Depletion of Albendazole and Its Metabolites and Their Impact on the Gut Microbial Community Following Multiple Oral Dosing in Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Chemical Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Residue Depletion of Albendazole and Its Metabolites
2.3.1. Administration and Sampling
2.3.2. Analytical Methods
2.3.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Effects on the Gut Microbial Community
2.4.1. Administration and Sampling
2.4.2. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification of Intestinal Samples
2.4.3. Purification and Mixing of PCR Products
2.4.4. Library Construction, On-Line Sequencing and Information Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Residue Depletion of Albendazole and Its Metabolites
3.1.1. Residue Concentrations of ABZ and Its Three Metabolites
3.1.2. Residue Depletion of ABZ and Its Three Metabolites
3.1.3. Withdrawal Period of ABZ After Multiple Oral Dosing
3.2. Gut Microbial Community Test
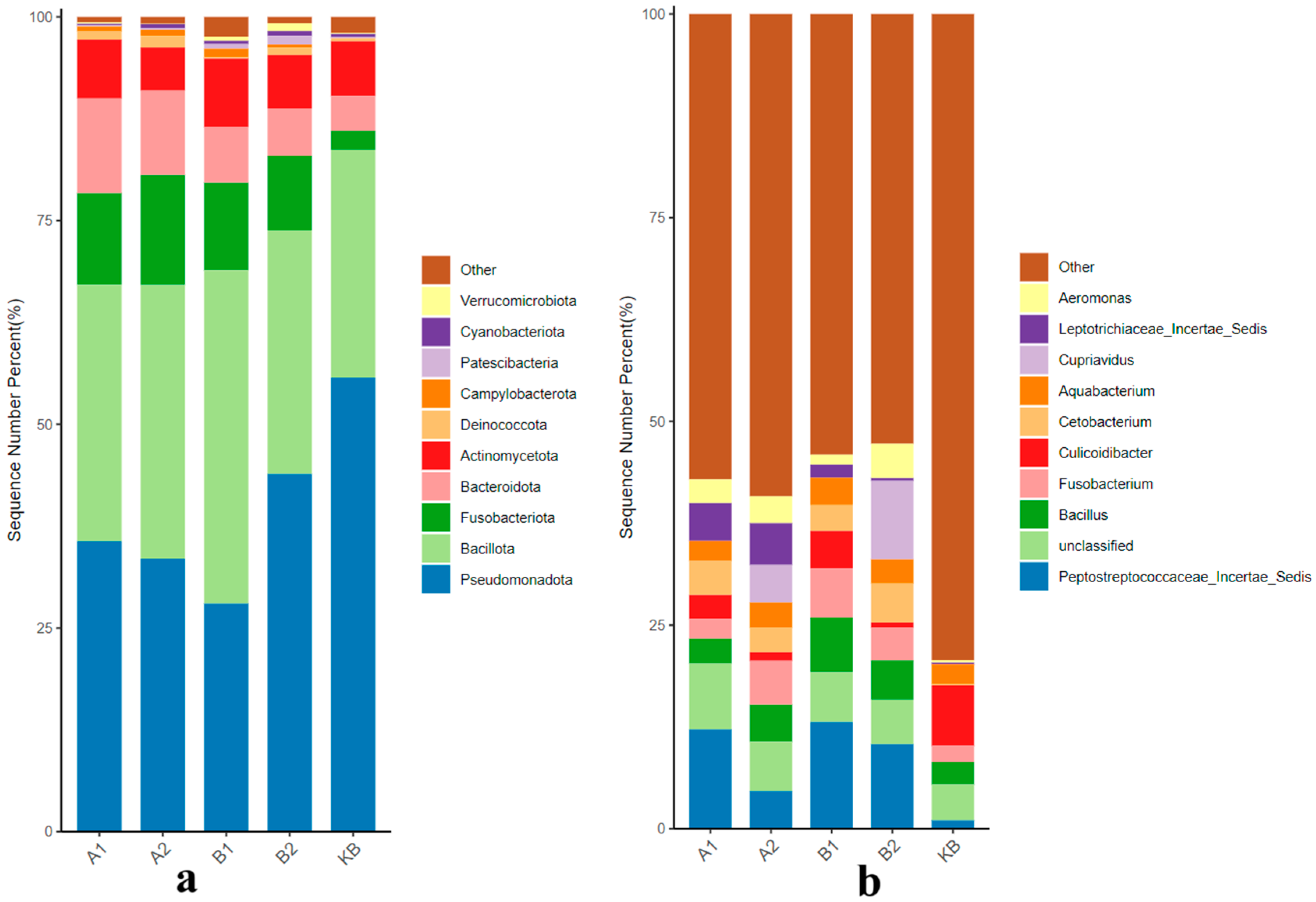
3.2.1. Effects of ABZ Oral Administration on the Gut Microbial Community of Yellow River Carp
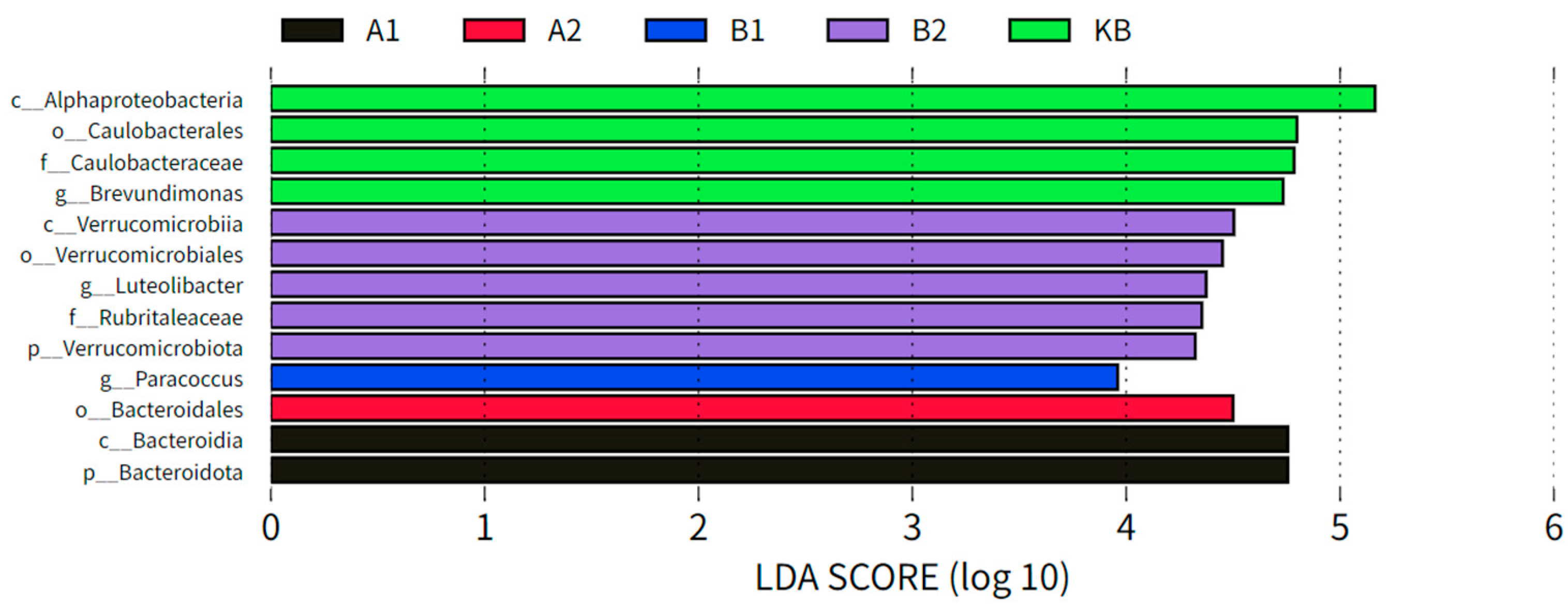
3.2.2. Differential Analysis of ABZ Oral Administration on Intestinal Bacterial Marker Species in Yellow River Carp
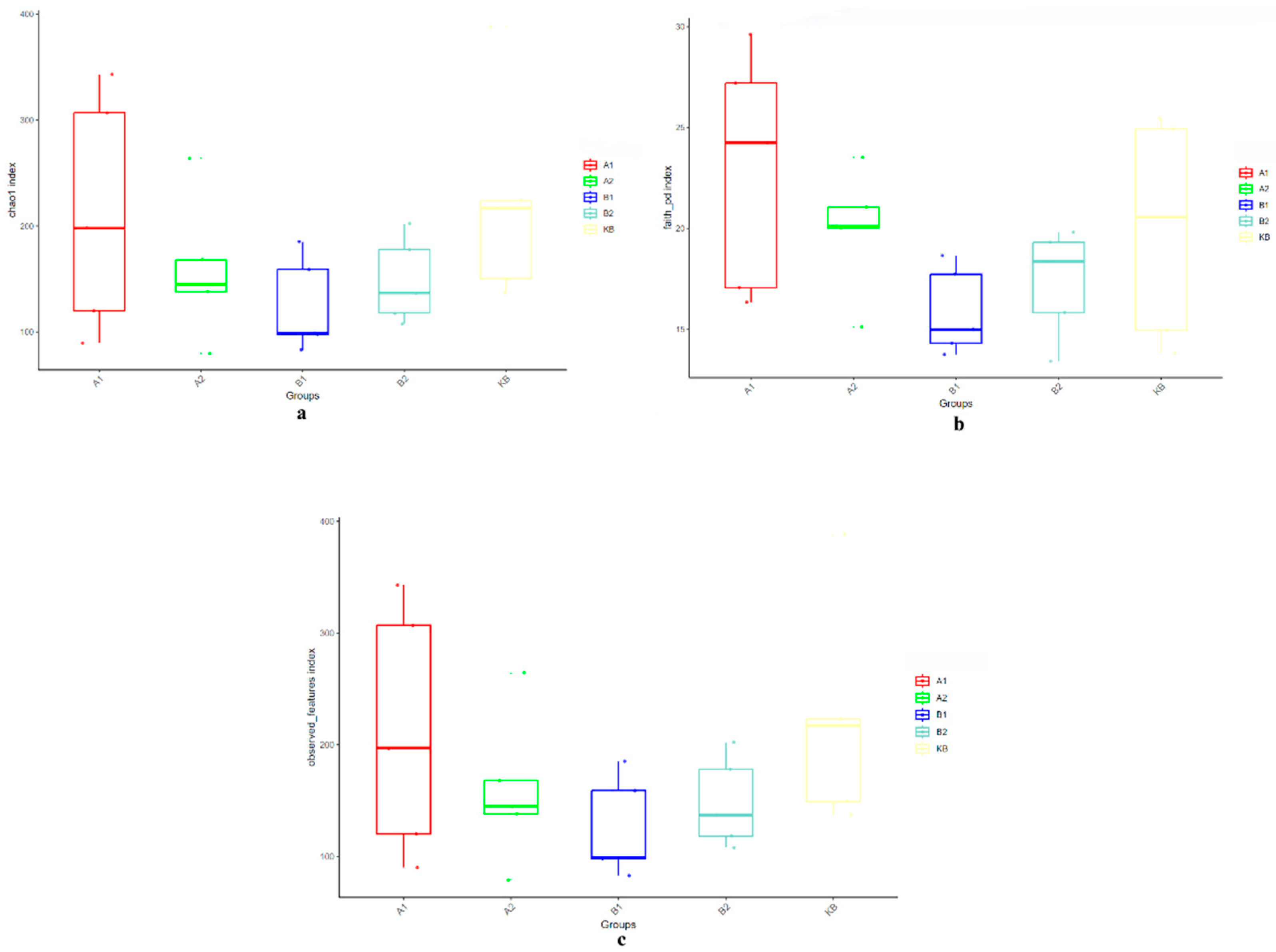
3.2.3. Effects of ABZ Oral Administration on the Number and Diversity of Intestinal Microbial OTUs in Yellow River Carp
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Honji, R.M.; Mello, P.H.; Araújo, B.C. Reproduction and development in fish: Solving bottlenecks in modern aquaculture. Animals 2025, 15, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrowska-Korczak, B.; Stawarska, A.; Szterk, A.; Ofiara, K.; Czerwonka, M.; Giebułtowicz, J. Determination of pharmaceuticals, heavy metals, and oxysterols in fish muscle. Molecules 2021, 26, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, J.L.; Liu, D.; Qin, C.B.; Yan, X.; Pang, P.; Yun, Y.H.; Wang, L.M.; Nie, G.X. Dietary (-)-Epicatechin supplementation regulates myofiber development, fillet quality, and antioxidant status of Yellow River carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 2023, 572, 739542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ma, K.L.