Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Probiotics and Prebiotics on Growth, Physiological Condition, and Resistance to Pathogens Challenge in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Conditions and Fish
2.2. Preparation of Experimental Feed
- Control variant (V0)—commercial feed, without probiotics and prebiotics;
- Probiotic variant (V1)—commercial feed supplemented with BetaPlus® probiotics–1% × BW;
- Prebiotic variant (V2)—commercial feed supplemented with TechnoMos® prebiotics–1% × BW;
- Synbiotic variant (V3)—commercial feed supplemented with BetaPlus® probiotics and TechnoMos® prebiotics–1:1% × BW.
2.3. Growth Measurements
2.4. Blood Samples, Hematological, Biochemical Parameters, and Oxidative Stress
2.4.1. Blood Sampling
2.4.2. Hematological, Biochemical Parameters, and Oxidative Stress
2.5. Challenge Tests
- Positive control (C+)—fish were injected with 0.5 ml of 0.85% saline solution;
- Aeromonas hydrophila (Ah)—fish were injected with 0.5 ml solution of Aeromonas hydrophila with a concentration of 1.3 × 109 CFU/mL;
- Pseudomonas fluorescens (Pf)—fish were injected with a 0.5 mL solution of Pseudomonas fluorescens with a concentration of 1.5 × 109 CFU/mL;
- Negative control (C−)—fish were not injected.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fish Growth Performance
3.2. Hematological and Biochemical Parameters
3.3. Challenge Tests
Hematological and Biochemical Parameters after the Challenge Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El Asely, A.; Amin, A.; El-Naby, A.S.A.; Samir, F.; El-Ashram, A.; Dawood, M.A.O. Ziziphus mauritiana supplementation of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) diet for improvement of immune response to Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 1561–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadifar, E.; Moghadam, M.S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Hoseinifar, S.H. Lactobacillus fermentum and/or ferulic acid improved the immune responses, antioxidative defence and resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fingerlings. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, D.; Faggio, C. Importance of prebiotics in aquaculture as immunostimulants. Effects on immune system of Sparus aurata and Dicentrarchus labrax. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, P.; Prakash, P.; Musthafa, M.S.; Faggio, C. Effect of alkoxy glycerol on growth performance, immune response and disease resistance in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 123, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichaiyo, N.; Tongsiri, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Dawood, M.A.; Jaturasitha, S.; Esteban, M.; Ringø, E.; Van Doan, H. The effects gotu kola (Centella asiatica) powder on growth performance, skin mucus, and serum immunity of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fingerlings. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 16, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doan, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Ringø, E.; Ángeles Esteban, M.; Dadar, M.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Faggio, C. Host-Associated Probiotics: A Key Factor in Sustainable Aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2019, 1, 16–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S. Efficiency of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum supplemental diets on red sea bream Pagrus major. Aquaculture 2015, 442, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Van Doan, H. Probiotic application for sustainable aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, B.P. Production, health aspects and potential food uses of dairy prebiotic galactooligosaccharides. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringø, E.; Olsen, R.; Gifstad, T.; Dalmo, R.; Amlund, H.; Hemre, G.-I.; Bakke, A. Prebiotics in aquaculture: A review. Aquac. Nutr. 2010, 16, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohani, F.; Islam, S.M.; Hossain, K.; Ferdous, Z.; Siddik, M.A.; Nuruzzaman, M.; Padeniya, U.; Brown, C.; Shahjahan, M. Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics improved the functionality of aquafeed: Upgrading growth, reproduction, immunity and disease resistance in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 120, 569–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.-G.; Shiu, Y.-L.; Nguyen, T.-P.; Truong, Q.-P.; Chen, J.-C.; Liu, C.