Sudden Changes in Water Hardness Do Not Impact Short-Term Rainbow Trout Survival
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods Common to Each Experiment
2.2. Trials
2.3. Statistical Analysis
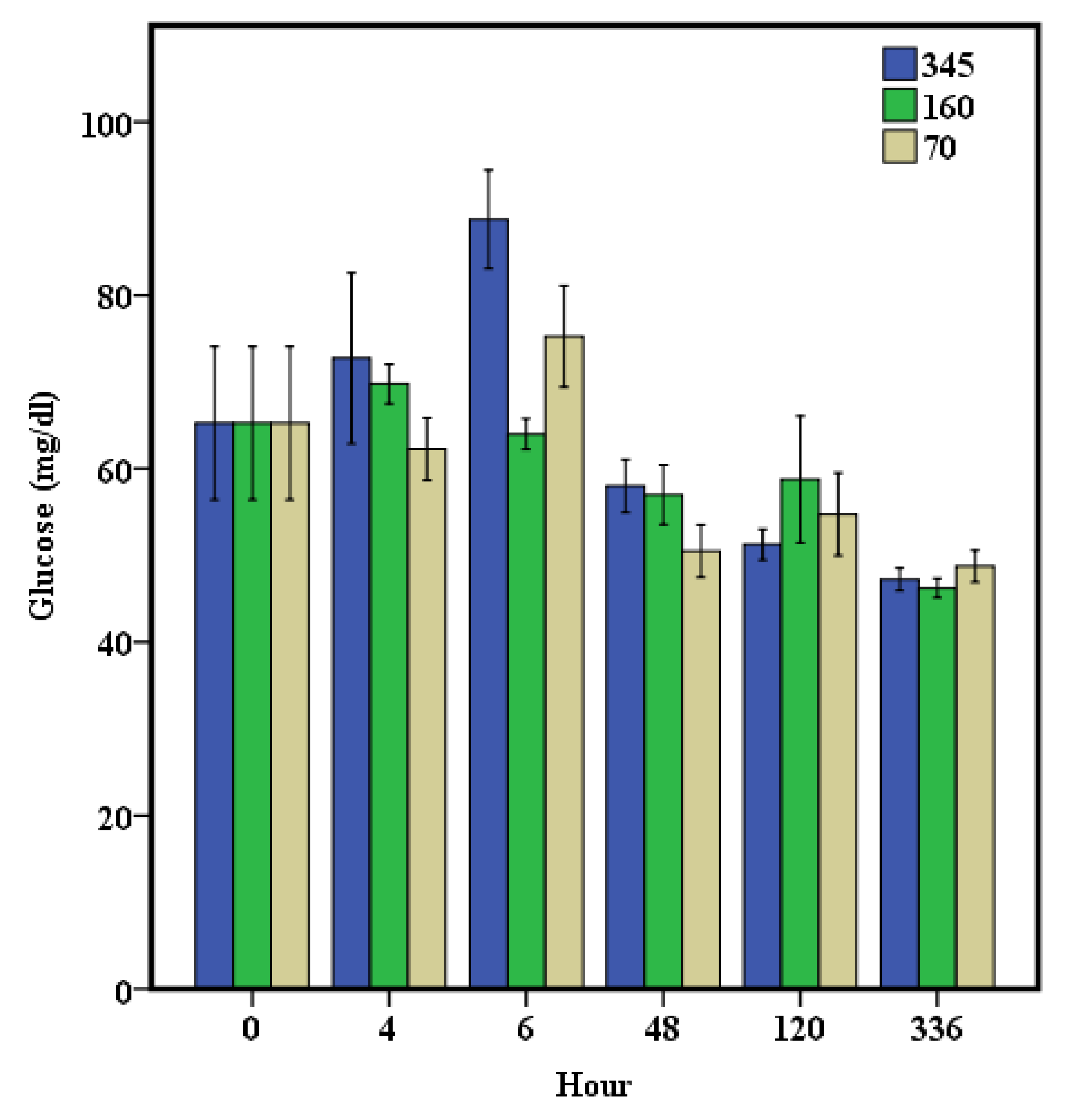
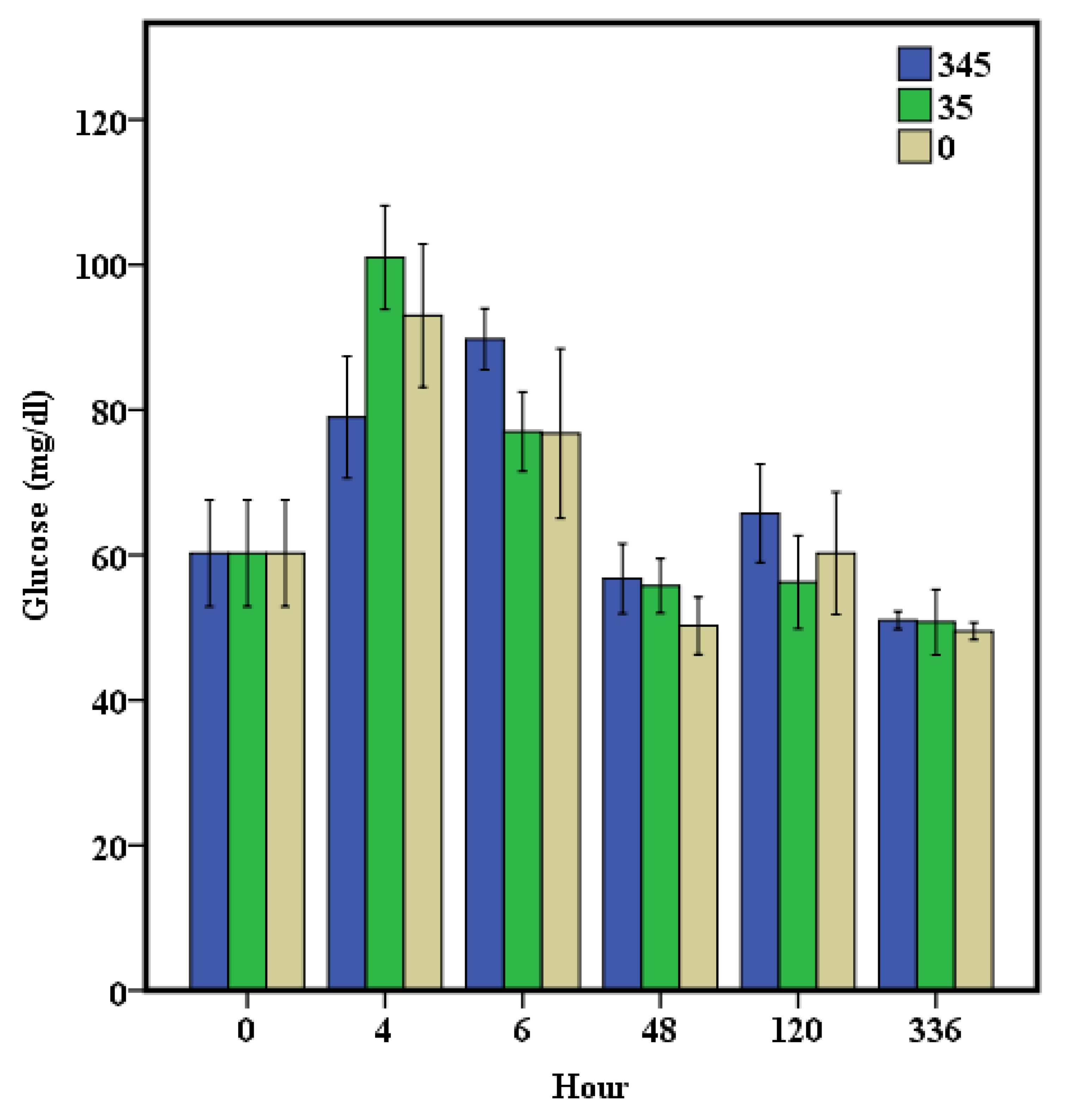
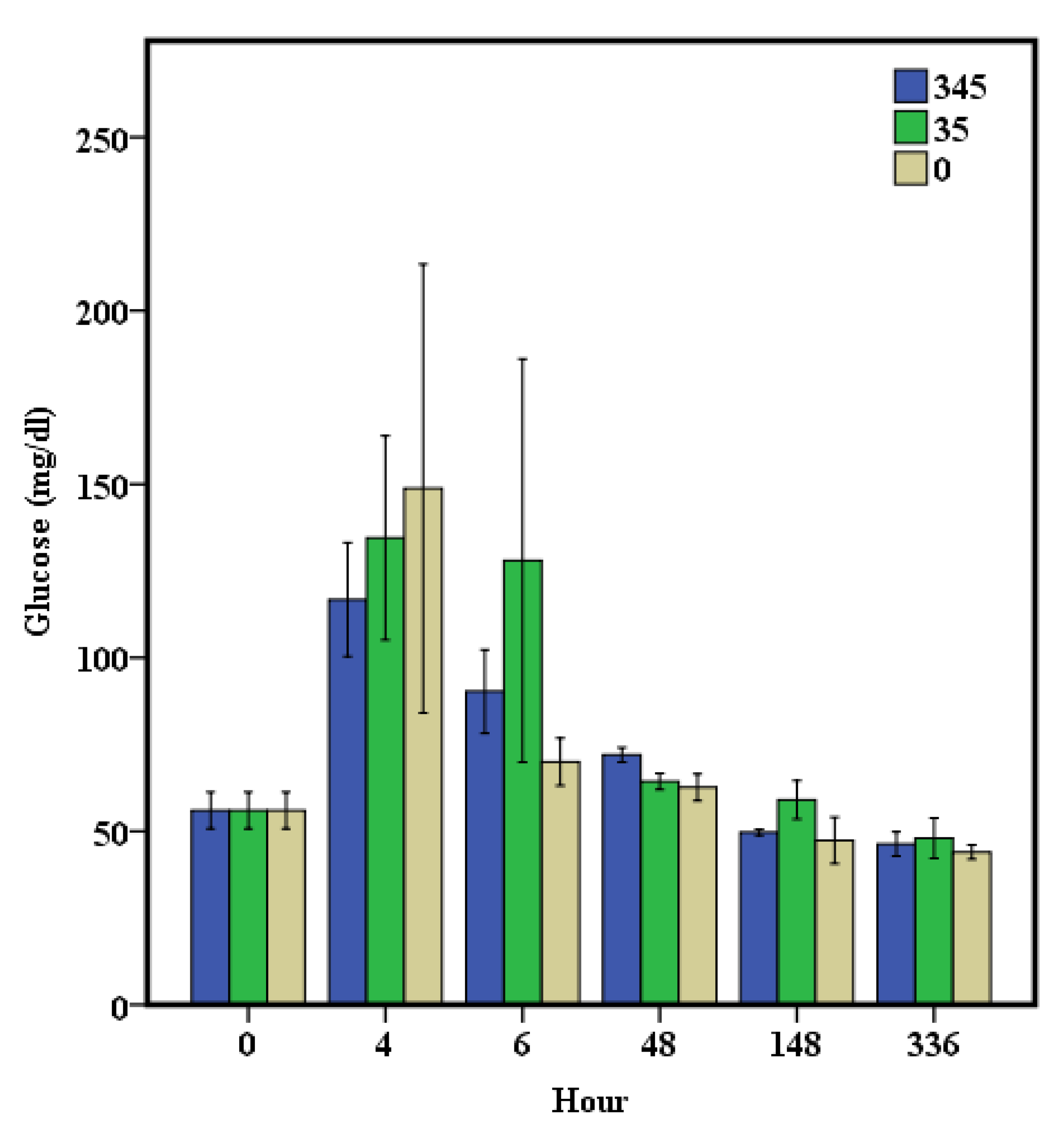
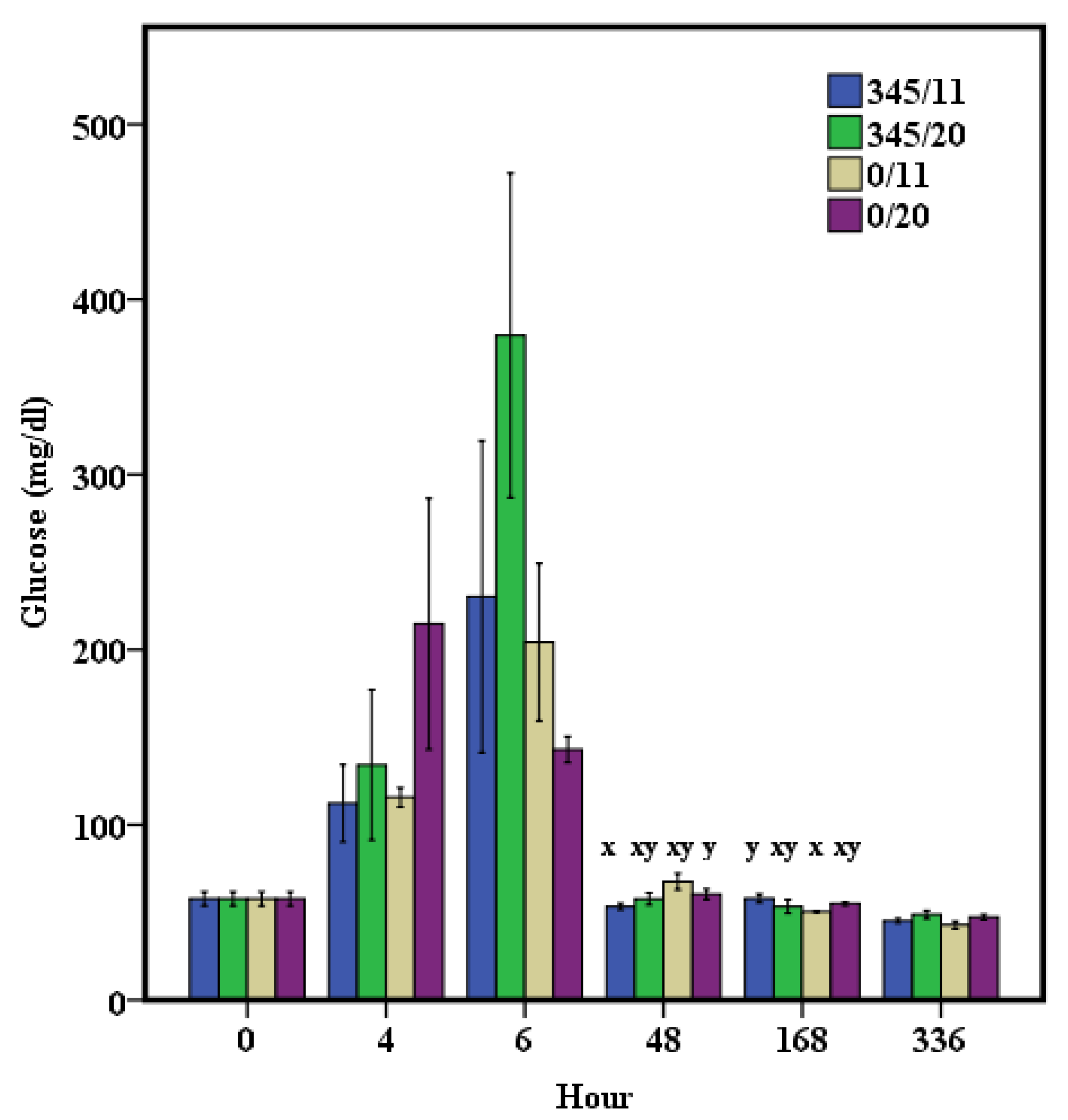
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brett, J.R. Tempering versus acclimation in the planting of speckled trout. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1941, 70, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, M.E.; Wahl, D.H. Comparative mortality of three escoids due to stocking stressors. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 46, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, G.A. Physiology of Intensive Culture Systems; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Clapp, D.F.; Bhagwat, Y.; Wahl, D.H. The effect of thermal stress on walleye fry and fingerling mortality. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1997, 17, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.A.; Hubert, W.A. Simulated thermal tempering versus sudden temperature change and short-term survival of fingerling rainbow trout. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2003, 65, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huysman, N.; Voorhees, J.M.; Krebs, E.; Barnes, M.E. Thermal tempering does not impact rainbow and brown trout survival. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, R.G.; McElwain, I.B.; Orme, L.E.; McCraren, J.P.; Fowler, L.G.; Leonard, J.R. Fish Hatchery Management; U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Noga, E.J. Fish Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Timmons, E.B.; Ebeling, J.B.; Wheaton, F.W.; Summerfelt, S.T.; Cayuga, B.J. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems; Cayuga Aqua Adventures: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002; No. SH137. R37. [Google Scholar]
