Abstract
Otoliths, calcified structures in the inner ears, are used to estimate fish age, and their shape is an efficient fish stock identification tool. Otoliths are thus very important for the management and assessment of commercial stocks. However, most studies have used left or right otoliths, chosen arbitrarily without evaluation of the difference between these otoliths. In this study, the asteriscii otoliths from 263 common carp (Cyprinus carpio; Linnaeus, 1758) were sampled in three Iraqi rivers to test the potential asymmetry and the geographical effect on otolith growth from three measurements (length, width and weight), and on shape from two shape indices (ellipticity and form-factor). Among all asteriscii otolith features, there was significant fluctuating asymmetry between fish length and every otolith descriptor. At one fish length, the size and/or the shape of otoliths could be different between two individuals and/or between left and right asteriscii otoliths for the same individual. Moreover, the relationship between fish length and otolith shape/growth was significantly dependent on the studied geographical area and, more especially, the environmental effects as the water temperature and pH. Finally, the relationships between fish length and otolith shape indices showed that the otolith evolves into the elliptical shape during the life of the fish. To use the otolith shape, it is essential to take into account the developmental stage of individuals to integrate the ontogenetic effect. Our results highlight the importance of verifying potential otolith asymmetry, especially for the asteriscii otoliths (lagenar otoliths) before their use in fisheries research.
Keywords:
asteriscus; side effect; growth; otolith shape; geographical effect; temperature effect; pH 1. Introduction
Otoliths, calcified structures in the inner ears [1,2], are used to identify species in taxonomic or phylogenic studies and to collect age data for management and assessment of stocks. The otoliths grow throughout the fish life and are metabolically inert [3], and their shape (i.e., their outline resulting from genetic, environmental and ontogenetic effects) is used as an efficient tool to recognize the species at the interspecific level and to identify the fish stocks at the intraspecific level (to see the Stock Identification Methods Working Group of which identifies all studies each year; SIMWG). Each head side (i.e., left and right inner ear), however, has three pairs of otoliths (sagittae, asteriscii and lapilli) [4]. Among the three different otoliths, the sagittal otolith is usually used due to its larger size and easier removal [5]. The asteriscii (lagenar otoliths) are the smallest otolith in marine species and so rarely used. Conversely, asteriscus otoliths are the most frequently used otoliths in Cypriniforms species such as common carp [6]. For these species, asteriscii are the largest of the three otolith pairs [6]. Several growth studies focused on the common carp have used asteriscii otoliths [6,7,8,9]; however, no study has focused on the astericus shape for this species.
Since 1990, when the first report on the asymmetry in fishes was published on fishes of Iraq [10], few scientific publications have appeared on the phenomenon of asymmetry in freshwater fish species. In total, there are four publications concerning the Iraqi waters reporting asymmetry in four fish species (Heteropneustes fossilis, Bloch, 1794; Mystus pelusius, Solander, 1794; Planiliza abu, Heckel, 1843; and Parasilurus triostegus, Heckel, 1843) related to different fish characters [10,11,12,13,14]. There are similarly few reports for the marine fish species of Iraq: the first publication on the asymmetry of this group was in 2020, with six reports studying otolith asymmetry in six marine species. The present study focuses on potential asymmetry and the geographical effects on otoliths growth and shape in common carp Cyprinus carpio, a freshwater species of Iraq. A recent study using the otolith shape to identify the stock structure of the bogue (Boops boops; Linnaeus, 1758) in the Mediterranean Sea showed that the significant asymmetry could modify the boundaries of stocks according to the use of the left or right otolith [15]. Moreover, this study showed that this significant asymmetry could be due to environmental differences. Consequently, the aims of this study are to compare the fluctuations in asymmetry of the asteriscus in the carp, Cyprinus carpio, and to identify if this asymmetry could be a possible response to the environmental variables in several rivers in Iraq.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
A total of 263 individual carp were collected in May–July 2021 from three different locations on the Euphrates (Nasiriya City; 31°2′28″ N, 46°14′45″ E; n = 90), Tigris (Amarah City; 31°51′25″ N, 47°8′15″ E; n = 89) and Shatt al-Arab (Basrah City; 30°33′41″ N, 47°47′41″ E; n = 84) rivers (Figure 1; Supplementary Table S1). All individuals were from commercial catches and macroscopic observation of the gonads did not identify sex with a good accuracy.
