Development and Seasonal Variations of the Larvae of Three Mesopelagic Fishes near Coral Reefs in the Red Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
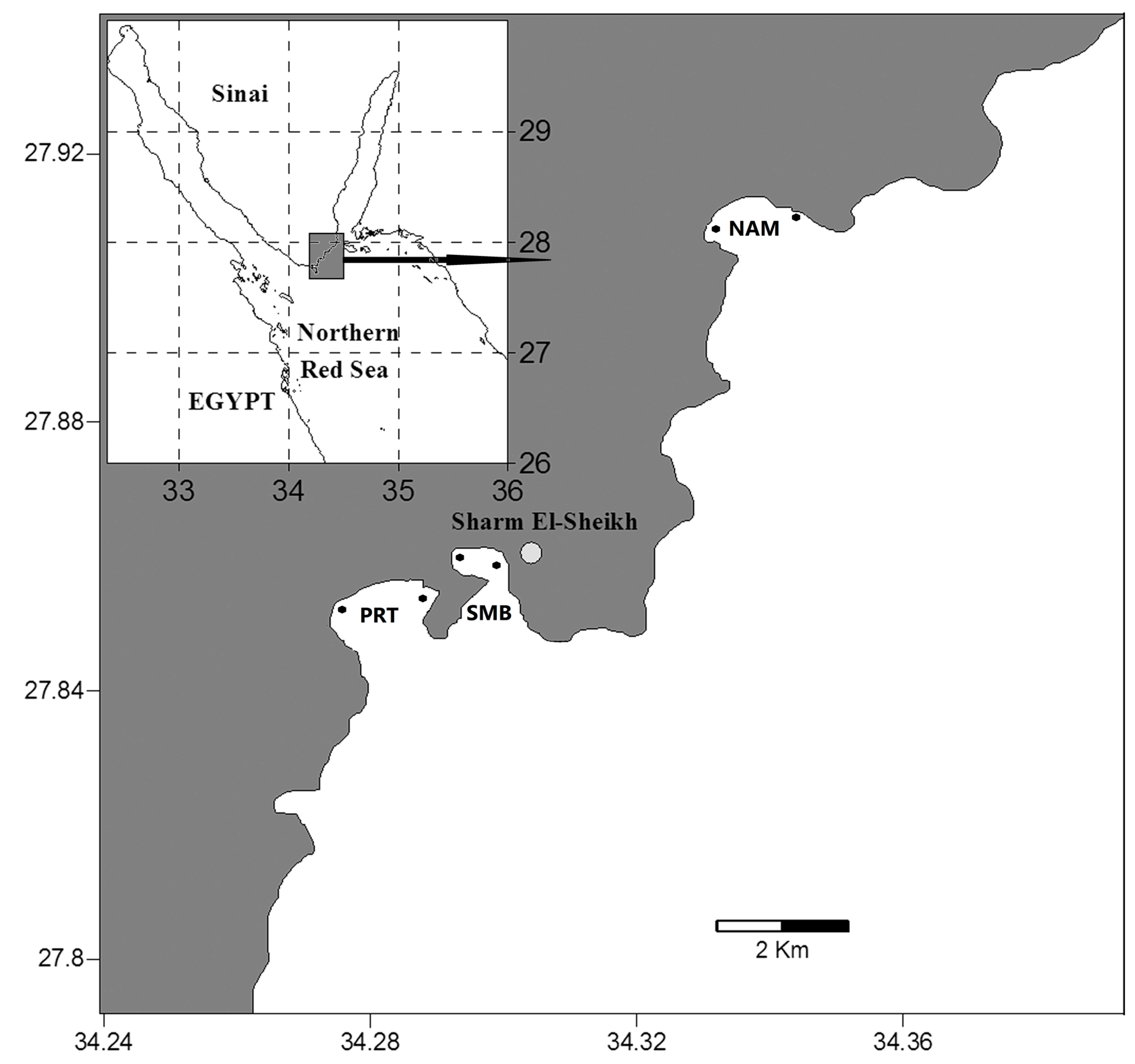
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Work
2.3. Laboratory Work
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Ethical Statement
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Conditions in the Study Area
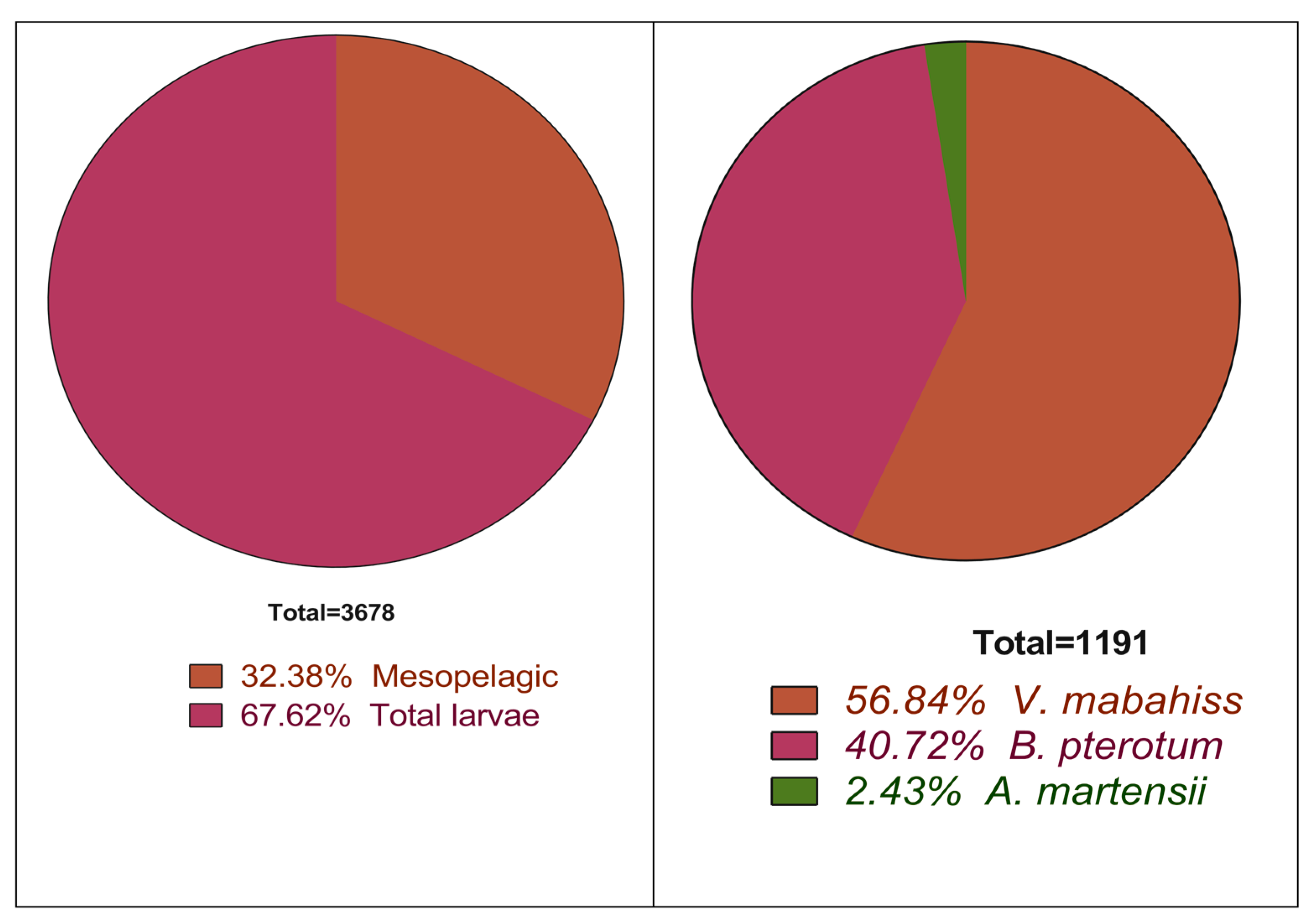
3.2. General Abundance of the Larvae of Mesopelagic Fish
3.3. Vinciguerria mabahiss
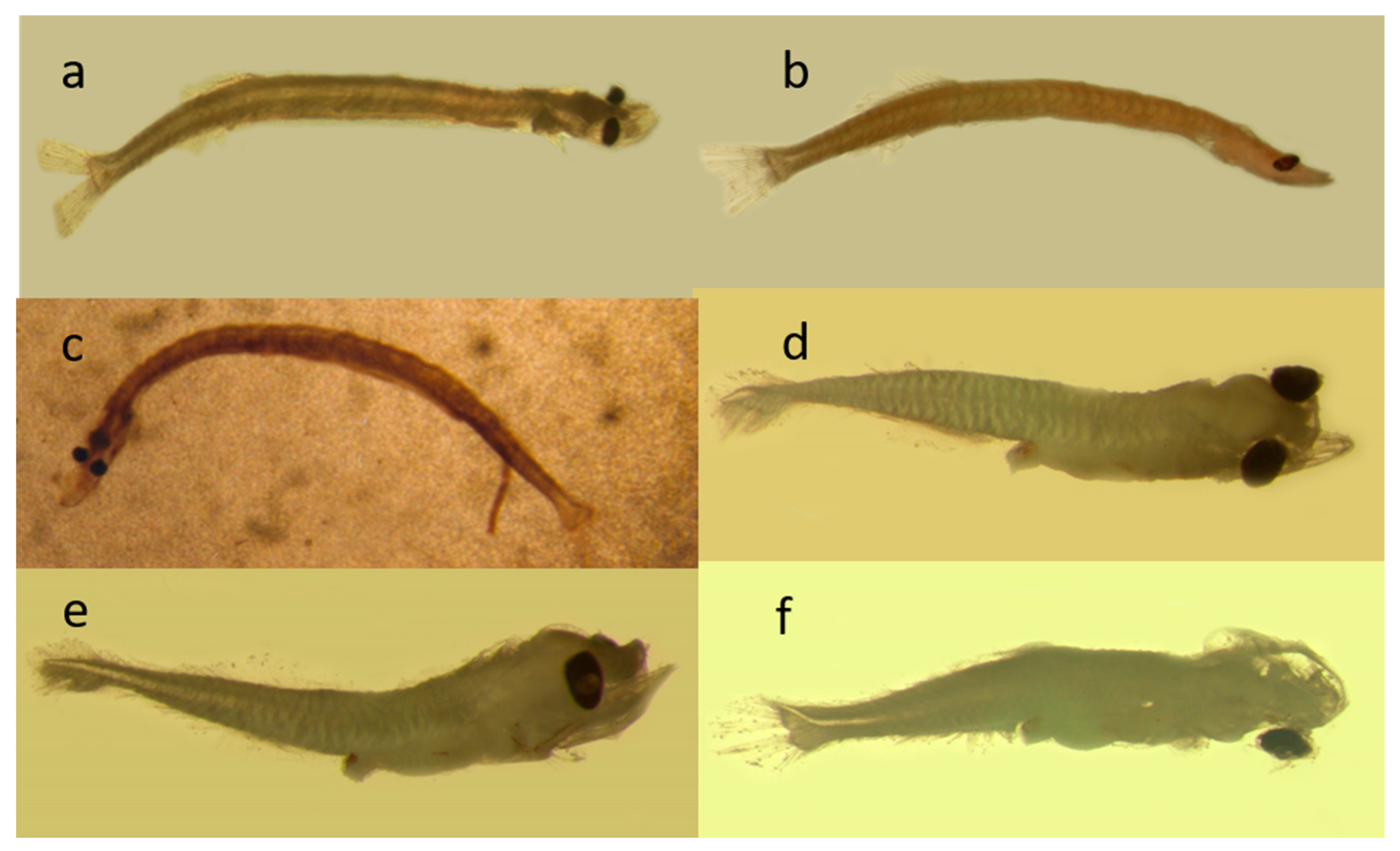
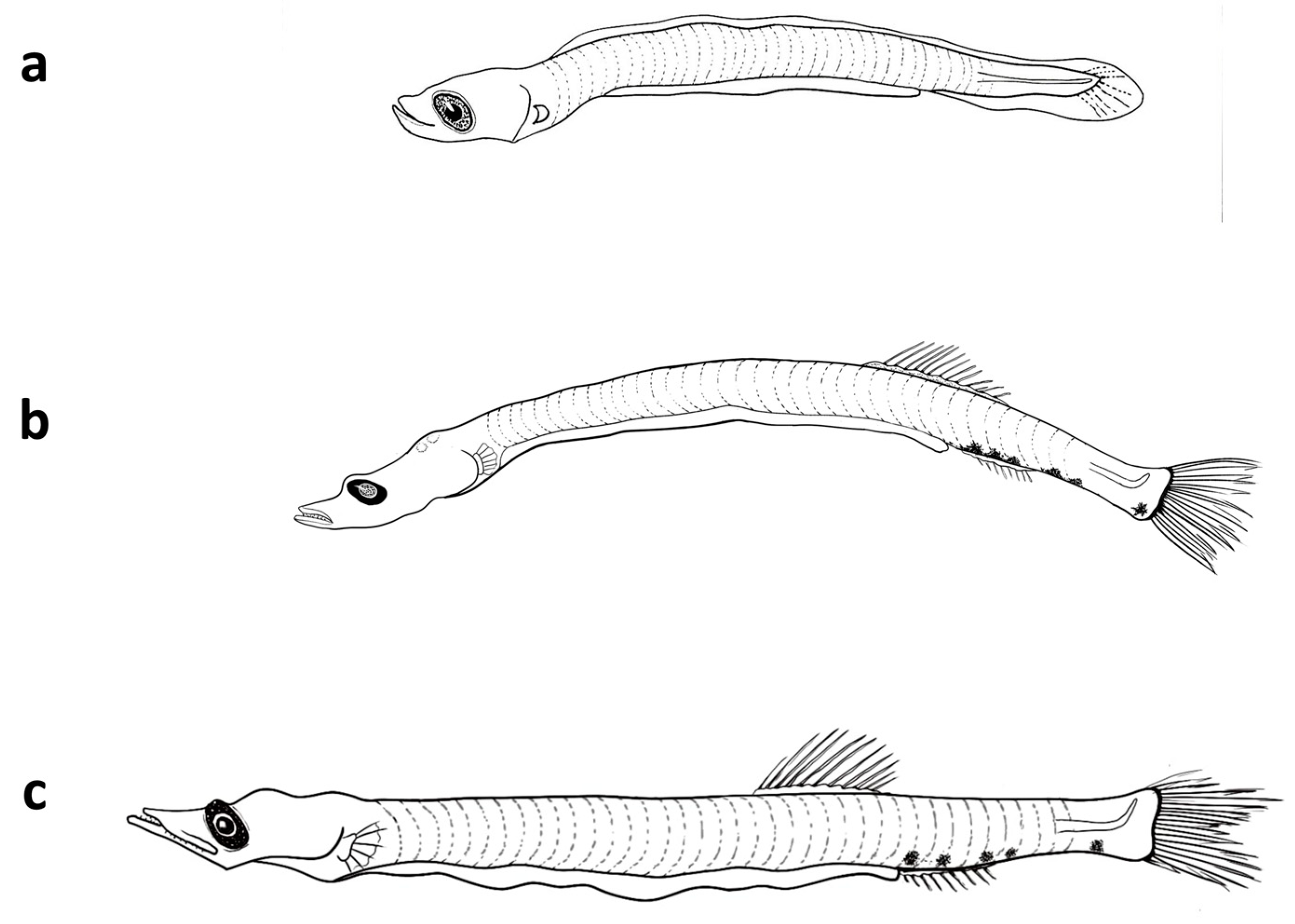
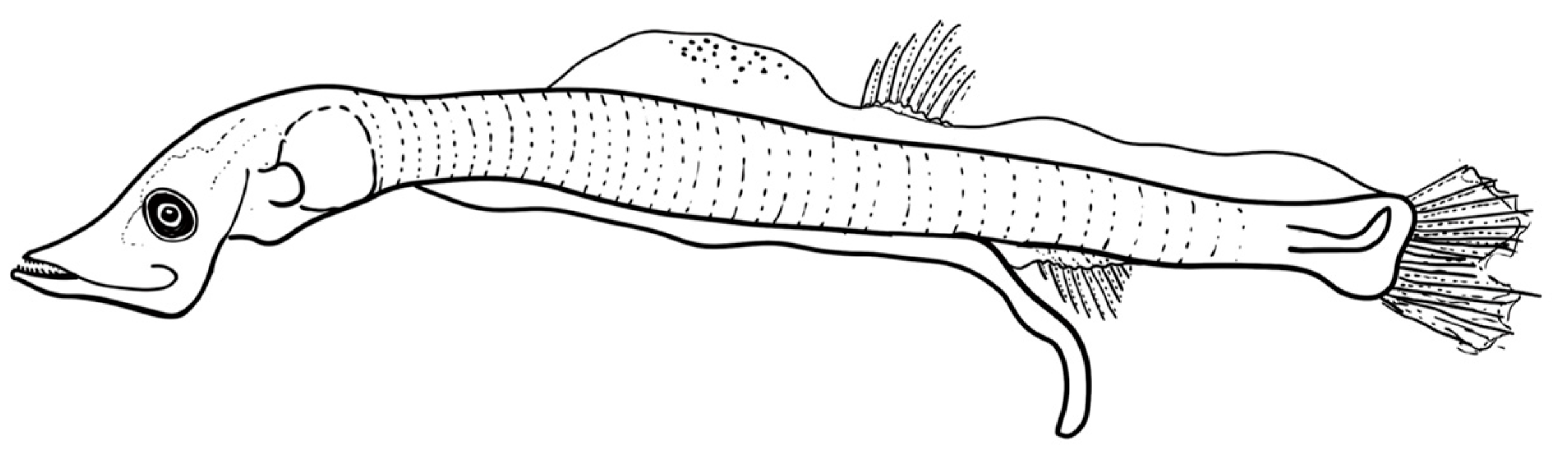
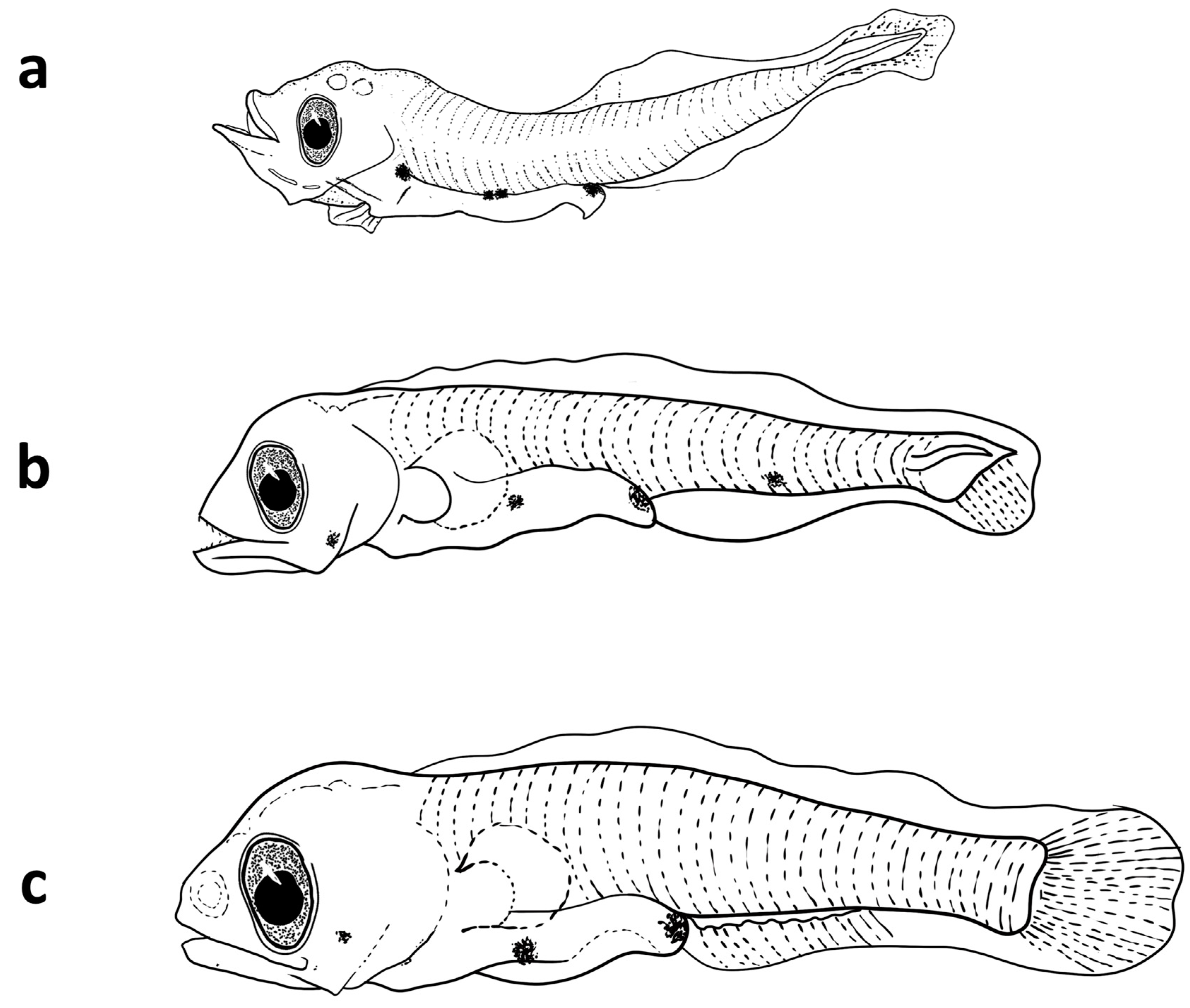
3.3.1. Description of the Larvae
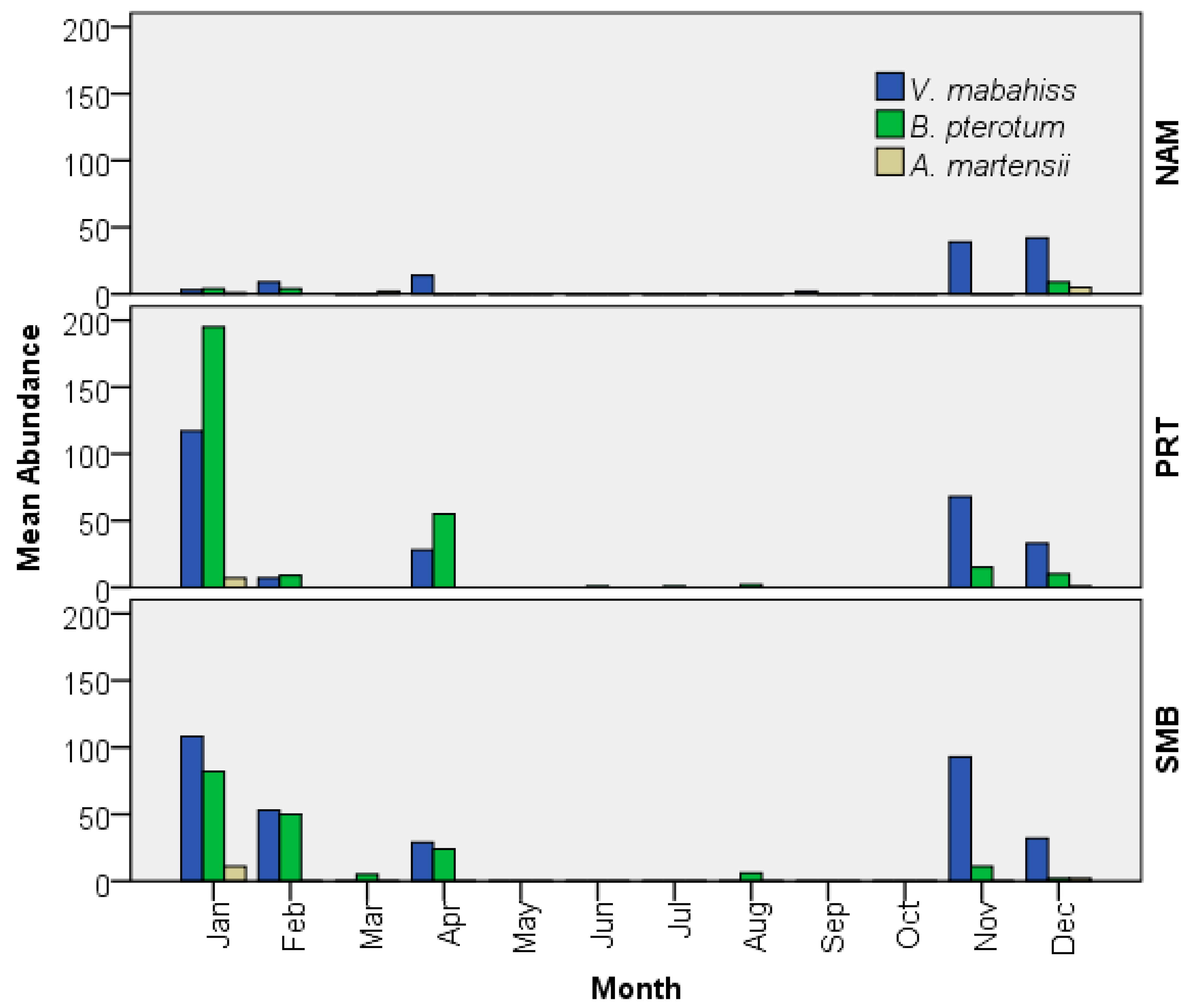
3.3.2. Abundance and Spawning Season of V. mabahiss
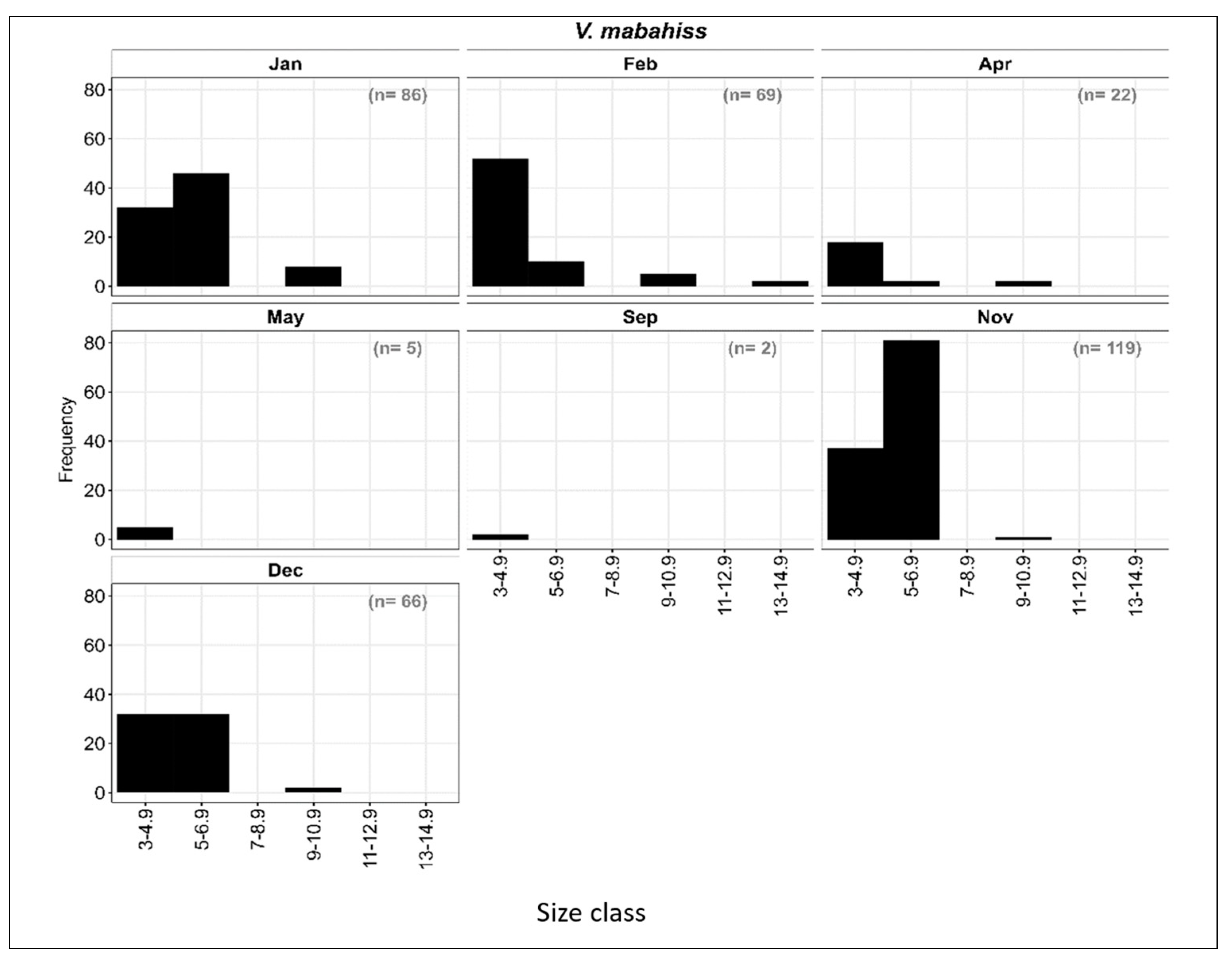
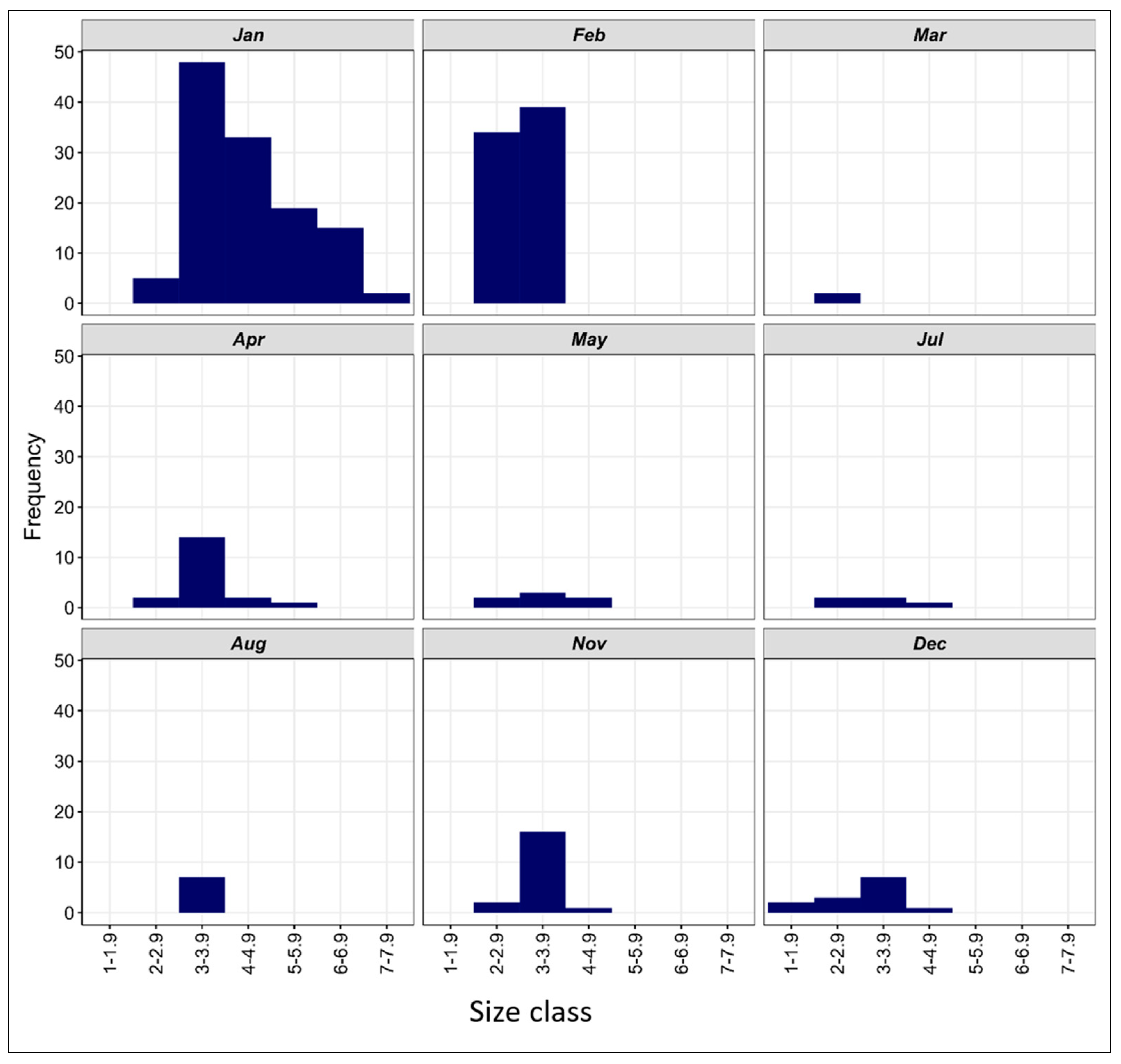
3.3.3. Length–Frequency Distribution of V. mabahiss Larvae
3.4. Astronesthes martensii
3.4.1. Description of the Larvae
3.4.2. Abundance and Spawning Season of A. martensii
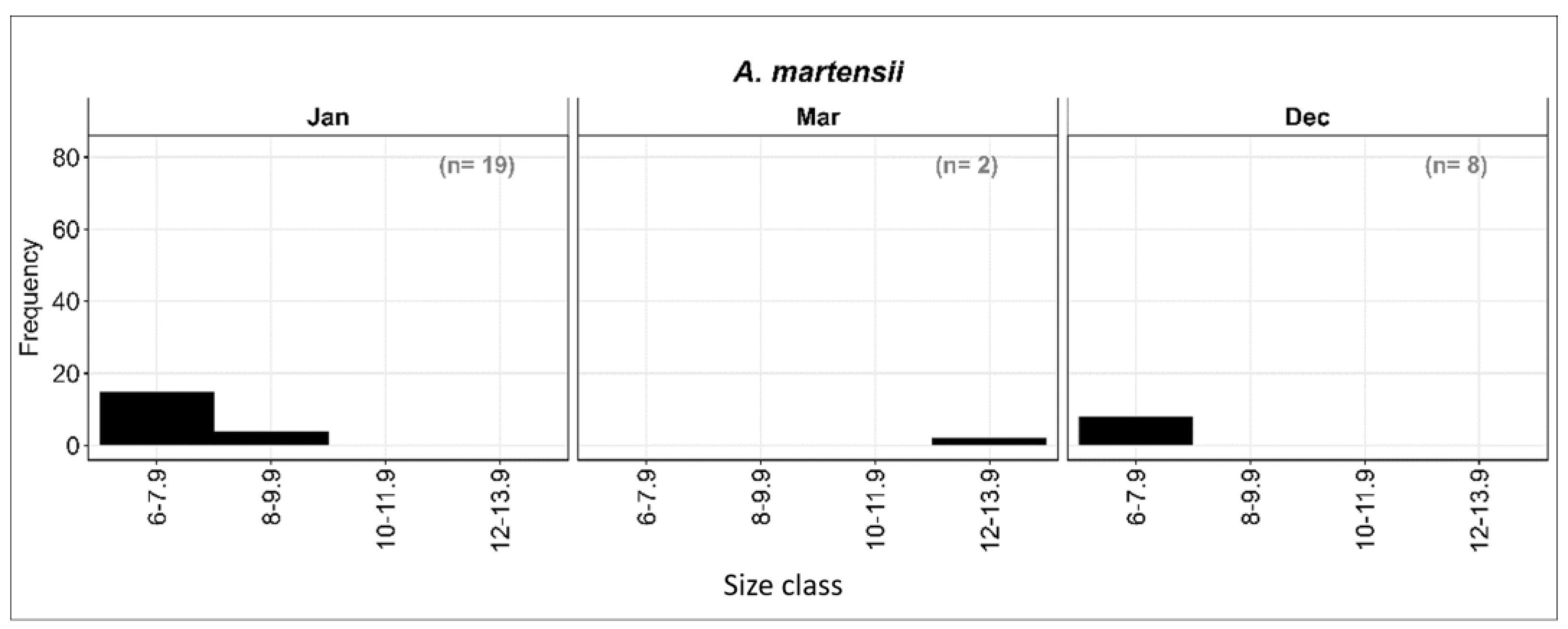
3.4.3. Length–Frequency Distribution of A. martensii
3.5. Benthosema pterotum
3.5.1. Description of the Larvae
3.5.2. Abundance and Spawning Season of B. pterotum
3.5.3. Length–Frequency Distribution of B. pterotum Larvae
4. Discussion
4.1. Diversity and Distribution of Mesopelagic Fish Larvae
