Abstract
Cysteine proteinase inhibitors (CPIs) protect tissues and organs against cysteine proteinases in animal blood and have attracted much attention for use in food processing and medical sciences for humans and animals. Several CPI proteins, which include stefins, cystatins, kininogens, histidine-rich glycoproteins (HRG) and fetuins, have been identified and characterized in mammals. Fish blood also contains high CPI activity, but the identity of the major protein responsible for this activity has not been clarified. This study was conducted to screen CPI activity by examining papain inhibitory activity from various different tissues in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus and to identify major proteins for the activity in the blood. CPI activity was highest in the serum among the tissues screened in this study (at least fourfold higher than in other tissues)(P < 0.05). Major proteins for CPI activity in serum were purified using a CNBr-activated sepharose 4B column, gel filtration and an ion exchange FPLC column. From these purifications, two proteins with strong CPI activity were isolated and partially sequenced. Based on their molecular weights and partial amino sequences, the two major proteins with CPI activity from the blood in this species were found to be fetuin B (60 kDa) and kininogen (54 kDa).
1. Introduction
The components contained in animal blood are used in various industries, including the food processing, medical and pharmaceutical sectors [1]. Blood from farmed fish could also be collected and utilized in the same way. It has been well demonstrated that fish blood inhibits autolysis of fish meat and increases the gel strength of fish surimi [2,3,4]. One of the main components that achieve this effect has been suggested to be cysteine proteinase inhibitors (CPIs) [4,5].
CPIs belong to a protein superfamily, cystatin. Based on classifications in mammals, this cystatin superfamily includes families of stefins, cystatins, kininogens, histidine-rich glycoproteins (HRG) and fetuins which contain at least one cystatin domain [6]. Most of these inhibitors exhibit papain (a cysteine proteinase) inhibitory activity, except fetuin in mammals. These inhibitors protect tissues and organs against cysteine proteinases that are released into the blood after cell death.
It has been reported that fish blood contains high CPI activity [7,8], but the exact identity of the protein responsible for the activity is not known. High activity of this inhibitor was also well reported in the blood of humans [9], chickens [5], frogs [10] and other animals, including fish [4]. Nevertheless, CPI in fish did not get much attention until recently when their names were mentioned concerning some important biological events in genomic, transcriptomic and proteomic analyses [11,12,13]. CPIs are involved in many important biological functions and have been suggested as potential medicinal substances and diagnostic tools [14,15]. For example, cystatin C, one of the major CPIs, is used as a marker for cardiovascular risk [9].
Several CPIs have been purified and characterized in fish (rainbow trout liver [16], salmon plasma [17], turbot mucosal barrier [18], salmon skin [19], salmon egg [20] and catfish muscle [21]), but the identity of the protein responsible for the CPI activity was not clarified in many cases. The CPI from rainbow trout liver was cystatin C with a molecular weight (MW) of 10–20 kDa [16]. Salmon plasma contained a 70 kDa protein with CPI activity, which was assumed to be kininogen [17]. CPI from the turbot mucosal barrier was suggested as fetuin B with some protective roles against pathogens [18]. However, the identities of CPIs from salmon skin [19] and egg [20] and also catfish muscle [21] were ambiguous. Moreover, to our best knowledge, information on plasma CPIs in fish is extremely limited.
Tilapia, a subtropical fish species, is a favorite aquaculture species, being cultured all around world including in many regions in Asia, Europe, America and Africa. This species grows fast with strong resistance to many diseases. Identification of major proteins responsible for CPI activity in the blood of this species could provide better opportunities for utilizing these substances in various ways, including as medicines or additives for food processing. We have screened several different tissues from the Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus for papain inhibitory activity and identified two major CPIs in the blood.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Samples
Adult female Nile tilapia (total length 13.9 ± 1.2 cm, body weight 55.6 ± 7.2 g, n = 5) were obtained from a local fish farm and maintained in fish-holding facilities until sacrificed for sampling. Fish were killed by overdoses of anesthetics (benzocaine). Blood was withdrawn, and the liver, kidney, ovary, muscle and heart were removed to screen for papain inhibitory activity.
