Transcriptome Analysis Provides an Overview of Genes Involved in the Peculiar Food Preference at First-Feeding Stage in Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish
2.2. Total RNA Extraction
2.3. cDNA Library Construction and RNA-seq
2.4. Data Processing and Mapping
2.5. Differential Expression Analysis
2.6. Functional Enrichment Analyses
2.7. Experimental Validation of DEGs by RT-qPCR
3. Results
3.1. Statistics of RNA-seq Data
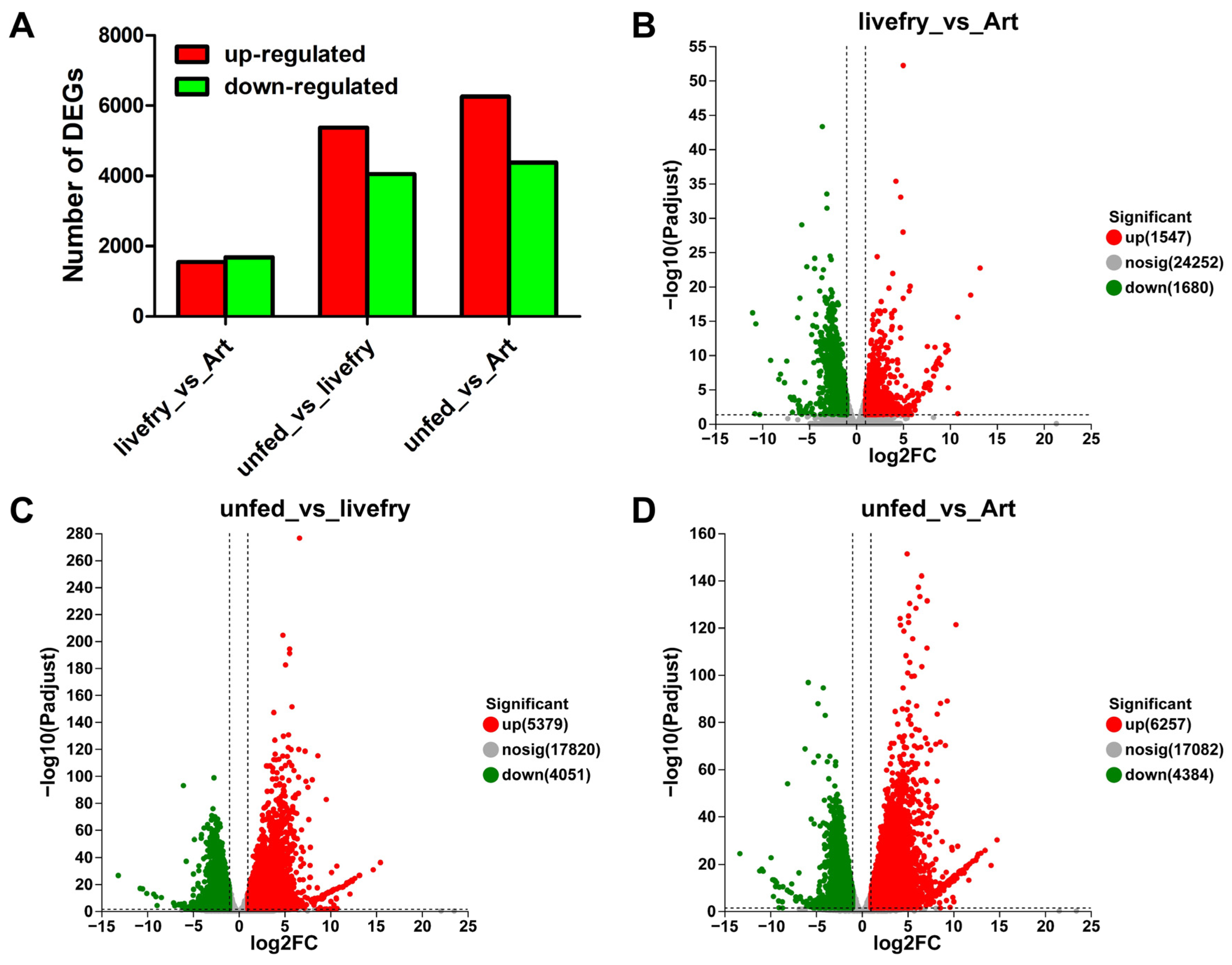
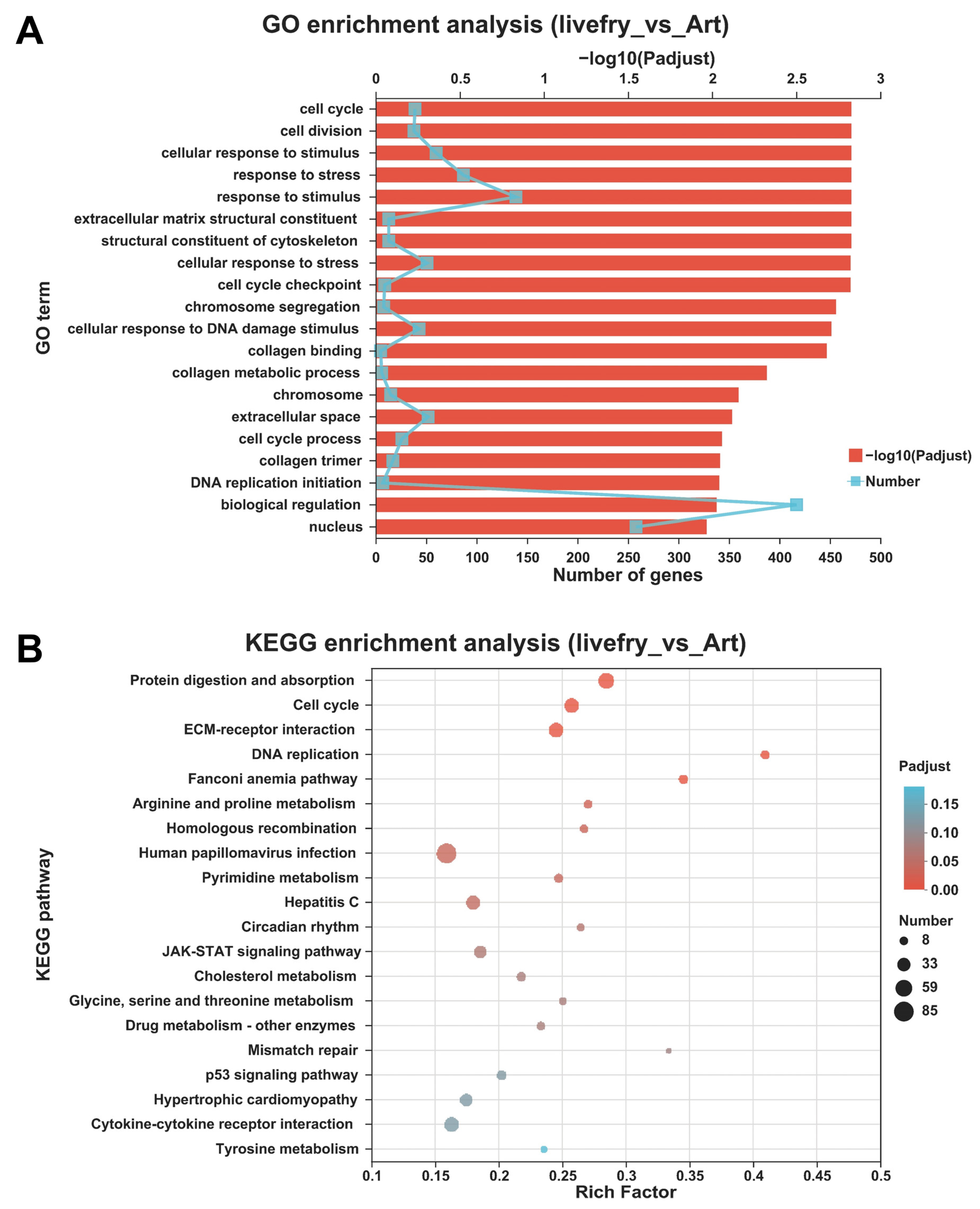
3.2. Differentially Expressed Genes between the Mandarin Fish Larvae Fed with Live Prey Fish and Brine Shrimp
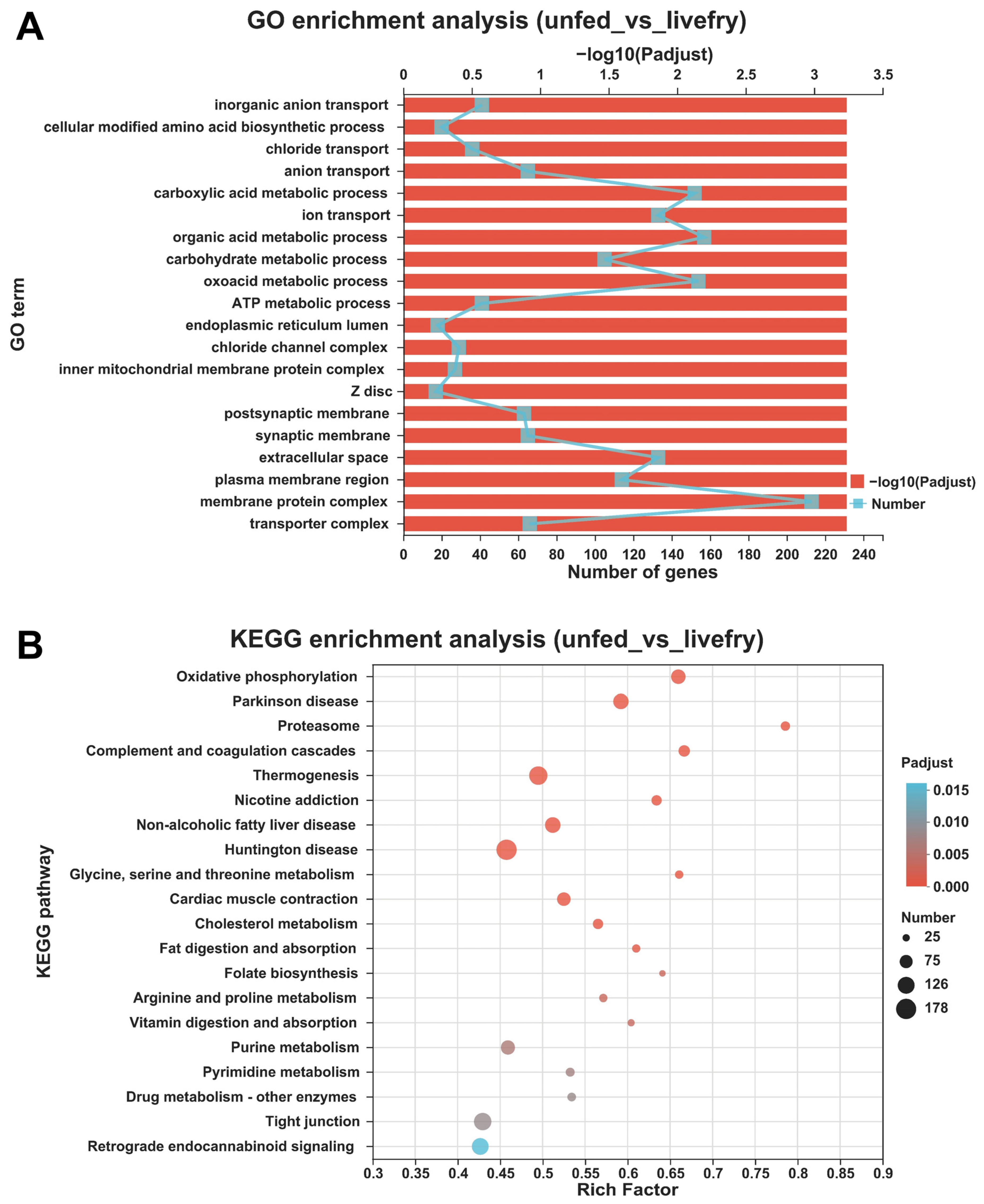
3.3. Differentially Expressed Genes between the Mandarin Fish Larvae Unfed and Fed with Live Prey Fish
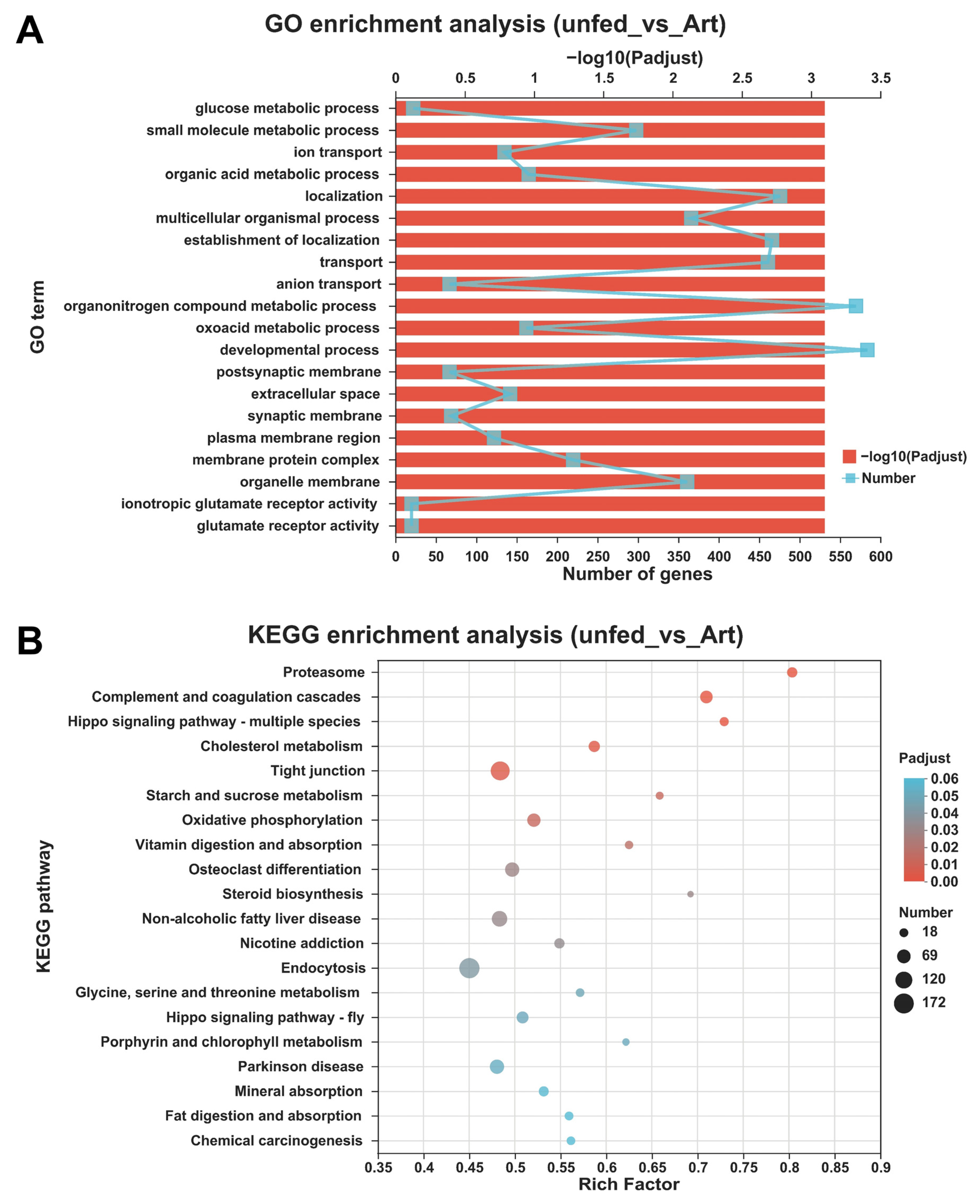
3.4. Differentially Expressed Genes between the Mandarin Fish Larvae Unfed and Fed with Brine Shrimp
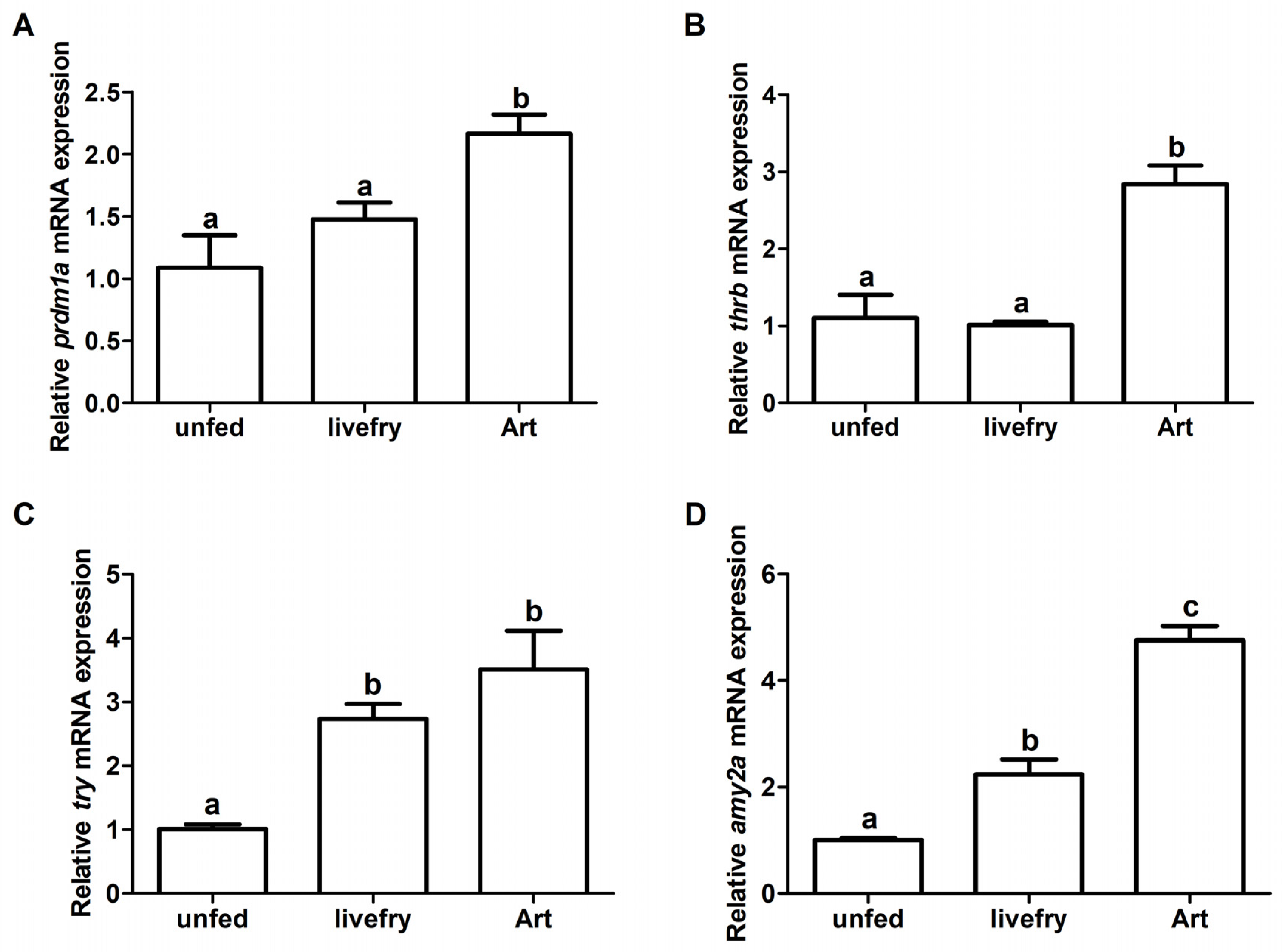
3.5. Experimental Validation of DEGs by RT-qPCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, X.F.; Oku, H.; Ogata, H.Y.; Liu, J.; He, X. Weaning Chinese perch Siniperca chuatsi (Basilewsky) onto artificial diets based upon its specific sensory modality in feeding. Aquac. Res. 2001, 32, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.-Y.; Sutcliffe, M.P.F.; Grabenhorst, F. Preferences for nutrients and sensory food qualities identify biological sources of economic values in monkeys. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101954118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasumyan, A.O. The taste system in fishes and the effects of environmental variables. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 95, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogdans, J. Sensory ecology of the fish lateral-line system: Morphological and physiological adaptations for the perception of hydrodynamic stimuli. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 95, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Liang, X.-F.; Sun, J.; Li, L.; Yu, Y.; Huang, W.; Qu, C.-M.; Cao, L.; Bai, X.-L.; Tao, Y.-X. Insights into food preference in hybrid F1 of Siniperca chuatsi (♀) × Siniperca scherzeri (♂) mandarin fish through transcriptome analysis. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.-Y.; Liang, X.-F.; He, S. Genome-wide identification and characterization of olfactory receptor genes in Chinese perch, Siniperca chuatsi. Genes 2019, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, S.; Lim, L.-S.; Shaleh, S.R.M.; Mukai, Y.; Anraku, K.; Kawamura, G. Ontogenetic eye development and related behavioural changes in larvae and juveniles of barramundi Lates calcarifer (Bloch). Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2011, 44, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.