Abstract
Vibrio parahaemolyticus belongs to an expanding group of aquatic pathogens that are widely distributed in aquatic environments. This species is a lethal pathogen for a number of economically important marine crabs. However, studies exploring host–vibrio interactions between V. parahaemolyticus and crabs are scarce, and therefore, the underlying molecular mechanisms are unclear. Herein, we performed a comprehensive proteomic analysis to investigate the immune response of Portunus trituberculatus hemocytes to V. parahaemolyticus infection. A total of 4433 proteins were identified using isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ), and 526 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) were subjected to Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis, with six DEPs further subjected to quantitative real-time PCR. Several identified DEPs were found to be mainly involved in the immune defense of the crustacean, such as a hemocyanin subunit, C-type lectin, α-2-macroglobulin, Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase, and heat shock protein 70, playing a key role in the response to V. parahaemolyticus infection. Moreover, many immune-related KEGG pathways were markedly altered, such as cell adhesion molecules, complement and coagulation cascades, and phagosomes. Our results provide insights into how V. parahaemolyticus overcomes the innate immunity of P. trituberculatus to induce pathological alterations in affected tissues. We report the first iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis and highlight the key pathways and proteins involved in the host–vibrio interactions between P. trituberculatus and V. parahaemolyticus. These findings should enhance our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying such interactions.
1. Introduction
As an important economic species in Asia-Pacific nations, Portunus trituberculatus has become a major aquaculture species in the coastal areas of China due to its fast growth rate and delicious taste, with its production reaching 105,283 tons in 2021 [1]. However, the stability of crab aquaculture was recently restricted by epidemic diseases caused by diverse pathogens [2,3]. Notably, Vibrio parahaemolyticus has had a significant impact on the sustainable aquaculture of P. trituberculatus, causing considerable economic losses since 2006 [4,5]. Therefore, for better cognition and to develop strategies to overcome this issue, further investigations on the response of P. trituberculatus against pathogens are needed. P. trituberculatus is reported to mainly rely on innate immunity capabilities, including humoral and cellular immune systems, to defend against invading pathogens, which is similar to other invertebrates [6,7]. Previous studies have reported that hemocytes are essential for the survival of crabs in the case of systemic infection and are the main targets during infections caused by V. parahaemolyticus [8].
Many approaches have been applied to study the immune mechanism of crustaceans, such as suppression subtractive hybridization, a simple gene investigation, high-throughput expressed sequence tag analysis, and proteomics [9,10,11,12]. Proteomics places additional value to the interpretation of biological functions inferred to facilitate the elucidation of molecular responses more directly comparing to conventional genomics [13]. Isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) have become a widely used method [12,14,15]. This technique uses four isobaric amine-specific tags and can help identify and quantify more proteins than most sensitive mass spectrometers.
iTRAQ has been applied to analyze proteomic profiles pre- and post-pathogen infection [16]. Moreover, iTRAQ-based proteomics has been used to study crustacean immune responses to bacterial or viral pathogens. For example, the immunological responses of Procambarus clarkii, Cherax quadricarinatus, Eriocheir sinensis, Macrobrachium rosenbergii, and Scylla paramamosain against Spiroplasma eriocheiris or WSSV infection have been investigated using iTRAQ-based proteomics [12,14,17,18,19]. Such studies have made us aware that iTRAQ-based proteomics could be a reliable and accurate method to investigate the immune relationship between pathogens and crustaceans.
A proteomic analysis to elucidate the immune response of P. trituberculatus to V. parahaemolyticus has not yet been reported. Our previous gene expression analysis helped us identify some genes that play important roles in the response of P. trituberculatus to a V. parahaemolyticus challenge [8,20]. The pertinent immune response remains to be explored. Here, we used proteomics to investigate the immune response of P. trituberculatus hemocytes to V. parahaemolyticus infection. Our findings should contribute to further understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying the immune response of crustaceans to bacterial pathogens.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Statement of Ethics
All experiments were performed in accordance with the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals in China. This study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of the Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences (Qingdao, China), under approval number YSFRI2022026.