2.2. Chemicals
α-N-benzoyl-DL-arginine-2-naphthylamide (BANA), dithiothreitol (DTT), ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), iodoacetic acid, papain (P4762), Bradford reagent, L-cysteine, polyoxyethylene 23 lauryl ester (Brij 35), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), sodium azide, 2-[3-(hydroxymercuri)-2-methoxypropyl] carbamoyl-phenoxy-acetic acid (mersalyl acid), 2-naphthylamine, fast Garnet GBC sulfate salt (4-amino-2′,3-dimethylazobenzene diazotated), acrylamide, sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), molecular-weight standard (SDS-6H) and dialysis membrane (D0405-100FT) were obtained from Sigma (St. louis, MO, USA). CNBr-activated Sepharose 4B and Mono Q were purchased from Pharmacia Biotech (Uppsala, Sweden).
2.3. Papain Inhibitory Activity in Different Tissues
Papain inhibitory activity as an indication of the presence of CPI in the sample was measured based on the previous methods [7,22,23,24] with some modifications. Tissues (serum, liver, kidney, ovary, muscle and heart) of Nile tilapia were homogenized in 100 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6.0) containing EDTA (1.33 mM) and cysteine (2.7 mM) and centrifuged at 4 °C at 10,000 rpm for 20 min. Tissue to buffer ratio (w:v) was 1:10 for the homogenization process. Each supernatant from different tissue sample (125 µL) was mixed with 50 µL of papain solution (45 ng/µL) and 1.5 mL of 100 mM phosphate buffer (88 mM KH2PO4, 12 mM Na2HPO4, 1.33 mM disodium EDTA, 2.7 mM cysteine, pH 6.0), and preincubated at 40 °C for 5 min. The mixture was then incubated together with 50 µL of an artificial substrate BANA solution (40 mg/mL in DMSO) at the same temperature for 10 min. A mixture (2 mL) of Fast Garnet GBC base solution (2.25 µg/mL), sodium nitrite (0.2 mM) and mersalyl-Brij solution (mersalyl acid 2.43 mg/mL and 2% Brij 35) was added to the incubation for color development. The developed red color, which indicates the residual papain activity, was analyzed at A520 using a spectrophotometer (Pharmacia). Inhibitory activity of CPI was measured three times for each tissue and calculated by using the following equation (1 unit of inhibitory activity is described as inhibition of one unit of papain):
Inhibitory activity = ODo − ODi/ODo × 0.0405 × F
ODo: A520 for reactant solution without inhibitor
ODi: A520 for reactant solution with inhibitor
0.0405: Unit of papain in the reaction mixture
F: Dilution factor
2.4. Isolation of CPIs from Tilapia Serum
Tilapia blood CPIs were isolated by using three steps: affinity chromatography, gel filtration and ion exchange FPLC column (mono Q HR 5/5) (Figure 1). FPLC was carried out in an AKTA FPLC system (Amersham Phamacia Biotech, Uppsala, Sweden). Volume of a fraction in all chromatographies was 0.5 mL. Blood serum was pooled and diluted threefold with loading buffer (20 mM phosphate buffer, 0.1 M NaCl, pH 6.0) and then dialyzed at 4 °C against the same buffer four times per day. CNBr-activated Sepharose 4B was coupled with papain in coupling buffer (0.2 M NaHCO3, 0.5 M NaCl, pH 8.3) at 4 °C overnight. The Sepharose 4B coupled with papain was equilibrated with the loading buffer and loaded in a column (2.5 × 30 mm). The dialyzed serum was applied to this Sepharose 4B column for affinity chromatography. Specifically bound protein to the Sepharose 4B coupled with papain was eluted using 20 mM trisodium phosphate buffer (pH 10.5) after the removal of unbound (buffer: 20 mM phosphate, 0.1 M NaCl, pH 6.0) and non-specifically bound proteins (buffer: 20 mM phosphate, 1 M NaCl, pH 6.0). Fractions were tested for papain inhibitory activity. Positive fractions for this test were concentrated (Stirred Ultrafiltration Cell YM3, dia 63.5 mm, dia 25 mm) and dialyzed using 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0).