- Harmon, T.S. Methods for reducing stressors and maintaining water quality associated with live fish transport in tanks: A review of the basics. Rev. Aquac. 2009, 1, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, F.; Wurts, W.A. Transportation of Warmwater Fish: Equipment and Guidelines; Southern Regional Aquaculture Center: Stoneville, MS, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Trushenski, J.T.; Larsen, D.A.; Middleton, M.A.; Jakaitis, M.; Johnson, E.L.; Kozfkay, C.C.; Kline, P.A. Search for the smoking gun: Identifying and addressing the causes of postrelease morbidity and mortality of hatchery-reared Snake River sockeye salmon smolts. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2019, 145, 875–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.G.; Rogano, M.S. Ion regulation by the Rainbow Trout, Salmo gairdneri, in ion-poor water. Physiol. Zool. 1986, 59, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.G.; Robinson, J.G. Physiological responses of Lake Trout to stress: Effects of water hardness and genotype. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1993, 122, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, A.M.; Gilmour, K.M.; Fenwick, J.C.; Perry, S.F. The effects of softwater acclimation on respiratory gas transfer in the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. J. Exp. Biol. 1995, 198, 2557–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, P.; Dunel-Erb, S.; Chevalier, C.; Lignon, J. Gill epithelial cell kinetics in a freshwater teleost, Oncorhynchus mykiss, during adaptation to ion-poor water and hormonal treatments. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1995, 13, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, S.F.; Reid, S.G.; Wankiewicz, E.; Iyer, V.; Gilmour, K.M. Physiological responses of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) to prolonged exposure to soft water. Physiol. Zool. 1996, 69, 1419–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, F.D.F.; Freire, C.A. An overview of stress physiology of fish transport: Changes in water quality as a function of transport duration. Fish Fish. 2016, 17, 1055–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.A.; Rodela, T.M.; Richards, J.G. Hardness does not affect the physiological responses of wild and domestic strains of diploid and triploid rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss to short-term exposure to pH 9.5. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 89, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, A.M. The known and possible role of minerals in trout nutrition and physiology. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1959, 88, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, B.A. Stress in fishes: A diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Soc. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnath, J.G. Hatchery disinfection and disposal of infected stocks. In A Guide to Integrated Fish Health Management in the Great Lakes Basin; Meyer, F.P., Warren, J.W., Carey, T.G., Eds.; Spec. Pub.: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1983; pp. 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, W.J.; Babcock-Johnson, L.; Culver, D.A. Field testing of protocols to prevent the spread of Zebra Mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) during fish hatchery and aquaculture activities. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2002, 64, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucherelli, S.F.; Portz, D.E.; Bloom, K.; Carmon, J.; Brenimer, S.; Hosler, D. Quagga mussel contamination of fish haul trucks by fish and development of effective potassium chloride and formalin treatments. J. Appl. Aquac. 2014, 26, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SDGFP (South Dakota Department of Game, Fish & Parks). 