Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Community in Kumamoto Oyster (Crassostrea sikamea) Larvae: Response to Antibiotics in Trace Concentration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. 16S rRNA and 18S rRNA Gene Library Construction and Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing Data Characteristics and Diversity
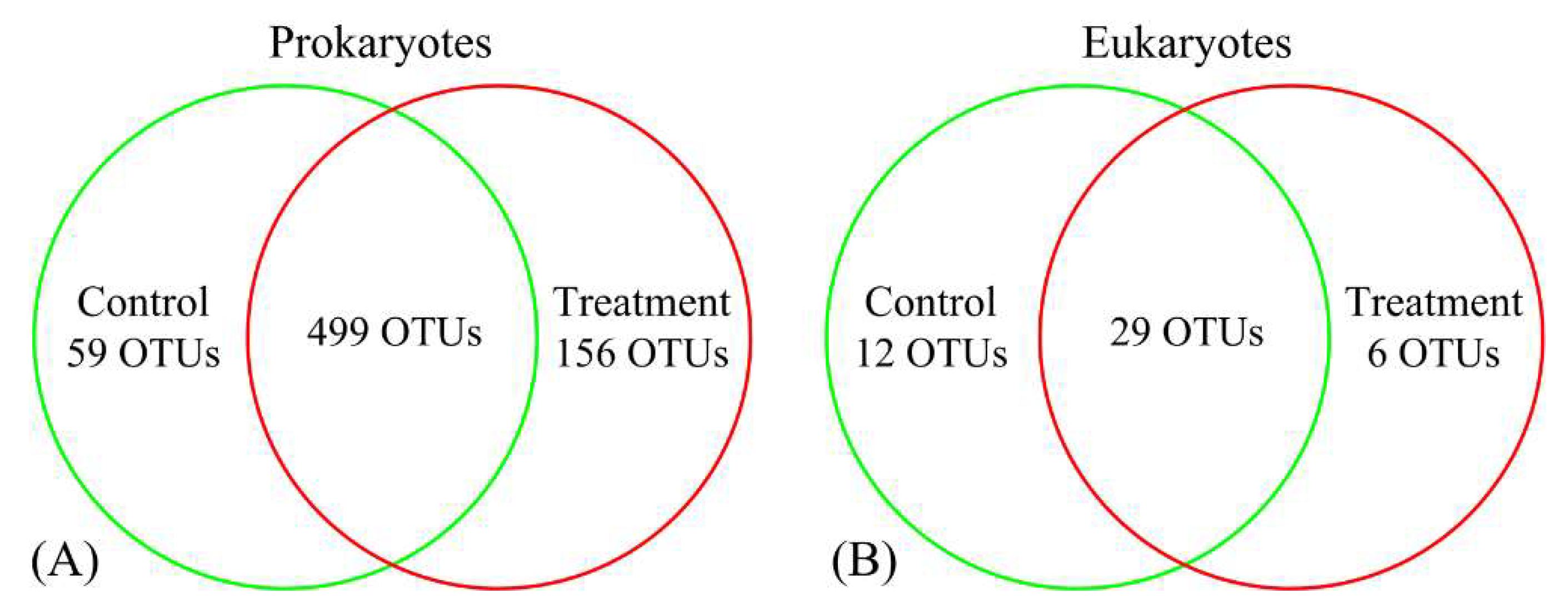
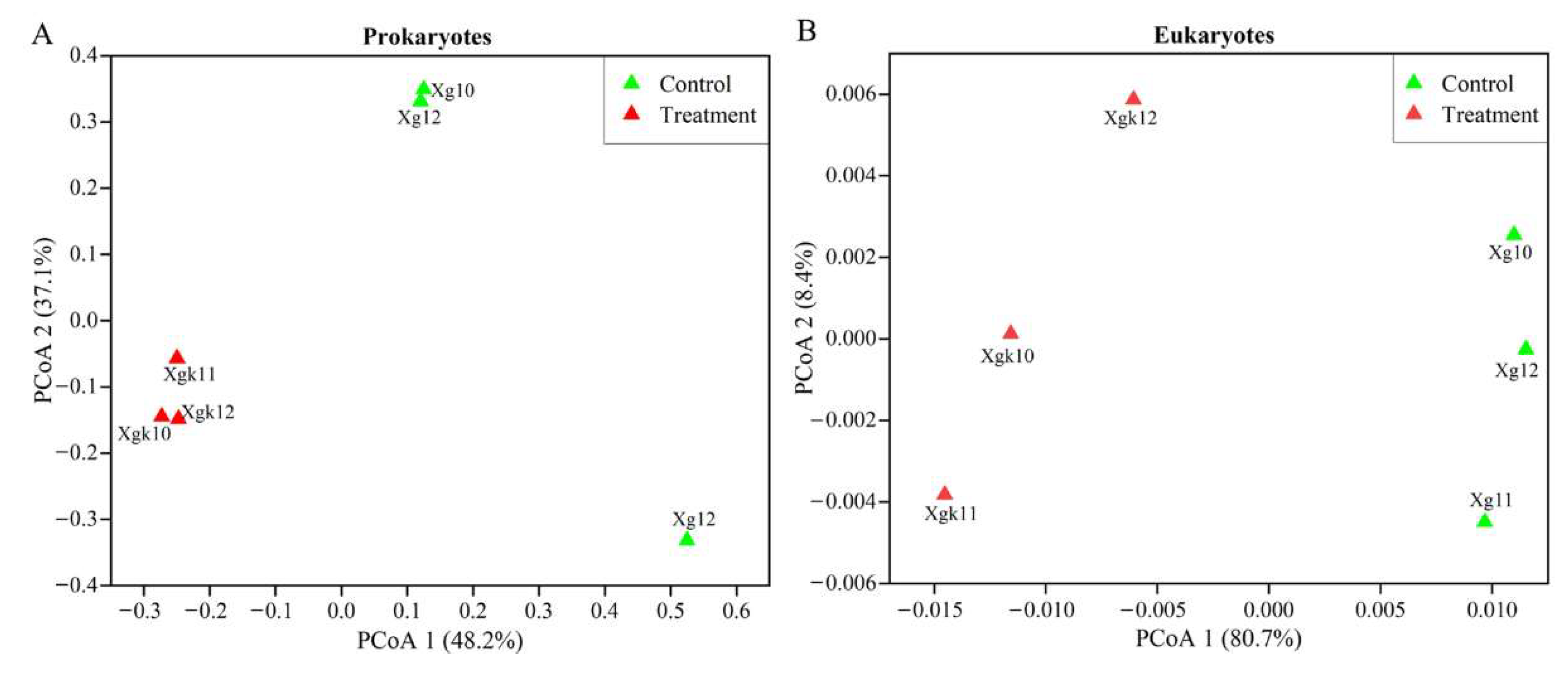
3.2. Variations in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Communities in Response to Antibiotics
3.3. Variations in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Compositions at Phylum Level
3.4. Variations in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Compositions at Family Level
3.5. Variations in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Compositions at Genus Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paillard, C.; Le Roux, F.; Borrego, J.J. Bacterial disease in marine bivalves, a review of recent studies: Trends and evolution. Aquat. Living Resour. 2004, 17, 477–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Balboa, S.; Romalde, J.L.; Figueras, M.J. Diversity and pathogenecity of Vibrio species in cultured bivalve molluscs. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, S.; Romalde, J.L.; Montes, J.; Barja, J.L. Pathogenic bacteria isolated from disease outbreaks in shellfish hatcheries. First description of Vibrio neptunius as an oyster pathogen. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2005, 67, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blogoslawski, W.J.; Stewart, M.E.; Rhodes, E.W. Bacterial disinfection in shellfish hatchery disease control. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting-World Mariculture Society; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1978; Volume 9, pp. 587–602. [Google Scholar]
- Keeney, K.M.; Yurist-Doutsch, S.; Arrieta, M.C.; Finlay, B.B. Effects of antibiotics on human microbiota and subsequent disease. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 68, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Shields, R.J.; Bricknell, I.R.; Birkbeck, T.H. Effects of different water treatment methods and antibiotic addition on larval survival and gut microflora development in Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.) yolk-sac larvae. Aquaculture 2004, 232, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekirov, I.; Tam, N.M.; Jogova, M.; Robertson, M.L.; Li, Y.; Lupp, C.; Finlay, B.B. Antibiotic-induced perturbations of the intestinal microbiota alter host susceptibility to enteric infection. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4726–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arfken, A.; Song, B.; Allen, S.K., Jr.; Carnegie, R.B. Comparing larval microbiomes of the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) raised in different hatcheries. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Nicolae, V.V.; Akileh, R.; Liu, T. A brief review of oyster-associated microbiota. Microbiol. Res. J. Int. 2017, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dai, W.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Gut eukaryotic disease-discriminatory taxa are indicative of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) white feces syndrome. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Dong, Y.; Ye, J.; Xue, Q.; Lin, Z. Gut microbiome composition likely affects the growth of razor clam Sinonovacula constricta. Aquaculture 2022, 550, 737847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.J.; Bohannan, B.J.; Young, V.B. From structure to function: The ecology of host-associated microbial communities. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabal Fernández, N.; Mazón-Suástegui, J.M.; Vázquez-Juárez, R.; Ascencio-Valle, F.; Romero, J. Changes in the composition and diversity of the bacterial microbiota associated with oysters (Crassostrea corteziensis, Crassostrea gigas and Crassostrea sikamea) during commercial production. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerissi, C.; Lorgeril, J.D.; Petton, B.; Lucasson, A.; Toulza, E. Diversity and stability of microbiota are key factors associated to healthy and diseased Crassostrea gigas oysters. BioRxiv 2018. BioRxiv:378125. [Google Scholar]
- Parfrey, L.W.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R. Microbial eukaryotes in the human microbiome: Ecology, evolution, and future directions. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massana, R.; Logares, R. Eukaryotic versus prokaryotic marine picoplankton ecology. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Yu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhen, T.; Xiong, J. The gut eukaryotic microbiota influences the growth performance among cohabitating shrimp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 6447–6457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyman, M.; Van Houten, M.A.; Watson, R.L.; Chu, M.L.J.; Arp, K.; De Waal, W.J.; Schiering, I.; Plötz, F.B.; Willems, R.J.L.; Schaik, W.; et al. Effects of early-life antibiotics on the developing infant gut microbiome and resistome: A randomized trial. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argentini, C.; Mancabelli, L.; Alessandri, G.; Tarracchini, C.; Barbetti, M.; Carnevali, L.; Longhi, G.; Viappiani, A.; Anzalone, R.; Milani, C.; et al. Exploring the ecological effects of naturally antibiotic-insensitive bifidobacteria in the recovery of the resilience of the gut microbiota during and after antibiotic treatment. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2022, 88, e00522-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patangia, D.V.; Anthony, R.C.; Dempsey, E.; Paul, R.R.; Stanton, C. Impact of antibiotics on the human microbiome and consequences for host health. MicrobiologyOpen 2022, 11, e1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Gonzalez, A.; Maeda-Martínez, A.; Sainz, J.; Ascencio-Valle, F. Comparative susceptibility of veliger larvae of four bivalve mollusks to a Vibrio alginolyticus strain. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2002, 49, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.K.; Waters, P.; Rikard, F.S. Oyster Hatchery Techniques; Southern Regional Aquaculture Center: Stoneville, MS, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Ren, T.; Zhang, L. Dix-seq: An integrated pipeline for fast amplicon data analysis. bioRxiv 2020. bioRxiv:2020.05.11.089748. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, R.; Miner, P.; Nicolas, J. Mortality control of scallop larvae in the hatchery. Aquacult. Int. 1996, 4, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, S. Microbiota Asociada a Criaderos de Moluscos: Patogénesis and Probiosis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jernberg, C.; Löfmark, S.; Edlund, C.; Jansson, J.K. Long-term impacts of antibiotic exposure on the human intestinal microbiota. Microbiology 2010, 156, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoah, K.; Dong, X.; Tan, B.; Zhang, S.; Chi, S.; Yang, Q.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. Administration of probiotic Bacillus licheniformis induces growth, immune and antioxidant enzyme activities, gut microbiota assembly and resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquacult. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1604–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandvang, D.; Skjoet-Rasmussen, L.; Cantor, M.D.; Mathis, G.F.; Lumpkins, B.S.; Blanch, A. Effects of feed supplementation with 3 different probiotic Bacillus strains and their combination on the performance of broiler chickens challenged with Clostridium perfringens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Sheng, Z.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Shrimp disease progression increases the gut bacterial network complexity and abundances of keystone taxa. Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Ye, J.; Liu, S.; Chang, G.; Xu, H.; Lin, Z.; Xue, Q. Bacterial Community Dynamics in Kumamoto Oyster Crassostrea sikamea Hatchery During Larval Development. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 933941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettcher, K.J.; Barber, B.J.; Singer, J.T. Additional evidence that juvenile oyster disease is caused by a member of the Roseobacter group and colonization of nonaffected animals by Stappia stellulata-like strains. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2000, 66, 3924–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, D.; Schubiger, C.; Lunda, S.; Mueller, R.S.; Langdon, C. A marine probiotic treatment against the bacterial pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus to improve the performance of Pacific (Crassostrea gigas) and Kumamoto (C. sikamea) oyster larvae. Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforest-Lapointe, I.; Arrieta, M.C. Microbial eukaryotes: A missing link in gut microbiome studies. MSystems 2018, 3, e00201-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooks, K.B.; O’Malley, M.A. Contrasting strategies: Human eukaryotic versus bacterial microbiome research. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2020, 67, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, M.R. Composition and functional roles of the gut microbiota in mosquitoes. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 28, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakke, I.; Coward, E.; Andersen, T.; Vadstein, O. Selection in the host structures the microbiota associated with developing cod larvae (Gadus morhua). Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3914–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Imai, I.; Yamaguchi, A.; Tuji, A.; Not, F.; Suzuki, N. Molecular phylogeny of the widely distributed marine protists, Phaeodaria (Rhizaria, Cercozoa). Protist 2015, 166, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Zeng, S.; Liu, J.; Yan, M.; Weng, S.; He, J.; Huang, Z. Characterization of prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbial community in pacific white shrimp ponds. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2016, 7, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Ye, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shao, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, C. Metabolic product response profiles of Cherax quadricarinatus towards white spot syndrome virus infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 61, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, J.H.; Dorweiler, B.; Woo, C.W. Interaction between gut microbiota and toll-like receptor: From immunity to metabolism. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, S.; Yeoman, C.J.; Sipos, M.; Torralba, M.; Wilson, B.A.; Goldberg, T.L.; Stumpf, R.M.; Leigh, S.R.; White, B.A.; Nelson, K.E. Characterization of the fecal microbiome from non-human wild primates reveals species specific microbial communities. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Treatment | Control | Treatment | |
| Reads | 83,534 | 83,354 | 83,738 | 83,573 |
| OTUs | 558 | 655 | 41 | 35 |
| Phylum | 15 | 15 | 8 | 10 |
| Class | 23 | 27 | 17 | 17 |
| Order | 43 | 49 | 21 | 21 |
| Family | 75 | 78 | 23 | 22 |
| Genus | 109 | 114 | 18 | 17 |
| Microbial Communities | Shannon Diversity | Chao 1 | Observed Species | Simpson Index | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Treatment | p | Control | Treatment | p | Control | Treatment | p | Control | Treatment | p | |
| Prokaryotes | 4.60 ± 0.40 | 5.80 ± 0.15 | 0.048 | 466.90 ± 18.26 | 528.87 ± 8.68 | 0.038 | 418.00 ± 32.62 | 504.67 ± 3.18 | 0.116 | 0.14 ± 0.04 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.089 |
| Eukaryotes | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.004 | 31.20 ± 5.27 | 29.77 ± 2.03 | 0.812 | 27.33 ± 3.84 | 28.33 ± 1.86 | 0.826 | 0.98 ± 0.00 | 0.95 ± 0.00 | 0.006 |