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.G.; Zhang, Y.N.; Dai, Y.; Duan, M.H.; Li, Z.E.; Yang, F. Tissue distribution and residue depletion of difloxacin in crucian carp (Carassius carassius) after multiple oral administration. Aquaculture 2024, 593, 741299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024–Blue Transformation in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, W.W.; Yu, X.M.; Liu, Q.S.; Tong, J.G. Brain and intestine transcriptome analyses and identification of genes involved in feed conversion efficiency of Yellow River carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol.—Part D 2019, 29, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jia, S.P.; Zhang, L.; Ma, F.R.; Zhang, M.; Yu, M.; Jiang, H.X.; Qiao, Z.G.; Li, X.J. Comparative study on nutritional quality and volatile flavor compounds of muscle in Cyprinus carpio haematopterus under wild, traditional pond and in-pond raceway system culture. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostock, J.; McAndrew, B.; Richards, R.; Jauncey, K.; Telfer, T.; Lorenzen, K.; Little, D.; Ross, L.; Handisyde, N.; Gatward, I.; et al. Aquaculture: Global status and trends. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 2897–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.N.; Qu, F.H.; Ge, Y.L.; Li, C.T.; Shi, X.D.; Hu, X.S.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, X.Y.; Jia, Z.Y. Effects of Dietary Protein Levels on the Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Indices of Juvenile Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Animals 2025, 15, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.R.; Majumder, S.; Chandra, K.J. Ecto—Parasitism in Juvenile Indian Major Carps of Difference Fish Farms of Mymensingh. Bangladesh J. Vet. Med. 2016, 2, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Qin, X.L.; Wang, C.F.; Liu, W.Q. Pharmacokinetics and tissue residues of albendazole sulphoxide and its metabolites in donkey after intramuscular injection. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.K.; Ji, Y.K.; Dong, W.S.; Mi, O.E. Application potential of albendazole as an aquatic animal drug based on its safety, efficacy, and residue profiles. Toxicol. Res. 2024, 40, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, D.M.; Patel, K.R.; Mistri, H.N.; Jangid, A.G.; Shrivastav, P.S.; Sanyal, M. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous determination of albendazole and albendazole sulfoxide in human plasma for bioequivalence studies. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzias, G.C.; Delis, G.A. Reversed-phase liquid chromatographic method with fluorescence detection for the simultaneous determination of albendazole sulphoxide, albendazole sulphone and albendazole 2-aminosulphone in sheep plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 805, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, B.; Rummel, N.; Gieseker, C.; Serfling, S.; Reimschuessel, R. Metabolism and residue depletion of albendazole and its metabolites in rainbow trout, tilapia and Atlantic salmon after oral administration. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 26, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baynes, R.E.; Dedonder, K.; Kissell, L.; Mzyk, D.; Marmulak, T.; Smith, G.; Tell, L.; Gehrin, R.; Davis, J.; Riviere, J.E. Health concerns and management of select veterinary drug residues. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 88, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hombu, A.; Yoshida, A.; Kikuchi, T.; Nagayasu, E.; Kuroki, M.; Maruyama, H. Treatment of larva migrans syndrome with long-term administration of albendazole. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorides, V.J.; Carakostas, M.C.; Colaianne, J.J.; Freeman, J.F.; Page, S.W. Safety of albendazole in developing bovine fetuses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 54, 2171–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 31650 2019; The National Standard for Food Safety-Maximum Residue Limit of Veterinary Drugs in Food. MARA (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China): Beijing, China, 2019. Available online: https://www.fas.usda.gov/data/china-china-publishes-maximum-residue-limits-veterinary-drugs-food (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- EU (European Union). Commission Regulation (EU) No 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in foodstuffs of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 20, L15/1–L15/72. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/files/eudralex/vol-5/reg_2010_37/reg_2010_37_en.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Chen, D.Y.; Jiang, W.D.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Ren, H.M.; Jin, X.W.; Zhou, X.Q.; Feng, L. Mechanism of fumonisin B1 on growth performance and intestinal structural integrity of juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Anim. Nutr. 2025, 21, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Zhou, X.Q.; Wu, P.; Jiang, W.D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.N.; Feng, L. New perspective into possible mechanism in growth promotion of potassium diformate (KDF) on the juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquaculture 2023, 576, 739850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Su, S.Y.; Dong, P.; Feng, W.R.