Biodiversity Assessment of the Ancient Submerged Port of Egnazia (Southern Adriatic Sea, Mediterranean Sea): New Evidence for Conservation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
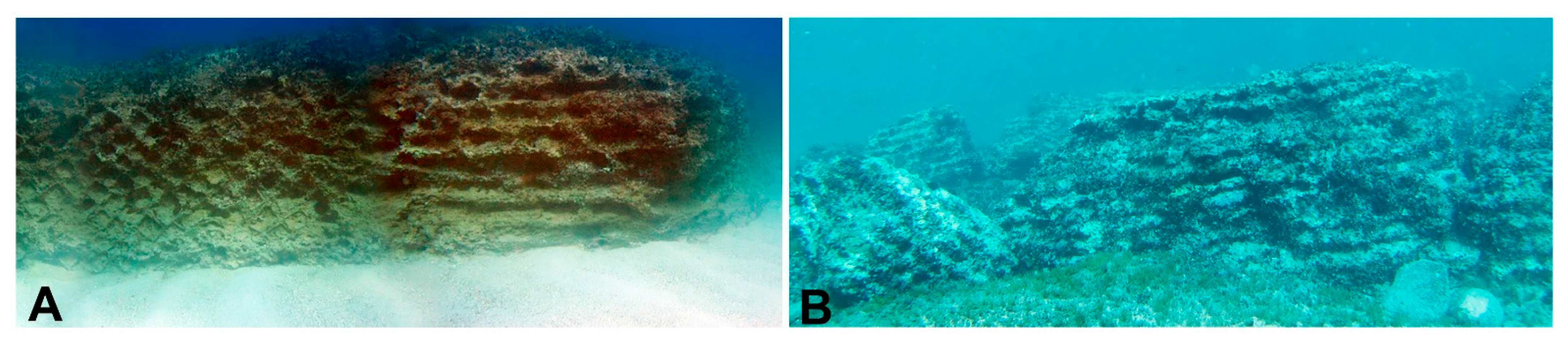
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Data Analysis
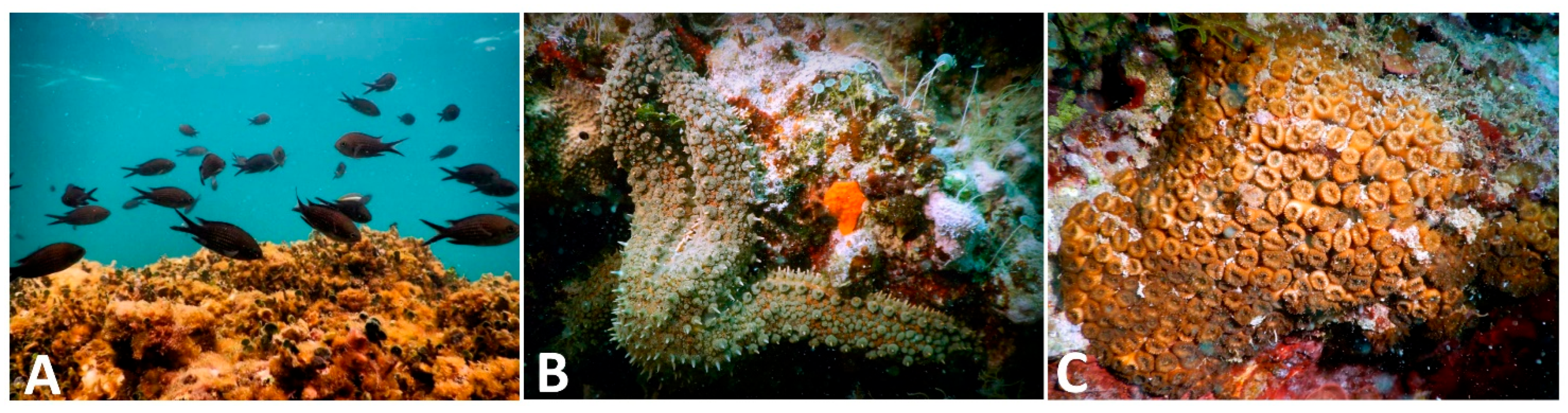
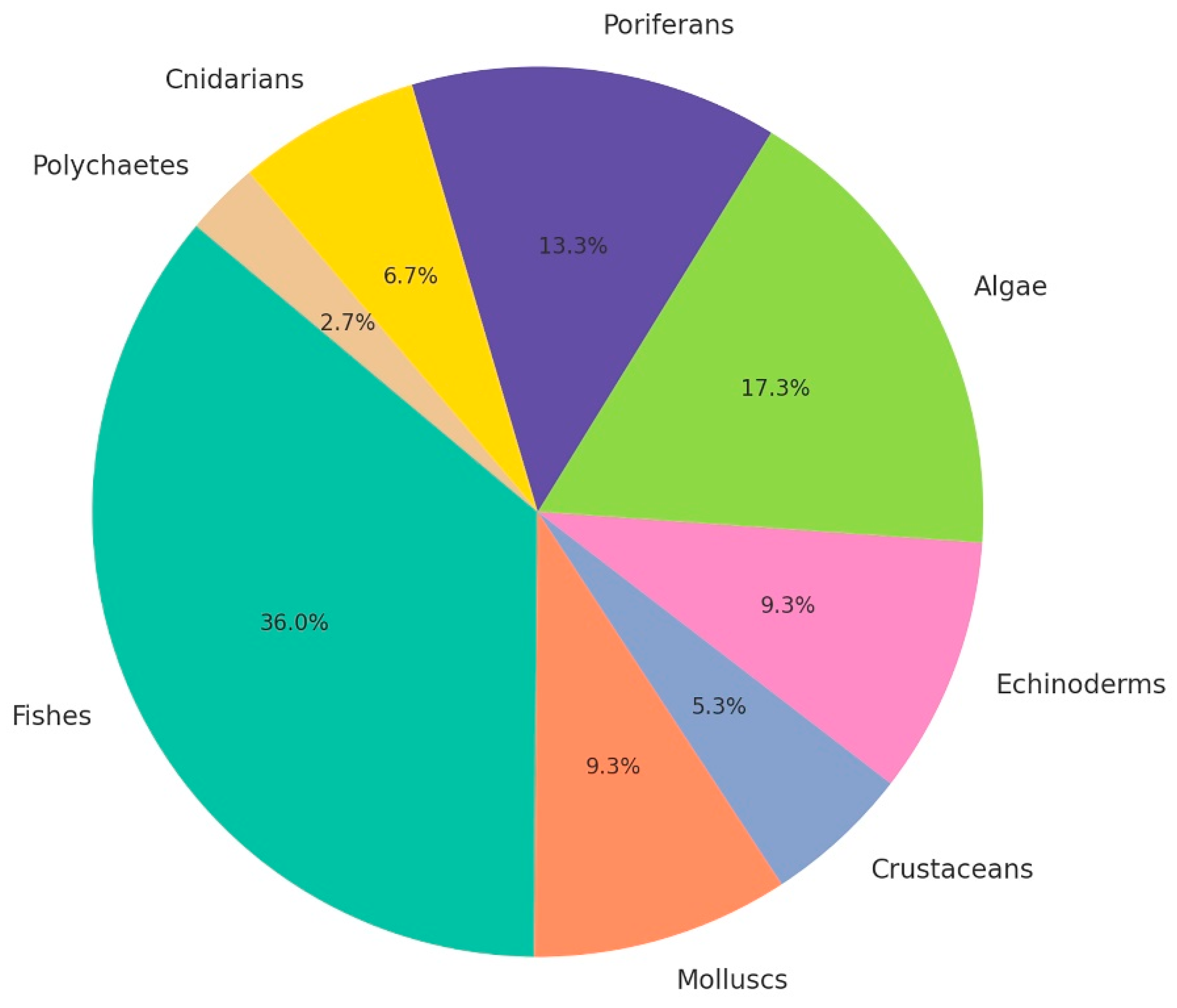
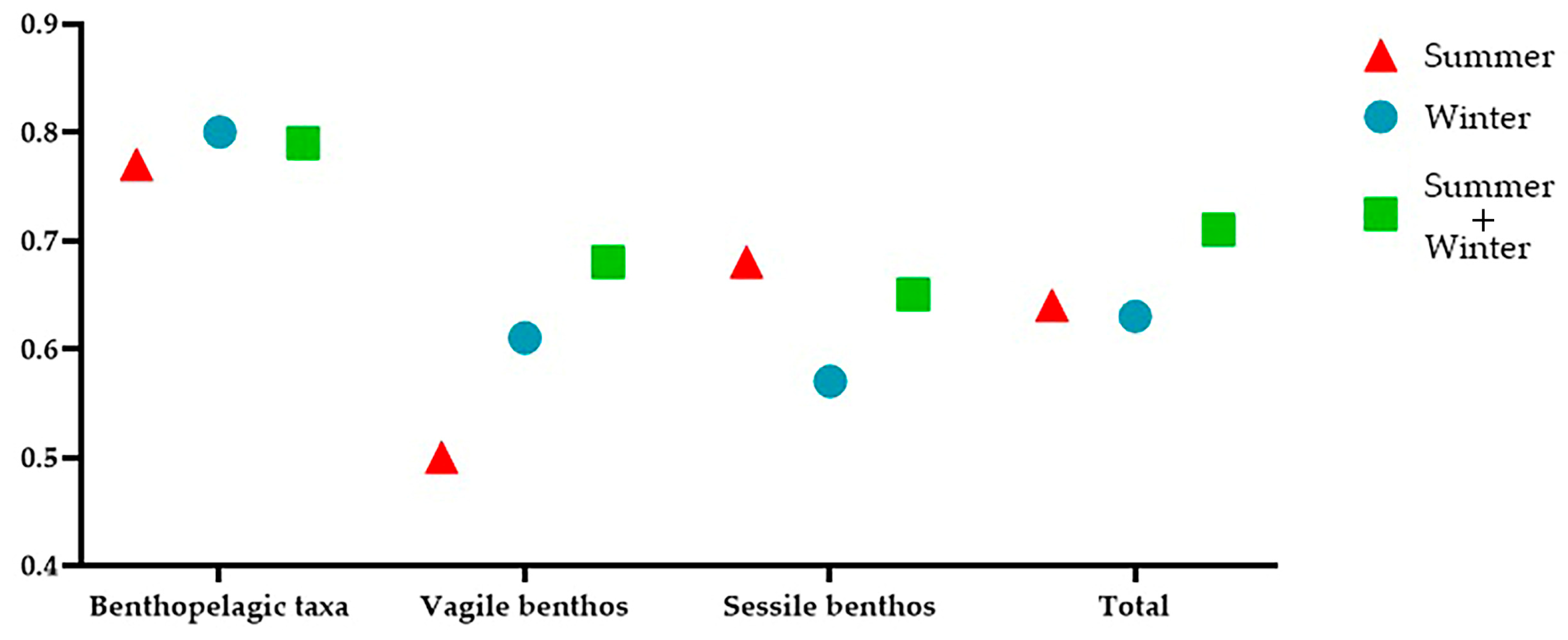
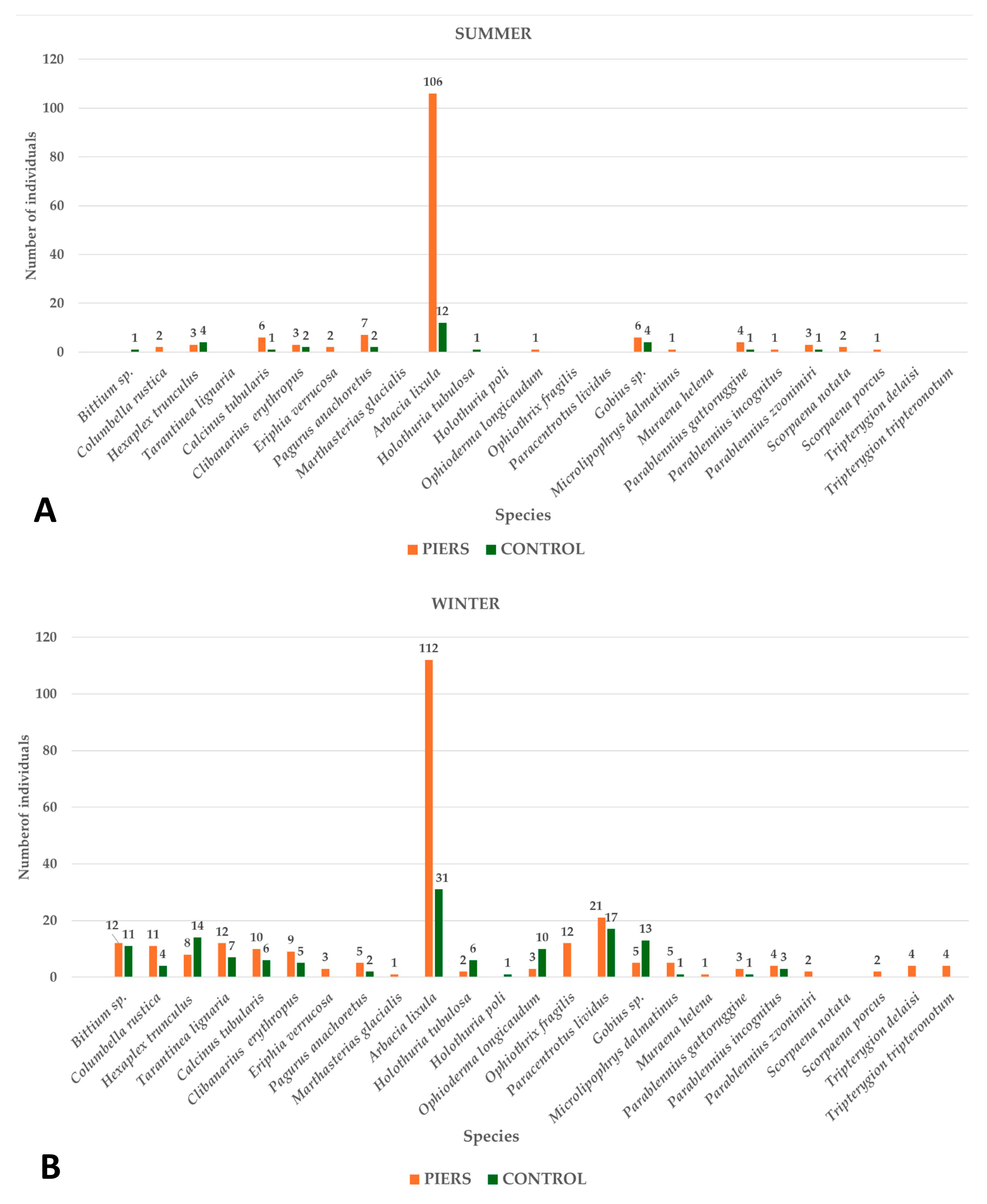
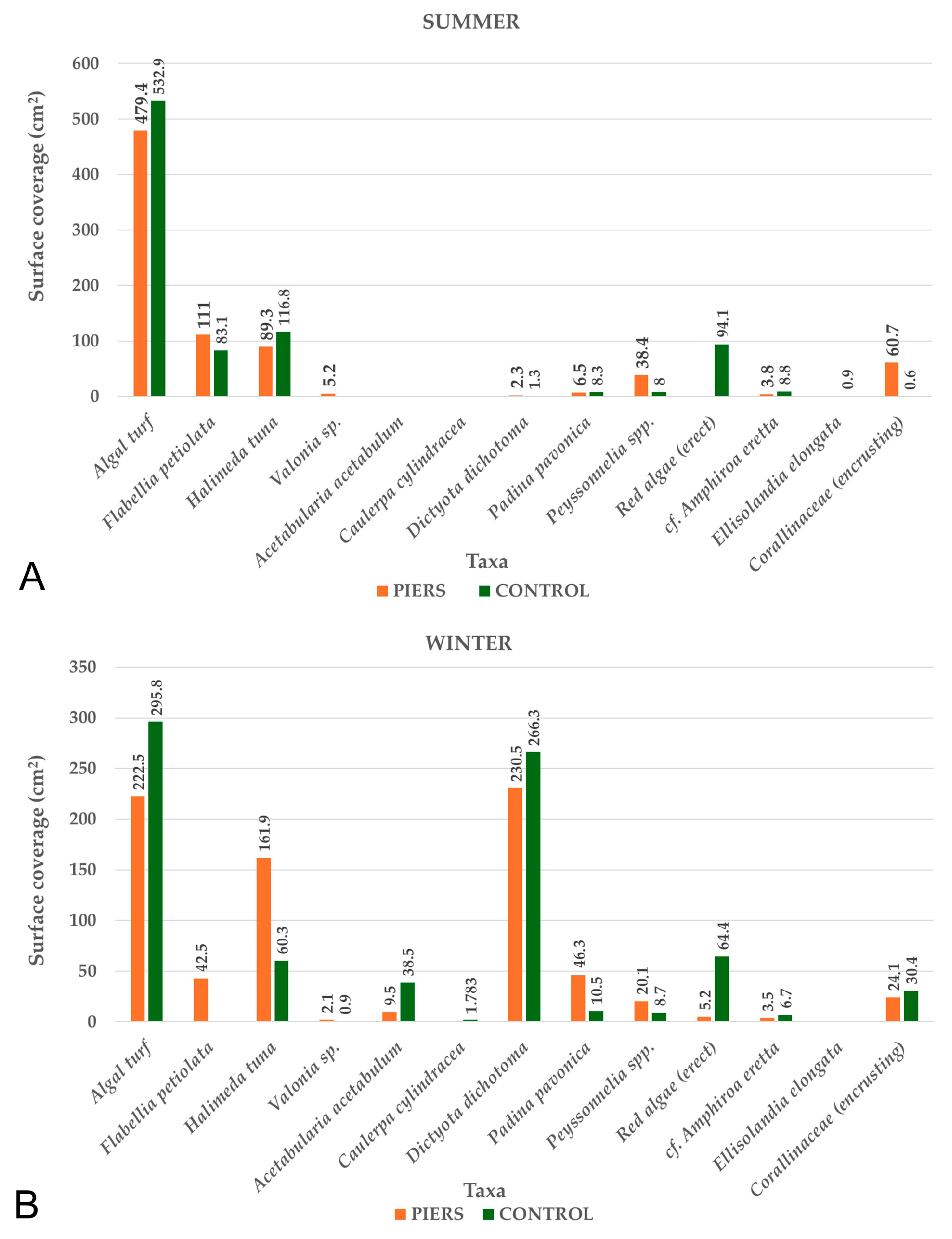
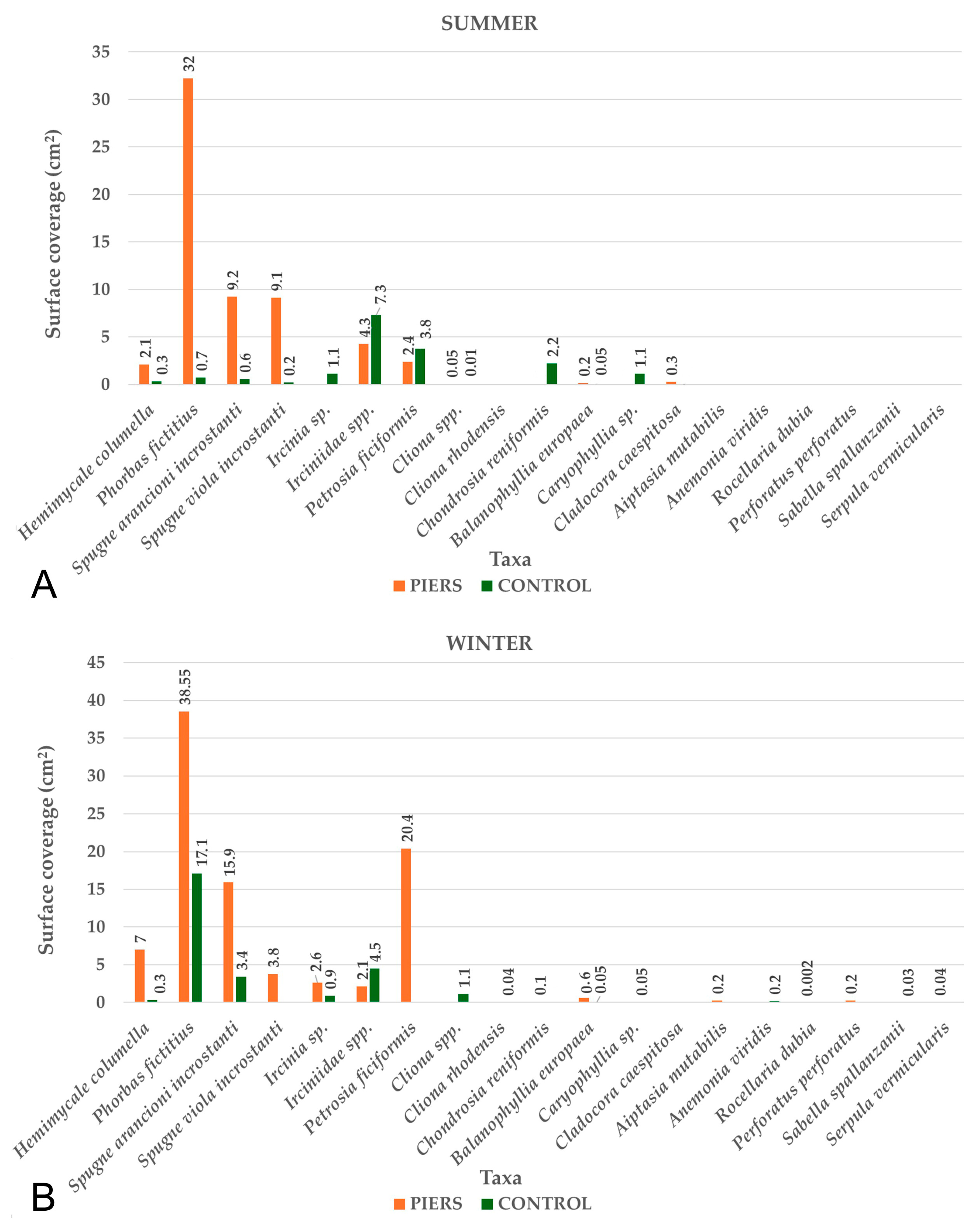
3. Results
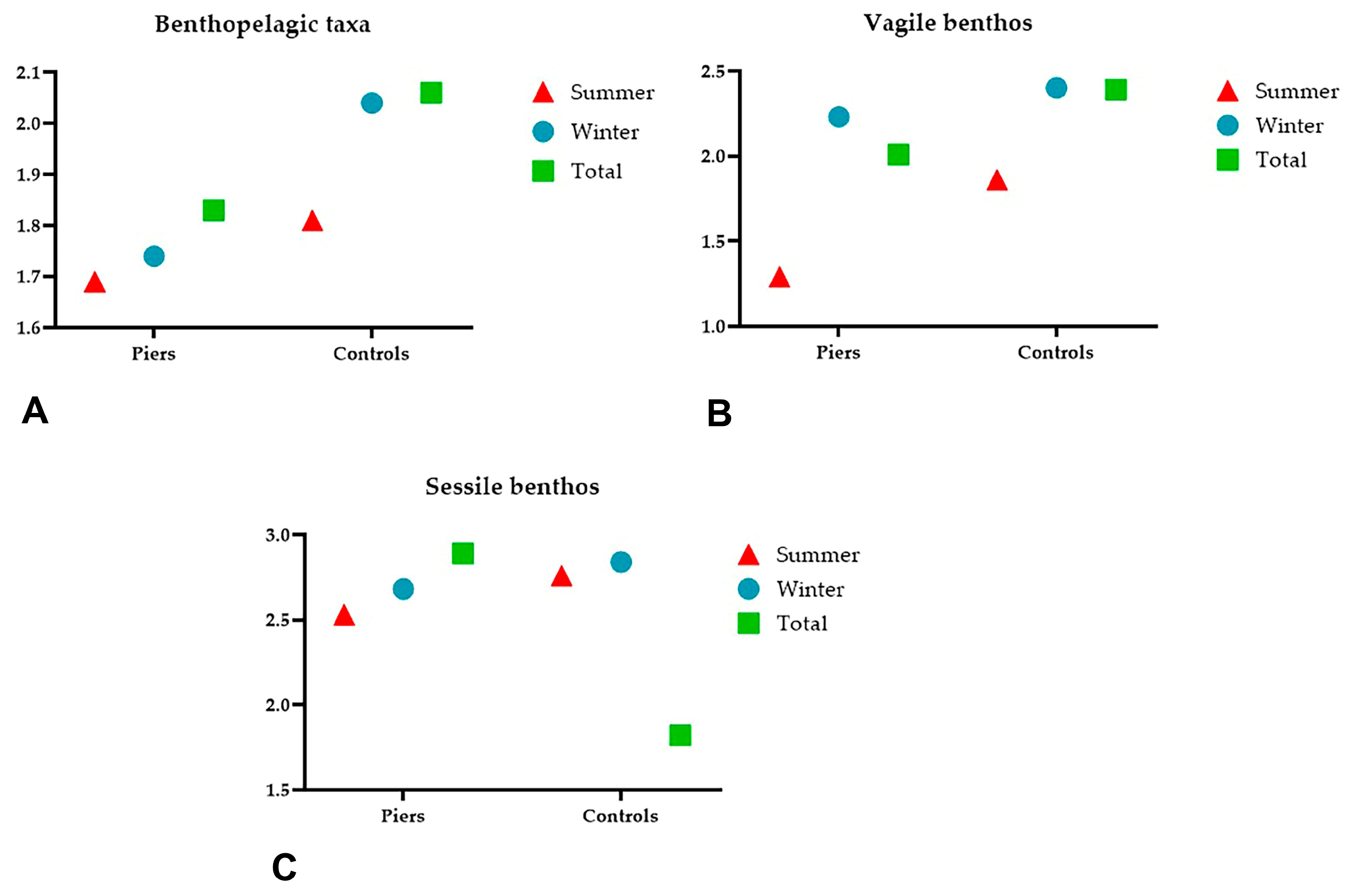
3.1. Benthopelagic Community
3.2. Vagile Benthic Community
3.3. Sessile Benthic Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNESCO. Convention on the Protection of the Underwater Cultural Heritage; UNESCO Publication: London, UK, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrakis, G.; Bonazza, A.; Bruno, F.; Ricca, M. A sustainable approach for the management and valorization of underwater cultural heritage: New perspectives from the TECTONIC project. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5000. [Google Scholar]
- Erlandson, J.M.; Rick, T.C. Archaeology meets marine ecology: The antiquity of maritime cultures and human impacts on marine fisheries and ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 231–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop Ristova, P.; Bienhold, C.; Wenzhöfer, F.; Rossel, P.E. Temporal and spatial variations of bacterial and faunal communities associated with deep-sea wood falls. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consoli, P.; Romeo, T.; Battaglia, P.; Castriota, L.; Esposito, V.; Andaloro, F. The effect of shipwrecks on associated fish assemblages in the central Mediterranean Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K. 2015, 95, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, M.I.; Torres, P.; Díaz, C.; Zamora, V.; López, J.; Olivares, G. Ecological succession of benthic organisms on niche-type artificial reefs. Ecol. Process. 2020, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, A.P.M.; Ferreira, B.P. Centenary shipwrecks reveal the limits of artificial habitats in protecting regional reef fish diversity. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, J.; Richards, J.; Rees, A.; Sheehan, E.V. Shipwrecks act as de facto Marine Protected Areas in areas of heavy fishing pressure. Mar. Ecol. 2024, 45, e1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco Perasso, C.; Antonelli, F.; Calcinai, B. The bioerosion of submerged archaeological artifacts in the Mediterranean Sea: An overview. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 888731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, A.B.; McGonigle, C.; Damour, M.; Holly, G. Shipwreck ecology: Understanding the function and processes from microbes to megafauna. BioScience 2024, 74, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marriner, N.; Morhange, C.; Flaux, C.; Carayon, N.; Kaniewski, D. Harbors and Ports, Ancient. Encycl. Geoarchaeol. 2023, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou, P.; Ioannidis, C.; Skarlatos, D. Automatic detection and 3D mapping of ancient harbors using UAV photogrammetry and GIS tools. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.C.; Barreiros, J.P. Are underwater archaeological parks good for fishes? Symbiotic relation between cultural heritage preservation and marine conservation in the Azores. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2018, 21, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavloudi, C.; Chatzinikolaou, E.; Keklikoglou, K. Seascape of soft bottom benthic communities in the Aegean Sea. In Aegean Sea: Significance for Europe and the Middle East; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 839–855. [Google Scholar]
- Galeandro, A. Routes, trade and commerce in the ancient port of Egnazia. Proc. Int. Conf. Ports Harb. Anc. Mediterr. 2013, 1, 105–123. [Google Scholar]
- Davidde Petriaggi, B.; Stefanile, M.; D’Agostino, M.; Sacco Perasso, C.; Ricci, S. MUSAS: An innovative project for the enhancement of the Underwater Cultural Heritage. In Proceedings of the International Conference in Management of Accessible Underwater, Cultural and Natural Heritage Sites: “Dive in Blue Growth”, Athens, Greece, 16–18 October 2019; pp. 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Jessop, S.A.; Saunders, B.J.; Goetze, J.S.; Harvey, E.S. A comparison of underwater visual census, baited, diver operated and remotely operated stereo-video for sampling shallow water reef fishes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 276, 108017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, G.; Thiriet, P.; Di Franco, A.; Francour, P. Enhancing fish Underwater Visual Census to move forward assessment of fish assemblages: An application in three Mediterranean Marine Protected Areas. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfsema, C.M.; Phinn, S.R.; Dennison, W.C.; Dekker, A.G.; Brando, V.E. Evaluating Benthic Survey Techniques for Validating Maps of Coral Reefs Derived from Remotely Sensed Images. In Proceedings of the 10th International Coral Reef Symposium, Okinawa, Japan, 28 June–2 July 2004; Volume 1, pp. 1771–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Facon, M.; Pinault, M.; Obura, D.; Pioch, S.; Pothin, K.; Bigot, L.; Quod, J.P.; Garnier, R. A comparative study of the accuracy and effectiveness of line and point intercept transect methods for coral reef monitoring in the southwestern Indian Ocean islands. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Maggi, E.; Bertocci, I.; Vaselli, S.; Maggi, E. Estimating the abundance of benthic invertebrates: A comparison of procedures and variability between observers. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 138, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Pandey, C.M.; Singh, U.; Gupta, A.; Sahu, C.; Keshri, A. Descriptive statistics and normality tests for statistical data. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2019, 22, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, M.L. Multiple comparison analysis testing in ANOVA. Biochem. Med. 2011, 21, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassallo, P.; Paoli, C.; Aliani, S.; Cocito, S.; Morri, C.; Bianchi, C.N. Benthic diversity patterns and predictors: A study case with inferences for conservation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, R.; Vargas, J.M. The Probabilistic Basis of Jaccard’s Index of Similarity. Syst. Biol. 1996, 45, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WoRMS Editorial Board. World Register of Marine Species. 2025. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2025, 2025–1, 1–1. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Spellerberg, I.F.; Fedor, P.J. A tribute to Shannon, evenness, and diversity. Biodivers. Conserv. 2003, 12, 441–452. [Google Scholar]
