Abstract
Bcl-2-like protein 13 (Bcl2l13) plays an important role in the cell apoptosis and mitochondrial autophagy of mammals. However, the role of bcl2l13 remains unclear in fish. Therefore, in this study, the function of Megalobrama amblycephala bcl2l13 gene in apoptosis and autophagy was investigated. The results showed that the overexpression of M. amblycephala bcl2l13 under hypoxic condition led to a reduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), an increase in the expression levels of autophagy-related genes (p62, lc3, pink1), and a disruption of mitochondrial structure. However, deleting its transmembrane (TM) and Bcl-2 homology no (BHNo) domains decreased the P62 protein level, suggesting its essential role in autophagy. Furthermore, bcl2l13 overexpression inhibited cell proliferation and increased apoptosis. Additional studies revealed that the permeability of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) increased after overexpression of bcl2l13, but decreased upon deletion of the TM domain. Additionally, hypoxia led to elevated Bcl2l13 and P62 levels, and caused mitochondrial damage in M. amblycephala liver after 48 h of treatment. In conclusion, bcl2l13 may induce autophagy, inhibit cell proliferation and promote apoptosis, while its TM and BHNo domains play pivotal roles in these processes.
Key Contribution:
In this study, it was found that overexpression of M. amblycephala bcl2l13 induces autophagy, inhibits cell proliferation, and triggers apoptosis via the endogenous mitochondrial pathway. The TM and BH domains of Bcl2l13 play a crucial role in both autophagy and apoptosis.
1. Introduction
Autophagy serves as the primary intracellular degradation system, responsible for transporting and breaking down cellular substances within lysosomes, which is vital for maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating energy metabolism [1,2,3,4,5]. Autophagy encompasses several distinct types, each with specific roles: macro-autophagy, micro-autophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy, mitophagy, and golgi autophagy [6]. Mitochondrial autophagy (mitophagy) selectively degrades damaged mitochondria and is responsible for their turnover and quality control [7]. Under hypoxic conditions, the mitochondrial electron transport chain produces high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage [8]. Elevated ROS levels can activate signaling pathways, such as Nrf2 and NF-κB, which promote the expression of autophagy-related genes, thereby enhancing the protective function of mitophagy [9,10,11]. Apoptosis is a programmed cell death, genetically determined to maintain homeostasis [12]. There are three main apoptotic pathways: the exogenous death receptor pathway, the endogenous mitochondrial pathway and the endoplasmic reticulum apoptotic pathway [13]. These pathways are triggered by environmental disturbances and are initiated by Caspase3 [14]. Together, autophagy and apoptosis ensure the maintenance of cellular and organismal homeostasis.
The Bcl-2 protein family is composed of three categories: anti-apoptotic proteins, pore-forming proteins, and Bcl-2 homology (BH) domain 3-only (BH3-only) proteins, according to the BH domain [15,16]. Studies have shown that this family, especially the BH domain, plays an important role in apoptosis and autophagy. Bcl2l13, as a member of the Bcl-2 family, contains four typical BH domains, one TM domain, and one BHNo domain [17]. Unlike other Bcl-2 proteins, the pro-apoptotic activity of Bcl2l13 stems from its BHNo domain rather than the typical BH domains [18], and its function is cell-type dependent. In prostate cancer cells (PC3) and lung adenocarcinoma cells (A549), Bcl2l13 promotes apoptosis through its interaction with adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT) and voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein (VDAC), affecting mitochondrial permeability [19,20]. In contrast, in brain tumor cells (SF767), the BHNo domain of Bcl2l13 inhibits apoptosis by binding Ceramidase 6 (CERS6) and CERS2, regulating the CERS2/6 heterodimer formation [21]. Additionally, Bcl2l13 also modulates mitophagy, sharing homology with yeast mitophagy receptor Atg32 [22,23].
Hypoxia is a common environmental stressor that affects aquatic organisms, including fish. To adapt to hypoxic environments, fish alter their energy metabolism, substance synthesis, immune response, and behavior [24,25]. Studies have shown that hypoxia can induce autophagy. In hypoxic environments, HIF-1 can induce the transcription of the bnip3 gene, and the BNIP3 protein displaces Beclin1 from Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL, allowing free Beclin1 to subsequently induce autophagy [26,27]. BNIP3 can also activate autophagy by inhibiting the Ras homolog enriched in brain (RHEB) protein [28]. In addition, hypoxia can also induce apoptosis. The Bcl-2/Bax ratio in the liver of golden pompano gradually decreased under hypoxia, thereby promoting hepatocyte apoptosis [29].
Megalobrama amblycephala is an important herbivorous freshwater economic fish in China. Compared with other cultured fishes of the family Cyprinidae, M. amblycephala is more sensitive to changes in dissolved oxygen in cultured water, which seriously affects its survival. A previous study found that mRNA expression of bcl2l13 and autophagy-related genes was significantly up-regulated by Hif-1α mediated pathway after hypoxia treatment in M. amblycephala, and the TM domain was very critical to its cellular localization [30]. However, the function of this gene and its different domains remains still unclear in fish. Therefore, in order to understand how M. amblycephala bcl2l13 gene regulates autophagy and apoptosis in response to hypoxic stress, we hypothesized that M. amblycephala Bcl2l13 and its different domains play important roles in response to hypoxia and other physiological functions. Studies have shown that the bcl2l13 gene in Pimephales promelas was highly conserved, sharing the same domains and high homology with the bcl2l13 gene in M. amblycephala. Therefore, the experiments in vitro were performed in the FHM cells, derived from Pimephales promelas [30,31]. In this manner, the effect of M. amblycephala bcl2l13 overexpression on ROS and mitochondrial structure was investigated and the function of its different domains in autophagy and apoptosis was also studied in FHM cells. These results will provide a theoretical reference for revealing the mechanism of autophagy and apoptosis in fish.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
The FHM cells (Cell Collection Centre for Freshwater Organisms, Huazhong Agricultural University) were maintained in M199 medium (Hyclone, Carlsbad, CA, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin at 28 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2.
2.2. Construction of bcl2l13 Mutants with the Deleting of Different Domains
The cDNA sequences of M. amblycephala bcl2l13 when deleting different domains were amplified and cloned into the pCMV-myc plasmids for construction of the pCMV-myc-Bcl2l13 vector with expressing Bcl2l13 protein (myc-Bcl2l13), the pCMV-myc-Bcl2l13 vector deleting the TM domain (ΔTM), the pCMV-myc-Bcl2l13 vector deleting the BHNo domain (ΔB), or both the BHNo and TM domains (ΔTB). The primers are shown in Table 1. FHM cells were seeded in 12-well plates. When cells reached 70–80% confluence, they were transfected with plasmids using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, the transfection mixture was prepared by combining 4 µL of Lipofectamine 2000 reagent and 1 µg of plasmid DNA in 100 µL of Opti-MEM reduced serum medium (Gibco, Grand Island, NE, USA). FHM cells were respectively transfected using the above constructed plasmids for 24 h, and collected for Western blotting, cell viability assay and real-time PCR. Cells were fixed in 2% glutaraldehyde for transmission electron microscopy. Cell viability was determined using the CCK-8 kit (Servicebio, Wuhan, China) according to the kit instructions.

Table 1.
Primers used in the experiments.
2.3. CoCl2 Treatment and ROS Detection
FHM cells were treated with 250 μmol/L CoCl2 for 24 h and then transfected by the pCMV-myc-Bcl2l13 vector. After transfection for 24 h, these cells were collected, and ROS was detected by using the ROS assay kit (Jiancheng Bioengineering institute, Nanjing, China) based on 2,7-Dichlorofuorescin Diacetate (DCFH-DA). Briefly, cells were washed with PBS twice. Cells were incubated with 10 μmol/L DCFH-DA solution (1: 1000, dissolved in culture medium) for 30 min at 28 °C, washed carefully with PBS three times and observed using a fluorescent microscope (Thermo, Waltham, MA, USA). Additionally, these cells were used for real-time PCR and Western blotting to detect the expression of autophagy-related genes after bcl2l13 overexpression for 24 h. Untreated cells were used as negative controls and hypoxia conditions as positive controls.
