Age and Growth of Diaphus brachycephalus in the South China Sea Using Sagittal Otolith Microstructure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
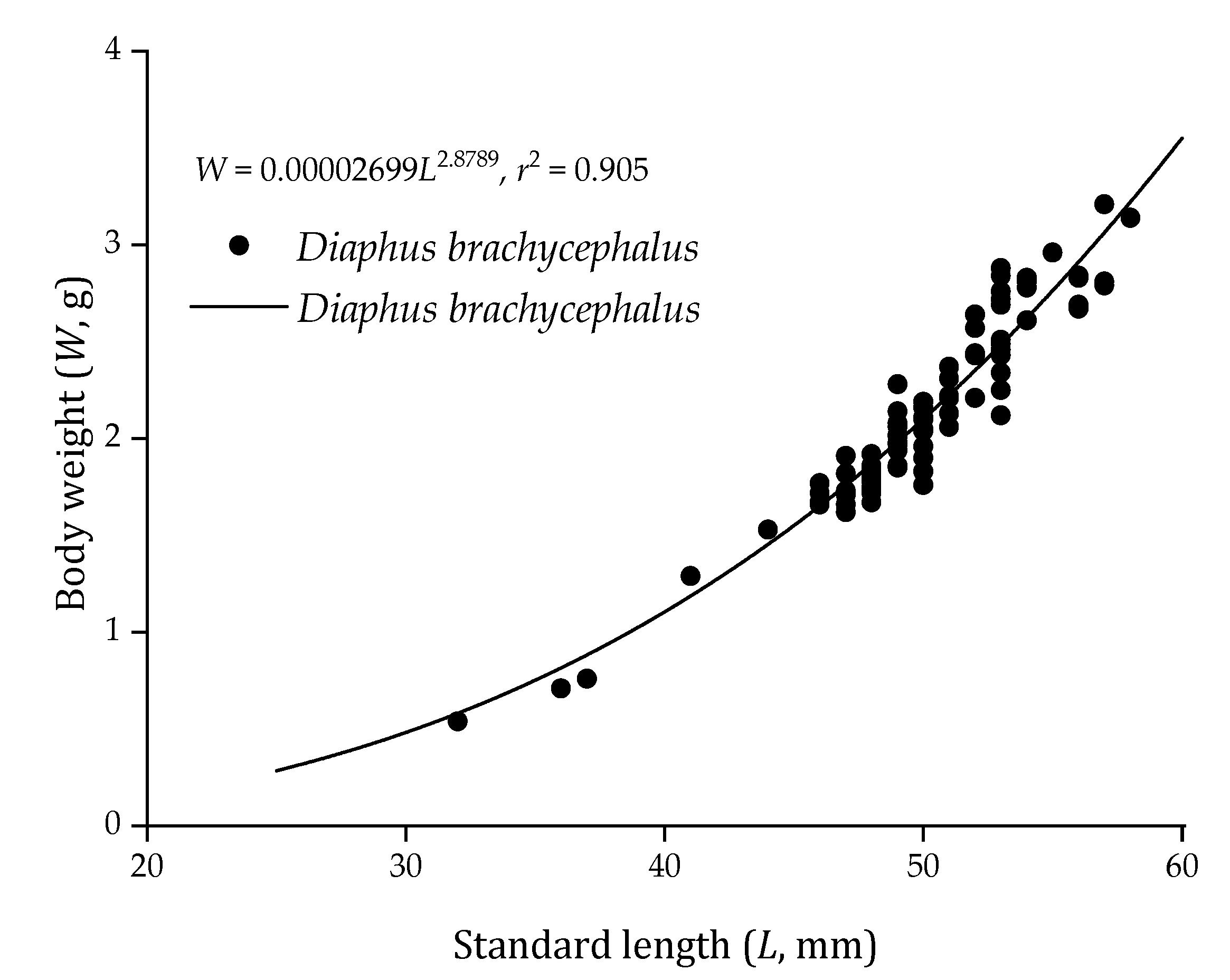
3.1. Body Length and Weight
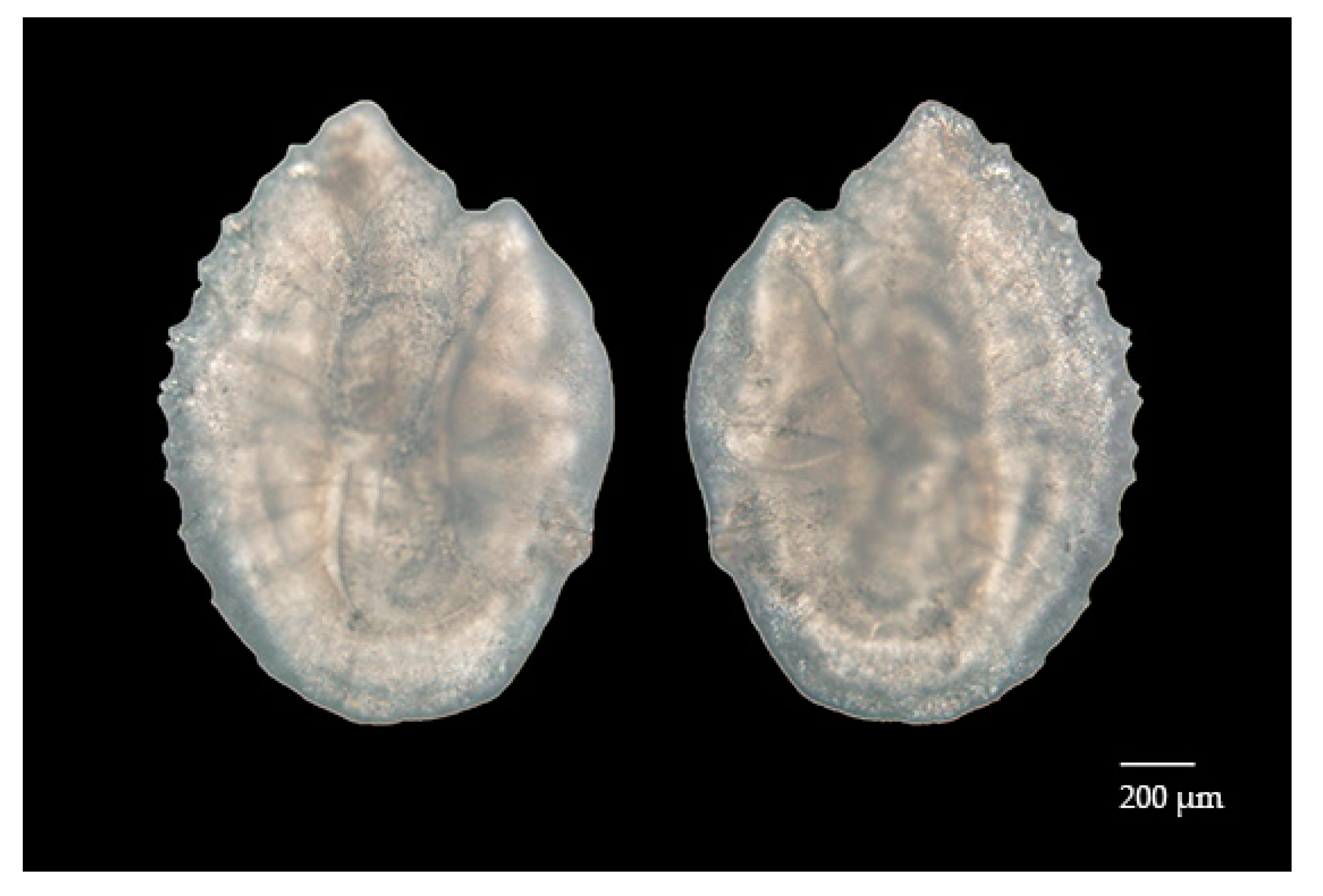
3.2. Sagittal Otolith Microstructure
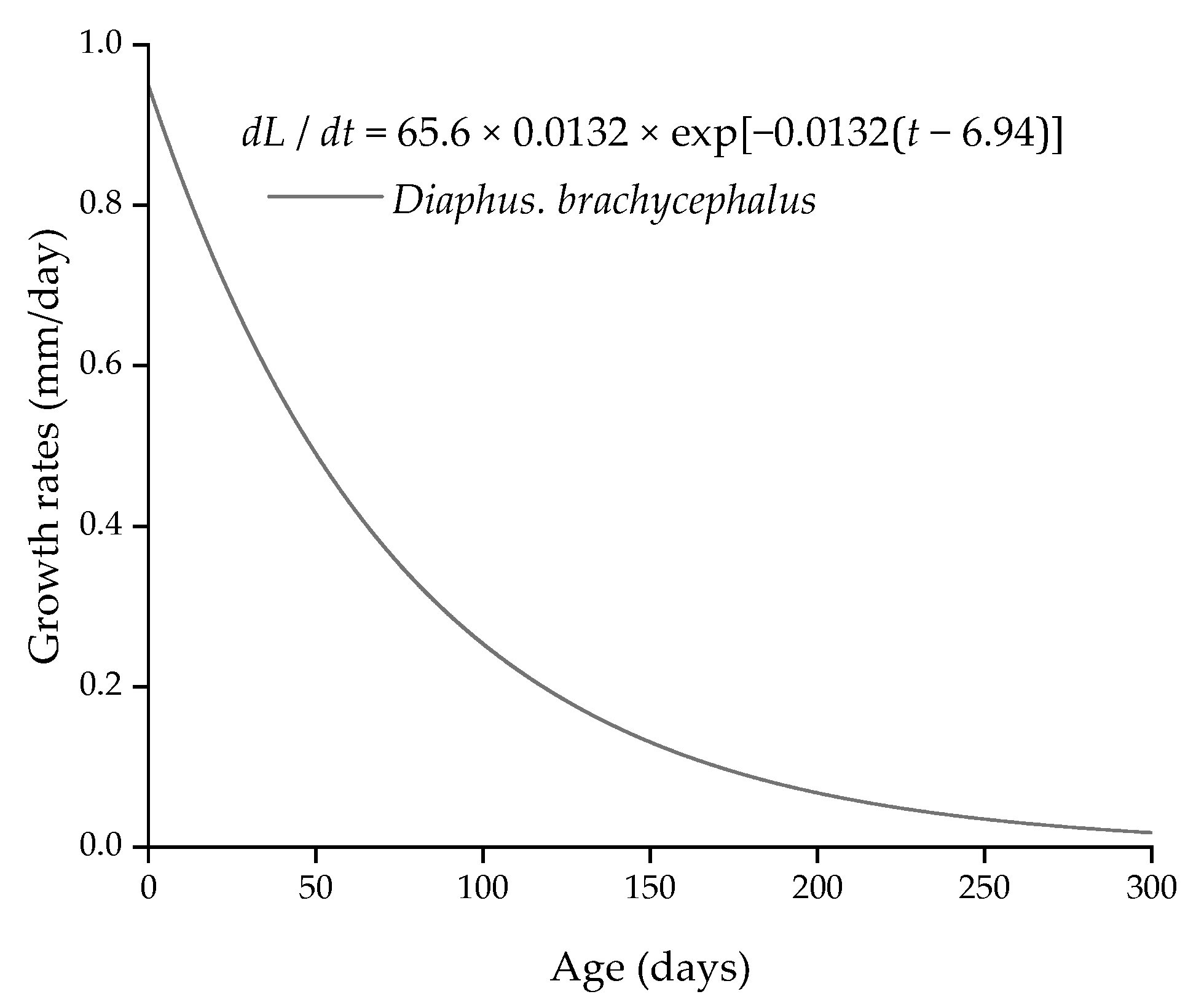
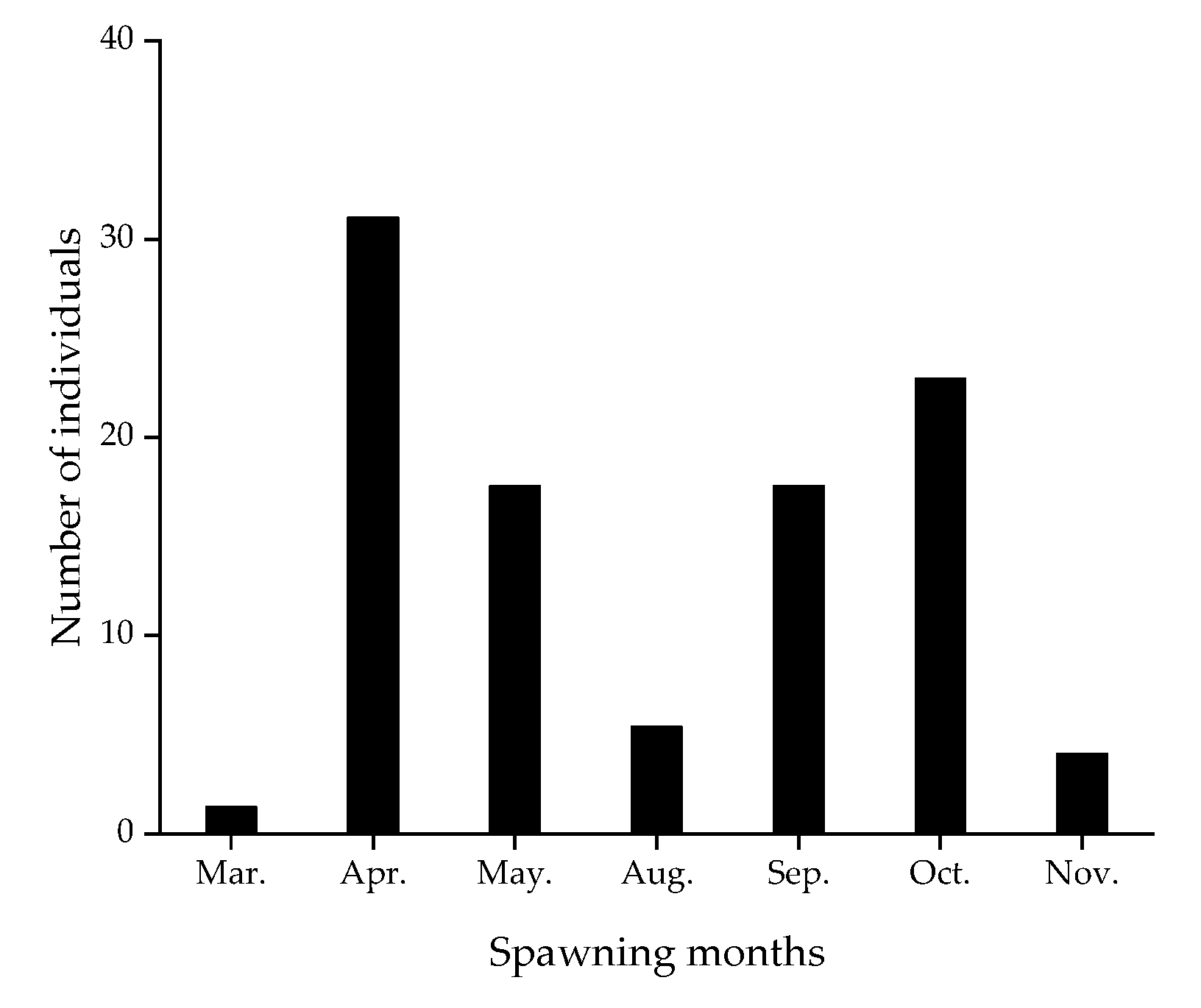
3.3. Age and Growth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.T.A.; Wang, S.L.; Wang, B.J.; Pai, S.C. Nutrient budgets for the South China Sea basin. Mar. Chem. 2001, 75, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.T.F.; Ku, T.L.; Mulholland, M.; Tseng, C.M.; Wang, D.P. The South East Asian time-series study (SEATS) and the biogeochemistry of the South China Sea—An overview. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2007, 54, 1434–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yizhuo, Z.; Huiwu, S. Development trends of marine capture fisheries in South China Sea. Agric. Outlook 2015, 11, 51–55, (In Chinese with English summary). [Google Scholar]
- Funge-Smith, S.; Briggs, M.; Miao, W. Regional Overview of Fisheries and Aquaculture in Asia and the Pacific 2012; RAP Publication 2012/26; Asia-Pacific Fishery Commission, FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific: Bangkok, Thailand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.W.; Chuang, C.T. Fishing capacity management in Taiwan: Experiences and prospects. Mar. Policy 2010, 34, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, L.S.L.; Witter, A.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Sumaila, U.R.; Yin, X. What is at stake? Status and threats to South China Sea marine fisheries. Ambio 2017, 46, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gjøsaeter, J.; Kawaguchi, K. A review of the world resources of mesopelagic fish. Food Agric. Organ. U. N. 1980, 193, 1–151. [Google Scholar]
- Klevjer, T.A.; Irigoien, X.; Røstad, A.; Fraile-Nuez, E.; Benítez-Barrios, V.M.; Kaartvedt, S. Large scale patterns in vertical distribution and behaviour of mesopelagic scattering layers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Proud, R.; Handegard, N.O.; Kloser, R.J.; Cox, M.J.; Brierley, A.S. From siphonophores to deep scattering layers: Uncertainty ranges for the estimation of global mesopelagic fish biomass. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 76, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGinnis, R.F. Biogeography of the lantern fishes (Myctophidae) south of 30° S. Antarctic Res. Ser. 1982, 35, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbase. Diaphus brachycephalus: List of Point Data. 2022. Available online: https://www.fishbase.se/map/OccurrenceMapList.php?genus=Diaphus&species=brachycephalus (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Stanton, T.K.; Sellers, C.J.; Jech, J.M. Resonance classification of mixed assemblages of fish with swimbladders using a modified commercial broadband acoustic echosounder at 1–6 kHz. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 854–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saunders, R.A.; Hill, S.L.; Tarling, G.A.; Murphy, E.J. Myctophid fish (family Myctophidae) are central consumers in the food web of the Scotia Sea (Southern Ocean). Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO Fisheries. Lanternfishes: A Potential Fishery in the Northern Arabian Sea. Roma, Italy, 1997. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/003/w4248e/w4248e34.htm (accessed on 26 March 2022).
