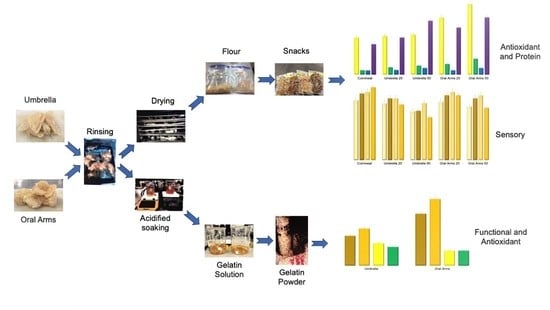
Conversion of Dry-Salted Cannonball Jellyfish (Stomolophus meleagris) Umbrella and Oral Arms to Cornmeal Snacks and Gelatin with Antioxidant Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material
2.2. Preliminary Characterization of Dry-Salted Umbrella and Oral Arms
2.3. Preparation of Rehydrated Umbrella Flour and Oral Arms Flour
2.4. Preparation of Cornmeal Snacks and Analysis
2.4.1. Chemical Analysis of Flour and Snacks
2.4.2. Antioxidant Activity of Flour and Snacks
2.4.3. Sensory Analysis of Snacks
2.5. Preparation and Analysis of Gelatin Powders
2.5.1. Chemical Analysis
2.5.2. Electrophoretic Profile (SDS-PAGE)
2.5.3. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance of Proton (1H-NMR)
2.5.4. Viscosity
2.5.5. Foaming Properties
2.5.6. Antioxidant Properties
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Characterization of Jellyfish Umbrella and Oral Arms
3.2. Snacks
3.2.1. Chemical Analysis of Flours and Snacks
3.2.2. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Flour and Snacks
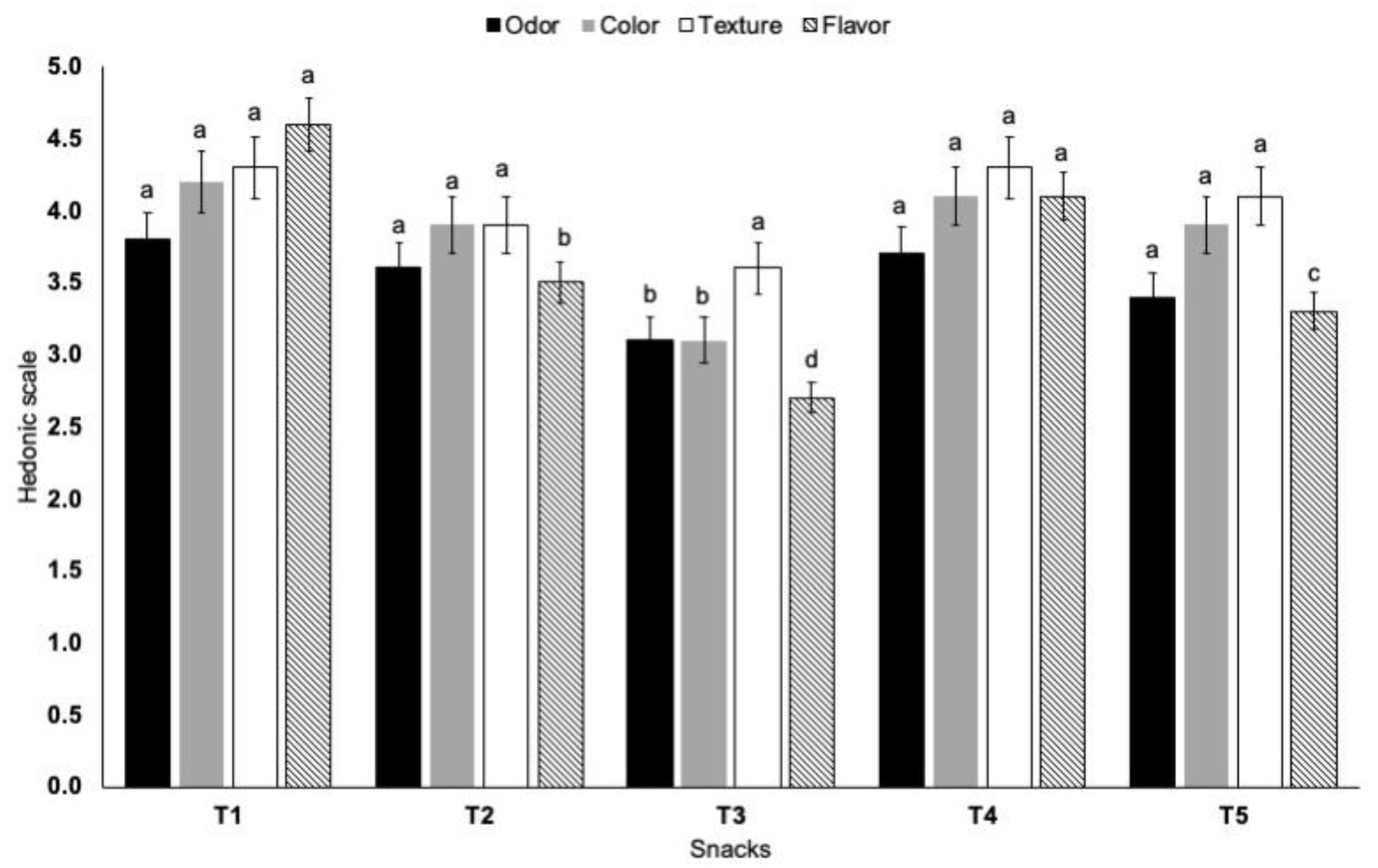
3.2.3. Sensory Analysis of Snacks
3.3. Gelatin
3.3.1. Yield
3.3.2. Chemical Composition
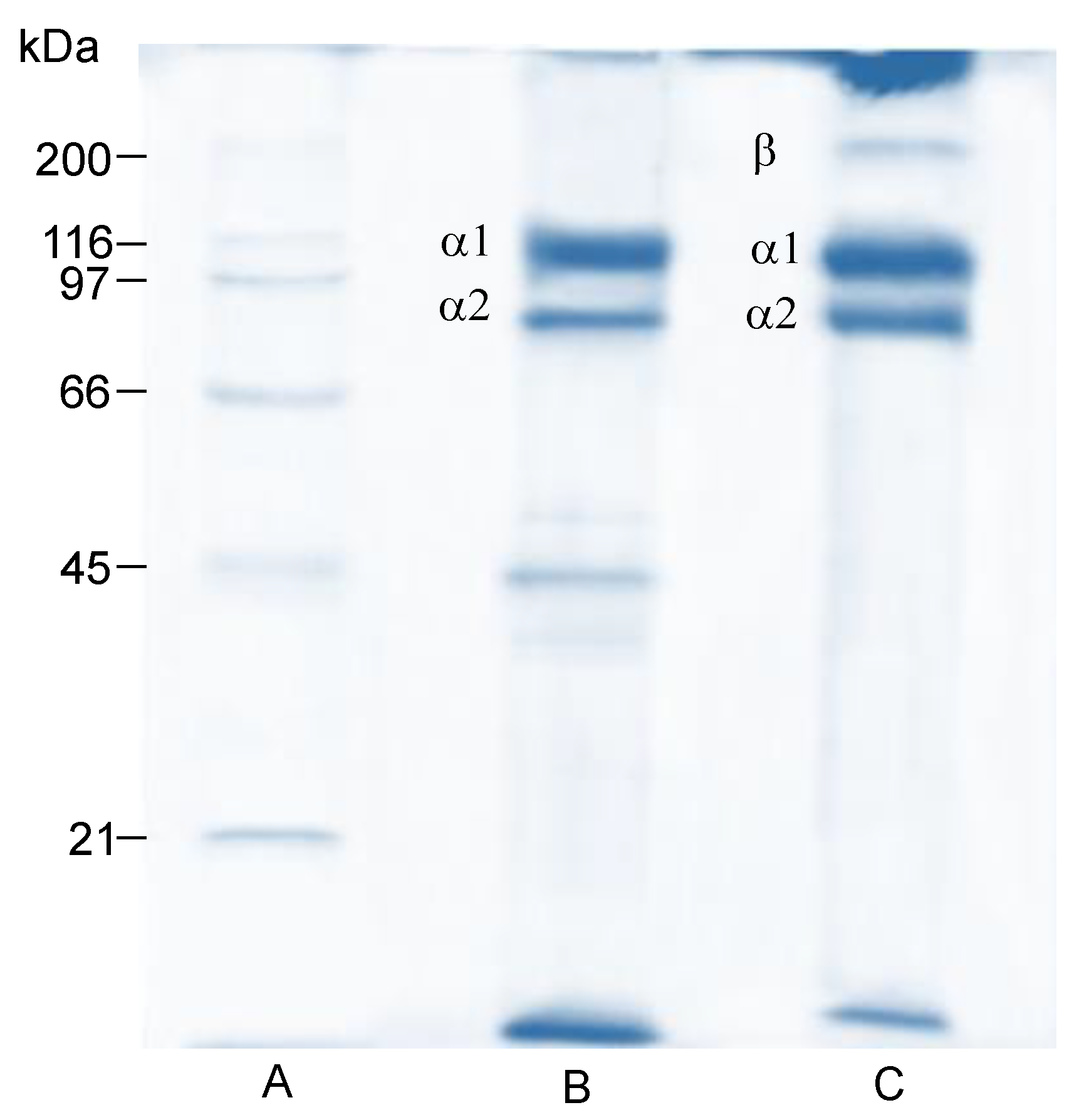
3.3.3. Electrophoretic Profile
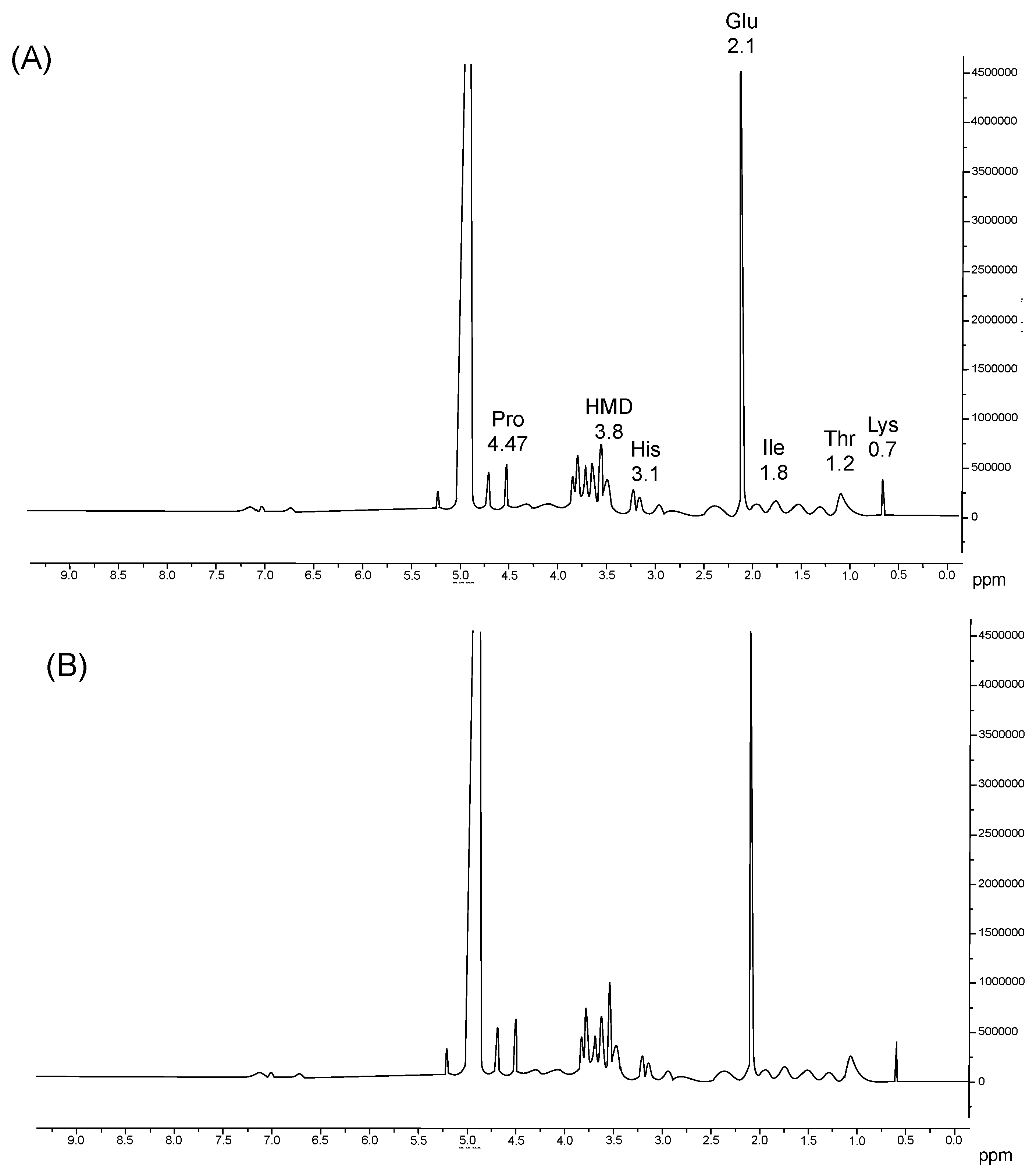
3.3.4. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance of Proton (1H-NMR)
3.3.5. Viscosity
3.3.6. Foaming Properties
3.3.7. Antioxidant Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bleve, G.L.; Ramires, F.A.; Gallo, A.; Leone, A. Identification of safety and quality parameters for preparation of jellyfish based novel food products. Foods 2019, 8, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.F.; Li, Y.-Y.; Xu, J.-J.; Su, X.R.; Gao, X.; Yue, F.-P. Study on effect of jellyfish collagen hydrolysate on anti-fatigue and anti-oxidant. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzideh, Z.; Latiff, A.A.; Gan, C.-Y.; Abedin, M.Z.; Alias, A.K. ACE inhibitory and antioxidant activities of collagen hydrolysates from the ribbon jellyfish (Chrysaora sp.). Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 52, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, A.; Lecci, R.M.; Durante, M.; Meli, F.; Piraino, S. The bright side of gelatinous blooms: Nutraceutical value and antioxidant properties of three Mediterranean jellyfish (Scyphozoa). Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4654–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khong, N.M.H.; Yusoff, F.M.; Jamilah, B.; Basri, M.; Maznah, I.; Chan, K.W.; Nishikawa, J. Nutritional composition and total collagen content of three commercially important edible jellyfish. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodsuwan, U.; Thumthanaruk, B.; Kerdchoechuen, O.; Laohakunjit, N. Functional properties of type A gelatin from jellyfish (Lobonema smithii). Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23, 507–514. Available online: http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my/23%20(02)%202016/(8).pdf (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Prieto, L.; Enrique-Navarro, A.; Volsi, R.L.; Ortega, M.J. The large jellyfish Rhizostoma luteum as sustainable a resource for antioxidant properties, nutraceutical value and biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, C.; Zhao, J.; Shi, X.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Fu, Y.; Jin, W.; Zhu, B. Separation and characterization of antioxidative and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from jellyfish gonad hydrolysate. Molecules 2018, 23, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, S.; De Rinaldis, G.; Paulmery, M.; Piraino, S.; Leone, A. Barrel jellyfish (Rhizostoma pulmo) as source of antioxidant peptides. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.; Lecci, R.M.; Milisenda, G.; Piraino, S. Mediterranean jellyfish as novel food: Effects of thermal processing on antioxidant, phenolic, and protein contents. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1611–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, P.G.; Pegg, R.B.; Kumar, D.; Sloval, K.M. Exploring the feasibility of developing novel gelatine powders from salted, dried cannonball jellyfish (Stomolophus meleagris). Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upata, M.; Siriwoharn, T.; Makkun, S.; Yarnpakdee, S.; Regenstein, J.M.; Wangtueai, S. Tyrosinase inhibitory and antioxidant activity of enzymatic protein hydrolysate from jellyfish (Lobonema smithii). Foods 2022, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, L.; Raposo, A.; Morais, Z.; Coimbra, A. Jellyfish ingestion was safe for patients with crustaceans, cephalopods, and fish allergy. Asia Pac. Allergy 2018, 8, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Martínez, J.; Álvarez-Tello, J. The jellyfish fishery in Mexico. Agric. Sci. 2013, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Future of Food. Available online: https://www.about.sainsburys.co.uk/~/media/Files/S/Sainsburys/pdf-downloads/futureoffood-10c.