Fish Diversity and Spatial Patterns in the Upper Yangtze River National Nature Reserve for Rare and Endemic Fish Based on Environmental DNA (eDNA) Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
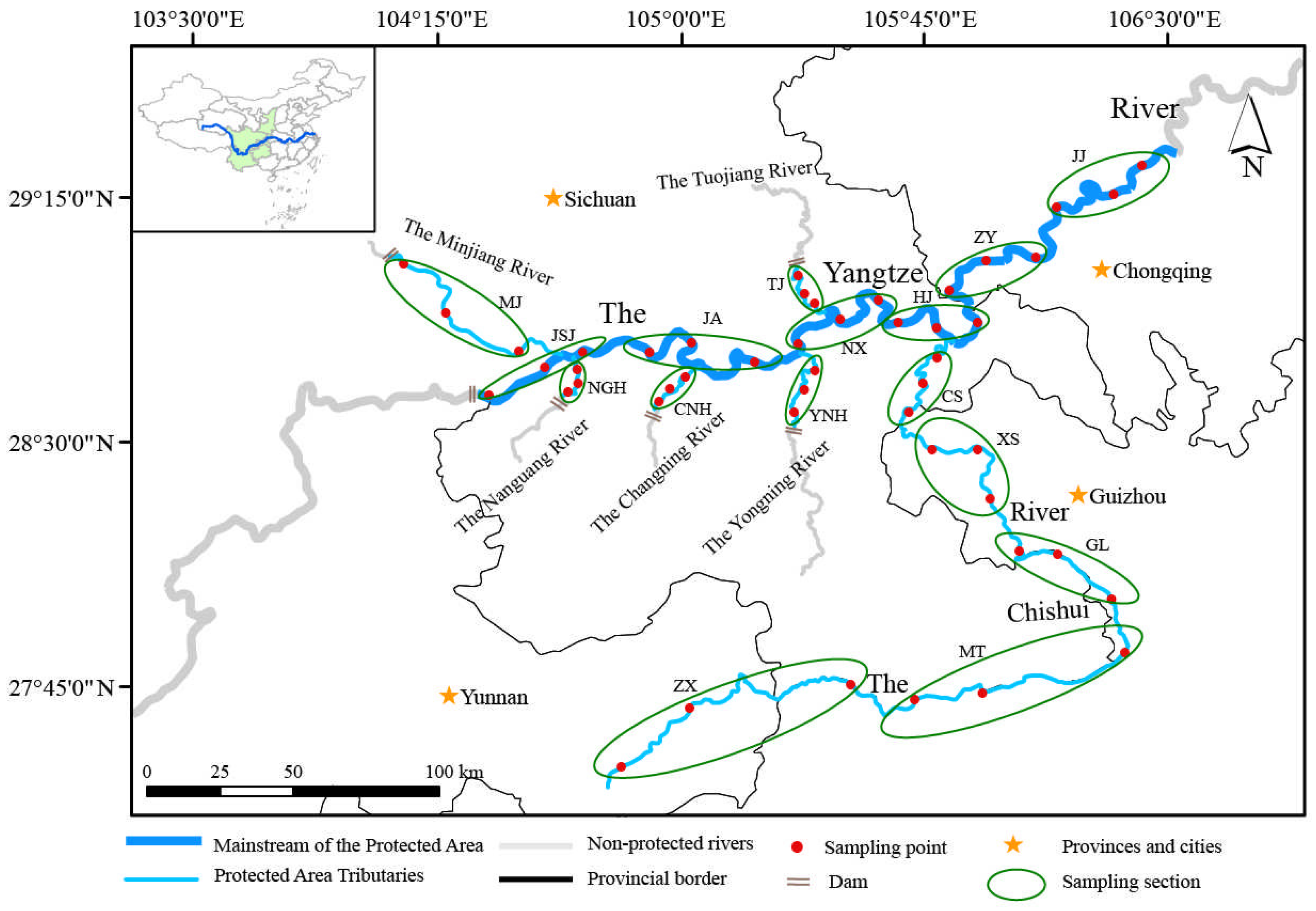
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Design