-S.; Mukai, Y. Morphogenesis of sense organs and behavioural changes in larvae of the brown-marbled grouper Epinephelus fuscoguttatus (Forsskål). Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2014, 47, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.L.; Flamarique, I.N.; Hárosi, F.I.; Rickers-Haunerland, J.; Haunerland, N.H. Photoreceptor layer of salmonid fishes: Transformation and loss of single cones in juvenile fish. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 495, 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, J.A.; Duston, J.; Croll, R.P. Superficial neuromasts facilitate non-visual feeding by larval striped bass (Morone saxatilis). J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 3522–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenzaki, A.; Okunishi, S.; Tomoda, T.; Shioura, Y.; Uchida, M.; Tezuka, N.; Maeda, H. Observation of the feeding behaviour of reared Japanese eel Anguilla japonica leptocephali fed picocyanobacteria Synechococcus spp. J. Fish Biol. 2022, 100, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasdi, N.W.; Qin, J.G. Improvement of copepod nutritional quality as live food for aquaculture: A review. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, L.E.C.; Yúfera, M.; Makridis, P.; Morais, S.; Dinis, M.T. Live feeds for early stages of fish rearing. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 613–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curnow, J.; King, J.; Bosmans, J.; Kolkovski, S. The effect of reduced Artemia and rotifer use facilitated by a new microdiet in the rearing of barramundi Lates calcarifer (BLOCH) larvae. Aquaculture 2006, 257, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giebichenstein, J.; Giebichenstein, J.; Hasler, M.; Schulz, C.; Ueberschär, B. Comparing the performance of four commercial microdiets in an early weaning protocol for European seabass larvae (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Hong, Y.; Hong, Y.; Sun, K.; Hong, Y. Study on formulated diet for large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae at the early feeding stage. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2021, 20, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Xiong, C.; Zhou, J.; Wei, K. Development of feeding organs and selective behavior on food of larval Chinese snake-head fish Channa argus. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 1997, 16, 399–407. [Google Scholar]
- Kolkovski, S. Microdiets as alternatives to live feeds for fish larvae in aquaculture: Improving the efficiency of feed particle utilization. In Advances in Aquaculture Hatchery Technology; Allan, G., Burnell, G., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Tortolero, D.A.; Vázquez-Islas, G.; Campos-Ramos, R. A transcriptome insight during early fish larval development followed by starvation in Seriola rivoliana. Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xu, G.; Xu, P. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals metabolism transformation in Coilia nasus larvae during the mouth-open period. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2020, 36, 100712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, L.; Lv, L.-Y.; Cai, W.-J.; Dou, Y.-Q.; Li, J.; Tang, S.-L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. Mandarin fish (Sinipercidae) genomes provide insights into innate predatory feeding. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.-C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopfenstein, D.V.; Zhang, L.; Pedersen, B.S.; Ramírez, F.; Vesztrocy, A.W.; Naldi, A.; Mungall, C.J.; Yunes, J.M.; Botvinnik, O.; Weigel, M.; et al. GOATOOLS: A Python library for Gene Ontology analyses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnsworth, D.R.; Posner, M.; Miller, A.C. Single cell transcriptomics of the developing zebrafish lens and identification of putative controllers of lens development. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 206, 108535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Corbo, J.C. Partitioning of gene expression among zebrafish photoreceptor subtypes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zele, A.J.; Feigl, B.; Adhikari, P.; Maynard, M.L.; Cao, D. Melanopsin photoreception contributes to human visual detection, temporal and colour processing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, W.; Nakane, Y.; Hattar, S.; Yoshimura, T. Impaired circadian photoentrainment in Opn5-null mice. iScience 2018, 6, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.-L.; Liang, X.-F.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Lu, K. Genome-wide identification and expression patterns of opsin genes during larval development in Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Gene 2022, 825, 146434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, J.A.; Reh, T.A. Photoreceptor cell fate specification in vertebrates. Development 2015, 142, 3263–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viets, K.; Eldred, K.C.; Johnston, R.J. Mechanisms of photoreceptor patterning in vertebrates and invertebrates. Trends Genet. 2016, 32, 638–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diacou, R.; Nandigrami, P.; Fiser, A.; Liu, W.; Ashery-Padan, R.; Cvekl, A. Cell fate decisions, transcription factors and signaling during early retinal development. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2022, 91, 101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A.; Furukawa, A.; Koike, C.; Tano, Y.; Aizawa, S.; Matsuo, I.; Furukawa, T. Otx2 homeobox gene controls retinal photoreceptor cell fate and pineal gland development. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodson, N.B.; Kaufman, M.A.; Park, K.U.; Brzezinski, J.A., IV. Simultaneous deletion of Prdm1 and Vsx2 enhancers in the retina alters photoreceptor and bipolar cell fate specification, yet differs from deleting both genes. Development 2020, 147, dev190272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, J.A., IV; Lamba, D.A.; Reh, T.A. Blimp1 controls photoreceptor versus bipolar cell fate choice during retinal development. Development 2010, 137, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquardt, T.; Ashery-Padan, R.; Andrejewski, N.; Scardigli, R.; Guillemot, F.; Gruss, P. Pax6 is required for the multipotent state of retinal progenitor cells. Cell 2001, 105, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, C.L.; Gregory-Evans, C.Y.; Furukawa, T.; Papaioannou, M.; Looser, J.; Ploder, L.; Bellingham, J.; Ng, D.; Herbrick, J.-A.S.; Duncan, A.; et al. Cone-rod dystrophy due to mutations in a novel photoreceptor-specific homeobox gene (CRX) essential for maintenance of the photoreceptor. Cell 1997, 91, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mears, A.J.; Kondo, M.; Swain, P.K.; Takada, Y.; Bush, R.A.; Saunders, T.L.; Sieving, P.A.; Swaroop, A. Nrl is required for rod photoreceptor development. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Khanna, H.; Oh, E.C.T.; Hicks, D.; Mitton, K.P.; Swaroop, A. Photoreceptor-specific nuclear receptor NR2E3 functions as a transcriptional activator in rod photoreceptors. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.; Hurley, J.B.; Dierks, B.; Srinivas, M.; Saltó, C.; Vennström, B.; Reh, T.A.; Forrest, D. A thyroid hormone receptor that is required for the development of green cone photoreceptors. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.M.; Park, L.; Stenkamp, D.L. Retinal homeobox 1 is required for retinal neurogenesis and photoreceptor differentiation in embryonic zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2009, 328, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, M.G.; Oel, A.P.; Allison, W.T. gdf6a is required for cone photoreceptor subtype differentiation and for the actions of tbx2b in determining rod versus cone photoreceptor fate. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Delfin, K.; Morris, A.C.; Snelson, C.D.; Gamse, J.T.; Gupta, T.; Marlow, F.L.; Mullins, M.C.; Burgess, H.A.; Granato, M.; Fadool, J.M. Tbx2b is required for ultraviolet photoreceptor cell specification during zebrafish retinal development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2023–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, A.K.; Peng, G.-H.; Chen, S. Regulation of photoreceptor gene expression by Crx-associated transcription factor network. Brain Res. 2008, 1192, 114–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Rattner, A.; Nathans, J. The rod photoreceptor-specific nuclear receptor Nr2e3 represses transcription of multiple cone-specific genes. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, N.B.; Jacobson, S.G.; Cideciyan, A.V.; Swiderski, R.; Streb, L.M.; Searby, C.; Beck, G.; Hockey, R.; Hanna, D.B.; Gorman, S.; et al. Mutation of a nuclear receptor gene, NR2E3, causes enhanced S cone syndrome, a disorder of retinal cell fate. Nat. Genet. 2000, 24, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Han, S.; Qu, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Yu, S.; Reilly, J.; Tu, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, Z.; et al. Knockout of Nr2e3 prevents rod photoreceptor differentiation and leads to selective L-/M-cone photoreceptor degeneration in zebrafish. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, L.I.; Kim-Han, J.S.; Saunders, L.M.; Poria, D.; Hughes, A.E.O.; Kefalov, V.J.; Parichy, D.M.; Corbo, J.C. Thyroid hormone receptors mediate two distinct mechanisms of long-wavelength vision. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15262–15269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveau, C.; Jiao, X.; Suzuki, S.C.; Krishnakumar, A.; Yoshimatsu, T.; Hejtmancik, J.F.; Nelson, R.F. Thyroid hormone receptor beta mutations alter photoreceptor development and function in Danio rerio (zebrafish). PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angueyra, J.; Kunze, V.P.; Patak, L.K.; Kim, H.; Kindt, K.S.; Li, W. Identification of transcription factors involved in the specification of photoreceptor subtypes. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, J.; Tang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, Y.; Chen, X. The digestive system of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) can adapt to domestication by feeding with artificial diet. Aquaculture 2021, 538, 736546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palińska-Żarska, K.; Woźny, M.; Kamaszewski, M.; Szudrowicz, H.; Brzuzan, P.; Żarski, D. Domestication process modifies digestion ability in larvae of Eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis), a freshwater Teleostei. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuvier-Péres, A.; Kestemont, P. Development of some digestive enzymes in Eurasian perch larvae Perca fluviatilis. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2001, 24, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Liang, X.-F.; He, S.; Tang, S.-L.; Peng, D. The potential use of Artemia for larval rearing of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primers | Sequence 5′–3′ | Amplification Efficiency (%) | Annealing Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| sc-rpl13a-F | TATCCCCCCACCCTATGACA | 100.6 | 59 |
| sc-rpl13a-R | ACGCCCAAGGAGAGCGAACT | ||
| sc-prdm1a-F | CTGACGAAACACTGGAGAAAGA | 93.7 | 55 |
| sc-prdm1a-R | GTCCTAGGTACGCTGGTTAAAG | ||
| sc-thrb-F | CAAGGATGAGCTCTGTGTAGTG | 91.0 | 55 |
| sc-thrb-R | GCGTAGGTTGGGTTGAGATT | ||
