The Impact of Multiple Pond Conditions on the Performance of Dike-Pond Extraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
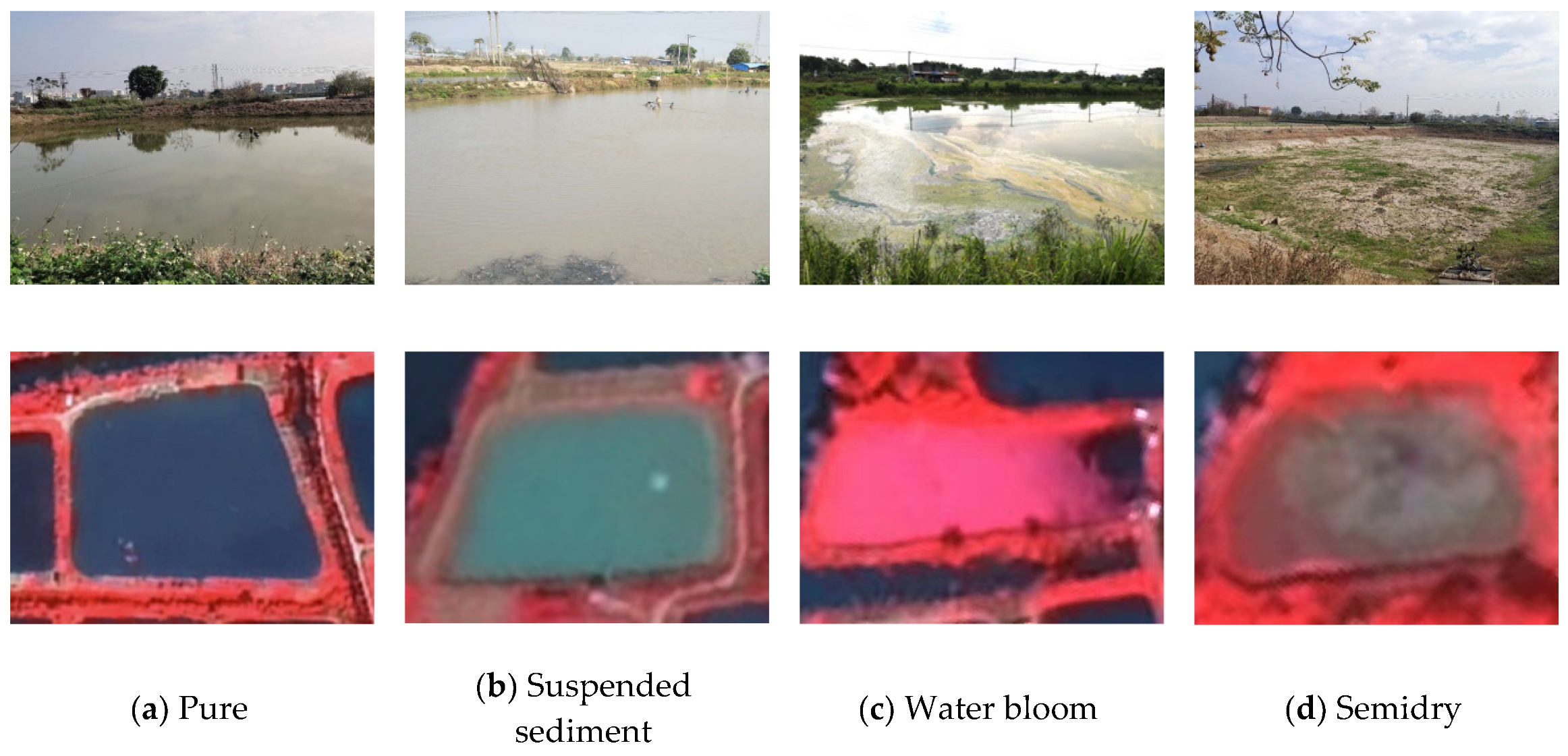
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
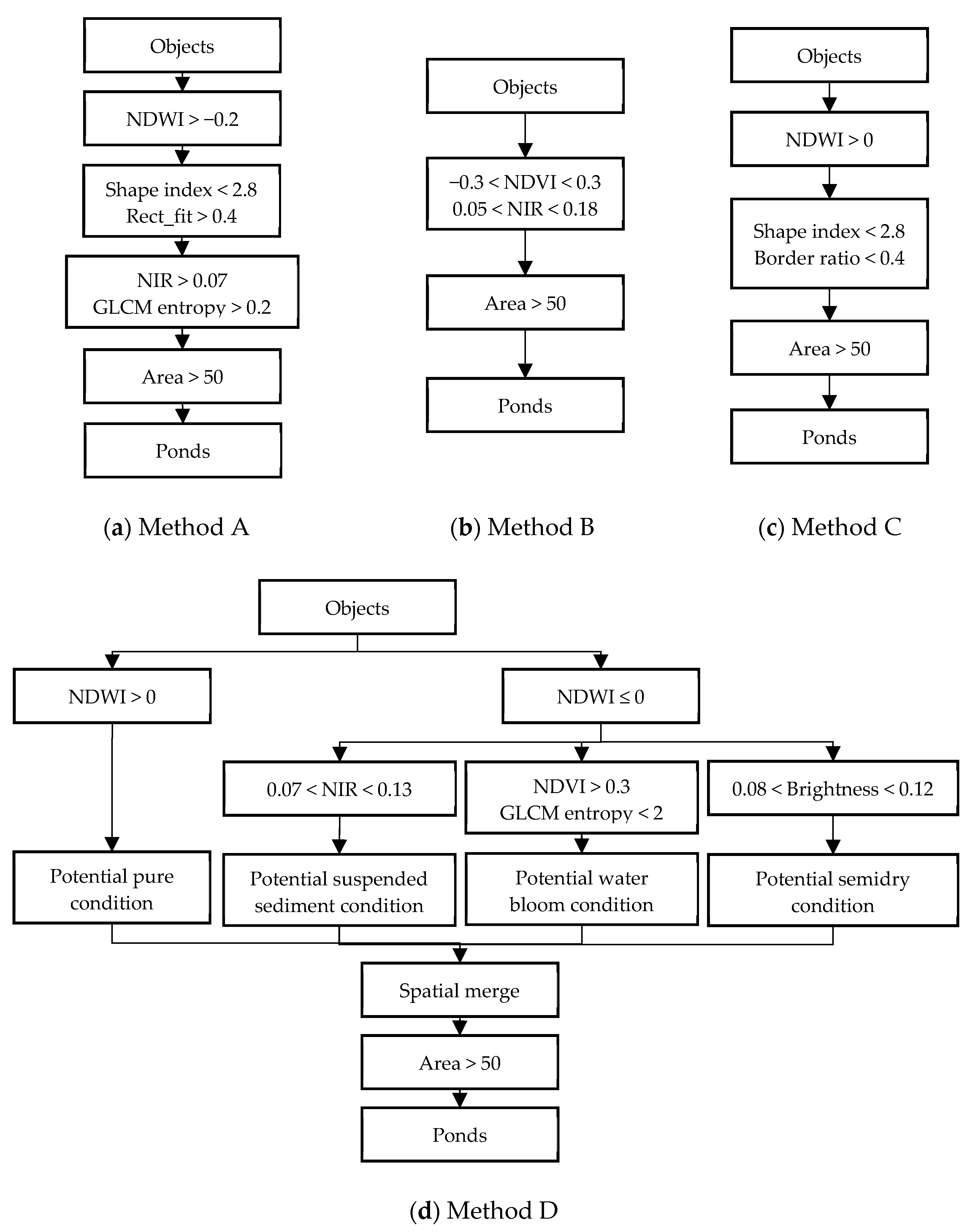
2.2.1. Rule-Based Methods
2.2.2. Image Segmentation
3. Results
3.1. Feature Analysis
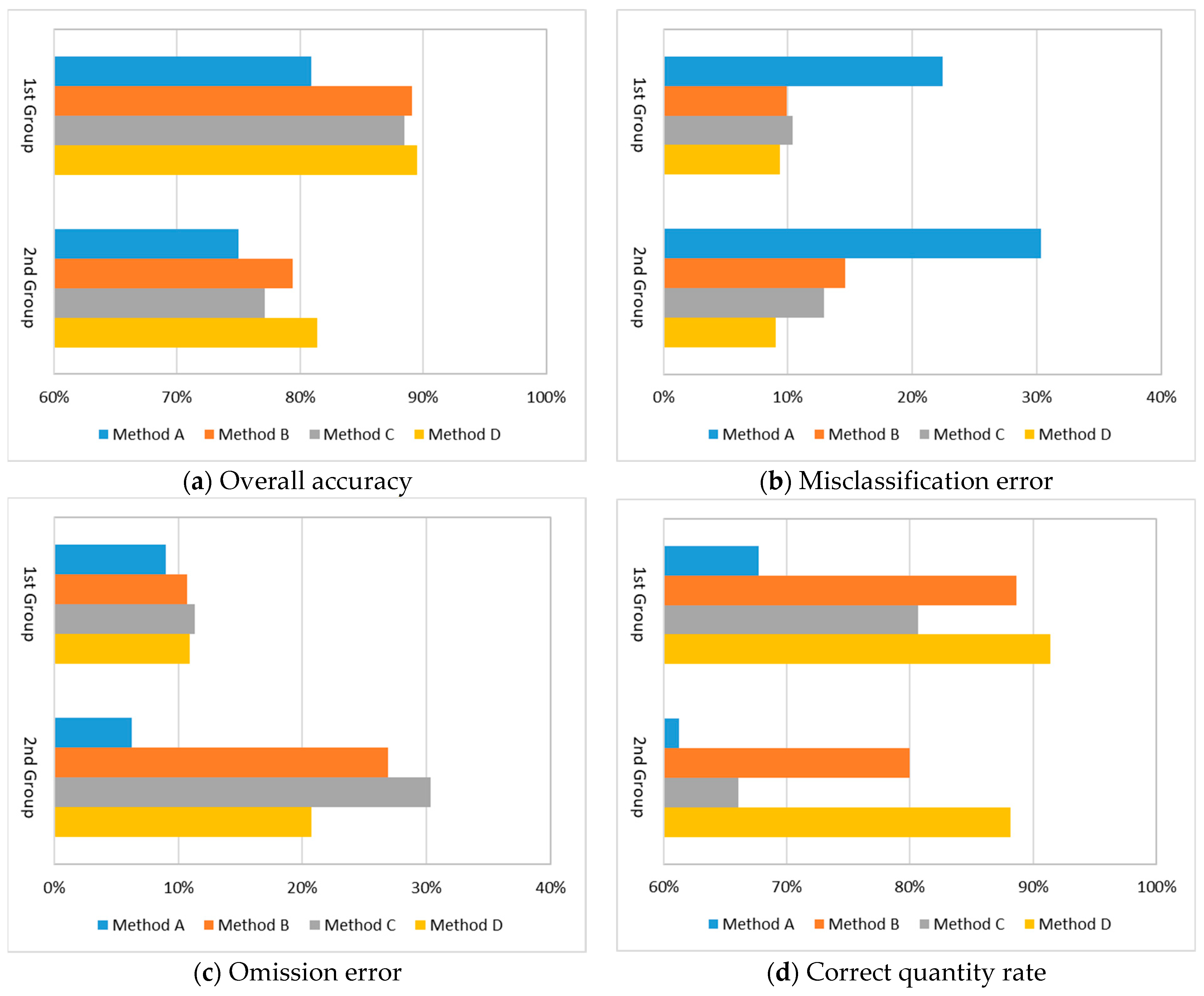
3.2. Impact Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, P. Aquaculture environment interactions: Past, present and likely future trends. Aquaculture 2015, 447, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamani, K.; Suresh, Y. Evaluation of coastal aquaculture ponds using remote sensing and GIS. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2019, 48, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Xi, Y.; Xiao, X.; Doughty, R.B.; Liu, M.; Jia, M.; et al. Rapid expansion of coastal aquaculture ponds in China from Landsat observations during 1984–2016. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2019, 82, 101902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.L. Aquaculture, Ecological Engineering: Lessons from China. Ambio 1993, 22, 491–494. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Q. A historical perspective of river basin management in the Pearl River Delta of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 1048–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.H.; Min, Q.W. Integrated farming systems an important approach toward sustainable agriculture in China. Ambio 1999, 28, 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S. The research into the world heritage value and tourism development of Dike-Pond agriculture in the pearl river delta. In Tourism and Hospitality Development Between China and EU; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 111–127. [Google Scholar]
- Gongfu, Z. The types, structure and results of the dike-pond system in South China. GeoJournal 1990, 21, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.P. Environmental impact on the development of agricultural technology in China: The case of the dike-pond ("jitang") system of integrated agriculture-aquaculture in the Zhujiang Delta of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1996, 60, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, M. The dike-pond concept: Sustainable agriculture and nutrient recycling in China. Ambio 1996, 25, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Wang, Y.L.; Jing, J.; Yue, J.; Li, W.F. Ecological development of coastal areas in China. Coast. Manag. 