-H. Current applications, selection, and possible mechanisms of actions of synbiotics in improving the growth and health status in aquaculture: A review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 64, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derome, N.; Gauthier, J.; Boutin, S.; Llewellyn, M. Bacterial Opportunistic Pathogens of Fish. In The Rasputin Effect: When Commensals and Symbionts Become Parasitic, Advances in Environmental Microbiology, Advances in Environmental Microbiology; Hurst, C.J., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 81–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, A.M.; El-Sayed, A.F.M.; Mahmoud, M.M. Effects of a novel marine probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum AH 78, on growth performance and immune response of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarahmadi, P.; Ghafarifarsani, H.; Khazaei, A.; Khodadadi, M.; Rashidiyan, G.; Jalali, M.A. Protective effects of the prebiotic on the immunological indicators of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, A.; Banerjee, G.; Dan, S.K.; Ghosh, P.; Ghosh, K.; Ray, A.K. Screening of Autochthonous Intestinal Microbiota as Candidate Probiotics Isolated from Four Freshwater Teleosts. Curr. Sci. 2017, 113, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, G.; Nandi, A.; Ray, A.K. Assessment of hemolytic activity, enzyme production and bacteriocin characterization of Bacillus subtilis LR1 isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of fish. Arch Microbiol. 2017, 199, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Bolívar, J.F.; Pardo, R.Y.R.; Hume, M.E.; Díaz, L.M.V. Multistrain probiotics use in main commercially cultured freshwater fish: A systematic review of evidence. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1758–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raida, M.K.; Larsen, J.L.; Nielsen, M.E.; Buchmann, K. Enhanced resistance of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), against Yersinia ruckeri challenge following oral administration of Bacillus subtilis and B. licheniformis (BioPlus2B). J. Fish Dis. 2003, 26, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, T.; Hedayati, S.A.; Yavari, V.; Alizade, M.; Farzanfar, A. Growth, survival and gut microbial load of rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss) fry given diet supplemented with probiotic during the two months of first feeding. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 8, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Bradley, G.; Baker, R.T.M.; Davies, S.J. Probiotic applications for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) II. Effects on growth performance, feed utilization, intestinal microbiota and related health criteria postantibiotic treatment. Aquac. Nutr. 2010, 16, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, S.; Khara, H.; Shakoori, M. Effects of probiotics and Fe ion on the growth and survival and body composition of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1792) frys. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2013, 41, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Dimitroglou, A.; Bradley, G.; Baker, R.T.M.; Davies, S.J. Probiotic applications for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) I. Effects on growth performance, feed utilization, intestinal microbiota and related health criteria. Aquac. Nutr. 2010, 16, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, R.A.; Lim, C.; Yildirim-Aksoy, M.; Delaney, M.A. Effects of Probiotic Diet Supplements on Disease Resistance and Immune Response of Young Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. J. Appl. Aquac. 2006, 18, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antache, A.; Cristea, V.; Grecu, I.; Dediu, L.; Cretu, M.; Bocioc, E.; Petrea, S.M. Effects of Dietary Supplementation at Nile tilapia with Thymus vulgaris, Trigonela foenum graecum and Azadirachta indica on Welfare Status. Bull. UASVM Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 71, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, R.d.A.; Costa, L.S.; Okamura, D.; Felipe, G.d.A.; Ribeiro, P.A.P.; Corrêa, F.M.; Priscila, V.R. Evaluation of 2-phenoxyethanol and menthol as anaesthetic agent in tilapia. Bol. Inst. 2012, 38, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Svobodová, Z.; Flajšhans, M.; Kolářová, J.; Modrá, H.; Svoboda, M.; Vajcová, V. Leukocyte profiles of diploid and triploid tench, Tinca tinca L. Aquaculture 2001, 198, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodova, Z.; Pravda, D.; Palackov, J. Unified Methods of Haematological Examination of Fish; Research Institute of Fish Culture and Hydrobiology: Vodnany, Czech Republic, 1991; p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Draper, H.; Hadley, M. Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid Peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.T.; Wang, S.F.; Cai, Y.; Guo, X.H.; Cao, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Liu, S.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Dietary administration of Bacillus subtilis HAINUP40 enhances growth, digestive enzyme activities, innate immune responses and disease resistance of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Zommara, M.; Eweedah, N.M.; Helal, A.I.; Aboel-Darag, M.A. The potential role of nano-selenium and vitamin C on the performances of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 9843–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.D.F.; Baldissera, M.D.; Verdi, C.M.; Santos, R.C.; Da Rocha, M.I.U.; da Veiga, M.L.; da Silva, A.S.; Baldisserotto, B. Oxidative stress and antioxidant responses in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus experimentally infected by Providencia rettgeri. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 131, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldissera, M.D.; Souza, C.F.; Doleski, P.H.; de Vargas, A.C.; Duarte, M.M.; Duarte, T.; Boligon, A.A.; Leal, D.B.; Baldisserotto, B. Melaleuca alternifolia essential oil prevents alterations to purinergic enzymes and ameliorates the innate immune response in silver catfish infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 109, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, R.C.; da Costa, M.M.; Baldisserotto, B.; Heinzmann, B.M.; Schmidt, D.; Caron, B.O.; Copatti, C.E. Antimicrobial and synergistic activity of essential oils of Aloysia triphylla and Lippia alba against Aeromonas spp. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fečkaninová, A.; Koščová, J.; Mudroňová, D.; Popelka, P.; Toropilová, J. The use of probiotic bacteria against Aeromonas infections in salmonid aquaculture. Aquaculture 2017, 469, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morselli, M.B.; Reis, J.H.; Baldissera, M.D.; Souza, C.F.; Baldisserotto, B.; Petrolli, T.G.; Paiano, D.; Lopes, D.L.; Da Silva, A.S. Benefits of thymol supplementation on performance, the hepatic antioxidant system, and energetic metabolism in grass carp. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 46, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morselli, M.B.; Baldissera, M.D.; Souza, C.F.; Reis, J.H.; Baldisserotto, B.; Sousa, A.A.; Zimmer, F.; Lopes, D.L.; Petrolli, T.G.; Da Silva, A.S. Effects of thymol supplementation on performance, mortality and branchial energetic metabolism in grass carp experimentally infected by Aeromonas hydrophila. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 139, 103915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rurangwa, E.; Verdegem, M.C.J. Microorganisms in recirculating aquaculture systems and their management. Rev. Aquac. 2014, 7, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Huang, L.; Liu, Z.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; Tacon, P.; Auclair, E.; Zhou, Z. A Comparison of the Beneficial Efects of Live and Heat-Inactivated Baker’s Yeast on Nile Tilapia: Suggestions on the Role and Function of the Secretory Metabolites Released from the Yeast. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145448. [Google Scholar]
- Irianto, A.; Austin, B. Use of dead probiotic cells to control furunculosis in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. Fish Dis. 2003, 26, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, Y.A.E.; Shalaby, A.M.E.; Sharaf Saffa, M.; El-Marakby, H.; RizlAlla, E.H. The physiological changes and growth performance of the Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus after feeding with Biogen® as growth promoter. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish 2004, 8, 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, K.A.; Badia, A.F.; Eid, A.M.S. Evaluation of using some feed additives on growth performance and feed utilization of monosex nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Fingerlings. Agric. Res. J. Suez Canal Univ. 2007, 7, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, J.-H.; Rahimnejad, S.; Yang, S.-Y.; Kim, K.-W.; Lee, K.-J. Evaluations of Bacillus spp. as dietary additives on growth performance, innate immunity and disease resistance of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) against Streptococcus iniae and as water additives. Aquaculture 2013, 50, 402–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Ray, A.K.; Ringø, E. Applications of plant ingredients for tropical and subtropical freshwater finfish: Possibilities and challenges. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 793–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, J.; Acosta, M.; Mendoza, G.; Pitones, V. Bacillus subtilis, an ideal probiotic bacterium to shrimp and fish aquaculture that increase feed digestibility, prevent microbial diseases, and avoid water pollution. Arch Microbiol. 2020, 202, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltan, M.A.; El-Laithy, S.M. Effect of probiotics and some spices as feed additives on the performance and behaviour of the Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Egypt J. Aquat. Biol. Fish 2008, 12, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazalah, A.A.; Ali, H.M.; Gehad, E.A.; Hammouda, Y.A. Effect of probiotics on performance and nutrients digestibility of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed low protein diets. Nat. Sci. 2010, 8, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Abarike, E.D.; Cai, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, L.; Jian, J.; Tang, J.; Jun, L.; Kuebutornye, F.K.A. Effects of a commercial probiotic BS containing Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis on growth, immune response and disease resistance in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarike, E.D.; Jian, J.; Tang, J.; Cai, J.; Yu, H.; Lihua, C.; Jun, L. Influence of traditional Chinese medicine and Bacillus species (TCMBS) on growth, immune response and disease resistance in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 