| sc-try-F | AGTAGGTGCAGAACACAATCA | 93.8 | 55 |
| sc-try-R | ACTCGTAGCCTCCAACAATC | ||
| sc-amy2a-F | TGCCTTTGGACGTGGTAATC | 93.0 | 55 |
| sc-amy2a-R | GCACCTGTTTCCTTCCTTCT |
| Gene ID | Description | Gene Symbol | Log2FC | Padjust | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lens development | |||||
| SC7-LG04_05276 | poly(U)-specific endoribonuclease | endou | 4.16 | 4.81 × 10−3 | up |
| phototransduction | |||||
| SC7-LG08_10491 | visinin-like | rcvrn3 | 1.76 | 2.80 × 10−4 | up |
| transcription factors | |||||
| SC7-LG01_00775 | general transcription factor IIF subunit 1 | gtf2f1 | −1.05 | 2.39 × 10−4 | down |
| SC7-LG04_05393 | period circadian protein homolog 3 | per3 | 1.40 | 1.55 × 10−4 | up |
| SC7-LG08_10567 | transcription elongation factor B polypeptide 3 | eloa/tceb3 | 1.77 | 6.36 × 10−3 | up |
| SC7-LG08_10670 | PR domain zinc finger protein 1a | prdm1a | 1.10 | 1.94 × 10−3 | up |
| SC7-LG08_11305 | thyroid hormone receptor beta | thrb | 1.55 | 3.77 × 10−2 | up |
| SC7-LG09_12670 | estrogen-related receptor gamma | esrrg | 1.16 | 1.96 × 10−3 | up |
| SC7-LG13_17911 | myocyte enhancer factor 2ca | mef2ca | −1.41 | 1.77 × 10−10 | down |
| SC7-LG16_20751 | nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group E, member 3 | nr2e3 | −1.10 | 7.21 × 10−3 | down |
| SC7-LG18_22664 | homeobox and leucine zipper protein a | homeza | 1.15 | 4.80 × 10−3 | up |
| SC7-LG21_27073 | early growth response protein 1 | egr1 | 1.03 | 6.87 × 10−3 | up |
| SC7-LG22_27752 | cone-rod homeobox | crx | −1.02 | 6.93 × 10−3 | down |
| opsins | |||||
| SC7-LG07_09212 | melanopsin A | opn4xb | 1.20 | 1.33 × 10−2 | up |
| SC7-LG10_13207 | opsin 5 | opn5 | 2.89 | 4.87 × 10−2 | up |
| Gene ID | Description | Gene Symbol | Log2FC | Padjust | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| protein digestion | |||||
| SC7-LG04_05415 | anionic trypsin-1-like | prss1 | 3.95 | 1.05 × 10−13 | up |
| SC7-LG05_06178 | carboxypeptidase A1 | cpa1 | 3.72 | 2.75 × 10−29 | up |
| SC7-LG05_06203 | carboxypeptidase A2-like | cpa2 | 4.66 | 3.03 × 10−6 | up |
| SC7-LG07_09459 | chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 2A | cela2a | 3.14 | 8.44 × 10−6 | up |
| SC7-LG08_10790 | trypsin-3-like | try | 4.66 | 2.60 × 10−8 | up |
| SC7-LG09_12234 | neprilysin | mme | 1.20 | 1.70 × 10−11 | up |
| SC7-LG10_13776 | chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 2A | cela2a | 2.47 | 1.88 × 10−7 | up |
| SC7-LG12_16603 | meprin A subunit alpha-like | mep1a.1 | 3.73 | 6.95 × 10−104 | up |
| SC7-LG12_16604 | meprin A subunit alpha-like | mep1a.2 | 3.41 | 1.38 × 10−34 | up |
| SC7-LG14_18622 | carboxypeptidase B2 | cpb2 | 5.12 | 6.99 × 10−17 | up |
| SC7-LG14_18753 | dipeptidyl peptidase 4-like | dpp4 | 3.08 | 1.90 × 10−21 | up |
| SC7-LG16_20581 | angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 | ace2 | 3.24 | 4.90 × 10−12 | up |
