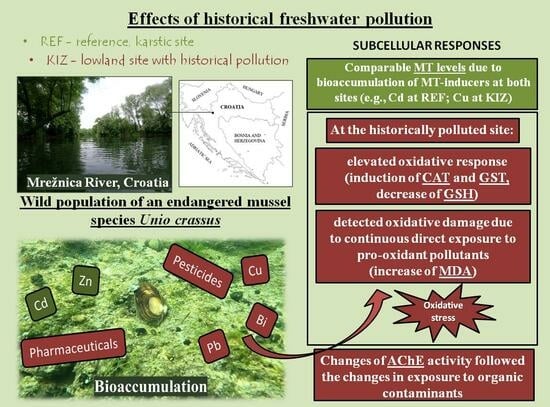
Changes in Subcellular Responses in the Digestive Gland of the Freshwater Mussel Unio crassus from a Historically Contaminated Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling of Mussels
2.2. Processing of the Mussel Digestive Gland Samples
2.3. Biomarker Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Biomarkers of Metal Exposure and General Stress
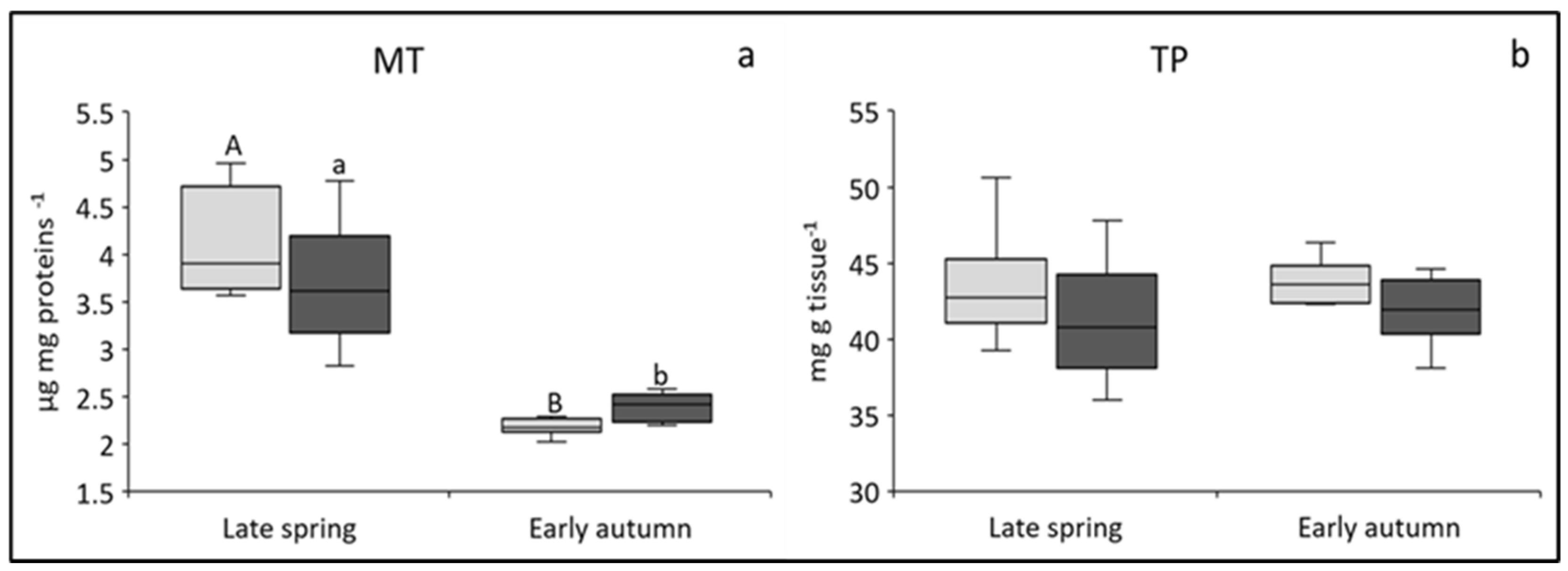
3.1.1. MT Concentrations
3.1.2. TP Concentrations
3.2. Changes in Biomarkers of Antioxidative Capacity (CAT, GSH), Xenobiotic Detoxification (GST), and Oxidative Damage (MDA)
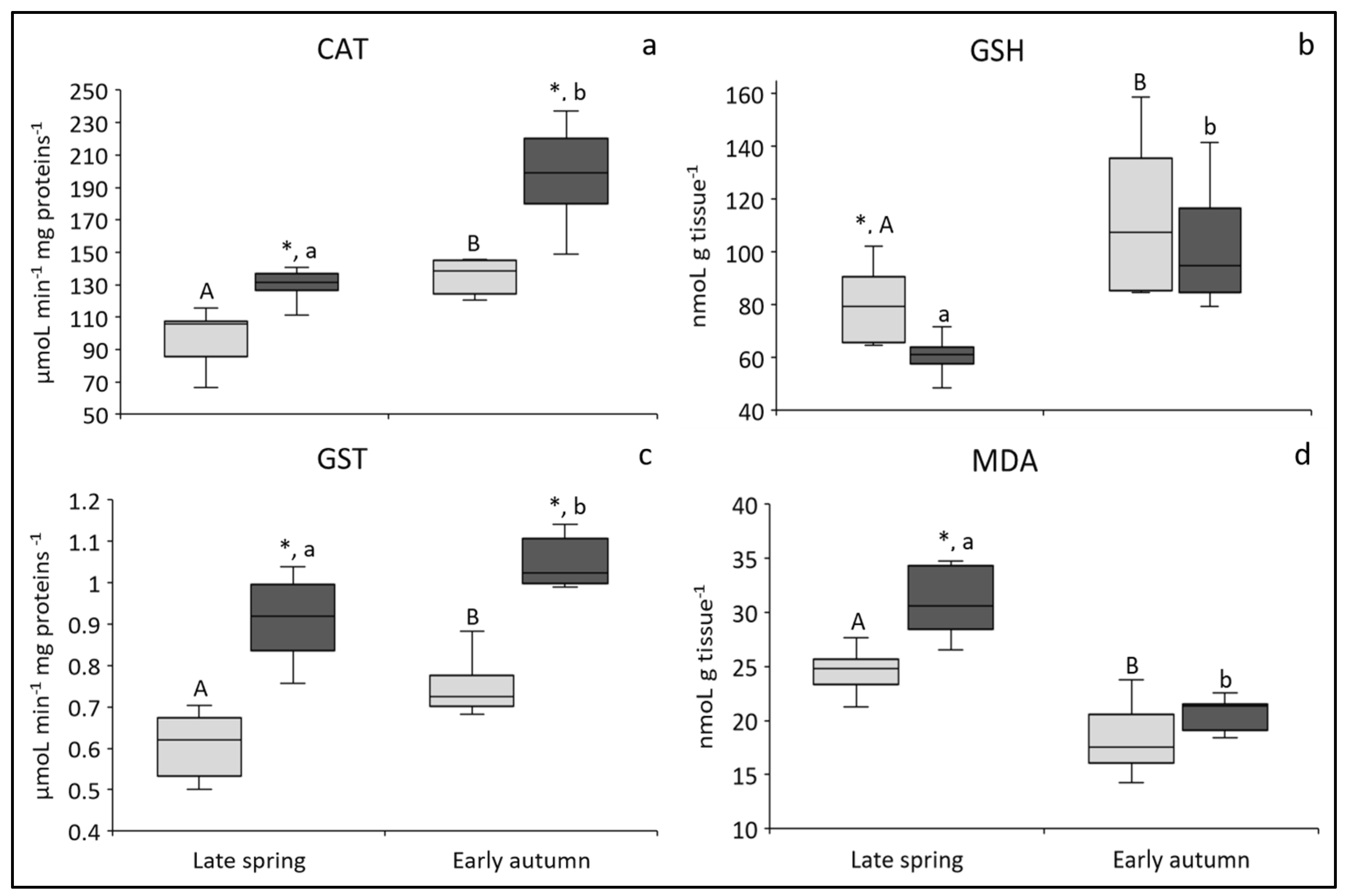
3.2.1. CAT Activity: Biomarker of Antioxidative Capacity
3.2.2. GSH Concentration: Biomarker of Antioxidative Capacity
3.2.3. GST Activity: Biomarker of Xenobiotic Detoxification
3.2.4. MDA Concentration: Biomarker of Oxidative Damage
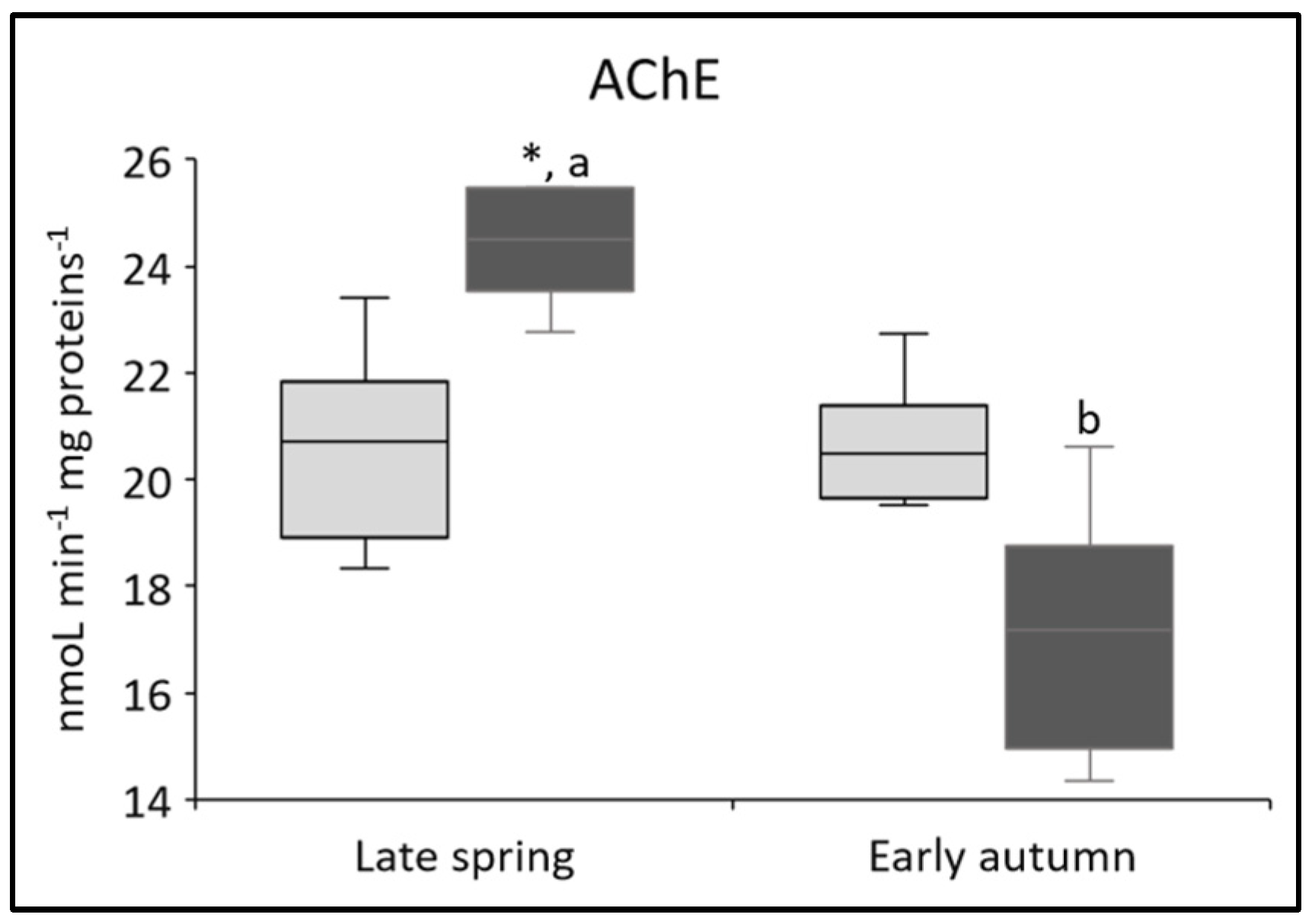
3.3. Changes in Biomarker of Neurotoxicity (AChE)
3.4. Season as a Common Factor Influencing Biomarker Responses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dragun, Z.; Stipaničev, D.; Fiket, Ž.; Lučić, M.; Udiković Kolić, N.; Puljko, A.; Repec, S.; Šoštarić Vulić, Z.; Ivanković, D.; Barac, F.; et al. Yesterday’s contamination—A problem of today? The case study of discontinued historical contamination of the Mrežnica River (Croatia). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, e157775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frančišković-Bilinski, S.; Bilinski, H.; Maldini, K.; Milović, S.; Zhang, Q.; Appel, E. Chemical and magnetic tracing of coal slag pollutants in karstic river sediments. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, R.R.; Rothwell, J.J.; Woodward, J.C. Metal contamination of bed sediments in the Irwell and Upper Mersey catchments, northwest England: Exploring the legacy of industry and urban growth. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 2648–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, S.M.; Rothwell, J.J. Mobilisation of sediment-associated metals from historical Pb working sites on the River Sheaf, Sheffield, UK. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 155, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suschka, J.; Ryborz, S.; Leszczynska, I. Surface water and sediment contamination in an old industrial region of Poland—Two critical examples. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 29, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stipaničev, D.; Dragun, Z.; Repec, S.; Ivanković, D.; Barac, F.; Kiralj, Z.; Kralj, T.; Valić, D. Dynamics of drug contamination of the river-water in the rural, semirural and urban areas of the Mrežnica River in Croatia during COVID-19 pandemic (2020–2021). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 93652–93666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiralj, Z.; Dragun, Z.; Lajtner, J.; Trgovčić, K.; Valić, D.; Ivanković, D. Accumulation of metal(loid)s in the digestive gland of the mussel Unio crassus Philipsson, 1788: A reliable detection of historical freshwater contamination. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoli, F.; Pellegrini, D.; Cicero, A.M.; Nigro, M.; Benedetti, M.; Gorbi, S.; Fattorini, D.; D’Errico, G.; Di Carlo, M.; Nardi, A.; et al. A multidisciplinary weight of evidence approach for environmental risk assessment at the Costa Concordia wreck: Integrative indices from Mussel Watch. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 96, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiard, J.C.; Amiard-Triquet, C.; Barka, S.; Pellerin, J.; Rainbow, P.S. Metallothioneins in aquatic invertebrates: Their role in metal detoxification and their use as biomarkers. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 76, 160–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanković, D.; Pavičić, J.; Erk, M.; Filipović-Marijić, V.; Raspor, B. Evaluation of the Mytilus galloprovincialis Lam. digestive gland metallothionein as a biomarker in a long-term field study: Seasonal and spatial variability. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanković, D.; Pavičić, J.; Beatović, V.; Klobučar, R.S.; Klobučar, G.I.V. Inducibility of metallothionein biosynthesis in the whole soft tissue of zebra mussels Dreissena polymorpha exposed to cadmium, copper, and pentachlorophenol. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 25, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspor, B.; Pavičić, J. Induction of metallothionein-like proteins in the digestive gland of Mytilus galloprovincialis after a chronic exposure to the mixture of trace heavy metals. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 1991, 3, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercal, N.; Gurer-Orhan, H.; Aykin-Burns, N. Toxic metals and oxidative stress. Part I: Mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2001, 1, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, S.S.; Harris, G.K.; Shi, X. Metal-induced oxidative stress and signal transduction. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 37, 1921–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viarengo, A.; Burlando, B.; Dondero, F.; Marro, A.; Fabbri, R. Metallothionein as a tool in biomonitoring programmes. Biomarkers 1999, 4, 455–466. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Rocha, C.P.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, F.J.M. Enzymes as useful biomarkers to assess the response of freshwater communities to pesticide exposure—A review. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, C.; Doyotte, A.; Babut, M.; Exinger, A.; Vasseur, P. Antioxidant biomarkers in freshwater bivalves, Unio tumidus, in response to different contamination profiles of aquatic sediments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2000, 45, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sárkány-Kiss, A.; Herczeg, I.; Palombi, B.; Grigorszky, I.; Antal, L.; Bácsi, I.; Mozsár, A.; Kalmár, A.F.; Nagy, S.A. Toxicity tests of chlorinated hydrocarbons on the river mussel, Unio crassus (Bivalvia, Unionidae). North-West. J. Zool. 2012, 8, 358–361. [Google Scholar]
- Třešňáková, N.; Çağlan Günal, A.; Başaran Kankılıç, G.; Paçal, E.; Nihan Tavşanoğlu, Ü; Uyar, R.; Erkoç, F. Sub-lethal toxicities of zinc pyrithione, copper pyrithione alone and in combination to the indicator mussel species Unio crassus Philipsson, 1788 (Bivalvia, Unionidae). Chem. Ecol. 2020, 36, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkmen, E.U.; Arslan, P.; Erkoç, F.; Günal, A.Ç.; Duran, H. The cerium oxide nanoparticles toxicity induced physiological, histological and biochemical alterations in freshwater mussels, Unio crassus. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 83, 127371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudhur, S.M.; Shekha, Y.A. Histopathological and biochemical biomarker response of mussel, Unio pictorum, to carbamate pesticide carbaryl: A laboratory study. Indian J. Anim. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köprücü, K.; Yonar, S.M.; Şeker, E. Effects of cypermethrin on antioxidant status, oxidative stress biomarkers, behavior, and mortality in the freshwater mussel Unio elongatulus eucirrus. Fish. Sci. 2010, 76, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paçal, E.; Gümüş, A.; Günal, Ç.; Erkmen, B.; Arslan, P.; Yıldırım, Z.; Erkoç, F. Oxidative stress response as biomarker of exposure of a freshwater invertebrate model organism (Unio mancus Lamarck, 1819) to antifouling copper pyrithione. Pestic. Fitomed. 