2366–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, S.; Carrias, A.A.; Williams, M.A.; Liles, M.R.; Terhune, J.S.; Davis, D.A. Effects of Bacillus subtilis Strains on Growth, Immune Parameters, and Streptococcus iniae Susceptibility in Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2017, 48, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Pereira, M.A.; Schwarz, M.; Delbos, B.; Rodrigues, R.V.; Romano, L.; Sampaio, L. Efectos probiớticos sobre las larvas de cobia Rachycentron canadum criadas en un sistema de recirculaciớn de agua, Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 42, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, C.; Kim, H.; Aalfin Emmanuel, S.; Kim, H.G.; Won, S.; Bae, J.; Bai, S.C.; Koh, S.C. Microbial community analysis of an eco-friendly recirculating aquaculture system for olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) using complex microbial probiotics. Korean J. Microbiol. 2018, 54, 369–378. [Google Scholar]
- Zibiene, G.; Zibas, A. Impact of commercial probiotics on growth parameters of European catfish (Silurus glanis) and water quality in recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 1751–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, K.R. Fish Hematology and Associated Disorders. Clin. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 681–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ologhobo, A.D. Nutritive Values of Some Tropical (West African) Legumes for Poultry. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 1992, 2, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rhman, A.M.A.; Khattab, Y.A.; Shalaby, A.M. Micrococcus luteus and Pseudomonas species as probiotics for promoting the growth performance and health of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 27, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.S.; Soltan, M.A.; Ghonemy, M.M.R. Effect of synbiotics between Bacillus licheniformis and yeast extract on growth, hematological and biochemical indices of the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, Z.; Firouzbakhsh, F.; Jafarpour, A. Effects of dietary supplementation of synbiotic on growth performance, serum biochemical parameters and carcass composition in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fingerlings. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 96, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, E.; Khara, H.; Ahmadnezhad, M. Effects of synbiotic (Biomin IMBO) on haematological and immunological components of Russian sturgeon, Acipenser guldenstadti. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 24, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nobi, G.; Hassanin, M.; Khalil, A.; Mohammed, A.; Amer, S.; Montaser, M.; El-Sharnouby, M. Synbiotic Effects of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Mannan Oligosaccharides, and β-Glucan on Innate Immunity, Antioxidant Status, and Disease Resistance of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; El-Sabagh, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Wang, W.L.; Yukun, Z.; Olivier, A. Physiological response, blood chemistry profile and mucus secretion of red sea bream (Pagrus major) fed diets supplemented with Lactobacillus rhamnosus under low salinity stress. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchini, S.; Terova, G.; Caricato, G.; Saroglia, M. Lysozyme activity in embryos and larvae of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.), spawned by broodstock fed with vitamin C enriched diets. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2000, 20, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Okey, I.B.; Gabriel, U.U.; Deekae, S.N. The Use of Synbiotics (Prebiotic and Probiotic) in Aquaculture Development. Sumer. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 1, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Adloo, M.N.; Soltanian, S.; Hafezieh, M.; Ghadimi, N. Effects of long term dietary administration of β-Glucan on the growth, survival, and some blood parameters of striped catfish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (Siluriformes: Pangasiidae). Iran. J. Ichthyol. 2015, 2, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S.; El Basuini, M.F.; Hossain, M.S.; Nhu, T.H.; Moss, A.S.; Dossou, S.; Wei, H. Dietary supplementation of β-glucan improves growth performance, the innate immune response and stress resistance of red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstad, R.E.; Robertsen, B.; Frivold, E. Yeast glucan induces increase in lysozyme and complement-mediated haemolytic activity in Atlantic salmon blood. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1992, 2, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Sun, G.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Effect of dietary β-glucan on growth, survival and regulation of immune processes in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) infected by Aeromonas salmonicida. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 64, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Sun, H.; Chen, T.