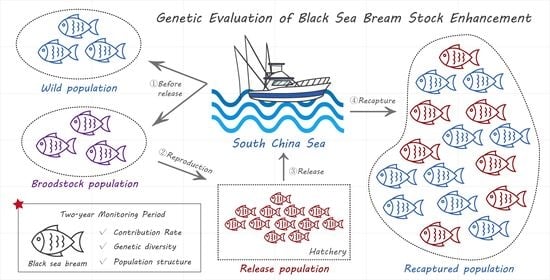
Genetic Evaluation of Black Sea Bream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii) Stock Enhancement in the South China Sea Based on Microsatellite DNA Markers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.2. Genotyping and Calculation of the Contribution Rate
2.3. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure
3. Results
3.1. Contribution Rate of Stock Enhancement
3.2. Genetic Diversity within Populations
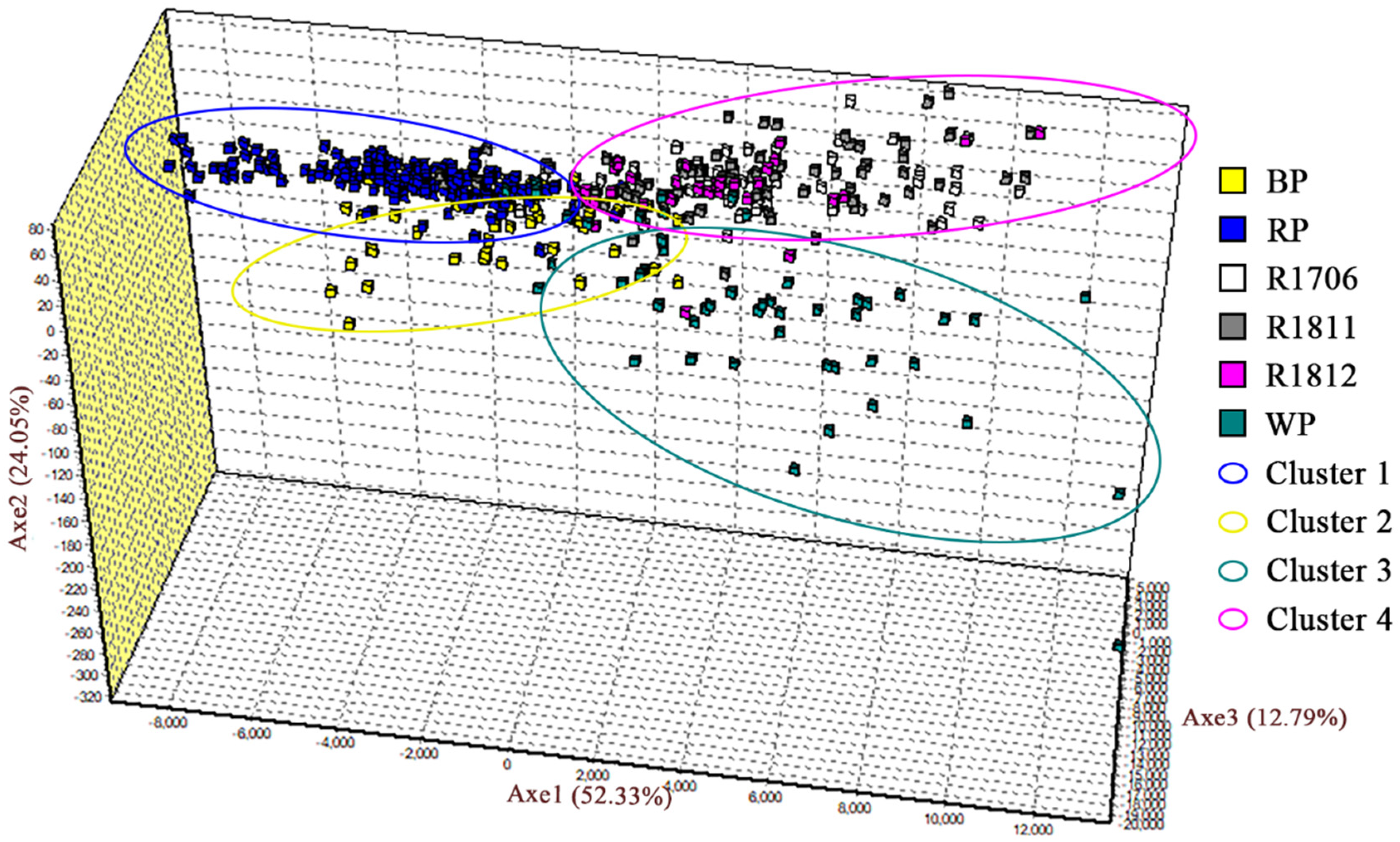
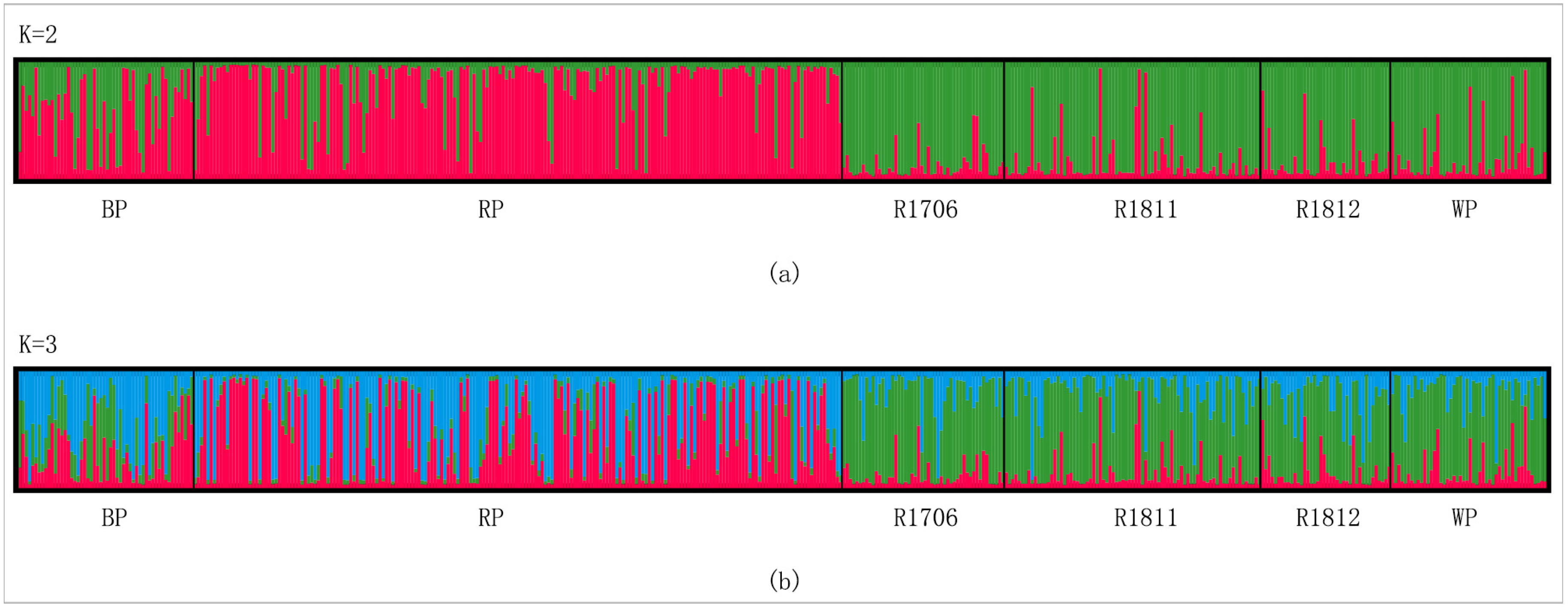
3.3. Genetic Differentiation among Populations
4. Discussion
4.1. The Contribution Rate of the Stock Enhancement
4.2. Genetic Evaluation of the Stock Enhancement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pauly, D.; Zeller, D. Comments on FAOs State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA 2016). Mar. Policy 2017, 77, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, S. Economic, ecological and genetic impacts of marine stock enhancement and sea ranching: A systematic review. Fish Fish. 2018, 19, 511–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, H.; Schmid, C. Is hatchery stocking a help or harm?: Evidence, limitations and future directions in ecological and genetic surveys. Aquaculture 2010, 308, S2–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.A.; Luo, Y.T.; Xu, D.P.; Yang, X.W.; Wang, X.H. Relationship between genetic risk and stock enhancement of the silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) in the Yangtze River. Fish Res. 2021, 235, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leber, K.M.; Arce, S.M. Stock enhancement in a commercial mullet, Mugil cephalus L., fishery in Hawaii. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 1996, 3, 261–278. [Google Scholar]
- R.L., W.; D.M., B. An Evaluation of Present Techniques for the Enhancement of Fisheries. Available online: www.fao.org/3/W8514E/W8514E01.htm (accessed on 6 July 2021).