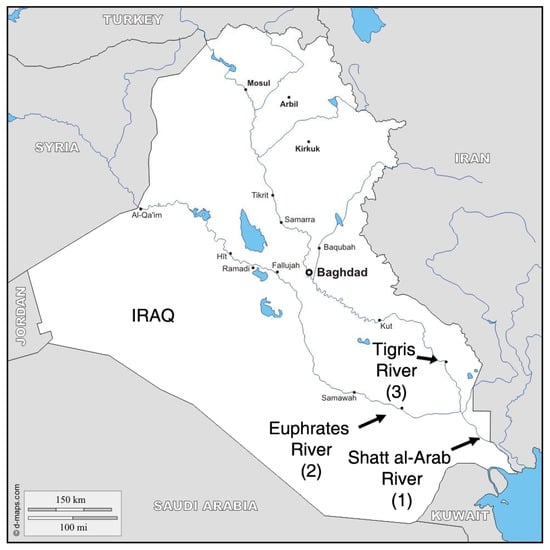
Figure 1.
Sampling locations where common carp (Cyprinus carpio) were collected: the Shatt al-Arab (1), Euphrates (2) and Tigris (3) rivers.
2.2. Study Areas
The Euphrates is the longest river in Western Asia (around 3000 km; [16,17,18,19]). At Nasiriya City, where the common carp specimens were collected for this study, the water of the Euphrates river is seasonally variable in temperature, salinity and hydrogen ion concentration. Water temperature ranged from 11 °C in January to 34 °C in July and pH values fluctuated from 7.12 in August to 8.43 in December [16].
The Tigris is 1750 km long, rising in the Taurus Mountains of eastern Turkey, about 25 km southeast of Elazig city and about 30 km from the headwaters of the Euphrates [20]. The water temperature of the Tigris river in Mysan Province varied between 15 °C and 25 °C and pH values from 7.05 to 7.8 [21].
The Shatt al-Arab river, around 200 km long, is formed at the confluence of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in al-Qurnah City in southern Iraq [22]. Currently, the river depends mainly on freshwater flow from the Tigris river [23,24]. The water flow in the Shatt Al-Arab river is affected by the tidal phenomenon of the Arabian Gulf, which has a semidiurnal pattern [25,26]. The recorded water temperature of the Shatt al-Arab river at Basrah City varied between 19 and 32 °C and the pH values between 7.86 and 8.07 [27,28].
2.3. Morphometrical Analysis
The commercial catches were sampled directly at the laboratory to limit the storage bias on the fish and otolith data. The first step was to measure the total length (TL ± 0.1 cm) of fish, then extract and clean both asteriscii otoliths. To describe the otolith shape, only univariate data as size parameters and shape factors were used. Asteriscii Otolith weight (OWEIGHT) was measured using a digital balance to the nearest 0.0001 g (Sartorius Precision Balance Entris; Model BCE6231-1CFR, Sartorius Lab Instruments GmbH & Co. KG Otto-Brenner-Strasse 20 37079 Goettingen, Germany). Otolith images were captured using a camera (Efix 07-45x, 13MP, Alibaba.com, China (accessed on 28 March 2022)) with a stereomicroscope. Asteriscii Otolith length (OLENGTH, mm) and width (OWIDTH, mm) were taken using image processing systems (detailed descriptions in Figure 2). Size parameters (otolith length, width and weight) are measurements linked directly to otolith size, and are linked to otolith growth. Conversely, shape indices are dimensionless (and thus independent from otolith size) measures of otolith morphology similarity (i.e., otolith shape), compared with ideal geometric shapes calculated using size features. Two shape indices were used: ellipticity (to quantify similarity to an ellipse) and aspect-ratio (to compare to a rectangle) [29].
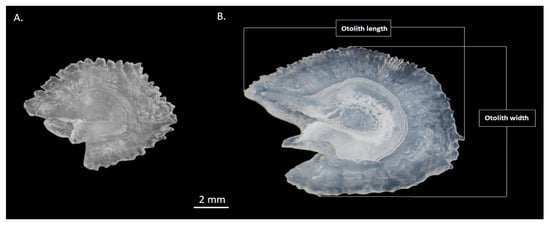
Figure 2.
Asteriscii otoliths of Cyprinus carpio illustrating different features of the otolith measurements for two life stages ((A): small individual, TL = 155 mm; (B): large individual, TL = 380 mm).