2022, 37, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falfushynska, H.I.; Gnatyshyna, L.L.; Gyori, J.; Stoliar, O.B. Metallothioneins, Caspase-3 and oxidative stress responses in the multi-marker study of freshwater mussel inhabiting sites of various human impact. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 14, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspor, B.; Dragun, Z.; Erk, M. Examining the suitability of mussel digestive gland to serve as a biomonitoring target organ. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2005, 56, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zając, K.; Zając, T.A.; Adamski, P.; Bielański, W.; Ćmiel, A.M.; Lipińska, A.M. Dispersal and mortality of translocated thick-shelled river mussel Unio crassus Philipsson, 1788 adults revealed by radio tracking. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 29, 331–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viarengo, A.; Ponzano, E.; Dondero, F.; Fabbri, R. A simple spectrophotometric method for metallothionein evaluation in marine organisms: An application to Mediterranean and Antarctic molluscs. Mar. Environ. Res. 1997, 44, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdineaud, J.-P.; Štambuk, A.; Šrut, M.; Radić Brkanac, S.; Ivanković, D.; Lisjak, D.; Sauerborn Klobučar, R.; Dragun, Z.; Bačić, N.; Klobučar, G. Gold and silver nanoparticles effects to the earthworm Eisenia fetida—The importance of tissue over soil concentrations. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 44, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Schellhorn, H. Rapid kinetic microassay for catalase activity. J. Biomol. Tech. 2007, 18, 185–187. [Google Scholar]
- Tietze, F. Enzymic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: Applications to mammalian blood and other tissues. Anal. Biochem. 1969, 27, 502–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, I.; Kode, A.; Biswas, S. Assay for quantitative determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide levels using enzymatic recycling method. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Jakoby, W.B. Glutathione S-transferase. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botsoglou, N.A.; Fletouris, D.J.; Papageorgiou, G.E.; Vassilopoulos, V.N.; Mantis, A.J.; Trakatelliss, A.G. Rapid, sensitive, and specific thiobarbituric acid method for measuring lipid peroxidation in animal tissue, food, and feedstuff samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijošek, T.; Filipović Marijić, V.; Dragun, Z.; Krasnići, N.; Ivanković, D.; Erk, M. Evaluation of multi-biomarker response in fish intestine as an initial indication of anthropogenic impact in the aquatic karst environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragun, Z.; Kiralj, Z.; Pećnjak, A.; Ivanković, D. The study of acidic/basic nature of metallothioneins and other metal-binding biomolecules in the soluble hepatic fraction of the northern pike (Esox lucius). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecoeur, S.; Videmann, B.; Berny, P. Evaluation of metallothionein as a biomarker of single and combined Cd/Cu exposure in Dreissena polymorpha. Environ. Res. 2004, 94, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoloğlu, E.; Uçkun, M.; Uçkun, A.A. Metal accumulation and biochemical variations in the freshwater mussels (Unio mancus) collected from Atatürk Dam Lake, Turkey. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2018, 79, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, E.H.; Mawgood, A.A.; Ghonim, A.Z.; Nagar, R.E. The possibility of using the fresh water bivalve, Spathopsis rubens, in the Nile River, El Mahmoudia water stream as bioindicator for pollution. Int. J. Limnol. 2018, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potet, M.; Devin, S.; Pain-Devin, S.; Rousselle, P.; Giambérini, L. Integrated multi-biomarker responses in two dreissenid species following metal and thermal cross-stress. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, A.A.D.S.; Wood, C.M.; Bianchini, A.; Gillis, P.L. Responses of biomarkers in wild freshwater mussels chronically exposed to complex contaminant mixtures. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyotte, A.; Cossu, C.; Jacquin, M.-C.; Babut, M.; Vasseur, P. Antioxidant enzymes, glutathione and lipid peroxidation as relevant biomarkers of experimental or field exposure in the gills and the digestive gland of the freshwater bivalve Unio tumidus. Aquat. Toxicol. 1997, 39, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pytharopoulou, S.; Grintzalis, K.; Sazakli, E.; Leotsinidis, M.; Georgiou, C.D.; Kalpaxis, D.L. Translational responses and oxidative stress of mussels experimentally exposed to Hg, Cu and Cd: One pattern does not fit at all. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Liñán, L.; Bellas, J.; Etxebarria, N.; Nieto, O.; Beiras, R. Glutathione S-transferase, glutathione peroxidase and acetylcholinesterase activities in mussels transplanted to harbour areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, N.S.; Shekha, Y.A. Acute toxicity of chlorpyrifos on the freshwater bivalves (Unio tigridis) and effects on bioindicators. Baghdad Sci. J. 2023, 21, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainy, A.C.D.; Gennari De Medeiros, M.H.; Di Mascio, P.; de Almeida, E.A. In vivo effects of metals on the acetylcholinesterase activity of the Perna perna mussel’s digestive gland. Rev. Biotemas 2006, 19, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Caen, J.P.; He, H.Y.; Jin, Q.H.; Guo, L.H.; Alemany, M.; Zhang, L.Y.; Shi, Y.F. Induction of acetylcholinesterase expression during apoptosis in various cell types. Cell Death Differ. 2002, 9, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaizer, R.R.; Corrêa, M.C.; Spanevello, R.M.; Morsch, V.M.; Mazzanti, C.M.; Gonçalves, J.F.; Schetinger, M.R.C. Acetylcholinesterase activation and enhanced lipid peroxidation after long-term exposure to low levels of aluminum on different mouse brain regions. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, C.; Gagné, F. Cumulative effects of ibuprofen and air emersion in zebra mussels Dreissena polymorpha. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 55, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, E.; Antal, L.; Stoyanova, S.; Aranudova, D.; Velcheva, I.; Iliev, I.; Vasileva, T.; Bivolarski, V.; Mitkovska, V.; Chassovnikarova, T.; et al. Biomarkers for pollution in caged mussels from three reservoirs in Bulgaria: A pilot study. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.-L.; Taylor, J.J. Effect of chronic administration of acetylcholinesterase activity in the hypothalamus and medulla oblongata of the rat brain. An ultrastructural study. Brain Res. 1973, 54, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selak, L. Biološke i Ekološke Značajke Slatkovodnog Školjkaša Unio crassus Philipsson, 1788. Bachelor’s Thesis, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2016. [Google Scholar]

| Period | Sampling Site | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| REF | KIZ | ||
| Metals in the Sediment [1] | |||
| Bi/µg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 0.330 ± 0.112 0.254 ± 0.030 | 0.416 ± 0.152 0.405 ± 0.052 |
