Rearing Time–Salinity Synergy in Osmoregulation: Ionic Homeostasis and Textural Enhancement in Adult Freshwater Drums (Aplodinotus grunniens)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish and Rearing Conditions
2.2. Determination of Growth Performance
2.3. Determination of Osmotic Pressure Analysis
2.4. Determination of Serum Biochemical Indices
2.5. Determination of Water-Holding Capacity Analysis
2.6. Determination of Texture Profile Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
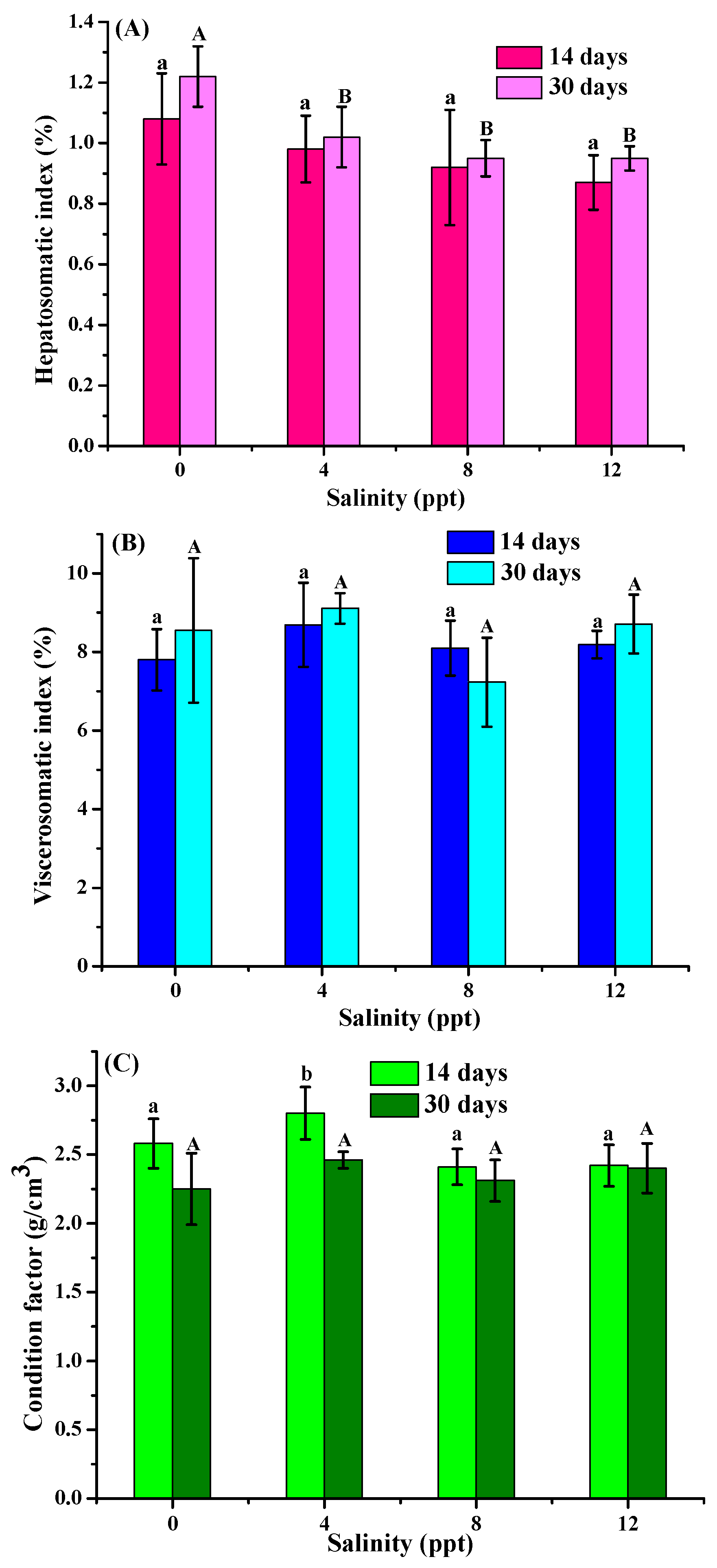
3.1. Morphological Index Analysis
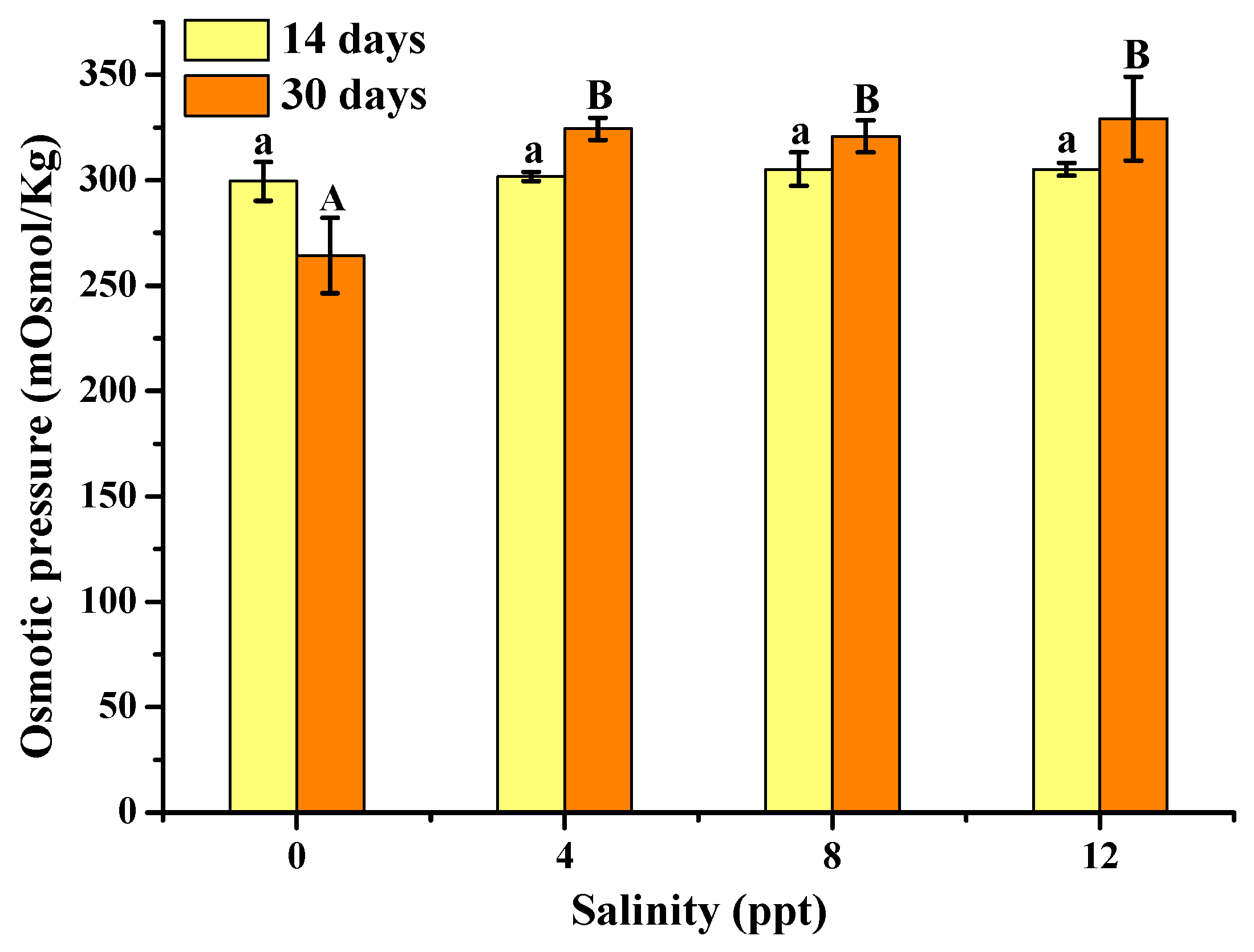
3.2. Osmotic Pressure Analysis
3.3. Serum Biochemical Indices Analysis
3.4. Inorganic Ion Analysis
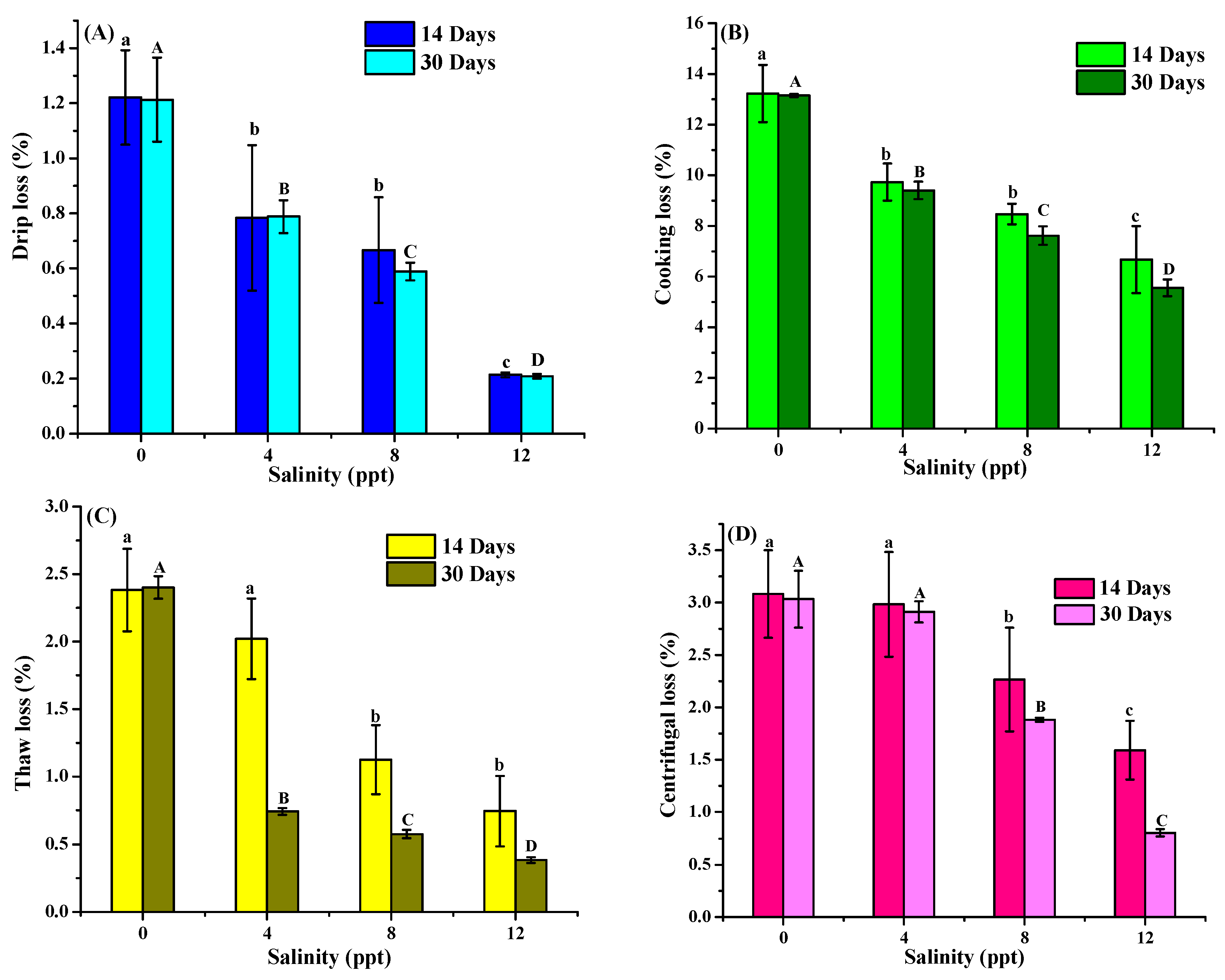
3.5. Water-Holding Capacity Analysis
3.6. Texture Profile Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Ahmed, H.A.; Shukry, M.; Khafaga, A.F.; Elkhayat, B.K.; Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Abd-elaziz, R.A. Growth performance, physiological responses, and histoarchitectural changes in juvenile pangasianodon hypophthalmus under different environmental salinities. Fishes 2023, 8, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wu, X.M.; Zheng, S.Y.; Song, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Chang, M.X. Effects and molecular regulation mechanisms of salinity stress on the health and disease resistance of grass carp. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 917497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soegianto, A.; Adhim, M.d.H.; Zainuddin, A.; Putranto, T.W.C.; Irawan, B. Effect of different salinity on serum osmolality, ion levels and hematological parameters of east java strain tilapia oreochromis niloticus. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2017, 50, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, B.C.; Enders, E.C.; Anderson, G.W. A salt on your senses: Influences of rearing environment on salinity preference and sensing in lake trout salvelinus namaycush. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2023, 106, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Dong, X.; Fu, Y.; Xie, X.; Miao, S. The impact of rearing salinity on flesh texture, taste, and fatty acid composition in largemouth bass micropterus salmoides. Foods 2022, 11, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Monroig, O.; Zhou, Q.; Tocher, D.R.