2019 Annual Technical Fish Stocking Report; Pierre, SD, USA, 2019. Available online: https://apps.sd.gov/GF56FisheriesReports (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- SDGFP (South Dakota Department of Game, Fish & Parks). Strategic Plan 2016–2020; Pierre, SD, USA, 2015. Available online: https://gfp.sd.gov/userdocs/docs/strategic-plan-2.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Kientz, J.L.; Barnes, M.E.; Durben, D.J. Concentration of stocked rainbow trout catch and harvest by a small number of recreational anglers. J. Fish. Sci. Com 2017, 11, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Harper, C.; Wolf, J.C. Morphologic effects of the stress response in fish. ILAR J. 2009, 50, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, K.J.; Preston, B. Stocking. In Fish Hatchery Management, 2nd ed.; Wedemeyer, G.A., Ed.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2001; pp. 661–686. [Google Scholar]
- Mazik, P.M.; Simco, B.A.; Parker, N.C. Influence of water hardness and salts on survival and physiological characteristics of striped bass during and after transport. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1991, 120, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.F.; Goss, G.G.; Fenwick, J.C. Interrelationships between gill chloride cell morphology and calcium uptake in freshwater teleosts. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1992, 10, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, S.F.; Goss, G.G.; Laurent, P.L. The interrelationships between gill chloride cell morphology and ionic uptake in four freshwater teleosts. Can. J. Zool. 1992, 70, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.F.; Laurent, P.L. Environmental effects on fish gill structure and function. In Fish Ecophysiology; Rankin, J.C., Jensen, F.B., Eds.; Chapman Hall: London, UK, 1993; pp. 231–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, P.R.; Behnke, R.J. The