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, X.; Shi, C.; Pan, H.; Chang, O.; Ren, P.; et al. Oral delivery of Bacillus subtilis spores expressing cysteine protease of Clonorchis sinensis to grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus): Induces immune responses and has no damage on liver and intestine function. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 64, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Yousefi, S.; Van Doan, H.; Ashouri, G.; Gioacchini, G.; Maradonna, F.; Carnevali, O. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense in Fish: The Implications of Probiotic, Prebiotic, and Synbiotics. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 29, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Abarike, E.D.; Lu, Y.; Hlordzi, V.; Sakyi, M.E.; Afriyie, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, C.X. Mechanisms and the role of probiotic Bacillus in mitigating fish pathogens in aquaculture. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 819–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, M.; Cordero, H.; Martínez-Tomé, M.; Jiménez-Monreal, A.; Bakhrouf, A.; Mahdhi, A. Effect of dietary supplementation of probiotics and palm fruits extracts on the antioxidant enzyme gene expression in the mucosae of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 39, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, M.B.; Hashim, R.; Chai, Y.H.; Marsh, T.L.; Nor, S.A. Dietary prebiotics and probiotics influence growth performance, nutrient digestibility and the expression of immune regulatory genes in snakehead (Channa striata) fingerlings. Aquaculture 2016, 460, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irianto, A.; Austin, B. Probiotics in aquaculture. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Mukherjee, S.C.; Ranjan, R.; Nayak, S.K. Enhanced innate immune parameters in Labeo rohita (Ham.) following oral administration of Bacillus subtilis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddik, M.A.; Foysal, J.; Fotedar, R.; Francis, D.S.; Gupta, S.K. Probiotic yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae coupled with Lactobacillus casei modulates physiological performance and promotes gut microbiota in juvenile barramundi, Lates calcarifer. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Multifaceted applications of probiotic Bacillus species in aquaculture with special reference to Bacillus subtilis. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 13, 862–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amphan, S.; Unajak, S.; Printrakoon, C.; Areechon, N. Feedingregimen of β-glucan to enhance innate immunity and disease resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus Linn., against Aeromonas hydrophila and Flavobacterium columnare. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjugam, M.; Vaseeharan, B.; Iswarya, A.; Gobi, N.; Divya, M.; Thangaraj, M.P.; Elumalai, P. Effect of β-1, 3 glucan binding protein based zinc oxide nanoparticles supplemented diet on immune response and disease resistance in Oreochromis mossambicus against Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 76, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S. Effects of partial substitution of fish meal by soybean meal with or without heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum (LP20) on growth performance, digestibility, and immune response of amberjack, Seriola dumerili juveniles. Biomed Res Int. 2015, 2015, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S. Effects of heat killed Lactobacillus plantarum (LP20) supplemental diets on growth performance, stress resistance and immune response of red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 2015, 442, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S. Interaction effects of dietary supplementation of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum and β-glucan on growth performance, digestibility and immune response of juvenile red sea bream, Pagrus major. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S.; El-Sabagh, M.; Billah, M.M.; Zaineldin, A.I.; Zayed, M.M.; Omar, A.A.E.-D. Changes in the growth, humoral and mucosal immune responses following β-glucan and vitamin C administration in red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 2017, 470, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iswarya, A.; Vaseeharan, B.; Anjugam, M.; Gobi, N.; Divya, M.; Faggio, C. β-1, 3 glucan binding protein based selenium nanowire enhances the immune status of Cyprinus carpio and protection against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 83, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Ke, F.; Zhang, Q.-Y. Effect of β-glucan on activity of antioxidant enzymes and Mx gene expression in virus infected grass carp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 27, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, J.; Wiegertjes, G.F. Long-lived effects of administering β-glucans: Indications for trained immunity in fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 64, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarski, F.; Ferreira de Oliveira, C.A.; Darpossolo de Souza, F.P.B.; Zanuzzo, F.S. Different β-glucans improve the growth performance and bacterial resistance in Nile tilapia. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.A.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Saavedra, M.J.; Enes, P.; Serra, C.R. Bacillus spp. as source of Natural Antimicrobial Compounds to control aquaculture bacterial fish pathogens. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Liu, H.; Yu, L.; Zha, J.; Wang, G. Probiotic potential of Bacillus velezensis JW: Antimicrobial activity against fish pathogenic bacteria and immune enhancement effects on Carassius auratus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 78, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholil, M.I.; Hossain, M.M.M.; Neowajh, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Kabir, M. Comparative efficiency of some commercial antibiotics against Pseudomonas infection in fish. Int. J. Fish Aquat. Stud. 2015, 2, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, T. Pseudomonas anguilliseptica infection as a threat to wild and farmed fish in the Baltic Sea. Microbiol. Aust. 2016, 37, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Korkea-Aho, T.; Heikkinen, J.; Thompson, K.; Von, W.A.; Austin, B. Pseudomonas sp. M174 inhibits the fish pathogen Flavobacterium psychrophilum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.S.; Sen, S.S.; Sukumaran, V. Effects of dietary supplementation of potential probiotic Pseudomonas aeruginosa VSG-2 on the innate immunity and disease resistance of tropical freshwater fish, Labeo rohita. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altinok, I.; Kayis, S.; Capkin, E. Pseudomonas putida infection in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.M.; Abdel-Galil Ahmed, Y.; Abdel-Aziz Ghareeb, A.; Mohamed, M.F. Studies on Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, as potential probiotics, on the immune response and resistance of Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus) to challenge infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, T.L.; Lim, C. Use of Probiotics in Diets of Tilapia. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hai, N. Research findings from the use of probiotics in tilapia aquaculture: A review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Elala, N.; Marzouk, M.; Moustafa, M. Use of different S. cerevisiae biotic forms as immune-modulator and growth promoter for Oreochromis niloticus challenged with some fish pathogens. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. Diagn. 2013, 1, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Mirvaghefi, A.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Sharifian, M.; Esteban, M. Modulation of innate immune response, mucosal parameters and disease resistance in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) upon synbiotic feeding. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimnejad, S.; Guardiola, F.A.; Leclercq, E.; Angeles Esteban, M.; Castex, M.; Sotoudeh, E.; Lee, S.-M. Effects of dietary supplementation with Pediococcus acidilactici MA18/5M, galactooligosaccharide and their synbiotic on growth, innate immunity and disease resistance of rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli). Aquaculture 2018, 482, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.-D.; Wang, K.; Li, F.-D.; Sun, Y.-Z. Single or combined effects of fructo- and mannan oligosaccharide supplements and Bacillus clausii on the growth, feed utilization, body composition, digestive enzyme activity, innate immune response and lipid metabolism of the Japanese flounder Paralichth. Aquac. Nutr. 2011, 17, e902–e911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Q.; Xu, H.; Mai, K.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Effects of dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis and fructooligosaccharide on growth performance, survival, non-specific immune response and disease resistance of juvenile large yellow croaker, Larimichthys crocea. Aquaculture 2011, 317, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Dong, X.-H.; Tan, B.-P.; Yang, Q.-H.; Chi, S.-Y.; Liu, H.-Y.; Liu, X.-Q. Effects of dietary chitosan and Bacillus subtilis on the growth performance, non-specific immunity and disease resistance of cobia, Rachycentron canadum. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galagarza, O.A.; Smith, S.A.; Drahos, D.J.; Eifert, J.D.; Williams, R.C.; Kuhn, D.D. Modulation of innate immunity in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis endospores. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 83, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newaj-Fyzul, A.; Al-Harbi, A.; Austin, B. Review: Developments in the use of probiotics for disease control in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2014, 431, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Jain, K.K.; Sardar, P.; Jayant, M.; Tok, N.C. Effect of dietary synbiotic on growth performance, body composition, digestive enzyme activity and gut microbiota in Cirrhinus mrigala (Ham.) fingerlings. Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukgehnaish, K.; Kumar, P.; Sivachandran, P.; Marimuthu, K.; Arshad, A.; Paray, B.A.; Arockiaraj, J. Gut microbiota metagenomics in aquaculture: Factors influencing gut microbiome and its physiological role in fish. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1903–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