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, T.; Lu, J.; Song, D.; Jiao, L.; Jin, M. Environmental salinity and dietary lipid nutrition strategy: Effects on flesh quality of the marine euryhaline crab scylla paramamosain. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharani, M.; Nayak, B.B.; Xavier, K.A.M.; Layana, P.; Balange, A.K. Meat quality assessment of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) reared in inland saline water. Indian J. Fish. 2024, 71, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wen, H.; Liu, G.; Ma, X.; Lv, G.; Wu, N.; Chen, J.; Xue, M.; Li, H.; Xu, P. Gut microbes reveal pseudomonas medicates ingestion preference via protein utilization and cellular homeostasis under feed domestication in freshwater drum, aplodinotus grunniens. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1259988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amankwah, J.F.; Jin, W.; Ma, X.; Xu, P.; Wen, H.; Amuneke, K.E.; Munganga, B.P.; Li, K.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Salinity tolerance in freshwater drum (Aplodinotus grunniens): Investigating biochemical, antioxidant, digestive enzyme, and gene expression responses to acute salinity stress. Animals 2025, 15, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, M.; Inanan, B.E.; Karasahin, T.; Dikel, S. Effects of glutamine on growth performance, nutrient content, fatty acid profile, and blood parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Fish Biol. 2024, 104, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Hong, G.-P. Comparison of superchilling and supercooling on extending the fresh quality of beef loin. Foods 2022, 11, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, B.; Kong, B.; Xia, X.; Bao, Y. Impact of ultrasound-assisted saline thawing on the technological properties of mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 86, 106014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Yun, Y.; Mi, J.; Luo, J.; Jin, M.; Nie, G.; Zhou, Q. Effects of faba bean on growth performance and fillet texture of yellow river carp, cyprinus carpio haematopterus. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningsih, L.; Sulmartiwi, L.; Lutfiyah, L. The profile of carassius auratus growth and hepatosomatic index in different salinity. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 441, 012114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Lu, Y.; Lai, W.