The Biogeographic Patterns of Two Typical Mesopelagic Fishes in the Cosmonaut Sea Through a Combination of Environmental DNA and a Trawl Survey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
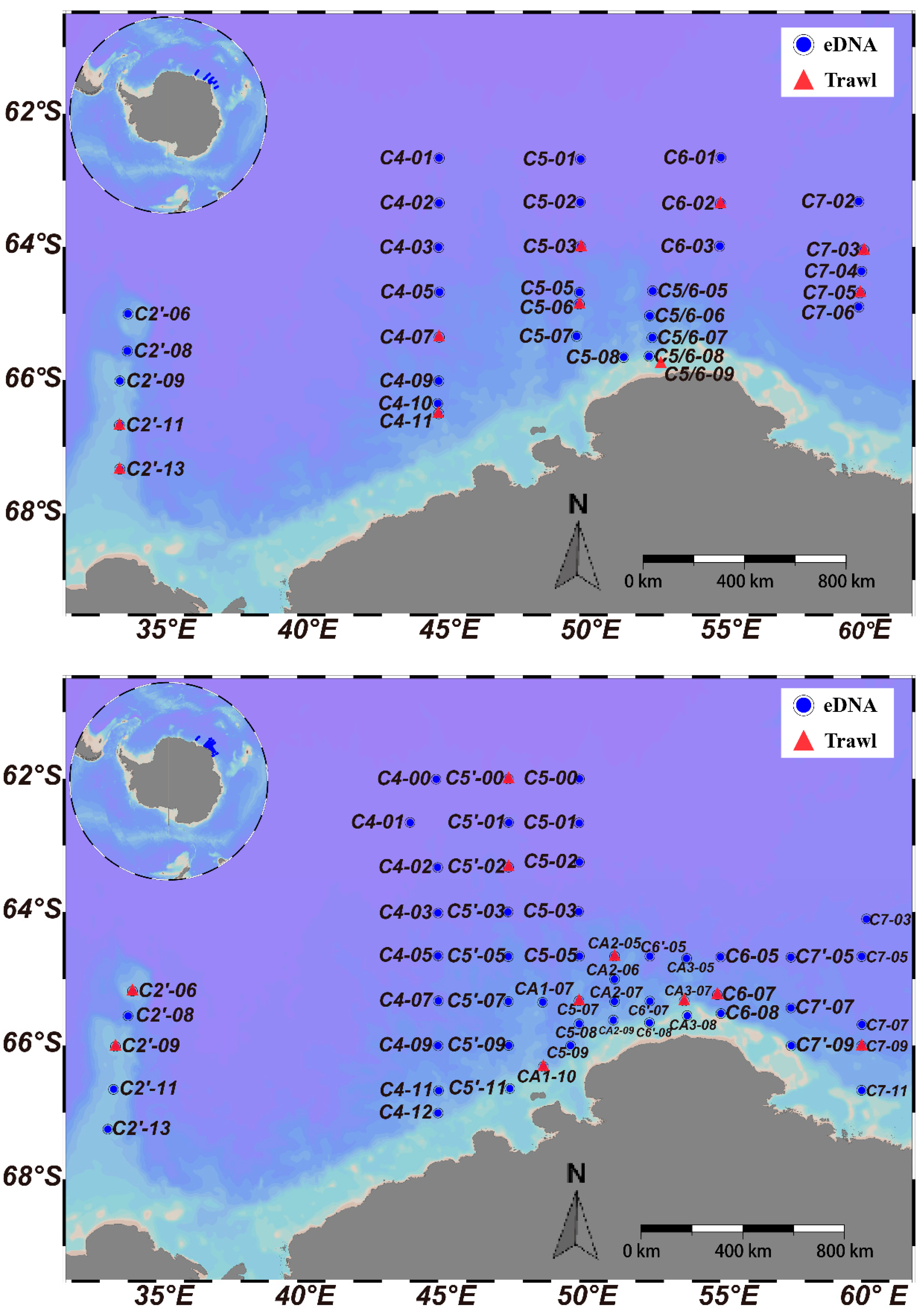
2.1. eDNA and Fish Sample Collection
2.2. Development of Specific Primers and Probes and qPCR Assays
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Primer and Probe Design
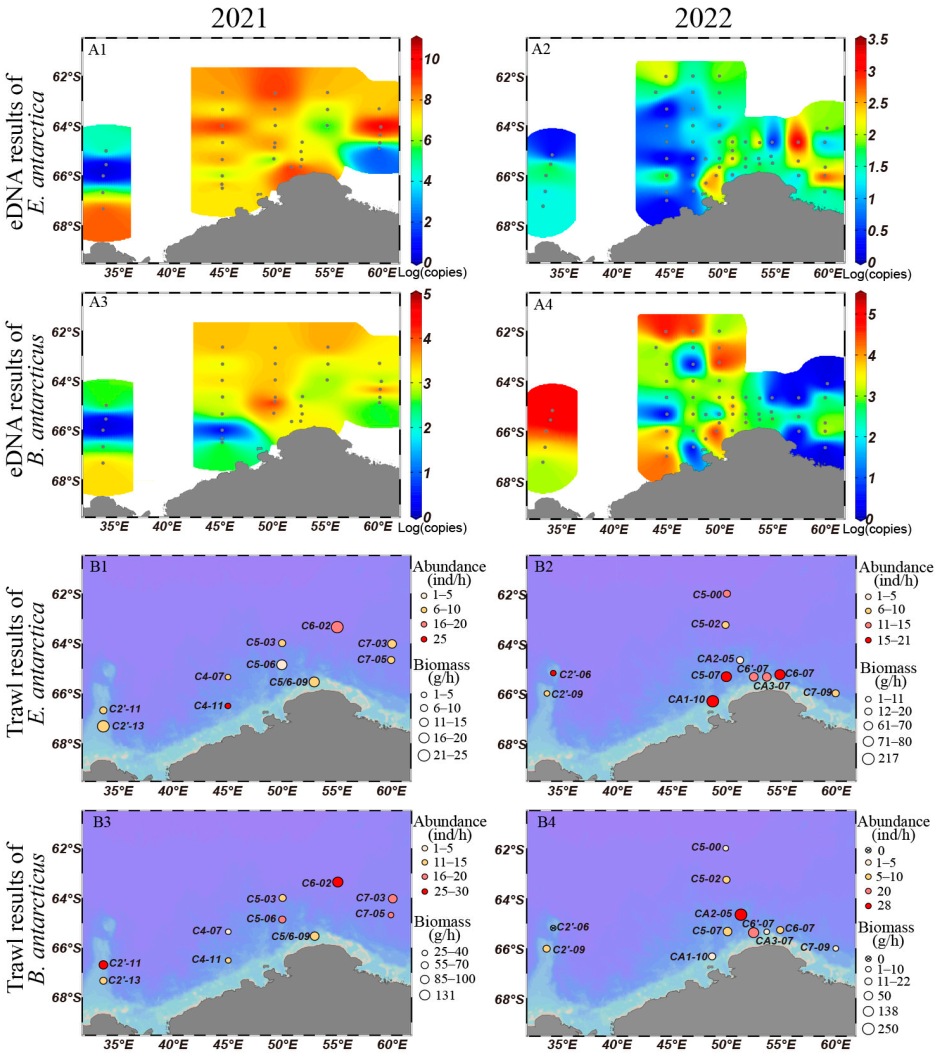
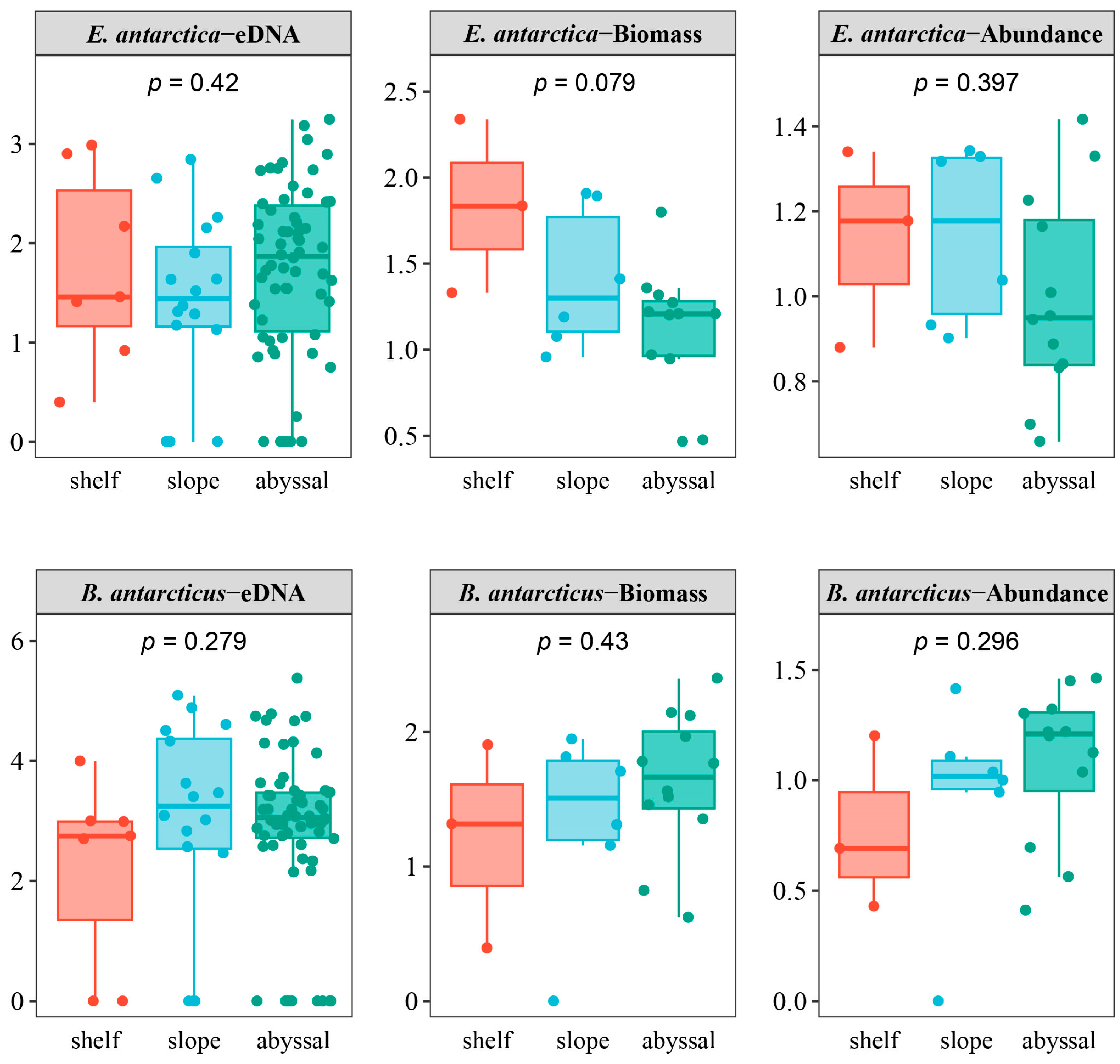
3.2. Comparison of Horizontal Distribution by eDNA and Trawling Methods
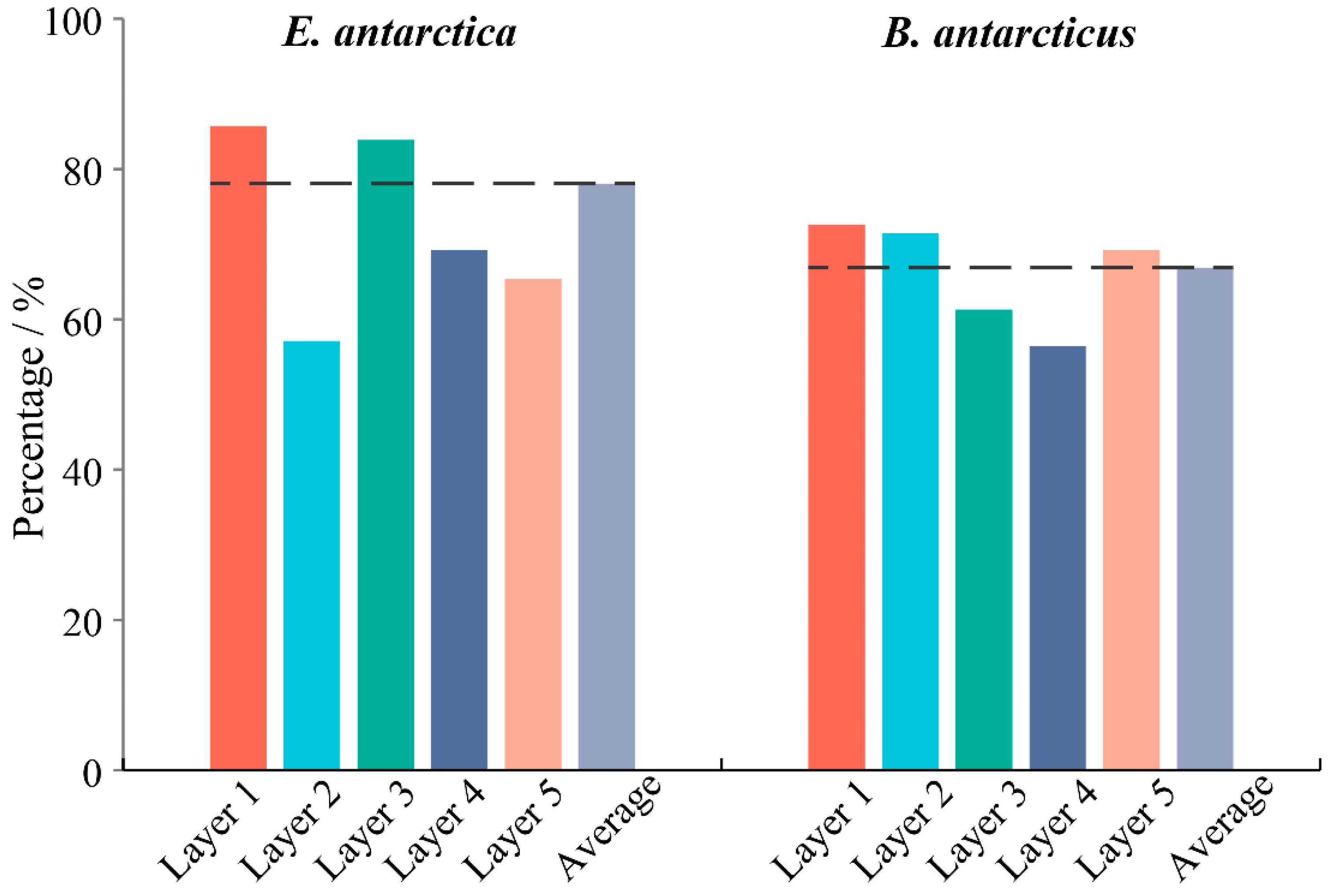
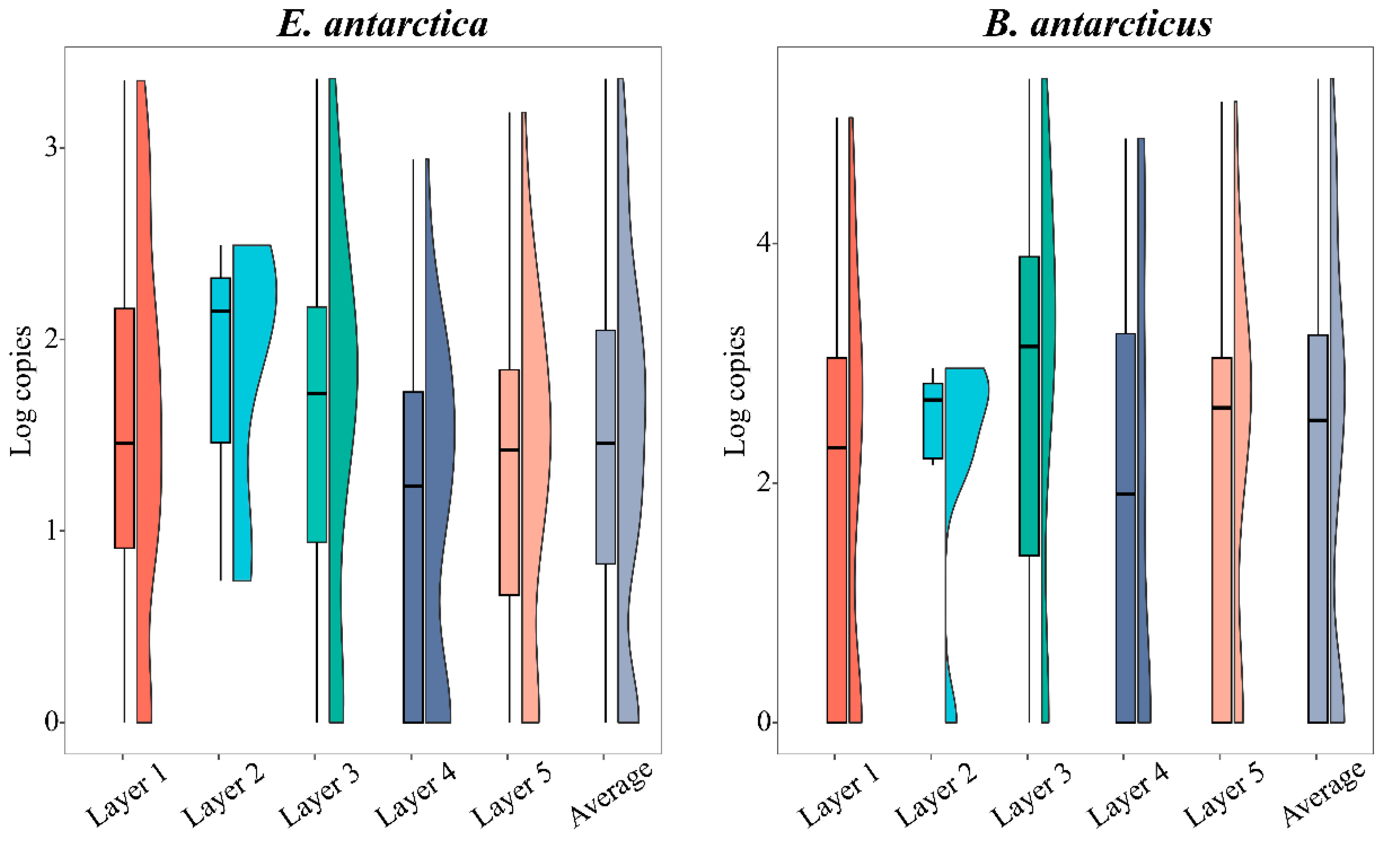
3.3. Comparison of Vertical Distribution by eDNA Method
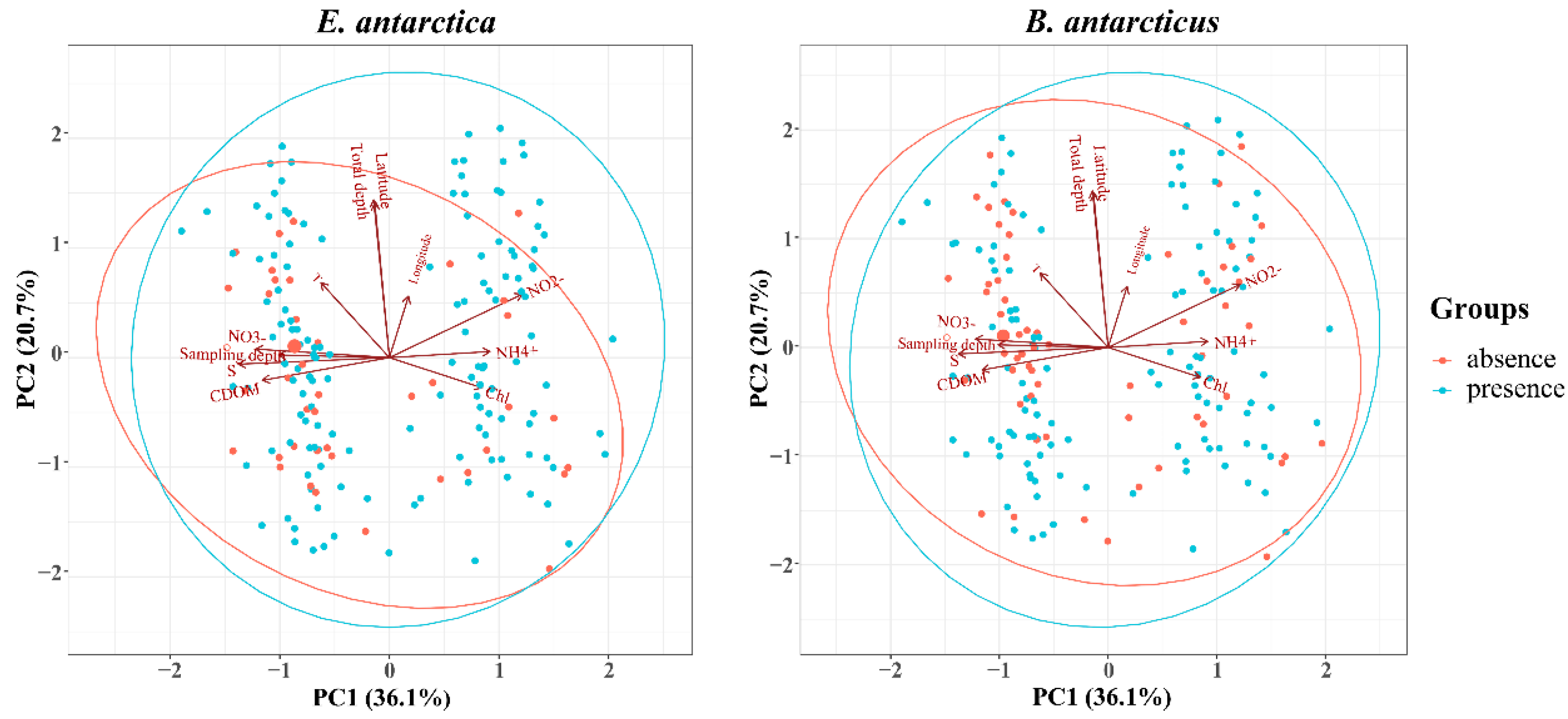
3.4. Environmental Factors Correlated with Distribution
4. Discussion
4.1. The Horizontal Distribution Patterns of Antarctic Lanternfish and Antarctic Deep-Sea Smelt
4.2. eDNA Reveals Different Vertical Distribution Structures in Two Fish Species
4.3. The Distribution of the Two Fish Species Is Affected by Different Environmental Factors
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cherel, Y.; Ducatez, S.; Fontaine, C.; Richard, P.; Guinet, C. Stable isotopes reveal the trophic position and mesopelagic fish diet of female southern elephant seals breeding on the Kerguelen Islands. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 370, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.D.M.; Brown, C.J.; Bulman, C.M.; Fulton, E.A.; Johnson, P.; Kaplan, I.C.; Lozano-Montes, H.; Mackinson, S.; Marzloff, M.; Shannon, L.J.; et al. Impacts of fishing low–trophic level species on marine ecosystems. Science 2011, 333, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, S.P.; Olson, R.J.; Watters, G.M. Complex wasp-waist regulation of pelagic ecosystems in the Pacific Ocean. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2013, 23, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irigoien, X.; Klevjer, T.A.; Røstad, A.; Martinez, U.; Boyra, G.; Acuña, J.L.; Bode, A.; Echevarria, F.; Gonzalez-Gordillo, J.I.; Hernandez-Leon, S.; et al. Large mesopelagic fishes biomass and trophic efficiency in the open ocean. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, H.; Dettai, A.; Heindler, F.M.; Collins, M.A.; Duhamel, G.; Hautecoeur, M.; Steinke, D.; Volckaert, F.A.; Van de Putte, A.P. Diversity of mesopelagic fishes in the Southern Ocean-a phylogeographic perspective using DNA barcoding. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Ashford, J.R.; Bestley, S.; Wei, X.; Walters, A.; Zhu, G. Otolith chemistry of Electrona antarctica suggests a potential population marker distinguishing the southern Kerguelen Plateau from the eastward-flowing Antarctic Circumpolar Current. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.A.; Stowasser, G.; Fielding, S.; Shreeve, R.; Xavier, J.C.; Venables, H.J.; Enderlein, P.; Cherel, Y.; Van de Putte, A. Latitudinal and bathymetric patterns in the distribution and abundance of mesopelagic fish in the Scotia Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2012, 59, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Zhang, C.; Luo, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, G.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, S.; Zhang, W.; et al. The feeding strategies of the antarctic lanternfish electrona antarctica (pisces: Myctophidae) in the amundsen and cosmonaut seas (Southern Ocean), assessed with a classification tree analysis. Polar Biol. 2024, 47, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Putte, A.P.; Jackson, G.D.; Pakhomov, E.; Flores, H.; Volckaert, F.A. Distribution of squid and fish in the pelagic zone of the Cosmonaut Sea and Prydz Bay region during the BROKE-West campaign. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moteki, M.; Horimoto, N.; Nagaiwa, R.; Amakasu, K.; Ishimaru, T.; Yamaguchi, Y. Pelagic fish distribution and ontogenetic vertical migration in common mesopelagic species off Lützow-Holm Bay (Indian Ocean sector, Southern Ocean) during austral summer. Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 1461–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koubbi, P.; Hulley, P.-A.; Pruvost, P.; Henri, P.; Labat, J.-P.; Wadley, V.; Hirano, D.; Moteki, M. Size distribution of meso-and bathypelagic fish in the Dumont d’Urville Sea (East Antarctica) during the CEAMARC surveys. Polar Sci. 2011, 5, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, H.; Van de Putte, A.P.; Siegel, V.; Pakhomov, E.A.; Van Franeker, J.A.; Meesters, E.H.; Volckaert, F.A. Distribution, abundance and ecological relevance of pelagic fishes in the Lazarev Sea, Southern Ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 367, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moteki, M.; Tsujimura, E.; Hulley, P.A. Developmental intervals during the larval and juvenile stages of the Antarctic myctophid fish Electrona antarctica in relation to changes in feeding and swimming functions. Polar Sci. 2017, 12, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, M.A.; Nichols, P.D.; Wilson, G. Fatty acid composition of lipid-rich myctophids and mackerel icefish (Champsocephalus gunnari)–Southern Ocean food-web implications. Polar Biol. 2002, 25, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.; Watkins, J.; Trathan, P.; Reid, K.; Meredith, M.; Thorpe, S.; Johnston, N.; Clarke, A.; Tarling, G.; Collins, M.; et al. Spatial and temporal operation of the Scotia Sea ecosystem: A review of large-scale links in a krill centred food web. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 113–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.A.; Hill, S.L.; Tarling, G.A.; Murphy, E.J. Myctophid fish (Family Myctophidae) are central consumers in the food web of the Scotia Sea (Southern Ocean). Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gon, O. A description of the postlarva of Cygnodraco mawsoni Waite, 1916 (Pisces, Bathydraconidae), from the Southern Ocean. Afr. Zool. 1987, 22, 321–322. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsworthy, S.D.; Lewis, M.; Williams, R.; He, X.; Young, J.W.; Van den Hoff, J. Diet of Patagonian toothfish (Dissostichus eleginoides) around Macquarie Island, South Pacific Ocean. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 53, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, S.A.; Melbourne-Thomas, J.; Trebilco, R.; Blanchard, J.L.; Raymond, B.; Constable, A. Decades of dietary data demonstrate regional food web structures in the Southern Ocean. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.A.; Collins, M.A.; Stowasser, G.; Tarling, G.A. Southern Ocean mesopelagic fish communities in the Scotia Sea are sustained by mass immigration. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 569, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freer, J.J.; Tarling, G.A.; Collins, M.A.; Partridge, J.C.; Genner, M.J. Predicting future distributions of lanternfish, a significant ecological resource within the Southern Ocean. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.T.; Amsler, M.O.; Aronson, R.B.; Thatje, S.; McClintock, J.B.; Vos, S.C.; Kaeli, J.W.; Singh, H.; La Mesa, M. Photographic survey of benthos provides insights into the Antarctic fish fauna from the Marguerite Bay slope and the Amundsen Sea. Antarct. Sci. 2013, 25, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; O’Brien, P.E.; Stark, J.S.; Johnstone, G.J.; Riddle, M.J. Integrating multibeam sonar and underwater video data to map benthic habitats in an East Antarctic nearshore environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 164, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehui, W.; Chunlin, L.; Mi, D.; Chi, Z.; Zhenjiang, Y.; Yang, L.; Yongjun, T.; Jianfeng, H. Community structure of mesopelagic fauna and the length-weight relationships of three common fishes in the Cosmonaut Sea, Southern Ocean. Adv. Polar Sci. 2022, 33, 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- Valentini, A.; Taberlet, P.; Miaud, C.; Civade, R.; Herder, J.; Thomsen, P.F.; Bellemain, E.; Besnard, A.; Coissac, E.; Boyer, F.; et al. Next-generation monitoring of aquatic biodiversity using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M. Environmental DNA Metabarcoding: A novel method for biodiversity monitoring of marine fish communities. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2022, 14, 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowart, D.A.; Murphy, K.R.; Cheng, C.H.C. Metagenomic sequencing of environmental DNA reveals marine faunal assemblages from the West Antarctic Peninsula. Mar. Genom. 2018, 37, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Miao, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, R.; Li, H.; Lin, L. First pelagic fish biodiversity assessment of Cosmonaut Sea based on environmental DNA. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 192, 106225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bao, Y.; Fang, X.; Ruan, Y.; Rong, Y.; Yang, G. A circumpolar study of surface zooplankton biodiversity of the Southern Ocean based on eDNA metabarcoding. Environ. Res. 2024, 255, 119183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Hajibabaei, M.; Rieseberg, L.H. Environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohmann, K.; Evans, A.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Carvalho, G.R.; Creer, S.; Knapp, M.; Yu, D.W.; De Bruyn, M. Environmental DNA for wildlife biology and biodiversity monitoring. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stat, M.; John, J.; DiBattista, J.D.; Newman, S.J.; Bunce, M.; Harvey, E.S. Combined use of eDNA metabarcoding and video surveillance for the assessment of fish biodiversity. Conserv. Biol. 2019, 33, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Lu, G.; Gao, T. Detection of an invasive species through an environmental DNA approach: The example of the red drum Sciaenops ocellatus in the East China Sea. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 815, 152865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, S.; Takahara, T.; Doi, H.; Shibata, N.; Yamanaka, H. The detection of aquatic macroorganisms using environmental DNA analysis—A review of methods for collection, extraction, and detection. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Poulsen, J.Y.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H.; et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, L.R.; Lawson Handley, L.; Hahn, C.; Boonham, N.; Rees, H.C.; Gough, K.C.; Lewis, E.; Adams, I.P.; Brotherton, P.; Phillips, S.; et al. Needle in a haystack? A comparison of eDNA metabarcoding and targeted qPCR for detection of the great crested newt (Triturus cristatus). Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 6330–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Ito, S.