2.2. Experimental Animals and Sample Collection
We captured 120 healthy P. trituberculatus (38.6 g ± 2 g) specimens from an aquaculture pond. In the indoor closed seawater tank (1000 L water, temperature 22 °C, salinity 30 ppt), the crabs were reared for 7 days, and then, the test treatment was carried out. After 7 days, 60 crabs were injected with 100 μL of V. parahaemolyticus (2.6 × 107 CFU/mL) according to a previous study [8,20,21]. The injection site was the juncture of the swimming foot. At 0 h, 36 h, and 72 h post-inoculation, hemolymph was extracted from 3 randomly chosen crabs, with the 0 h sample as the control group. The hemolymph samples were centrifuged at 700× g for 10 min at 4 °C. Next, the hemocytes were washed 3 times with 1× PBS to remove hemocyanin and other impurities, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C. During the experimental period, the crabs were fed clam meat.
2.3. Protein Preparation
The hemocytes were disrupted in lysis buffer (with enzyme inhibitors). The mixtures were centrifuged and mixed with 5 volumes of cold acetone after removing the supernatant. The mixture was subsequently re-centrifuged, and the obtained pellets were dissolved. Next, dithiothreitol and iodoacetamide were added and incubated successively. Subsequently, 5 volumes of cold acetone were added, and the solution was incubated at –20 °C for 2 h. After centrifugation, the pellet was dissolved. The protein concentration was determined, and the solution was stored at −80 °C.
2.4. iTRAQ Labeling and Reversed-Phase (RP) Fractionation
The total protein (100 μg) in each sample was digested for 4 h at 37 °C with Trypsin Gold (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Subsequently, Trypsin Gold was re-added and the duration of digestion was 8 h. Formic acid was mixed with the digested sample, the pH was adjusted under 3, and the solution was centrifuged at 12,000× g for 5 min at room temperature. The supernatant was slowly loaded to the C18 desalting column, washed with washing buffer (0.1% formic acid, 3% acetonitrile) 3 times, and then eluted by some elution buffer (0.1% formic acid, 70% acetonitrile). The eluents of each sample were collected and lyophilized. Peptides were then reconstituted in 20 μL of 1 Mtriethylammoniumbicarbonate. iTRAQ labeling of the peptide samples was performed using an iTRAQ Reagent 8Plex Kit (AB Sciex, Foster City, CA, USA). Next, the isobaric-tag-labeled peptides were pooled and dried by vacuum centrifugation. The iTRAQ-labeled peptides were then fractionated using a C18 column (Waters BEH C18, 4.6 × 250 mm, 5 μm) on a RIGOL L3000 HPLC system, and the column oven temperature was set to 45 °C. The eluates were monitored at UV 214 nm, collected for a tube per minute, and combined into 10 fractions finally. All fractions were dried under vacuum and then reconstituted in 0.1% (v/v) formic acid (FA) in water.
2.5. Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray Ionization–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS)
UHPLC-MS/MS analyses were performed using an EASY-nLCTM 1200 UHPLC system (Thermo Fisher, Bremen, Germany) coupled with a Q ExactiveTM HF-X (Thermo Fisher, Germany) in Novogene Bioinformatics Technology Co., Ltd.(Beijing, China). Peptides were separated on a Reprosil-Pur 120 C18-AQ analytical column (15 cm × 150 μm, 1.9 μm) using a 60 min linear gradient from 5% to 100% eluent B (0.1% FA in 80% acetonitrile (ACN)) in eluent A (0.1% FA in H2O) at a flow rate of 600 nL/min. The solvent gradient was as follows: 5–10% B, 2 min; 10–30% B, 49 min; 30–50% B, 2 min; 50–90% B, 2 min; and 90–100% B, 5 min.
The separated peptides were analyzed using a Q ExactiveTM HF-X mass spectrometer under data-dependent acquisition (DDA) mode, with an ion source of Nanospray Flex™ (ESI), a spray voltage of 2.1 kV, and an ion transport capillary temperature of 320 °C. The full scan ranged from m/z 407 to 1500 with a resolution of 60,000 (at m/z 200), the automatic gain control (AGC) target value was 3 × 106, and the maximum ion injection time was 20 ms. The top 40 precursors of the highest abundance in the full scan were selected and fragmented by higher-energy collisional dissociation (HCD) and analyzed by MS/MS, where the resolution was 15,000 (at m/z 200), the automatic gain control (AGC) target value was 5 × 104, the maximum ion injection time was 45 ms, the normalized collision energy was set to 32%, the intensity threshold was 2.2 × 104, and the dynamic exclusion parameter was 20 s.