2005, 33, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astudillo, M.F.; Thalwitz, G.; Vollrath, F. Modern analysis of an ancient integrated farming arrangement: Life cycle assessment of a mulberry dyke and pond system. Int. J. Life Cycle Ass. 2015, 20, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, K.; Tang, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, H. Analyzing trends of dike-ponds between 1978 and 2016 using multi-source remote sensing images in shunde district of south China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, M. Seeing from above: Observation of contemporary dike-pond landscape. Landsc. Archit. Front. 2019, 7, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V. Fisheries applications of remote sensing: An overview. Fish. Res. 2013, 148, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottinger, M.; Clauss, K.; Kuenzer, C. Opportunities and challenges for the estimation of aquaculture production based on earth observation data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kourti, N.; Shepherd, I.; Greidanus, H.; Alvarez, M.; Aresu, E.; Bauna, T.; Chesworth, J.; Lemoine, G.; Schwartz, G. Integrating remote sensing in fisheries control. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2005, 12, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, A.; Zainuddin, M. Application of remotely sensed satellite data to identify Skipjack Tuna distributions and abundance in the coastal waters of Bone Gulf. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 241, 12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, S.; Mugo, R.; Radiarta, I.N.; Asaga, S.; Takahashi, F.; Hirawake, T.; Ishikawa, Y.; Awaji, T.; In, T.; Shima, S. Some operational uses of satellite remote sensing and marine GIS for sustainable fisheries and aquaculture. Ices J. Mar. Sci. 2011, 68, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, T.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; Chen, B.; Yan, M. Spatio-temporal patterns and sustainable development of coastal aquaculture in Hainan Island, China: 30 Years of evidence from remote sensing. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 214, 105897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Spatial-temporal Change of Sanshui district’s Dike-pond from 1979–2009. Phys. Procedia 2012, 25, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y. The dynamic of dike-pond system in the pearl river delta during 1964–2012. In Global Changes and Natural Disaster Management: Geo-Information Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Li, J. Tracking dike-pond landscape dynamics in a core region of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area based on topographic maps and remote sensing data during 1949–2020. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, A.W.C. New developments in integrated dike-pond agriculture-aquaculture in the Zhujiang Delta, China: Ecological implications. Ambio 1999, 28, 529–533. [Google Scholar]
