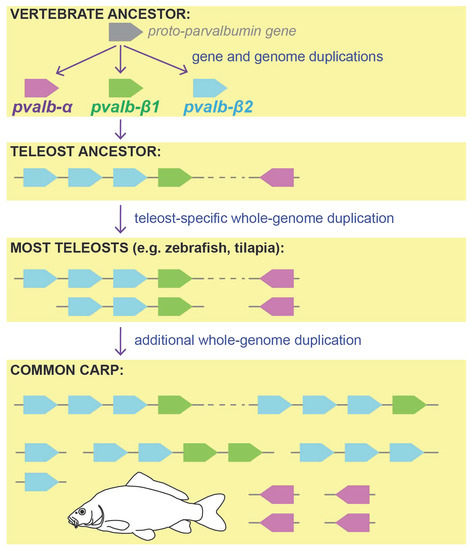
Evolution of the Parvalbumin Genes in Teleost Fishes after the Whole-Genome Duplication
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genomic and Transcriptomic Data Set
2.2. Parvalbumin Genomic Repertoire and Phylogenetic Reconstruction of the Parvalbumin Genes
2.3. Transcriptomic Analysis in the Common Carp Tissues
3. Results and Discussion
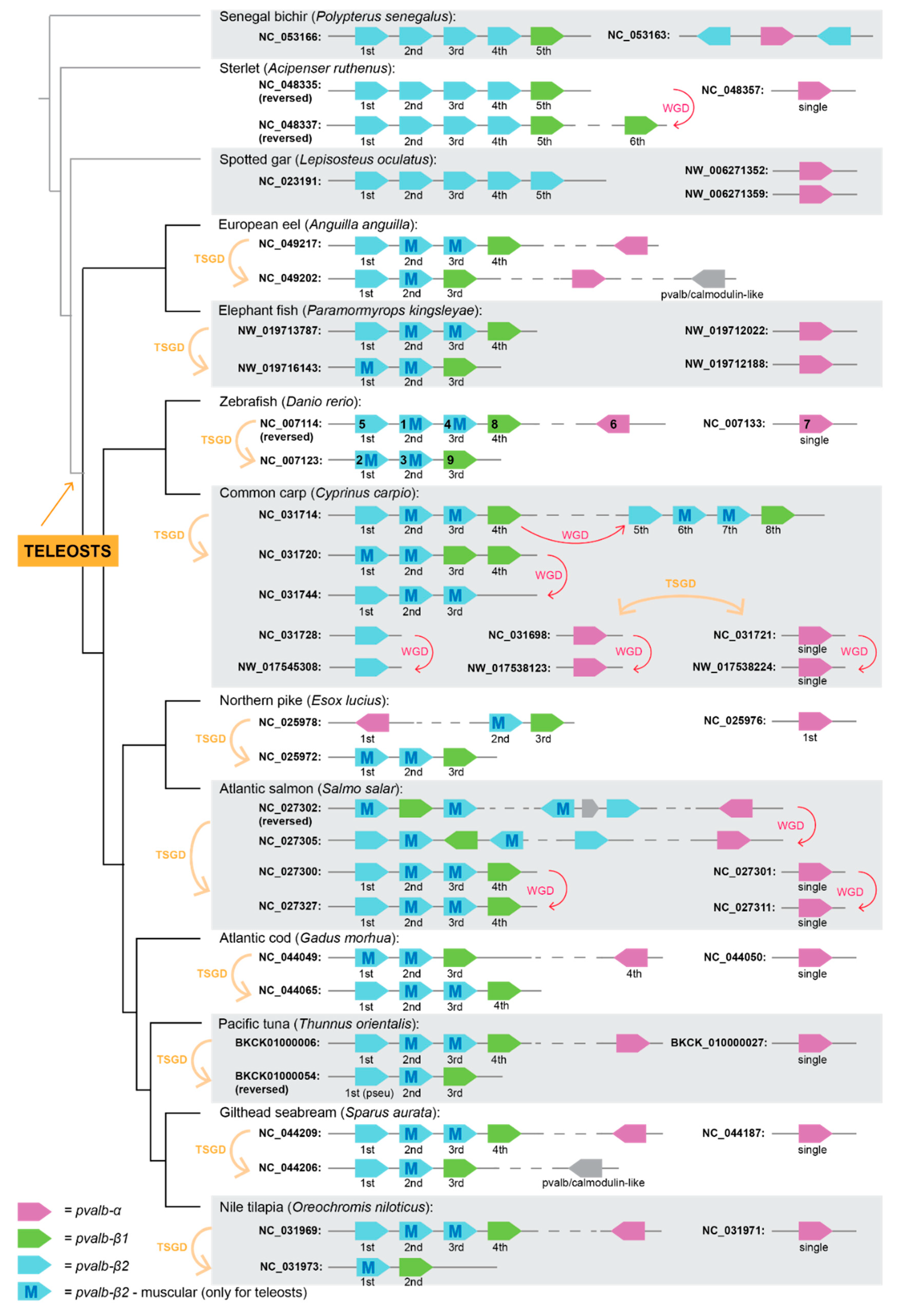
3.1. Parvalbumin Gene Repertoire in Teleost Fishes

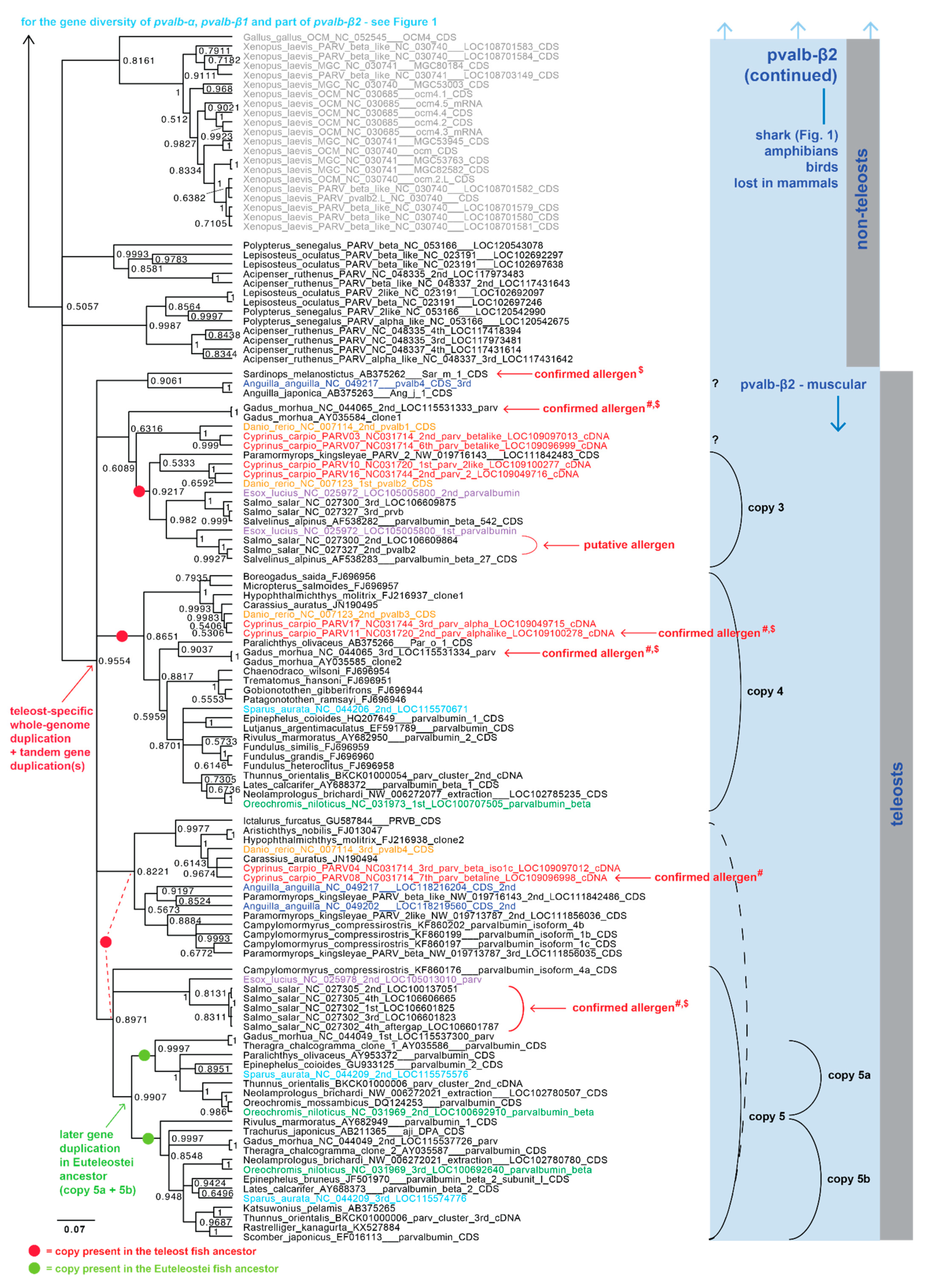
3.2. Whole-Genome Duplications Have Boosted Parvalbumin Gene Diversity
3.3. Gene Expression of Parvalbumin Genes in the Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio)
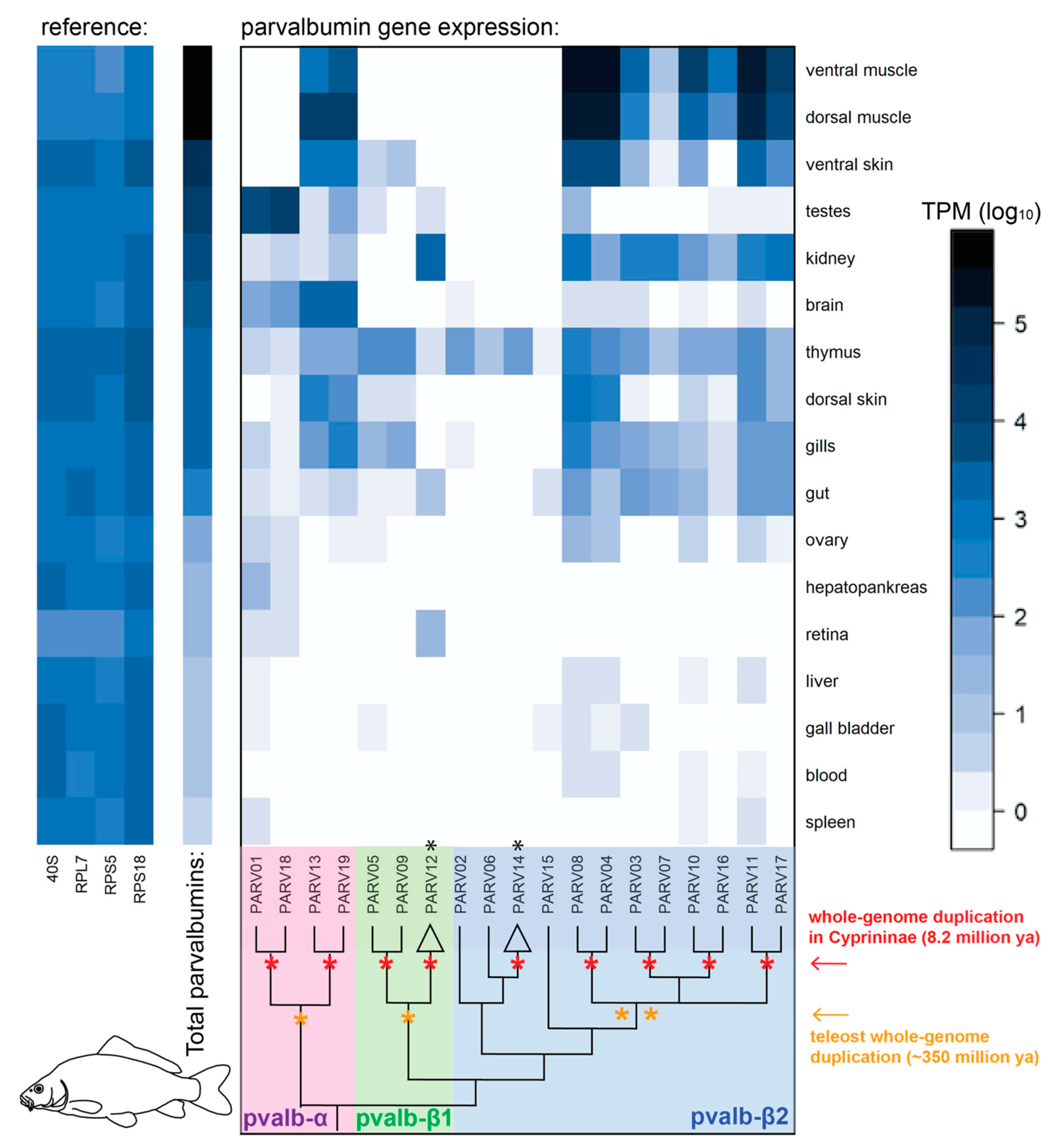
3.4. Fish Allergenicity and the Muscle Parvalbumins
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swoboda, I.; Bugajska-Schretter, A.; Valenta, R.; Spitzauer, S.J.A. Recombinant fish parvalbumins: Candidates for diagnosis and treatment of fish allergy. Allergy 2002, 57, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, M.L.; Goodman, M.; Berger-Cohn, J.; Demaille, J.G.; Matsuda, G. The early adaptive evolution of calmodulin. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1984, 1, 442–455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Climer, L.K.; Cox, A.M.; Reynolds, T.J.; Simmons, D.D. Oncomodulin: The enigmatic parvalbumin protein. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrell, M.S.; Lyne, M.; Carr, A.R.; Zakon, H.H.; Buckley, D.; Campbell, A.S.; Davis, M.C.; Micklem, G.; Baker, C.V. Insights into electrosensory organ development, physiology and evolution from a lateral line-enriched transcriptome. eLife 2017, 6, e24197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Liang, C.Z.; Gao, H.W.; Lin, C.; Deng, M.J. Detection of parvalbumin, a common fish allergen gene in food, by real-time polymerase chain reaction. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanak, P.; Laknerova, I.; Svatora, M. Second intron in the protein-coding region of the fish parvalbumin gene-a promising platform for polymerase chain reaction-based discrimination of fish meat of various species. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 51, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, A.; Rehbein, H. The differentiation of tuna (family: Scombridae) products through the PCR-based analysis of the cytochrome b gene and parvalbumin introns. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhatova, D.; Laknerova, I.; Zdenkova, K.; Olafsdottir, G.; Magnusdottir, S.; Piknova, L.; Kyrova, V.; Lerch, Z.; Hanak, P. International interlaboratory study on TaqMan real-time polymerase chain reaction authentication of black seabream (Spondyliosoma cantharus). J. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 57, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg, F. Parvalbumin isoforms in zebrafish. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2005, 32, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchtold, M.W.; Epstein, P.; Beaudet, A.L.; Payne, M.E.; Heizmann, C.W.; Means, A.R. Structural organization and chromosomal assignment of the parvalbumin gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 8696–8701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrotte, J.G. A crystalline constituent from myogen of carp muscles. Nature 1952, 169, 968–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntener, M.; Kaser, L.; Weber, J.; Berchtold, M.W. Increase of skeletal-muscle relaxation speed by direct injection of parvalbumin cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 6504–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Lo, L.C.; Wang, C.M.; Lin, G.; Feng, F.; Yue, G.H. Characterization of two parvalbumin genes and their association with growth traits in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). Anim. Genet. 2006, 37, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rall, J.A. Role of parvalbumin in skeletal muscle relaxation. News Physiol. Sci. 1996, 11, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca, N.; Deng, P.; Linberg, K.A.; Lewis, G.P.; Fisher, S.K.; Kolb, H. The neurons of the ground squirrel retina as revealed by immunostains for calcium binding proteins and neurotransmitters. J. Neurocytol. 2002, 31, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Thalmann, I.; Thalmann, R.; Simmons, D.D. Expression of α and β parvalbumin is differentially regulated in the rat organ of corti during development. J. Neurobiol. 