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, C.F.; Tang, Y.K. Effects of simulated winter short photoperiods on the microbiome and intestinal metabolism in Huanghe carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1293749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, G.D.; Balcázar, J.L. A review on the interactions between gut microbiota and innate immunity of fish. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 52, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimundo, R.J.K.; Carliane, M.G.A.; Marcos, S.B.O.; Clara, B.S.; Abthyllane, A.C.; Marcela, N.V.; Eliane, T.O.Y.; Marcos, T.D. Albendazol tem eficácia em controlar monogenéticos em Colossoma macropomum (Serrasalmidae): Banhos terapêuticos e seus efeitos fisiológicos e histopatológicos. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Veterinária 2024, 33, e004924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carliane, M.G.A.; Joziele, N.N.; Isaac, B.B.; Joilson, R.D.S.; Gracienhe, G.S.; Marcos, T.D. Albendazole, levamisole and ivermectin are effective against monogeneans of Colossoma macropomum (Pisces: Serrasalmidae). J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, E.E.B.; Ángel, G.L.C.; Gustavo, A.R.M.O.; Selene, M.A.R.; Daniela, A.M.I.; Edén, A.R.V.; Zohar, I.Z.; Mayra, I.G.M. Effective control and treatment of Rhabdosynochus viridisi (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) in Centropomus viridis (Teleostei: Centropomidae) in marine aquaculture. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2025, 53, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speare, D.J.; Athanassopoulou, F.; Daley, J.; Sanchez, J.G. A Preliminary Investigation of Alternatives to Fumagillin for the Treatment of Loma salmonae Infection in Rainbow Trout. J. Comp. Pathol. 1999, 121, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caio, F.S.F.; Franmir, R.B.; Fernanda, A.S.; Damy, C.M.; Patrícia, C.M.; Cláudia, M.; Edsandra, C.C. Albendazole and praziquantel for the control of Neoechinorhynchus buttnerae in tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum). Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaelle, P.C.; Patrícia, A.C.B.; Maria, J.S.R.; Edsandra, C.C.; Felix, G.R.R. Depletion study and estimation of the withdrawal period for albendazole in tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) parasitised by acanthocephalan (Neoechinorhynchus buttnerae) treated with albendazole-containing feed. Food Addit. Contam.: Part A 2021, 38, 1883–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Yang, F.; Li, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.G.; Li, Z.E.; Duan, M.H.; Zhang, Y.N.; Yang, F. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Albendazole and Its Three Metabolites in Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus) after Single Oral Administration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 1824–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacrămioara, G.N.; Lorena, D.; Mirela, C.; Cristian, R.; Angelica, D.; Iulia, G.; Floricel, M.D.; Maria, D.S.; Camelia, V. The Protective Effects of Korill Product on Carp Fingerlings Reared in High Densities and Challenged with Albendazole Treatment. Fishes 2023, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damte, D.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Cho, B.H.; Kim, J.C.; Park, S.C. Evaluation of linear regression statistical approaches for withdrawal time estimation of veterinary drugs. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M. Pharmacokinetic and Residue Elimination Studies of Albendazole and Its Sulfoxide in Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus auratus). Master’s Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Corum, O.; Corum, D.D.; Terzi, E.; Uney, K. Pharmacokinetics, Tissue Residues, and Withdrawal Times of Oxytetracycline in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after Single- and Multiple-Dose Oral Administration. Animals 2023, 13, 3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Chen, C.L.; Ai, D.Y.; Wang, C.M.; Li, J.; Qi, Y.H.; Yi, W.X.; Shen, H.C.; Cao, J.Y. Pharmacokinetics and tissue residues of hydrochloric acid albendazole sulfoxide and its metabolites in crucian carp (Carassius auratus) after oral administration. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 33, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anadón, A. Perspectives in Veterinary Pharmacology and Toxicology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, S.K. Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1553–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Cheng, M.Q.; Xue, X.; Guan, Y.J.; Wang, Z.Z. Characterization of tetracycline effects on microbial community, antibiotic resistance genes and antibiotic resistance of Aeromonas spp. in gut of goldfish Carassius auratus Linnaeus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.T.