An Ecosystem-Based Approach to Evaluating Impacts of Fisheries Management on Ecosystem Restoration in a Chinese Subtropical Yangming Reservoir
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
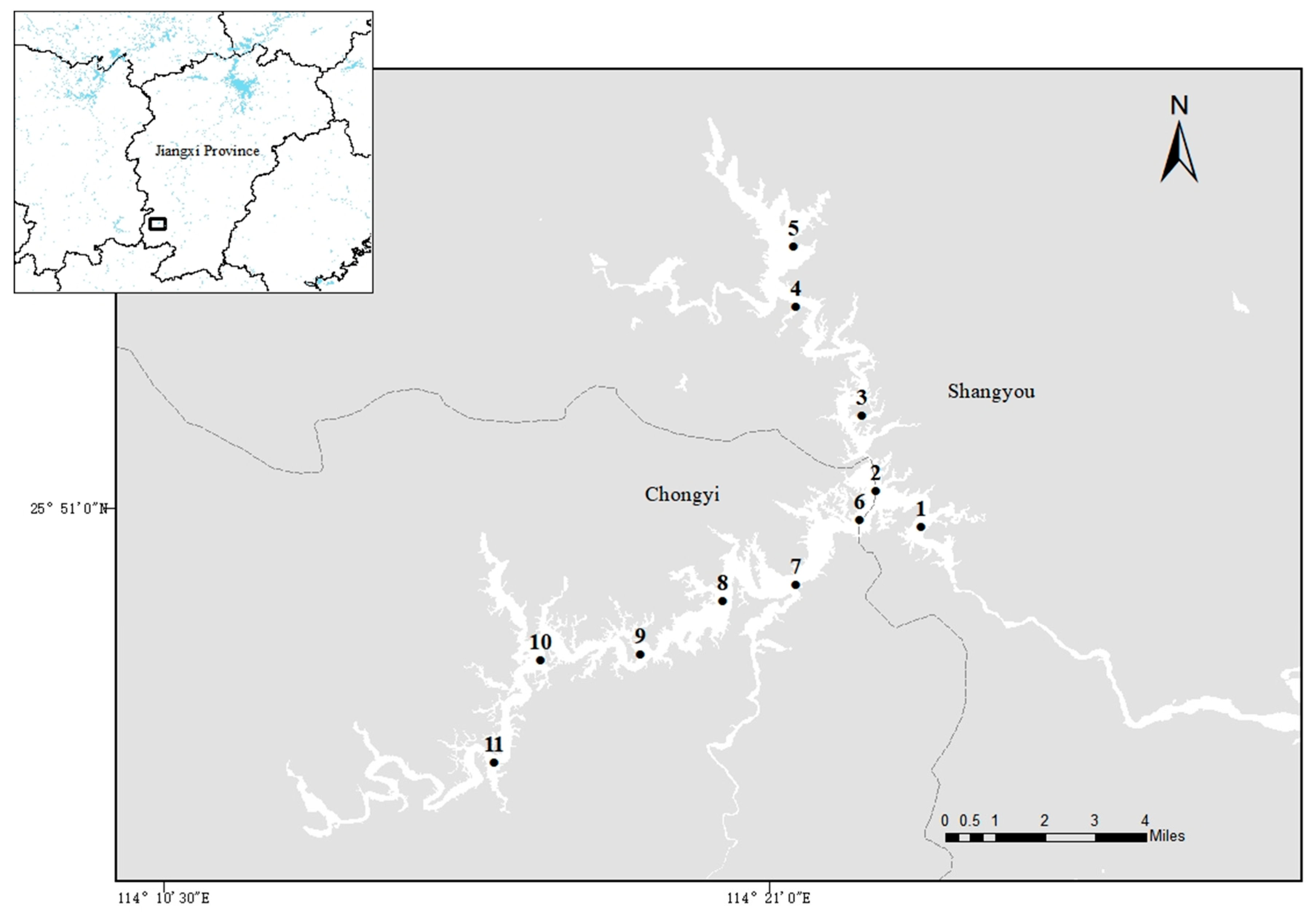
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Ecopath with Ecosim Modelling Approach
2.2.1. Functional Groups
2.2.2. Fish
2.2.3. Zoobenthos and Planktons
2.2.4. Detritus
2.2.5. Diet
2.2.6. Model Balance and Data Analysis
3. Results
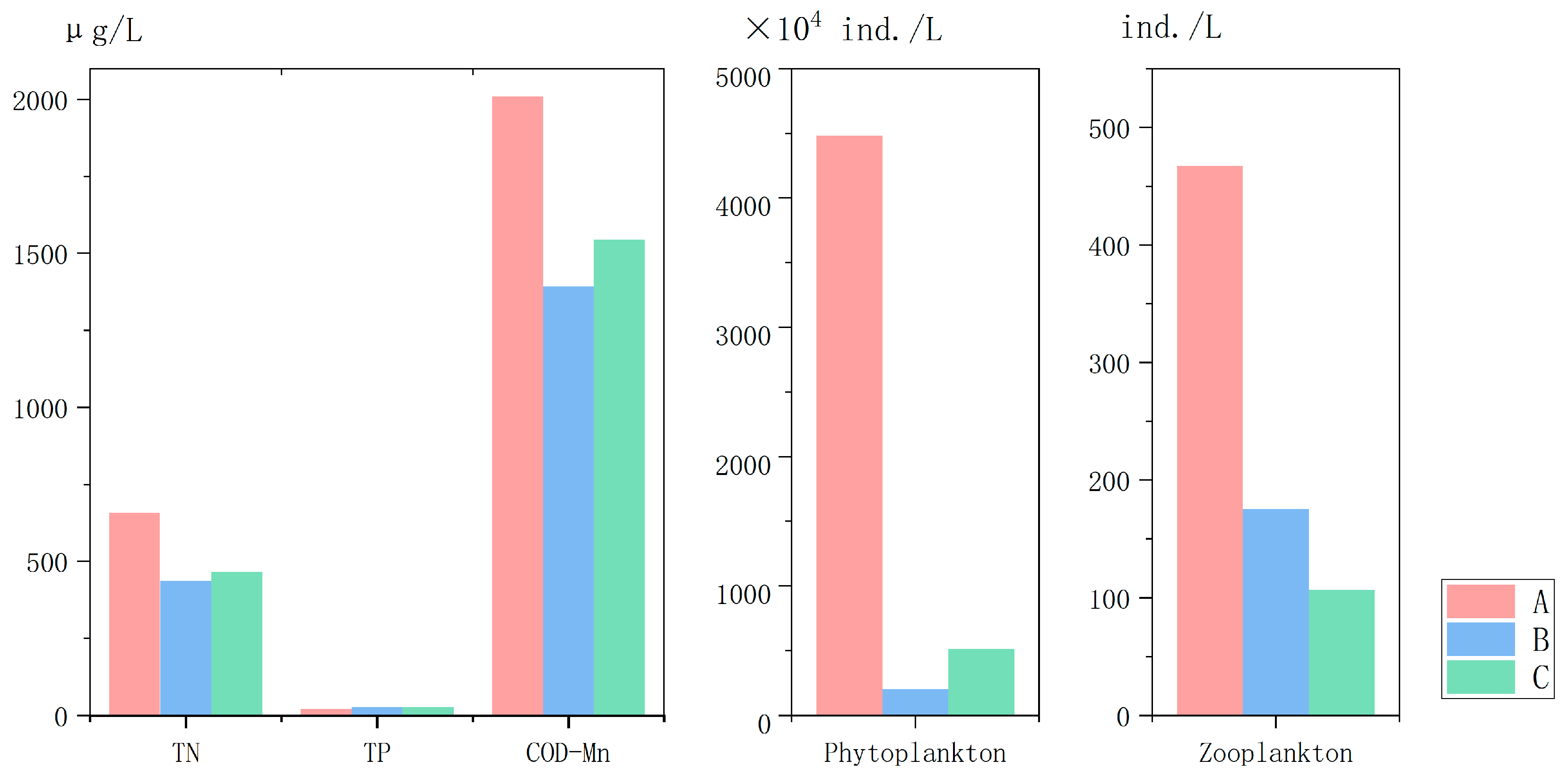
3.1. Phytoplankton and Water Quality
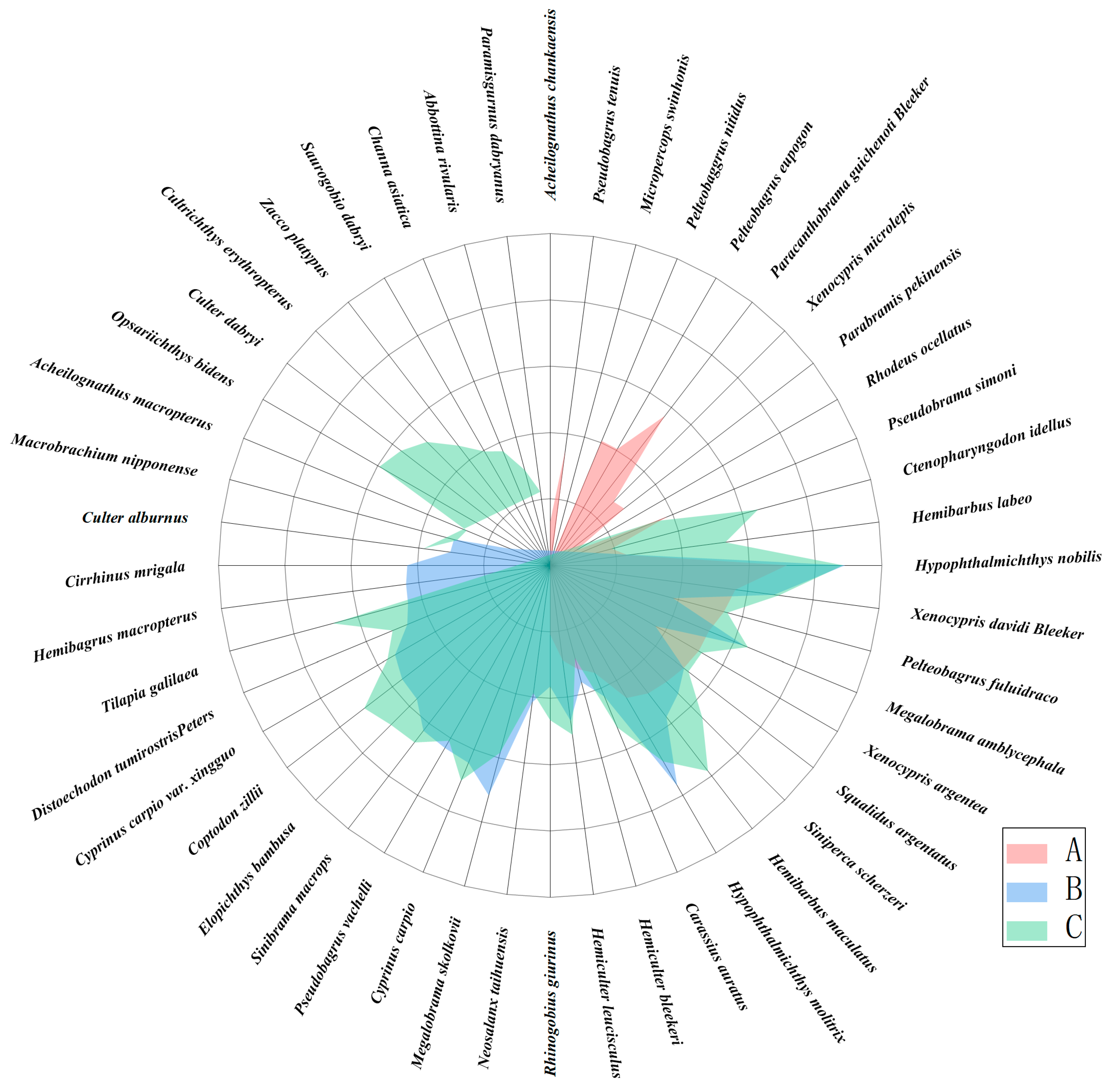
3.2. Fish Community
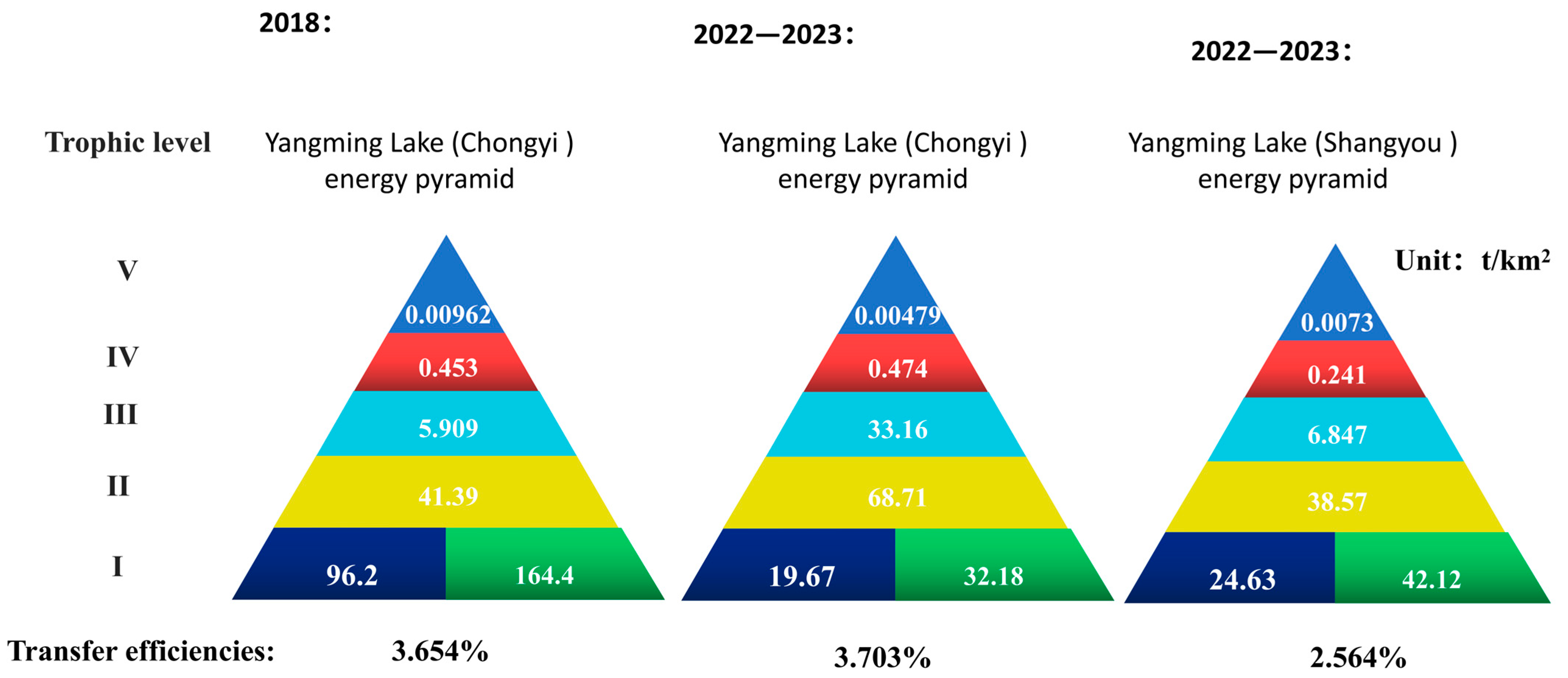
3.3. Model Basic Estimations
3.4. Model System Statistics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amoros, C.; Bornette, G. Connectivity and biocomplexity in waterbodies of riverine floodplains. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymans, J.; Ulanowicz, R.; Bondavalli, C. Network analysis of the South Florida Everglades graminoid marshes and comparison with nearby cypress ecosystems. Ecol. Model. 2002, 149, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Song, C.; Deng, J.; Xue, B.; Gong, Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Shi, K.; et al. Importance and main cological and environmental problems of lakes in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 3503–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, J.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Tong, Y. Importance and vulnerability of lakes and reservoirs supporting drinking water in China. Fundam. Res. 2023, 3, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, J.S. Aquaculture Production and Biodiversity Conservation. BioScience 2009, 59, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2014; ISBN 9789251082751. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor, R.L.; Goldburg, R.J.; Primavera, J.H.; Kautsky, N.; Beveridge, M.C.; Clay, J.; Folke, C.; Lubchenco, J.; Mooney, H.; Troell, M. Effect of aquaculture on world fish supplies. Nature 2000, 405, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charvet, P.; Occhi, T.V.T.; Faria, L.; Carvalho, B.M.; Pedroso, C.R.; Carneiro, L.; Freitas, M.O.; Petrere-junior, M.; Vitule, J.R.S. Tilapia farming threatens Brazil’s waters. Science 2021, 371, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.; Neal, C.; Jarvie, H.; Doody, D. Agriculture and Eutrophication: Where Do We Go from Here? Sustainability 2014, 6, 5853–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M. Impacts of cage fish farms in a large reservoir on water and sediment chemistry. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, É.A.T.; da Silva, G.M.N.; de Oliveira, C.R.; Cunha, M.C.C.; Sobral, M.d.C. Assessing the negative impact of an aquaculture farm on effluent water quality in Itacuruba, Pernambuco, Brazilian semiarid region. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veer, G.v.d.; Nentwig, W. Environmental and economic impact assessment of alien and invasive fish species in Europe using the generic impact scoring system. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2015, 24, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Berthou, E. The characteristics of invasive fishes: What has been learned so far? J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, J.; Kotusz, J.; Witkowski, A. Alien invasive fish species in Polish waters: An overview. Folia Zool. 2010, 59, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.J.; Chart, T.E.; Trammell, M.A.; Wullschleger, J.G.; Bergersen, E.P. Fish species composition before and after construction of a main stem reservoir on the White River, Colorado. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1994, 40, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, J.R.; Davies, G.D.; Harrod, C. Trophic interactions and consequent impacts of the invasive fish Pseudorasbora parva in a native aquatic foodweb: A field investigation in the UK. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budy, P.; Thiede, G.P.; Lobón-Cerviá, J.; Fernandez, G.G.; McHugh, P.; McIntosh, A.; Vøllestad, L.A.; Becares, E.; Jellyman, P. Limitation and facilitation of one of the world’s most invasive fish: An intercontinental comparison. Ecology 2013, 94, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wan, C.; Ding, Q.; Pan, L.; Wu, S.; Gao, S. Effect of reservoir fisheries on water quality of Chinese reservoirs and bionomic control countermeasures. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Lazar, L.; Vlas, O.; Pantea, E.; Boicenco, L.; Marin, O.; Abaza, V.; Filimon, A.; Bisinicu, E. Black Sea Eutrophication Comparative Analysis of Intensity between Coastal and Offshore Waters. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Yu, Q.; Huang, X. Evaluation of the Nutritional Status of Water Bodies in Nine Large Reservoirs in the Yangtze River Basin. J. Hydroecol. 2001, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, C.; Huang, S.; Wu, M.; Du, S. Effect of fish stocking with bait on phytoplankton and water quality in Panjiakou Reservoir enclosures. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2011, 31, 525–532. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Industry Standards of the People’s Republic of China; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Technical specifications for monitoring and evaluating algal bloom based on remote sensing and field monitoring(HJ 1098-2020). 2020. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/other/qt/202002/t20200213_762889.shtml (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- Bișinicu, E.; Boicenco, L.; Pantea, E.; Timofte, F.; Lazăr, L.; Vlas, O. Qualitative Model of the Causal Interactions between Phytoplankton, Zooplankton, and Environmental Factors in the Romanian Black Sea. Phycology 2024, 4, 168–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Han, S.; Su, H.; Xia, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ke, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. Nontraditional biomanipulation: A powerful ecotechnology to combat cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic freshwaters. Innov. Life 2023, 1, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, F.; Xia, J. Research on Development Status, Issues and Countermeasures for Ecological Fishery of Large-Scale Water. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 38, 142–148. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, Z.; Bi, Y.; Li, Z. Analysis on the development strategies and key techniques of ecological fisheries in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2015, 39, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, L. The Dilemma and Path Choice of Reservoir Fishery Sustainable Development Based on the Perspective of Ecology: Verified by the Illustration of Qiandao Lake Aquatic Environment Protection Oriented Fishery. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Development Status and Countermeasures of Cage Fish Farming Industry in Doushui Lake, Shangyou County. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 12, 324–325. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=XMmmt_ij6VHME3s1JGji4HuMeuabbkhZsMtDQE90PknImgS67x81cIzCRoRWiotD34TLIQVLperu901TTO0YeUpRllTBGXEzFchWQes3nRUAgpgMJV-ObD14hnGGtZChlbkxzmHfk-BW900ykPZwjDChx-L9Re2olrwSYnFICJEo9QDvIwN9MA==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 7 March 2024). (In Chinese).