-I.; Wong, M.K.-S.; Yoshizawa, S.; Inoue, J.; Itoh, S.; Yukami, R.; Ishikawa, K.; Guo, C.; Ijichi, M.; et al. Comparison of species-specific qPCR and metabarcoding methods to detect small pelagic fish distribution from open ocean environmental DNA. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Minami, K.; Fukaya, K.; Takahashi, K.; Sawada, H.; Murakami, H.; Tsuji, S.; Hashizume, H.; Kubonaga, S.; Horiuchi, T.; et al. Environmental DNA as a ‘snapshot’ of fish distribution: A case study of Japanese jack mackerel in Maizuru Bay, Sea of Japan. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149786. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Lin, H.J.; Li, B.Y.; Du, H.; Yan, Z.G. Environmental DNA reveals the spatiotemporal distribution and migration characteristics of the Yangtze Finless Porpoise, the sole aquatic mammal in the Yangtze River. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, J.; Duan, M.; Tian, Y. Age and growth of Antarctic deep-sea smelt (Bathylagus antarcticus), an important mesopelagic fish in the Southern Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2022, 201, 105122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, B.P.V.; Pakhomov, E.A.; Trotsenko, B.G. The macrozooplankton of the Cosmonaut Sea, east Antarctica (30 E–60 E), 1987–1990. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2007, 54, 1042–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancraft, T.M.; Hopkins, T.L.; Torres, J.J.; Donnelly, J. Oceanic micronektonic/macrozooplanktonic community structure and feeding in ice covered Antarctic waters during the winter (AMERIEZ 1988). Polar. Biol. 1991, 11, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, Y.; Gao, L.; Guo, G.; Fang, Y. Changes of Circumpolar Deep Water between 2006 and 2020 in the south-west Indian Ocean, East Antarctica. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2022, 197, 105043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, N.; Liu, S.; Chen, Z.; Xu, A.; Gao, T. DNA barcoding of fishes from Zhoushan coastal waters using mitochondrial COI and 12S rRNA genes. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2023, 41, 1997–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R.; Hebert, P.D. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R package for multivariate analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Wood, S.; Wood, M.S. Package ‘mgcv’, R package version 1.9-3; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015.
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S.; Adler, D.; Bates, D.; Baud-Bovy, G.; Ellison, S.; Firth, D.; Friendly, M.; Gorjanc, G.; Graves, S.; et al. Package ‘car’, Version 3.1-3; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2012.