2.4. Hypoxia Treatment of M. amblycephala
M. amblycephala (about 30 g) was obtained from the Wuchang fish stock farm in Ezhou City, Hubei Province, China. Before the formal experiment, these fish were fed twice daily in a tank of 80 L with a recirculating water system (water temperature 25 ± 1 °C), with a commercial pellet feed equivalent to 3% of body weight. M. amblycephala was treated with hypoxia by filling the water with nitrogen gas. Each group contained 30 fish (totally 120 fish). Dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration was 1.8 ± 0.2 mg/L in the hypoxia group and 7.5 ± 0.5 mg/L in the control group. M. amblycephala was anesthetized by MS-222 (3-Aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester methanesulfonate). The liver tissues were rinsed with cold PBS to remove any residual blood and contaminants. The tissues were then snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until further study. The liver was collected for protein expression detection by Western blotting and ultrastructural observation by transmission electron microscopy after hypoxia treatment for 12 h, 24 h and 48 h.
2.5. Real-Time PCR
Total RNAs from FHM cells and M. amblycephala liver tissues were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, Waltham, USA). Total RNA (1 µg) was reverse-transcribed into cDNA using a reverse transcription kit (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA). Relative mRNA expression levels were examined using real-time PCR and the CFX96™ real-time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The conditions were as follows: 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 5 s, 60 °C for 20 s, 72 °C for 30 s. The primers are shown in Table 1. All of the samples were analyzed in triplicate, and the expression of bcl2l13, the mitochondrial respiratory chain (ndufa2, cox17, sdha), autophagy (beclin1, pik3ca, lc3, pink1 and p62) and apoptosis (caspase3, cyt-c, grp78 and fas) related genes was calculated as relative folds of the expression of the reference gene according to the ∆∆Ct method [32]. β-actin was used as the internal control [30].
2.6. Ultrastructural Observation
To observe the effect of bcl2l13 overexpression on cellular ultrastructure, the FHM cells were respectively transfected using the pCMV-myc (negative control) and pCMV-myc-Bcl2l13 vector for 24 h. Samples were fixed in 2% glutaraldehyde for 4 h. After initial fixation, samples were washed three times with 0.1 M phosphate buffer for 10 min each. They were then post-fixed in 1% osmium tetroxide in 0.1 M phosphate buffer for 1 h at room temperature and then dehydrated using a series of increasing concentrations of ethanol (30%, 50%, 70%, 90%, and 100% ethanol). Dehydrated samples were infiltrated with a mixture of ethanol and epoxy resin (1:1) for 1 h, followed by pure epoxy resin overnight. The next day, samples were embedded in fresh epoxy resin and polymerized in a 60 °C oven for 48 h. Polymerized blocks were trimmed and sectioned using an ultramicrotome (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) to obtain ultrathin sections (approximately 70 nm thick). Sections were collected on copper grids, stained with 2% uranyl acetate for 15 min and then with lead citrate for 5 min to enhance contrast. Stained grids were air-dried and observed by transmission electron microscopy (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). Additionally, cells treated with autophagy inhibitor 3-MA (1 mmol/L) were used as the positive control.
2.7. Western Blot
Protein extracts from cells and tissues were generated using RIPA buffer (Beyotime Biotechnology). The RIPA buffer recipe contained sodium chloride (5M) 3 mL, Tris-HCl (1M, pH = 7.4) 5 mL, Nonidet P-40 1 mL, Sodium deoxycholate (10%) 5 mL, SDS (10%) 1 mL and ddH2O (UP to 100 mL). Samples were centrifuged at 4 °C, 12,000 r/min, for 10 min and quantified using the Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Scientific). Standard Western blotting was performed with the following primary antibodies: Bcl2l13 (M. amblycephala specific antibodies, made in our laboratory, Supplementary Materials), LC3 (Proteintech, Wuhan, China), P62 (ABclonal, Wuhan, China), β-actin (ABclonal, Wuhan, China) and mouse anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Dingguo Biotechnology, Beijing). Equal amounts of protein were separated by SDS–PAGE and transferred to PVDF membranes. Membranes were blocked with 5% non-fat dry milk in TBS-T (Tris-buffered saline with 0.1% Tween-20) for 2 h at room temperature and then incubated with primary antibodies (dilution ratio 1:1000) overnight at 4 °C. After washing with TBS-T, membranes were incubated with secondary antibodies (dilution ratio, 1:5000) for 1 h at room temperature.
2.8. Hoechst 33258 Staining
The transfected cells were washed twice with PBS and incubated with Hoechst 33258 (1 μg/mL) for 5 min at room temperature away from light, then washed once again with PBS. Cell apoptosis was observed by fluorescence microscopy under excitation light of 330–380 nm. The negative controls without any DNA transfection (mock) and positive controls with transfecting pCMV-myc empty vector (myc-N) were also analyzed.
2.9. Annexin V FITC/PI Assay
FHM cells were digested with EDTA-free trypsin and collected by centrifugation at 1000 r/min for 5 min. These cells were washed twice with PBS and stained with FITC and PI. Cells were detected by flow cytometry (Beckman, Brea, CA, USA) within 1 h. The negative controls without any DNA transfection (mock) and positive controls with transfecting pCMV-myc empty vector (myc-N) were also analyzed.
2.10. Calcein AM-CoCl2 Staining
The mPTP in each group was detected using the mPTP Fluorescence Assay Kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Adherent cells were detached using pancreatic enzyme digestion and resuspended in culture medium to form a single-cell suspension. After counting, an appropriate volume was centrifuged at 1000× g for 5 min at room temperature. The cell pellet was resuspended in detection buffer containing Calcein AM staining solution and fluorescence quenching working solution, adjusted to a final density of 1 × 106 cells/mL (1 mL each sample). The suspensions were incubated in the dark at 37 °C for 30 min, then centrifuged at 1000 g for 5 min. The cells were resuspended in 400 µL detection buffer for analysis. For flow cytometry analysis, a negative control was set up with detection buffer only, and fluorescence was measured at 494 nm excitation and 517 nm emission.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
All experimental data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (mean ± SEM). To ensure the reliability and reproducibility of the results, each experiment was conducted in triplicate, with three independent trials performed. Data analysis was carried out using SPSS 17.0 statistical software. To evaluate differences between groups, we employed either Student’s t-test for comparing two groups, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) or two-way ANOVA for comparing more than two groups. For cases involving multiple comparisons, post hoc analysis was performed using the Duncan method, which is suitable for identifying significant differences among group means while controlling for Type I error. Bonferroni correction was applied to address the issue of multiple comparisons, resulting in a corrected p-value of 0.01. The significance levels were set at follows: * for p < 0.05, ** for p < 0.01; *** for p < 0.001, **** for p < 0.0001.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of bcl2l13 Overexpression on ROS Levels After Hypoxic Stimulation
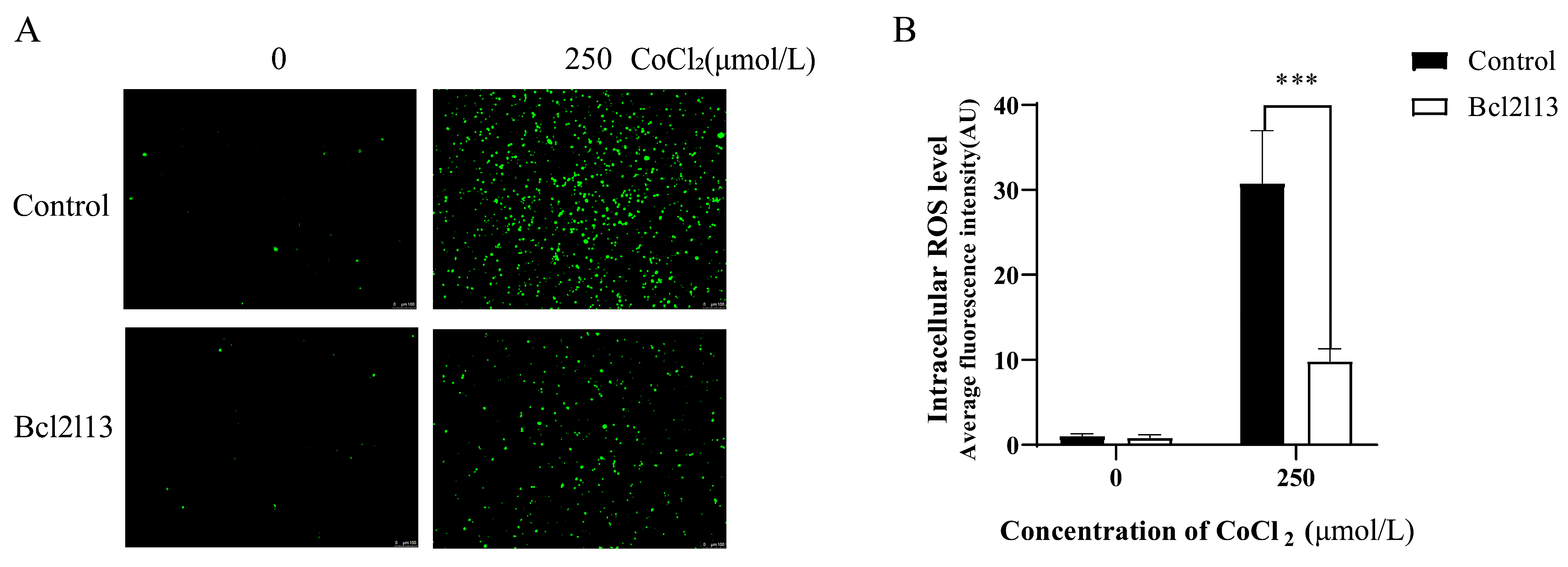
Hypoxia leads to an increase in ROS levels. To investigate the function of bcl2l13 in hypoxia mediated ROS production, a bcl2l13 overexpression assay was carried out in FHM cells, and ROS levels were subsequently measured following hypoxia treatment with CoCl2. The results showed that hypoxia caused a significant increase in ROS levels. Bcl2l13 overexpression alone did not significantly change the ROS levels. However, the ROS levels were significantly reduced in cells overexpressing bcl2l13 following CoCl2 treatment (Figure 1). These results indicate that overexpression of bcl2l13 could remove excessive ROS in cells under hypoxic condition.
