, J.E.; Robins, C.R. The taxonomic position of the West Atlantic goby, Eviota personata, with descriptions of two new related species. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila. 1962, 114, 175–189. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase. Coryphopterus lipernes. 2023. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=276431 (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Taylor, M.S.; Hellberg, M.E. Genetic evidence for local retention of pelagic larvae in a Caribbean reef fish. Science 2003, 299, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.S.; Ruben, P. Cleaning behavior of Bodianus rufus, Thalassoma bifasciatum, Gobiosoma evelynae, and Periclimenes pedersoni along a depth gradient at Salt River Submarine Canyon, St. Croix. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1988, 23, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, E.A.; Côté, I.M. Sex differences in cleaning behaviour and diet of a Caribbean cleaning goby. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2002, 82, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnal, C.; Côté, I.M. Diet of broadstripe cleaning gobies on a Barbadian reef. J. Fish Biol. 2000, 57, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.A.; Almany, G.R.; Houck, L.D.; Hixon, M.A. Experimental analysis of monogamy in the Caribbean cleaner goby, Gobiosoma evelynae. Anim. Behav. 2003, 65, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, E.A.; Côté, I.M. Social monogamy in the cleaning goby Elacatinus evelynae: Ecological constraints or net benefit? Anim. Behav. 2003, 66, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.; Osenberg, C.W. Experimental and observational patterns of density-dependent settlement and survival in the marine fish Gobiosoma. Oecologia 2002, 130, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteman, E.A.; Côté, I.M. Cleaning activity of two Caribbean cleaning gobies: Intra- and interspecific comparisons. J. Fish Biol. 2002, 60, 1443–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittey, K.E.; Dunkley, K.; Young, G.C.; Cable, J.; Perkins, S.E. Microhabitats of sharknose goby (Elacatinus evelynae) cleaning stations and their links with cleaning behaviour. Coral Reefs 2021, 40, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.L.; Tyler, J.C. Redescription of the gobiid fish Coryphopterus lipernes Böhlke and Robins: With notes on its habits and relationships. Am. Mus. Novit. 1977, 2616, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Luckhurst, B.E.; Luckhurst, K. Recruitment patterns of coral reef fishes on the fringing reef of Curaçao, Netherlands Antilles. Can. J. Zool. 1977, 55, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sais, J.R. Reef habitats and associated sessile-benthic and fish assemblages across a euphotic-mesophotic depth gradient in Isla Desecheo, Puerto Rico. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, P.L. The Neon Gobies: The Comparative Biology of the Gobies of the Genus Gobiosoma, Subgenus Elacatinus, (Pisces: Gobiidae) in the Tropical Western North Atlantic Ocean; T.F.H. Publications: Neptune, NJ, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Bak, R.P.M. Ecological aspects of the distribution of reef corals in the Netherlands Antilles. Bijdr. Dierk. 1975, 45, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duyl, F.C. Atlas of the Living Reefs of Curaçao and Bonaire (Netherlands Antilles); Foundation for Scientific Research in Surinam and the Netherlands Antilles: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Bongaerts, P.; Baldwin, C.C. High coral cover at lower mesophotic depths: A dense Agaricia community at the leeward side of Curaçao, Dutch Caribbean. Mar. Biodivers. 