- Renzi, M.; Romeo, T.; Guerranti, C.; Perra, G.; Canese, S.; Consoli, P.; Focardi, S.E.; Berti, C.; Sprovieri, M.; Gherardi, S.; et al. Are shipwrecks a real hazard for the ecosystem in the Mediterranean Sea? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercader, M.; Blazy, C.; Di Pane, J.; Devissi, C.; Mercière, A.; Cheminée, A.; Thiriet, P.; Pastor, J.; Crec’Hriou, R.; Verdoit-Jarraya, M.; et al. Is artificial habitat diversity a key to restoring nurseries for juvenile coastal fish? Ex situ experiments on habitat selection and survival of juvenile seabreams. Restor. Ecol. 2019, 27, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relini, G. The Loano Artificial Reef. In Artificial Reefs in European Seas; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 129–149. [Google Scholar]
- Consoli, P.; Romeo, T.; Giongrandi, U.; Andaloro, F. Differences among fish assemblages associated with a nearshore vermetid reef and two other rocky habitats along the shores of Cape Milazzo. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2008, 88, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheminée, A.; Pastor, J.; Bianchimani, O.; Thiriet, P.; Sala, E.; Cottalorda, J.M.; Francour, P. Juvenile fish assemblages in temperate rocky reefs are shaped by the presence of macro-algae canopy and its three-dimensional structure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinopoli, M.; Cattano, C.; Chemello, R.; Timpanaro, A.; Milisenda, G.; Gristina, M. Nest-mediated parental care in a marine fish: Are large-scale nesting habitats selected and do these habitats respond to small-scale requirements? Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2018, 19, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francour, P.; Charbonnel, E.; Harmelin, J.G.; Ody, D. Effects of artificial reef design on associated fish assemblages in the Côte Bleue Marine Park (Mediterranean Sea, France). In Artificial Reefs in European Seas; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 359–376. [Google Scholar]
- Ntouni, M.M.; Lazaris, A.; Tzanatos, E. Patterns of fish occupancy of artificial habitats in the eastern Mediterranean shallow littoral. Mar. Biol. 2023, 170, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.; Minchin, D.; Clements, M.; Deaker, D.J. The Waiting Stage, Prolonged Residency in Nursery Habitats by Juveniles of the Predatory Sea Star Marthasterias glacialis. Biol. Bull. 2021, 241, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, P.; Terlizzi, A.; Boero, F. Effects of the edible sea urchin, Paracentrotus lividus, fishery along the Apulian rocky coast (SE Italy, Mediterranean Sea). Fish. Res. 2004, 66, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, F.; Ferrario, F.; Abbiati, M. Chasing genetic structure in coralligenous reef invertebrates: Patterns, criticalities and conservation issues. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacobbe, S.; Renda, W. Infralittoral molluscs from the Scilla cliff (Strait of Messina, Central Mediterranean). Biodivers. J. 2018, 9, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrell, C.L.; McCook, L.J.; Willis, B.L. Effects of algal turfs and sediment on coral settlement. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, B.P.; Allen, R.; Agostini, S.; Hoffmann, L.J.; Kon, K.; Summerfield, T.C.; Wada, S.; Hall-Spencer, J.M. Feedback mechanisms stabilise degraded turf algal systems at a CO2 seep site. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffredo, S.; Mancuso, A.; Caroselli, E.; Prada, F.; Dubinsky, Z.; Falini, G.; Levy, O.; Fantazzini, P.; Pasquini, L. Skeletal mechanical properties of Mediterranean corals along a wide latitudinal gradient. Coral Reefs 2015, 34, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellani, V.; Oliva, M.; Pretti, C.; Renzi, M. Stress-related molecular biomarkers to monitor the effects of global changes on calcifying reef-forming organisms: A review in the Mediterranean. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morri, C.; Oprandi, A.; Peirano, A.; Montefalcone, M. Population structure change in a temperate reef coral after a quarter of century. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 270, 107851. [Google Scholar]
- Toso, A.; Necci, F.; Martines, A.; Lacorte, R.; Toso, Y.; Gianguzza, P.; Deidun, A.; Ungaro, N.; Costantino, G.; Caforio, M.; et al. Overfishing and sea warming drive the collapse of Paracentrotus lividus. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 18733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weilgart, L.S. The impact of ocean noise pollution on fish and invertebrates: A review of scientific findings and potential policy responses. OceanCare 2018, 1, 1–30. [Google Scholar]



| Phylum | Class | Family | Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| Algal turf (OTU) | |||
| ANNELIDA | Polychaeta | Sabellidae | Sabella spallanzanii (Gmelin, 1791) (3) |