2.6. Data Analyses
All resulting spectra from LC-MS/MS were searched against the reference proteome generated by genome sequencing using Proteome Discoverer 2.2. The retrieved results were filtered using Proteome Discoverer v. 2.2 peptide-spectrum matches (PSMs), with 95% confidence intervals. Proteins with at least one unique peptide fragment were considered reliable. The reliable PSMs and proteins were verified with other reliable proteins. Peptide fragments and proteins with false discovery rates (FDRs) of >5% were excluded. The protein quantitation results were statistically analyzed using a t-test. Differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) were determined by the t-test when there was a significant change (p < 0.05) in expression levels (fold-change ≥ 1.2).
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
qRT-PCR was used to evaluate the correlation between mRNA expression and protein abundance. Primers are listed in Table 1. Total RNA was extracted from hematocrit samples using TRIzol reagent, and cDNA was synthesized using a PrimeScript™ RT reagent kit with gDNA Eraser (Perfect Real Time; TaKaRa, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR was performed on an ABI 7500 RT-PCR instrument using a 20 µL reaction system. The procedures and methods of qRT-PCR were the same as used by Gao et al. [22].

Table 1.
qRT-PCR primers used in this study.
3. Results
3.1. Protein Profiling
A total of 924,144 spectra were detected, including 195,272 unique spectra. A total of 4433 proteins were identified and distributed in different ranges of peptide sequence coverage (Figure 1; Table S1). Among them, 1857 proteins were annotated into three major ontologies—biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components—by Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analyses (Table S2). Biological processes had 0.74% of proteins involved in immune system process terms (Figure 2). In addition, 2125 proteins were mapped and classified into 24 different cluster of orthologous group (COG) categories. In the COG category, 9 proteins were annotated to the V category “defense mechanisms” (Figure 3; Table S3). Of the identified proteins, 3498 were annotated with 301 Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways, of which 2.89% were involved in the phagosome pathway (Table S4)
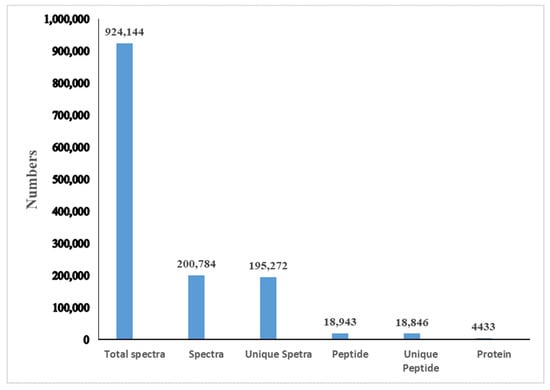
Figure 1.
Summary of the proteome profile in P. trituberculatus hemocytes by iTRAQ. “Total spectra” are the secondary mass spectra, and “Spectra” are the secondary mass spectra after quality control. “Unique Peptide” is the identified peptides that belong only to a group of proteins.
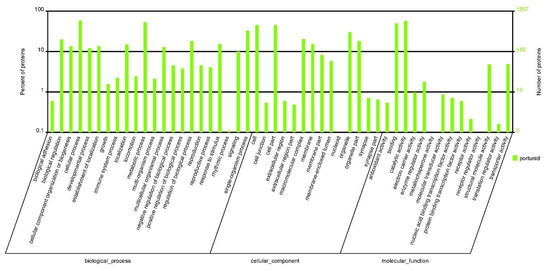
Figure 2.
Gene Ontology analysis of the identified proteins in hemocytes. These proteins were classified into different categories based on three major ontologies, including biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components.
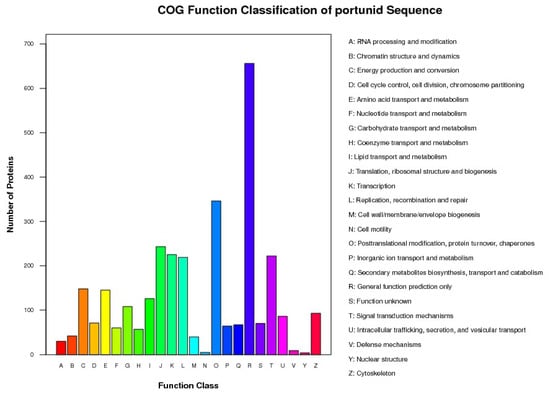
Figure 3.