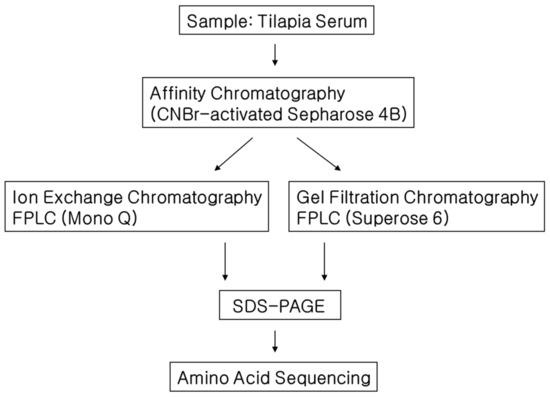
Figure 1.
Strategy for the purification of cysteine proteinase inhibitor (CPI) from the blood of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus.
Fractions with strong papain inhibitory activity were then subjected to ion exchange FPLC column (mono Q HR 5/5). The proteins were eluted using linear NaCl gradient (0–0.5 M) at a flow rate of 1 mL min−1. Papain inhibitory fraction was also subjected to gel filtration chromatography to estimate molecular weight of papain inhibiting proteins in tilapia serum by comparing the elution results to gel filtration with standard proteins (ovalbumin 45 kDa, bovine serum albumin 66 kDa and aldorase 158 kDa).
Fractions with strong papain inhibitory activity from ion exchange chromatography was further separated to obtain single protein band by SDS-PAGE using 12% polyacrylamide gel [25]. The gels were stained with 0.1% Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 to visualize proteins.
2.5. Amino Acid Sequencing
Potential CPI bands were excised from the gel and destained with destaining solution (50% methanol in 10% acetic acid) by shaking. The gel piece with a protein band was digested by trypsin (Promega) overnight at 37 °C. Digested peptide mixture was then desalted and concentrated prior to mass spectrometric analysis. MS/MS of this peptide mixture was carried out by nano-ESI on a Q-TOF2 mass spectrometer (Micromass, Manchester, UK). All MS/MS spectra recorded on the tryptic peptides derived from the gel piece were searched against protein sequences from NCBI nr and EST databases using the MASCOT search program (www.matrixscience.com, accessed on 22 June 2022).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Tissue Distribution of CPI Activity
Analysis of CPI activity in the serum, liver, kidney, ovary, muscle and heart of Nile tilapia revealed that the activity was far higher in the serum than the activity in other tissues (4–25 times higher depending on tissues) (Figure 2). Not many studies have investigated CPI activity by tissue type so far. In a few studies, differences in the tissue distribution of some CPI have been suggested. In mouse, cystatin C protein was more abundant in the muscle, kidney and spleen than in the liver but not investigated in the blood [26]. In silver carp, the expression level of cystatin C mRNA was highest in the muscle but low in the liver and spleen (no data available for blood [27]). In turbot (Scophthalmus maximus), stefin B mRNA was expressed severalfold more in the muscle than in other tissues (no data available for blood, [28]).
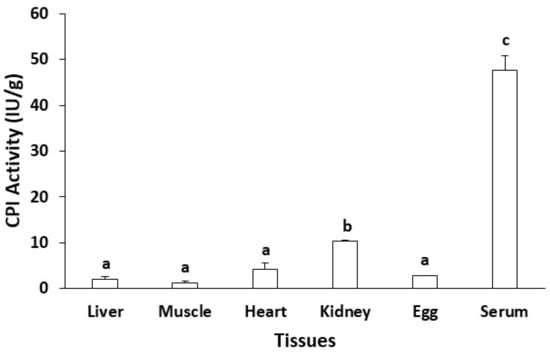
Figure 2.
Differential activity of CPI in various tissues of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Different letters on top of each column indicate significant difference in CPI activity between tissues (Tukey’s multiple comparison, p < 0.05).