- Virdis, S.G.P. An object-based image analysis approach for aquaculture ponds precise mapping and monitoring: A case study of Tam Giang-Cau Hai Lagoon, Vietnam. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Tian, B.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Sengupta, D.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y. Tracking changes in aquaculture ponds on the China coast using 30 years of Landsat images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2021, 102, 102383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhou, Z.; She, X.; Zhou, L.; Ren, T.; Liu, S.; Lu, J. Identifying dike-pond system using an improved cascade R-CNN model and High-Resolution satellite images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhou, C.; Su, F. Automatic mapping aquaculture in coastal zone from TM imagery with OBIA approach. In Proceedings of the 2010 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Loberternos, R.A.; Porpetcho, W.P.; Graciosa, J.C.A.; Violanda, R.R.; Diola, A.G.; Dy, D.T.; Otadoy, R.E.S. An object-based workflow developed to extract aquaculture ponds from airborne lidar data: A test case in central visayas, philippines. In International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences; ISPRS Congress: Prague, Czech Republic, 2016; Volume 41, pp. 1147–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Ottinger, M.; Clauss, K.; Kuenzer, C. Large-Scale assessment of coastal aquaculture ponds with sentinel-1 time series data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y. Estimation of Ponds Area Based on Object-Oriented Classification Method with Remote Sensing Data: A Case of Taishan; Nanjing University: Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, M.; Gong, J.; Li, T. Analysis on Landscape Pattern Based on Extraction of Dike-Pond Ecosystem Using Object-Oriented Classification Method in Shunde District. Ecol. Sci. 2018, 37, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Liu, L.; Peng, L. Remote sensing classification for dike-pond system based on Worldview-2 data. Wetl. Sci. 2018, 16, 587–596. [Google Scholar]
- Al Sayah, M.J.; Nedjai, R.; Abdallah, C.; Khouri, M. On the use of remote sensing to map the proliferation of aquaculture ponds and to investigate their effect on local climate, perspectives from the Claise watershed, France. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, A.M. The derivation of global estimates from a confusion matrix. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1988, 9, 1395–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcfeeters, S.K. The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W. Monitoring Vegetation Systems in the Great Plains with Erts. In Proceedings of the Third ERTS Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 December 1973; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1973; pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Duan, Q. Estimating the aquatic-plant area on a pond surface using a hue-saturation-component combination and an improved Otsu method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 188, 106372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Stumpf, R.P.; Meredith, A. Evaluation of RapidEye data for mapping algal blooms in inland waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 2811–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edna, G.; Fernandez-Figueroa, A.E.W.S. Commercially available unoccupied aerial systems for monitoring harmful algal blooms: A comparative study. Limnol. Oceanogr. Meth. 2022, 20, 146–158. [Google Scholar]
- Volpe, V.; Silvestri, S.; Marani, M. Remote sensing retrieval of suspended sediment concentration in shallow waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, R.R.; Harmel, T.; Martinez, J.; Filizola Junior, N.P. Spatiotemporal dynamics of suspended sediments in the negro river, amazon basin, from in situ and sentinel-2 remote sensing data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wei, Y.; Xu, J.; Yuan, Z. Remote sensing estimation of Chlorophyll a and suspended sediment concentration in turbid water based on spectral separation. Optik 2013, 124, 6815–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, M.; Allen, D.; Neeson, T.; Hong, Y. Monitoring drought through the lens of landsat: Drying of rivers during the california droughts. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Han, X.; Zhang, L. Spatial-temporal wetland landcover changes of Poyang lake derived from landsat and HJ-1A/B data in the dry season from 1973–2019. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.S.; King, O.; Miles, E.S.; Quincey, D.J. Optimising NDWI supraglacial pond classification on Himalayan debris-covered glaciers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondejar, J.P.; Tongco, A.F. Near infrared band of Landsat 8 as water index: A case study around Cordova and Lapu-Lapu City, Cebu, Philippines. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2019, 29, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, G.; Baek, I.; Stocker, M.D.; Smith, J.E.; Van Tassell, A.L.; Qin, J.; Chan, D.E.; Pachepsky, Y.; Kim, M.S. Hyperspectral imaging from a multipurpose floating platform to estimate chlorophyll-a concentrations in irrigation pond water. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briem, G.J.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Multiple classifiers applied to multisource remote sensing data. IEEE T. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2291–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talukdar, S.; Singha, P.; Mahato, S.; Shahfahad; Pal, S.; Liou, Y.; Rahman, A. Land-Use Land-Cover classification by machine learning classifiers for satellite observations—A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quantifying suspended sediment dynamics in mega deltas using remote sensing data: A case study of the Mekong floodplains. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 68, 105–115.