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, W.J.; Fan, Z.C. Biological toxicity effects of florfenicol on antioxidant, immunity and intestinal flora of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 265, 115520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Older, C.E.; Griffin, M.J.; Richardson, B.M.; Waldbieser, G.C.; Reifers, J.G.; Goodman, P.M.; Ware, C.; Gatlin, D.M.; Wise, D.J.; Yamamoto, F.Y. Influence of probiotic and prebiotic supplementation on intestinal microbiota and resistance to Edwardsiella ictaluri infection in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) following florfenicol administration. J. Fish Dis. 2024, 47, e13910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Song, T.; Li, D.; Chen, M.F.; Wang, P.; Ye, J.D. Effect of dietary Clostridium butyricum supplementation on growth performance, immune function, and intestinal health of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus ♀ × Epinephelus lanceolatus ♂). Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1557256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Villalta, D.; Gómez-Espinoza, O.; Guillén-Watson, R.; Murillo-Vega, F.; Villalta- Romero, F.; Vaquerano-Pineda, F.; Chicas, M.; Guerrero, M.; Núñez-Montero, K. Impact of Arthrospira maxima Feed Supplementation on Gut Microbiota and Growth Performance of Tilapia Fry (Oreochromis niloticus). Fishes 2024, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theriot, C.M.; Koenigsknecht, M.J.; Carlson, P.E.; Hatton, G.E.; Nelson, A.M.; Li, B.; Huffnagle, G.B.; Li, J.Z.; Young, V.B. Antibiotic-induced shifts in the mouse gut microbiome and metabolome increase susceptibility to Clostridium difficile infection. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountfort, D.O.; Campbell, J.; Clements, K.D. Hindgut fermentation in three species of marine herbivorous fish. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terutoyo, Y. Streptococcosis in aquaculture. Fish Pathol. 2016, 51, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.H.; Xu, D.H.; Shoemaker, C. Experimental induction of motile Aeromonas septicemia in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) by waterborne challenge with virulent Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquac. Rep. 2015, 3, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