| Polychaeta | Serpulidae | Serpula vermicularis (Linnaeus, 1767) (3) | |
| ARTHROPODA | Thecostraca | Balanidae | Perforatus perforatus (Bruguière, 1789) (3) |
| Malacostraca | Diogenidae | Calcinus tubularis (Linnaeus, 1767) (2) | |
| Malacostraca | Diogenidae | Clibanarius erythropus (Latreille, 1818) (2) | |
| Malacostraca | Eriphiidae | Eriphia verrucosa (Forskål, 1775) (2) | |
| Malacostraca | Paguridae | Pagurus anachoretus (Risso, 1827) (2) | |
| CHLOROPHYTA | Ulvophyceae | Caulerpaceae | Caulerpa cylindracea (Sonder, 1845) |
| Ulvophyceae | Halimedaceae | Flabellia petiolata (Nizamuddin, 1987) | |
| Ulvophyceae | Halimedaceae | Halimeda tuna (J.V.Lamouroux, 1816) | |
| Ulvophyceae | Polyphysaceae | Acetabularia acetabulum ((Linnaeus) P.C. Silva, 1952) (3) | |
| Ulvophyceae | Valoniaceae | Valonia sp. (3) | |
| CHORDATA | Teleostei | Blenniidae | Microlipophrys dalmatinus (Steindachner & Kolombatovic, 1883) (2) |
| Teleostei | Blenniidae | Parablennius gattoruggine (Linnaeus, 1758) (2) | |
| Teleostei | Blenniidae | Parablennius incognitus (Bath, 1968) (2) | |
| Teleostei | Blenniidae | Parablennius zvonimiri (Kolombatovic, 1892) (2) | |
| Chondrichthyes | Dasyatidae | Dasyatis pastinaca (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Gobiidae | Gobius sp. (2) | |
| Teleostei | Labridae | Coris julis (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Labridae | Symphodus cinereus (Bonnaterre, 1788) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Labridae | Symphodus doderleini (Jordan, 1890) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Labridae | Symphodus ocellatus (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Labridae | Symphodus tinca (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Labridae | Thalassoma pavo (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Mullidae | Mullus surmuletus (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Muraenidae | Muraena helena (Linnaeus, 1758) (2) | |
| Teleostei | Pomacentridae | Chromis chromis (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Sciaenidae | Sciaena umbra (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Scorpaenidae | Scorpaena notata (Rafinesque, 1810) (2) | |
| Teleostei | Scorpaenidae | Scorpaena porcus (Linnaeus, 1758) (2) | |