| SC7-LG16_20935 | chymotrypsin A-like | ctra | 5.76 | 1.31 × 10−39 | up |
| SC7-LG16_20936 | chymotrypsin B | ctrb | 5.23 | 6.54 × 10−28 | up |
| SC7-LG17_21412 | trypsinogen-like protein 3 | trp3 | 4.25 | 1.34 × 10−41 | up |
| SC7-LG17_21428 | trypsin-like | prss59.1 | 5.17 | 2.94 × 10−47 | up |
| SC7-LG17_21430 | trypsin-1 | prss59.1 | 6.11 | 1.86 × 10−49 | up |
| SC7-LG17_21862 | chymotrypsin-like protease CTRL-1 | ctrl | 4.61 | 1.35 × 10−3 | up |
| SC7-LG17_21865 | chymotrypsin-like protease CTRL-1 | ctrl | 6.39 | 7.98 × 10−6 | up |
| SC7-LG17_21899 | pancreatic trypsin | try | 4.65 | 1.79 × 10−39 | up |
| SC7-LG19_24660 | dipeptidyl peptidase 4-like | fap | 1.69 | 7.34 × 10−5 | up |
| SC7-LG20_25447 | chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 3B | cela3b | 4.62 | 7.14 × 10−12 | up |
| SC7-LG21_26716 | xaa-Pro aminopeptidase 2 | xpnpep2 | 1.86 | 3.14 × 10−13 | up |
| SC7-LG24_30459 | carboxypeptidase B | cpb1 | 1.30 | 1.02 × 10−3 | up |
| fat digestion | |||||
| SC7-LG03_04160 | group XIIB secretory phospholipase A2-like protein | pla2g12b | 4.30 | 4.77 × 10−52 | up |
| SC7-LG13_17222 | bile salt-activated lipase-like | cel | −1.57 | 1.86 × 10−3 | down |
| SC7-LG13_17255 | phospholipase A2-like | pla2g1b | 2.99 | 1.46 × 10−12 | up |
| SC7-LG13_17854 | group 3 secretory phospholipase A2-like | pla2g3 | 1.43 | 1.30 × 10−3 | up |
| SC7-UN_52_31480 | bile salt-activated lipase-like | cel | 1.62 | 3.33 × 10−2 | up |
| carbohydrate digestion | |||||
| SC7-LG18_23440 | pancreatic alpha-amylase-like | amy2a | 1.69 | 2.15 × 10−4 | up |
| SC7-LG19_24913 | lactase-phlorizin hydrolase-like | lct | 1.99 | 9.21 × 10−5 | up |
| Gene ID | Description | Gene Symbol | Log2FC | Padjust | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| protein digestion | |||||
| SC7-LG04_05415 | anionic trypsin-1-like | prss1 | 5.23 | 4.46 × 10−23 | up |
| SC7-LG05_06178 | carboxypeptidase A1 | cpa1 | 4.30 | 1.41 × 10−21 | up |
| SC7-LG05_06203 | carboxypeptidase A2-like | cpa2 | 5.70 | 8.36 × 10−7 | up |
| SC7-LG07_09459 | chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 2A | cela2a | 4.30 | 5.07 × 10−8 | up |
| SC7-LG08_10790 | trypsin-3-like | try | 5.76 | 4.92 × 10−12 | up |
| SC7-LG09_12234 | Neprilysin | mme | 1.19 | 8.21 × 10−9 | up |
| SC7-LG10_13776 | chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 2A | cela2a | 1.91 | 8.19 × 10−3 | up |
| SC7-LG12_16603 | meprin A subunit alpha-like | mep1a.1 | 2.91 | 2.92 × 10−23 | up |
| SC7-LG12_16604 | meprin A subunit alpha-like | mep1a.2 | 3.19 | 4.46 × 10−29 | up |
| SC7-LG14_18622 | carboxypeptidase B2 | cpb2 | 4.12 | 8.56 × 10−12 | up |
| SC7-LG14_18753 | dipeptidyl peptidase 4-like | dpp4 | 2.44 | 8.45 × 10−10 | up |
| SC7-LG16_20581 | angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 | ace2 | 2.87 | 1.54 × 10−7 | up |