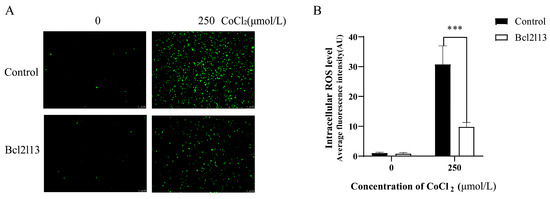
Figure 1.
The ROS levels in FHM cells after hypoxic stimulation and bcl2l13 overexpression. (A) Detection of ROS levels. (B) Fluorescence values of intracellular ROS quantified with ImageJ2, data are shown as mean ± SD. “***” means p < 0.001. Control: without bcl2l13 overexpression; Bcl2l13: bcl2l13 overexpression; 0: without hypoxia treatment; 250: hypoxia treatment with 250 μmol/L CoCl2. Scale size = 100 µm, n = 3.
3.2. Effect of bcl2l13 Overexpression on Autophagy-Related Gene Expression and Cell Ultrastructure
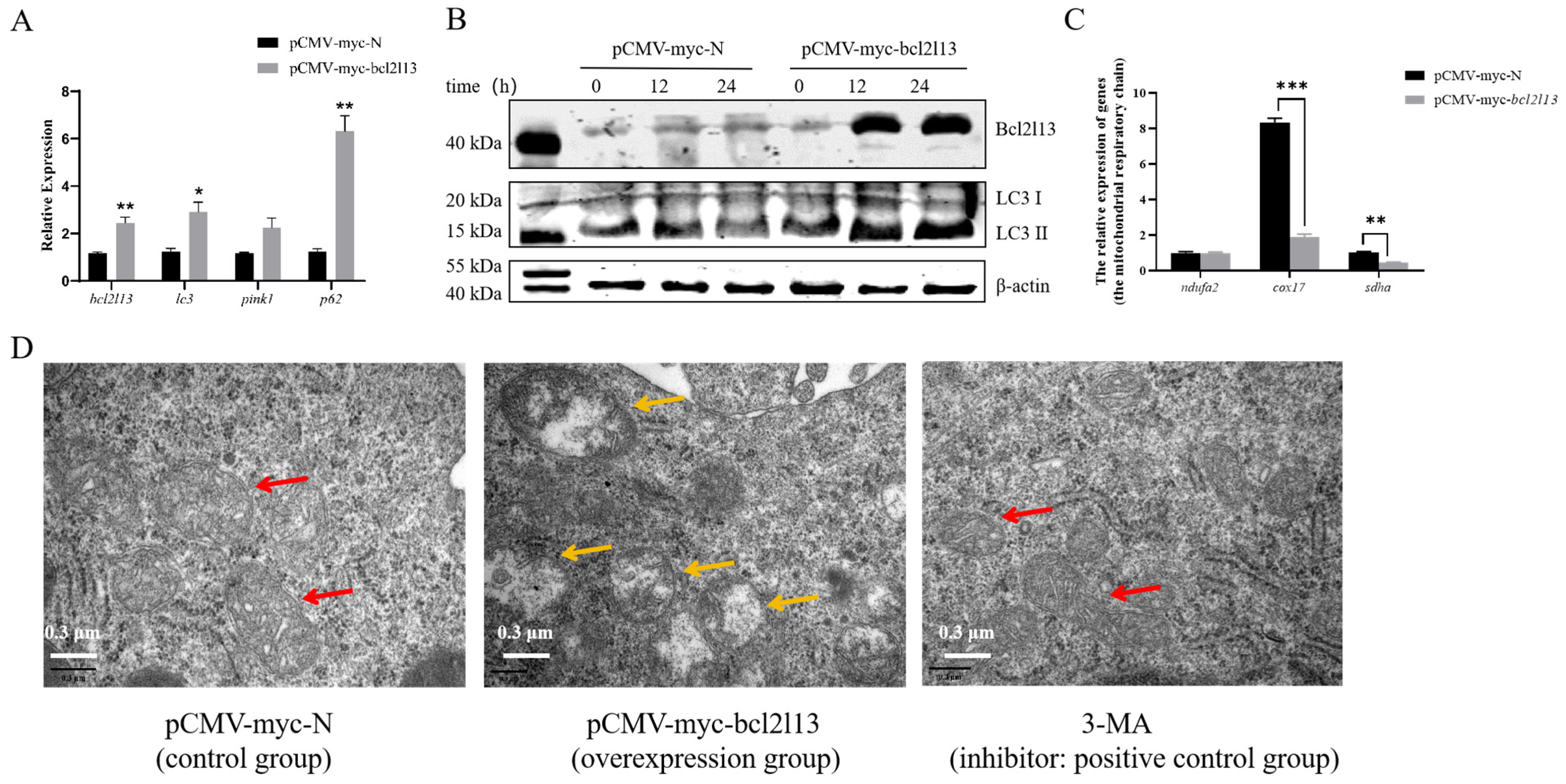
To study the function of M. amblycephala bcl2l13 gene in autophagy, the expression of autophagy-related genes was detected after bcl2l13 overexpression based on real-time PCR and Western blotting. The results revealed that the mRNA and protein levels of Bcl2l13 was significantly increased in the FHM cells transfected with bcl2l13 overexpression vector, compared to the control (Figure 2A,B). Moreover, the expression of autophagy-related genes lc3 and p62 was also significantly elevated (Figure 2A). Meanwhile, the LC3-II steady-state level gradually increased with extended transfection time (Figure 2B). In addition, cox17 and sdha related with the mitochondrial respiratory chain were significantly downregulated after bcl2l13 overexpression (Figure 2C). Cell ultrastructure observation based on transmission electron microscopy further showed that, after bcl2l13 overexpression, the mitochondria were enlarged, the matrix became less dense, and the cristae became shorter, or even disappeared. There was no obvious difference between the control group and the 3-MA treatment group (Figure 2D). These findings demonstrated that bcl2l13 was probably involved in autophagy.
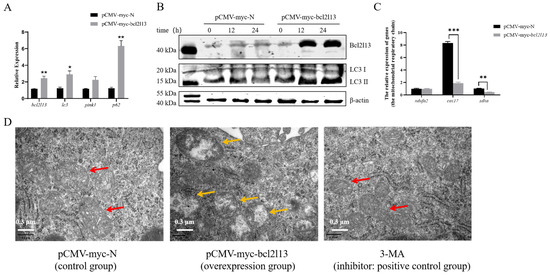
Figure 2.
Bcl2l13 overexpression caused up-regulated expression of autophagy-related genes and changes of cell ultrastructure in FHM cells. (A) Expression changes of mitophagy-related genes after bcl2l13 overexpression based on real-time PCR. “*” stands for p < 0.05, “**” stands for p < 0.01, n = 3. (B) Expression of Bcl2l13 and LC3 proteins based on Western blotting. FHM cells were transfected with pCMV-myc (control) and pCMV-myc-Bcl2l13 plasmids for 0 h, 12 h and 24 h, n = 3. (C) Expression changes of genes related with the mitochondrial respiratory chain after bcl2l13 overexpression. “**” stands for p < 0.01, “***” stands for p < 0.001. (D) Observation of the cell ultrastructure based on transmission electron microscopy after bcl2l13 overexpression. pCMV-myc-N: the control group transfected with pCMV-myc plasmid; pCMV-myc-bcl2l13: the overexpression group transfected with pCMV-myc-Bcl2l13 plasmid for 24 h; 3-MA: the positive group treated by an autophagy inhibitor, 3-methyladenine (3-MA) with a final concentration of 1 mmol/L for 24 h. The red arrow indicates normal mitochondria, while the yellow arrow indicates mitochondria with morphological abnormalities. Scale size = 0.3 µm, n = 3.