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Effects of salinity on growth, physiology, biochemistry and gut microbiota of juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 258, 106482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghaed, A.T.; Ghelichpour, M. Effects of anesthesia and salt treatment on stress responses, and immunological and hydromineral characteristics of common carp (Cyprinus carpio, linnaeus, 1758) subjected to transportation. Aquaculture 2019, 501, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, B.P.; Lerner, D.T.; Grau, E.G.; Seale, A.P. The effects of acute salinity challenges on osmoregulation in mozambique tilapia reared in a tidally changing salinity. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, M.A.; Glover, C.N. Effect of salinity on osmoregulation, metabolism and nitrogen excretion in the amphidromous fish, inanga (Galaxias maculatus). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 473, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordlie, F.G. Environmental influences on regulation of blood plasma/serum components in teleost fishes: A review. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2009, 19, 481–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavya, K.S.; Kulkarni, R.S.; Jadesh, M. Some blood biochemical changes in response to saline exposure in the fresh water fish, notopterus notopterus (Pallas). Int. Lett. Nat. Sci. 2015, 49, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahirwal, S.K.; Das, P.C.; Sarma, K.; Kumar, T.; Singh, J.; Kamble, S.P. Effect of salinity changes on growth, survival and biochemical parameters of freshwater fish Gibelion catla (Hamilton, 1822). J. Environ. Biol. 2021, 42, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahim, M.M.; Lotfy, A.M.; Toutou, M.M.; Aly, H.A.; Sallam, G.R.; Abdelaty, B.S.; Helal, A.M. Effects of salinity level on the survival, growth, feed utilization, carcass composition, haematological and serum biochemical changes of juvenile meagre (Argyrosomus regius) (asso, 1801) grown in ground saltwater. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Alvarez, R.M.