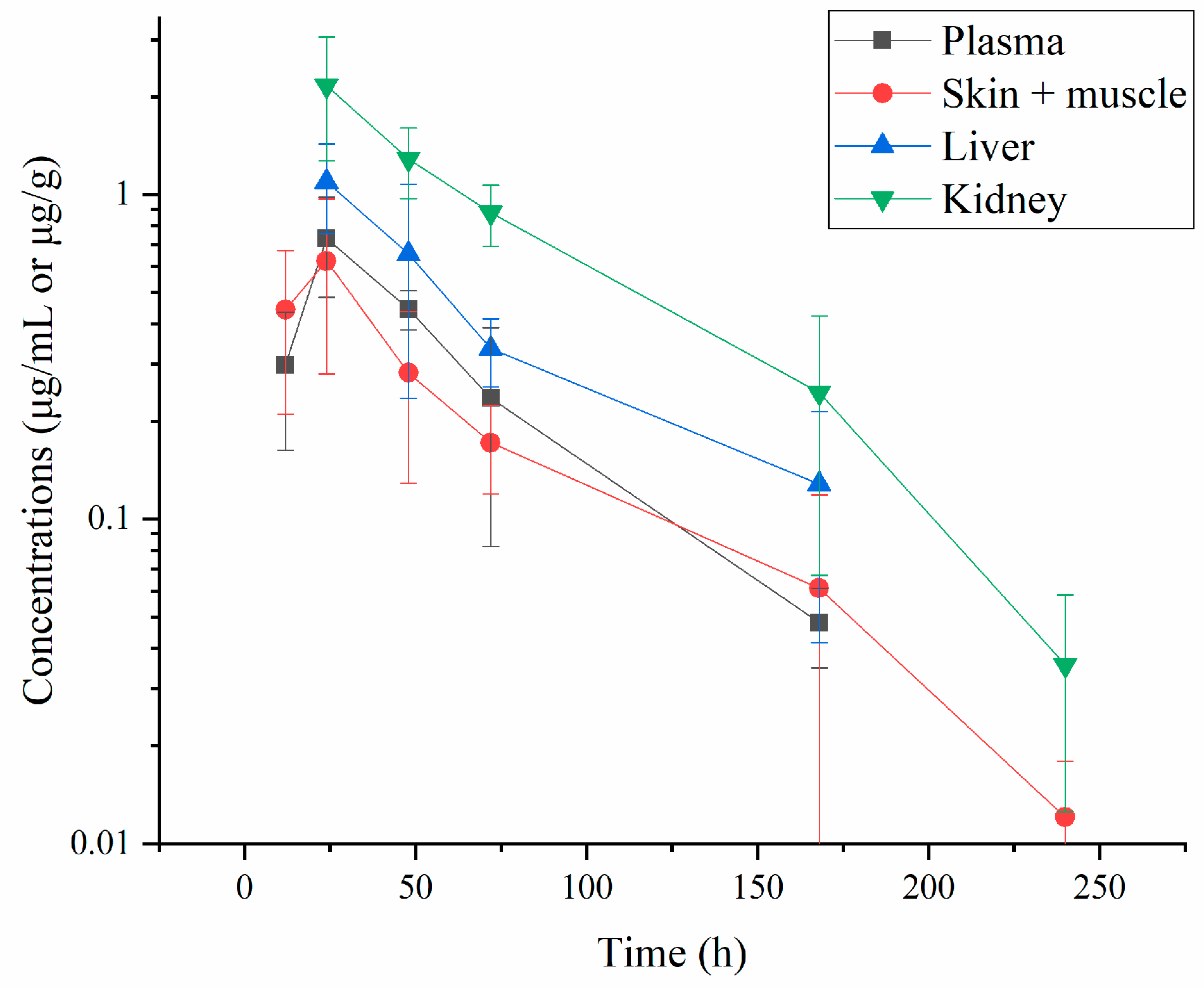

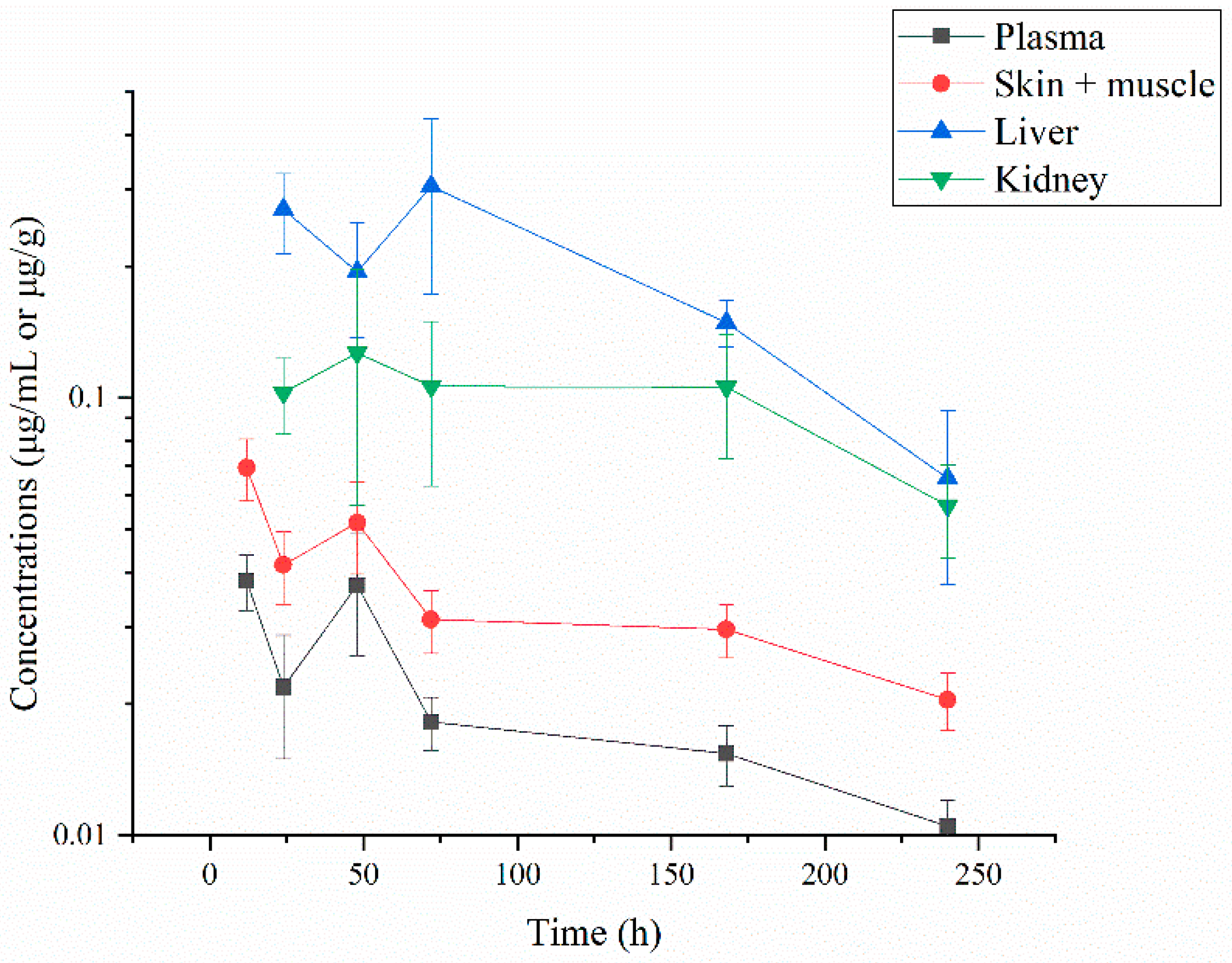



| Time (h) | Plasma | Skin-Muscle | Liver | Kidney |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 0.298 ± 0.135 | 0.442 ± 0.231 | 1.094 ± 0.336 | 2.164 ± 0.892 |
| 24 | 0.733 ± 0.250 | 0.624 ± 0.344 | 0.656 ± 0.420 | 1.287 ± 0.315 |
| 48 | 0.444 ± 0.062 | 0.282 ± 0.153 | 0.335 ± 0.080 | 0.880 ± 0.188 |
| 72 | 0.236 ± 0.154 | 0.172 ± 0.052 | 0.128 ± 0.086 | 0.245 ± 0.178 |
| 120 | 0.048 ± 0.013 | 0.061 ± 0.057 | 1.094 ± 0.336 | 0.035 ± 0.023 |
| 240 | ND | 0.012 ± 0.006 | ND | ND |
| 360 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Time (h) | Plasma | Skin-Muscle | Liver | Kidney |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 1.203 ± 0.103 | 1.479 ± 0.115 | ND | ND |
| 24 | 1.559 ± 0.327 | 2.198 ± 0.277 | 4.145 ± 1.759 | 2.455 ± 0.512 |
| 48 | 1.397 ± 0.187 | 1.334 ± 0.160 | 3.296 ± 0.574 | 3.347 ± 0.704 |
| 72 | 0.691 ± 0.245 | 0.702 ± 0.128 | 2.023 ± 0.366 | 1.867 ± 0.236 |
| 120 | 0.545 ± 0.174 | 0.466 ± 0.237 | 1.221 ± 0.535 | 1.039 ± 0.333 |
| 240 | 0.078 ± 0.022 | 0.076 ± 0.028 | 0.304 ± 0.086 | 0.394 ± 0.085 |
| 360 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Time (h) | Plasma | Skin-Muscle | Liver | Kidney |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 0.038 ± 0.006 | 0.069 ± 0.011 | ND | ND |
| 24 | 0.022 ± 0.007 | 0.042 ± 0.008 | 0.270 ± 0.056 | 0.103 ± 0.020 |
| 48 | 0.037 ± 0.012 | 0.052 ± 0.012 | 0.194 ± 0.057 | 0.127 ± 0.070 |
| 72 | 0.018 ± 0.003 | 0.031 ± 0.005 | 0.304 ± 0.131 | 0.106 ± 0.043 |
| 120 | 0.015 ± 0.002 | 0.030 ± 0.004 | 0.149 ± 0.018 | 0.106 ± 0.033 |
| 240 | 0.011 ± 0.002 | 0.020 ± 0.003 | 0.066 ± 0.028 | 0.057 ± 0.014 |
| 360 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Time (h) | Plasma | Skin-Muscle | Liver | Kidney |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | ND | 0.0748 ± 0.0078 | ND | ND |
| 24 | ND | 0.0402 ± 0.0114 | ND | 0.0655 ± 0.0351 |
| 48 | ND | 0.0757 ± 0.0257 | ND | 0.0350 ± 0.0104 |
| 72 | ND | 0.0655 ± 0.0137 | ND | 0.0418 ± 0.0201 |
| 120 | ND | 0.0542 ± 0.0191 | ND | 0.0669 ± 0.0515 |
| 240 | ND | 0.0234 ± 0.0024 | ND | ND |
| 360 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Parameters | Unit | Plasma | Skin-on Muscle | Liver | Kidney |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λZ | 1/h | 0.018 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.018 |
| t1/2λZ | h | 38.56 | 44.77 | 55.04 | 38.53 |