2.2. Water Collection and eDNA Enrichment
2.3. PCR Amplification
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
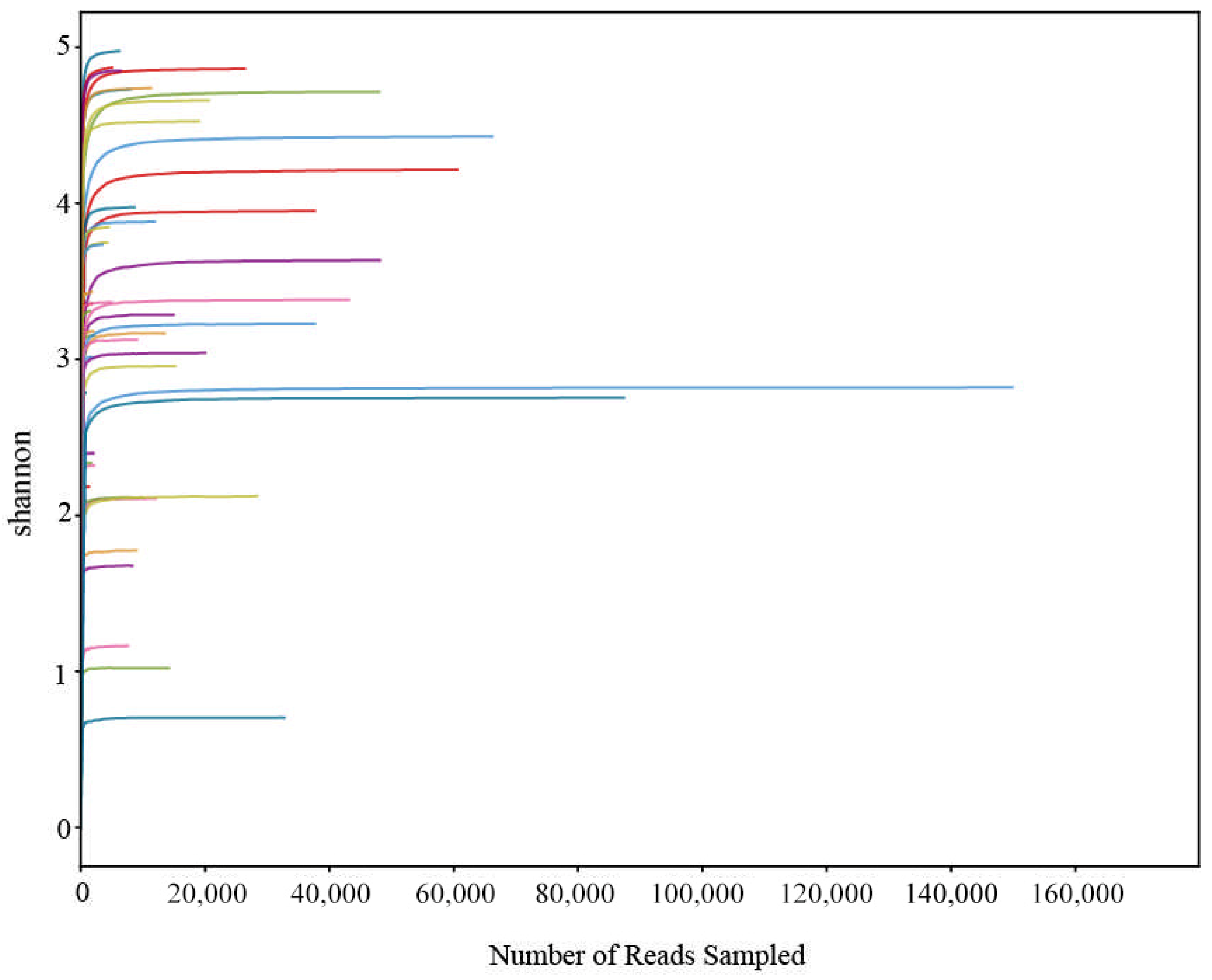
3.1. eDNA Sequencing Overview and Data Quality
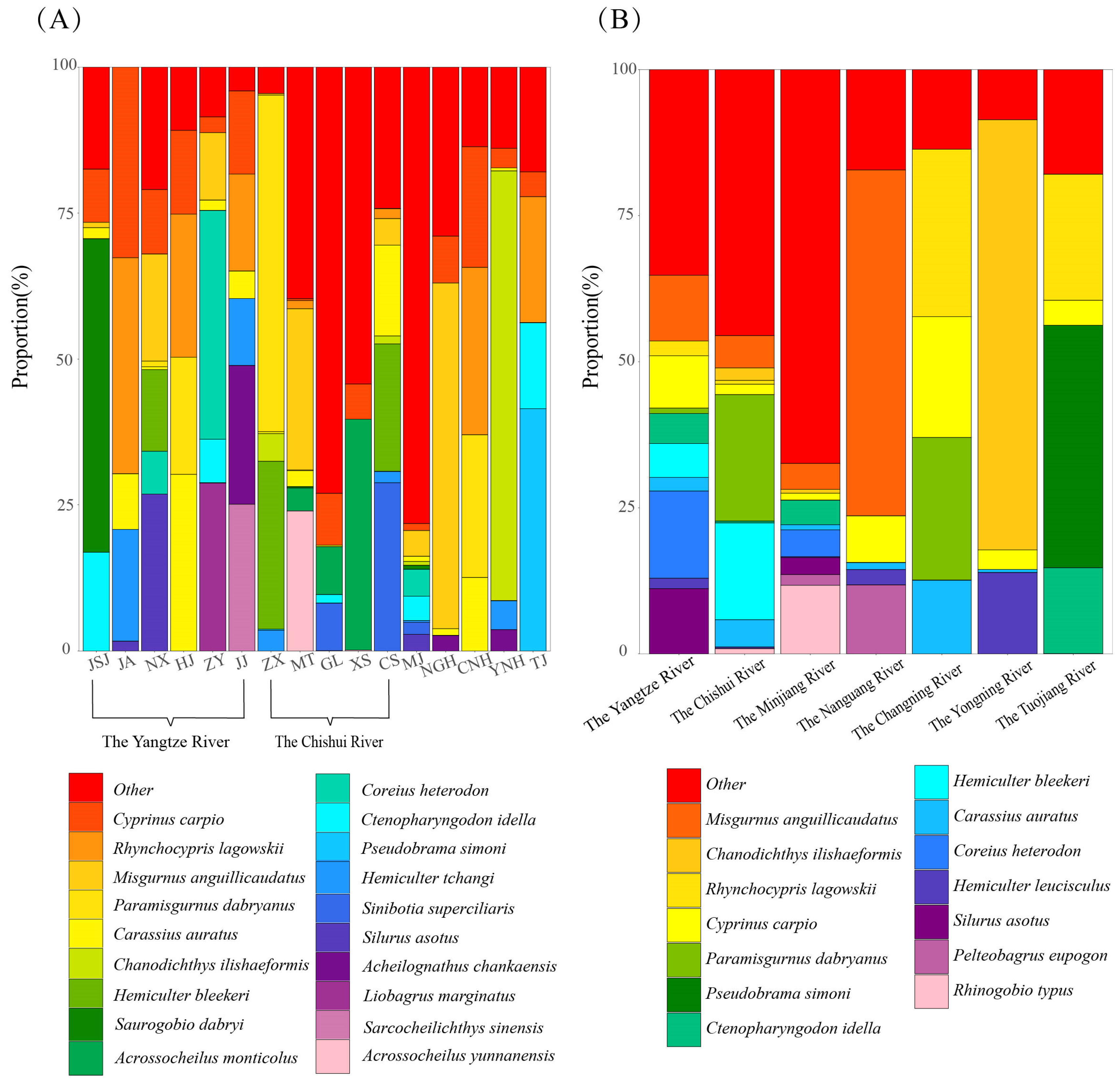
3.2. Fish Community Composition and Structure