3.3. Roles of Different Domains of Bcl2l13 in Autophagy and Apoptosis
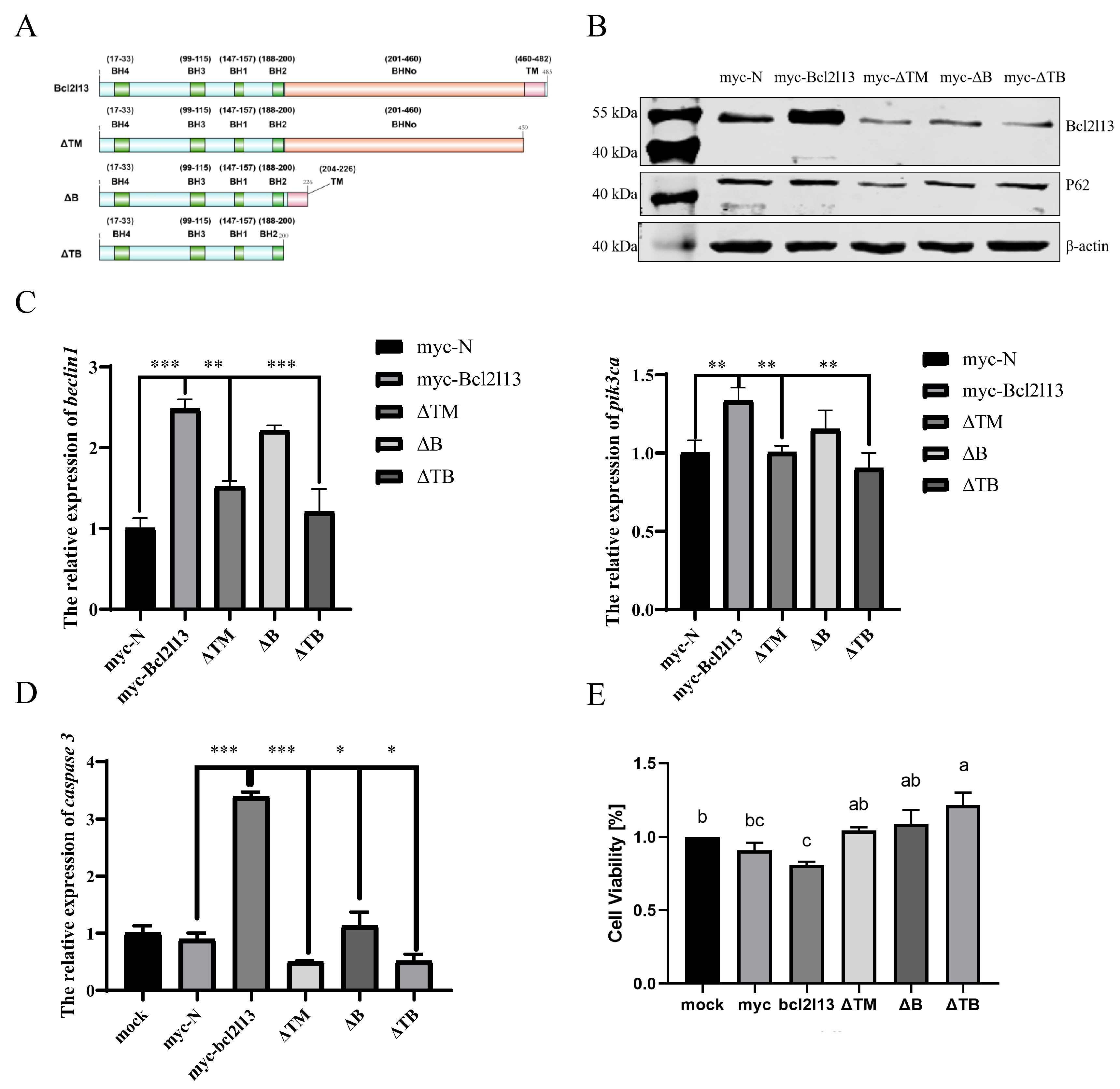
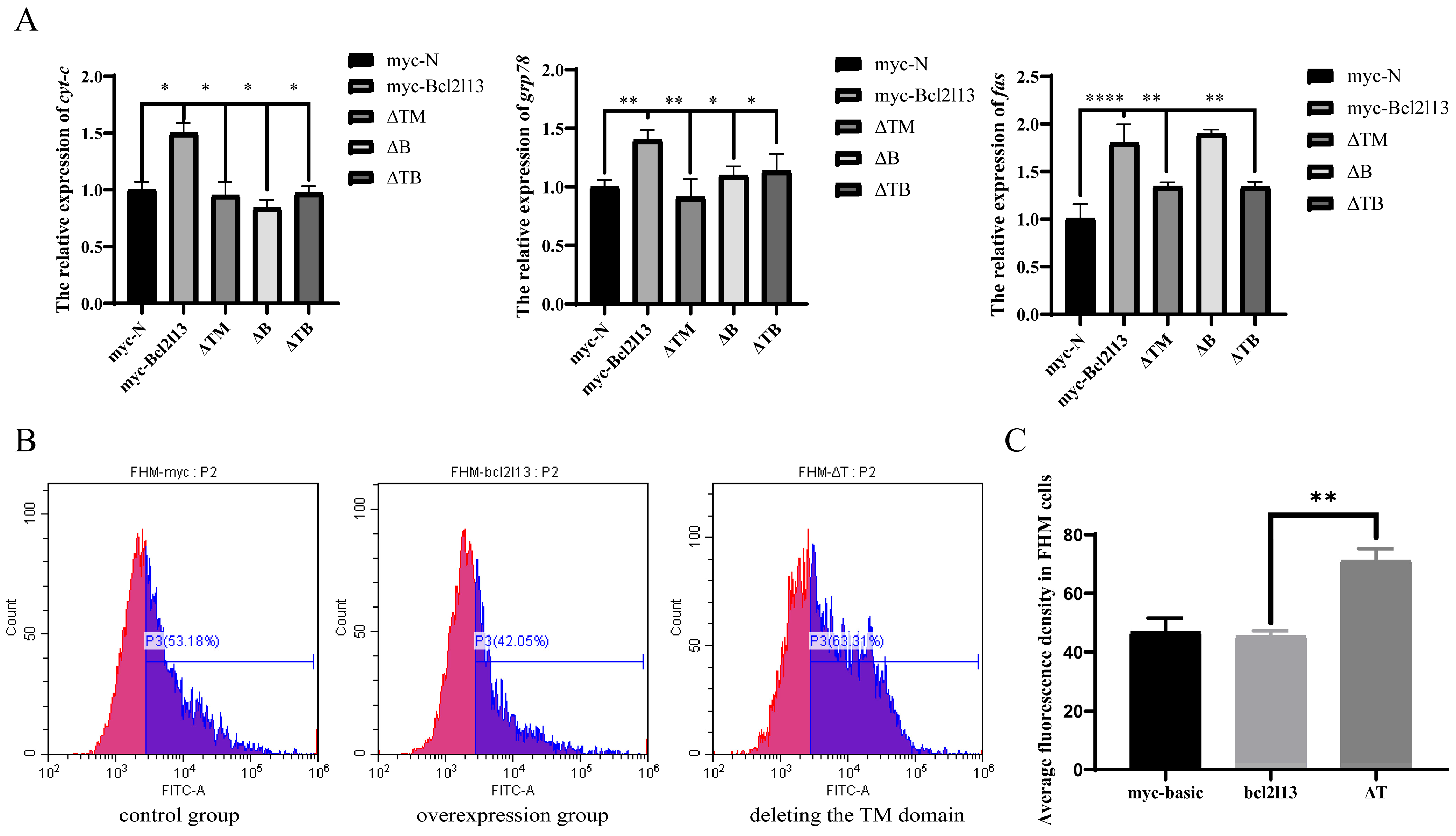
The Bcl2l13 protein of M. amblycephala contains four BH, one TM and BHNo domains [30]. To analyze the function of different domains in autophagy and apoptosis, three mutants with deleting different domains, ΔTM (deleting TM domain), ΔB (deleting BHNo domain), and ΔTB (deleting both TM and BHNo domains) were constructed, respectively (Figure 3A), and transfected into the FHM cells. It was found that the protein levels of Bcl2l13 and P62 were significantly increased after bcl2l13 overexpression but decreased after the deletion of the TM and/or BHNo domains (Figure 3B). The expression of beclin1 and pik3ca was significantly increased after bcl2l13 overexpression, but significantly decreased after the deletion of domains, especially when deleting the TM domain (Figure 3C).