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Jozinović, A.; Šubarić, D.; Ačkar, Đ.; Babić, J.; Orkić, V.; Guberac, S.; Miličević, B. Food industry by-products as raw materials in the production of value-added corn snack products. Foods 2021, 10, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.; Skonberg, D.; Camire, M.; Dougherty, M.; Bayer, R.; Briggs, J. Chemical composition and physical properties of extruded snacks containing crab-processing by-product. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, G.; Gautam, A. Hydrolyzed fish muscle as a modifier of rice flour extrudate characteristics. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez-Netto, J.; Campagnoli-de Oliveira, P.; Lapa-Guimarães, J.; Villegas, M. Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of snack made with minced Nile tilapia. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 34, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaviklo, A.R. Fish snacks from value addition of low value fish and processing by-products. Infofish Inter. 2012, 5, 42–44. Available online: www.infofish.org (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Shaviklo, A.R.; Azaribeh, M.; Moradi, Y.; Zangeneh, P. Formula optimization and storage stability of extruded puffed corn-shrimp snacks. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish gelatin: Properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Ahn, J.R.; Koo, J.S.; Kim, S.B. Physicochemical properties of gelatin from jellyfish Rhopilema hispidum. Fish. Aquatic Sci. 2014, 17, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancharern, P.; Laohakunjit, N.; Kerdchoechuen, O.; Thumthanaru, B. Extraction of type A and type B gelatin from jellyfish (Lobonema smithii). Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23, 419–424. Available online: www.ifrj.upm.edu.my/23%20(01)%202016/(63).pdf (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Lueyot, A.; Rungsardthong, V.; Vatanyoopaisarn, S.; Hutangura, P.; Wonganu, B.; Wongsa-Ngsari, P.; Charoenlappanit, S.; Roytrakul, S.; Thumthanaruk, B. Influence of collagen and some proteins on gel properties of jellyfish gelatin. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, W. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 17th ed.; The Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Protoggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J.J. Ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay: Direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fluids and modified version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilgaard, M.C.; Civille, G.V.; Caar, B.T. Sensory Evaluation Techniques, 4th ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Codex Alimentarius, Normas Internacionales de los Alimentos. Norma del Codex para galletas de pescado marino y de agua dulce y de mariscos, crustáceos y moluscos. Organización de las Naciones Unidas, Organización Mundial de la Salud, 2001, CXS 222-2001. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius.org (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- Sarbon, N.M.; Badii, F.; Howell, N.K. Preparation and characterisation of chicken skin gelatin as an alternative to mammalian gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Ortíz, F.A.; Morón-Fuenmayor, O.E.; González-Méndez, N.F. Hydroxyproline Measurement by HPLC: Improved Method of Total Collagen Determination in Meat Samples. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. 2004, 27, 2771–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabia-Sainz, H.M.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Márquez-Ríos, E.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.C.; Rouzaud-Sández, O.; Valenzuela-Soto, E.M.; Burgara-Estrella, A.J.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Interrelation of collagen chemical structure and nanostructure with firmness of three body regions of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas). Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzapour-Kouhdasht, A.; Sabzipour, F.; Taghizadeh, M.S.; Moosavi-Nasab, M. Physicochemical, rheological, and molecular characterization of colloidal gelatin produced from common carp by-products using microwave and ultrasound-assisted extraction. J. Texture Stud. 2019, 50, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uriarte-Montoya, M.H.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J.; Rouzaud-Sández, O.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Giant squid skin gelatin: Chemical composition and biophysical characterization. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 3243–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffman, C.W.; Garcia, V.V. Functional properties and amino acid content of protein isolate from mung bean flour. J. Food Technol. 1977, 12, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, C.; He, C.; Wang, H. Mechanical properties, anisotropic swelling behaviours and structures of jellyfish mesoglea. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 6, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, A.; Xiong, Z.; Li, Q.; Xiong, H.; Irshad, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, M.; Hina, S.; Regenstein, J.M. Evaluation of physicochemical, textural and sensory quality characteristics of red fish meat-based fried snacks. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5771–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipal, J.; Mohd Pu’ad, N.A.S.; Lee, T.C.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Sahari, N.; Basri, H.; Idris, M.I.; Abdullah, H.Z. A review of gelatin: Properties, sources, process, applications, and commercialization. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Compendium of Food Additive Specifications; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006; ISSN 1817-7077. [Google Scholar]
- Ledward, D.A. Gelation of gelatin. In Functional Properties of Food Macromolecules; Mitchell, J.R., Ledward, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 1986; pp. 171–201. [Google Scholar]
- Klaiwong, T.; Hutangura, P.; Rutatip, S.; Wongsa-ngasri, P.; Thumthanaruk, B. Comparative properties of pepsin hydrolyzed jellyfish protein from salted jellyfish. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. B 2014, 4, 555–564. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, S.; Miyauchi, Y.; Uchida, N. Scale and bone type I collagens of carp (Cyprinus carpio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1991, 99, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, M.; Karube, S.; Hayashi, Y.; Shindo, H.; Igarashi, M. Direct measurement of collagen crosslinks with automatic amino acid analyzer—Identification of peaks due to crosslinks. FEBS Lett. 1976, 63, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen Lin, C.; Kuei Chiou, T.; Chieh Sung, W. Characteristics of gelatin from giant grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus) skin. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 2339–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Properties of emulsion stabilized with milk proteins: Overview of some recent development. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 2607–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.M.; Zabik, M.E. Ultrastructural examination of egg albumen protein foams. J. Food Sci. 1981, 46, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.-L.; Zhoa, X.; Li, B.F. Optimization of antioxidant activity by response surface methodology in hydrolysates of jellyfish (Rhopilema esculentum) umbrella collagen. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2009, 10, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample | SUM | SOA | UMF | OAF | CM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 1.02 ± 0.26 c | 1.35 ± 0.15 c | 17.52 ± 0.29 a | 16.94 ± 1.02 a | 7.86 ± 0.38 b |
| Protein | 19.42 ± 1.66 b | 23.65 ± 1.29 a | 18.56 ± 1.14 b | 22.67 ± 1.31 a | 12.12 ± 0.80 c |
| Lipids | 1.15 ± 0.11 b | 1.23 ± 0.16 b | 1.33 ± 0.15 b | 1.59 ± 0.21 b | 6.91 ± 0.17 a |
| Ash | 78.35 ± 1.31 a | 73.57 ± 1.71 b | 37.65 ± 0.66 a | 35.37 ± 0.35 b | 1.71 ± 0.20 c |
| DPPH | 18.9 ± 0.81 b | 24.8 ± 0.99 a | 17.70 ± 1.20 b | 23.40 ± 1.08 a | 16.98 ± 1.13 b |
| ABTS | 7.1 ± 0.52 b | 11.6 ± 0.60 a | 6.04 ± 0.42 b | 10.90 ± 0.90 a | 2.91 ± 0.68 c |
| FRAP | 2.05 ± 0.25 a | 2.75 ± 0.38 a | 1.94 ± 0.63 a | 2.26 ± 0.48 a | 2.02 ± 0.35 a |
| Sample | Moisture (%) | Protein (%) | Lipids (%) | Ash (%) | Carbohydrate-Free Nitrogen (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 5.30 ± 0.43 c | 8.63 ± 0.66 f | 5.00 ± 0.29 b | 4.71 ± 0.28 d | 76.37 ± 0.41 a |
| T2 | 4.48 ± 1.06 c | 11.30 ± 0.72 e | 4.40 ± 0.25 c | 24.21 ± 0.29 c | 55.62 ± 0.58 c |
| T3 | 4.36 ± 0.97 c | 15.78 ± 0.53 d | 4.23 ± 0.35 c | 22.15 ± 0.64 c | 53.48 ± 0.62 c |
| T4 | 4.60 ± 0.35 c | 13.63 ± 1.02 de | 4.10 ± 0.20 c | 22.20 ± 0.42 c | 55.47 ± 0.50 c |
| T5 | 4.69 ± 0.55 c | 17.12 ± 1.09 c | 4.40 ± 0.30 c | 20.45 ± 1.77 c | 53.34 ± 0.93 c |
| Sample | DPPH (%) | ABTS (μM TE/g dm) | FRAP (μM TE/g dm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 11.18 ± 1.15 e | 1.50 ± 0.22 d | 1.14 ± 0.27 a |
| T2 | 12.43 ± 0.81 e | 2.12 ± 0.44 cd | 1.32 ± 0.58 a |
| T3 | 13.23 ± 1.21 e | 2.62 ± 0.54 cd | 1.86 ± 0.83 a |
| T4 | 16.73 ± 1.14 d | 3.09 ± 0.68 c | 1.27 ± 0.42 a |
| T5 | 21.30 ± 0.75 c | 4.71 ± 0.79 b | 1.91 ± 0.46 a |
| Analysis | Umbrella | Oral Arms |