| Cd/µg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 0.509 ± 0.067 0.516 ± 0.047 | 0.537 ± 0.021 0.582 ± 0.058 |
| Cr/µg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 52.6 ± 17.5 37.9 ± 5.4 | 81.0 ± 13.9 84.4 ± 3.1 |
| Cs/µg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 2.02 ± 0.85 1.87 ± 0.19 | 4.13 ± 0.94 5.04 ± 0.41 |
| Cu/µg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 19.4 ± 6.0 15.3 ± 2.5 | 31.7 ± 8.9 38.9 ± 1.8 |
| Fe/mg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 11.7 ± 3.7 9.69 ± 1.24 | 21.9 ± 5.4 20.1 ± 1.7 |
| Ni/µg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 25.8 ± 6.6 23.6 ± 3.0 | 48.8 ± 5.8 54.2 ± 8.3 |
| Pb/µg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 13.3 ± 6.0 9.95 ± 0.86 | 26.9 ± 21.8 20.6 ± 1.7 |
| Rb/µg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 28.0 ± 12.7 25.4 ± 2.7 | 38.8 ± 11.7 45.2 ± 5.2 |
| Sb/µg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 0.537 ± 0.229 0.434 ± 0.062 | 0.799 ± 0.337 4.19 ± 5.66 |
| U/µg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 1.18 ± 0.48 1.08 ± 0.12 | 3.75 ± 0.76 3.94 ± 0.37 |
| V/µg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 38.6 ± 15.4 36.6 ± 4.8 | 63.0 ± 11.1 71.1 ± 6.5 |
| Zn/µg g−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 49.1 ± 19.9 36.1 ± 2.1 | 93.2 ± 30.2 68.2 ± 1.1 |
| Organic contaminants in the water [1,6] | |||
| Herbicides/µg L−1 A | April 2021 September 2021 | 0.007 0.002 | 0.029 0.002 |
| Insecticides/µg L−1 B | April 2021 September 2021 | 0.198 0.347 | 0.309 0.578 |
| Total drugs/ng L−1 C | April 2021 September 2021 | 10.6 443 | 429 491 |
| DF | MT | TP | CAT | GSH | GST | MDA | AChE | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | ||
| Site | 1 | 1.19 | 0.286 | 1.25 | 0.275 | 36.8 | <0.001 | 4.15 | 0.052 | 89.6 | <0.001 | 8.97 | 0.006 | 1.09 | 0.307 |
| Season | 1 | 47.2 | <0.001 | 0.168 | 0.685 | 56.9 | <0.001 | 27.5 | <0.001 | 19.4 | <0.001 | 38.1 | <0.001 | 9.34 | 0.005 |
| Interaction | 1 | 2.78 | 0.107 | 0.946 | 0.341 | 2.22 | 0.149 | 0.527 | 0.475 | 0.019 | 0.889 | 3.89 | 0.060 | 8.01 | 0.009 |
| Period | Sampling Site | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| REF | KIZ | ||
| Ag/ng g−1 | June 2021 October 2021 | 3.81 ± 0.55 5.22 ± 1.13 | 5.47 ± 0.79 11.8 ± 5.5 |
| Bi/ng g−1 | June 2021 October 2021 | 2.55 ± 0.34 2.37 ± 0.57 | 3.89 ± 0.34 3.72 ± 0.78 |
| Cd/ng g−1 | June 2021 October 2021 | 1149 ± 284 222 ± 47.8 | 96.0 ± 12.3 49.9 ± 7.9 |
| Cu/µg g−1 | June 2021 October 2021 | 1.41 ± 0.21 0.99 ± 0.13 | 3.67 ± 0.57 2.02 ± 0.25 |