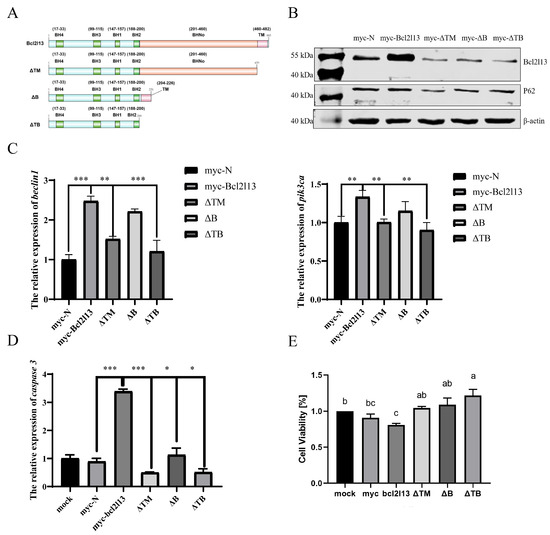
Figure 3.
Different domains of Bcl2l13 regulate autophagy and apoptosis. (A) Construction of Bcl2l13 deletion mutants. (B) The protein levels of Bcl2l13 and P62 after bcl2l13 overexpression and when deleting TM, BHNo or both of them. myc–N: control with transfecting pCMV–myc empty vector; myc–Bcl2l13: the overexpression of bcl2l13; ΔTM: the mutant with deleting the TM domain; ΔB: the mutant with deleting the BHNo domain; ΔTB: the mutant with deleting both the TM and BHNo domains. (C,D) Expression of caspase3, beclin1 and pik3ca mRNA after overexpression of bcl2l13 and their mutants with deleting different domains. n = 3, “*” stands for p < 0.05, “**” stands for p < 0.01, “***” stands for p < 0.001. (E) Effect of deletion for different domains of Bcl2l13 on cell proliferation based on CCK–8. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among groups (p < 0.05), n = 3. If two groups have the same letter (a, b, c), there is no significant difference between these two groups. If two groups have different letters, there is a significant difference between the two groups.
To further investigate the function of Bcl2l13 different domains in cell proliferation and apoptosis, the expression of caspase3 was detected by qPCR. It was found that the expression of caspase3 was significantly increased after bcl2l13 overexpression, but significantly decreased after the deletion of domains, especially deleting the TM domain (Figure 3D). Additionally, cell viability was assessed by the CCK–8 kit. The results revealed that cell proliferation was reduced after bcl2l13 overexpression; however, the inhibitory effect of bcl2l13 on cell proliferation was weakened after deleting the TM and/or BHNo domains, especially when deleting both the TM and BHNo domains (Figure 3E). These findings suggest that different domains of M. amblycephala Bcl2l13 play distinct roles in regulating autophagy, apoptosis and cell proliferation. The TM domain appears particularly important for apoptosis, as its deletion significantly attenuates caspase3 expression and weakens the inhibitory effect on cell proliferation.
3.4. The TM Domain of Bcl2l13 Was Critical to Apoptosis
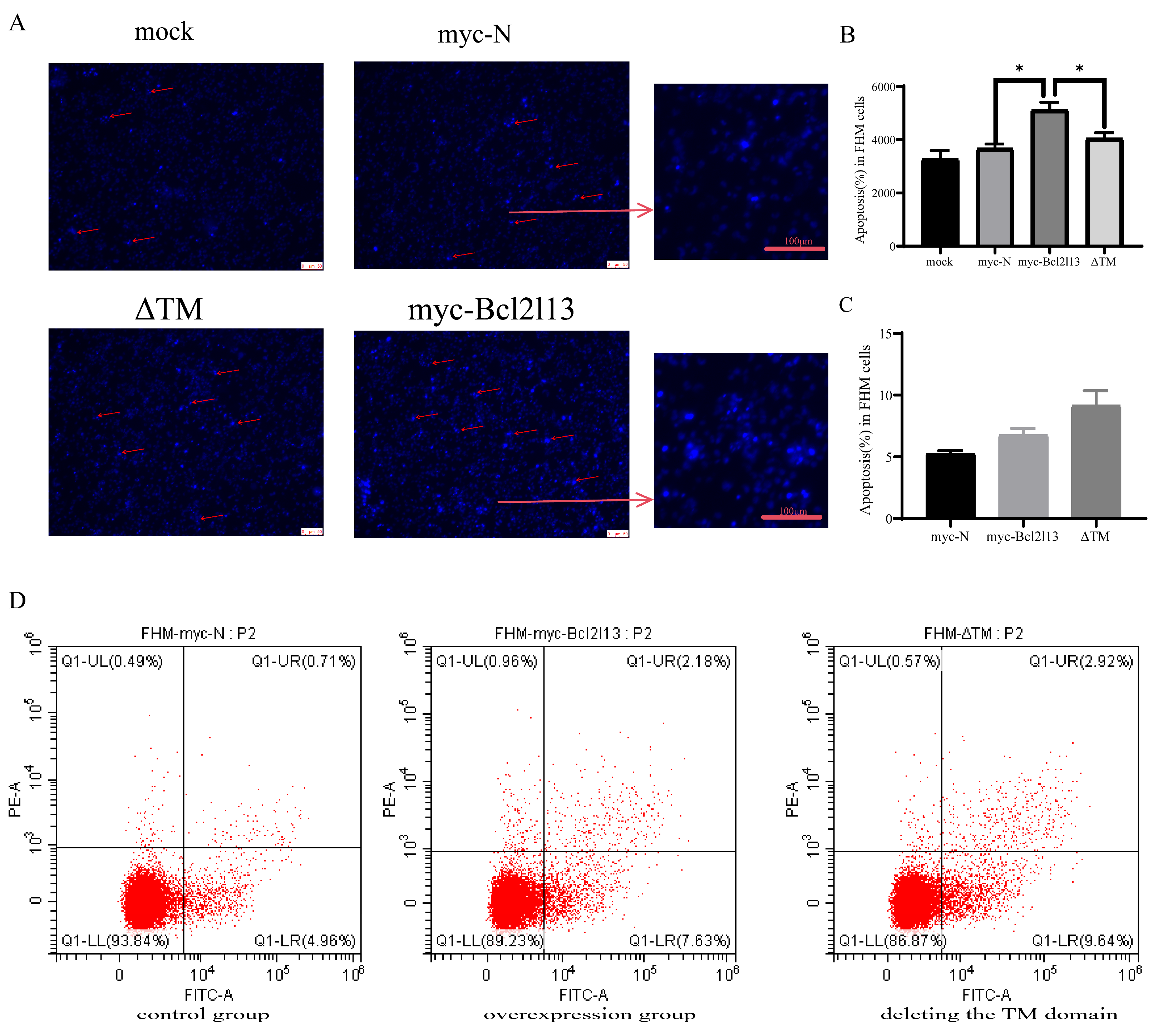
To further investigate the function of the TM domain in apoptosis, apoptosis in FHM cells was detected by Hoechst 33258 staining and Annexin V FITC/PI. Hoechst 33258 staining results showed that bcl2l13 overexpression led to a significant increase in the number of cells with nuclear condensation; however, there was no significant difference from the control group after the TM domain was removed (Figure 4A,B). The apoptosis rate was found to increase after bcl2l13 overexpression based on Annexin V FITC/PI; however, deletion of the TM domain did not impair the pro-apoptotic effect of bcl2l13 (Figure 4C,D).
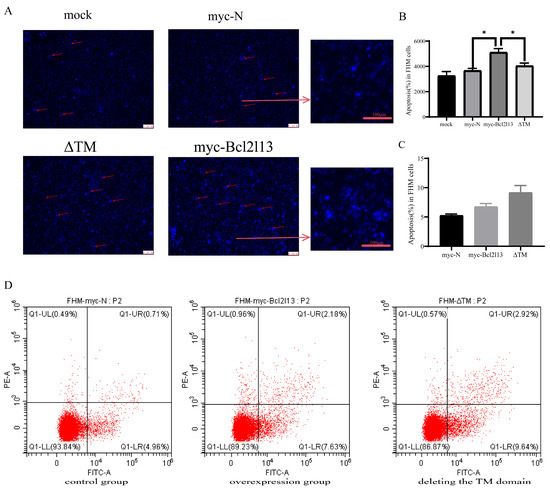
Figure 4.