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, D.; Tan, W.; Huang, J. Extracting aquaculture ponds from natural water surfaces around inland lakes on medium resolution multispectral images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2019, 80, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, D.; Tan, W.; Yu, G.; You, J.; Lv, B.; Wu, Z. RCSANet: A full convolutional network for extracting inland aquaculture ponds from High-Spatial-Resolution images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinhao, Z.; Xiaojun, H.; Ningchuan, X.; Zeming, L.; Manqi, L. Comparison and application of spatial pattern measurement methods for water surface of dike-pond. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Cheng, Z.; Qiu, J.; Park, E.; Ran, L.; Xie, X.; Yang, X. Spatiotemporal Changes in Mulberry-Dyke-Fish Ponds in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area over the Past 40 Years. Water 2021, 13, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhw, A.; Kcc, A.; Ay, B.; Ckcw, A. The Dyke-pond systems in south china: Past, present and future—ScienceDirect. In Wetlands Ecosystems in Asia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, C.; Luo, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y. The dike-pond system in the Pearl River Delta: Degradation following recent land use alterations and measures for their ecological restoration. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2003, 23, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, F.; Liang, S.; Hu, Y. The Impact of Multiple Pond Conditions on the Performance of Dike-Pond Extraction. Fishes 2022, 7, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7040144
Zhou J, Zhou W, Zhou Q, Zhu Y, Xie F, Liang S, Hu Y. The Impact of Multiple Pond Conditions on the Performance of Dike-Pond Extraction. Fishes. 2022; 7(4):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7040144
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jinhao, Wu Zhou, Qiqi Zhou, Yuanhui Zhu, Fei Xie, Shen Liang, and Yueming Hu. 2022. "The Impact of Multiple Pond Conditions on the Performance of Dike-Pond Extraction" Fishes 7, no. 4: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7040144
APA StyleZhou, J., Zhou, W., Zhou, Q., Zhu, Y., Xie, F., Liang, S., & Hu, Y. (2022). The Impact of Multiple Pond Conditions on the Performance of Dike-Pond Extraction. Fishes, 7(4), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7040144