| SC7-LG16_20935 | chymotrypsin A-like | ctra | 6.16 | 1.80 × 10−26 | up |
| SC7-LG16_20936 | chymotrypsin B | ctrb | 5.60 | 4.95 × 10−22 | up |
| SC7-LG17_21412 | trypsinogen-like protein 3 | trp3 | 4.48 | 7.89 × 10−60 | up |
| SC7-LG17_21428 | trypsin-like | prss59.1 | 5.97 | 2.44 × 10−27 | up |
| SC7-LG17_21430 | trypsin-1 | prss59.1 | 6.87 | 8.66 × 10−31 | up |
| SC7-LG17_21862 | chymotrypsin-like protease CTRL-1 | ctrl | 5.45 | 5.81 × 10−5 | up |
| SC7-LG17_21865 | chymotrypsin-like protease CTRL-1 | ctrl | 7.19 | 3.37 × 10−7 | up |
| SC7-LG17_21899 | pancreatic trypsin | try | 4.90 | 1.30 × 10−19 | up |
| SC7-LG20_25299 | meprin A subunit beta-like | mep1b | −1.87 | 3.39 × 10−3 | down |
| SC7-LG20_25447 | chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 3B | cela3b | 3.94 | 3.14 × 10−7 | up |
| SC7-LG21_26716 | xaa-Pro aminopeptidase 2 | xpnpep2 | 1.83 | 9.35 × 10−16 | up |
| SC7-LG23_29643 | elastase-1-like | zgc:112285 | 2.35 | 4.83 × 10−10 | up |
| SC7-LG24_30459 | carboxypeptidase B | cpb1 | 1.50 | 1.73 × 10−3 | up |
| fat digestion | |||||
| SC7-LG03_04160 | group XIIB secretory phospholipase A2-like protein | pla2g12b | 3.94 | 1.15 × 10−24 | up |
| SC7-LG13_17222 | bile salt-activated lipase-like | cel | −2.15 | 4.31 × 10−7 | down |
| SC7-LG13_17223 | bile salt-activated lipase-like | cel | 1.71 | 3.40 × 10−2 | up |
| SC7-LG13_17255 | phospholipase A2-like | pla2g1b | 3.19 | 2.44 × 10−6 | up |
| SC7-UN_52_31480 | bile salt-activated lipase-like | cel | 1.67 | 3.53 × 10−2 | up |
| carbohydrate digestion | |||||
| SC7-LG18_23440 | pancreatic alpha-amylase-like | amy2a | 2.88 | 3.21 × 10−7 | up |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Tang, S.-L.; He, S.; Liang, X.-F. Transcriptome Analysis Provides an Overview of Genes Involved in the Peculiar Food Preference at First-Feeding Stage in Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Fishes 2023, 8, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8010017
Li L, Tang S-L, He S, Liang X-F. Transcriptome Analysis Provides an Overview of Genes Involved in the Peculiar Food Preference at First-Feeding Stage in Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Fishes. 2023; 8(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ling, Shu-Lin Tang, Shan He, and Xu-Fang Liang. 2023. "Transcriptome Analysis Provides an Overview of Genes Involved in the Peculiar Food Preference at First-Feeding Stage in Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi)" Fishes 8, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8010017
APA StyleLi, L., Tang, S.-L., He, S., & Liang, X.-F. (2023). Transcriptome Analysis Provides an Overview of Genes Involved in the Peculiar Food Preference at First-Feeding Stage in Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Fishes, 8(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8010017