| Tmax | h | 24.00 | 24.00 | 24.00 | 24.00 |
| Cmax | μg/mL or μg/g | 0.73 | 0.62 | 1.09 | 2.16 |
| AUC0–∞ | h·μg/mL or h·μg/g | 46.49 | 40.12 | 77.96 | 160.03 |
| AUMC0–∞ | h 2·μg/mL or h 2·μg/g | 2861.11 | 2654.70 | 6274.72 | 11,038.61 |
| MRT | h | 61.54 | 66.16 | 80.48 | 68.98 |
| AUC% | % | 5.62 | 2.34 | 12.50 | 1.57 |
| Parameters | Unit | Plasma | Skin-on Muscle | Liver | Kidney |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λZ | 1/h | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.0090 |
| t1/2λZ | h | 53.73 | 54.19 | 61.74 | 77.46 |
| Tmax | h | 24.00 | 24.00 | 24.00 | 48.00 |
| Cmax | μg/mL or μg/g | 1.54 | 2.29 | 4.51 | 3.35 |
| AUC0–∞ | h·μg/mL or h·μg/g | 175.94 | 185.60 | 458.89 | 403.47 |
| AUMC0–∞ | h 2·μg/mL or h 2·μg/g | 16,687.22 | 15,934.63 | 46,240.91 | 49,205.87 |
| MRT | h | 94.85 | 85.85 | 100.77 | 121.96 |
| AUC% | % | 4.97 | 4.68 | 7.31 | 12.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Wang, W.-R.; Chen, Y.-X.; Jin, Y.-G.; Sun, L.-J.; Li, S.-H.; Yang, F.; Li, X.-P.; et al. Depletion of Albendazole and Its Metabolites and Their Impact on the Gut Microbial Community Following Multiple Oral Dosing in Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Fishes 2025, 10, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080410
Liu Y, Dai Y, Zhang Y-N, Wang W-R, Chen Y-X, Jin Y-G, Sun L-J, Li S-H, Yang F, Li X-P, et al. Depletion of Albendazole and Its Metabolites and Their Impact on the Gut Microbial Community Following Multiple Oral Dosing in Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Fishes. 2025; 10(8):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080410
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yue, Yan Dai, Yan-Ni Zhang, Wen-Rui Wang, Yu-Xin Chen, Yang-Guang Jin, Long-Ji Sun, Shi-Hao Li, Fang Yang, Xing-Ping Li, and et al. 2025. "Depletion of Albendazole and Its Metabolites and Their Impact on the Gut Microbial Community Following Multiple Oral Dosing in Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus)" Fishes 10, no. 8: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080410
APA StyleLiu, Y., Dai, Y., Zhang, Y.-N., Wang, W.-R., Chen, Y.-X., Jin, Y.-G., Sun, L.-J., Li, S.-H., Yang, F., Li, X.-P., & Yang, F. (2025). Depletion of Albendazole and Its Metabolites and Their Impact on the Gut Microbial Community Following Multiple Oral Dosing in Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Fishes, 10(8), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080410