- He, Y.; Zhang, X. Thinking of Ecological Fisheries Development in Shangyou County. Jiangxi Fish. Sci. Technol. 2014, 1, 7–9. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=XMmmt_ij6VGBUjWAgBE_XdqwiARwgIhoTxXnNFEr4ReLv6V3-Q6SYvhDiOpiA4NdCX6jE5GeSsqOD4rn7pyeNidTT3_UO6rhA-ZPd2zrdTPlv8Yo_5IOc5RlerPCpxJBw0lEvyK_goZA9aVK5iV6S8F6ptjZ_qEhxIR4yBkcQVaU0RRw2w-VFw==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Yangming Lake Ganzhou City Jiangxi Province—Beauiful Rivers and Lakes. China Ecol. Civiliz. 2024, 62–63. (In Chinese)
- Christensen, V.; Pauly, D. Trophic Models of Aquatic Ecosystems; WorldFish: Penang, Malaysia, 1993; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.K. Studies on Ecology of the East Lake; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Xue, T.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X.P. Community structure and environmental determinants of Macrozoobenthos in the Doushui Lake Basin. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Val. 2019, 28, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippsen, J.S.; Minte-Vera, C.V.; Coll, M.; Angelini, R. Assessing fishing impacts in a tropical reservoir through an ecosystem modeling approach. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2019, 29, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Gong, L.; Chen, Y.; Ni, L.; Pitcher, T.J.; Kang, B.; Guo, L. Modeling ecosystem impacts of the invasive Japanese smelt Hypomesus nipponensis in Lake Erhai, southwestern China. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 67, 101488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianneke, V.W.; Kong, X.; Knap, H.; Janssen, A.B.G. A serious game approach for lake modeling and management: The EscapeBLOOM. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 173, 105941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, B.; Francesca, L.M.; Teresa, M.; Ceferina, V.; Giuseppe, P.; Anna, N. The quality of meat in milk fed lambs is affected by the ewe diet: A review. Meat Sci. 2024, 207, 109374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, D.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Leng, X.; Zhao, D.; An, S. Effects of a Fishing Ban on the Ecosystem Stability and Water Quality of a Plateau Lake: A Case Study of Caohai Lake, China. Water 2024, 16, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Liu, H.; Wei, N.; Meng, Z.; Hu, F.; Li, X. Comparing Ecosystem Structure and Function of the Geheyan Reservoir Based on the Ecopath Model After a Fishing Ban. Fishes 2025, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chang, J. Evaluation of the effect of stocking silver carp and binghead carp on the ecosystem of Qiandao Lake using Ecopath model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 6853–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutopoulos, D.K.; Douligeri, A.S.; Ziou, A.; Kiriazis, N.; Korakis, A.; Petsis, N.; Katselis, G.N. A Modelling Approach for the Management of Invasive Species at a High-Altitude Artificial Lake. Limnol. Rev. 2024, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubiani, É.A.; Angelini, R.; Vieira, L.C.G.; Gomes, L.C.; Agostinho, A.A. Trophic models in Neotropical reservoirs: Testing hypotheses on the relationship between aging and maturity. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 3838–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y. Ecological safety Assessment and Research of the Lake of Doushui Based on F-IBI and Nutrient Criterion. Master’s Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, V.; Walters, C.J. Ecopath with Ecosim: Methods, capabilities and limitations. Ecol. Model. 2004, 172, 109–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Gurski, L.; Bleninger, T.; Rohr, H.; Wolf, N.; Lorke, A. Hydrodynamic Drivers of Nutrient and Phytoplankton Dynamics in a Subtropical Reservoir. Water 2022, 14, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, K.M.; Smith, R.S.; Raimondi, P.; Reed, D. Sensitivity analysis to reduce sampling effort of a long-term monitoring program. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, M.J.; Beaty, K.G.; Findlay, D.L.; Findlay, W.J.; Schiff, S.L.; St. Louis, V.L.; Venkiteswaran, J.J. Long-term changes in nutrient dynamics and plankton communities following the creation of a new reservoir. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 76, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Green, S.A.; Cook, A.J.; Johnson, S.A.; Kerr, J.G.; O’Brien, K.R. Sources and fate of nutrients in a subtropical reservoir. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 74, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, V.; Walters, C.; Pauly, D. Ecopath with Ecosim: A User’s Guide. 2005. Volume 12. Available online: https://ecopath.org/ (accessed on 7 May 2022).
- Polovina, J. An overview of the ECOPATH model. Fishbyte 1984, 2, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Liao, F.; Yang, X.; Xie, Z.; Song, R. Fishes of Hunan; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, Z.; He, X.; Jin, W.; Chen, Y. Colored Atlas of Fishes in Sichuan; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Fishes of Jiangxi; Jiangxi Science and Technology Press: Nanchang, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Atlas of Common Aquatic Organism in China Basin; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Palomares, M.L.D.; Pauly, D. Predicting food consumption of fish populations as functions of mortality, food type, morphometrics, temperature and salinity. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1998, 49, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beverton, R.J.H.; Holt, S.J. A Review of Methods for Estimating Mortality Rates in Exploited Fish Populations, with Special Reference to Sources of Bias in Catch Sampling. Agric. Sci. 1956, 140, 67–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Sun, J.; Duan, Z.; Xiang, Y. Study on The Population Growth and mortality of Paracanthobrama Guichenoti Bleeker in Wanghu Lake. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1994, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Song, X. The preliminary investigation of the biological characteristics of the Rhinogobius giurinus in Paiyang Lake. Hebei Fish. 2013, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J. Studies on Fisheries Ecology in a Large Yunnan Plateau Lake, Lake Erhai, China; The Chinese Academy of Sciences: Wuhan, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Chen, F.; Changyan, F.; Luo, J. Studies on age and growth of Channa asiatica. J. Fish. Sci. China 1999, 6, 10–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D. Yangtze River Aquatic Biological Resources Monitoring Manual; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment (China). Water Quality—Determination of Phytoplankton—Filtration Membrane-Microscope Counting Method. 2021, HJ1215. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/202201/W020220121590258111680.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2022).