Cluster of orthologous group (COG) classification of the identified proteins in hemocytes.
3.2. iTRAQ Quantification
Using a 1.2-fold increase or decrease in protein expression as a benchmark for physiologically significant changes, we found that 214 (93) and 303 (78) proteins were significantly downregulated (upregulated) at 36 h and 72 h, respectively, between the experimental and control groups. Moreover, in the experimental group, 55 (33) proteins were significantly downregulated (upregulated) at 36 h in comparison to 72 h (Figure 4).
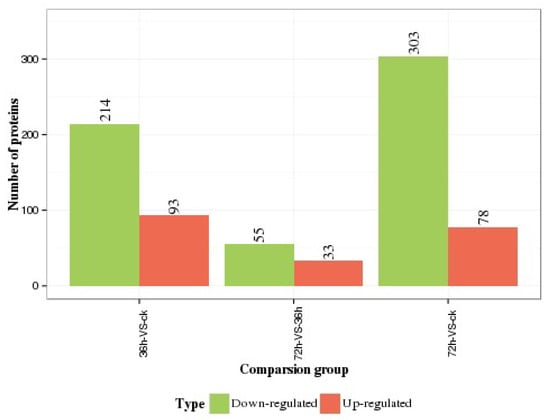
Figure 4.
Numbers of differentially expressed proteins in hemocytes.
iTRAQ analysis helped in the reliable identification and quantification of 526 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs): 143 were upregulated, and 419 were downregulated. Moreover, 36 DEPs with fluctuant changes were identified (Figure 5).
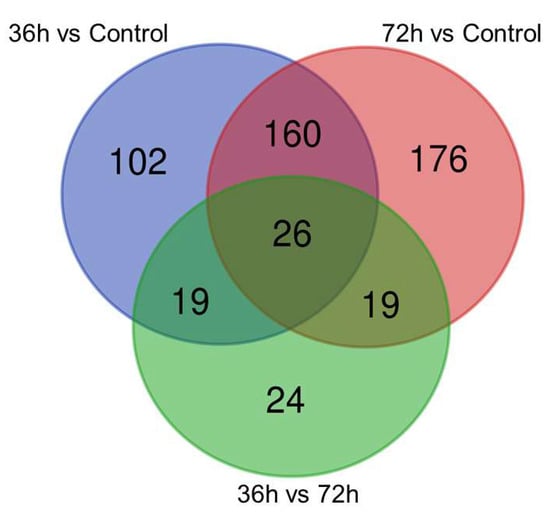
Figure 5.
Venn diagram of the altered hemocyte proteome profiles between different time points after the V. parahaemolyticus challenge. The numbers of unique and common differentially expressed proteins between the time points are indicated.
3.3. GO Enrichment Analysis
In the GO enrichment analysis of DEPs between the experimental and control groups at 36 h after the V. parahaemolyticus challenge, 126 significantly enriched GO terms (p < 0.05) were identified, including 96, 19, and 11 terms associated with biological processes, cellular components, and molecular functions, respectively. In the GO enrichment analysis of DEPs between the experimental and control groups at 72 h after the V. parahaemolyticus challenge, 71 significantly enriched GO terms (p < 0.05) were identified, including 50, 10, and 11 terms associated with biological processes, cellular components, and molecular functions, respectively (Table S5).
3.4. Immune-Related KEGG Pathways
The KEGG pathway analysis of DEPs at 36 h and 72 h after the V. parahaemolyticus challenge was performed. At 36 h after the V. parahaemolyticus challenge, the KEGG pathway analysis revealed altered immune pathways, including cell adhesion molecules, complement and coagulation cascades, phagosomes, lysosomes, tight junctions, ECM–receptor interactions, the MAPK signaling pathway, metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450, focal adhesion, peroxisomes, the B cell receptor signaling pathway, Toll-like receptor signaling, TNF signaling, and the T cell receptor signaling pathway. Similarly, at 72 h after the V. parahaemolyticus challenge, the KEGG pathway analysis revealed altered immune pathways, including complement and coagulation cascades, cell adhesion molecules, focal adhesion, ECM–receptor interactions, phagosomes, lysosomes, tight junctions, the MAPK signaling pathway, antigen processing and presentation, the B cell receptor signaling pathway, the metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450, the Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, peroxisomes, TNF signaling, and the T cell receptor signaling pathway”. Further details are provided in Table 2 and Figure 6.