- Hoddell, R.J.; Crossley, A.C.; Williams, R.; Hosie, G.W. The distribution of Antarctic pelagic fish and larvae (CCAMLR division 58.4.1). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2000, 47, 2519–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Oro, E. The role of fish in the Antarctic marine food web: Differences between inshore and offshore waters in the southern Scotia Arc and west Antarctic Peninsula. Antarct. Sci. 2002, 14, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moteki, M.; Koubbi, P.; Pruvost, P.; Tavernier, E.; Hulley, P.A. Spatial distribution of pelagic fish off Adélie and George V Land, East Antarctica in the austral summer 2008. Polar Sci. 2011, 5, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, B.L.; Van de Putte, A.P.; Hindell, M.A.; Raymond, B.; Saunders, R.A.; Walters, A.; Trebilco, R. Species distribution models describe spatial variability in mesopelagic fish abundance in the Southern Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 981434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, S.; Pauly, T.; Bindoff, N.L.; Strutton, P.G. “BROKE” a biological/oceanographic survey off the coast of East Antarctica (80–150° E) carried out in January–March 1996. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2000, 47, 2281–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeunen, G.; Lamare, M.D.; Knapp, M.; Spencer, H.G.; Taylor, H.R.; Stat, M.; Bunce, M.; Gemmell, N.J. Water stratification in the marine biome restricts vertical environmental DNA (eDNA) signal dispersal. Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhamel, G.; Hulley, P.A.; Causse, R.; Koubbi, P.; Vacchi, M.; Pruvost, P.; Vigetta, S.; Irisson, J.O.; Mormede, S.; Belchier, M.; et al. Biogeographic patterns of fish. In Biogeographic atlas of the Southern Ocean; Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 328–362. [Google Scholar]
- Piatkowski, U.; Rodhouse, P.G.; White, M.G.; Bone, D.G.; Symon, C. Nekton community of the Scotia Sea as sampled by the RMT 25 during austral summer. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 112, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Kielgast, J.; Iversen, L.L.; Wiuf, C.; Rasmussen, M.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Orlando, L.; Willerslev, E. Monitoring endangered freshwater biodiversity using environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2565–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Inui, R.; Akamatsu, Y.; Kanno, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Takahara, T.; Minamoto, T. Environmental DNA analysis for estimating the abundance and biomass of stream fish. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Masuda, R.; Sato, Y.; Sado, T.; Araki, H.; Kondoh, M.; Minamoto, T.; Miya, M. Environmental DNA metabarcoding reveals local fish communities in a species-rich coastal sea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusch, C.; Hulley, P.A.; Kock, K.H. Community structure and feeding ecology of mesopelagic fishes in the slope waters of King George Island (South Shetland Islands, Antarctica). Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2004, 51, 1685–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.B.; Sunday, J.M.; Rogers, S.M. Predicting the fate of eDNA in the environment and implications for studying biodiversity. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20191409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2019, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, D.G.; Lewis, M.R.; Worm, B. Global phytoplankton decline over the past century. Nature 2010, 466, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Duan, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Ma, S.; Ju, P.; Shi, W.; et al. Ontogenetic shift in feeding habits of Antarctic deep-sea smelt Bathylagus antarcticus in the Cosmonaut Sea, East Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2025, 48, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andruszkiewicz, E.A.; Koseff, J.R.; Fringer, O.B.; Ouellette, N.T.; Lowe, A.B.; Edwards, C.A.; Boehm, A.B. Modeling environmental DNA transport in the coastal ocean using Lagrangian particle tracking. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Yoon, S.; Kasai, A.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Sakata, M.K.; Horiuchi, T.; Sawada, H.; Kondoh, M.; Yamashita, Y.; et al. Dispersion and degradation of environmental DNA from caged fish in a marine environment. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzafesta, E.; Shokri, M. The combined negative effect of temperature, UV radiation and salinity on eDNA detection: A global meta-analysis on aquatic ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 176, 113669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Oligo Sequences | Assay Performance | Amplicon Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. antarctica | Forward: 5′-CCCTATTTGTCTGAGCCGTCCTC-3′ | PCR efficiency: 98.32% R2 = 0.9995 LOD: 8 LOQ: 14 | 107 bp |
| Reverse: 5′-GGTGTTTAGGTTCCGGTCCGTTAA-3′ | |||
| Probe: 5′FAM-TGCTCCTCTCACTCCCTGTACTAGCTGCCG-3′BHQ1 | |||
| B. antarcticus | Forward: 5′-CATGCAGGAGCTTCCGTAGAC-3′ | PCR efficiency: 90.60% R2 = 0.9993 LOD: 12 LOQ: 18 | 153 bp |
| Reverse: 5′-GACAGACCAAATAAAGAGGGGAGTC-3′ | |||
| Probe: 5′FAM-ACCATCTTCTCCCTCCACCTCGCTGGG-3′BHQ1 |