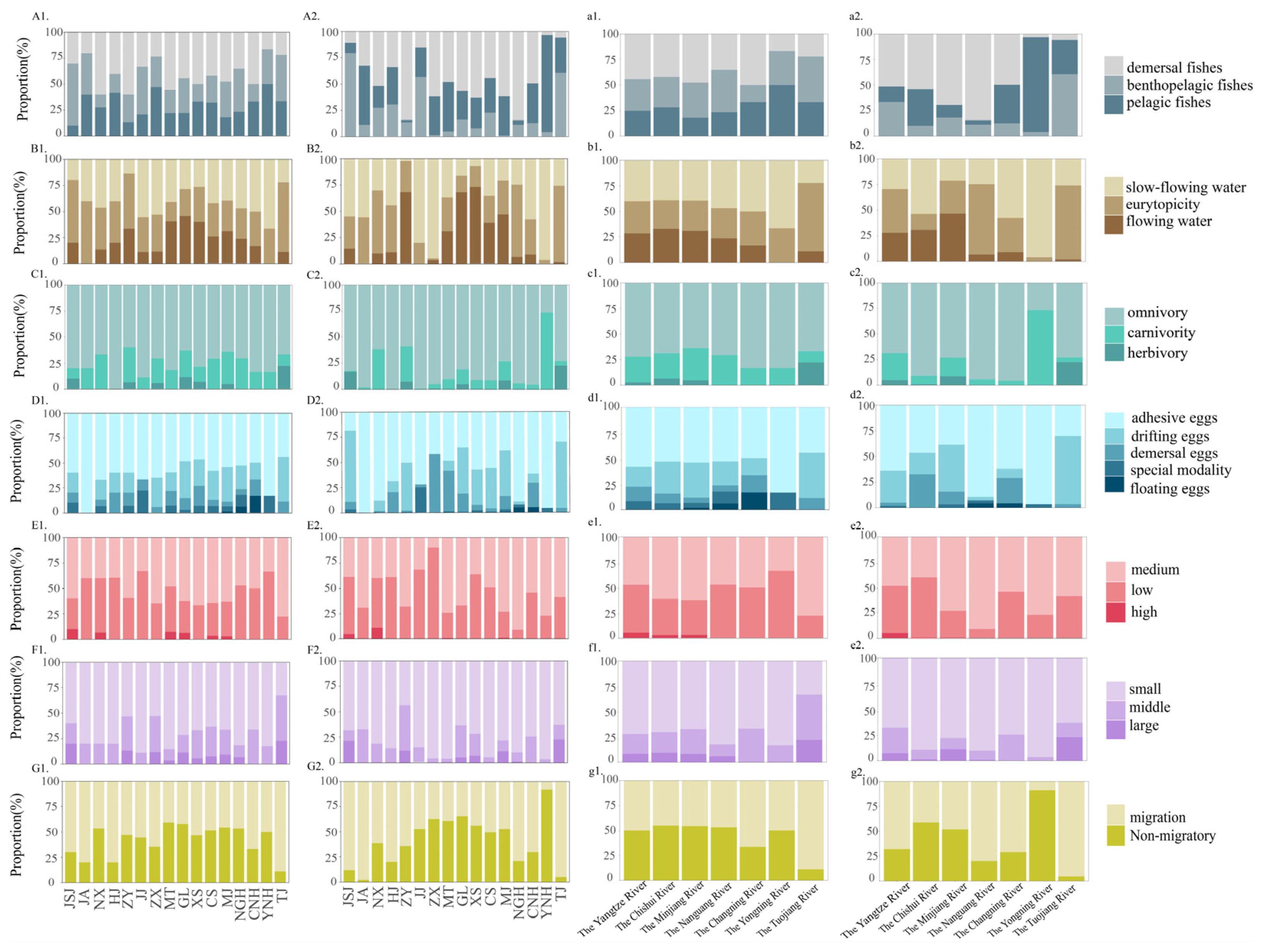
3.3. Ecological Types of Species
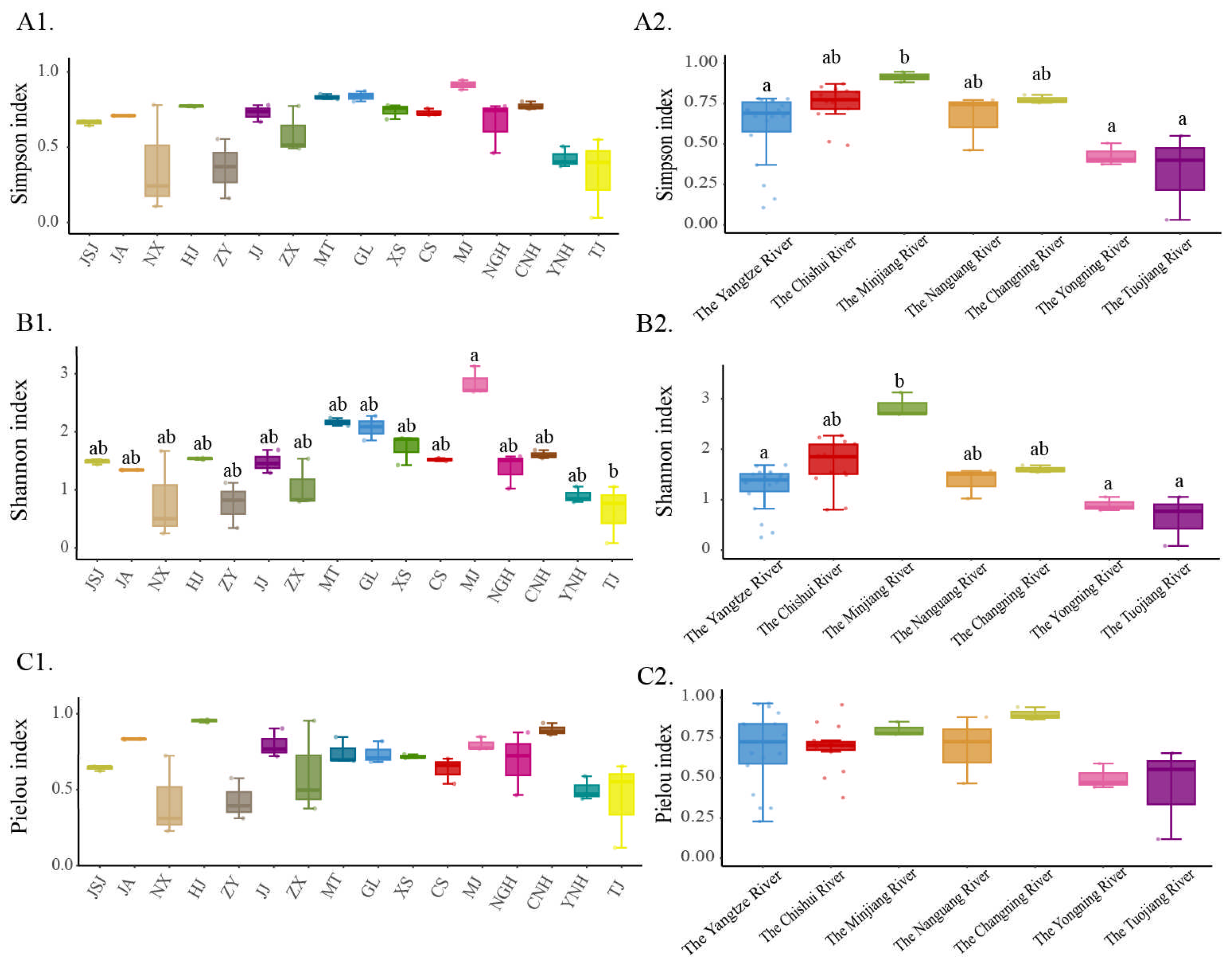
3.4. Spatial Patterns of Fish Alpha Diversity
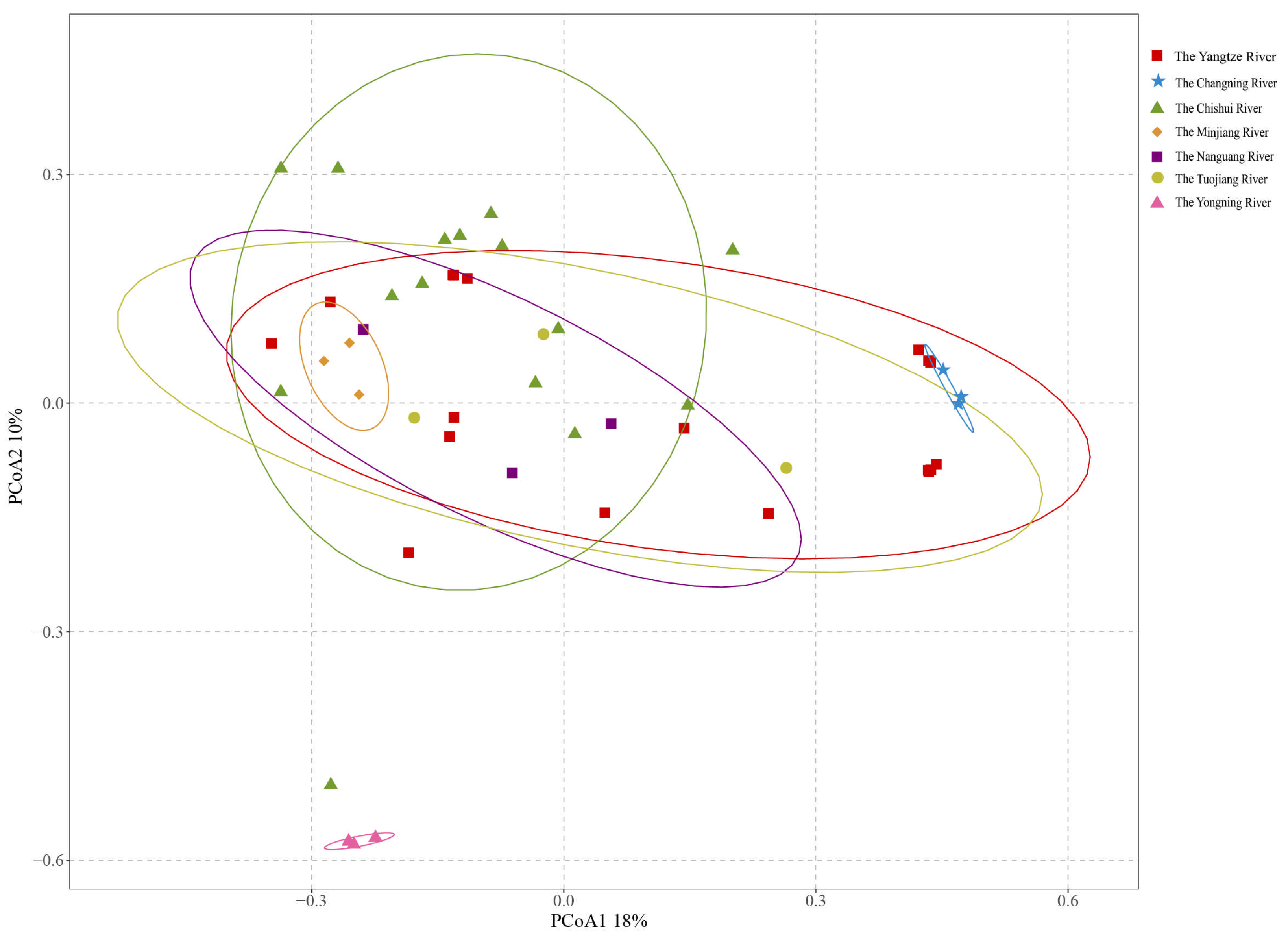
3.5. Fish Community Beta Diversity and Structural Differentiation
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal Changes in Fish Community Composition and Potential Drivers
4.2. Ecological Type Structure and Habitat Adaptation
4.3. Spatial Patterns of Fish Diversity and Their Potential Drivers
4.4. Applicability and Limitations of the eDNA Method
4.5. Conservation Implications and Management Recommendations
- (1)
- Implement systematic ecological flow management, incorporating seasonal flow releases timed to key natural hydrological and thermal spawning cues (e.g., spring runoff pulses, temperature thresholds), to restore longitudinal connectivity for fish migration and rehabilitate critical spawning habitats.