Table 2.
KEGG immune-related pathways and their associated differentially expressed proteins identified in hemocytes by iTRAQ. Fold-changes were calculated in comparison with the control group.
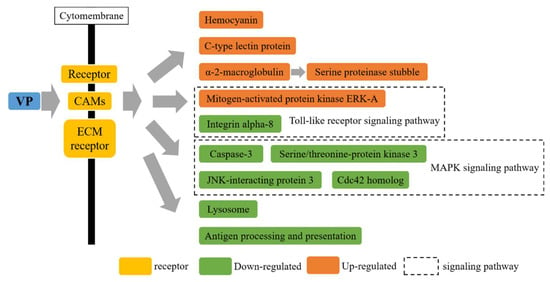
Figure 6.
Immune system of P. trituberculatus reacted to V. parahaemolyticus infection.
3.5. Validation of Proteomic Data by qRT-PCR
To confirm our iTRAQ results, the mRNA transcript levels of six immune-related DEPs, including two significantly downregulated (ribosomal protein L10, scavenger receptor class B) and four significantly upregulated (hemocyanin subunit 3, C-type lectin containing a domain protein, clip domain serine proteinase 2, serine protease) proteins at 36 h after the V. parahaemolyticus challenge, were validated by qRT-PCR (Figure 7). The mRNA transcript levels of most genes showed a consistent alteration trend with the corresponding proteins, but a disparity was noted between the mRNA transcript levels and protein abundance of C-type lectin containing a domain protein at 72 h after the V. parahaemolyticus challenge.
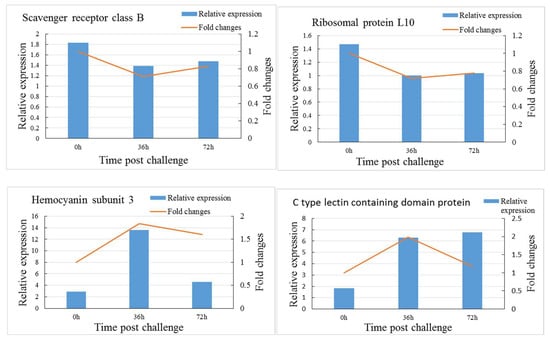
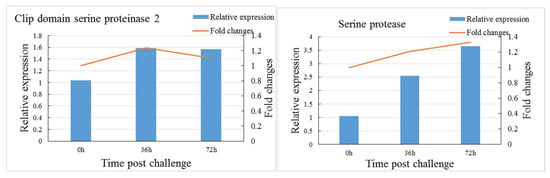
Figure 7.
Comparison of transcriptional analysis and iTRAQ-based proteomic results for six differentially expressed proteins.
4. Discussion
In recent years, V. parahaemolyticus has had a considerable impact on the sustainable aquaculture of P. trituberculatus [4,5], Scylla serrate [23,24], and Penaeus vannamei [25]. V. parahaemolyticus infection can lead to major economic losses; therefore, elucidating the mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of this infection has become pivotal for achieving sustainable crustacean production. iTRAQ has emerged as a highly efficient, reliable, and widely used method for protein identification as well as quantification. In our previous studies, the injected V. parahaemolyticus could establish an infection of P. trituberculatus, which could cause crab death and tissues lesions [8,20,26].
Herein, we used an iTRAQ-based approach to analyze the immune responses of P. trituberculatus hemocytes to V. parahaemolyticus infection. We could identify a total of 4433 proteins; 526 DEPs were subjected to GO enrichment and KEGG pathway analyses. Our findings indicated that V. parahaemolyticus considerably alters the host immune system, for example, by affecting immune-related KEGG pathways, such as CAMs, focal adhesion, and ECM-receptor interaction.