origin of hatchery rainbow trout. Progress. Fish-Cult. 1962, 24, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, E.R. Effects of stocking catchable-size hatchery rainbow trout on two wild trout species in the Madison River and O’Dell Creek, Montana. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1987, 7, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.E.; Simpson, G.; Durben, D.J. Post-stocking harvest of catchable-sized rainbow trout enhanced by dietary supplementation with a fully fermented commercial yeast culture during hatchery rearing. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2009, 29, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Wilhite, J.W.; Simpson, G.; Barnes, M.E.; Bertrand, K.N.; Willis, D.W. Contributions of stocked and naturally reproduced rainbow trout in Deerfield Reservoir System. Prairie Nat. 2013, 45, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, S.; Poupin, J. A study of the effects of water carbonate alkalinity on some parameters of blood acid-base status in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri R.). J. Comp. Physiol. B 1985, 156, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchot, J.P.; Forgue, J. Effect of water alkalinity on gill CO2 exchange and internal Pco2 in aquatic animals. Comp. Biochem. Phys. A 1998, 119, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; Tucker, C.S.; Somridhivej, B. Alkalinity and hardness: Critical but elusive concepts in aquaculture. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2016, 47, 6–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurts, W.A.; Perschbacher, P.W. Effects of bicarbonate alkalinity and calcium on the acute toxicity of copper to juvenile channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture 1994, 125, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, E.J.; Bosakowski, T.; Interlmann, S. Combined effects of temperature and high pH on mortality and the stress response of rainbow trout after stocking. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1997, 126, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, H.D.; Coates, G.I.; Wilhelm, S. Impacts of increased tempering lengths on twenty-four-hour survival of hybrid striped bass fry. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2000, 62, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial | Hardness (mg/L CaCO3) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 70 | 11 |
| 160 | 11 | |
| 345 | 11 | |
| 2 | 0 | 11 |
| 35 | 11 | |
| 345 | 11 | |
| 3 | 0 | 11 |
| 35 | 11 | |
| 345 | 11 | |
| 4 | 0 | 11 |
| 0 | 20 | |
| 345 | 11 | |
| 345 | 20 |
| Trial | Survival (%) | Days Alive | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 14 | |
| 100 | 14 | N/A | |
| 100 | 14 | ||
| 2 | 100 | 14 | 0.34 |
| 100 | 14 | ||
| 75 | 13 ± 1 | ||
| 3 | 100 | 14 | 0.34 |
| 75 | 11 ± 3 | ||
| 100 | 14 | ||
| 4 | 100 | 14 | N/A |
| 100 | 14 | ||
| 100 | 14 | ||
| 100 | 14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huysman, N.; Voorhees, J.M.; Krebs, E.; Barnes, M.E. Sudden Changes in Water Hardness Do Not Impact Short-Term Rainbow Trout Survival. Fishes 2022, 7, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010044
Huysman N, Voorhees JM, Krebs E, Barnes ME. Sudden Changes in Water Hardness Do Not Impact Short-Term Rainbow Trout Survival. Fishes. 2022; 7(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuysman, Nathan, Jill M. Voorhees, Eric Krebs, and Michael E. Barnes. 2022. "Sudden Changes in Water Hardness Do Not Impact Short-Term Rainbow Trout Survival" Fishes 7, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010044
APA StyleHuysman, N., Voorhees, J. M., Krebs, E., & Barnes, M. E. (2022). Sudden Changes in Water Hardness Do Not Impact Short-Term Rainbow Trout Survival. Fishes, 7(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7010044