2017, 47, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frade, P.R.; Bongaerts, P.; Baldwin, C.C.; Trembanis, A.C.; Bak, R.P.M.; Vermeij, M.J.A. Bonaire and Curaçao. In Mesophotic Coral Ecosystems. Coral Reefs of the World; Loya, Y., Puglise, K., Bridge, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 12, pp. 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humann, P.; Deloach, N. Reef Coral Identification: Florida, the Caribbean and the Bahamas, 3rd ed.; New World Publications Inc.: Jacksonville, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; van der Loos, L.M.; van Moorsel, G.W.N.M. Coral diversity matches marine park zonation but not economic value of coral reef sites at St. Eustatius, eastern Caribbean. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Studio Team. R Studio: Integrated Development Environment for R; R Studio: Boston, MA, USA, 2021; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogle, D.H.; Doll, J.C.; Wheeler, P.; Dinno, A. FSA: Fisheries Stock Analysis (R Package Version 0.9.3). 2022. Available online: https://github.com/fishR-Core-Team/FSA/releases (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Mangiafico, S.S. Rcompanion: Functions to Support Extension Education Program Evaluation (Version 2.4.30); Rutgers Cooperative Extension: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 2023; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rcompanion/ (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.M. glmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartig, F. DHARMa: Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-Level/Mixed) Regression Models (Art. R Package Version 0.4.4). 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=DHARMa (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Bolker, B. bbmle: Tools for General Maximum Likelihood Estimation (R Package Version 1.0.25); R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=bbmle (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- McGehee, M.A. Correspondence between assemblages of coral reef fishes and gradients of water motion, depth, and substrate size off Puerto Rico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 105, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, M.W.; Graham, N.A.J.; Jones, G.P. Depth gradients in diversity, distribution and habitat specialisation in coral reef fishes: Implications for the depth-refuge hypothesis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 540, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellington, G.M. Habitat selection and juvenile persistence control the distribution of two closely related Caribbean damselfishes. Oecologia 1992, 90, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, L. Habitat selection by recruits establishes local patterns of adult distribution in two species of damselfishes: Stegastes dorsopunicans and S. planifrons. Oecologia 1998, 115, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, T.P. Hard-coral distribution and cold-water disturbances in South Florida: Variation with depth and location. Coral Reefs 1985, 4, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, J.M. Vertical distribution behaviour and its spatial variation in late-stage larvae of coral-reef fishes during the day. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2007, 37, 65–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, J.M. Vertical distribution of fish larvae in the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon, Australia. Mar. Biol. 1991, 109, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, I.E.; Wilson, D.; Meekan, M. Vertical distributions of late stage larval fishes in the nearshore waters of the San Blas Archipelago, Caribbean Panama. Coral Reefs 2001, 20, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, P.; Robert, D.; Bouchard, C.; Dower, J.F.; Falardeau, M.; Fortier, L.; Jenkins, G.P.; Leclerc, V.; Levesque, K.; Llopiz, J.K.; et al. Once upon a larva: Revisiting the relationship between feeding success and growth in fish larvae. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 72, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veron, J.E.N.; Stafford-Smith, M.G.; Turak, E.; De Vantier, L.M. Corals of the World. Available online: http://www.coralsoftheworld.org/coral_geographic/interactive_map/ (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Meesters, E.H.; Mueller, B.; Nugues, M.M. Caribbean free-living coral species co-occurring deep off the windward coast of Curaçao. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lo, C.M.; Morand, S.; Galzin, R. Parasite diversity\host age and size relationship in three coral-reef fishes from French Polynesia. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 1695–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abele, L.G.; Patton, W.K. The size of coral heads and the community biology of associated decapod crustaceans. J. Biogeogr. 1976, 3, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitburg, D.L. Settlement patterns and presettlement behavior of the naked goby, Gobiosoma bosci, a temperate oyster reef fish. Mar. Biol. 1991, 109, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, P.A.; Barber, I.; Forsgren, E. Shoaling behaviour of the two-spotted goby. J. Fish Biol. 2000, 56, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweatman, H. Field evidence that settling coral reef fish larvae detect resident fishes using dissolved chemical cues. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1988, 124, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
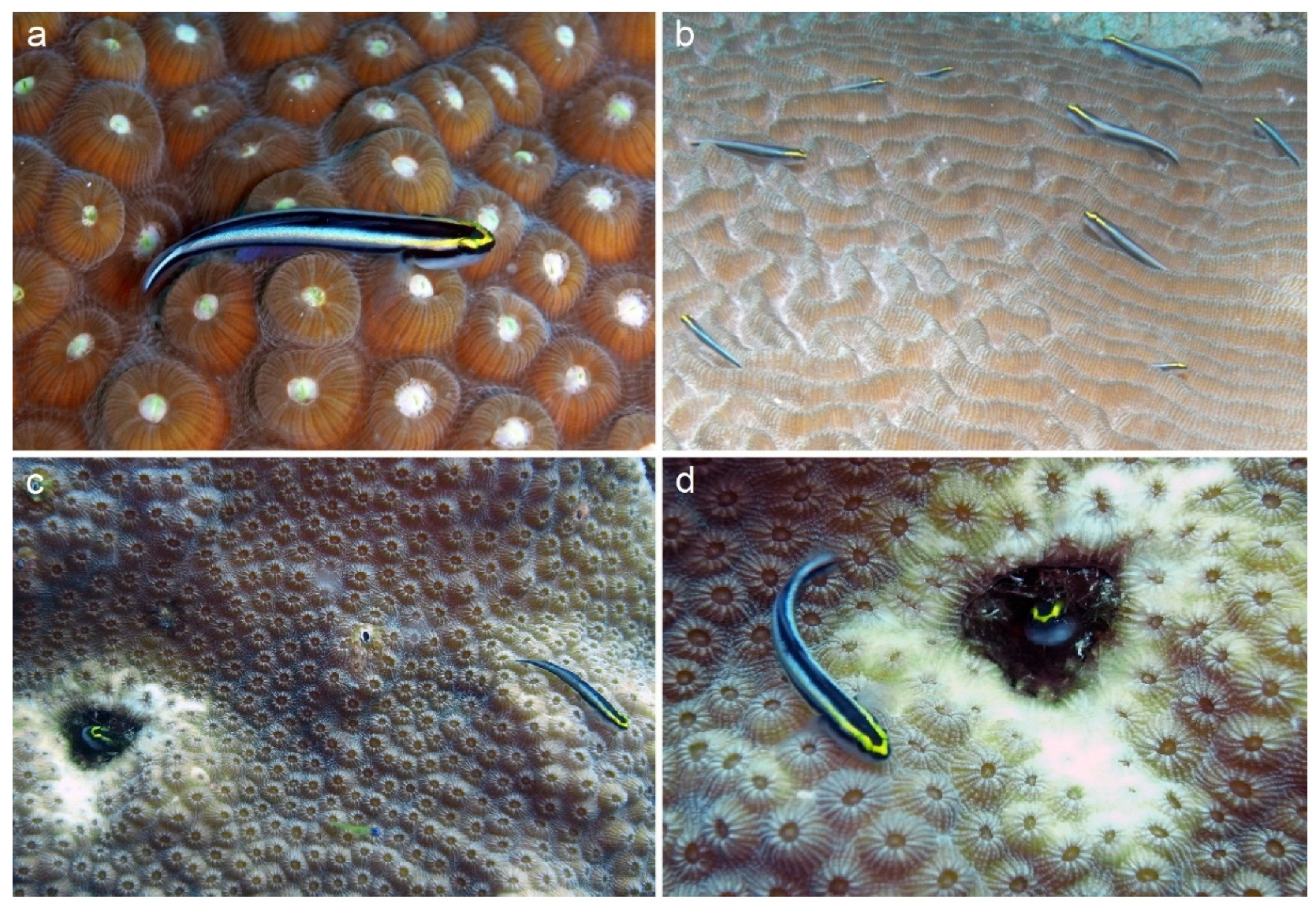


| Coral Species | Small | Medium | Large |
|---|---|---|---|
| Montastraea cavernosa | ≤600 cm2 | ≤1200 cm2 | >1200 cm2 |
| Colpophyllia natans | ≤1200 cm2 | ≤2400 cm2 | >2400 cm2 |
| Pseudodiploria strigosa | ≤800 cm2 | ≤1600 cm2 | >1600 cm2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziebell, A.-C.; Vogel, M.L.; Ratajczak, N.K.; Hoeksema, B.W. Habitat Use of Two Coral-Associated Cryptobenthic Gobiid Fishes (Family: Gobiidae) in the Southern Caribbean. Fishes 2023, 8, 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100531
Ziebell A-C, Vogel ML, Ratajczak NK, Hoeksema BW. Habitat Use of Two Coral-Associated Cryptobenthic Gobiid Fishes (Family: Gobiidae) in the Southern Caribbean. Fishes. 2023; 8(10):531. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100531
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiebell, Ann-Christin, Maite L. Vogel, Niklas Kjell Ratajczak, and Bert W. Hoeksema. 2023. "Habitat Use of Two Coral-Associated Cryptobenthic Gobiid Fishes (Family: Gobiidae) in the Southern Caribbean" Fishes 8, no. 10: 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100531
APA StyleZiebell, A.-C., Vogel, M. L., Ratajczak, N. K., & Hoeksema, B. W. (2023). Habitat Use of Two Coral-Associated Cryptobenthic Gobiid Fishes (Family: Gobiidae) in the Southern Caribbean. Fishes, 8(10), 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100531






