Current Challenges and Issues in the Application of Astaxanthin
Abstract
1. Introduction
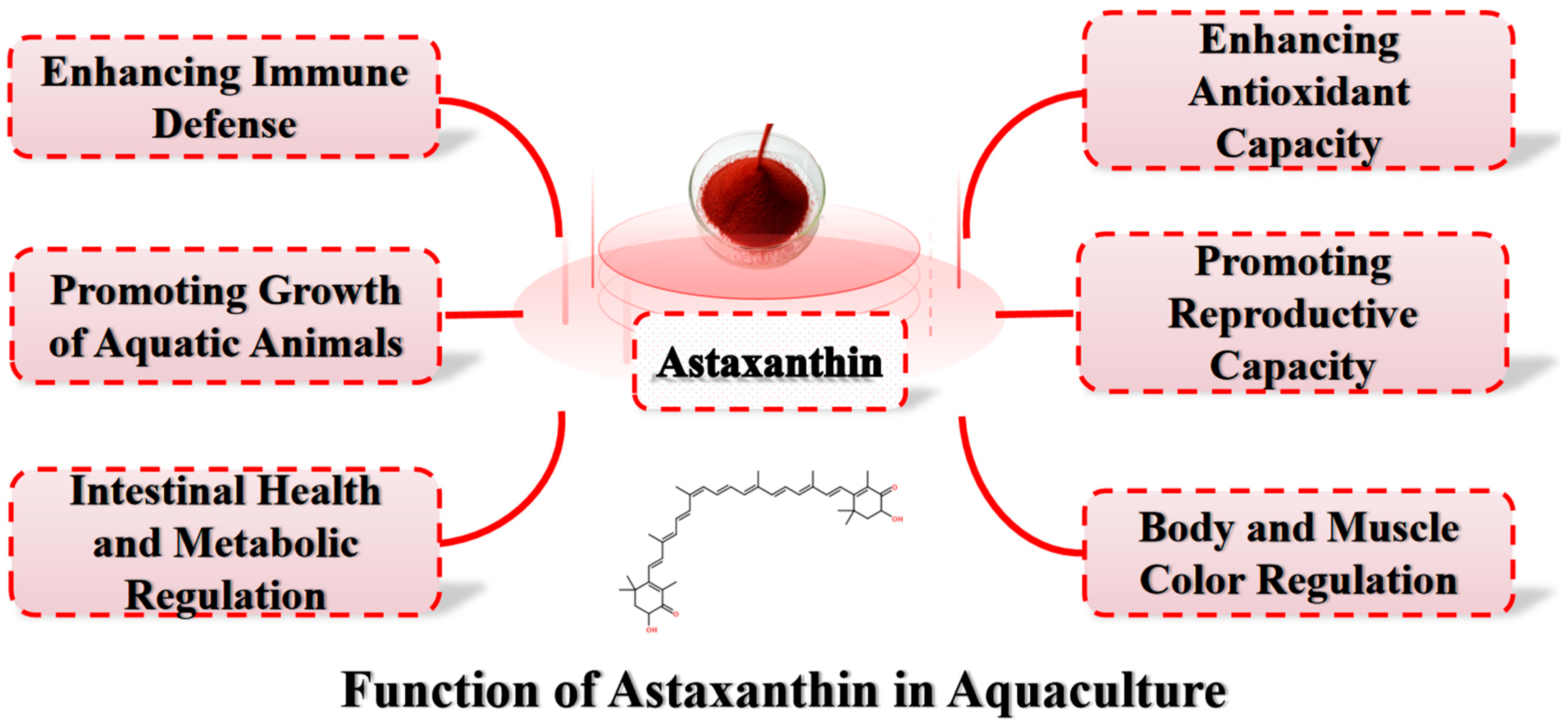
2. The Growth-Promoting Effects of Astaxanthin in Aquatic Animals
3. The Role of Astaxanthin in Enhancing Antioxidant Capacity in Aquatic Animals
4. The Role of Astaxanthin in Immune Regulation in Aquatic Animals
5. The Impact of Astaxanthin on the Reproductive Capacity of Aquatic Animals
6. The Role of Astaxanthin in Intestinal Health and Metabolic Regulation in Aquatic Animals
7. The Impact of Astaxanthin on the Body and Muscle Color of Aquatic Animals
8. Current Challenges and Issues in the Application of Astaxanthin
8.1. Challenges and Solutions for Improving the Bioavailability of Astaxanthin in Aquaculture
8.2. Current Status of Astaxanthin Production and Strategies for Reducing Production Costs
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eldessouki, E.A.A.; Elshopakey, G.E.; Elbahnaswy, S.; Shakweer, M.S.; Abdelwarith, A.A.; Younis, E.M.; Davies, S.J.; Mili, A.; Abd El-Aziz, Y.M.; Abdelnour, S.A.; et al. Influence of astaxanthin-enriched Haematococcus pluvialis microalgae on the growth efficacy, immune response, antioxidant capacity, proinflammatory cytokines, and tissue histomorphology of hybrid red tilapia. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 7447–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.C.; Yusoff, F.M.; Shariff, M.; Kamarudin, M.S. Astaxanthin as feed supplement in aquatic animals. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 738–773. [Google Scholar]
- Higuera-Ciapara, I.; Félix-Valenzuela, L.; Goycoolea, F.M. Astaxanthin: A review of its chemistry and applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 185–196. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, R.T.; Cysewski, G.R. Commercial potential for Haematococcus microalgae as a natural source of astaxanthin. Trends Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Britton, G.; Liaaen-Jensen, S.; Pfander, H. (Eds.) Carotenoids, Vol. 4: Natural Functions; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.W.; Yin, P.; Tian, L.X.; Yu, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Niu, J. Dietary Supplementation of Astaxanthin Improved the Growth Performance, Antioxidant Ability and Immune Response of Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Fed High-Fat Diet. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.H.; Gong, N.Y.; Chen, F.T.; Hu, S.R.; Zhou, Q.X.; Gao, X. The Effects of Astaxanthin on Metabolic Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, L.; Liu, W.J.; Xu, Y.W.; Zhang, B.; Meng, L.N.; Yin, R.; Chen, H.J. New insights into micro-algal astaxanthin’s effect on deoxynivalenol-induced spleen lymphocytes pyroptosis in Cyprinus carpio: Involving mitophagy and mtROS-NF-xB-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 144, 109259. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Sifuentes, L.; Marszalek, J.E.; Hernández-Carbajal, G.; Chuck-Hernández, C. Importance of Downstream Processing of Natural Astaxanthin for Pharmaceutical Application. Front. Chem. Eng. 2021, 2, 601483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, C.T.; Betancor, M.B.; Torrecillas, S.; Sprague, M.; Larroquet, L.; Véron, V.; Panserat, S.; Izquierdo, M.S.; Kaushik, S.J.; Fontagné-Dicharry, S. More Than an Antioxidant: Role of Dietary Astaxanthin on Lipid and Glucose Metabolism in the Liver of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Antioxidants 2023, 12, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; Chang, J.J.; Huang, H.T.; Lee, C.P.; Hu, Y.F.; Wu, M.L.; Huang, C.Y.; Nan, F.H. Improving red-color performance, immune response and resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus on white shrimp Penaeus vannamei by an engineered astaxanthin yeast. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2248. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.K.; Yang, Y.S.; Xu, H.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Dong, F.; Chen, Q.; Han, T.; Wang, J.T.; Wu, C.L. Effects of dietary astaxanthin on growth performance, immunity, and tissue composition in largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1404661. [Google Scholar]