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Domezain, A.; Morales, A.E.; García-Gallego, M.; Sanz, A. Physiological changes of sturgeon acipenser naccarii caused by increasing environmental salinity. J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 3699–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imanpoor, M.R.; Najafi, E.; Kahir, M. Effect of different salinity and temperatures on the growth, survival, hematocrit, and serum biochemistry of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonas, C.C.; Pavlidis, M.; Papandroulakis, N.; Zaiss, M.M.; Tsafarakis, D.; Papadakis, I.E.; Varsamos, S. Growth performance and osmoregulation in the shi drum (Umbrina cirrosa) adapted to different environmental salinities. Aquaculture 2009, 287, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Mu, C.; Shi, C.; Liu, L. Effects of light intensity on growth performance, biochemical composition, fatty acid composition and energy metabolism of scylla paramamosain during indoor overwintering. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-H.; Cheng, M.-L.; Lo, C.-J.; Fan, C.-M.; Wu, Y.-R.; Chen, C.-M. Alternations of lipoprotein profiles in the plasma as biomarkers of huntington’s disease. Cells 2023, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Tsujino, T.; Masuyama, T.; Ishihara, M. Crosstalk between iron and arteriosclerosis. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2022, 29, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroldogan, O.T.; Kumlu, M. Growth performance, body traits and fillet composition of the european sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) reared in various salinities and fresh water. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2002, 26, 993–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, P.T.; Huon, D.T.T. The osmoregulation and growth of hybrid yellow catfish juvenile (Clarias macrocephalus gunther x Clarias gariepinus) exposed to the different salinities. Can Tho Univ. J. Sci. 2011, 20, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ge, J.; Davis, D.A.; Dong, Y.; Gao, Q.; Dong, S. Growth, serum biochemical parameters, salinity tolerance and antioxidant enzyme activity of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in response to dietary taurine levels. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.; Qi, T.; Xi, R.; Li, L.; Tang, R.; Li, D. Slight increases in salinity improve muscle quality of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Fishes 2012, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Chen, Z.; Qin, J.; Huang, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, C.; Pan, X.; Lin, Y. Effects of salinity on muscle nutrition, fatty acid composition, and substance anabolic metabolism of blue tilapia oreochromis aureus. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2024, 2024, 5549406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Serum Biochemical Indices | Salinity (ppt) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 Days | 0 | 4 | 8 | 12 |
| Total protein (g/L) | 52.6 ± 4.47 a | 37.96 ± 11.75 b | 36.80 ± 0.17 b | 41.2 ± 2.95 ab |
| Albumin (g/L) | 15.96 ± 0.92 a | 11.13 ± 3.82 b | 10.83 ± 0.15 b | 12.43 ± 0.47 ab |
| Globulin (g/L) | 36.66 ± 3.74 a | 26.83 ± 7.95 b | 25.96 ± 0.25 b | 28.76 ± 2.63 ab |
| Albumin/Globulin | 0.43 ± 0.02 a | 0.41 ± 0.03 a | 0.41 ± 0.01 a | 0.43 ± 0.02 a |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 7.89 ± 1.86 a | 3.09 ± 1.02 b | 3.35 ± 0.63 b | 1.72 ± 0.23 b |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 11.93 ± 1.36 a | 8.11 ± 1.36 b | 6.89 ± 0.67 b | 8.96 ± 1.05 b |
| High-density lipoprotein (mmol/L) | 1.68 ± 0.18 a | 1.67± 0.02 a | 1.51 ± 0.06 a | 2.15 ± 0.28 b |
| Low-density lipoprotein (mmol/L) | 1.76 ± 0.41 a | 1.00 ± 0.30 b | 0.79 ± 0.26 b | 1.06 ± 0.18 b |
| Arteriosclerosis index | 6.16 ± 1.45 a | 3.86 ± 0.90 b | 3.56 ± 0.28 b | 3.16 ± 0.15 b |
| Serum Biochemical Indices | Salinity (ppt) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 Days | 0 | 4 | 8 | 12 |
| Total protein (g/L) | 40.60 ± 8.77 a | 33.23 ± 5.76 a | 35.80 ± 14.12 a | 40.26 ± 5.02 a |
| Albumin (g/L) | 12.40 ± 3.29 a | 9.60 ± 1.73 a | 10.53 ± 4.57 a | 12.00 ± 0.96 a |
| Globulin (g/L) | 28.20 ± 5.49 a | 23.63 ± 4.09 a | 25.26 ± 9.57 a | 28.26 ± 4.14 a |
| Albumin/Globulin | 0.43 ± 0.03 a | 0.40 ± 0.02 a | 0.41 ± 0.03 a | 0.42 ± 0.03 a |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 4.62 ± 1.53 a | 3.45 ± 1.73 a | 2.48 ± 1.02 a | 2.14 ± 0.83 a |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 8.07 ± 3.50 a | 7.24 ± 1.58 a | 6.00 ± 3.26 a | 8.17 ± 0.61 a |
| High-density lipoprotein (mmol/L) | 0.74 ± 0.24 a | 1.73 ± 0.17 b | 1.54 ± 0.44 b | 2.08 ± 0.17 b |
| Low-density lipoprotein (mmol/L) | 0.90 ± 0.50 a | 0.85 ± 0.28 a | 0.90 ± 0.83 a | 1.01 ± 0.24 a |
| Arteriosclerosis index | 9.83 ± 2.02 a | 3.23 ± 1.23 b | 2.76 ± 0.92 b | 2.96 ± 0.55 b |
| Inorganic Ions (mmol/L) | Salinity (ppt) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 days | 0 | 4 | 8 | 12 |