2004, 58, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toury, R.; Belqasmi, F.; Hauchecorne, M.; Leguellec, D.; Heizmann, C.W.; Balmain, N. Localization of the Ca2+-binding α-Parvalbumin and its mRNA in epiphyseal plate cartilage and bone of growing rats. Bone 1995, 17, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, J.M.; Arnold, J.; Beach, G.G.; Ragland, W.L.; Wunderlich, J.K. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of tissue-specific parvalbumins from chicken muscle and thymus and possible evolutionary significance. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 181, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchtold, M.W.; Wilson, K.J.; Heizmann, C.W. Isolation of neuronal parvalbumin by high-performance liquid chromatography. Characterization and comparison with muscle parvalbumin. Biochemistry 1982, 21, 6552–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berchtold, M.W.; Celio, M.R.; Heizmann, C.W. Parvalbumin in non-muscle tissues of the rat. Quantitation and immunohistochemical localization. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 5189–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, P.P.; Keyser, K.T.; Celio, M.R.; Karten, H.J.; Bloom, F.E. Distribution of parvalbumin immunoreactivity in the vertebrate retina. Brain Res. 1993, 600, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesmeier, U.; Vázquez-Cortés, S.; Bublin, M.; Radauer, C.; Ma, Y.; Briza, P.; Fernández-Rivas, M.; Breiteneder, H. Expression levels of parvalbumins determine allergenicity of fish species. Allergy 2010, 65, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, A.; Scheuermann, T.; Hilger, C.; Hentges, F. Important variations in parvalbumin content in common fish species: A factor possibly contributing to variable allergenicity. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 153, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.W.; Nordlee, J.A.; Koppelman, S.J.; Baumert, J.L.; Taylor, S.L. Measuring parvalbumin levels in fish muscle tissue: Relevance of muscle locations and storage conditions. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, A.; Tanaka, H.; Hamada, Y.; Ishizaki, S.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Comparison of allergenicity and allergens between fish white and dark muscles. Allergy 2006, 61, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.C.; Neo, K.H.; Goh, D.M.; Shek, L.C.; Lee, B.W. Missing parvalbumin: Implications in diagnostic testing for tuna allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 