The difference in CPI activity or expression level might be associated with CPI protein types between different tissues. In a previous study, the thermal stability of blood CPI was found to be higher than that of egg CPI [7]. In addition, the pH stability between blood CPI and egg CPI was different (data not shown). All of these results indicate that, in fish, major CPIs in the blood are different from major CPIs in the eggs, although they share the function of papain inhibition. In this study, blood protein with papain inhibitory activity was isolated and partially characterized (identified by means of amino acid sequencing).
3.2. Isolation of CPIs from Tilapia Serum
Tilapia serum was subjected to affinity chromatography utilizing papain-coupled CNBr-activated sepharose 4B column. Specifically bound protein to this sepharose 4B coupled with papain was eluted after the removal of unbound and non-specifically bound proteins by changing the conditions of the elution buffer. Fractions collected using appropriate buffer conditions were screened for papain inhibitory activity (Figure 3), resulting in fraction no 22–24 and 32 with strong CPI activity. The fractions corresponding to this strong activity were then pooled and subjected to gel filtration chromatography to estimate molecular weight of the papain-inhibiting proteins in tilapia serum. As a result, the molecular weight of potential CPI proteins in tilapia serum ranged between 45 and 66 kDa (Figure 4) when compared to the results of gel filtration chromatography with standard proteins. Molecular weights (MW) of well-known CPIs are generally divided into three groups: stefins 10–14 kDa, cystatins 10–14 kDa and kininogens >50 kDa [29]. From this, it can be suggested kninogen or some high-MW CPI is responsible for the high CPI activity in tilapia serum, while fractions with weak CPI activity, which were excluded from the pooling, may have contained stefins or cystatins.
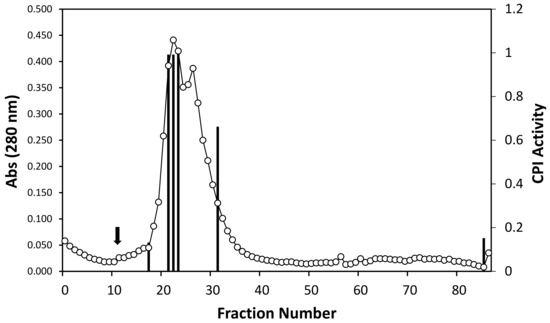
Figure 3.
Elution profile from affinity chromatography on CNBr-activated papain Sepharose 4B column. Tilapia serum was applied to the column, and the column was washed to remove unbound and non-specifically bound proteins. Target protein was then eluted by adding 20 mM tri-sodium phosphate buffer (pH 10.5). Black arrow indicates the adding timing of elution buffer. Fractions were collected and screened for papain inhibitory activity (as CPI activity). Black columns show fractions with distinct CPI activity.
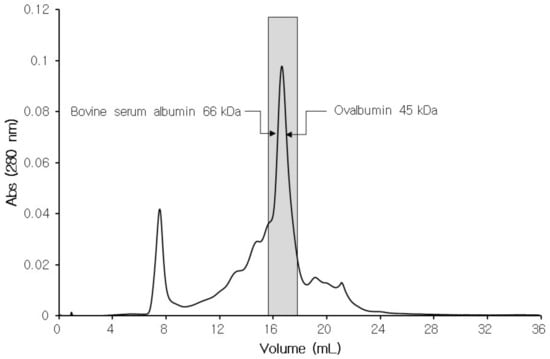
Figure 4.
Fractions with CPI activity obtained from the affinity chromatography were pooled and subjected to gel filtration chromatography (Superose 6, FPLC). The peak in the bar area indicates fractions showing strong CPI activity, with molecular weights estimated between 45 and 66 kDa by comparing to results from standard proteins.