| Explanatory Variable | Accumulation of Deviance Explanation/% | Importance/% | p | AIC (Akaike Information Criterion) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log—E. antarctica | NO3− | 12 | 12 | 0.28 | 493.8053 |
| Longitude | 21.6 | 9.6 | <0.05 | 484.9752 | |
| Chl | 24.6 | 3 | <0.01 | 480.255 | |
| Salinity | 25.7 | 1.1 | <0.05 | 478.748 | |
| NH4+ | 27 | 1.3 | 0.10 | 477.5129 | |
| 0/1—E. antarctica | NO2− | 3.6 | 3.6 | 0.09 | 197.7437 |
| Longitude | 12.9 | 9.3 | 0.06 | 193.4223 | |
| Chl | 17.6 | 4.7 | 0.19 | 191.4463 | |
| sampling depth | 19.9 | 2.3 | 0.06 | 189.6297 | |
| Latitude | 21.7 | 1.8 | 0.27 | 188.7583 | |
| Biomass—E. antarctica | Chl | 93.2 | 93.2 | <0.01 | 184.7565 |
| DO | 100 | 6.8 | <0.01 | 38.87483 | |
| Abundance—E. antarctica | PO4− | 80 | 80 | <0.01 | 125.6865 |
| NO3− | 99.4 | 19.4 | <0.01 | 68.78184 | |
| Log—B. antarcticus | CDOM | 11.3 | 11.3 | <0.01 | 699.667 |
| Chl | 15 | 3.7 | <0.01 | 693.4619 | |
| Latitude | 17.9 | 2.9 | 0.31 | 692.783 | |
| 0/1—B. antarcticus | T | 11.1 | 11.1 | <0.01 | 234.8247 |
| total depth | 19 | 7.9 | <0.01 | 224.4735 | |
| Biomass—B. antarcticus | PO4− | 45.4 | 45.4 | <0.01 | 232.3302 |
| NO3− | 57.7 | 12.3 | <0.01 | 230.5606 | |
| Abundance—B. antarcticus | PO4− | 63.5 | 63.5 | <0.01 | 142.2869 |
| NH4+ | 72.8 | 9.3 | <0.01 | 138.3001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Duan, M.; Ju, P.; Zhang, W.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; He, J.; Shi, W.; Tian, Y. The Biogeographic Patterns of Two Typical Mesopelagic Fishes in the Cosmonaut Sea Through a Combination of Environmental DNA and a Trawl Survey. Fishes 2025, 10, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070354
Wang Y, Liu C, Duan M, Ju P, Zhang W, Ma S, Li J, He J, Shi W, Tian Y. The Biogeographic Patterns of Two Typical Mesopelagic Fishes in the Cosmonaut Sea Through a Combination of Environmental DNA and a Trawl Survey. Fishes. 2025; 10(7):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070354
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yehui, Chunlin Liu, Mi Duan, Peilong Ju, Wenchao Zhang, Shuyang Ma, Jianchao Li, Jianfeng He, Wei Shi, and Yongjun Tian. 2025. "The Biogeographic Patterns of Two Typical Mesopelagic Fishes in the Cosmonaut Sea Through a Combination of Environmental DNA and a Trawl Survey" Fishes 10, no. 7: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070354
APA StyleWang, Y., Liu, C., Duan, M., Ju, P., Zhang, W., Ma, S., Li, J., He, J., Shi, W., & Tian, Y. (2025). The Biogeographic Patterns of Two Typical Mesopelagic Fishes in the Cosmonaut Sea Through a Combination of Environmental DNA and a Trawl Survey. Fishes, 10(7), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070354