874–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilger, C.; Thill, L.; Grigioni, F.; Lehners, C.; Falagiani, P.; Ferrara, A.; Romano, C.; Stevens, W.; Hentges, F. IgE antibodies of fish allergic patients cross-react with frog parvalbumin. Allergy 2004, 59, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Do, T.; Elsayed, S.; Florvaag, E.; Hordvik, I.; Endresen, C. Allergy to fish parvalbumins: Studies on the cross-reactivity of allergens from 9 commonly consumed fish. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rencova, E.; Kostelnikova, D.; Tremlova, B. Detection of allergenic parvalbumin of Atlantic and Pacific herrings in fish products by PCR. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2013, 30, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrøm, C.D.; van Dô, T.; Hordvik, I.; Endresen, C.; Elsayed, S. Cloning of two distinct cDNAs encoding parvalbumin, the major allergen of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Scand J. Immunol. 1996, 44, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Griesmeier, U.; Susani, M.; Radauer, C.; Briza, P.; Erler, A.; Bublin, M.; Alessandri, S.; Himly, M.; Breiteneder, H.; et al. Comparison of natural and recombinant forms of the major fish allergen parvalbumin from cod and carp. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, S196–S207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Colmenero, M.; Rahman, S.; Martínez, J.L.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. High variability in parvalbumin beta 1 genes offers new molecular options for controlling the mislabeling in commercial Salmonids. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretsinger, R.H. Structure and evolution of calcium-modulated protein. CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem. 1980, 8, 119–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, M.; Pechere, J.-F. The evolution of muscular parvalbumins investigated by the Maximum Parsimony method. J. Mol. Evol. 1977, 9, 131–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapak, R.C.; Zhao, H.; Boschi, J.M.; Henzl, M.T. Novel avian thymic parvalbumin displays high degree of sequence homology to oncomodulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 5288–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, S. Evolution by Gene Duplication; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.S.; Van de Peer, Y.; Meyer, A. Genome duplication, divergent resolution and speciation. Trends Genet. 