We believe that the DEPs identified by us play a pivotal role in the immune response of P. trituberculatus hemocytes to V. parahaemolyticus infection. For example, hemocyanin is an immunoglobulin superfamily molecule, which is one of the important host factors against pathogenic invasion [27,28]. More recent reports have indicated that hemocyanin plays a key role in the immune defense mechanisms of shrimp. In addition, hemocyanin isolated from L. vannamei and Penaeus monodon reportedly shows antiviral and antibacterial properties [29,30]. In this study, the expression level of hemocyanin in response to V. parahaemolyticus infection was upregulated, which is consistent with previously reported results [31,32,33]. In invertebrates, C-type lectins recognize and eliminate pathogens efficiently, which play an important role in the innate immunity system [34]. A study reported that under acute ammonia stress, the expression level of C-type lectins is significantly affected in the hepatopancreas of shrimp [35]; this result is in line with our observations. We also found that α-2-macroglobulin (A2M) and serine proteinase stubble are significantly upregulated in response to V. parahaemolyticus infection. A2M is a key component of the crustacean innate immunity system and plays an important role in defending against invading pathogens; melanization through the prophenol oxidase (proPO) cascade is one of the many innate immune mechanisms. Briefly, the proPO system is a principal component of the humoral immune response in crustaceans and can be activated even by little amounts of microbial components [7,36]. On infecting Fenneropenaeus chinensis with WSSV or a Vibrio species, the increased expression level of A2M inhibited the activation of the proPO system by inhibiting the serine protease activity [37]. Similar results were reported after subjecting P. trituberculatus hepatopancreas to a Hematodinium challenge [38], and we observed similar results in this study, too.
The Toll-like receptor signaling pathways and phagosomes are key in protecting crustaceans against pathogenic infections [38,39,40]. Herein, the phagosome and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways were affected in response to V. parahaemolyticus, with 24 DEPs identified in the two pathways. The complement and coagulation cascades pathways have been reported to play an important role in the immune response of P. trituberculatus to Hematodinium infection [38], Larimichthys crocea to Cryptocaryon irritans [41], and E. sinensis to S. eriocheiris [42]. In this study, the complement and coagulation cascades pathways were remarkably affected, with five relevant proteins being differentially expressed in the hemocytes of P. trituberculatus, including A2M and serine proteinase stubble. CAMs play an important role in mediating the migration of immune cells and maintaining tissue integrity [43,44,45]. The CAM pathway was also influenced (18 DEPs identified) in response to the V. parahaemolyticus challenge. The protein levels of some important CAMs (integrin α-8, laminin subunit β-1 and γ-1, and fasciclin-2) were significantly induced. In addition, the ECM–receptor interactions, focal adhesion, lysosomes, tight junctions, and MAPK signaling pathway were considerably affected(19, 21, 10, 10, and 10 DEPs identified, respectively) in response to V. parahaemolyticus infection. The metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450, peroxisomes, antigen processing and presentation, T and B cell receptor signaling pathways, and the TNF signaling pathway were all found to be significantly affected, too. To summarize, our results indicate that these pathways play an important role in the immune response of P. trituberculatus to V. parahaemolyticus infection
5. Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive proteomic analysis to highlight the key proteins and pathways involved in the host–vibrio interaction between P. trituberculatus and V. parahaemolyticus. The results of the study will enhance our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying this interaction.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fishes7050259/s1, Table S1: Annotation of identified proteins; Table S2: Annotation of GO; Table S3: Annotation of COG; Table S4: Different Proteins with pathway annotation; Table S5: In the enrichment analysis of GO for the DEPs between the experiment and control group after the V. parahemolyticus challenge.