The relationship between fish total length and each asteriscii otolith feature (otolith length, width, weight, ellipticity and aspect-ratio) according to the geographical position (River) and head side (Side) was modelled according to Equation (3):
TL ~ Otolith feature + Otolith feature:River + Otolith feature:Side + Otolith feature:River:Side
One generalized linear model was performed by each otolith feature (otolith length, width, weight, ellipticity and aspect-ratio). The geographical (Asteriscii Otolith feature:River) and side (Asteriscii Otolith feature:Side) effects and their interaction (Otolith feature:River:Side) were tested by the relationships between fish length and otolith feature. A second model was applied to evaluate the environmental effects (water temperature: T °C and acidification: pH) on the relationship between fish size and all otolith features according to the head side (Equation (4)). The environmental data were extracted from the literature for each location [16,21,27,28]. To test the environmental parameters, we used three values by factor with the annual mean value, the minimum and the maximum values registered by area.
TL ~ Otolith feature:T °C:Side + Otolith feature:pH:Side
The normality and the homoscedasticity of the residuals were assessed by visual inspection of diagnostic plots. The significance of explanatory variables was tested by likelihood ratio tests between nested models, while respecting the marginality of the effects (type 2 tests [29]) that are supposed to follow an χ2 distribution under the null hypothesis, while correcting for multiple comparisons using a Bonferroni procedure. Statistical analyses were performed in the R statistical environment [30], using car [31], sp. [32], HH [33], vegan [34] and ggplot2 [35] packages.
3. Results
There were some differences between left and right asteriscii otoliths from the same individuals with the right otolith being bigger (i.e., otolith length and width) than the left otolith (Figure 3). Analysis of the relationships between fish length and each otolith feature (three size parameters and two shape indices) showed that there was a significant relationship between only two otolith size descriptors (length and width) with the total length of fish (column “TL”, Table 1). For three other otoliths features, the relationship with the total length was not significant (Figure 4).
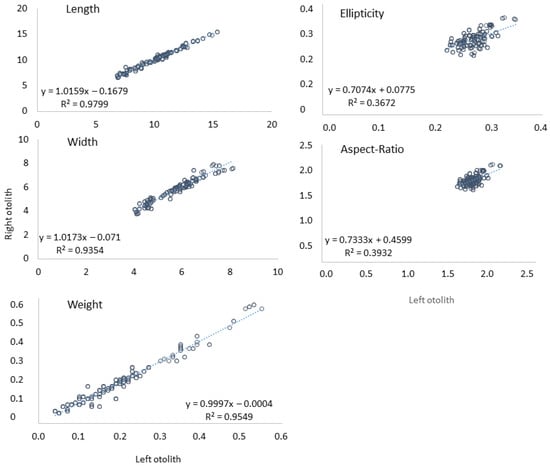
Figure 3.
Difference between left and right otoliths of Cyprinus carpio for each otolith measurement.

Table 1.
p-values of generalized linear models for the relationship between fish length and each otolith variable for Cyprinus carpio collected from three localities in Iraqi rivers with by geographical and Side effects (observed from the interaction between Otolith feature and river or side in the GLM: Otolith feature: River/Side). The environmental effects on the relationship between fish length and each otolith variable (Otolith feature: T °C/Side and Otolith feature: pH/Side) were tested with three different values (mean, minimal and maximum). Grey cases show significant effects (p < 0.05).
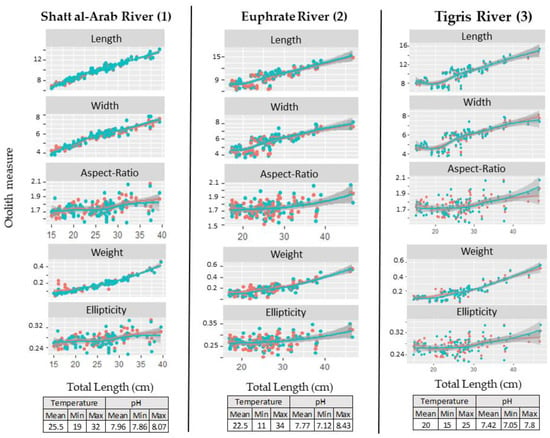
Figure 4.
Relationships between fish length and asteriscii otolith morphological features (red points and line = left otolith, and green points and line = right otolith) according to the head side of Cyprinus carpio for each Iraqi River (for each river, the environmental data are presented).