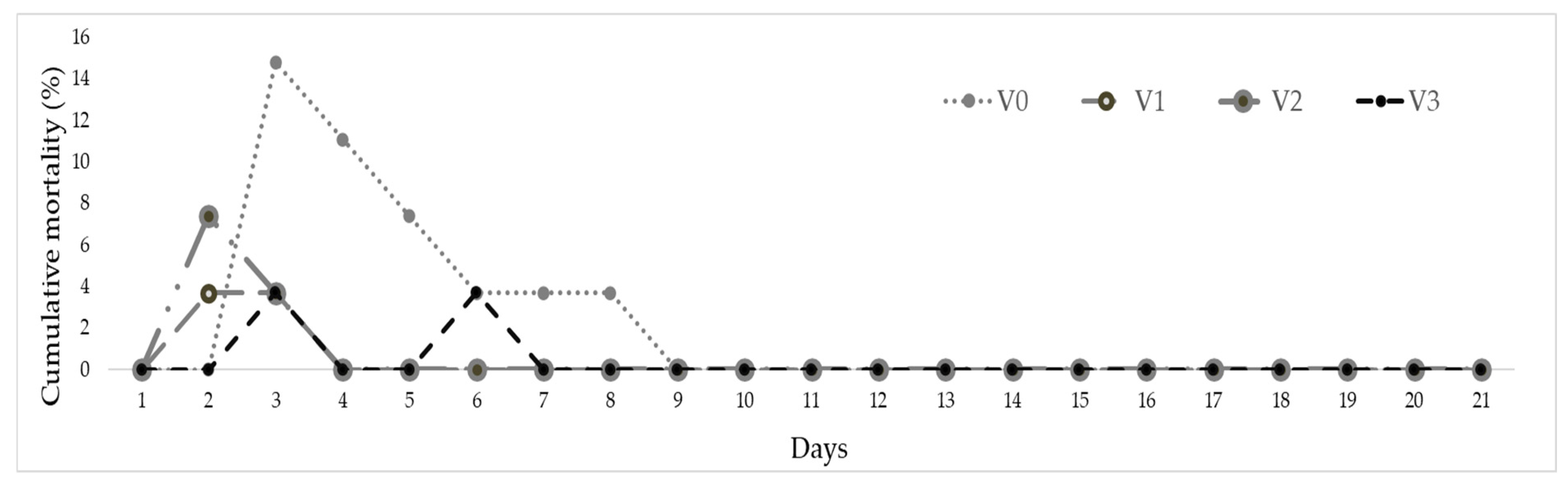

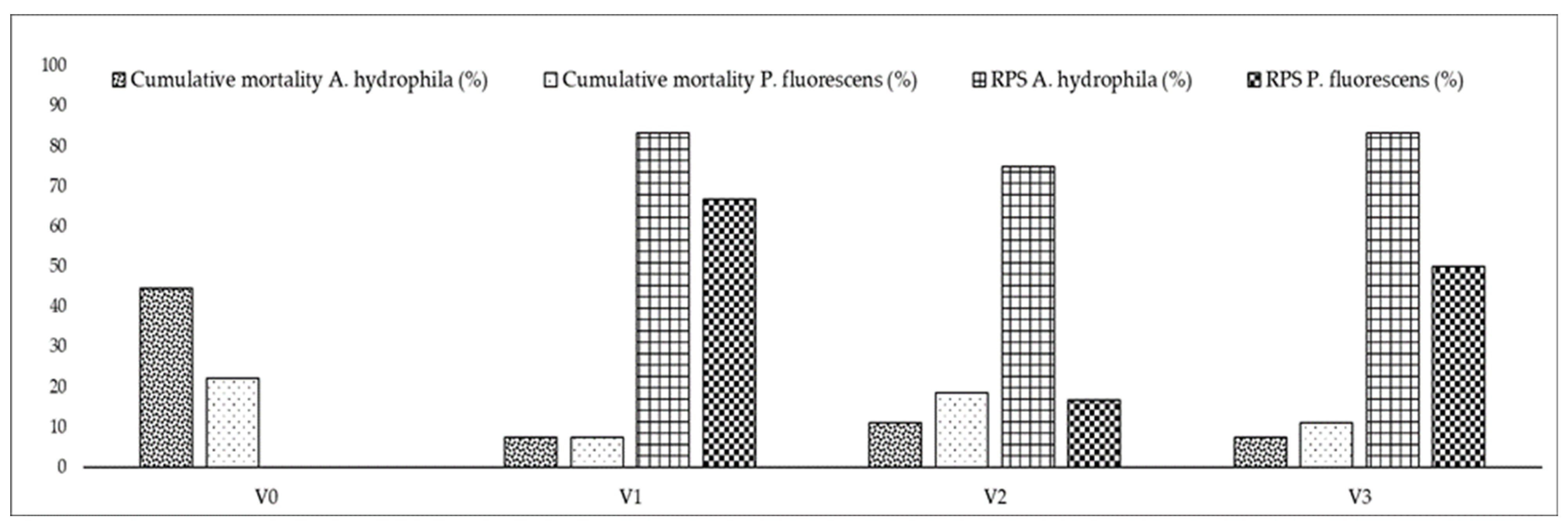

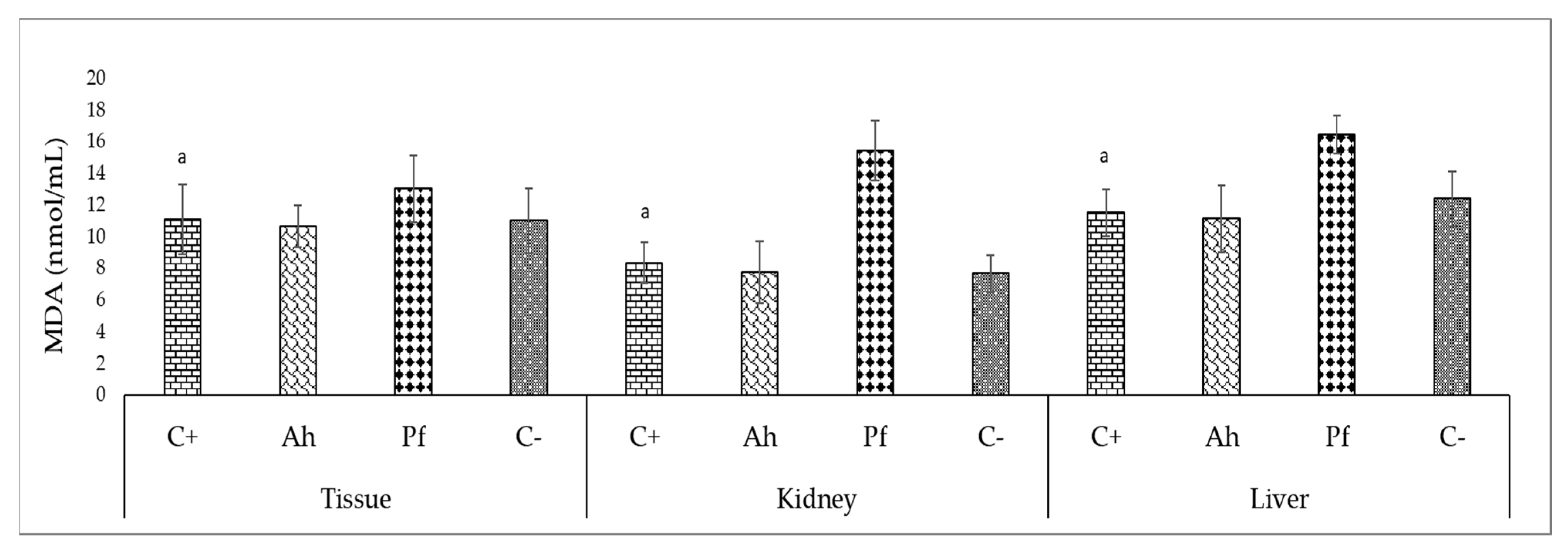
| Experimental Variant | Experimental Stage I | Experimental Stage II | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SGR | FCR | PER | SGR | FCR | PER | |
| Control (V0) | 6.38 ± 0.01 | 0.92 ± 0.01 | 1.71 ± 0.01 | 1.99 ± 0.02 | 1.01 ± 0.02 a | 2.21 ± 0.04 a |
| Probiotic (V1) | 6.72 ± 0.06 | 0.90 ± 0.03 | 1.73 ± 0.05 | 1.94 ± 0.04 | 0.97 ± 0.03 a | 2.29 ± 0.07 a |
| Prebiotic (V2) | 6.74 ± 0.03 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | 1.71 ± 0.02 | 1.89 ± 0.03 | 1.12 ± 0.03 b | 1.98 ± 0.06 b |
| Synbiotic (V3) | 6.85 ± 0.03 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 1.77 ± 0.03 | 1.98 ± 0.01 | 1.00 ± 0.01 a | 2.21 ± 0.02 a |
| Hematological Parameters | Experimental Stage (I, II) | Control | Probiotic | Prebiotic | Synbiotic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (V0) | (V1) | (V2) | (V3) | ||
| RBCc (×106 cells/µL) | I | 1.74 ± 0.05 b | 1.59 ± 0.06 a | 1.57 ± 0.03 a | 1.50 ± 0.04 a |
| II | 1.82 ± 0.09 | 1.65 ± 0.09 | 1.69 ± 0.07 | 1.75 ± 0.05 | |
| PVC (%) | I | 25.20 ± 1.11 | 25.80 ± 0.80 | 26.00 ± 0.74 | 27.07 ± 0.67 |
| II | 22.00 ± 1.50 a | 25.07 ± 1.09 a | 27.27 ± 1.38 b | 27.27 ± 1.22 b | |
| Hb (g/dL) | I | 7.88 ± 0.26 a | 7.22 ± 0.24 a | 8.05 ± 0.22 b | 7.58 ± 0.19 a |
| II | 7.78 ± 0.14 | 7.68 ± 0.12 | 7.70 ± 0.22 | 8.00 ± 0.13 | |
| MCV (µm3) | I | 146.08 ± 6.57 a | 165.12 ± 6.46 b | 166.62 ± 6.36 b | 183.04 ± 7.21 b |
| II | 123.89 ± 8.63 a | 159.70 ± 12.05 b | 168.83 ± 15.02 b | 156.41 ± 6.44 b | |
| MCH (pg) | I | 46.35 ± 2.61 | 46.31 ± 2.00 | 51.35 ± 1.37 | 51.18 ± 1.85 |
| II | 44.11 ± 1.90 | 48.88 ± 2.97 | 47.17 ± 3.00 | 46.33 ± 1.53 | |
| MCHC (g/dL) | I | 32.01 ± 1.53 | 28.20 ± 0.92 | 31.43 ± 1.41 | 28.27 ± 1.04 |
| II | 37.28 ± 2.12 b | 31.40 ± 1.39 a | 29.55 ± 1.92 a | 30.34 ± 1.70 a | |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | II | 103.17 ± 1.46 a | 111.93 ± 1.25 b | 104.29 ± 1.95 a | 102.83 ± 1.24 a |
| Total proteins (g/dL) | II | 6.73 ± 0.23 b | 6.04 ± 0.18 a | 6.41 ± 0.28 a | 5.76 ± 0.16 a |
| Lysozyme (U/mL) | II | 11.79 ± 0.29 a | 13.09 ± 0.3 b | 12.29 ± 0.3 a | 13.6 ± 0.52 b |
| Agranulocytes Granulocytes | Experimental Stage (I, II) | Control | Probiotic | Prebiotic | Synbiotic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (V0) | (V1) | (V2) | (V3) | ||
| Leukocytes (×1000 cell./mm3) | I | 65.25 ± 3.32 b | 58.04 ± 6.72 b | 46.25 ± 2.22 a | 48.99 ± 3.67 a |
| II | 52.65 ± 3.94 | 51.64 ± 6.25 | 60.76 ± 6.36 | 56.31 ± 3.75 | |
| Lymphocytes small (×1000 cell./mm3) | I | 65.58 ± 3.25 b | 55.49 ± 6.52 b | 43.70 ± 2.24 a | 46.72 ± 3.50 a |
| II | 48.22 ± 3.77 | 47.05 ± 5.88 | 55.37 ± 4.03 | 51.00 ± 3.35 | |
| Lymphocytes large (×1000 cell./mm3) | I | 1.11 ± 0.14 | 1.09 ± 0.22 | 0.94 ± 0.12 | 0.83 ± 0.08 |
| II | 0.61 ± 0.08 a | 1.12 ± 0.19 b | 1.10 ± 0.17 b | 1.14 ± 0.09 b | |
| Monocytes (×1000 cell./mm3) | I | 0.54 ± 0.11 | 0.55 ± 0.08 | 0.50 ± 0.06 | 0.36 ± 0.05 |
| II | 0.65 ± 0.09 | 0.64 ± 0.11 | 0.53 ± 0.07 | 0.81 ± 0.17 | |
| Neutrophilic granulocytes (×1000 cell./mm3) | I | 1.01 ± 0.19 | 0.89 ± 0.19 | 1.18 ± 0.11 | 1.09 ± 0.13 |
| II | 3.16 ± 0.70 | 2.92 ± 0.38 | 2.63 ± 0.46 | 3.21 ± 0.58 | |
| Platelets (×1000 cell./mm3) | I | 23.10 ± 4.01 | 20.72 ± 2.34 | 21.52 ± 2.06 | 15.84 ± 2.20 |
| II | 32.82 ± 3.06 | 27.84 ± 3.15 | 25.57 ± 4.38 | 29.79 ± 3.79 |
| Hematological Parameters | Experimental Variant | Control Positive | Aeromonas hydrophyla | Pseudomonas fluorescens | Control Negative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (C+) | (Ah) | (Pf) | (C−) | ||
| RBCc (×106 cells/µL) | V0 | 1.15 ± 0.06 a | 1.07 ± 0.02 b | 1.01 ± 0.03 b | 1.15 ± 0.06 a |
| V1 | 1.27 ± 0.08 | 1.21 ± 0.08 | 1.31 ± 0.04 | 1.27 ± 0.08 | |
| V2 | 1.30 ± 0.04 | 1.35 ± 0.03 | 1.29 ± 0.09 | 1.30 ± 0.04 | |
| V3 | 1.25 ± 0.02 | 1.14 ± 0.06 | 1.23 ± 0.03 | 1.25 ± 0.02 | |
| PVC (%) | V0 | 21.33 ± 0.67 a | 16.33 ± 1.20 b | 15.00 ± 0.58 b | 17.67 ± 1.67 a |
| V1 | 22.33 ± 1.33 | 22.00 ± 1.73 | 18.67 ± 0.67 | 15.33 ± 1.75 | |
| V2 | 19.33 ± 1.67 | 23.00 ± 1.00 | 19.67 ± 1.76 | 18.33 ± 1.86 | |
| V3 | 20.00 ± 1.73 | 23.33 ± 1.45 | 22.00 ± 1.15 | 21.00 ± 1.00 | |
| Hb (g/dL) | V0 | 7.65 ± 0.64 a | 6.58 ± 0.28 b | 7.35 ± 0.31 a | 7.36 ± 0.13 a |
| V1 | 7.62 ± 0.39 a | 7.26 ± 0.31 a | 5.67 ± 0.38 b | 7.29 ± 0.30 a | |
| V2 | 7.50 ± 0.22 | 8.03 ± 0.38 | 6.13 ± 0.51 | 7.15 ± 0.10 | |
| V3 | 7.11 ± 0.48 | 7.46 ± 0.18 | 7.50 ± 0.40 | 7.48 ± 0.07 | |
| MCV (µm3) | V0 | 186.49 ± 4.42 a | 218.37 ± 5.93 b | 149.28 ± 5.24 a | 145.98 ± 14.57 a |
| V1 | 176.01 ± 9.71 | 170.66 ± 3.99 | 146.16 ± 2.85 | 126.99 ± 5.49 | |
| V2 | 148.56 ± 8.19 | 181.61 ± 3.99 | 150.30 ± 2.01 | 147.27 ± 8.09 | |
| V3 | 159.56 ± 13.62 | 144.93 ± 3.86 | 178.15 ± 5.30 | 164.88 ± 15.70 | |
| MCH (pg) | V0 | 66.73 ± 4.23 a | 61.83 ± 2.41 a | 73.20 ± 4.01 b | 60.77 ± 1.70 a |