- Wang, L.J.; Wu, Z.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, M.X.; Song, A.H.; Liu, H.J.; You, F. Genetic Assessment of a Black Rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii, Stock Enhancement Program in Lidao Bay, China Based on Mitochondrial and Nuclear DNA Analysis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Furukawa, M.; Kubota, M.; Harada, Y. Effects of stocking hatchery fish on the phenotype of indigenous populations in the amago salmon Oncorhynchus masou ishikawae in Japan. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 81, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, K.; Toriya, S.; Shishidou, H.; Sugaya, T.; Kitada, S. Genetic effects of hatchery fish on wild populations in red sea bream Pagrus major (Perciformes, Sparidae) inferred from a partial sequence of mitochondrial DNA. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 2123–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Villaizán Romo, M.D.M.; Aritaki, M.; Taniguchi, N. Pedigree analysis of recaptured fish in the stock enhancement program of spotted halibut Verasper variegatus. Fish. Sci. 2006, 72, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, A.T.; Bradley, D.G.; Cunningham, E.P. Microsatellite genetic variation between and within farmed and wild Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) populations. Aquaculture 1999, 180, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lyu, D.; Wang, M.; Liu, K.; Kong, J.; Shan, X.; Jin, X. Research in migration route of hatchery released Chinese shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis) in the Bohai Bay using method of SSR marker. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.H.; Huang, C.W.; Lee, H.T.; Kuo, Y.H.; Liu, K.M.; Lin, C.H.; Gong, H.Y. Population genetic analysis for stock enhancement of silver sea bream (Rhabdosargus sarba) in Taiwan. Fishes 2020, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.D.; Becker, A.; Quinn, J.; Lowry, M.B.; Fielder, S.; Knibb, W. Stock structure of dusky flathead (Platycephalus fuscus) to inform stocking management. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 71, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, C.D.; Carpenter, K.E.; Mann, B.Q.; Pollard, D.; Russell, B.; Liao, W.; Shao, K. Acanthopagrus schlegelii. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-3.RLTS.T170153A20567110.en (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Shan, B.; Liu, Y.; Song, N.; Ji, D.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, T.; Sun, D. Genetic diversity and population structure of black sea bream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii) based on mitochondrial control region sequences: The genetic effect of stock enhancement. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 35, 101188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuyuki, A.; Umino, T. Spatial movement of black sea bream Acanthopagrus schlegelii around the oyster farming area in Hiroshima Bay, Japan. Fish. Sci. 2017, 83, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Shan, B.; Sun, D.; Liu, S.; Li, T.; Lliu, M.; Xie, Q. Investiqation of a mark-recapture method of black porąy, Acanthopaqrus schlegelii, in Daya Bay usinq plastic oval tags. J. Fish. Sci. China 2019, 26, 63–70. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.-W. The Biology and Fisheries Status of Seabreams (Family: Sparidae) in Hong Kong and Adjacent Waters; The University of Hong Kong: Hong Kong, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, E.B.; Nagasawa, K.; Umino, T. Stock enhancement program for black sea bream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii) in Hiroshima Bay: Monitoring the genetic effects. Aquaculture 2008, 276, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.-S.; Gonzalez, E.B.; Morishima, K.; Arai, K.; Umino, T. Parentage assignment of stocked black sea bream Acanthopagrus schlegelii in Hiroshima Bay using microsatellite DNA markers. Fish. Sci. 2007, 73, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- An, H.S.; Hong, S.W.; Lee, J.U.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, K.-K. Genetic diversity of wild and farmed black sea bream populations in Jeju. Anim. Cells Syst. 2010, 14, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Changping, Y.; Binbin, S.; Dianrong, S.; Shengnan, L.; Teng, L.; Manting, L.; Qijian, X. Investigation of a mark-recapture method of black porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegelii, in Daya Bay using plastic oval tags. J. Fish. Sci. China 2019, 26, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Sanchez, G.; Kawai, K.; Tomano, S.; Fujita, H.; Umino, T. The role of the isolation of the marginal seas during the Pleistocene in the genetic structure of black sea bream Acanthopagrus schlegelii (Bleeker, 1854) in the coastal waters of Japan. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.S.W.; Sadovy de Mitcheson, Y. Reproductive biology of black seabream Acanthopagrus schlegelii, threadfin porgy Evynnis cardinalis and red pargo Pagrus major in the northern South China Sea with consideration of fishery status and management needs. J. Fish Biol. 2017, 91, 101–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinis, M.T. Practical flatfish culture and stock enhancement—Edited by H.V. Daniels and W.O. Watanabe. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 81, 1145–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Chen, T.; Chen, L.; Guo, J. The techniques of Sparus macrocephalus tagged and released in Daya Bay. J. Fish. China 2001, 25, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Wu, L.; Huang, W.; Wu, R.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Meng, Z. Genetic evidence for the mating system and reproductive success of black sea bream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii). Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 4483–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, S.T.; Taper, M.L.; Marshall, T.C. Revising how the computer program cervus accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. genalex 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudet, J. FSTAT, a program to estimate and test gene diversities and fixation indices, version 2.9. 3. Available online: http://www2.unil.ch/popgen/softwares/fstat.html (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Eecoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhir, K. GENETIX 4.05, logiciel Sous Windows TM Pour la génétique des Populations. Available online: http://www.genetix.univ-montp2.fr/genetix/genetix.html (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, D.A.; VonHoldt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A. CLUMPP: A cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, N.A. distruct: A program for the graphical display of population structure. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R.W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 32, 314–331. [Google Scholar]
- Umino, T.; Hayashi, M.; Miyatake, J.; Nakayama, K.; Sasaki, T.; Okada, K.; Nakagawa, H. Significance of release of black sea bream at 20-mm size on stock enhancement in Daiô Bay, Hiroshima. Suisanzoshoku 1999, 47, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Carson, E.W.; Bumguardner, B.W.; Fisher, M.; Saillant, E.; Gold, J.R. Spatial and temporal variation in recovery of hatchery-released red drum Sciaenops ocellatus in stock-enhancement of Texas bays and estuaries. Fish Res. 2014, 151, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Umino, T.; Hayashi, M.; Sasaki, T.; Okada, K. Changes in biochemical composition of black sea bream released at 20 mm size in Daio Bay, Hiroshima. Suisanzoshoku 2000, 48, 643–648. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Enriquez, R.; Takemura, M.; Tabata, K.; Taniguchi, N. Genetic diversity of red sea bream Pagrus major in western Japan in relation to stock enhancement. Fish. Sci. 2001, 67, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sánchez-Lamadrid, A. Effectiveness of releasing gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) for stock enhancement in the bay of Cádiz. Aquaculture 2004, 231, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryman, N.; Utter, F. Population Genetics & Fishery Management; The Blackburn Press: Caldwell, ID, USA, 1987; Volume 1990, pp. 141–159. [Google Scholar]
- Asahida, T.; Shinotsuka, Y.; Saitoh, K.; Tsuzaki, T.; Aritaki, M.; Yamashita, Y. Parental Contributions in a Japanese Flounder Hatchery Inferred from Mitochondrial DNA Haplotypes. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2004, 35, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D. The importance of identifying spatial population structure in restocking and stock enhancement programmes. Fish Res. 2006, 80, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-Schiaffino, G.; Dopico, E.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. Genetic variation losses in Atlantic salmon stocks created for supportive breeding. Aquaculture 2007, 264, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.H.