Among the five asteriscii otolith features (size parameters or shape indices), there is always a significant effect of the head side on the relationship between fish length and each otolith descriptor (observed from the interaction between otolith feature and area or side in the GLM: Otolith feature: River/Side; Table 1). The relationship between fish length and otolith shape (i.e., two shape indices) was significantly dependent on the studied geographical area (i.e., river). The data collected in Tigris river presented the highest level of the fluctuating asymmetry in asteriscii otoliths of common carp collected from three localities in Iraqi Rivers. The relationship between fish and otolith growth was not directly linked to the location of sampling (Table 1). Finally, this generalized linear model showed that the relationship between fish length and otolith shape described by ellipticity and aspect-ratio is significantly different between the right and left otoliths, and this result was also linked to the location of sampling. Moreover, two mainly environmental factors were tested on the side effect applied to the relationship between fish length and each otolith descriptor. The results showed the interaction between both water temperature and pH and head side on the relationship between fish length and each otolith descriptor, especially with the minimum and mean values of these factors (Table 1). The Tigris river, which presented the lowest value of water pH and temperature, was the location with the highest level of the fluctuating asymmetry in asteriscii otoliths.
The significant correlation between fish total length and otolith growth showed that the following factors of otolith size also increased with an increase in total length: length, width and weight (Figure 4). The relationship between body length and otolith shape indices showed that the otolith shape evolves into a rectangular or elliptical shape during the life of the fish. The difference between the shape of the left and right otoliths in the same fish increased mainly in large individuals over 40 cm. This asymmetry is explained mainly by the width of the asteriscii otolith (Figure 4).
4. Discussion
The morphogenesis of the otolith is the result of a combination of exogenous (environment), endogenous (genetics) and developmental (ontogeny) factors [36,37]. Thus, the variability of these different factors and the biological scale at which they are expressed will determine the variation in the growth and shape of the otolith. Environmental factors that influence the morphogenesis of the otolith are separated into two groups: firstly, there are abiotic factors with temperature [38,39], pH [40], the depth of the water in which the fish live [41], the nature of the substrate [42] and salinity [43]. The growth and the morphogenesis of otoliths during the early life stages of fish are due to ontogenetic effects, but they also temperature-dependent [38]. In the same way, water acidification can also alter otolith shape [40]. For several species, individuals exposed to high pCO2 had a larger otolith area and maximum length compared with controls; the increases were larger than could be explained by an increase in CaCO3 precipitation in the otoliths driven by the modification of the pH regulation in the endolymph [44,45,46,47]. Our study corroborated that the water temperature and pH modified the relationship between fish length and each otolith measure (i.e., otolith length and width) and shape (i.e., ellipticity and aspect-ratio). Secondly, biotic factors such as the quantity [48] and specific composition [49] of the food available to the fish also affect the morphogenesis of the otolith. Genetic variability is also a strong factor influencing this morphogenesis process [50,51,52,53,54,55]. Ontogeny is also a factor generating shape variability, which can be reflected in effects of sex, age [53], body size [48] or the stage of sexual maturity [42,50,53] of the individual. The development of the otolith is spatially heterogeneous. The otoliths are paired structures present in the right and left inner ears, and an asymmetry between the two otoliths, or fluctuating asymmetry (FA), can be measured. This fluctuating asymmetry is related to the developmental trajectory of the otoliths, which is itself guided by developmental regulatory processes, such as the evolutionary canalization [54]. Fluctuating asymmetry may be related to developmental instability and thus provide an indicator measure of stress or micro-environmental variability [55,56,57,58]. In particular, Lemberget and McCormick [56] identify FA as an indicator of fish health as this type of asymmetry can directly affect the balance and hearing performance of the fish. This asymmetry can also be a functional adaptation to the environment. Our study showed the significant interaction between the level of asymmetry and the environmental factors (water temperature and pH). The acidification and the lowest temperature (i.e., lowest value of pH and temperature of water) observed in the Tigris river showed the highest level of asymmetry registered in Iraqi Rivers. As the trends of pH and temperature between the three locations were the same direction, it was not possible to dissociate the acidification and the temperature effects. The asymmetry can be measured in the otolith growth from the morphological descriptors (i.e., the relationship between fish length and otolith descriptors such as weight, length and width) and/or the otolith shape from univariate (i.e., Shape index) or multivariate (i.e., Elliptic Fourier Descriptors) measures. Otolith mass asymmetry is the most commonly used measure to compare the growth between left and right otoliths. Our results showed that there was a significant asymmetry in otolith growth of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) observed from all otolith descriptors (i.e., length, width and weight). This asymmetry corroborates that observed in previous studies on other marine and freshwater species [49,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67]. In contrast, one study focused on Cyprinid fishes from Turkish inland waters observed no difference in the relationship between otolith descriptors and fish length according to the side effect [68]. However, the previous study on common carp (Cyprinus carpio) estimated that this species showed fluctuating asymmetry in otolith weight [69].