- (2)
- Develop an integrated early-warning and control system for invasive species that combines high-sensitivity eDNA monitoring with conventional methods. This system should establish molecular-based alert thresholds to trigger confirmatory on-ground surveys and targeted netting for rapid response. This initiative must be coupled with strict regulations to prevent invasions from aquaculture escapes and unauthorized fish releases.
- (3)
- Improve the management of fish stock enhancement to ensure that species introductions are scientifically sound and ecologically appropriate, enhancing the effectiveness of artificial breeding and release programs.
- (4)
- Strengthen policy guidance by implementing differentiated management strategies—such as designating “core natural river zones” (e.g., the Chishui River) and “ecological restoration zones” (e.g., the Tuojiang River)—to simultaneously advance conservation and rehabilitation goals.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.; Jiao, L.; Ni, L.; Wang, M.; You, P. Bridging the gap: The integration of eDNA techniques and traditional sampling in fish diversity analysis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1289589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloranta, A.P.; Kahilainen, K.K.; Amundsen, P.A.; Knudsen, R.; Harrod, C.; Jones, R.I. Lake size and fish diversity determine resource use and trophic position of a top predator in high-latitude lakes. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 1664–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yuan, T.; Xiong, M.; Zhao, X.; Ma, P.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Dong, F.; Li, J. Fish Diversity Investigation in the Three-River Headwater Region and Strategies for Conservation. J. Hydroecol. 2024, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Wang, M.; Ma, W.; Gu, D.; Jin, Z.; Yang, R.; Qian, Z.; Song, C.; Wang, Z.; Jin, S. Environment DNA Reveals Fish Diversity in a Canyon River within the Upper Pearl River Drainage. Animals 2024, 14, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, C.R.; Punt, A.E.; Cope, J.M. The effect of reduced data on the ability to monitor rebuilding of overfished fish stocks. Fish. Bull. 2018, 116, 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Hubert, N.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gan, X.; Peng, Z.; He, S. DNA barcoding the ichthyofauna of the Yangtze River: Insights from the molecular inventory of a mega-diverse temperate fauna. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Chang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, T. Influence of Three Gorges Dam on Downstream Low Flow. Water 2019, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinho, A.A.; Pelicice, F.M.; Gomes, L.C. Dams and the fish fauna of the Neotropical region: Impacts and management related to diversity and fisheries. Braz. J. Biol. 2008, 68 (Suppl. S4), 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, M.S.D.J.; Ludwig, S.; Resende, C.L.; Dias, P.F.P.B.; Pereira, A.H.; Abreu, N.L.d.; Rosse, I.C.; Martins, A.P.V.; Facchin, S.; Lopes, J.D.M.; et al. Genetic evaluation of migratory fish: Implications for conservation and stocking programs. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 10314–10324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarossa, V.; Schmitt, R.J.P.; Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Zarfl, C.; King, H.; Schipper, A.M. Impacts of current and future large dams on the geographic range connectivity of freshwater fish worldwide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3648–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.B.; Braga-Silva, A.; Freitas, P.D.; Galetti, P.M., Jr. Damming shapes genetic patterns and may affect the persistence of freshwater fish populations. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 67, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liermann, R.C.; Nilsson, C.; Robertson, J.; Rebecca, Y.N. Implications of Dam Obstruction for Global Freshwater Fish Diversity. BioScience 2012, 62, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R. Dam-building threatens Mekong fisheries. Science 2016, 354, 1084–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessey, C.; Jarman, S.N.; Berry, O.; Olsen, Y.S.; Bunce, M.; Simpson, T.; Power, M.; McLaughlin, J.; Edgar, G.J.; Keesing, J. Maximizing fish detection with eDNA metabarcoding. Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merin, C.R.; Florian, A.; Fabian, F.; Antoine, G.; Thomas, K.; Arnaud, L.; Pierre-Louis, R.; Eilísh, R.; Alice, V.; Conor, W.; et al. Catchment-based sampling of river eDNA integrates terrestrial and aquatic biodiversity of alpine landscapes. Oecologia 2023, 202, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, A.M.; Turner, R.C. The ecology of environmental DNA and implications for conservation genetics. Conserv. Genet. 2016, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Walser, J.; Mächler, E.; Altermatt, F. Choice of capture and extraction methods affect detection of freshwater biodiversity from environmental DNA. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, A.; Taberlet, P.; Miaud, C.; Civade, R.; Herder, J.; Thomsen, P.F.; Bellemain, E.; Besnard, A.; Coissac, E.; Boyer, F.; et al. Next-generation monitoring of aquatic biodiversity using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, N.T.; Li, Y.; Renshaw, M.A.; Olds, B.P.; Deiner, K.; Turner, C.R.; Jerde, C.L.; Lodge, D.M.; Lamberti, G.A.; Pfrender, M.E. Fish community assessment with eDNA metabarcoding: Effects of sampling design and bioinformatic filtering. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coble, A.A.; Flinders, C.A.; Homyack, J.A.; Penaluna, B.E.; Cronn, R.C.; Weitemier, K. eDNA as a tool for identifying freshwater species in sustainable forestry: A critical review and potential future applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Turner, C.R.; Deiner, K.; Klymus, K.E.; Thomsen, P.F.; Murphy, M.A.; Spear, S.F.; McKee, A.; Oyler-McCance, S.J.; Cornman, R.S.; et al. Critical considerations for the application of environmental DNA methods to detect aquatic species. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Miaud, C.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Chadderton, W.L.; Lodge, D.M. “Sight-unseen” detection of rare aquatic species using environmental DNA. Conserv. Lett. 2011, 4, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, J.; Hui, Z.; Weiwei, X. Fish Diversity Monitored by Environmental DNA in the Yangtze River Mainstream. Fishes 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Tong, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Geng, X.; Gao, C.; Wang, Y. Towards a comprehensive assessment of ichthyofaunal diversity in the Yangtze River estuary: Leveraging environmental DNA technology and bottom trawl surveys. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Luo, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y. Application of eDNA metabarcoding for monitoring the fish diversity of the Jiangjin to Fuling section of the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 4067–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shen, L.; He, Y.; Tian, H.; Gao, L.; Wu, J.; Mei, Z.; Wei, N.; Wang, L.; Zhu, T. Status of aquatic organisms resources and their environments in Yangtze River system (2017–2021). Aquacult. Fish. 2024, 9, 833–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y. Protection of the rare and endemic fish in the conservation area located in the upstream of the Yangtze River. Freshw. Fish. 2014, 44, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.; Wang, C.; Liu, F.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Zhu, X. Current status and conservation planning of fish biodiversity in the upper Yangtze River Basin in the context of hydropower development. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin 2019, 43, 130–143. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Lin, P.C.; Li, M.Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, H.Z. Situations and conservation strategies of fish resources in the Yangtze river basin. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2019, 43 (Suppl. S1), 144–156. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Duan, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y. Fish Diversity in Chongqing Section of the National Nature Reserve for Rare and Endemic Fish in the Upper Yangtze River Based on eDNA Technology. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2022, 46, 2–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q. Scientific Investigation Report on National Nature Reserve for the Rare and Endemic Fishes in the Upper Reaches of the Yangtze River; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012; Volume 208, p. 214. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, K.; Ma, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, J. Using environmental DNA to assess population-wide spatiotemporal reserve use. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Chen, F.; Shen, Y. Insights into the Process of Fish Diversity Pattern Changes and the Current Status of Spatiotemporal Dynamics in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area Using eDNA. Fishes 2025, 10, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Dong, X.; Huang, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, W.; Shen, Y. Environmental DNA Insights into the Spatial Status of Fish Diversity in the Mainstem of the Jialing River. Animals 2025, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Poulsen, J.Y.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H.; et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohl, D.; Vangay, P.; Garbe, J.; Maclean, A.; Hauge, A.; Becker, A.; Trevor, G.; Jonathan, C.; Timothy, J.; Ryan, H.; et al. Systematic improvement of amplicon marker gene methods for increased accuracy in microbiome studies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R. The Fish of Sichuan; Sichuan Science and Technology Press: Chengdu, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L. Guizhou Fish Fauna; Guizhou People’s Publishing House: Guiyang, China, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, E.C. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C.J. The measurement of diversity in different typesof biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Fan, G.; Hu, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, C. Integrating environmental DNA technology and traditional fish survey to reveal the diversityof fishes in the rivers on the Chongming lsland. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 2022, 31, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T.H.; Tian, H.W.; Ye, C.; Duan, X.B. Diversity and composition of fish in the mainstream of national nature reserve of rare and endemic fish in the upper Yangtze River. Freshw. Fish. 2013, 43, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Deng, H.T.; Tian, H.W.; Wu, X.H.; Tang, X.; Pu, Y.; Wang, D.Q.; Duan, X.B.; Liu, S.P.; Chen, D.Q. Analysis on the characteristics of fish community structure in the main stream section of the National Nature Reserve for Rare and Endemic Fish in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. J. Fish. China 2023, 47, 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, H.; Miao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J. Status and conservation of fish resources in the Chishui River. Biol. Divers. 2010, 18, 162–172. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H. Application of environmental DNA metabarcoding in ecology. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 4573–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qin, J.; Xu, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Biodiversity decline of fish assemblages after the impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2019, 29, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cao, J.; Zhou, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, Q. Early Stage Resource Status of Fish Species Spawning Drifting Eggs in the Jiangjin Section of the Upper Yangtze River and Their Hydrologic Requirements. J. Hydroecol. 