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Lo, L.C.; Wang, C.M.; Lin, G.; Feng, F.; Pang, H.Y.; Li, J.; Gong, P.; Liu, H.M.; et al. Genetic variation and population structure of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) in the Asia-Pacific region. Aquaculture 2009, 293, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xia, J.-H.; Bai, Z.-Y.; Fu, J.-J.; Li, J.-L.; Yue, G.H. High genetic diversity and substantial population differentiation in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) revealed by microsatellite analysis. Aquaculture 2009, 297, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létourneau, J.; Ferchaud, A.L.; Le Luyer, J.; Laporte, M.; Garant, D.; Bernatchez, L. Predicting the genetic impact of stocking in Brook Charr (Salvelinus fontinalis) by combining RAD sequencing and modeling of explanatory variables. Evol. Appl. 2018, 11, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.S.; Umino, T.; Kuroda, K.; Hayashi, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Kang, J.C.; Morishima, K.; Arai, K. Genetic divergence and population structure of black sea bream Acanthopagrus schlegeli inferred from microsatellite analysis. Fish. Sci. 2003, 69, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, M.J.; McCauley, D.E. Extinction and recolonization: Their effects on the genetic differentiation of local populations. Evolution 1988, 42, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, G.; Bai, Z. Genetic variability in four wild and two farmed stocks of the Chinese freshwater pearl mussel (Hyriopsis cumingii) estimated by microsatellite DNA markers. Aquaculture 2009, 287, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, D.J. How well can captive breeding programs conserve biodiversity? A review of salmonids. Evol. Appl. 2008, 1, 535–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orita, R.; Nagano, Y.; Kawamura, Y.; Kimura, K.; Kobayashi, G. Genetic diversity and population structure of razor clam Sinonovacula constricta in Ariake Bay, Japan, revealed using RAD-Seq SNP markers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, J.; Maria Porta, J.; Cañavate, P.; Martínez-Rodríguez, G.; Carmen Alvarez, M. Substantial loss of genetic variation in a single generation of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) culture: Implications in the domestication process. J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Meng, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Genetic diversity and differentiation of the orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) between and within cultured stocks and wild populations inferred from microsatellite DNA analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 4378–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bert, T.M.; Crawford, C.R.; Tringali, M.D.; Seyoum, S.; Galvin, J.L.; Higham, M.; Lund, C. Genetic Management of Hatchery-Based Stock Enhancement. In Ecological and Genetic Implications of Aquaculture Activities; Bert, T.M., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 123–174. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Song, N.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Gao, T. Genetic diversity of swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) from four broodstock populations in stock enhancement inferred from mitochondrial control region. J. Fish. China 2014, 38, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, R.M.; Perez-Enriquez, R.; Takagi, M.; Taniguchi, N. Selective recovery of founder genetic diversity in aquacultural broodstocks and captive, endangered fish populations. Genetica 2001, 111, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Recaptured Sample | Broodstock | Mismatched Loci | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1706-042 | ♀23-♂17 | 0 | * |
| R1812-040 | ♀03 | 0 | * |
| Locus | Parameter | BP n = 54 | RP n = 200 | R1706 n = 50 | R1811 n = 79 | R1812 n = 40 | WP n = 48 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M320 | Na | 4.00 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 3.00 |
| Ne | 1.47 | 1.42 | 1.08 | 1.03 | 1.10 | 1.24 | |
| Ho | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.17 | |
| He | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.19 | |
| PIC | 0.30 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.18 | |
| Ar | 3.98 | 2.74 | 2.00 | 1.76 | 2.00 | 3.00 | |
| M414 | Na | 5.00 | 4.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 4.00 | 7.00 |
| Ne | 2.81 | 2.43 | 2.64 | 2.63 | 2.61 | 2.68 | |