- SC/T 9102.3-2007; Specification for Ecological Environment Monitoring of Fisheries. Part 3: Freshwater. National Library of Digital Standards: Beijing, China, 2007. Available online: https://www.ndls.org.cn/standard/detail/748ebe4b689fbe01399797d8fa505998 (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Moraes, C.R.F.d.; Attayde, J.L.d.; Henry-Silva, G.G. Stable isotopes of C and N as dietary indicators of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cultivated in net cages in a tropical reservoir. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, H.; Yao, X.; Zhao, K.; Qiu, B.; Dai, M. Research on spatial difference of diet of cultured abalone by stable carbon and nitrogen isotope. J. Fuzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2017, 45, 454–458. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J. Ecological Studies on the Food Web Structures and Trophic Relationships of Freshwater Lakes in China Using Stable Carbon and Nitrogen Isotopes. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Deehr, R.A.; Luczkovich, J.J.; Hart, K.J.; Clough, L.M.; Johnson, B.J.; Johnson, J.C. Using stable isotope analysis to validate effective trophic levels from Ecopath models of areas closed and open to shrimp trawling in Core Sound, NC, USA. Ecol. Model. 2014, 282, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkas, L.; Oliphant, M.S.; Iverson, I.L.K. Fish Bulletin 152. Food Habits of Albacore, Bluefin Tuna, and Bonito In California Waters. Scripps Inst. Oceanography Library. 1970. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/7t5868rd (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Ulanowicz, R.; Puccia, C. Mixed trophic impacts ecosystems. Coenoses 1990, 5, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Valls, A.; Coll, M.; Christensen, V. Keystone species: Toward an operational concept for marine biodiversity conservation. Ecol. Monogr. 2015, 85, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libralato, S.; Christensen, V.; Pauly, D. A method for identifying keystone species in food web models. Ecol. Model. 2006, 195, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barausse, A.; Duci, A.; Mazzoldi, C.; Artioli, Y.; Palmeri, L. Trophic network model of the Northern Adriatic Sea: Analysis of an exploited and eutrophic ecosystem. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 83, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, E.P. The Strategy of Ecosystem Development: An understanding of ecological succession provides a basis for resolving man’s conflict with nature. Science 1969, 164, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. Ecological Diversity; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1975; Volume 22, p. 174. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhm, J.L. Use of Biomass Units in Shannon’s Formula. Ecology 1968, 49, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morissette, L. Complexity, cost and quality of ecosystem models and their impact on resilience: A comparative analysis, with emphasis on marine mammals and the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Brithish Columbia, Vancouver, BC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, T.; Xin, K. Public health: A sustainable plan for China’s drinking water. Nature 2014, 511, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauda, A.B.; Ajadi, A.; Tola-Fabunmi, A.S.; Akinwole, A.O. Waste production in aquaculture: Sources, components and managements in different culture systems. Aquac. Fish. 2019, 4, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-F.; Xu, P.; Wu, X.; Xu, Z.-H.; Xu, Z.-H. Present condition of aquaculture nitrogen and phosphorus environmental pollution and future development strategy. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 34, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China Development of China’s Distant-Water Fisheries. Beijing, China; 2023. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/202310/content_6911268.htm (accessed on 29 October 2023).
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, K.; Zhu, K.; Xu, C.; Xie, J.; Xu, J. Aquaculture Impacts on China’s Marine Wild Fisheries Over the Past 30 Years. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 710124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeman, R.L. The Trophic-Dynamic Aspect of Ecology. Ecology 1942, 23, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Meng, Z.; HU, F.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, D. Nitrogen and phosphorus emissions from cage fish culture. Freshw. Fish. 2020, 50, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Wu, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Pan, J. Study on the influence of cage fish culture on water environment of Qiandao Lake. Agric. Technol. 2022, 42, 119–121. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, D.; Xia, T. Impacts of cage-culture of Oreochromis niloticus on organic matter content, fractionation and sorption of phosphorus, and alkaline phosphatase activity in a hypereutrophic lake, People’s Republic of China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 73, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Wang, Q.; Gao, C.; Zhao, J. Analysis of phytoplankton community characteristics and influencing factors in the Yangtze River Estuary. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2024, 39, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, R.T. Food Web Complexity and Species Diversity. Am. Nat. 1966, 100, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, R. Fluctuations of Animal Populations and a Measure of Community Stability. Ecology 1955, 36, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimm, S.L. Food Webs; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Khatun, M.H.; Barman, P.P.; Yi, J.; Lupa, S.T.; Zahangir, M.M.; Liu, Q. A preliminary snapshot of the trophic model and ecosystem attributes of Kaptai reservoir ecosystem, Bangladesh. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, R.S.T.d.; Angelini, R.; Henry-Silva, G.G. Interactions between cage fish farms and fishing in Brazilian semiarid reservoirs: An ecosystemic approach. Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, S.M.; Kovalenko, K.E.; Havel, J.E.; Kats, L.B. Aquatic invasive species: General trends in the literature and introduction to the special issue. Hydrobiologia 2015, 746, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, V. Ecosystem maturity—Towards quantification. Ecol. Model. 1995, 77, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, H.; Lobón-Cerviá, J.; Ramos, I.P.; Souto, A.C.; Nobile, A.B.; Zica, É.d.O.P.; Carvalho, E.D. Influence of a cage farming on the population of the fish species Apareiodon affinis (Steindachner, 1879) in the Chavantes reservoir, Paranapanema River SP/PR, Brazil. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2012, 24, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossaina, M.M.; Matsuishia, T.; Arhonditsisb, G. Elucidation of ecosystem attributes of an oligotrophic lake in Hokkaido, Japan, using Ecopath with Ecosim (EwE). Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Guo, C.; Gozlan, R.E.; Liu, J. Tilapia introduction in China: Economic boom in aquaculture versus ecological threats to ecosystems. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 15, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, R.J.; Huenneke, L.F. Disturbance, Diversity, and Invasion: Implications for Conservation. Conserv. Biol. 1992, 6, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, K.; Chesson, P.; Shea, K.; Chesson, P. Community ecology theory as a framework for biological invasions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2002, 17, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Brockway, D.G.; Larson, D.L.; Wang, D.; Ren, H. Improving Ecological Restoration to Curb Biotic Invasion—A Practical Guide. Invasive Plant Sci. Manag. 2018, 11, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; LIU, Z.; LIU, Q.; Guo, C.; Liao, C.; LI, W.; Guo, C.; ZHang, T.; Liu, J. Comparative Study on Reproductive Biology of Two Coinvasion Tilapia Species in the Shanmei Reservoir. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2023, 47, 657–665. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, M.N.; Derek Aday, D.; Rice, J.A.; Layman, C.A. Assessing the Influence of Tilapia on Sport Fish Species in North Carolina Reservoirs. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2018, 147, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022: Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Assessment of the Maximum Sustainable Yield of Portunus trituberculatus in the Northern Areas of the East China Sea Under the Impact of Stock Enhancement. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2022, 53, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.Y.; Bai, X.L., Xu; Wang, X.N.; Lv, Y.B.; Hou, J.; He, X.G. Analysis of ecological system characteristics and ecological capacity of Hypophthalmichthys molitrix and Aristichthys nobilis in the Weishui Reservoir based on Ecopath model. J. Fish. Sci. China 2021, 28, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, J. The effects of microorganisms on the migration and transformation of nitrogen in the polyculture system of Plagiogathops microlepis Bleeker, Hypophthalmichthys molitrix and Aristichthys nobilis. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramidas, I.; Dimarchopoulou, D.; Ofir, E.; Scotti, M.; Tsikliras, A.C.; Gal, G. Ecotrophic perspective in fisheries management: A review of Ecopath with Ecosim models in European marine ecosystems. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1182921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Bundy, A.; Shannon, L.J. Ecosystem Modelling Using the Ecopath with Ecosim Approach. In Computers in Fisheries Research; Megrey, B.A., Moksness, E., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 225–291. [Google Scholar]


| Year | Policy/Event | Impact on Fisheries in Yangming Lake (Jiangxi Province) | Wider Context/Policy Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre- 2017 | Cage fishing dominant in Yangming Lake. | Traditional cage farming using feed and cages was the primary fishery mode, introducing non-native species and contributing to water quality degradation (e.g., eutrophication from nutrient inputs). | Global concerns over aquaculture’s ecological impacts (e.g., cage fisheries linked to biodiversity loss and water pollution) [8,9,10,11,19]. |
| 2018 | Ecological fisheries pilot launched in Yangming Lake. | Shangyou County and Chongyi County initiated ecological fisheries via two fishery companies, shifting to “human-stocked, naturally-grown” models without feed/fertilizer/cages. | China’s growing emphasis on ecological protection; Jiangxi Province’s role in Yangtze River Basin sustainability [23,24]. |
| 2020 | Yangtze River Basin decade-long fishing ban implemented. | Shangyou County’s portion of Yangming Lake halted all fishery activities (including ecological fisheries) due to the ban. | Nationwide policy to prohibit natural water fishing/aquaculture, aiming to restore aquatic ecosystems [31,32]. |
| Chongyi County continued ecological fisheries (selective stocking of filter-feeding fish like silver carp/bighead carp). | Aligned with UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for life below water (SDG 14). | ||
| 2023 | Yangming Lake listed as “Second Batch of Outstanding Cases of Beautiful River and Lakes”. | Ecological fisheries in Chongyi County demonstrated improved water quality and biodiversity, serving as a model for sustainable fishery practices under the ban. | National recognition of successful ecosystem restoration; policy emphasis on balancing fishery development with ecological conservation [29]. |
| No. | Function Group | Code | Composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bottom piscivorous | BOP | Siniperca scherzeri |
| 2 | Yellow-head catfish | PEL | Pelteobagrus eupogon, P. nitidus, Tachysurus fulvidraco, Pseudobagrus tenuis |
| 3 | Paracanthobrama guichenoti Bleeker | PGB | Paracanthobrama guichenoti Bleeker |
| 4 | Xenocypris | XEN | Xenocypris davidi, Xenocyprisargentea, Xenocypris microlepis |
| 5 | Hemibarbus maculatus | HES | Hemibarbus maculatus |
| 6 | Hemiculter | HEM | Hemiculter leucisculus, |
| 7 | Crucian | CAR | Carassius auratus |