- Elbahnaswy, S.; Elshopakey, G.E. Recent progress in practical applications of a potential carotenoid astaxanthin in aquaculture industry: A review. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 50, 97–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.; Yin, P.; Zhou, W.W.; Tian, L.X.; Liu, Y.J.; Xu, D.H.; Niu, J. Astaxanthin Attenuates Fish Oil-Related Hepatotoxicity and Oxidative Insult in Juvenile Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Lu, J.H.; Liu, Z.; Quan, J.Q.; Zhu, L.R.; Kucharczyk, D. Effects of Astaxanthin on Growth Performance, Gut Structure, and Intestinal Microorganisms of Penaeus vannamei under Microcystin-LR Stress. Animals 2024, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panase, P.; Vongkampang, T.; Wangkahart, E.; Sutthi, N. Impacts of astaxanthin-enriched Paracoccus carotinifaciens on growth, immune responses, and reproduction performance of broodstock Nile tilapia during winter season. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 50, 1205–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.X.; Liu, Y.T.; Huang, W.X.; Yao, C.W.; Yin, Z.Y.; Mai, K.S.; Ai, Q.H. Effects of dietary supplementation of astaxanthin (Ast) on growth performance, activities of digestive enzymes, antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 4605–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.M.; Gao, C.S.; Du, X.Y.; Yao, J.M.; He, F.F.; Niu, X.T.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, D.M. Effects of dietary astaxanthin on the growth, innate immunity and antioxidant defence system of Paramisgurnus dabryanus. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.M.; Li, M.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Xia, C.G.; Niu, X.T.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, D.M. Effects of dietary astaxanthin on growth, blood biochemistry, antioxidant, immune and inflammatory response in lipopolysaccharide-challenged Channa argus. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.L.; Li, X.X.; Huang, D.; Guo, Y.L.; Deng, J.M.; Zhou, W.Y.; Zhang, W.B.; Mai, K.S. Effects of dietary chromium yeast and astaxanthin on the growth performance, anti-oxidative capacity, and resistance to heat stress of abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, Y.; Berg, P.C.; Shakersain, B.; Hecht, K.; Takikawa, A.; Tao, R.H.; Kakuta, Y.; Uragami, C.; Hashimoto, H.; Misawa, N.; et al. Astaxanthin: Past, Present, and Future. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.J.; Liu, J.G. Astaxanthin isomers: Selective distribution and isomerization in aquatic animals. Aquaculture 2020, 520, 734915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, T.; Bandyopadhyay, T.K.; Vanitha, K.; Bobby, M.N.; Tiwari, O.N.; Bhunia, B.; Muthuraj, M. Astaxanthin from microalgae: A review on structure, biosynthesis, production strategies and application. Food Res. Int. 2024, 176, 113841. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Li, J.T.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Zhao, F.Z. Antioxidant, Transcriptome and the Metabolome Response to Dietary Astaxanthin in Exopalaemon carinicauda. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 859305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.W.; Lyu, X.; Lu, W.Y.; Peng, S.; Jia, X.Y.; Zhou, W.L.; Kang, J. Transcriptional analysis combined with intestinal microbiota sequencing to unveil the effects of astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis on pearl gentian grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀ x Epinephelus lanceolatu ♂). Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, Y.; Hosokawa, M.; Mikami, N.; Miyashita, K.; Tanaka, T. Dietary astaxanthin inhibits colitis and colitis-associated colon carcinogenesis in mice via modulation of the inflammatory cytokines. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2011, 193, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldessouki, E.A.A.; Diab, A.M.; Selema, T.; Sabry, N.M.; Abotaleb, M.M.; Khalil, R.H.; El-Sabbagh, N.; Younis, N.A.; Abdel-Tawwab, M. Dietary astaxanthin modulated the performance, gastrointestinal histology, and antioxidant and immune responses and enhanced the resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei against Vibrio harveyi infection. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 1869–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Kohandel, Z.; Farkhondeh, T.; Aschner, M.; Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Samarghandian, S. Anti-inflammatory action of astaxanthin and its use in the treatment of various diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, S.; Abbaszadeh, F.; Dargahi, L.; Jorjani, M. Astaxanthin: A mechanistic review on its biological activities and health benefits. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 136, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.M.; Ahmed, F.; Lin, B.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.H.; Sun, G.; Ding, H.; Wang, C.; Meng, C.X.; Gao, Z.Q. The Effects of Plant Growth Regulators on Cell Growth, Protein, Carotenoid, PUFAs and Lipid Production of Chlorella pyrenoidosa ZF Strain. Energies 2017, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolnourian, A.; Galea, I.; Bulters, D. Neuroprotective Role of the Nrf2 Pathway in Subarachnoid Haemorrhage and Its Therapeutic Potential. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 6218239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Liu, J.L.; Yu, H.J.Y.; Tian, H.Q.; Wu, G.L.; Liu, B.Y.; Dong, P.; Li, J.; Liang, X.G. Water-dispersible astaxanthin-rich nanopowder: Preparation, oral safety and antioxidant activity in vivo. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.D.; Chen, Y.F.; Xie, X.N.; Yao, D.; Ding, C.; Chen, M.Y. Astaxanthin prevents against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and sepsis via inhibiting activation of MAPK/NF-κB. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar]
- Echavarri-Erasun, C.; Johnson, E.A. Stimulation of astaxanthin formation in the yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous by the fungus Epicoccum nigrum. Fems Yeast Res. 2004, 4, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Gao, C.S.; Du, X.Y.; Zhao, L.; Niu, X.T.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, D.M. Amelioration of LPS-induced inflammatory response and oxidative stress by astaxanthin in Channa argus lymphocyte via activating glucocorticoid receptor signalling pathways. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 2687–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Guo, W.Q.; Guo, G.L.; Zhu, X.M.; Niu, X.T.; Shan, X.F.; Tian, J.X.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, D.M. Effects of dietary astaxanthin on lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress, immune responses and glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-related gene expression in Channa argus. Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lixi, F.; Vitiello, L.; Giannaccare, G. Marine Natural Products Rescuing the Eye: A Narrative Review. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salares, V.R.; Young, N.M.; Bernstein, H.J.; Carey, P.R. Mechanisms of spectral shifts in lobster carotenoproteins. The resonance Raman spectra of ovoverdin and the crustacyanins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1979, 576, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Q.; Li, L.P.