| Potassium | 1.36 ± 0.43 a | 1.43 ± 0.66 a | 0.92 ± 0.30 a | 0.95 ± 0.50 a |
| Sodium | 167.20 ± 19.29 a | 151.56 ± 17.06 a | 148.83 ± 15.94 a | 164.20 ± 16.62 a |
| Chlorine | 119.63 ± 19.71 a | 122.00 ± 13.09 a | 125.03 ± 15.63 a | 135.36 ± 15.88 a |
| Calcium | 4.19 ± 0.22 a | 2.83 ± 0.39 b | 2.60 ± 0.30 b | 2.82 ± 0.29 b |
| Phosphate | 3.07 ± 0.75 a | 2.46 ± 0.39 ab | 1.94 ± 0.07 b | 1.89 ± 0.19 b |
| Magnesium | 2.03 ± 0.15 a | 1.43 ± 0.19 b | 1.19 ± 0.12 b | 1.32 ± 0.14 b |
| Inorganic Ions (mmol/L) | Salinity (ppt) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 days | 0 | 4 | 8 | 12 |
| Potassium | 1.09 ± 0.38 a | 0.86 ± 0.35 a | 1.00 ± 0.20 a | 1.46 ± 1.09 a |
| Sodium | 130.00 ± 19.96 a | 151.10 ± 21.77 a | 161.13 ± 38.48 a | 161.36 ± 12.87 a |
| Chlorine | 53.10 ± 13.58 a | 115.63 ± 18.36 b | 124.46 ± 30.83 b | 127.76 ± 12.80 b |
| Calcium | 3.45 ± 0.70 a | 2.55 ± 0.38 a | 2.88 ± 1.17 a | 3.16 ± 0.39 a |
| Phosphate | 2.85 ± 0.83 a | 2.11 ± 0.60 a | 2.92 ± 0.98 a | 2.36 ± 0.34 a |
| Magnesium | 1.83 ± 0.47 a | 1.55 ± 0.31 a | 1.57 ± 0.48 a | 1.64 ± 0.24 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miraji, S.M.; Chen, W.; Wen, H.; Wang, L.; Jin, W.; Ma, X.; Xu, P.; Cheng, H. Rearing Time–Salinity Synergy in Osmoregulation: Ionic Homeostasis and Textural Enhancement in Adult Freshwater Drums (Aplodinotus grunniens). Fishes 2025, 10, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090437
Miraji SM, Chen W, Wen H, Wang L, Jin W, Ma X, Xu P, Cheng H. Rearing Time–Salinity Synergy in Osmoregulation: Ionic Homeostasis and Textural Enhancement in Adult Freshwater Drums (Aplodinotus grunniens). Fishes. 2025; 10(9):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090437
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiraji, Sharifa Mohamed, Wanwen Chen, Haibo Wen, Liufu Wang, Wu Jin, Xueyan Ma, Pao Xu, and Hao Cheng. 2025. "Rearing Time–Salinity Synergy in Osmoregulation: Ionic Homeostasis and Textural Enhancement in Adult Freshwater Drums (Aplodinotus grunniens)" Fishes 10, no. 9: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090437
APA StyleMiraji, S. M., Chen, W., Wen, H., Wang, L., Jin, W., Ma, X., Xu, P., & Cheng, H. (2025). Rearing Time–Salinity Synergy in Osmoregulation: Ionic Homeostasis and Textural Enhancement in Adult Freshwater Drums (Aplodinotus grunniens). Fishes, 10(9), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090437