The role of the TM domain of Bcl2l13 in apoptosis. (A) Detection of the number of nuclei consolidated after overexpression of bcl2l13 and the mutant with deleting the TM domain based on Hoechst 33258 staining, Scale size = 40 µm, n = 3. The red arrows indicate nuclear condensation. (B) The statistics of apoptosis ratio based on Hoechest 33258 staining. mock: the detection of control without any DNA transfection. “*” stands for p < 0.05. (C) The statistics of apoptosis ratio based on Annexin V FITC/PI. (D) Flow cytometry in FHM cells. control group: transfection of pCMV–myc in FHM cells; overexpression group: overexpression of bc2l13 in FHM cells; deleting the TM domain group: overexpression of the mutant with deleting the TM domain in FHM cells, n = 3.
3.5. Bcl2l13 Mediated Apoptosis Through the Endogenous Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway
To further investigate the pathways through which bcl2l13 mediates apoptosis, bcl2l13 was overexpressed in the FHM cells and expression of apoptotic pathway-related genes (cyt-c, grp78 and fas) was detected by real-time PCR. The results showed that the expression of cyt-c, grp78 and fas was significantly up-regulated after bcl2l13 overexpression but significantly decreased after the deletion of the domains (Figure 5A). These findings suggested that bcl2l13 may act in a regulatory role within the apoptotic pathways. To further investigate bcl2l13 mediated apoptosis, mitochondrial transition pore permeability (mPTP) was detected by Calcein AM-CoCl2 staining. The result showed that, compared with the control group, bcl2l13 overexpression decreased the fluorescence value, and increased mPTP. However, deletion of the TM domain led to a significant decrease in mPTP (Figure 5B,C). These findings collectively suggested that bcl2l13 regulated apoptosis by influencing the endogenous mitochondrial pathway. Specifically, bcl2l13 appeared to enhance mitochondrial permeability through its TM domain, potentially contributing to its pro-apoptotic function.
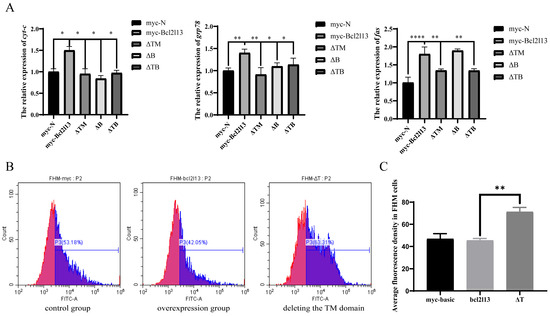
Figure 5.
Bcl2l13 mediated apoptosis through the endogenous mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. (A) Expression of cyt-c, grp78 and fas mRNA after overexpression of bcl2l13 and their mutants with deleting different domains. n = 3, “*” stands for p < 0.05, “**” stands for p < 0.01, “****” stands for p < 0.0001. (B) Calcein AM–CoCl2 staining of FHM cells. The control group: transfection of pCMV–myc in FHM cells; the overexpression group: overexpression of bc2l13 in FHM cells; deleting the TM domain group: overexpression of the mutant with deleting the TM domain in FHM cells. n = 3. (C) Statistics of average fluorescence value in FHM cells. “**” stands for p < 0.01.
3.6. Effect of Hypoxia on Bcl2l13 Expression and Tissue Ultrastructure at the Individual Level
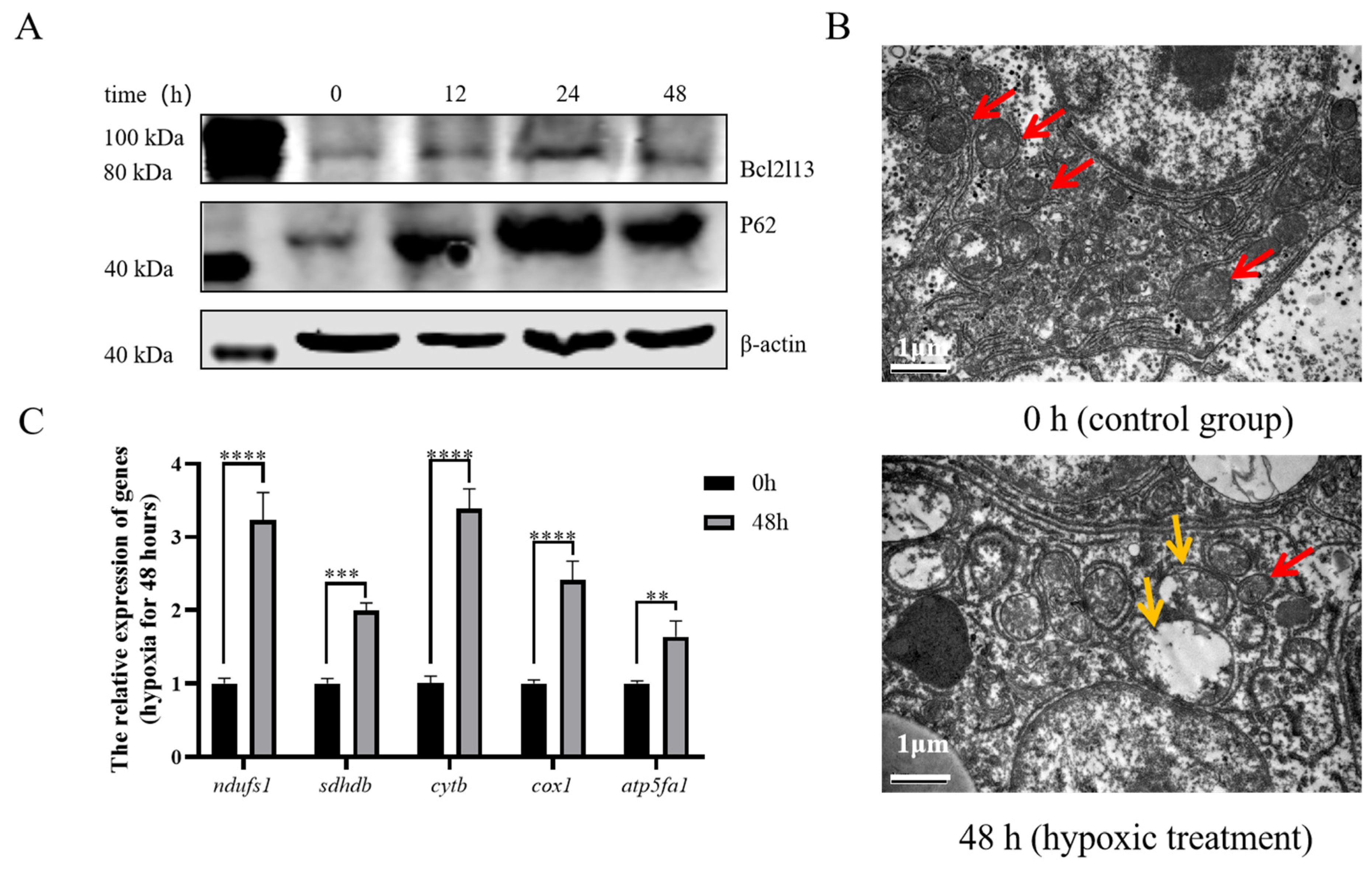
To investigate the regulatory mechanism of bcl2l13 in hypoxia-mediated autophagy at the individual level, M. amblycephala was subjected to a hypoxia condition. The results revealed that, in the liver of M. amblycephala, hypoxic treatment led to elevated levels of Bcl2l13 and P62 proteins (Figure 6A). Electron microscopy analysis further demonstrated significant alterations in mitochondrial ultrastructure in the liver of M. amblycephala after hypoxic treatment, characterized by mitochondrial swelling, matrix vacuolation, and reduction or even disappearance of mitochondrial crests (Figure 6B). Expression of the mitochondrial respiratory chain-related genes (ndufs1, sdhdb, cytb, cox1 and atp5fa1) was significantly up-regulated in the liver of M. amblycephala after 48 h of hypoxia treatment (Figure 6C).