4.2. The Diagnostic Features of Vinciguerria Species, B. pterotum, and A. martensii
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clavel-Henry, M.; Piroddi, C.; Quattrocchi, F.; Macias, D.; Christensen, V. Spatial distribution and abundance of mesopelagic fish biomass in the Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 573986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prášil, O.; Kaiser, M.J.; Attrill, M.J.; Jennings, S.; Thomas, D.N.; Barnes, D.K.A.; Brierley, A.S.; Polunin, N.V.C.; Raffaelli, D.G.; Williams, P.J.L.B. Marine Ecology: Processes, Systems, and Impacts; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. GBP 25–99. ISBN 0-19-924975-X. [Google Scholar]
- Olivar, M.P.; Bernal, A.; Molí, B.; Peña, M.; Balbín, R.; Castellón, A.; Miquel, J.; Massutí, E. Vertical distribution, diversity and assemblages of mesopelagic fishes in the western Mediterranean. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2012, 62, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, K. Fish production in open ocean ecosystems. In Flows of Energy and Materials in Marine Ecosystems: Theory and Practice; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1984; pp. 435–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valinassab, T.; Pierce, G.; Johannesson, K. Lantern fish (Benthosema pterotum) resources as a target for commercial exploitation in the Oman Sea. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2007, 23, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.A.; Hill, S.L.; Tarling, G.A.; Murphy, E.J. Myctophid fish (Family Myctophidae) are central consumers in the food web of the Scotia Sea (Southern Ocean). Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, I.D.; Polunin, N.V.; Hendrick, V.J. Limits to grazing by herbivorous fishes and the impact of low coral cover on macroalgal abundance on a coral reef in Belize. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 222, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würtz, M. Mediterranean Pelagic Habitat: Oceanographic and Biological Processes, An Overview; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland; Malaga, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Giménez, J.; Marçalo, A.; García-Polo, M.; García-Barón, I.; Castillo, J.J.; Fernández-Maldonado, C.; Saavedra, C.; Santos, M.B.; de Stephanis, R. Feeding ecology of Mediterranean common dolphins: The importance of mesopelagic fish in the diet of an endangered subpopulation. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2018, 34, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, R.T.; Anker-Nilssen, T.; Gabrielsen, G.W.; Chapdelaine, G. Food consumption by seabirds in Norwegian waters. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 59, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, P. The Biology of the Deep Ocean; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Salvanes, A.; Kristoffersen, J. Mesopelagic Fishes; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitzch Sierra, V.S.; Berumen, M.L. Recruitment of coral reef fishes along a cross-shelf gradient in the Red Sea peaks outside the hottest season. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 1565–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golani, D.; Fricke, R. Checklist of the Red Sea fishes with delineation of the Gulf of Suez, Gulf of Aqaba, endemism and Lessepsian migrants. Zootaxa 2018, 4509, 1–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, M.; Hanafy, M.; Dorgham, M. Mesozooplankton dynamics in the coastal waters of Sharm El-Sheikh, Red Sea, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 563–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El-Regal, M.; Abu Zeid, M.; Hellal, A.; Maaty, M. Abundance and diversity of reef fish larvae in Mabahiss Bay, on the Egyptian Red Sea coast. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2014, 18, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smith, P.E.; Richardson, S. Standard Techniques for Pelagic Fish Eggs and Larvae; FAO Fisheries Technical Paper No. 175; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Abu El-Regal, M. Abundance and diversity of coral reef fish larvae at Hurghada, Egyptian Red Sea. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2008, 12, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dytham, C. Choosing and Using Statistics: A Biologist’s Guide; Wiley-Blackwell, A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis; Pearson Education India: Noida, India, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Klevjer, T.A.; Torres, D.J.; Kaartvedt, S. Distribution and diel vertical movements of mesopelagic scattering layers in the Red Sea. Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 1833–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dypvik, E.; Kaartvedt, S. Vertical migration and diel feeding periodicity of the skinnycheek lanternfish (Benthosema pterotum) in the Red Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2013, 72, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isari, S.; Pearman, J.K.; Casas, L.; Michell, C.T.; Curdia, J.; Berumen, M.L.; Irigoien, X. Exploring the larval fish community of the central Red Sea with an integrated morphological and molecular approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El-Regal, M. Adult and larval reef fish communities in coastal reef lagoon at Hurghada, Red Sea, Egypt. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 4, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Aldanondo, N.; Kaartvedt, S.; Irigoien, X. Growth patterns of two Red Sea mesopelagic fishes. Mar. Biol. 2023, 170, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, J.M. The Pelagic Stage of Reef Fishes: The Larval Biology of Coral Reef Fishes; University of Tasmania: Hobart, Australia, 1991; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/102.100.100/490411 (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- De Falco, C.; Desbiolles, F.; Bracco, A.; Pasquero, C. Island mass effect: A review of oceanic physical processes. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 894860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renjith, R.K.; Jha, P.N.; Michael, B.; MP, R. Length weight relationship of five deep sea fishes from Kerala, south west coast of India. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2020, 36, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Shekarabi, S.; Valinassab, T.; Bystydzieńska, Z.; Linkowski, T. Age and growth of Benthosema pterotum (Alcock, 1890) (Myctophidae) in the Oman Sea. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2015, 31, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjøsæter, J.; Tilseth, S. Spawning behaviour, egg and larval development of the myctophid fish Benthosema pterotum. Mar. Biol. 1988, 98, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassa, C.; Takahashi, M.; Tsukamoto, Y. Distribution, hatch-date, growth, and mortality of larval Benthosema pterotum (Pisces: Myctophidae) in the shelf region of the East China Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2015, 95, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassa, C.; Ohshimo, S.; Tanaka, H.; Tsukamoto, Y. Reproductive biology of Benthosema pterotum (Teleostei: Myctophidae) in the shelf region of the East China Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2014, 94, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalpadado, P.; Gjøsæter, J. Observations on mesopelagic fish from the Red Sea. Mar. Biol. 1987, 96, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalpadado, P. Biology of the Lanternfish Benthosema pterotum from the Indian Ocean. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Aglen, A.; Gjøsæter, J.; Myrseth, B.; Tilseth, S. Surveys of Mesopelagic Fish Resources in the Gulf of Oman and the Gulf of Aden, Jul–Aug 1979 and Jan–Feb 1981; Institute of Marine Research: Bergen, Norway, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.K.; Feltes, R.M. A New Species of Vinciguerria (Salmoniformes, Phosichthyidae) from the Red Sea and Gulf of Aqaba, with Comments on the Depauperacy of the Red Sea Mesopelagic Fish Fauna; Field Museum of Natural History: Chicago, IL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlstrom, E.; Elbert, H.; Counts, R. Development and Distribution of Vinciguerria lucetia and Related Species in the Eastern Pacific; Fishery Bulletin of the Fish and Wildlife Service; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1958.