| 8 | Other fish | OTF | Abbottina rivularis, Acheilognathus chankaensis, Rhodeus ocellatus, Pseudobrama simoni |
| 9 | Goby | RhI | Rhinogobius giurinus |
| 10 | Silver gobio | SQA | Squalidus argentatus, |
| 11 | Bream | MPC | Megalobrama amblycephala, Parabramis pekinensis, Ctenopharyngodon idella |
| 12 | Silver carp | SIC | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix |
| 13 | Bighead carp | BIC | Aristichthys nobilis |
| 14 | Benthos | BEH | Anodonta, bellamya, Chironomid, Annelida, Arthropoda |
| 15 | Zooplankton | ZOP | Rotifera, Cladocera, Copepods |
| 16 | Phytoplankton | PHP | Cyanophyta, Bacillariophyta, Chlorophyta |
| 17 | Detritus | DET | Detritus |
| SYL | CYL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Function Group | Code | Composition | No. | Function Group | Code | Composition |
| 1 | Large carnivorous fish | ElB | Elopichthys bambusa | 1 | Large carnivorous fish | ElB | Elopichthys bambusa |
| 2 | Culter | CUT | Cultrichthys erythropterus, Culter alburnus, Culter dabryi dabryi | 2 | Culter | CUT | Cultrichthys erythropterus, Culter alburnus, Culter dabryi dabryi |
| 3 | Botton piscivorous | BOP | Siniperca scherzeri, Channa asiatica | 3 | Botton piscivorous | BOP | Siniperca scherzeri, Channa asiatica |
| 4 | Opsariichthys | OPS | Opsariichthys bidens, Zacco platypus | 4 | Yellow-head catfish meat | PEL | Pelteobagrus fulvidraco, Pelteobagrus vachelli, |
| 5 | Icefish | ICF | Neosalanx taihuensis | 5 | Sinibrama macrops | SIN | Sinibrama macrops |
| 6 | Yellow-head catfish meat | PEL | Pelteobagrus fulvidraco, Pelteobagrus vachelli, | 6 | Xenocypris | XEN | Xenocypris davidi, Distoechodon tumirostrisPeters, Xenocyprisargentea |
| 7 | Sinibrama macrops | SIN | Sinibrama macrops | 7 | Gobio | HES | Hemibarbus maculatus, Hemibarbus labeo, Saurogobio dabryi |
| 8 | Xenocypris | XEN | Xenocypris davidi, Distoechodon tumirostrisPeters, Xenocyprisargentea | 8 | Hemiculter | HEM | Hemiculter leucisculus, |
| 9 | Gobio | HES | Hemibarbus maculatus, Hemibarbus labeo, Saurogobio dabryi | 9 | Tilapia | TIL | Coptodon zillii, Tilapia galilaea |
| 10 | Hemiculter | HEM | Hemiculter leucisculus | 10 | Crucian | CAR | Carassius auratus |
| 11 | Tilapia | TIL | Coptodon zillii, Tilapia galilaea | 11 | Other fish | OTF | Rhodeus ocellatus, Acheilognathus macropterus, Abbottina rivularis, |
| 12 | Crucian | CAR | Carassius auratus | 12 | Carp | CYP | Cyprinus carpio, Cyprinus carpiouar singuonensis |
| 13 | Other fish | OTF | Rhodeus ocellatus, Acheilognathus macropterus, Abbottina rivularis | 13 | Goby | RhI | Rhinogobius giurinus |
| 14 | Carp | CYP | Cyprinus carpio, Cyprinus carpiouar singuonensis | 14 | Silver Gobio | SQA | Squalidus argentatus, |
| 15 | Goby | RhI | Rhinogobius giurinus | 15 | Bream | MPC | Megalobrama amblycephala, Parabramis pekinensis, Ctenopharyngodon idella |
| 16 | silver Gobio | SQA | Squalidus argentatus | 16 | Silver carp | SIC | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix |
| 17 | Bream | MPC | Megalobrama amblycephala, Parabramis pekinensis, Ctenopharyngodon idella | 17 | Bighead carp | BIC | Aristichthys nobilis |
| 18 | Silver carp | SIC | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 18 | Shrimps | SHP | Macrobrachium nipponens |
| 19 | Bighead carp | BIC | Aristichthys nobilis | 19 | Benthos | BEH | Anodonta, bellamya, Chironomid, Annelida, Arthropoda |
| 20 | Shrimps | SHP | Macrobrachium nipponens | 20 | Zooplankton | ZOP | Rotifera, Cladocera, Copepds |
| 21 | Benthos | BEH | Anodonta, bellamya, Chironomid, Annelida, Arthropoda | 21 | Phytoplankton | PHP | Cyanophyta, Bacillariophyta, Chlorophyta |
| 22 | Zooplankton | ZOP | Rotifera, Cladocera, Copepodas | 22 | Detritus | DET | Detritus |
| 23 | Phytoplankton | PHP | Cyanophyta, Bacillariophyta, Chlorophyta | ||||
| 24 | Detritus | DET | Detritus | ||||
| 2018 CYL | 2022 CYL | 2022 SYL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| H′ | 2.198 | 2.579 | 2.823 |
| J′ | 0.675 | 0.758 | 0.770 |
| D | 4.169 | 4.282 | 5.033 |
| Parameter (Unit) | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| SC (t/km2/year) | 1310.678 | 5438.05 | 4553.905 |
| SE (t/km2/year) | 19,178.850 | 3029.287 | 4523.993 |
| SRF (t/km2/year) | 546.743 | 832.031 | 530.638 |
| SFID (t/km2/year) | 19,634.560 | 5039.543 | 5565.581 |
| TST (t/km2/year) | 40,670.830 | 14,338.91 | 15,174.120 |
| SP (t/km2/year) | 19,885.970 | 4724.484 | 6053.789 |
| CNPP (t/km2/year) | 19,725.600 | 3861.6 | 5054.616 |
| TPP/TR (t/km2/year) | 36.078 | 4.641174 | 9.526 |
| NSP (t/km2/year) | 19,178.860 | 3029.569 | 4523.978 |
| TPP/TB | 93.167 | 30.046 | 57.575 |
| TB (excluding detritus) (t/km2) | 211.724 | 128.5228 | 87.792 |
| CI | 0.242 | 0.225 | 0.214 |
| SOI | 0.086 | 0.175 | 0.158 |
| TC (including detritus) (t/km2/year) | 222.0 | 2920.000 | 1342.000 |
| FCI (% of total throughput) | 0.546 | 19.030 | 8.845 |
| FMPL | 2.062 | 3.975 | 3.002 |
| Ecopath pedigree | 0.419 | 0.667 | 0.689 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, H.; Yin, C.; Yu, J.; Xiao, J.; Yu, Z.; Fu, X.; Huang, B.; Wu, X.; Li, C. An Ecosystem-Based Approach to Evaluating Impacts of Fisheries Management on Ecosystem Restoration in a Chinese Subtropical Yangming Reservoir. Fishes 2025, 10, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060246
Gong H, Yin C, Yu J, Xiao J, Yu Z, Fu X, Huang B, Wu X, Li C. An Ecosystem-Based Approach to Evaluating Impacts of Fisheries Management on Ecosystem Restoration in a Chinese Subtropical Yangming Reservoir. Fishes. 2025; 10(6):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060246
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Haibo, Chengjie Yin, Jinxiang Yu, Jun Xiao, Zhijie Yu, Xuejun Fu, Bin Huang, Xiya Wu, and Caigang Li. 2025. "An Ecosystem-Based Approach to Evaluating Impacts of Fisheries Management on Ecosystem Restoration in a Chinese Subtropical Yangming Reservoir" Fishes 10, no. 6: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060246
APA StyleGong, H., Yin, C., Yu, J., Xiao, J., Yu, Z., Fu, X., Huang, B., Wu, X., & Li, C. (2025). An Ecosystem-Based Approach to Evaluating Impacts of Fisheries Management on Ecosystem Restoration in a Chinese Subtropical Yangming Reservoir. Fishes, 10(6), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060246