| Teleostei | Serranidae | Serranus cabrilla (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Serranidae | Serranus hepatus (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Serranidae | Serranus scriba (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Sparidae | Diplodus sargus (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Sparidae | Diplodus vulgaris (Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1817) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Sparidae | Lithognathus mormyrus (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Sparidae | Oblada melanura (Linnaeus, 1758) (1) | |
| Teleostei | Tripterygiidae | Tripterygion delaisi (Cadenat & Blache, 1970) (2) | |
| Teleostei | Tripterygiidae | Tripterygion tripteronotum (Risso, 1810) (2) | |
| CNIDARIA | Anthozoa | Metridioidea | Aiptasia mutabilis (Gravenhorst, 1831) (3) |
| Anthozoa | Actiniidae | Anemonia viridis (Forsskål, 1775) (3) | |
| Anthozoa | Charyophylliidae | Balanophyllia europaea (Risso, 1827) (3) | |
| Anthozoa | Charyophylliidae | Caryophyllia sp. (3) | |
| Anthozoa | Cladocoridae | Cladocora caespitosa (Linnaeus, 1767) (3) | |
| CYANOBACTERIA | Cyanobacteria | ||
| ECHINODERMATA | Echinoidea | Arbacidae | Arbacia lixula (Linnaeus, 1758) (2) |
| Holothuroidea | Holotidae | Holothuria tubulosa (Gmelin, 1791) (2) | |
| Holothuroidea | Holotidae | Holothuria poli (Delle Chiaje, 1824) (2) | |
| Asteroidea | Marthidae | Marthasterias glacialis (Linnaeus, 1758) (2) | |
| Ophiuroidea | Ophioidae | Ophioderma longicaudum (Bruzelius, 1805) (2) | |
| Ophiuroidea | Ophiothricidae | Ophiothrix fragilis (Abildgaard in O.F. Müller, 1789) (2) | |
| Echinoidea | Paracidae | Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck, 1816) (2) | |
| MOLLUSCA | Bivalvia | Gastrochaenidae | Rocellaria dubia (Pennant, 1777) (3) |
| Gastropoda | Cerithiidae | Bittium sp. (2) | |
| Gastropoda | Columbellidae | Columbella rustica (Linnaeus, 1758) (2) | |
| Gastropoda | Fasciolariidae | Tarantinaea lignaria (Linnaeus, 1758) (2) | |
| Gastropoda | Muricidae | Hexaplex trunculus (Linnaeus, 1758) (2) | |
| Gastropoda | Plakobranchidae | Thuridilla hopei (Vérany, 1853) (2) | |
| OCHROPHYTA | Phaeophyceae | Dictyotaceae | Dictyota dichotoma ((Hudson) J.V.Lamouroux, 1809) (3) |
| Phaeophyceae | Erect brown algae (OTU) (3) | ||
| Phaeophyceae | Dictyotaceae | Padina pavonica ((Linnaeus) Thivy, 1960) (3) | |