2001, 17, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A. Birth and death of duplicated genes in completely sequenced eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 2001, 17, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.; Schartl, M. Gene and genome duplications in vertebrates: The one-to four (-to-eight in fish) rule and the evolution of novel gene functions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1999, 11, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Cheng, H.; Tiersch, T.R. Differential genome duplication and fish diversity. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2002, 11, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.; Van de Peer, Y. From 2R to 3R: Evidence for a fish-specific genome duplication (FSGD). Bioessays 2005, 27, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amores, A.; Force, A.; Yan, Y.L.; Joly, L.; Amemiya, C.; Fritz, A.; Ho, R.K.; Langeland, J.; Prince, V.; Wang, Y.L.; et al. Zebrafish hox clusters and vertebrate genome evolution. Science 1998, 282, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemons, D.; McGinnis, W. Genomic evolution of Hox gene clusters. Science 2006, 313, 1918–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.J.; Holland, P.W. Diversification of Hox gene clusters in Osteoglossomorph fish in comparison to other teleosts and the spotted gar outgroup. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2017, 328, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, S.; Koop, B.F.; Sandve, S.R.; Miller, J.R.; Kent, M.P.; Nome, T.; Hvidsten, T.R.; Leong, J.S.; Minkley, D.R.; Zimin, A.; et al. The Atlantic salmon genome provides insights into rediploidization. Nature 2016, 533, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Kuang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zheng, X.; Ren, L.; Wang, G.; et al. Genome sequence and genetic diversity of the common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Stöck, M.; Kneitz, S.; Klopp, C.; Woltering, J.M.; Adolfi, M.C.; Feron, R.; Prokopov, D.; Makunin, A.; Kichigin, I.; et al. The sterlet sturgeon genome sequence and the mechanisms of segmental rediploidization. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postlethwait, J.H.; Woods, I.G.; Ngo-Hazelett, P.; Yan, Y.L.; Kelly, P.D.; Chu, F.; Huang, H.; Hill-Force, A.; Talbot, W.S. Zebrafish comparative genomics and the origins of vertebrate chromosomes. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 1890–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.; Force, A. The probability of duplicate gene preservation by subfunctionalization. Genetics 2000, 154, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortesi, F.; Musilová, Z.; Stieb, S.M.; Hart, N.S.; Siebeck, U.E.; Malmstrøm, M.; Tørresen, O.K.; Jentoft, S.; Cheney, K.L.; Marshall, N.J.; et al. Ancestral duplications and highly dynamic opsin gene evolution in percomorph fishes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortesi, F.; Camacho, D.; Luehrmann, M.; Sommer, G.M.; Musilova, Z. Multiple ancestral duplications of the red-sensitive opsin gene (LWS) in teleost fishes and convergent spectral shifts to green vision in gobies. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musilova, Z.; Salzburger, W.; Cortesi, F. The visual opsin gene repertoires of teleost fishes: Evolution, ecology, and function. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 37, 441–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.C.; Chen, L. Evolution of an antifreeze glycoprotein. Nature 1999, 401, 443–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.I.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FigTree. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 31 January 2016).
- Sayers, E.W.; Barrett, T.; Benson, D.A.; Bolton, E.; Bryant, S.H.; Canese, K.; Clark, K.; Connor, R.; Fiorini, N.; Funk, K.; et al. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 36, D13–D25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushnell, B. BBMap Short-Read Aligner, and Other Bioinformatics Tools; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015; Available online: Sourceforge.net/projects/bbmap (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yuan, X.; Yuan, S.; Dai, L.; Dong, S.; Liu, J.; Peng, L.; Wang, M.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, Y. Optimal reference genes for gene expression analysis in polyploid of Cyprinus carpio and Carassius auratus. BMC Genet. 2020, 21, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 31 December 2020).