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhao, Y.T.; Yu, X.Y. Chemical inducers regulate ROS signalling to stimulate astaxanthin production in Haematococcus pluvialis under environmental stresses: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 136, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, J.; Cai, X.N.; Ai, Y.; Long, H.; Ren, W.; Huang, A.Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Z.Y. Dietary supplementation of astaxanthin is superior to its combination with Lactococcus lactis in improving the growth performance, antioxidant capacity, immunity and disease resistance of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastak, Y.; Pelletier, W. Captivating Colors, Crucial Roles: Astaxanthin’s Antioxidant Impact on Fish Oxidative Stress and Reproductive Performance. Animals 2023, 13, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, N.; Canada, P.; Caboz, J.; Andrade, C.; Cordeiro, N. Effect of different levels of synthetic astaxanthin on growth, skin color and lipid metabolism of commercial sized red porgy (Pagrus pagrus). Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 276, 114916. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Long, X.W.; Li, Y.P.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.H.; Wu, X.G. Effects of Three Sources of Astaxanthin on the Growth, Coloration, and Antioxidant Capacity of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during Long-Term Feeding. Fishes 2024, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yao, R.; Wei, H.L.; Guo, Y.C.; Chen, A.Q.; Chen, B.Y.; Jin, N. Astaxanthin, bile acid and chlorogenic acid attenuated the negative effects of high-fat diet on the growth, lipid deposition, and liver health of Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 2023, 567, 739255. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Che, H.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Jin, Y.C.; Yu, H.; Wang, C.Q.; Fu, Y.R.; Li, N.; Zhang, J. Astaxanthin Alleviates Aflatoxin B1-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in IPEC-J2 Cells via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Toxins 2023, 15, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciapala, K.; Rojewska, E.; Pawlik, K.; Ciechanowska, A.; Mika, J. Analgesic Effects of Fisetin, Peimine, Astaxanthin, Artemisinin, Bardoxolone Methyl and 740 Y-P and Their Influence on Opioid Analgesia in a Mouse Model of Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhzadeh, N.; Panchah, I.K.; Asadpour, R.; Tayefi-Nasrabadi, H.; Mahmoudi, H. Effects of Haematococcus pluvialis in maternal diet on reproductive performance and egg quality in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2012, 130, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; Failla, M.L. Bioaccessibility of all trans-Astaxanthin from Salmon. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 38. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gamal, M.M.; Othman, S.I.; Abdel-Rahim, M.M.; Mansour, A.T.; Alsaqufi, A.S.; El Atafy, M.M.; Mona, M.H.; Allam, A.A. Palaemon and artemia supplemented diet enhances sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax, broodstock reproductive performance and egg quality. Aquaculture. Rep. 2020, 16, 100290. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.X.; Yang, F.M.; Zhu, L.L.; Zhan, L.L.; Numasawa, T.; Deng, J.M. Effects of dietary astaxanthin supplementation on growth performance, antioxidant status, immune response, and intestinal health of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Anim. Nutr. 2024, 17, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Zhao, W.; Lu, D.Q.; Xie, J.J.; He, X.S.; Fang, H.H.; Liao, S.Y. Dual-Function Analysis of Astaxanthin on Golden Pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) and Its Role in the Regulation of Gastrointestinal Immunity and Retinal Mitochondrial Dysfunction Under Hypoxia Conditions. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 568462. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, W.H.; Liao, Z.B.; Yu, G.J.; Xu, H.G.; Liang, M.Q.; Mai, K.S.; Zhang, Y.J. The effects of dietary astaxanthin on intestinal health of juvenile tiger puffer Takifugu rubripes in terms of antioxidative status, inflammatory response and microbiota. Aquac. Nutr. 2019, 25, 466–476. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.L.; Liu, M.T.; Fawzy, S.; Xue, Y.C.; Wu, M.Q.; Huang, X.X.; Yi, G.F.; Lin, Q. Effects of Dietary Phaffia rhodozyma Astaxanthin on Growth Performance, Carotenoid Analysis, Biochemical and Immune-Physiological Parameters, Intestinal Microbiota, and Disease Resistance in Penaeus monodon. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 762689. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, S.; Nishida, A.; Nishino, K.; Ohno, M.; Imaeda, H.; Andoh, A. Astaxanthin, a xanthophyll carotenoid, suppresses the development of experimental colitis by inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and AP-1. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, S573. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Bui, A.T.P.; Le, N.T.H.; Vo, H.T.N.; Nguyen, A.H.; Pham, T.D.; Hara, T.; Yokota, K.; Matsutani, M.; Takatsuka, Y.; et al. Heat-stable spores of carotenoid-producing Bacillus marisflavi and non-pigmented Bacillus subtilis cooperatively promote growth, quality, and gut microbiota of white-leg shrimp. Benef. Microbes 2023, 14, 623–640. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Luo, K.; Zhang, S.K.; Wei, C.; Wang, L.B.; Qiu, Y.G.; Tian, X.L. Biotic potential of the red yeast Rhodotorula mucilaginosa strain JM-01 on the growth, shell pigmentation, and immune defense attributes of the shrimp, Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2023, 572, 739543. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Su, W.T.; Zhang, X.D.; Tan, M.Q. Visual foodborne nanoparticles for oral site-specific delivery of anthocyanins in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Mater. Today Nano 2023, 24, 100431. [Google Scholar]
- Boe, M.R.; Vo, T.T.M.; Hansen, A.K.G.; Lerfall, J. Effect of natural carotenoids obtained from Haematococcus pluvialis, Paracoccus carotinifaciens, and Phaffia rhodozyma on flesh pigmentation and related biochemical mechanisms in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2025, 596, 741743. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zheng, X.; Du, R.H.; Xu, J.H.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.Q.; Liang, X.; Liang, H. Astaxanthin Protects against Alcoholic Liver Injury via Regulating Mitochondrial Redox Balance and Calcium Homeostasis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 19531–19550. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, X.W.; Xu, W.; Zhou, H.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Luo, Y.W.; Zhang, W.B.; Mai, K.S. Effects of dietary astaxanthin and xanthophylls on the growth and skin pigmentation of large yellow croaker Larimichthys croceus. Aquaculture 2014, 433, 377–383. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, L.; Chin, Y.X.; Liu, F.; Li, R.W.; Yuan, S.H.; Xue, C.H.; Xu, J.; Tang, Q.J. Astaxanthin n-Octanoic Acid Diester Ameliorates Insulin Resistance and Modulates Gut Microbiota in High-Fat and High-Sucrose Diet-Fed Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.J.; Morais, R.; Choubert, G. Effect of carotenoid source and dietary lipid content on blood astaxanthin concentration in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 1999, 176, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Ishizaki, S.; Nagashima, Y.; Watabe, S. Functional and structural properties of red color-related pigment-binding protein from the shell of Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar]