Otolith mass asymmetry has been used as an indicator to evaluate condition between several habitats [70], in particular, as a consequence of environmental stress, human activities, genetic disposition and a combination of these factors [71]. Our results showed that there was a significant asymmetry in otolith shape of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) observed from two shape indices (i.e., ellipticity and form factor) with increased asymmetry with size. During the life of the fish, the ontogenetic effect on the shape of the otolith decreased, unlike the environmental effects (temperature, food, etc. [36,39,42]). Consequently, this observed trend showed that asymmetry could be the result of the environmental conditions in each river. The water temperature and pH showed that the fluctuating asymmetry could be linked significantly to these two environmental factors. Our results corroborate those of previous studies on other marine and freshwater species [54,72,73,74,75].
5. Conclusions
This study showed that the observed asymmetry level was significantly linked to the geographical area, with the otolith shape being linked only to the environmental effect (i.e., water temperature and pH). In the climate change context, the temperature and pH are mainly environmental factors, which will be modified. Consequently, in the future, the asymmetry level may change and alter the balance and hearing performance of the fish. Sagittal otoliths, such as asteriscii, may also show significant asymmetry. Moreover, the experimental approach should be used to better understand the factors controlling otolith shape, integrating the ontogenetic effect, as has been undertaken for other species. Finally, this is the first study showing that it is necessary to estimate the level of asymmetry between otolith pairs to limit the potential bias due to a difference between left and right sides when using otoliths, and that the asymmetry could be linked directly to environment factors such as temperature and pH.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fishes7020091/s1, Table S1: Size ranges of Cyprinus carpio collected from three localities in Iraq Rivers by head side (sample size, characteristics of fish length and each otolith variable).
Author Contributions
L.J. and K.M. designed the research; L.J. realized the sampling. K.M. performed the statistical analyses. All authors provided input for the results and discussion and wrote the paper. All authors provided critical comments and were involved in the writing of the manuscript. All authors accepted the final version of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, because the fish were obtained from fisheries and were already dead when the otoliths were extracted.
Data Availability Statement
Data Availability Statements in section “MDPI Research Data Policies” at https://www.mdpi.com/ethics (accessed on 28 March 2022).
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to all people involved in the collection of samples required in this study. We would especially thank Kirsteen MacKenzie for her valuable help in editing this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Popper, A.N.; Lu, Z. Structure-function relationships in fish otolith organs. Fish. Res. 2000, 46, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Iglio, C.; Natale, S.; Albano, M.; Savoca, S.; Famulari, S.; Gervasi, C.; Lanteri, G.; Panarello, G.; Spanò, N.; Capillo, G. Otolith Analyses Highlight Morpho-Functional Differences of Three Species of Mullet (Mugilidae) from Transitional Water. Sustainability 2022, 14, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casselman, J.M. Determination of age and growth. In The Biology of Fish Growth; Weatherley, A.H., Gill, H.S., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 209–242. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, P.J.; Panfili, J.; Morales-Nin, B.; Geffen, A.J. Types of calcified structures. A. Otoliths. In Manual of Fish Sclerochronology; Panfili, J., de Pontual, H., Troadec, H., Wright, P.J., Eds.; Ifremer-IRD Coédition: Brest, France, 2002; pp. 31–57. [Google Scholar]
- Panfili, J.; de Pontual, H.; Troadec, H.; Wright, P.J. Manual of Fish Sclerochronology; Coédition Ifremer-IRD: Brest, France, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Phelps, Q.E.; Edwards, K.R.; Willis, D.W. Precision of five structures for estimating age of common carp. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2007, 27, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilizzi, L.; Walker, K.F. Age and growth of common carp, Cyprinus carpio, in the River Murray, Australia: Validation, consistency of age interpretation and growth models. Env. Biol. Fish. 1999, 54, 77–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Green, C.; Sivakumaran, K.P.; Stoessel, D.; Giles, A. Validating otolith annuli for annual age determination of commoncarp. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2004, 133, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, H.; Weyl, O.L.; Booth, A.J.; Ellender, B.R. Life history and population dynamics of invasive common carp, Cyprinus carpio, within a large turbid African impoundment. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hassan, L.A.J.; Al-Dubaikel, A.Y.; Wahab, N.K.; Al-Daham, N.K. Asymmetry analysis in the catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis collected from Shatt Al-Arab River, Basrah, Iraq. Riv. Idrobiol. 1990, 29, 775–780. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hassan, L.A.J.; Hassan, S.S. Asymmetry study in Mystus pelusius collected from Shatt al-Arab River, Basrah, Iraq. Pak. J. Zool. 1994, 26, 276–278. [Google Scholar]
