Effect of a Peracetic Acid-Based Disinfectant on Growth, Hematology and Histology of Juvenile Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bacterial Load in Fish Skin and Water Column
2.2. Growth Performances
2.3. Hematological Findings
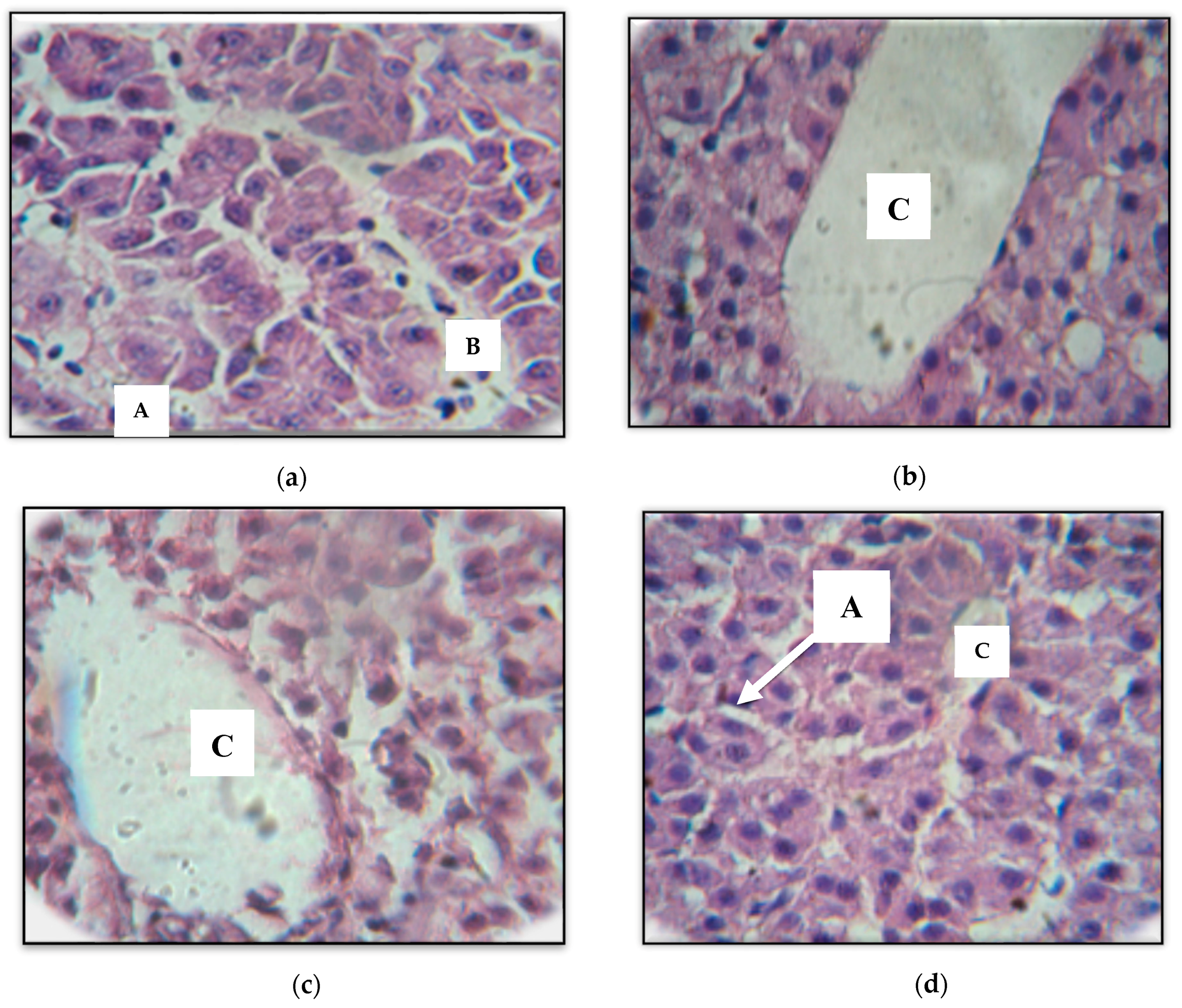
2.4. Histological Findings
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Treatment of Fish
4.2. Growth Performance
4.3. Hematological Assays
4.4. Quantification of Bacterial Load of Fish Skin and Water Column
4.5. Histological Studies
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Fisheries and Aquaculture Statistics; FAO Year Book; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017; p. 78. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D. Bacterial Fish Pathogens—Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish; Springer: London, UK, 2007; p. 512. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, L.F.; Pedersen, P.B. Hydrogen peroxide application to a commercial recirculating aquaculture system. Aquacult. Eng. 2012, 46, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, S.S. Peroxygen compounds. In Disinfection, Sterilization, and Preservation, 5rd ed.; Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins Publishers: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1991; pp. 185–205. [Google Scholar]
- Straus, D.L.; Meinelt, T.; Farmer, B.D.; Mitchell, A.J. Peracetic acid is effective for controlling fungus on channel catfish eggs. J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straus, D.L.; Meinelt, T.; Farmer, B.D.; Beck, B.H. Acute toxicity and histopathology of channel catfish fry exposed to peracetic acid. Aquaculture 2012, 342, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, L.F.; Meinelt, T.; Straus, D.L. Peracetic acid degradation in freshwater aquaculture systems and possible practical implications. Aquacult. Eng. 2013, 53, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldry, M.G.C.; Fraser, J.A.L. Disinfection with peroxygens. In Industrial Biocides; Payne, K.R., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1988; pp. 91–116. [Google Scholar]
- Monarca, S.; Richardson, S.D.; Feretti, D.; Grottolo, M.; Thruston, A.D.; Zani, C.; Navazio, G.; Ragazzo, P.; Zerbini, I.; Alberti, A. Mutagenicity and disinfection by-products in surface drinking water disinfected with peracetic acid. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinelt, T.; Matzke, S.; Stüber, A.; Pietrock, M.; Wienke, A.; Mitchell, A.J.; Straus, D.L. Toxicity of peracetic acid (PAA) to tomonts of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2009, 86, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudová, S.; Straus, D.L.; Wienke, A.; Meinelt, T. Evaluation of continuous 4-day exposure to peracetic acid as treatment for Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. J. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 106, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, P.A.; Phan, T.M.; Straus, D.L.; Farmer, B.D.; Stüber, A.; Meinelt, T. Reduction of in vitro growth in Flavobacterium columnare and Saprolegnia parasitica by products containing peracetic acid. Aquacult. Res. 2012, 43, 1861–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinelt, T.; Phan, T.M.; Behrens, S.; Wienke, A.; Pedersen, L.F.; Liu, D.; Straus, D.L. Growth inhibition of Aeromonas salmonicida and Yersinia ruckeri by disinfectants containing peracetic acid. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 113, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Behrens, S.; Pedersen, L.F.; Straus, D.L.; Meinelt, T. Peracetic acid is a suitable disinfectant for recirculating fish-microalgae integrated multi-trophic aquaculture systems. Aquacult. Rep. 2016, 4, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Straus, D.L.; Pedersen, L.F.; Meinelt, T. Periodic bacterial control with peracetic acid in a recirculating aquaculture system and its long-term beneficial effect on fish health. Aquaculture 2018, 485, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshangi, R.; Soltani, M.; Hosseini Shekarabi, S.P. Determination of Aquastart median lethal dose (LC50) as a disinfectant agent and study of the gill pathological effects on fry rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Pathobiol. 2017, 14, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar]
- Kitis, M. Disinfection of wastewater with peracetic acid: A review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Straus, D.L.; Pedersen, L F.; Meinelt, T. Pulse versus continuous peracetic acid applications: Effects on rainbow trout performance, biofilm formation and water quality. Aquacult. Eng. 2017, 77, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulsford, A.L.; Lemaire-Gony, S.; Tomlinson, M.; Collingwood, N.; Glynn, P.J. Effects of acute stress on the immune system of the dab, Limanda limanda. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1994, 109, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groff, J.M.; Zinkl, J.G. Hematology and clinical chemistry of cyprinid fish: Common carp and goldfish. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 1999, 2, 741–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.; Bromage, N. Intensive Fish Farming; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1992; p. 416. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.H.; Shiau, S.Y. Dietary lipid requirement of grouper Epinephelus malabaricus, and effects on immune responses. Aquaculture 2003, 225, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxhall, P.C.; Daisley, K.W. Routine haematological methods for use with fish blood. Fish Biol. 1973, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.W.; Davey, F.R. Basic examination of blood. In Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods; Henry, J.B., Ed.; Saunders Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996; pp. 549–593. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, L. Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics; TH-Books Verlagsgesellschaft Publisher: Frankfurt, Germany, 1998; p. 1527. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, S.A.; Reza, M.S.; Sharker, M.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.A. Effectiveness of oxytetracycline in reducing the bacterial load in rohu fish (Labeo rohita, Hamilton) under laboratory culture condition. J. Coast. Life Med. 2014, 2, 259–263. [Google Scholar]