- Williams, A.; Koslow, J.A.; Terauds, A.; Haskard, K. Feeding ecology of five fishes from the mid-slope micronekton community off southern Tasmania, Australia. Mar. Biol. 2001, 139, 1177–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, P.C.; Checkley, D.M.; Koslow, J.A.; Barlow, J. Carbon export mediated by mesopelagic fishes in the northeast Pacific Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2013, 116, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjøsæter, J. Growth, production and reproduction of myctophid fish Benthosema glaciale from western Norway and adjacent seas. Fiskeridir. Skr. Ser. Havunders. 1981, 17, 79–108. [Google Scholar]
- Catul, V.; Gauns, M.; Karuppasamy, P.K. A review on mesopelagic fishes belonging to family myctophidae. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2011, 21, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkowski, T.B. Otolith microstructure and growth patterns during the early life history of lanternfishes (family Myctophidae). Can. J. Zool. 1991, 69, 1777–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- José, I.Z.; Claudia, A.B.; Mauricio, F.L. Larval growth, condition and fluctuating asymmetry in the otoliths of a mesopelagic fish in an area influenced by a large Patagonian glacier. Mar. Biol. Res. 2014, 10, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlstrom, D. A crystallographic study of vertebrate otoliths. Biol. Bull. 1963, 125, 441–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Jun, Z.; Zuozhi, C.; Yane, J.; Shannan, X.; Zhongyi, L.; Xinliang, W.; Yiping, Y.; Xianyong, Z.; Meng, Z. Age and growth of Myctophum asperum in the South China Sea based on otolith microstructure analysis (Article). Deep-Sea Res. Part II 2019, 167, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Z.; Yan, W.; Zuozhi, C.; Yane, J.; Shannan, X. Age and growth of Ceratoscopelus warmingii (Myctophidae) in the South China Sea based on sagittal otolith microstructure. Mar. Biol. Res. 2021, 17, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, J.V. Life histories of three species of lanternfishes (Pisces: Myctophidae) from the eastern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Biol. 1991, 111, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, P.; Malara, D.; Romeo, T.; Andaloro, F. Relationships between otolith size and fish size in some mesopelagic and bathypelagic species from the Mediterranean Sea (Strait of Messina. Italy). Sci. Mar. 2010, 74, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, X.; Jian, Y.; Tao, J.; Hongbo, L.; Xiaming, Z.; Jianhua, T. Early life history of the small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) in sandy ridges of the South Yellow Sea. Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, V.E. Miktofovye Ryby Mirovogo Okeana. In Myctophid Fishes of the World Ocean; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1983; pp. 1–246. [Google Scholar]
- Nafpaktitis, B.G.; Robertson, D.A.; Paxton, J.R. Four new species of the lanternfish genus Diaphus (Myctophidae) from the Indo-Pacific. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1995, 29, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarzhans, W.A. Comparative morphological study of the recent otoliths of the genera Diaphus, Idiolychnus and Lobianchia (Myctophidae). Palaeoichthyologica 2013, 13, 41–82. [Google Scholar]
- Prokofiev, A.M.; Emelyanova, O.R.; Orlov, A.M.; Orlova, S.Y. A New Species of Diaphus Associated with Seamounts of the Emperor Chain, North-Western Pacific Ocean (Teleostei: Myctophiformes: Myctophidae). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullis, H.R.; Thompson, J.R. Collections by the Exploratory Fishing Vessels Oregon, Silver Bay, Combat, and Pelican Made during 1956 to 1960 in the Southwestern North Atlantic; United States Fish and Wildlife Service Special Scientific Reports–Fisheries; U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Commercial Fisheries: Washington, DC, USA, 1965; p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Backus, R.H.; Craddock, J.E.; Haedrich, R.L.; Shores, D.L. Mesopelagic fishes and thermal fronts in the western Sargasso Sea. Mar. Biol. 1969, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulley, P.A.; Quero, J.C.; Hureau, J.C.; Karrer, C.; Post, A.; Saldanha, L. Myctophidae. Check-List of the Fishes of the Eastern Tropical Atlantic (CLOFETA); JNICT: Lisbon, Portugal; SEI: Paris, France; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1990; pp. 398–467. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Ying, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, M. Vertical distribution and diel migration of mesopelagic fishes on the northern slope of the South China sea. Deep-Sea Res. Part II 2019, 167, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, S. Community structure of mesopelagic fish species in northern slope of South China Sea. South China Fish. Sci. 2018, 14, 85–91, (In Chinese with English summary). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Yane, J.; Jun, Z.; Zuozhi, C.; Shannan, X.; Jiangfeng, Z. A preliminary study on the community structure of mesopelagic fish in the cold seep area of Xisha Islands. South China Fish. Sci. 2022. accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Gong, Y.; Ying, Y.; Li, Z.; Kong, X.; Chen, G.; et al. Species composition and biomass density of mesopelagic nekton of the South China Sea continental slope. Deep-Sea Res. Part II 2019, 167, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motomura, H. Fish Collection Building and Procedures Manual; Ishikawa, S., Ed.; The Kagoshima University Museum: Kagoshima, Japan; The Research Institute for Humanity and Nature: Kyoto, Japan, 2013; p. 70. ISBN 978-4-905464-01-3. [Google Scholar]
- Beamish, R.J.; Leask, K.D.; Ivanov, O.A.; Balanov, A.A.; Orlov, A.M.; Sinclair, B. The ecology, distribution, and abundance of midwater fishes of the subarctic pacific gyres. Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 43, 399–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Seoane, E.; Meneses, I.; Silva, A. Microstructure of the otoliths of the glacier lanternfish, Benthosema glaciale. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 66, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigarosov, V.Y.; Ovcharov, O.P. Age and growth of the lantern fish Myctophum nitidulum (Myctophidae) from the tropical Atlantic. J. Ichthyol. 1992, 32, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bystydzieńska, Z.E.; Phillips, A.J.; Linkowski, T.B. Larval stage duration, age and growth of blue lanternfish Tarletonbeania crenularis (Jordan and Gilbert, 1880) derived from otolith microstructure. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2010, 89, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseini-Shekarabi, S.P.; Valinassab, T.; Bystydzieńska, Z.; Linkowski, T. Age and growth of Benthosema pterotum (Alcock, 1890) (Myctophidae) in the Oman Sea. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2015, 31, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R. Cube law, condition factor and weight-length relationships: History meta-analysis and recommendations. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2006, 22, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M. Fisheries Biology: Assessment and Management; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 1995; p. 341. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, T.A. Sex-ratios and sexual differences in size among mesopelagic fishes from the central Pacific Ocean. Mar. Biol. 1983, 73, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.W.; Bulman, C.M.; Blaber, S.J.M.; Wayte, S.E. Age and growth of the lanternfish Lampanyctodes hectoris (Myctophidae) from eastern Tasmania, Australia. Mar. Biol. 1988, 99, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassa, C.; Tanaka, H.; Ohshimo, S. Comparative reproductive biology of three dominant myctophids of the genus Diaphus on the slope region of the East China Sea. Deep-Sea Res. Part I 2016, 115, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppasamy, P.K.; George, S.; Menon, N.G. Length-weight relationship of Benthosema pterotum (myctophid) in the deep scattering layer (DSL) of the eastern Arabian Sea. Indian J. Fish. 2008, 55, 301–303. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, R.H.; Krueger, W.H. Biology of Midwater Fishes of the Bermuda Ocean Acre; Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology: Washington, DC, USA, 1987; pp. 1–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Perez, C.; Olivar, M.P.; Hulley, P.A.; Tuset, V.M. Length-weight relationships of mesopelagic fishes from the equatorial and tropical Atlantic waters: Influence of environment and body shape. J. Fish Biol. 2020, 96, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, T.A. Some Aspects of the Ecology of Lanternfishes (Myctophidae) in the Pacific Ocean near Hawaii. Fish Bull. 1973, 71, 401–434. [Google Scholar]
- Loeb, V.J. Vertical distribution and development of larval fishes in the North Pacific central gyre during summer. Fish Bull. 1980, 77, 777–793. [Google Scholar]
- Lisovenko, L.A.; Prut’ko, V.G. Reproductive biology of Diaphus suborbitalis (Myctophidae) in the equatorial part of the Indian Ocean. 2. Fecundity and reproductive potential. J. Ichthyol. 1987, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gjøsæter, J.; Tilseth, S. Spawning behavior, egg and larval development of the myctophid fish Benthosema pterotum. Mar. Biol. 1988, 98, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento-Lezcano, A.N.; Triay-Portell, R.; Castro, J.J.; Rubio-Rodríguez, U.G.; Pajuelo, J.G. Age-based life-history parameters of the mesopelagic fish Notoscopelus resplendens (Richardson, 1845) in the Central Eastern Atlantic. Fish Res. 2018, 204, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkowski, T.B. Morphological Variation, Systematics and Speciation of the Ceratosco-pelus townsendi−C. warmingii Complex (Osteichthyes: Myctophidae) Based on the Studies on the Morphology and Microstructure of Otoliths; Morski Instytut Rybacki: Gdynia, Poland, 1997; (In Polish with English summary). [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, K.; Yatsu, A.; Moku, M.; Sassa, C. Age and growth of lanternfishes, Symbolophorus californiensis and Ceratoscopelus warmingii (Myctophidae) in the Kuroshio-Oyashio Transition zone. Ichthyol. Res. 2006, 53, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moku, M.; Ishimaru, K.; Kawaguchi, K. Growth of larval and juvenile Diaphus theta (Pisces: Myctophidae) in the transitional waters of the western North Pacific. Ichthyol. Res. 2001, 48, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Starting Location | Finishing Location | Trawl Depth | Mean Towing Speed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Time | M/D/Y | Lat. (N)/Long. (E) | Lat. (N)/Long. (E) | (m) | (m/s) |
| 18:17~19:51 | 01/27/2015 | 15°21.45′/115°11.07′ | 15°19.93′/115°04.40′ | 75 | 2.3 |
| 21:30~22:30 | 06/20/2015 | 19°48.04′/115°48.90′ | 19°45.44′/115°51.90′ | 75 | 1.8 |
| M/D/Y | Sexes | L (mean ± SD, mm) | W (mean ± SD, g) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01/27/2015 | male | 49.6 ± 6.2 | 1.98 ± 0.62 | 9 |
| 01/27/2015 | female | 50.4 ± 5.1 | 2.27 ± 0.57 | 37 |
| 06/20/2015 | male | 49.6 ± 3.5 | 2.15 ± 0.42 | 7 |
| 06/20/2015 | female | 49.7 ± 2.7 | 2.15 ± 0.42 | 34 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J. Age and Growth of Diaphus brachycephalus in the South China Sea Using Sagittal Otolith Microstructure. Fishes 2022, 7, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7040169
Tian H, Jiang Y, Zhang J, Xu S, Chen Z, Zhu J. Age and Growth of Diaphus brachycephalus in the South China Sea Using Sagittal Otolith Microstructure. Fishes. 2022; 7(4):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7040169
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Han, Yane Jiang, Jun Zhang, Shannan Xu, Zuozhi Chen, and Jiangfeng Zhu. 2022. "Age and Growth of Diaphus brachycephalus in the South China Sea Using Sagittal Otolith Microstructure" Fishes 7, no. 4: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7040169
APA StyleTian, H., Jiang, Y., Zhang, J., Xu, S., Chen, Z., & Zhu, J. (2022). Age and Growth of Diaphus brachycephalus in the South China Sea Using Sagittal Otolith Microstructure. Fishes, 7(4), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7040169