| V1 | 59.99 ± 2.49 | 59.55 ± 1.70 | 47.45 ± 1.09 | 58.91 ± 2.05 | |
| V2 | 58.00 ± 3.15 | 60.24 ± 1.49a | 43.34 ± 1.68 | 59.84 ± 3.56 | |
| V3 | 56.77 ± 3.82 a | 66.07 ± 4.86 a | 60.98 ± 4.37 c | 58.59 ± 3.85 a | |
| MCHC (g/dL) | V0 | 35.79 ± 2.19 a | 28.52 ± 2.67 a | 49.01 ± 0.30 b | 42.25 ± 3.17 a |
| V1 | 34.14 ± 0.52 | 34.90 ± 0.47 | 32.98 ± 3.27 | 40.21 ± 2.36 | |
| V2 | 39.53 ± 4.47 | 33.22 ± 1.31 | 29.01 ± 1.29 | 47.41 ± 2.14 | |
| V3 | 35.69 ± 0.78 a | 46.04 ± 2.73 b | 34.34 ± 2.88 a | 35.77 ± 1.44 b | |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | V0 | 55.33 ± 1.17 | 57.01 ± 3.90 | 51.41 ± 0.50 | 62.44 ± 3.04 |
| V1 | 60.55 ± 1.38 | 61.38 ± 4.39 | 59.52 ± 2.48 | 71.03 ± 0.64 | |
| V2 | 56.32 ± 2.36 | 60.94 ± 3.16 | 59.26 ± 1.19 | 76.56 ± 3.97 | |
| V3 | 60.42 ± 0.46 | 62.69 ± 1.72 | 57.46 ± 0.88 | 67.10 ± 4.81 | |
| Total proteins (g/dL) | V0 | 5.01 ± 0.29 | 4.86 ± 0.18 | 4.82 ± 0.11 | 5.64 ± 0.24 |
| V1 | 5.33 ± 0.18 | 5.25 ± 0.16 | 5.10 ± 0.15 | 5.00 ± 0.17 | |
| V2 | 5.52 ± 0.19 | 5.47 ± 0.18 | 5.22 ± 0.43 | 5.32 ± 0.11 | |
| V3 | 5.03 ± 0.19 | 4.96 ± 0.92 | 5.00 ± 0.18 | 5.21 ± 0.25 | |
| Lysozyme (U/mL) | V0 | 10.58 ± 0.39 | 10.62 ± 0.63 | 10.02 ± 0.33 | 11.38 ± 0.21 |
| V1 | 11.99 ± 0.10 | 10.62 ± 0.36 | 11.37 ± 0.44 | 10.43 ± 0.54 | |
| V2 | 11.40 ± 0.36 | 10.81 ± 0.32 | 10.25 ± 0.67 | 11.10 ± 0.10 | |
| V3 | 11.89 ± 0.44 | 10.75 ± 0.29 | 10.89 ± 0.15 | 10.67 ± 0.67 |
| Experimental Challenge Test Variant | Experimental Growth Variant | Leukocytes | Lm | LM | M | GN | Platelets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (×1000 cell./mm3) | |||||||
| Control positive (C+) | V0 | 53.63 ± 6.86 a | 50.11 ± 14.12 a | 0.90 ± 0.29 a | 0.79 ± 0.23 b | 1.58 ± 0.41 a | 16.87 ± 0.66 a |
| V1 | 61.99 ± 5.53 | 59.78 ± 16.76 | 0.29 ± 0.08 | 0.29 ± 0.08 | 1.63 ± 0.43 | 16.72 ± 4.73 | |
| V2 | 84.02 ± 28.70 b | 79.29 ± 20.96 b | 1.54 ± 0.40 b | 1.16 ± 0.38 c | 2.03 ± 0.62 b | 14.47 ± 4.56 a | |
| V3 | 65.05 ± 8.16 a | 62.82 ± 17.58 a | 0.49 ± 0.14 a | 0.63 ± 0.16 b | 1.11 ± 0.29 a | 23.05 ± 2.11 b | |
| Aeromonas hydrophila (Ah) | V0 | 48.34 ± 5.12 a | 41.23 ± 12.56 a | 1.54 ± 0.40 a | 1.56 ± 0.42 b | 4.00 ± 1.29 b | 7.74 ± 2.09 a |
| V1 | 69.49 ± 6.31 b | 62.59 ± 19.56 b | 2.31 ± 0.83 b | 1.06 ± 0.29 a | 3.53 ± 1.08 b | 14.59 ± 6.48 c | |
| V2 | 74.28 ± 16,41 b | 65.73 ± 17.08 b | 3.40 ± 0.88 b | 2.05 ± 0.53 b | 3.10 ± 1.03 b | 13.50 ± 8.99 c | |
| V3 | 53.25 ± 5.43 a | 50.02 ± 14.59 a | 1.19 ± 0.35 a | 0.84 ± 0.22 a | 1.19 ± 0.35 a | 10.64 ± 5.84 b | |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens (Pf) | V0 | 38.21 ± 0.01 a | 35.18 ± 11.14 a | 0.19 ± 0.06 a | 1.23 ± 0.33 a | 1.61 ± 0.51 b | 16.03 ± 7.82 b |
| V1 | 41.65 ± 10.14 b | 37.88 ± 9.97 a | 0.94 ± 0.25 a | 0.82 ± 0.21 a | 2.00 ± 0.89 b | 19.54 ± 4.96 b | |
| V2 | 29.86 ± 2.73 | 27.99 ± 8.00 | 0.59 ± 0.19 | 0.74 ± 0.19 | 0.53 ± 0.14 | 3.52 ± 1.52 | |
| V3 | 52.90 ± 0.71 b | 49.97 ± 15.55 b | 1.01 ± 0.31 b | 1.14 ± 0.52 a | 0.76 ± 0.20 a | 10.57 ± 8.59 b | |
| Control negative (C−) | V0 | 77.14 ± 5.77 a | 74.66 ± 22.35 b | 0.98 ± 0.32 a | 0.94 ± 0.24 a | 0.57 ± 0.16 a | 14.62 ± 6.66 b |
| V1 | 61.14 ± 6.90 a | 58.47 ± 16.73 a | 0.60 ± 0.17 a | 0.43 ± 0.11 a | 1.63 ± 0.52 b | 10.82 ± 0.29 a | |
| V2 | 69.09 ± 17.51 a | 63.40 ± 16.39 b | 1.45 ± 0.38 b | 0.63 ± 0.16 a | 1.56 ± 0.40 b | 13.25 ± 2.42 b | |
| V3 | 58.40 ± 2.05 a | 55.73 ± 17.60 a | 1.07 ± 0.33 a | 0.53 ± 0.17 a | 1. 07 ± 0.33 a | 14.84 ± 4.86 b | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sîrbu, E.; Dima, M.F.; Tenciu, M.; Cretu, M.; Coadă, M.T.; Țoțoiu, A.; Cristea, V.; Patriche, N. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Probiotics and Prebiotics on Growth, Physiological Condition, and Resistance to Pathogens Challenge in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fishes 2022, 7, 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050273
Sîrbu E, Dima MF, Tenciu M, Cretu M, Coadă MT, Țoțoiu A, Cristea V, Patriche N. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Probiotics and Prebiotics on Growth, Physiological Condition, and Resistance to Pathogens Challenge in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fishes. 2022; 7(5):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050273
Chicago/Turabian StyleSîrbu, Elena, Maricel Floricel Dima, Magdalena Tenciu, Mirela Cretu, Marian Tiberiu Coadă, Aurelia Țoțoiu, Victor Cristea, and Neculai Patriche. 2022. "Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Probiotics and Prebiotics on Growth, Physiological Condition, and Resistance to Pathogens Challenge in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)" Fishes 7, no. 5: 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050273
APA StyleSîrbu, E., Dima, M. F., Tenciu, M., Cretu, M., Coadă, M. T., Țoțoiu, A., Cristea, V., & Patriche, N. (2022). Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Probiotics and Prebiotics on Growth, Physiological Condition, and Resistance to Pathogens Challenge in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fishes, 7(5), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050273