- Cardiff, R.D.; Miller, C.H.; Munn, R.J. Manual hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse tissue sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2014, 4, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Experimental Group | Time | Microbial Population | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Column (CFU/mL) | Fish Skin (CFU/cm2) | ||
| Control | Before exposure | 8.3 × 103 ± 1.3 × 102 a | 2.4 × 106 ± 2.2 × 104 a |
| Treated trout | Before exposure | 6.8 × 103 ± 6.6 × 10 c | 2.0 × 106 ± 1.1 × 104 b |
| Control | After exposure | 8.5 × 103 ± 3.4 × 102 a | 2.5 × 10 ± 2.2 × 104 a |
| Treated trout | After exposure | 7.5 × 10 ± 3.5 × 10 d | 1.2 × 104 ± 4.2 × 102 c |
| Experimental Group | FCR | SGR (%) | BWG (%) | CF (%) | SR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.43 ± 0.77 | 0.745 ± 0.01 | 29.97 ± 1.09 | 1.22 ± 0.14 | 53.33 ± 1.92 b |
| Treated trout | 1.52 ± 0.13 | 0.723 ± 0.09 | 28.47 ± 1.12 | 1.13 ± 0.13 | 70.00 ± 1.33 a |
| Control | Treatment after 30 min Exposure | After 60 Days | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Treated Trout | |||
| HCT (%) | 30.45 ± 0.71 d | 40.40 ± 0.85 a | 32.45 ± 0.63 c | 38.50 ± 0.71 b |
| Hb (g/d) | 9.82 ± 0.25 d | 13.47 ± 0.28 a | 10.82 ± 0.21 c | 12.83 ± 0.24 b |
| RBC (106 cells/mL) | 4.91 ± 0.13 d | 6.73 ± 0.14 a | 5.41 ± 0.11 c | 6.42 ± 0.12 b |
| MCV (fL) | 59.75 ± 0.35 a | 59.78 ± 0.32 a | 59.75 ± 0.35 a | 59.75 ± 0.35 a |
| MCH (pg) | 19.80 ± 0.00 b | 20.00 ± 0.00 a | 20.00 ± 0.00 a | 19.95 ± 0.07 a |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 32.97 ± 0.52 a | 32.67 ± 0.94 a | 33.17 ± 0.24 a | 33.17 ± 0.24 a |
| WBC (106 cells/mL) | 7.55 ± 0.64 d | 12.50±0.85a | 8.60 ± 0.85 c | 10.50 ± 0.71 b |
| Neut (%) | 9.50 ± 0.71 b | 4.60 ± 0.23 d | 17.35 ± 0.78 a | 8.50 ± 0.71 c |
| Lymp (%) | 90.00 ± 1.44 c | 94.50 ± 0.90 a | 83.50 ± 0.87 d | 92.50 ± 1.05 b |
| Mono (%) | 1.50 ± 0.71a | 1.50 ± 0.71 a | N/A | N/A |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hushangi, R.; Hosseini Shekarabi, S.P. Effect of a Peracetic Acid-Based Disinfectant on Growth, Hematology and Histology of Juvenile Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fishes 2018, 3, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3010010
Hushangi R, Hosseini Shekarabi SP. Effect of a Peracetic Acid-Based Disinfectant on Growth, Hematology and Histology of Juvenile Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fishes. 2018; 3(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleHushangi, Ramtin, and Seyed Pezhman Hosseini Shekarabi. 2018. "Effect of a Peracetic Acid-Based Disinfectant on Growth, Hematology and Histology of Juvenile Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)" Fishes 3, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3010010
APA StyleHushangi, R., & Hosseini Shekarabi, S. P. (2018). Effect of a Peracetic Acid-Based Disinfectant on Growth, Hematology and Histology of Juvenile Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fishes, 3(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3010010