- Zeileis, A.; Fisher, J.C.; Hornik, K.; Ihaka, R.; McWhite, C.D.; Murrell, P.; Stauffer, R.; Wilke, C.O. Colorspace: A Toolbox for Manipulating and Assessing Colors and Palettes. J. Stat. Softw. 2020, 96, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opazo, J.C.; Butts, G.T.; Nery, M.F.; Storz, J.F.; Hoffmann, F.G. Whole-genome duplication and the functional diversification of teleost fish hemoglobins. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Nikaido, M.; Hagino-Yamagishi, K.; Okada, N. Distinct functions of two olfactory marker protein genes derived from teleost-specific whole genome duplication. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquier, J.; Cabau, C.; Nguyen, T.; Jouanno, E.; Severac, D.; Braasch, I.; Journot, L.; Pontarotti, P.; Klopp, C.; Postlethwait, J.H.; et al. Gene evolution and gene expression after whole genome duplication in fish: The PhyloFish database. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallant, J.R.; Hopkins, C.D.; Deitcher, D.L. Differential expression of genes and proteins between electric organ and skeletal muscle in the mormyrid electric fish Brienomyrus brachyistius. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215, 2479–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ma, K.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, X.; Li, J. Transcriptomic analysis reveals growth-related genes in juvenile grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella. Aquac. Fish. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaalund, S.S.; Riise, J.; Broberg, B.V.; Fabricius, K.; Karlsen, A.S.; Secher, T.; Plath, N.; Pakkenberg, B. Differential expression of parvalbumin in neonatal phencyclidine-treated rats and socially isolated rats. J. Neurochem. 2013, 124, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filice, F.; Janickova, L.; Henzi, T.; Bilella, A.; Schwaller, B. The parvalbumin hypothesis of autism spectrum disorder. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 577525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, E.; Rivas, M.V.; Ward, J.M.; Okanoya, K.; Jarvis, E.D. Convergent differential regulation of parvalbumin in the brains of vocal learners. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownridge, P.; de Mello, L.V.; Peters, M.; McLean, L.; Claydon, A.; Cossins, A.R.; Whitfield, P.D.; Young, I.S. Regional variation in parvalbumin isoform expression correlates with muscle performance in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Tavarez, R.; Carrera, M.; Pedrosa, M.; Quirce, S.; Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Gasset, M. Reconstruction of fish allergenicity from the content and structural traits of the component β-parvalbumin isoforms. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Scheme 1. | GenBank Accession Number | Total pvalb Genes | pvalb-α | pvalb-β1 | pvalb-β2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| other vertebrates: | |||||
| Sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) | GCA_010993605.1 | 1 + 6 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ghostshark (Callorhinchus milii) | GCA_018977255.1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis) | GCA_017654675.1 | 28 | 3 | 3 | 22 |
| Chicken (Gallus gallus) | GCA_016699485.1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Human (Homo sapiens) | GCA_000001405.28 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Mouse (Mus musculus) | GCA_000001635.9 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| ray-fined non-teleost fishes: | |||||
| Senegal bichir (Polypterus senegalus) | GCA_016835505.1 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) | GCA_010645085.1 | 12 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Spotted gar (Lepisosteus oculatus) | GCA_000242695.1 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 5 |
| teleost fishes: | |||||
| European eel (Anguilla anguilla) | GCA_013347855.1 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Elephantfish (Paramormyrops kingsleyae) | GCA_002872115.1 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Common carp (Cyprinus carpio) | GCA_018340385.1 | 21 | 4 | 4 | 13 |
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | GCA_000002035.4 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Northern pike (Esox lucius) | GCA_011004845.1 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) | GCA_000233375.4 | 22 | 4 | 4 | 14 |
| Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) | GCA_902167405.1 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Pacific bluefin tuna (Thunnus orientalis) | GCA_009176245.1 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) | GCA_900880675.1 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | GCA_001858045.3 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mukherjee, S.; Bartoš, O.; Zdeňková, K.; Hanák, P.; Horká, P.; Musilova, Z. Evolution of the Parvalbumin Genes in Teleost Fishes after the Whole-Genome Duplication. Fishes 2021, 6, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040070
Mukherjee S, Bartoš O, Zdeňková K, Hanák P, Horká P, Musilova Z. Evolution of the Parvalbumin Genes in Teleost Fishes after the Whole-Genome Duplication. Fishes. 2021; 6(4):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040070
Chicago/Turabian StyleMukherjee, Subham, Oldřich Bartoš, Kamila Zdeňková, Petr Hanák, Petra Horká, and Zuzana Musilova. 2021. "Evolution of the Parvalbumin Genes in Teleost Fishes after the Whole-Genome Duplication" Fishes 6, no. 4: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040070
APA StyleMukherjee, S., Bartoš, O., Zdeňková, K., Hanák, P., Horká, P., & Musilova, Z. (2021). Evolution of the Parvalbumin Genes in Teleost Fishes after the Whole-Genome Duplication. Fishes, 6(4), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040070