| Cs/ng g−1 | June 2021 October 2021 | 0.67 ± 0.11 0.86 ± 0.06 | 1.54 ± 0.21 2.95 ± 0.30 |
| Pb/ng g−1 | June 2021 October 2021 | 31.7 ± 6.6 18.6 ± 1.3 | 48.2 ± 8.1 66.5 ± 18.8 |
| Sb/ng g−1 | June 2021 October 2021 | 1.06 ± 0.10 0.77 ± 0.08 | 2.41 ± 0.14 2.27 ± 0.17 |
| Tl/ng g−1 | June 2021 October 2021 | 1.42 ± 0.28 1.52 ± 0.12 | 1.96 ± 0.24 2.33 ± 0.19 |
| U/ng g−1 | June 2021 October 2021 | 24.4 ± 3.1 17.5 ± 2.9 | 43.6 ± 3.8 41.1 ± 2.9 |
| V/ng g−1 | June 2021 October 2021 | 129 ± 8.6 102 ± 20.4 | 166 ± 18 141 ± 16 |
| Period | Sampling Site | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| REF | KIZ | ||
| Dissolved oxygen /mg L−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 10.1 11.4 | 9.24 11.3 |
| Conductivity /µS cm−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 375 333 | 366 327 |
| pH | April 2021 September 2021 | 8.30 8.08 | 8.38 8.26 |
| Nitrates /mg N L−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 0.28 0.07 | 0.29 0.08 |
| Total phosphorus /mg P L−1 | April 2021 September 2021 | 0.017 0.013 | 0.022 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiralj, Z.; Dragun, Z.; Lajtner, J.; Trgovčić, K.; Mijošek Pavin, T.; Bušić, B.; Ivanković, D. Changes in Subcellular Responses in the Digestive Gland of the Freshwater Mussel Unio crassus from a Historically Contaminated Environment. Fishes 2025, 10, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070317
Kiralj Z, Dragun Z, Lajtner J, Trgovčić K, Mijošek Pavin T, Bušić B, Ivanković D. Changes in Subcellular Responses in the Digestive Gland of the Freshwater Mussel Unio crassus from a Historically Contaminated Environment. Fishes. 2025; 10(7):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070317
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiralj, Zoran, Zrinka Dragun, Jasna Lajtner, Krešimira Trgovčić, Tatjana Mijošek Pavin, Bruno Bušić, and Dušica Ivanković. 2025. "Changes in Subcellular Responses in the Digestive Gland of the Freshwater Mussel Unio crassus from a Historically Contaminated Environment" Fishes 10, no. 7: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070317
APA StyleKiralj, Z., Dragun, Z., Lajtner, J., Trgovčić, K., Mijošek Pavin, T., Bušić, B., & Ivanković, D. (2025). Changes in Subcellular Responses in the Digestive Gland of the Freshwater Mussel Unio crassus from a Historically Contaminated Environment. Fishes, 10(7), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10070317