Author Contributions
B.G. and X.R. conceived and designed the experiment. J.L. (Jianjian Lv) raised the crabs. X.M. dissected and collected crab tissue samples. B.G. completed the bioinformatics analysis and drafted the manuscript. J.L. (Jian Li) and P.L. revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the earmarked fund for CARS48 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 41876186).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The studies on Portunus trituberculatus were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute (approval number YSFRI2022026, approved on 7 August 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fishery Bureau, Ministry of Agriculture, China. China Fisheries Yearbook 2022; Chinese Agriculture Express: Being, China, 2022; Volume 22. (In Chinese)
- Wang, G.L.; Shan, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z. Study on pathogens and pathogenesis of emulsification disease of Portunus trituberculatus. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2006, 24, 527–531. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wan, X.; Fang, W. Analysis of major infectious diseases and their causative agents of Chinese sea crabs. Mar. Sci. 2014, 38, 102–106. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.L.; Qin, G.M.; Bao, Z.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Bi, K.R.; Qin, L. Isolation and identification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus from diseased Portunus trituberculatus. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2010, 29, 560–566. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, G.H.; Zhao, C.L.; Cui, Z.J. Main Reasons and Control Methods of Artificial Seedling Raising and Disease of Portunus trituberculatus. Shandong Fish. 2006, 23, 36–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Amparyup, P.; Charoensapsri, W.A. Tassanakajon, Prophenoloxidase system and its role in shrimp immune responses against major pathogens. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 34, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerenius, L.; Lee, B.L.; Soderhall, K. The proPO-system: Pros and cons for its role in invertebrate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lü, J.J.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.H. Cloning of Toll4 in Portunus trituberculatus and its expression in responding to pathogenic infection and low salinity stress. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2018, 39, 146–155. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Robalino, J.; Carnegie, R.B.; O‘Leary, N.; Ouvry-Patat, S.A.; de la Vega, E.; Prior, S.; Gross, P.S.; Browdy, C.L.; Chapman, R.W.; Schey, K.L.; et al. Contributions of functional genomics and proteomics to the study of immune responses in the Pacific white leg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 128, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, J.-H.; Chang, C.-C.; Wu, J.-L.; Hsu, C.-W.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T.; Juan, H.-F.; Lo, C.-F.; Kou, G.-H.; Huang, H.-C. Comparative analysis of differentially expressed genes in normal and white spot syndrome virus infected Penaeus monodon. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojtinnakorn, J.; Hirono, I.; Itami, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Aoki, T. Gene expression in haemocytes of kuruma prawn, Penaeus japonicus, in response to infection with WSSV by EST approach. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2002, 13, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.B.; Shi, J.Y.; Hao, W.J.; Xiang, T.; Zhou, H.F.; Wang, W.; Meng, Q.; Ding, Z. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis of Procambarus clakii hemocytes during Spiroplasma eriocheiris infection. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 7, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.L.; Anderson, N.G. Proteome and proteomics: New technologies, new concepts, and new words. Electrophoresis 1998, 19, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.B.; Xiu, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Gua, W.; Wang, W.; Meng, Q.G. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis of Macrobrachium rosenbergii hemocytes during Spiroplasma eriocheiris infection. J. Proteom. 2016, 136, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhu, F. A proteomic study of hemocyte Proteins from Mud crab (Scylla paramamosain) infected with White spot syndrome Virus or Vibrio alginolyticus. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, A.; Unwin, R.D.; Evans, C.A.; Griffiths, S.; Carney, L.; Zhang, L. Eightchannel iTRAQ enables comparison of the activity of six leukemogenic tyrosine kinases. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Hou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Xia, S.; Gu, W.; Wang, W. iTRAQ based proteomic study of the effects of Spiroplasma eriocheiris on Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis hemocytes. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeswin, J.; Xie, X.L.; Ji, Q.L.; Wang, K.J.; Liu, H.P. Proteomic analysis by iTRAQ in red claw crayfish, Cherax quadricarinatus, hematopoietic tissue cells post white spot syndrome virus infection. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 50, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saray, P.; Roytrakul, S.; Pangeson, T.; Phetrungnapha, A. Comparative proteomic analysis of hepatopancreas in Macrobrachium rosenbergii responded to Poly (I:C). Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 75, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lü, J.J.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.H. Cloning of HMGBa in Portunus trituberculatus and its expression in responding to pathogenic infection. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2017, 41, 1193–1199. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Lv, J.J.; Wang, L.; Sun, D.F.; Gao, B.Q.; Liu, P. Characterization of a chitinase-1 gene (PtCht-1) from a marine crab Portunus trituberculatus and its response to immune stress. Gene 2020, 741, 144523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.Q.; Sun, D.F.; Lv, J.J.; Ren, X.Y.; Liu, P.; Li, J. Transcriptomic analysis provides insight into the mechanism of salinity adjustment in swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus. Genes Genom. 