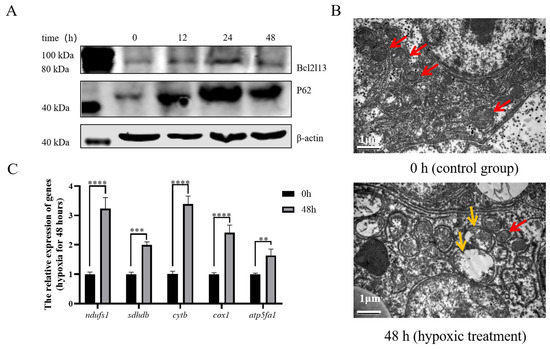
Figure 6.
Hypoxia affected Bcl2l13 and P62 protein levels and mitochondrial ultrastructure. (A) Effects of hypoxia on the expression of autophagy-related proteins in the liver of M. amblycephala. (B) Electron microscopy of the liver of M. amblycephala. 0 h: control group, without hypoxic treatment; 48 h: hypoxia treatment for 48 h. The red arrow indicates normal mitochondria, while the yellow arrow indicates mitochondria with morphological abnormalities. Scale size = 1 µm, n = 3. (C) Expression of genes related to the mitochondrial respiratory chain after hypoxia for 48 h. n = 3, “**” stands for p < 0.01, “***” stands for p < 0.001, “****” stands for p < 0.0001.
4. Discussion
The description of Bcl2l13 as a member of the Bcl-2 family with conserved BH1-BH4 domains and a unique BHNo domain aligns with its known structural characteristics in mammals. In mammals, Bcl2l13 plays important roles in regulating apoptosis and mitophagy, but its functions in bony fish, including M. amblycephala, remain largely unexplored. Consequently, this study aimed to elucidate the involvement of M. amblycephala bcl2l13 and its domains in autophagy and apoptosis.
The previous study found that the expression of bcl2l13 mRNA was significantly up-regulated in various tissues of M. amblycephala after hypoxic treatment, appearing to be regulated by Hif-1α [30]. After hypoxic stimulation, oxygen availability is reduced, which disrupts the electron transport chain (ETC) in mitochondria, leading to the generation of ROS [33]. Overexpression of Bcl-2 reduces ROS levels in glutathione-depleted cells and increases intracellular levels of reduced glutathione, suggesting that Bcl-2 enhances the antioxidant function of cells, thereby enhancing the ROS clearance mechanism [34]. Our results showed that the content of ROS in FHM cells increased after hypoxic treatment but greatly reduced by overexpression of bcl2l13 after hypoxic treatment in FHM cells. It indicated that overexpression of bcl2l13 could remove excess ROS from cells after hypoxic stimulation.
The accumulation of ROS can damage biomolecules and organelles, triggering both autophagy and apoptosis through ROS-FoxO3-LC3/Bnip3, ROS-Nrf2-P62, ROS-Hif1-Bnip3/Nix, and ROS-Tigar, etc. [35,36,37]. LC3 is a crucial protein marker for autophagy activation, while the ratio of LC3-II/LC3-I is indicative of the level of autophagy [38]. Additionally, P62 serves as a connector protein linking mitochondria and LC3, playing a role in autophagic vesicle formation [39]. The LC3-interacting region (LIR) domain of human Bcl2l13 has been shown to selectively bind to LC3C, GABARAP and GABARAPL1, thereby promoting mitochondrial autophagy [40]. During mitophagy, the number of mitochondria decreases and mitochondrial cristae are absent [41]. In this study, the results revealed that the expression of LC3 and P62 was significantly up-regulated after overexpression of bcl2l13. Besides, after overexpression of bcl2l13, mitochondria were enlarged, the matrix became less dense, and the cristae became shorter, or even disappeared. This suggests that bcl2l13 may induce autophagy, thereby eliminating excess ROS in cells. Hypoxic treatment was also carried out in M. amblycephala, and it was shown that the protein levels of Bcl2l13 and P62 increased in the liver of M. amblycephala, and mitochondria were also damaged in a similar manner to those in FHM cells. Moreover, expression of the mitochondrial respiratory chain-related genes was significantly downregulated after bcl2l13 overexpression, indicating damage to mitochondrial respiration. However, after hypoxic treatment of M. amblycephala, an opposite trend was observed, which may be a compensatory mechanism.
M. amblycephala Bcl2l13 shares sequence similarities with human Bcl2l13, possessing BH1-4, BHNo, and TM domains [30]. In mammals, the domains of Bcl2l13 play an important role in its promotion of mitophagy. Mutations in the BH and TM domains inhibit the mitochondrial fragmentation process promoted by Bcl2l13 [22]. In this study, overexpression of bcl2l13 significantly increased the protein levels of both Bcl2l13 and P62. This increase indicates that Bcl2l13 may play a role in enhancing autophagic activity, as P62 is a key autophagy-related protein involved in the formation of autophagosomes. However, deletion of the TM and/or BHNo domains led to a significant decrease in these protein levels. This suggested that both the TM and BHNo domains are essential for the function of Bcl2l13 in promoting autophagy. Beclin1 is a central regulator of autophagy initiation, while Pik3ca is involved in the signaling pathway that promotes autophagy [42,43]. The significant increase of beclin1 and pik3ca after bcl2l13 overexpression supported the hypothesis that Bcl2l13 enhances autophagic activity. Conversely, deletion of the TM domain led to a significant decrease in the expression of these autophagy-related genes. This highlights the critical role of the TM domain in mediating the autophagic function of Bcl2l13.
Bcl2l13 exhibits dual roles in apoptosis regulation depending on cellular context and structural domains. In various cell lines, such as 293T, HeLa, PC3, and A549, BCL2L13 demonstrates a pro-apoptotic effect while, in SF767 human brain tumor cells, it acts as an inhibitor of apoptosis [18,19,20,21]. Specifically, in 293T cells, the BH domain alone is insufficient to induce apoptosis, whereas the BHNo and TM domains exhibit pro-apoptotic effects [19]. Additionally, in SF767 cells, the BHNo domain inhibits the formation of the CERS2/6 heterodimer, thus negatively regulating apoptosis [18]. In this study, the results showed that bcl2l13 overexpression inhibited cell proliferation in FHM cells, but the deletion of the TM and BHNo domains weakened the inhibitory function of Bcl2l13. Furthermore, the expression of caspase3 was up-regulated after bcl2l13 overexpression, while the deletion of the TM and BHNo domains effectively down-regulated caspase3 expression, especially the TM domain. Subsequently, it was found that the level of nuclear condensation was increased after bcl2l13 overexpression, and the deletion of the TM domain can effectively reduce this increase. These results illustrate that the deletion of the BHNo domain reduces the pro-apoptotic activity of Bcl2l13, while the deletion of the TM domain leads to a complete loss of its pro-apoptotic activity.
The intricate regulation of apoptosis involves the dynamic interplay among various members of the Bcl-2 protein family, which control mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). BH3-only pro-apoptotic proteins can induce MOMP either directly or by inhibiting anti-apoptotic members, leading to the activation of BAK or BAX and subsequent release of Cyt-c from the mitochondrial intermembrane space into the cytoplasm [17]. In PC3 cells, Bcl2l13 interacts with ANT via its TM domain, facilitating the release of Cyt-c through conformational conversion of mPTP [19]. Similarly, in 293T cells VDAC, functionally equivalent to ANT, interacts with Bcl2l13 to modulate mPTP, leading to the release of Cyt-c and subsequent activation of Caspase3 [20]. In this study, it was found that bcl2l13 overexpression resulted in significant down-regulation of cyt-c, grp78 and fas expression, indicating its involvement in both the endogenous mitochondrial pathway and the death receptor pathway. Moreover, bcl2l13 overexpression significantly elevated the mPTP in FHM cells, while the deletion of the TM domain reduced mPTP. These results suggest that bcl2l13 controls apoptosis by regulating mPTP, with the TM domain playing a crucial role in this process. Overall, the mechanism by which M. amblycephala bcl2l13 regulates apoptosis shares similarities with the mammalian apoptotic regulation pathway, emphasizing the importance of bcl2l13 in mediating mitochondrial permeability and apoptosis.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this study delved into understanding the function of M. amblycephala Bcl2l13 and its domains concerning autophagy and apoptosis. Bcl2l13 plays a role in autophagy under hypoxic conditions of eliminating excess ROS in the cells. Meanwhile, Bcl2l13 mediates apoptosis, potentially through the endogenous mitochondrial pathway. The study significantly advances our understanding of how bcl2l13 influences cellular processes, like autophagy and apoptosis, in fish. However, further research is needed to fully elucidate the specific pathways and mechanisms through which Bcl2l13 interacts with other autophagy and apoptosis-related proteins, especially in response to oxidative stress. In future study, by targeting Bcl2l13, it may be possible to develop interventions that mitigate cellular damage caused by oxidative stress, which is a common issue in various diseases and environmental stressors. Future studies should aim to validate these findings in more diverse models and investigate the therapeutic potential of Bcl2l13 modulation in both fish and other organisms.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fishes10060247/s1, M. amblycephala specific antibodies of Bcl2l13.