Fractions (2–24 and 32 from the affinity chromatography) with strong papain inhibitory activity were further separated by ion exchange FPLC column (mono Q HR 5/5) (Figure 5A,B). The proteins were eluted using linear NaCl gradient (0–0.5 M) at a flow rate of 1 mL min−1. From this column, eight fractions showed distinct papain inhibitory activity and out of these, the six fractions, including fraction numbers 20 and 27, that had highest activity were selected for SDS-PAGE using 12% polyacrylamide gel. SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis of the fractions (fraction numbers 2, 18, 19, 20, 22, 27) showing high CPI activity from ion exchange chromatography resulted in several single-protein bands (86 kDa in fraction number, 60 kDa in fraction numbers 19, 20, 22 and 54 and 100 kDa in fraction numbers 22 and 27) (Figure 6).
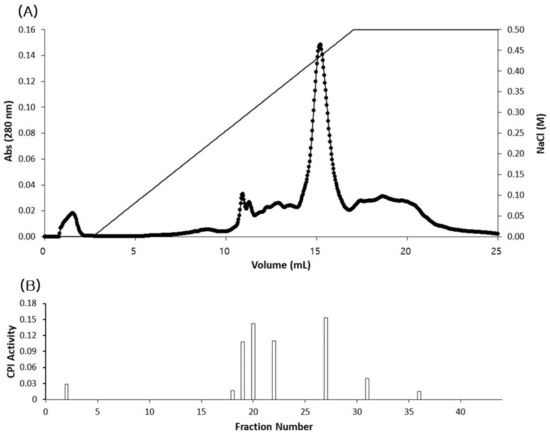
Figure 5.
Fractions with CPI activity obtained from the affinity chromatography were pooled and subjected to ion exchange FPLC column (mono Q) (A). The proteins were eluted with a 0–0.5 M NaCl gradient. CPI activity was analyzed for fractions obtained from the ion exchange column, and the fractions with distinct levels of CPI activity are shown (B).
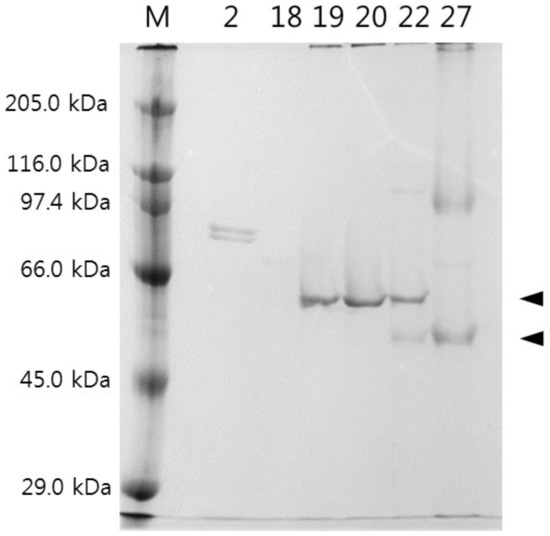
Figure 6.
SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis of fractions (tube numbers 2, 18, 19, 20, 22, 27) that showed CPI activity in the ion exchange chromatography. M: protein marker. Arrows indicate the protein bands (60 and 54 kDa) that were chosen for partial amino acid sequencing.
3.3. Amino Acid Sequencing and Identification of Major Blood CPIs in Nile Tilapia
Two protein bands (60 kDa band from fraction number 20 and 54 kDa band from fraction number 27) that were within the estimated MW range by gel filtration in this study were excised from the SDS-PAGE gel, and amino acid sequences of the digested fragments of these two proteins were determined (Table 1). Amino acid sequences of the digested fragments of the 60 kDa band matched well to the predicted sequences of tilapia fetuin B based on the genomic sequence of this species. Similarly, sequences of digested fragments of the 54 kDa band matched well to the predicted sequences of tilapia kininogen-1. From these, it seems obvious that the two major CPIs in terms of inhibiting activity in tilapia blood are fetuin B and kininogen. The sequences of these two were highly homologous to each other and similar even with another CPI, HRG. This is quite understandable because these three CPIs (kininogen, fetuin, HRG) are closely related proteins that evolved from the protein cystatin by gene duplication and exchange of gene segments [30].

Table 1.
Partial amino acid sequences of the two isolated proteins with CPI activity.