| Ho | 0.76 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.58 | 0.55 | 0.65 | |
| He | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.63 | |
| PIC | 0.58 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.56 | |
| Ar | 5.00 | 3.96 | 4.80 | 4.51 | 4.00 | 6.50 | |
| M448 | Na | 15.00 | 10.00 | 15.00 | 14.00 | 13.00 | 14.00 |
| Ne | 8.03 | 6.56 | 9.73 | 7.90 | 9.28 | 9.52 | |
| Ho | 0.89 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.80 | 0.98 | 0.75 | |
| He | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.89 | |
| PIC | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.89 | |
| Ar | 14.06 | 8.38 | 14.35 | 11.96 | 13.00 | 13.75 | |
| M473 | Na | 7.00 | 3.00 | 5.00 | 6.00 | 5.00 | 12.00 |
| Ne | 2.33 | 2.17 | 2.78 | 2.63 | 2.62 | 3.88 | |
| Ho | 0.63 | 0.50 | 0.68 | 0.52 | 0.58 | 0.85 | |
| He | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.64 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.74 | |
| PIC | 0.54 | 0.48 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.72 | |
| Ar | 6.66 | 3.00 | 5.00 | 5.01 | 5.00 | 11.60 | |
| M478 | Na | 10.00 | 8.00 | 10.00 | 13.00 | 10.00 | 5.00 |
| Ne | 5.02 | 3.36 | 3.95 | 3.96 | 4.64 | 3.79 | |
| Ho | 0.76 | 0.52 | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.83 | 0.50 | |
| He | 0.80 | 0.70 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.74 | |
| PIC | 0.78 | 0.66 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.69 | |
| Ar | 9.20 | 6.18 | 9.16 | 10.14 | 10.00 | 5.00 | |
| M417 | Na | 4.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 7.00 |
| Ne | 2.89 | 2.26 | 2.53 | 2.27 | 2.75 | 3.96 | |
| Ho | 0.48 | 0.32 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 1.00 | |
| He | 0.65 | 0.56 | 0.61 | 0.56 | 0.64 | 0.75 | |
| PIC | 0.59 | 0.49 | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.57 | 0.71 | |
| Ar | 4.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 6.67 | |
| M454 | Na | 7.00 | 7.00 | 7.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 8.00 |
| Ne | 2.97 | 2.33 | 4.01 | 4.34 | 3.48 | 3.34 | |
| Ho | 0.37 | 0.45 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.38 | 0.25 | |
| He | 0.66 | 0.57 | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.70 | |
| PIC | 0.62 | 0.50 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.67 | 0.65 | |
| Ar | 6.72 | 4.60 | 6.92 | 5.88 | 6.00 | 7.61 | |
| Mean | Na | 7.43 | 5.43 | 6.71 | 7.00 | 6.29 | 8.00 |
| Ne | 3.65 | 2.93 | 3.82 | 3.54 | 3.78 | 4.06 | |
| Ho | 0.58 | 0.46 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.60 | |
| He | 0.65 | 0.59 | 0.62 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.66 | |
| PIC | 0.61 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.63 | |
| Ar | 7.09 | 4.55 | 6.46 | 6.04 | 6.29 | 7.73 |
| BP | RP | R1706 | R1811 | R1812 | WP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP | \ | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * |
| RP | 0.014 | \ | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * |
| R1706 | 0.036 | 0.068 | \ | 0.126 | 0.054 | 0.000 * |
| R1811 | 0.031 | 0.068 | 0.006 | \ | 0.324 | 0.000 * |
| R1812 | 0.018 | 0.057 | 0.010 | 0.005 | \ | 0.000 * |
| WP | 0.030 | 0.061 | 0.015 | 0.026 | 0.022 | \ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Weng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Hua, S.; Zhang, H.; Meng, Z. Genetic Evaluation of Black Sea Bream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii) Stock Enhancement in the South China Sea Based on Microsatellite DNA Markers. Fishes 2021, 6, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040047
Wang X, Weng Z, Yang Y, Hua S, Zhang H, Meng Z. Genetic Evaluation of Black Sea Bream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii) Stock Enhancement in the South China Sea Based on Microsatellite DNA Markers. Fishes. 2021; 6(4):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xi, Zhuoying Weng, Yang Yang, Sijie Hua, Hanfei Zhang, and Zining Meng. 2021. "Genetic Evaluation of Black Sea Bream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii) Stock Enhancement in the South China Sea Based on Microsatellite DNA Markers" Fishes 6, no. 4: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040047
APA StyleWang, X., Weng, Z., Yang, Y., Hua, S., Zhang, H., & Meng, Z. (2021). Genetic Evaluation of Black Sea Bream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii) Stock Enhancement in the South China Sea Based on Microsatellite DNA Markers. Fishes, 6(4), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040047