- Goren, M.; Dor, M. An Updated Checklist of the Fishes of the Red Sea: CLOFRES II; The Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities: Jerusalem, Israel, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.-L.; Kim, J.-K.; Yu, H.-J.; Kim, J.-N. Ontogenetic comparison of larvae and juveniles of Diaphus garmani and Benthosema pterotum (Myctophidae, Pisces) collected from Korea. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Moser, H.G. Stomiatoidea: Development and Relationships. In Ontogeny and Systematics of Fishes, Special Publication 1; Moser, H.G., Richards, W.J., Cohen, D.M., Fahay, M.P., Kendall, A.W., Jr., Richardson, S.L., Eds.; American Society of Ichthyologists and Herptetologists: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1984; Volume 760, pp. 168–180. [Google Scholar]

| Order | Family | Species |
|---|---|---|
| Stomiiformes | Phosichthyidae | Vinciguerria mabahiss (Johnson and Feltes 1984) |
| Stomiidae | ||
| Subfam: Astronesthinae | Astronesthes martensii (Klunzinger 1871) | |
| Subfam: Stomiinae | Chauliodus sloani (Bloch and Schneider 1801) | |
| Stomias affinis (Günther 1887) | ||
| Sternoptychidae | Maurolicus mucronatus (Klunzinger 1871) | |
| Myctophiformes | Myctophidae | Benthosema fibulatum (Gilbert and Cramer 1897) |
| Benthosema pterotum (Alcock 1890) | ||
| Diaphus coeruleus (Klunzinger 1871) | ||
| Ateleopodiformes | Ateleopodididae | Ateleopus japonicus (Bleeker 1853) |
| Scombriformes | Trichiuridae | Evoxymetopon moricheni (Fricke, Golani, and Appelbaum-Golani 2014) |
| Tentoriceps cristatus (Klunzinger 1884) | ||
| Trichiurus auriga (Klunzinger 1884) | ||
| Trichiurus lepturus (Linnaeus 1758) | ||
| Gempylidae | Thyrsitoides marleyi (Fowler 1929) | |
| Aulopiformes | Paralepididae | Lestidiops jayakari (Boulenger 1889) |
| Lestrolepis luetkeni (Ege 1933) |
| Site Name | Code | Coordinates | Habitat | Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naama Bay | NAM | 27°55′ N and 34°20′ E, | Mainly coral reef | 100 m |
| Port Bay | PRT | 27°51′ N and 34°16.7′ E | Mainly coral reef | 35 m |
| Sharm El-Maya | SMB | 27°51.8′ N and 34°18.1′ E | Mainly seagrass | 10 m |
| Month | V. mabahiss | B. pterotum | A. martensii | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAM | PRT | SMB | NAM | PRT | SMB | NAM | PRT | SMB | |
| Aug | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sep | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Oct | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nov | 39 | 68 | 93 | 0 | 15 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Dec | 42 | 33 | 32 | 9 | 10 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 |
| Jan | 3 | 117 | 108 | 4 | 195 | 82 | 1 | 7 | 11 |
| Feb | 9 | 7 | 53 | 4 | 9 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mar | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Apr | 14 | 28 | 29 | 0 | 55 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| May | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Jun | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Jul | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sum | 109 | 253 | 315 | 17 | 288 | 180 | 8 | 8 | 13 |
| Meristics | V. mabahiss | B. pterotum | A. martensii |
|---|---|---|---|
| Myomeres | 37–39 | 30 | 50 |
| Preanal | 25 | 19 | 35 |
| Postanal | 12 | 11 | 15 |
| Doral fin spines | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Doral fin rays | 13 | 12 | 10–21 |
| Anal fin spines | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Anal fin rays | 13 | 18 | 12–22 |
| Pelvic | 7 | 8 | 5–9 |
| Pectoral | 10 | 19 | 5–9 |
| Caudal | 19 | 19 | NA |
| V. mabahiss | B. pterotum | A. martensii | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preflexion | Postflexion | Preflexion | Postflexion | Preflexion | Postflexion | |
| Snl/HL | 37% | 33–40% | 33–40% | 25–30% | 25% | 30% |
| ED/HL | 25% | 22–26% | 33–40% | 16–20% | 18% | 35% |
| HL/BL | 26% | 16–20% | 20–25% | 25–26% | 16% | 36% |
| PAL/BL | 83% | 74–77% | 50–60% | 55–60% | trailing gut | trailing gut |
| PDL/BL | --- | 61–63% | --- | 44–50% | ---- | 61% |
| BD/BL | 13–15% | 15–17% | % | 6% | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu El-Regal, M.A.; Ditty, J.G. Development and Seasonal Variations of the Larvae of Three Mesopelagic Fishes near Coral Reefs in the Red Sea. Fishes 2023, 8, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100500
Abu El-Regal MA, Ditty JG. Development and Seasonal Variations of the Larvae of Three Mesopelagic Fishes near Coral Reefs in the Red Sea. Fishes. 2023; 8(10):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100500
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu El-Regal, Mohamed Ahmed, and James G. Ditty. 2023. "Development and Seasonal Variations of the Larvae of Three Mesopelagic Fishes near Coral Reefs in the Red Sea" Fishes 8, no. 10: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100500
APA StyleAbu El-Regal, M. A., & Ditty, J. G. (2023). Development and Seasonal Variations of the Larvae of Three Mesopelagic Fishes near Coral Reefs in the Red Sea. Fishes, 8(10), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100500