| PORIFERA | Demospongiae | Clionaidae | Cliona sp. (3) |
| Demospongiae | Clionaidae | Cliona rhodensis (Rützler & Bromley, 1981) (3) | |
| Demospongiae | Chondrosiidae | Chondrosia reniformis (Nardo, 1847) (3) | |
| Demospongiae | Hymedesmiidae | Hemimycale columella (Bowerbank, 1874) (3) | |
| Demospongiae | Hymedesmiidae | Phorbas fictitius (Bowerbank, 1866) (3) | |
| Demospongiae | Encrusting orange sponges (OTU) (3) | ||
| Demospongiae | Encrusting purple sponges (OTU) (3) | ||
| Demospongiae | Irciniidae | Ircinia sp. (3) | |
| Demospongiae | Irciniidae | Irciniidae spp. (3) | |
| Demospongiae | Petrosiidae | Petrosia ficiformis (Poiret, 1789) (3) | |
| RHODOPHYTA | Florideophyceae | Corallinaceae | Ellisolandia elongata (J.Ellis & Solander) K.R.Hind & G.W.Saunders, 2013 (3) |
| Florideophyceae | Corallinaceae | Encrusting Corallinaceae (OTU) (3) | |
| Florideophyceae | Lithophyllaceae | cf. Amphiroa eretta (3) | |
| Florideophyceae | Peyssonnelliaceae | Peyssonnelia spp. (3) | |
| Florideophyceae | Erect red algae (OTU) (3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basile, V.; Mezzasalma, M.; Talarico, F.; La Russa, M.F.; Brunelli, E. Biodiversity Assessment of the Ancient Submerged Port of Egnazia (Southern Adriatic Sea, Mediterranean Sea): New Evidence for Conservation. Fishes 2025, 10, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090431
Basile V, Mezzasalma M, Talarico F, La Russa MF, Brunelli E. Biodiversity Assessment of the Ancient Submerged Port of Egnazia (Southern Adriatic Sea, Mediterranean Sea): New Evidence for Conservation. Fishes. 2025; 10(9):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090431
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasile, Valentina, Marcello Mezzasalma, Federica Talarico, Mauro Francesco La Russa, and Elvira Brunelli. 2025. "Biodiversity Assessment of the Ancient Submerged Port of Egnazia (Southern Adriatic Sea, Mediterranean Sea): New Evidence for Conservation" Fishes 10, no. 9: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090431
APA StyleBasile, V., Mezzasalma, M., Talarico, F., La Russa, M. F., & Brunelli, E. (2025). Biodiversity Assessment of the Ancient Submerged Port of Egnazia (Southern Adriatic Sea, Mediterranean Sea): New Evidence for Conservation. Fishes, 10(9), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090431