From the full sequences of these CPIs, several strongly conserved regions were noticeable. The most notable was a glutamine-valine-valine-alanine-glycine, QVVAG (Table 1). This sequence had been suggested to be the active site sequence involved in forming hairpin loops that bind proteinase in previous studies [31,32]. The consensus sequence is currently referred to as QxVxG, where x could be one of several amino acids. In some fetuins and HRGs of mammals, this sequence has been extensively altered, resulting in the loss of CPI activity.
Kininogen is known to constitute a major cysteine protease inhibitory activity in the circulation. This protein is also the precursor of bradykinin and involved in many important biological processes, including blood coagulation, vascularization, epithelial cell apoptosis and platelet activation [14]. A presumptive kininogen had been detected from tilapia blood by hybridization with a polyclonal bradykinin antiserum in a previous study [33]. MW of the presumptive kininogen was about 54 kDa, same as the kininogen in the present study.
Fetuins were first identified as major proteins during fetal life, mostly in the blood and brain [34]. These proteins are involved in fatty acid transport, osteogenesis and bone resorption and responding to systemic inflammation. Despite belonging to cystatin superfamily, fetuins did not seem to inhibit cysteine proteinases in various mammals [30]. Contrary to mammalian fetuins, fish fetuin showed strong CPI activity in the present study. Fetuin in rainbow trout was also shown to have CPI activity [35]. The biological significance of fetuin in fish has not been studied much, but the fetuin B gene was downregulated in zebrafish when infected by bacteria [11].
4. Conclusions
Proteinase inhibitors are known to be the third largest functional group of plasma proteins after albumin and immunoglobulins [35]. In support of this, tilapia blood also contained far higher activity of CPI than other tissues investigated in this study. The major CPIs responsible for this activity in tilapia serum were found to be fetuin B and kininogen based on partial amino acid sequences and MW of purified proteins. This study also confirms that fish fetuins possess papain inhibitory activity, unlike mammalian fetuins. Further studies are required to clarify the physiological roles of these proteins in fish blood.
Author Contributions
S.H.M.: Data acquisition, statistical analysis, writing; J.Y.K.: conceptualization, writing, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Sun Moon University Research Grant of 2019.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the SM Review Board for Animal Welfare and Ethical issues (protocol code: SM-2021-03-01, approval date: 1 March 2021).
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank S.H. Choi and H.C. Kwon for their help in analyzing CPI activity and protein purification.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- Bah, C.S.F.; Bekhit, A.E.A.; Carne, A.; McConnell, M.A. Slaughterhouse blood: An emerging source of bioactive compounds. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.K.; Lin, H.; Kim, S.M. Effect of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) plasma protein on the gelation of Alaska pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) surimi. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, C227–C234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, M.R.; Park, J.W. Effect of salmon plasma protein on Pacific whiting surimi gelation under various ohmic heating conditions. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, M.R.; Park, J.W. Salmon blood plasma: Effective inhibitor of protease-laden Pacific whiting surimi and salmon mince. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawdkuen, S.; Lanier, T.C.; Visessanguan, W.; Benjakul, S. Cysteine proteinase inhibitor from chicken plasma: Fractionation, characterization and autolysis inhibition of fish myofibrillar proteins. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.M.; Dziegielewska, K.M. Friends and relations of the cystatin superfamily-new members and their evolution. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.H.; Kwon, H.C.; Kwon, J.Y. Thermal stability of cysteine proteinase inhibitor of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) egg and serum. Dev. Reprod. 2006, 10, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Nopianti, R.; Baehaki, A.; Ridhowati, S.; Suhartono, M.T. Protease Inhibitory activity and protein analysis of catfish (Pangasius hypothalamus) and swamp eel (Monopterus albus) blood plasma. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2019, 42, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Taglieri, N.; Koenig, W.; Kaski, J.C. Cystatin C and cardiovascular risk. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1932–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mashiko, H.; Takahashi, H. Bullfrog plasma cysteine proteinase inhibitor (CPI). Immunophamacology 1996, 32, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Lu, C. Transcriptome profiling of zebrafish infected with Streptococcus suis. Microb. Pathog. 2010, 48, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, M.A.; Arnold, G.J.; Nynca, J.; Frohlich, T.; Otte, K.; Ciereszko, A. Characterization of carp seminal plasma proteome in relation to blood plasma. J. Proteomics 2014, 98, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakharuthai, C.