- Jawad, L.A. Asymmetry analysis in the mullet, Liza abu collected from Shatt al-Arab River, Basrah, Iraq. Bol. Mu. Reg. Sci. Nat. Torino 2004, 21, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Jawad, L.A.; Al-Janabi, M.I.; Rutkayová, J. Directional fluctuating asymmetry in certain morphological characters as a pollution indicator: Tigris catfish collected from the Euphrates, Tigris, and Shatt al-Arab Rivers in Iraq. Fish. Aquat. Life 2020, 28, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, L.A.; Abed, J.M. Morphological asymmetry in the greater lizardfish Saurida tumbil (Bloch, 1795) collected from the marine waters of Iraq. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 159, 111523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahé, K.; Ider, D.; Massaro, A.; Hamed, O.; Jurado-Ruzafa, A.; Goncalves, P.; Anastasopoulou, A.; Jadaud, A.; Mytilineou, C.; Elleboode, R.; et al. Directional bilateral asymmetry in otolith morphology may affect fish stock discrimination based on otolith shape analysis. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 76, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.D. Modelling Approaches to Understand Salinity Variations in a Highly Dynamic Tidal River, the Case of the Shatt Al-Arab River; dissertation of Delft University of Technology and of the Academic Board of the UNESCO-IHE; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- IME. Iraqi Ministries of Environment, Water Resources and Municipalities and Public Works, Volume I: Overview of Present Conditions and Current Use of the Water in the Marshlands Area/Book 1: Water Resources, New Eden Master Plan for Integrated Water Resources Management in the Marshlands Areas; New Eden Group: Brescia, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Daoudy, M. Le Partage des Eaux Entre la Syrie, l’Irak et la Turquie. Négociation, Sécurité et Asymétrie des Pouvoirs, Moyen-Orient (in French), Paris. 2005. Available online: http://books.openedition.org/editionscnrs/2449 (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Zarins, J. Euphrates. In The Oxford Encyclopedia of Archaeology in the Ancient Near East; Meyers, E.M., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Isaev, V.A.; Mikhailova, M.V. The hydrology, evolution, and hydrological regime of the mouth area of the Shatt al-Arab River. Wat. Res. 2009, 36, 380–395. [Google Scholar]
- Lazem, I.I.; Al-Naqeeb, N.A. Measuring pollution based on total petroleum hydrocarbons and total organic carbon in Tigris River, Maysan Province, Southern Iraq. Casp. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 19, 535–545. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Asadi, S.A.; Abdullah, S.S.; Al-Mahmood, H.K. Estimation of minimum amount of the net discharge in the Shatt Al-Arab River (south of Iraq). J. Adab Al-Basrah 2015, 2, 285–314. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Asadi, S.A. The future of freshwater in Shatt Al-Arab River (Southern Iraq). J. Geogr. Geol. 2017, 9, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Tememi, M.K.; Hussein, M.A.; Khaleefa, U.Q.; Ghalib, H.B.; AL-Mayah, A.M.; Ruhmah, A.J. The salts diffusion between East Hammar marsh area and Shatt Al-Arab River Northern Basra City. Marsh. Bull. 2015, 10, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ramadhan, B.; Pastour, M. Tidal characteristics of Shatt Al-Arab River. Mesopotamian J. Mar. Sci. 1987, 2, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, A.H.J. Evaluation of fish assemblages’ composition in the Euphrates River, southern Thiqar province, Iraq. Mesopot. J. Mar. Sci. 2020, 35, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Asadi, S.A.; Al Hawash, A.B.; Alkhlifa, N.H.A.; Ghalib, H.B. Factors affecting the levels of toxic metals in the Shatt Al-Arab River, Southern Iraq. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 3, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatea, M.H. Study of water quality changes of Shatt Al-Arab River, south of Iraq. J. Univ. Babylon Eng. Sci. 2018, 26, 228–241. [Google Scholar]