Author Contributions
X.L.: validation, data analysis. D.W.: validation, data analysis. S.W.: Writing—original draft, review and editing. H.W.: Writing—review and editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition. H.L.: Supervision. Z.G.: Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Natural Science Foundation of China (32072965), the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-45-01), and the Key R&D projects in Hubei Province (2022BBA0050).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The experiments on fish in this study were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Huazhong Agricultural University (Wuhan, China, HZAUFI-2020-0022, 5 January 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BH | BCL-2 homology domain |
| BHNo | Bcl-2 homology no domain |
| TM | Transmembrane domain |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| mPTP | Mitochondrial permeability transition pore |
| BH3-only | Bcl-2 homology domain 3-only |
| ANT | Adenine nucleotide translocator |
| VDAC | Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein |
| CERS6 | Ceramidase 6 |
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiforme |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-B |
| PC3 | Prostate cancer cells |
| A549 | Adenocarcinoma cells |
| SF767 | Brain tumor cells |
| mitophagy | Mitochondrial autophagy |
| KHEB | Ras homolog enriched in brain |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| DCFH-CA | 2,7-Dichlorofuorescin Diacetate |
| ETC | Electron transport chain |
| LIR | LC3-interacting region |
| MOMP | Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization |
References
- Wang, J.; Chen, A.; Xue, Z.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, A.; et al. BCL2L13 promotes mitophagy through DNM1L-mediated mitochondrial fission in glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Komatsu, M. Autophagy: Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell 2011, 147, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuma, A.; Mizushima, N. Physiological role of autophagy as an intracellular recycling system: With an emphasis on nutrient metabolism. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.R.; Thorburn, A. Autophagy and organelle homeostasis in cancer. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 906–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, Y.; Jeon, T.; Kim, M.S.; Kang, C. All cells are created equal in the sight of autophagy: Selective autophagy maintains homeostasis in senescent cells. Autophagy 2021, 17, 3260–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deretic, V.; Kroemer, G. Autophagy in metabolism and quality control: Opposing, complementary or interlinked functions? Autophagy 2022, 18, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Ballabio, A.; Boya, P.; Pedro, J.M.B.; Cecconi, F.; Choi, A.M.; Chu, C.T.; Codogno, P.; Colombo, M.I.; et al. Molecular definitions of autophagy and related processes. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 1811–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickles, S.; Vigié, P.; Youle, R.J. Mitophagy and Quality Control Mechanisms in Mitochondrial Maintenance. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R170–R185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, Q. Hypoxia activation of mitophagy and its role in disease pathogenesis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gibson, S.B. Is mitochondrial generation of reactive oxygen species a trigger for autophagy? Autophagy 2008, 4, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Kurokawa, H.; Waguri, S.; Taguchi, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Ichimura, Y.; Sou, Y.S.; Ueno, I.; Sakamoto, A.; Tong, K.I.; et al. The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djavaheri-Mergny, M.; Maiuri, M.C.; Kroemer, G. Cross talk between apoptosis and autophagy by caspase-mediated cleavage of Beclin 1. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1717–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igney, F.H.; Krammer, P.H. Death and anti-death: Tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornberry, N.A.; Lazebnik, Y. Caspases: Enemies within. Science 1998, 281, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desagher, S. Mitochondrial as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2000, 10, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, B.; Sinha, S.; Kroemer, G. Bcl-2 family members: Dual regulators of apoptosis and autophagy. Autophagy 2008, 4, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-D.; Qin, Z.-H. Beclin 1, Bcl-2 and Autophagy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1206, 109–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, T.; Holler, N.; Micheau, O.; Martinon, F.; Tinel, A.; Hofmann, K.; Tschopp, J. Bcl-rambo, a novel Bcl-2 homologue that induces apoptosis via its unique C-terminal extension. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 19548–19554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; So, K.-J.; Lee, S.; Park, J.-H. Bcl-rambo induces apoptosis via interaction with the adenine nucleotide translocator. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3142–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, H.; Tanaka, R.; Tateishi, T.; Yoshida, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kataoka, T. Corrigendum to: The human Bcl-2 family member Bcl-rambo and voltage-dependent anion channels manifest a genetic interaction in Drosophila and cooperatively promote the activation of effector caspases in human cultured cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 405, 112711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, S.A.; Calvert, A.E.; Volpert, G.; Kouri, F.M.; Hurley, L.A.; Luciano, J.P.; Wu, Y.; Chalastanis, A.; Futerman, A.H.; Stegh, A.H. Bcl2L13 is a ceramide synthase inhibitor in glioblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5682–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakawa, T.; Yamaguchi, O.; Hashimoto, A.; Hikoso, S.; Takeda, T.; Oka, T.; Yasui, H.; Ueda, H.; Akazawa, Y.; Nakayama, H.; et al. Bcl-2-like protein 13 is a mammalian Atg32 homologue that mediates mitophagy and mitochondrial fragmentation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrete, B., Jr.; Ackerly, K.L.; Esbaugh, A.J. Hypoxia-acclimation adjusts skeletal muscle anaerobic metabolism and burst swim performance in a marine fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2024, 297, 111734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pu, D.; Zheng, J.; Li, P.; Lü, H.; Wei, X.; Li, M.; Li, D.; Gao, L. Hypoxia-induced physiological responses in fish: From organism to tissue to molecular levels. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.B.; Gibson, S.B. Role of BNIP3 in proliferation and hypoxia-induced autophagy: Implications for personalized cancer therapies. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1210, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, S.; Jain, K.; Basu, A. Regulation of autophagy by kinases. Cancers 2011, 3, 2630–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kim, E.; Beemiller, P.; Wang, C.-Y.; Swanson, J.; You, M.; Guan, K.-L. Bnip3 mediates the hypoxia-induced inhibition on mammalian target of rapamycin by interacting with Rheb. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35803–35813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Sun, J.L.; Yao, F.C.; Jiang, T.; Jin, C.X.; Shi, L.P.; Sun, S.K.; Song, F.B.; Luo, J. Long-term hypoxia and reoxygenation induced oxidative stress lead to immunosuppression and apoptosis in golden pompano (Trachinotus blochii). Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1212571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Guo, X.; Bao, K.; Wu, D.; Liu, H.; Gao, Z.; Wang, H. Molecular Characterization and Expression Changes of the bcl2l13 Gene in Response to Hypoxia in Megalobrama amblycephala. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 6, 1136–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravell, M.; Malsberger, R.G. A permanent cell line from the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1965, 126, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆Ct Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherz, S.R.; Elazar, Z. Regulation of autophagy by ROS: Physiology and pathology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susnow, N.; Zeng, L.; Margineantu, D.; Hockenbery, D.M. Bcl-2 family proteins as regulators of oxidative stress. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2009, 19, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Xu, X.; Sho, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.; Yao, J.; Xu, J. ROS-induced autophagy regulates porcine trophectoderm cell apoptosis, proliferation, and differentiation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 316, C198–C209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Yin, H.; Li, S.; Gao, X.-J. TBBPA induced ROS overproduction promotes apoptosis and inflammation by inhibiting autophagy in mice lung. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 252, 114607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tan, J.; Miao, Y.; Lei, P.; Zhang, Q. ROS and Autophagy: Interactions and Molecular Regulatory Mechanisms. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 35, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Han, H.; Zhao, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tian, J.; Bing, G.; Zhao, L. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy alleviates chlorpyrifos-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicology 2015, 334, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, S.R.; Mizushima, N. Autophagy machinery in the context of mammalian mitophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 2797–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L. Cellular mitophagy: Mechanism, roles in diseases and small molecule pharmacological regulation. Theranostics 2023, 13, 736–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jia, J.; Zhang, X.; Dai, H. Selective binding of mitophagy receptor protein Bcl-rambo to LC3/GABARAP family proteins. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Commun. 2020, 530, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattingre, S.; Tassa, A.; Qu, X.; Garuti, R.; Liang, X.H.; Mizushima, N.; Packer, M.; Schneider, M.D.; Levine, B. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell. 2005, 122, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; Li, G.; Xia, D.; Hongdu, B.; Xu, C.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y. PRKCI negatively regulates autophagy via PIK3CA/AKT-MTOR signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).