2019, 41, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.K.; Sun, L.B.; Wu, H.J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, W.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Wen, X. The intestinal microbial diversity in mud crab (Scylla paramamosain) as determined by PCR-DGGE and clone library analysis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Xia, X.A.; Wu, Q.Y.; Liu, W.H.; Lin, Y.S. Infection with Hematodinium sp. in mud crabs Scylla serrata cultured in low salinity water in southern China. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 82, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.T.; Chen, I.T.; Lee, C.T.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, S.S.; Hor, L.I. Draft genome sequences of four strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, three of which cause early mortality syndrome/acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease in shrimp in China and Thailand. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00816-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L. Functional identification of chitinase gene family and its immune mechanism in response to salinity changes in Portunus trituberculatus. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2019; p. 50. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, S.Y.; Xu, A.L.; Chen, J.; Lin, B.K.; Peng, X.X. Affinity proteomic approach for identification of an IgA-like protein in Litopenaeus vannamei and study on its agglutination characterization. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachea, E.; Mialhe, E.; Noel, D.; Bouloa, V.; Morvana, A.; Rodriguezc, J. Knowledge and research prospects in marine mollusc and crustacean immunology. Aquaculture 1995, 132, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, L.; Lu, X.; Lu, H.; Wang, F.; Zhong, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y. Evidences of abundant hemocyanin variants in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 77, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Qin, Q. Antiviral properties of hemocyanin isolated from shrimp Penaeus monodon. Antivir. Res. 2004, 61, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.K.; Dettori, A.; Roux, M.M.; Klimpel, K.R.; Read, B. Identification of differentially expressed genes in shrimp (Penaeus stylirostris) infected with white spot syndrome virus by cDNA microarrays. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 2381–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, P.S.; Bartlett, T.C.; Browdy, C.L.; Chapman, R.W.; Warr, G.W. Immune gene discovery by expressed sequence tag analysis of hemocytes and hepatopancreas in the Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, and the Atlantic white shrimp, L-setiferus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lin, Q.; Lim, T.K.; Liu, T.; Hew, C. White spot syndrome virus proteins and differentially expressed host proteins identified in shrimp epithelium by shotgun proteomics and cleavable isotope-coded affinity tag. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11681–11689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Luan, S.; Dai, P.; Meng, X.H.; Cao, B.X.; Luo, K.; Kong, J. iTRAQ-based comparative proteome analysis for molecular mechanism of defense against acute ammonia toxicity in Pacific White shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 74, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Jiang, S.; Huang, J.; Zhou, F.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Yang, L. C-type lectin response to bacterial infection and ammonia nitrogen stress in tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 90, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerenius, L.; Kawabata, S.I.; Lee, B.L.; Nonaka, M.; Söderhäll, K. Proteolytic cascades and their involvement in invertebrate immunity. Trends Biochemical. Sci. 2010, 35, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.Q.; Li, F.H.; Xiang, J.H. Multiple forms of alpha-2 macroglobulin in shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinesis and their transcriptional response to WSSV or Vibrio pathogen infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, C. Proteomic analysis highlights the immune responses of the hepatopancreas against Hematodinium infection in Portunus trituberculatus. J. Proteom. 2019, 197, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xiang, J. Recent advances in researches on the innate immunity of shrimp in China. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 39, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Song, S. Molecular characterization and expression of a novel Toll gene from the swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Gao, Q.; Tang, B.; Sun, P.; Han, K.; Huang, W. Transcriptome and analysis on the complement and coagulation cascades pathway of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) to ciliate ectoparasite Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 50, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larvie, M.; Takahashi, K. Fluid phase barrier immunity and serine protease cascades–the essential roles of the coagulation system. J. Hematol. Thromboembolic Dis. 2014, 2, 1000158. [Google Scholar]
- Ponprateep, S.; Vatanavicharn, T.; Lo, C.F.; Tassanakajon, A.; Rimphanitchayakit, V. Alpha-2-macroglobulin is a modulator of prophenoloxidase system in pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamai. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 62, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prota, A.E.; Campbell, J.A.; Schelling, P.; Forrest, J.C.; Watson, M.J.; Peters, T.R.; Aurrand-Lions, M.; Imhof, B.A.; Dermody, T.S.; Stehle, T. Crystal structure of human junctional adhesion molecule 1: Implications for reovirus binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5366–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostrewa, D.; Brockhaus, M.; D’Arcy, A.; Dale, G.E.; Nelboeck, P.; Schmid, G.; Mueller, F.; Bazzoni, G.; Dejana, E.; Bartfai, T.; et al. X-ray structure of junctional adhesion molecule: Structural basis for hemophilic adhesion via a novel dimerization motif. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 4391–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).