|---|---|---|
| Yield (g/100 g jellyfish, wet basis) | 4.13 ± 1.23 b | 6.81 ± 1.26 a |
| Moisture (%) | 13.86 ± 0.62 a | 13.60 ± 0.46 a |
| Protein (%) | 71.23 ± 1.38 b | 71.67 ± 1.55 a |
| Lipids (%) | 1.17 ± 0.21 a | 1.49 ± 0.31 a |
| Ash (%) | 13.32 ± 0.52 a | 13.13 ± 0.81 a |
| Proline (mg/100 g) | 13.60 ± 0.42 a | 15.26± 0.25 a |
| Hydroxyproline (mg/100 g) | 18.65 ± 0.38 b | 22.87 ± 0.16 a |
| Imino acids 2 | 32.25 ± 0.40 b | 38.13 ± 0.21 a |
| Analysis | Umbrella | Oral Arms |
|---|---|---|
| VIS (cp) | 4.63 ± 0.60 b | 7.30 ± 0.56 a |
| FC (%) | 51.90 ± 2.30 a | 81.69 ± 3.29 a |
| IC50 DPPH (mg protein/mL) | 2.54 ± 0.47 a | 1.95 ± 0.07 b |
| IC50 ABTS (mg protein/mL) | 2.47 ± 0.02 a | 2.09 ± 0.08 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
del Sol Villalba-Urquidy, B.; Velazquez-Valdez, L.P.; Bracamontes-Picos, S.J.; Del Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Chan-Higuera, J.E.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Conversion of Dry-Salted Cannonball Jellyfish (Stomolophus meleagris) Umbrella and Oral Arms to Cornmeal Snacks and Gelatin with Antioxidant Properties. Fishes 2022, 7, 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050277
del Sol Villalba-Urquidy B, Velazquez-Valdez LP, Bracamontes-Picos SJ, Del Toro-Sánchez CL, Chan-Higuera JE, Ezquerra-Brauer JM. Conversion of Dry-Salted Cannonball Jellyfish (Stomolophus meleagris) Umbrella and Oral Arms to Cornmeal Snacks and Gelatin with Antioxidant Properties. Fishes. 2022; 7(5):277. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050277
Chicago/Turabian Styledel Sol Villalba-Urquidy, Blanca, Luis Pablo Velazquez-Valdez, Samantha Jaqueline Bracamontes-Picos, Carmen Lizette Del Toro-Sánchez, Jesús Enrique Chan-Higuera, and Josafat Marina Ezquerra-Brauer. 2022. "Conversion of Dry-Salted Cannonball Jellyfish (Stomolophus meleagris) Umbrella and Oral Arms to Cornmeal Snacks and Gelatin with Antioxidant Properties" Fishes 7, no. 5: 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050277
APA Styledel Sol Villalba-Urquidy, B., Velazquez-Valdez, L. P., Bracamontes-Picos, S. J., Del Toro-Sánchez, C. L., Chan-Higuera, J. E., & Ezquerra-Brauer, J. M. (2022). Conversion of Dry-Salted Cannonball Jellyfish (Stomolophus meleagris) Umbrella and Oral Arms to Cornmeal Snacks and Gelatin with Antioxidant Properties. Fishes, 7(5), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050277