- Henmi, H.; Hata, M.; Takeuchi, M. Studies on the carotenoids in the muscle of salmon--V. Combination of astaxanthin and canthaxanthin with bovine serum albumin and egg albumin. Comp. Biochem. Physiology. B Comp. Biochem. 1991, 99, 609–612. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.P.; Tian, C.X.; Zhu, K.C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, M.Y.; Zhu, C.H.; Li, G.L. Effects of Natural and Synthetic Astaxanthin on Growth, Body Color, and Transcriptome and Metabolome Profiles in the Leopard Coralgrouper (Plectropomus leopardus). Animals 2023, 13, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.T.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, M.M.; Chen, S.M.; Dai, J.Y.; Qian, Y.X.; Gong, Y.Y.; Han, T. Synthetic astaxanthin has better effects than natural astaxanthins on growth performance, body color and n-3 PUFA deposition in black tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon). Aquaculture. Rep. 2023, 33, 101816. [Google Scholar]
- Yi-oh, k.; Lee, S.-M. Effects of Dietary Lipid and Paprika Levels on Growth and Skin Pigmentation of Red- and White-colored Fancy Carp Cyprinus carpio var. koi. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 45, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, N.P.C.; Ha, N.N.; Linh, N.T.T.; Tri, N.N. Effect of astaxanthin and spirulina levels in black soldier fly larvae meal-based diets on growth performance and skin pigmentation in discus fish, Symphysodon sp. Aquaculture 2022, 553, 738048. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.J.; Hossain, A.; Shahidi, F. Dietary lipid and astaxanthin contents affect the pigmentation of Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus). Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2024, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.W.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.P.; Sun, W.H.; Wu, X.G. Effects of long-term Haematococcus pluvialis astaxanthin feeding on the growth, coloration, and antioxidant capacity of commercial-sized Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 30, 101603. [Google Scholar]
- Osuna-Salazar, A.; Hernández, C.; Lizárraga-Velázquez, C.E.; Gutiérrez, E.Y.S.; Hurtado-Oliva, M.Á.; Benitez-Hernández, A.; Ibarra-Castro, L. Improvement in spotted rose snapper growth and skin coloration after incorporation of shrimp head meal in diet. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 30, 101599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Zhang, S.Z.; McClements, D.J.; Wang, D.F.; Xu, Y. Design of Astaxanthin-Loaded Core-Shell Nanoparticles Consisting of Chitosan Oligosaccharides and Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid): Enhancement of Water Solubility, Stability, and Bioavailability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5113–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Zhao, Y.M.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.L.; Chen, X.; Han, J. Development and Evaluation of Astaxanthin as Nanostructure Lipid Carriers in Topical Delivery. AAPS Pharmscitech 2020, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Li, D.H.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, G.M.; Wang, Y.B.; Tan, B. Dietary fatty acid-mediated protein encapsulation simultaneously improving the water-solubility, storage stability, and oral absorption of astaxanthin. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107152. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.X.; Xu, Y.X.; Wu, S.; Zheng, W.Y.; Song, S.; Ai, C.Q. Fabrication of astaxanthin-enriched colon-targeted alginate microspheres and its beneficial effect on dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 396–409. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.N.; Su, W.T.; Tie, S.S.; Cui, W.A.; Yu, X.T.; Zhang, L.J.; Hua, Z.; Tan, M.Q. Orally deliverable sequence-targeted astaxanthin nanoparticles for colitis alleviation. Biomaterials 2023, 293, 121976. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, E.J.; Jeong, Y.I.; Lee, K.J.; Yu, Y.B.; Ohk, S.H.; Lee, S.Y. Anticancer Activity of Astaxanthin-Incorporated Chitosan Nanoparticles. Molecules 2024, 29, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wei, Z.; Xue, C. Recent research advances in astaxanthin delivery systems: Fabrication technologies, comparisons and applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 63, 3497–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, R.R.; Phang, S.M.; Ravi, S.; Aswathanarayana, R.G. Astaxanthin: Sources, extraction, stability, biological activities and its commercial applications—A review. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussagy, C.U.; Pereira, J.F.; Dufossé, L.; Raghavan, V.; Santos-Ebinuma, V.C.; Pessoa, A., Jr. Advances and trends in biotechnological production of natural astaxanthin by Phaffia rhodozyma yeast. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1862–1876. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, N.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. De novo synthesis of astaxanthin: From organisms to genes. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 162–171. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadkelayeh, S.; Hawboldt, K. Extraction of lipids and astaxanthin from crustacean by-products: A review on supercritical CO2 extraction. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 94–108. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.W.; Sun, J.N.; Liu, Z.; Huang, W.C.; Secundo, F.; Zhao, Y.H.; Xue, C.H.; Mao, X.Z. Highly efficient preparation of free all-trans-astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis extract by a rapid biocatalytic method based on crude extracellular enzyme extract. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 376–386. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.B.; Deng, J.Y.; Wang, J.M.; Ge, C.J.; Yang, H. Adverse effects of microplastics on the growth, photosynthesis, and astaxanthin synthesis of Haematococcus pluvialis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176427. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, D.D.; Jin, J.; Liu, D.; Jia, B.; Yuan, Y.J. In vitro and in vivo recombination of heterologous modules for improving biosynthesis of astaxanthin in yeast. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Quintana-López, A.; Hernández, C.; Palacios, E.; Manzano-Sarabia, M.; Hurtado-Oliva, M.A. Do by-products derived from farmed and wild shrimp contain the same quantities of astaxanthin? J. Crustac. Biol. 2021, 41, ruab065. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Ju, J.; Li, M.; Ma, Z.Y.; Lu, W.Y.; Yang, H. Dose-dependent effects of polystyrene nanoplastics on growth, photosynthesis, and astaxanthin synthesis in Haematococcus pluvialis. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 359, 124574. [Google Scholar]