| Phyla in Prokaryotic Community | Control | Treatment | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proteobacteria | 79.41% ± 2.81% | 85.51% ± 2.81% | 0.20 |
| Bacteroidetes | 11.25% ± 5.42% | 3.77% ± 0.63% | 0.04 |
| Firmicutes | 6.28% ± 6.16% | 0.31% ± 0.01% | 0.04 |
| Chlamydiae | 0.55% ± 0.02% | 5.04% ± 1.04% | 0.01 |
| Actinobacteria | 0.46% ± 0.16% | 1.52% ± 0.14% | 0.01 |
| Candidatus Saccharibacteria | 0.08% ± 0.02% | 0.09% ± 0.03% | 0.74 |
| Verrucomicrobia | 0.04% ± 0.01% | 0.03% ± 0.02% | 0.77 |
| Planctomycetes | 0.04% ± 0.01% | 0.10% ± 0.02% | 0.07 |
| Fusobacteria | 0.10% ± 0.01% | 0.00% ± 0.00% | 0.37 |
| Tenericutes | 0.01% ± 0.00% | 0.07% ± 0.03% | 0.11 |
| SR1 | 0.01% ± 0.01% | 0.00% ± 0.00% | 0.42 |
| Parcubacteria | 0.01% ± 0.00% | 0.11% ± 0.05% | 0.16 |
| Campilobacterota | 0.00% ± 0.00% | 0.06% ± 0.05% | 0.38 |
| Spirochaetes | 0.00% ± 0.00% | 0.01% ± 0.01% | 0.14 |
| Abditibacteriota | 0.00% ± 0.00% | 0.01% ± 0.01% | 0.42 |
| Unclassified | 1.86% ± 0.81% | 3.37% ± 1.26% | 0.37 |
| Phyla in eukaryotic community | Control | Treatment | p-value |
| Metazoa | 99.37% ± 0.30% | 99.46% ± 0.11% | 0.78 |
| Streptophyta | 0.53% ± 0.28% | 0.07% ± 0.05% | 0.18 |
| Perkinsea | 0.03% ± 0.03% | 0.00% ± 0.00% | 0.42 |
| Ochrophyta | 0.02% ± 0.01% | 0.01% ± 0.00% | 0.21 |
| Fungi | 0.02% ± 0.01% | 0.01% ± 0.01% | 0.40 |
| Chlorophyta | 0.01% ± 0.00% | 0.07% ± 0.01% | 0.02 |
| Cercozoa | 0.00% ± 0.00% | 0.32% ± 0.07% | 0.01 |
| Haptophyta | 0.00% ± 0.00% | 0.02% ± 0.00% | 0.01 |
| Sagenista | 0.00% ± 0.00% | 0.02% ± 0.01% | 0.07 |
| Unclassified | 0.00% ± 0.00% | 0.02% ± 0.00% | 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, W.; Ye, J.; Liu, S.; Xu, H.; Liu, M.; Lin, Z.; Xue, Q. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Community in Kumamoto Oyster (Crassostrea sikamea) Larvae: Response to Antibiotics in Trace Concentration. Fishes 2022, 7, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050272
Dai W, Ye J, Liu S, Xu H, Liu M, Lin Z, Xue Q. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Community in Kumamoto Oyster (Crassostrea sikamea) Larvae: Response to Antibiotics in Trace Concentration. Fishes. 2022; 7(5):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050272
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Wenfang, Jing Ye, Sheng Liu, Hongqiang Xu, Minhai Liu, Zhihua Lin, and Qinggang Xue. 2022. "Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Community in Kumamoto Oyster (Crassostrea sikamea) Larvae: Response to Antibiotics in Trace Concentration" Fishes 7, no. 5: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050272
APA StyleDai, W., Ye, J., Liu, S., Xu, H., Liu, M., Lin, Z., & Xue, Q. (2022). Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Community in Kumamoto Oyster (Crassostrea sikamea) Larvae: Response to Antibiotics in Trace Concentration. Fishes, 7(5), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050272