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Schrama, D.; Kumkhong, S.; Boonanuntanasarn, S. Effects of different dietary vegetable lipid sources on health status in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Haematological indices, immune response parameters and plasma proteome. Animals 2020, 10, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubin, G. Proteinaceous cysteine protease inhibitors. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghys, L.; Paepe, D.; Smets, P.; Lefebvre, H.; Delanghe, J.; Daminet, S. Cystatin C: A new renal marker and its potential use in small animal medicine. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 1152–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; An, H.; Seymour, T.A.; Bradford, C.S.; Morrissey, M.T.; Bailey, G.S.; Helmrich, A.; Barnes, D.W. Molecular cloning, sequence analysis and expression distribution of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cystatin C. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B 1998, 121, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.K.; Lin, H.; Kim, S.M. Purification and characterization of a cysteine protease inhibitor from chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) plasma. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, C.; Fu, Q.; Su, B.; Chen, J. Identification and expression analysis of fetuin B (FETUB) in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) mucosal barriers following bacterial challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 68, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synnes, M. Purification and characterization of two cysteine proteinase inhibitors from the skin of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B 1998, 121, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.; Konagaya, S. A novel cysteine protease inhibitor of the egg of chum salmon, containing a cysteine-rich thyroglobulin-motif. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 1282–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nurhayati, T.; Rusyadi, S.; Suwandi, R.; Nugraha, R. Purification and characterization of a cathepsin inhibitor from catfish (Pangasius sp.) of Indonesian water. Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 20, 941–946. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; An, H.; Seymour, T.A.; Barnes, D.W. Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cystatin C: Expression in Escherichia coli and properties of the recombinant protease inhibitor. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B 2000, 123, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, A.J. A new assay for cathepsin B1 and other thiol proteinases. Anal. Biochem. 1972, 47, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, A.J.; Kirschke, H. Cathepsin B, cathepsin H, and cathepsin L. Meth. Enzymol. 1981, 80, 535–561. [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakansson, K.; Huh, C.; Grubb, A.; Karlsson, S.; Abrahamson, M. Mouse and rat cystatin C: Escherichia coli Production, characterization and tissue distribution. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1996, 114B, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tan, X.; Li, S.; Jin, Y.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Takala, T.M.; Saris, P.E.J. Cloning, expression, characterization, and tissue distribution of cystatin C from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 5144–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.-P.; Hu, Y.-H.; Sun, L. Scophthalmus maximus Cystatin B enhances head kidney macrophage-mediated bacterial killing. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentandreu, M.A.; Coulis, G.; Ouali, A. Role of muscle endopeptidases and their inhibitors in meat tenderness. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 400–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzanowski, A.; Barker, W.C.; Hunt, L.T.; Seibel-Ross, E. Cystatin domains in alpha-2-HS glycoprotein and fetuin. FEBS Lett. 1988, 227, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jerala, R.; Trstenjak-Prebanda, M.; Kroon-Zitko, L.; Lenarcic, B.; Turk, V. Mutations in the QVVAG region of the cysteine proteinase inhibitor stefin B. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1990, 371, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.K.S.; Takei, Y. Lack of plasma kallikrein-kinin system cascade in teleosts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81057. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, W.M.; Saunders, N.R.; Mollgard, K.; Diegielewska, K.M. Fetuin–an old friend revisited. BioEssays 1992, 14, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nynca, J.; Slowinska, M.; Dietrich, M.A.; Bilinska, B.; Kotula-Balak, M.; Ciereszko, A. Isolation and identification if fetuin-B-like protein from rainbow trout seminal plasma and its localization in the reproductive system. Comp. Biochem. Physio Part B 2011, 158, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibbetts, K.; Hines, B.; Williams, D. An overview of proteinase inhibitors. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1999, 13, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).