- Simat, V.; Rathod, N.B.; Cagalj, M.; Hamed, I.; Mekinic, I.G. Astaxanthin from Crustaceans and Their Byproducts: A Bioactive Metabolite Candidate for Therapeutic Application. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.R.; Sindhuja, H.N.; Dharmesh, S.M.; Sankar, K.U.; Sarada, R.; Ravishankar, G.A. Effective Inhibition of Skin Cancer, Tyrosinase, and Antioxidative Properties by Astaxanthin and Astaxanthin Esters from the Green Alga Haematococcus pluvialis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3842–3851. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.; Narasimhan, A.L.; Moon, G.; Kim, Y.E.; Park, M.; Kim, B.; Mahadi, R.; Chung, S.; Oh, Y.K. Room-Temperature Cell Disruption and Astaxanthin Recovery from Haematococcus lacustris Cysts Using Ultrathin α-Quartz Nanoplates and Ionic Liquids. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denga, M.; Qu, Y.; Wu, T.X.; Na, Y.; Liang, N.; Zhao, L.S. Amino acid-based natural deep eutectic solvent combined with ultrasonic extraction: Green extraction of astaxanthin from shrimp shells. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 24631–24640. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, Y.M.; Li, Z.X.; Yu, F.Q.H. Recent Advances in Astaxanthin as an Antioxidant in Food Applications. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, A.F.; Tran, T.L.N.; Abramov, T.; Jehalee, F.; Miglani, M.; Liu, Z.Q.; Rochfort, S.; Gupta, A.; Cheirsilp, B.; Adhikari, B.; et al. Marine Protists and Rhodotorula Yeast as Bio-Convertors of Marine Waste into Nutrient-Rich Deposits for Mangrove Ecosystems. Protist 2020, 171, 125738. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.A.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, J.; Huh, Y.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Cho, D.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.; An, H.R.; et al. Biocompatible liquid-type carbon nanodots (C-paints) as light delivery materials for cell growth and astaxanthin induction of Haematococcus pluvialis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 109, 110500. [Google Scholar]
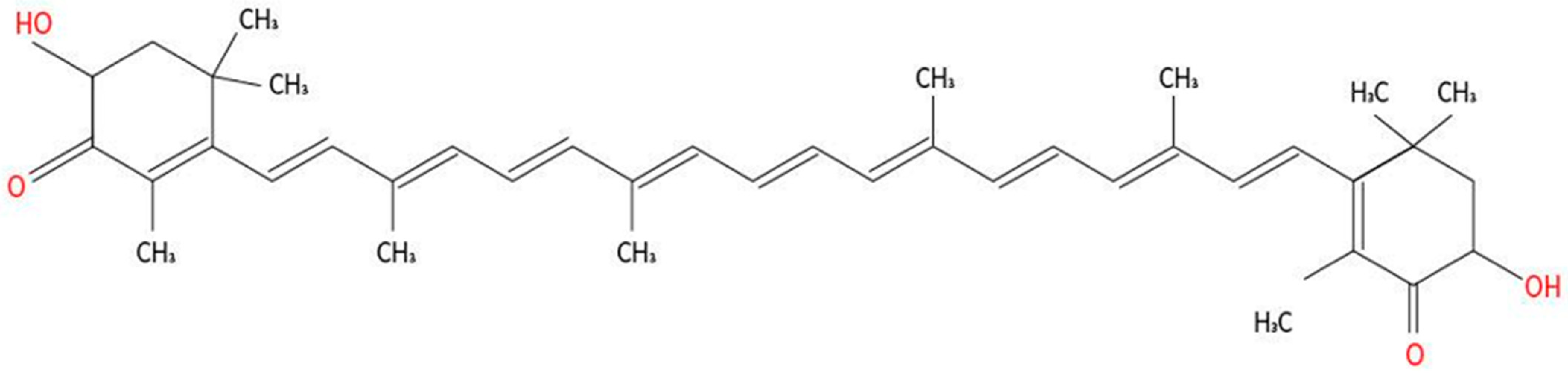
| Delivery System | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Nanoemulsions | Simple preparation process | Low encapsulation efficiency; prone to phase separation and flocculation |
| Microcapsule | Effective protection of active compounds; sustained release | Residual organic solvents; high cost of freeze-drying |
| Nanoparticle | Small particle size; high drug-loading capacity; biodegradable | Stability easily affected by environmental conditions |
| Liposome | Small particle size; high encapsulation efficiency; good biocompatibility | Use of cholesterol and organic solvents; limited industrial scalability |
| Nanostructured lipid carrier | Non-toxic; high drug-loading capacity; controlled release | Strict requirements for processing conditions |
| Astaxanthin Source | Estimated Production Cost (USD/kg) | Relative Bioavailability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| H. pluvialis | 1500–7000 | High | Natural source, high bioavailability due to esterified form; widely used. |
| P. rhodozyma | 1000–3000 | Medium | Natural source, used mainly in aquaculture feed. |
| Chemical synthesis | 500–1000 | Low | Racemic mixture; not approved for human use in some regions. |
| Crustacean by-products | 100–500 | Low–Medium | From shrimp/crab shells; low yield and stability. |
| Genetically engineered microorganisms | 500–2000 | Medium–High | Emerging technology; cost-effective and scalable. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yang, H. Current Challenges and Issues in the Application of Astaxanthin. Fishes 2025, 10, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040159
Peng L, Zhang Z, Li Q, Yang H. Current Challenges and Issues in the Application of Astaxanthin. Fishes. 2025; 10(4):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040159
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Limin, Zhiqiang Zhang, Qing Li, and Hui Yang. 2025. "Current Challenges and Issues in the Application of Astaxanthin" Fishes 10, no. 4: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040159
APA StylePeng, L., Zhang, Z., Li, Q., & Yang, H. (2025). Current Challenges and Issues in the Application of Astaxanthin. Fishes, 10(4), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040159