2024, 45, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Fan, J.; Guo, F.; Carpenter-Bundhoo, L.; Huang, G.; Shi, Y.; Ao, Y.; Wang, J. Assessing the impact of river connectivity on fish biodiversity in the Yangtze River Basin using a multi-index evaluation framework. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Yu, F.; Xia, Z.; Qin, Q.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, H. Changes in fish assemblages following the implementation of a complete fishing closure in the Chishui River. Fish. Res. 2021, 243, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, R.; Yang, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Duan, C.; Hu, J. Spatial distribution characteristics of fish community composition and diversity in the National Nature Reserve of Rare and Endemic Fishes in the Upper Yangtze River based on environmental DNA Matabarcoding. J. Hydroecol. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, R.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y. Fish diversity of the cascade hydropower reservoir area of the Wujiang River based on environmental DNA technology. J. Fish. China 2025, 49, 140–157. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, T.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, J.; He, B. Investigation and Analysis of Fish Resources in Minjiang River. Acta Ecol. Anim. Domastici 2022, 43, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Hao, L.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Cao, M. Confluence characteristics and regulation stage of shoals at Minjiang River mouth. Adv. Water Sci. 2024, 35, 645–656. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Chen, S.; Hua, Q.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q.; Hu, M. Fish community and its relationships with environmental variables in the channel connecting Poyang Lake and the Yangtze River. Aquat. Sci. 2024, 86, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, H.V.; Van Densen, W.L.T. Assessing the opportunities for upstream migration of non-salmonid fishes in the weir-regulated River Vecht. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2001, 8, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, L.; Zhi, X.; Hu, P.; Shang, C.; Zhao, B. Characteristics of the macroinvertebrate community structure and their habitat suitability conditions in the Chishui River. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2025, 12, 1459468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Shen, M.; Xiao, N.; Gao, X.; Guo, X.; Li, J. Distribution characteristics of autumn fish diversity in Chishui River based on environmental DNA metabarcoding technology. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 1676–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Analysis of changes of main water quality pollution indicators and driving factors in Tuojiang River Basin. Yangtze River 2025, 56, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X.; Ren, L.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, L.; Che, Q.; et al. Screening of ecological impact assessment indicators in urban water body restoration process itle. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.J.; Yu, F.D.; Tang, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Deng, B.L.; Liu, D.M.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.W. Site uniqueness contributions to fish β diversity in the Chishui River basin, Southwestern China. J. Fish. China 2023, 47, 128–142. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Q.; Guan, X.; Fu, B. Chishui River Health Assessment Based on Fish Biotic Integrity Index. Res. Environ. Sci. 2023, 36, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Zeng, H.; Xiong, F.; Yao, M.; He, S. Advances in environmental DNA monitoring: Standardization, automation, and emerging technologies in aquatic ecosystems. Sci. China Life Sci. 2024, 67, 1368–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.; Farrell, E.; Reaume, A.M.; Eble, J.A.; Gaither, M.R. One size does not fit all: Tuning eDNA protocols for high- and low-turbidity water sampling. Environ. DNA 2022, 4, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickler, M.K.; Fremier, K.A.; Goldberg, S.C. Quantifying effects of UV-B, temperature, and pH on eDNA degradation in aquatic microcosms. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Eble, J.E.; Gaither, M.R. A practical guide to sample preservation and pre-PCR processing of aquatic environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Ludwig, A.; Peng, Z. Standards for Methods Utilizing Environmental DNA for Detection of Fish Species. Genes 2020, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champlot, S.; Berthelot, C.; Pruvost, M.; Bennett, E.A.; Grange, T.; Geigl, E.M. An efficient multistrategy DNA decontamination procedure of PCR reagents for hypersensitive PCR applications. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, X.; Huang, J.; Qi, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, Q.; Shen, Y. Fish Diversity and Spatial Patterns in the Upper Yangtze River National Nature Reserve for Rare and Endemic Fish Based on Environmental DNA (eDNA) Technology. Fishes 2025, 10, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110595
Dong X, Huang J, Qi Z, Wang Z, Zuo Q, Shen Y. Fish Diversity and Spatial Patterns in the Upper Yangtze River National Nature Reserve for Rare and Endemic Fish Based on Environmental DNA (eDNA) Technology. Fishes. 2025; 10(11):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110595
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Xiaohan, Jiaxin Huang, Zongqiang Qi, Ziwei Wang, Qing Zuo, and Yanjun Shen. 2025. "Fish Diversity and Spatial Patterns in the Upper Yangtze River National Nature Reserve for Rare and Endemic Fish Based on Environmental DNA (eDNA) Technology" Fishes 10, no. 11: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110595
APA StyleDong, X., Huang, J., Qi, Z., Wang, Z., Zuo, Q., & Shen, Y. (2025). Fish Diversity and Spatial Patterns in the Upper Yangtze River National Nature Reserve for Rare and Endemic Fish Based on Environmental DNA (eDNA) Technology. Fishes, 10(11), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110595