- Russ, J. Computer-Assisted Microscopy: The Measurement and Analysis of Image; Plenum Press Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. Multivariate Linear Models in R: An R Companion to Applied Regression; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, LA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bivand, R.S.; Pebesma, E.; Gomez-Rubio, V. Applied Spatial Data Analysis with R, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Heiberger, R.M.; Holland, B. Statistical Analysis and Data Display: An Intermediate Course with Examples in R, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mille, T. Sources de Variation Intra-Populationelle de la Morphologie des Otolithes: Asymétrie Directionnelle et Régime Alimentaire. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lille 1—Sciences et Technologies, Lille, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vignon, M. Disentangling and quantifying sources of otolith shape variation across multiple scales using a new hierarchical partitioning approach. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 534, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahé, K.; Gourtay, C.; Bled Defruit, G.; Chantre, C.; de Pontual, H.; Amara, R.; Claireaux, G.; Audet, C.; Zambonino-Infante, J.L.; Ernande, B. Do environmental conditions (temperature and food composition) affect otolith shape during fish early-juvenile phase? An experimental approach applied to European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2019, 521, e151239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolles, K.L.; Begg, G.A. Distinction between silver hake (Merluccius bilineariz) stocks in U.S. waters of the northwest Atlantic using whole otolith morphometric. Fish. Bull. 2000, 98, 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg, R.J.; Wilcox-Freeburg, E.; Rhyne, A.L.; Tlusty, M.F.; Stebbins, A.; Nye, S.W., Jr.; Honig, A.; Johnston, A.E.; San Antonio, C.M.; Bourque, B.; et al. Ocean acidification alters morphology of all otolith types in Clark’s anemonefish (Amphiprion clarkii). PeerJ 2019, 7, e6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombarte, A.; Lleonart, J. Otolith size changes related with body growth, habitat depth and temperature. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1993, 37, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mille, T.; Mahé, K.; Villanueva, M.C.; De Pontual, H.; Ernande, B. Sagittal otolith morphogenesis asymmetry in marine fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2015, 87, 646–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capoccioni, F.; Costa, C.; Aguzzi, J.; Menesatti, P.; Lombarte, A.; Ciccotti, E. Ontogenetic and environmental effects on otolith shape variability in three Mediterranean European eel (Anguilla anguilla, L.) populations. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 397, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Checkley, D.M.; Dickson, A.G.; Takahashi, M.; Radich, J.A.; Eisenkolb, N.; Asch, R. Elevated CO2 Enhances Otolith Growth in Young Fish. Science 2009, 324, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.L.; Gagliano, M.; Donelson, J.M.; Dixson, D.L.; Thorrold, S.R. Ocean acidification does not affect the early life history development of a tropical marine fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 423, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Réveillac, E.; Lacoue-Labarthe, T.; Oberhänsli, F.; Teyssié, J.L.; Jeffree, R.; Gattuso, J.P.; Martin, S. Ocean acidification reshapes the otolith-body allometry of growth in juvenile sea bream. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2015, 463, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coll-Lladó, C.; Giebichenstein, J.; Webb, P.B.; Bridges, C.R.; Garcia de la Serrana, D. Ocean acidification promotes otolith growth and calcite deposition in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) larvae. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hüssy, K. Otolith shape in juvenile cod (Gadus morhua): Ontogenetic and environmental effects. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 364, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mérigot, B.; Letourneur, Y.; Lecomte-Finiger, R. Characterization of local populations of the common sole Solea solea (Pisces, Soleidae) in the NW Mediterranean through otolith morphometrics and shape analysis. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, M.; Doerin-Arjes, P.; Kastowsky, M.; Mosegaard, H. Effects of sex, stock, and environment on the shape of known-age Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) otoliths. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 61, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadrin, S.X.; Friedland, K.D. The utility of image processing techniques for morphometric analysis and stock identification. Fish. Res. 1999, 43, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castonguay, M.; Simard, P.; Gagnon, P. Usefulness of Fourier analysis of otolith shape for Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus) stock discrimination. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1999, 48, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lleonart, J.; Salat, J.; Torres, G.J. Removing allometric effects of body size in morphological analysis. J. Theor. Biol. 2000, 205, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahé, K. Sources de Variation de la Forme des Otolithes: Implications Pour la Discrimination des Stocks de Poissons. Ph.D. Thesis, Université du Littoral Côte d’Opale, Boulogne-sur-mer, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dowhower, J.F.; Blumer, L.S.; Lejeune, P.; Gaudin, P.; Marconato, A.; Bisazza, A. Otolith asymmetry in Cottus bairdi and Cottus gobio. Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1990, 37, 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Lemberget, T.; Mccormick, M.I. Replenishment success linked to fluctuating asymmetry in larval fish. Oecologia 2009, 159, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Gil, C.; Palmer, M.; Catalán, I.A.; Alós, J.; Fuiman, L.A.; García, E.; del Mar Gil, M.; Grau, A.; Kang, A.; Maneja, R.H.; et al. Otolith fluctuating asymmetry: A misconception of its biological relevance? ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 72, 2079–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbig, R.; Anken, R.; Rahmann, H. On the origin of susceptibility to kinetotic swimming behaviour in fish: A parabolic aircraft flight study. J. Vest. Res. 2003, 12, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lychakov, D.V. Behavioural lateralization and otolith asymmetry. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2003, 49, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lychakov, D.V.; Rebane, Y.T.; Lombarte, A.; Demestre, M.; Fuiman, L.A. Saccular otolith mass asymmetry in adult flatfishes. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 2579–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jawad, L.A.; Al-Mamry, J.; Al-Busaidi, H. Relationship between fish length and otolith length and width in the lutjanid fish, Lutjanus bengalensis (Lutjanidae) collected from muscat city coast on the sea of oman. J. Black Sea/Mediterr. Environ. 2011, 17, 116–126. [Google Scholar]
- Jawad, L.A.; Sadighzadeh, Z. Otolith mass asymmetry in the mugilid fish, Liza klunzingeri (Day, 1888) collected from Persian Gulf near Bandar Abbas. Anal. Biol. 2013, 35, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, L.A. Otolith Mass Asymmetry in Carangoides caerulepinnatus (Rüppell, 1830) (Family: Carangidae) Collected from the Sea of Oman. Croat. J. Fish. 2013, 71, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jawad, L.A.; Park, J.M.; Kwak, S.N.; Ligas, A. Study of the relationship between fish size and otolith size in four demersal species from the south-eastern yellow sea. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2017, 58, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Jawad, L.A.; Qasim, A.M.; Al-Faiz, N.A. Bilateral asymmetry in size of otolith of Otolithes ruber (Bloch & Schneider, 1801) collected from the marine waters of Iraq. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2021, 165, 112110. [Google Scholar]
- Yedier, S.; Bostanci, D.; Kontaş, S.; Kurucu, G.; Polat, N. Comparison of Otolith Mass Asymmetry in Two Different Solea solea Populations in Mediterranean Sea. J. Sci. Tech. 2018, 8, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, Y.A.A.; Mahé, K.; El-Mahdy, S.M.; Mohammad, A.S.; Mehanna, S.F. Relationship between Body and Otolith Morphological Characteristics of Sabre Squirrelfish (Sargocentron spiniferum) from the Southern Red Sea: Difference between Right and Left Otoliths. Oceans 2021, 2, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, N. Biometric Relation between Asteriscus Otolith Size and Fish Total Length of Seven Cyprinid Fish Species from Inland Waters of Turkey. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 20, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Takabayashi, A.; Ohmura-Iwasaki, T. Functional asymmetry estimated by measurements of otolith in fish. Biol. Sci. Space. 2003, 17, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gronkjaer, P.; Sand, M.K. Fluctuating asymmetry and nutritional condition of Baltic cod (Gadus morhua) larvae. Mar. Biol. 2003, 143, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.R. What determines direction of asymmetry: Genes, environment or chance? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trojette, M.; Ben Faleh, A.; Fatnassi, M.; Marsaoui, B.; Mahouachi, N.H.; Chalh, A.; Quignard, J.-P.; Trabelsi, M. Stock discrimination of two insular populations of Diplodus annularis (Actinopterygii: Perciformes: Sparidae) along the coast of Tunisia by analysis of otolith shape. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2015, 45, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bostanci, D.; Yilmaz, M.; Yedier, S.; Kurucu, G.; Kontas, S.; Darçin, M.; Polat, N. Sagittal otolith morphology of sharpsnout seabream Diplodus puntazzo (Walbaum, 1792) in the Aegean sea. Int. J. Morphol. 2016, 34, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Ye, Z.; Li, Z.; Wan, R.; Ren, Y.; Dou, S. Population structure of Japanese Spanish mackerel Scomberomorus niphonius in the Bohai Sea, the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea: Evidence from retom forests based on otolith features. Fish. Sci. 2016, 82, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebaya, M.; Ben Faleh, A.R.; Allaya, H.; Khedher, M.; Trojette, M.; Marsaoui, B.; Fatnassi, M.; Chalh, A.; Quignard, J.P.; Trabelsi, M. Otolith shape discrimination of Liza ramada (Actinopterygii: Mugiliformes: Mugilidae) from marine et estuarine populations in Tunisia. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2017, 47, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).