Estimating Whale Shark, Rhincodon typus, Length Using Multi-Stereo-Image Measurement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen and Rearing Conditions
2.2. Stereo-Video Recording
2.3. Video Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Stereo-Video Image Calibration
3.2. Whale Shark Length Estimation
3.3. The Precision of Stereo-Image Measurements
3.4. The Accuracy of Stereo-Image Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meekan, M.G.; Virtue, P.; Marcus, L.; Clements, K.D.; Nichols, P.D.; Revill, A.T. The world’s largest omnivore is a fish. Ecology 2022, 103, e3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigmann, S. Annotated checklist of the living sharks, batoids and chimaeras (Chondrichthyes) of the world, with a focus on biogeographical diversity. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 837–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowat, D.; Brooks, K.S. A review of the biology, fisheries and conservation of the whale shark Rhincodon typus. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 1019–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, B.A.; Jonsen, I.D.; Jorgensen, S.J.; Winship, A.J.; Shaffer, S.A.; Bograd, S.J.; Hazen, E.L.; Foley, D.G.; Breed, G.A.; Harrison, A.-L.; et al. Tracking apex marine predator movements in a dynamic ocean. Nature 2011, 475, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequeira, A.M.M.; Mellin, C.; Fordham, D.A.; Meekan, M.G.; Bradshaw, C.J.A. Predicting current and future global distributions of whale sharks. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequeira, A.M.M.; Mellin, C.; Meekan, M.G.; Sims, D.W.; Bradshaw, C.J.A. Inferred global connectivity of whale shark Rhincodon typus populations. J. Fish Biol. 2013, 82, 367–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meekan, M.G.; Bradshaw, C.J.; Press, M.; McLean, C.; Richards, A.; Quasnichka, S.; Taylor, J.G. Population size and structure of whale sharks Rhincodon typus at Ningaloo Reef, Western Australia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 319, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, A.M.M.; Thums, M.; Brooks, K.; Meekan, M.G. Error and bias in size estimates of whale sharks: Implications for understanding demography. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 150668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speakman, J.R. Body size, energy metabolism and lifespan. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, J.K.; Myers, R.A.; Kehler, D.G.; Worm, B.; Harley, S.J.; Doherty, P.A. Collapse and Conservation of Shark Populations in the Northwest Atlantic. Science 2003, 299, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, J.A.; Myers, R.A.; García, V.B.; Lucifora, L.O.; Kuparinen, A. Life-history correlates of extinction risk and recovery potential. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Norman, B. A preliminary survey of whale shark Rhincodon typus catch and trade in China: An emerging crisis. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, M.J.; Harman, A.; Rees, R.G. Evidence of continued hunting of whale sharks Rhincodon typus in the Maldives. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2009, 86, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speed, C.W.; Meekan, M.G.; Rowat, D.; Pierce, S.J.; Marshall, A.D.; Bradshaw, C.J.A. Scarring patterns and relative mortality rates of Indian Ocean whale sharks. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 1488–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amandè, M.J.; Ariz, J.; Chassot, E.; de Molina, A.D.; Gaertner, D.; Murua, H.; Pianet, R.; Ruiz, J.; Chavance, P. Bycatch of the European purse seine tuna fishery in the Atlantic Ocean for the 2003–2007 period. Aquat. Living Resour. 2010, 23, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, S.J.; Norman, B. Rhincodon typus. In IUCN Red List Threatened Species; IUCN Biodiversity Assessment & Knowledge Team: Cambridge, UK, 2016; p. e.T19488A2365291. [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw, C.J.A.; Fitzpatrick, B.M.; Steinberg, C.C.; Brook, B.W.; Meekan, M.G. Decline in whale shark size and abundance at Ningaloo Reef over the past decade: The world’s largest fish is getting smaller. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, A.M.M.; Mellin, C.; Delean, S.; Meekan, M.G.; Bradshaw, C.J.A. Spatial and temporal predictions of inter-decadal trends in Indian Ocean whale sharks. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 478, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffreys, G.L.; Rowat, D.; Marshall, H.; Brooks, K. The development of robust morphometric indices from accurate and precise measurements of free-swimming whale sharks using laser photogrammetry. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2013, 93, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, J.; Norman, B.; Arzoumanian, Z. Estimating population size, structure, and residency time for whale sharks Rhincodon typus through collaborative photo-identification. Endanger. Species Res. 2009, 7, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, C.T.; Figueiredo, J.; Vaudo, J.J.; Hancock, J.; Rees, R.; Shivji, M. Comparing length-measurement methods and estimating growth parameters of free-swimming whale sharks (Rhincodon typus) near the South Ari Atoll, Maldives. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintner, S.P. Preliminary Study of Vertebral Growth Rings in the Whale Shark, Rhincodon typus, from the East Coast of South Africa. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2000, 59, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzoumanian, Z.; Holmberg, J.; Norman, B. An astronomical pattern-matching algorithm for computer-aided identification of whale sharks Rhincodon typus. J. Appl. Ecol. 2005, 42, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.T.; Roberts, C.M. Assessing the size, growth rate and structure of a seasonal population of whale sharks (Rhincodon typus Smith 1828) using conventional tagging and photo identification. Fish. Res. 2007, 84, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, B.M.; Stevens, J.D. Size and maturity status of the whale shark (Rhincodon typus) at Ningaloo Reef in Western Australia. Fish. Res. 2007, 84, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, E.; Fletcher, D.; Shortis, M.R.; Kendrick, G.A. A comparison of underwater visual distance estimates made by scuba divers and a stereo-video system: Implications for underwater visual census of reef fish abundance. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2004, 55, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacy, C.; Olsen, A.; Howey, L.; Chapman, D.; Brooks, E.; Bond, M. Affordable and accurate stereo-video system for measuring dimensions underwater: A case study using oceanic whitetip sharks Carcharhinus longimanus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 574, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, E.; Fletcher, D.; Shortis, M. Estimation of reef fish length by divers and by stereo-video: A first comparison of the accuracy and precision in the field on living fish under operational conditions. Fish. Res. 2002, 57, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torisawa, S.; Kadota, M.; Komeyama, K.; Suzuki, K.; Takagi, T. A digital stereo-video camera system for three-dimensional monitoring of free-swimming Pacific bluefin tuna, Thunnus orientalis, cultured in a net cage. Aquat. Living Resour. 2011, 24, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torisawa, S.; Komeyama, K.; Takagi, T. A Technique of Three-Dimensional Monitoring for Free-Swimming Pacific Bluefin Tuna 71hunnusOrientaliCsulturedin a Net Cage Using a Digital Stereo-Video Camera System. Fish. Eng. 2012, 49, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeya, K.; Torisawa, S.; Yamane, H.; Mitsunaga, Y. Estimating the total length of Mekong giant catfish, Pangasianodon gigas, in an aquarium via stereo-video shooting and direct linear transformation. Zoo Biol. 2022, 41, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, N.; Shortis, M.R.; Harvey, E.S. A comparison of calibration methods and system configurations of underwater stereo-video systems for applications in marine ecology. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2015, 13, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsunaga, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Suzuki, K.; Yamane, T. Convenient Analysis of Swimming Mechanism of Largemouth Bass Using Digital Video Cameras. Fish. Eng. 2005, 41, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, S.; Kang, I.J.; Moroishi, J.; Nakamura, A. The application of entropy for detecting behavioral responses in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) exposed to different toxicants. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 25, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, B.H.; Spence-Chorman, N.; Gahtan, E. Three-dimensional motion tracking reveals a diving component to visual and auditory escape swims in zebrafish larvae. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 3981–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Ikeda, R.; Yuta, Y.; Tsurukawa, K.; Nakamura, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Komeyama, K. Annual monitoring of growth of red sea bream by multi-stereo-image measurement. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]

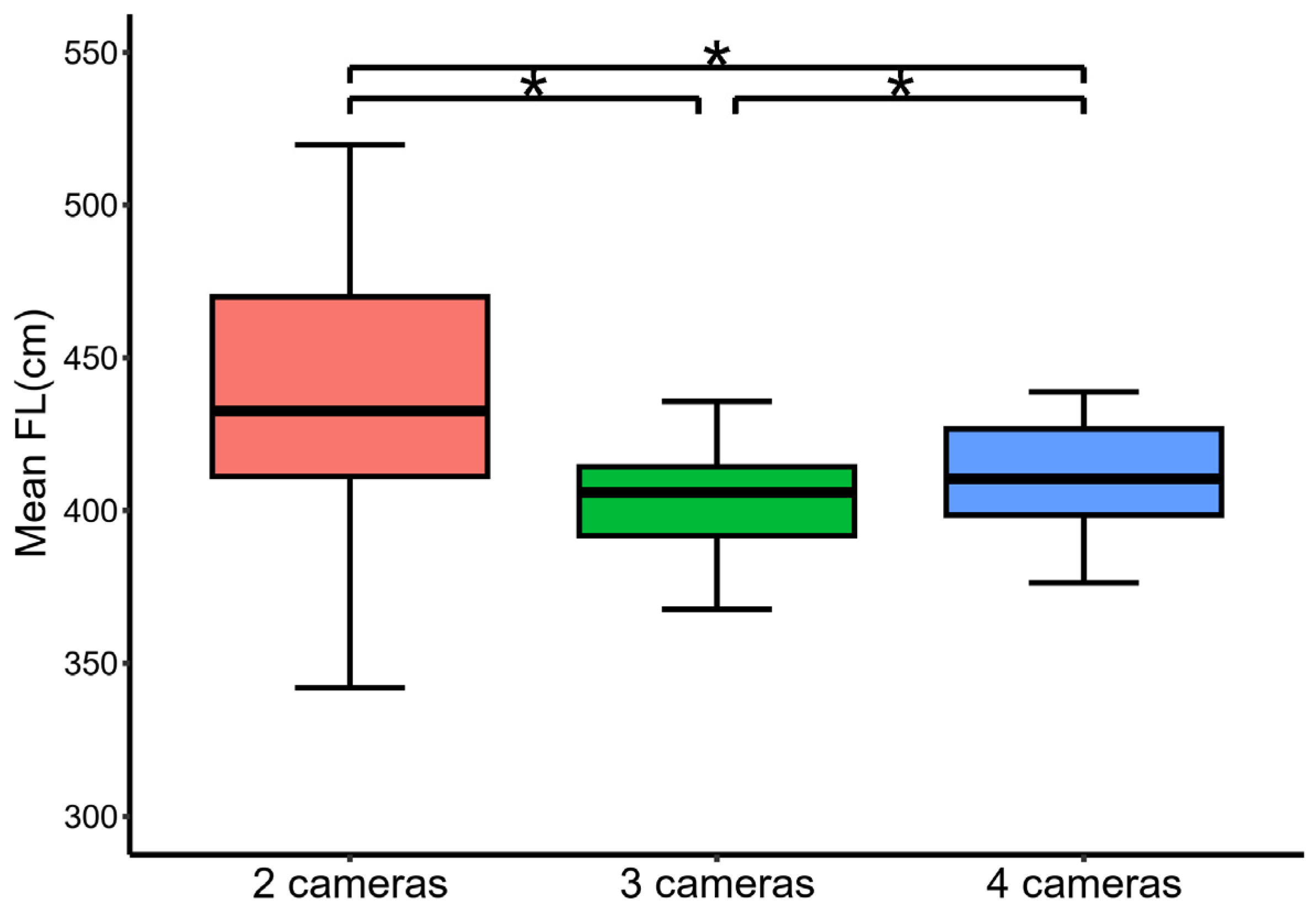
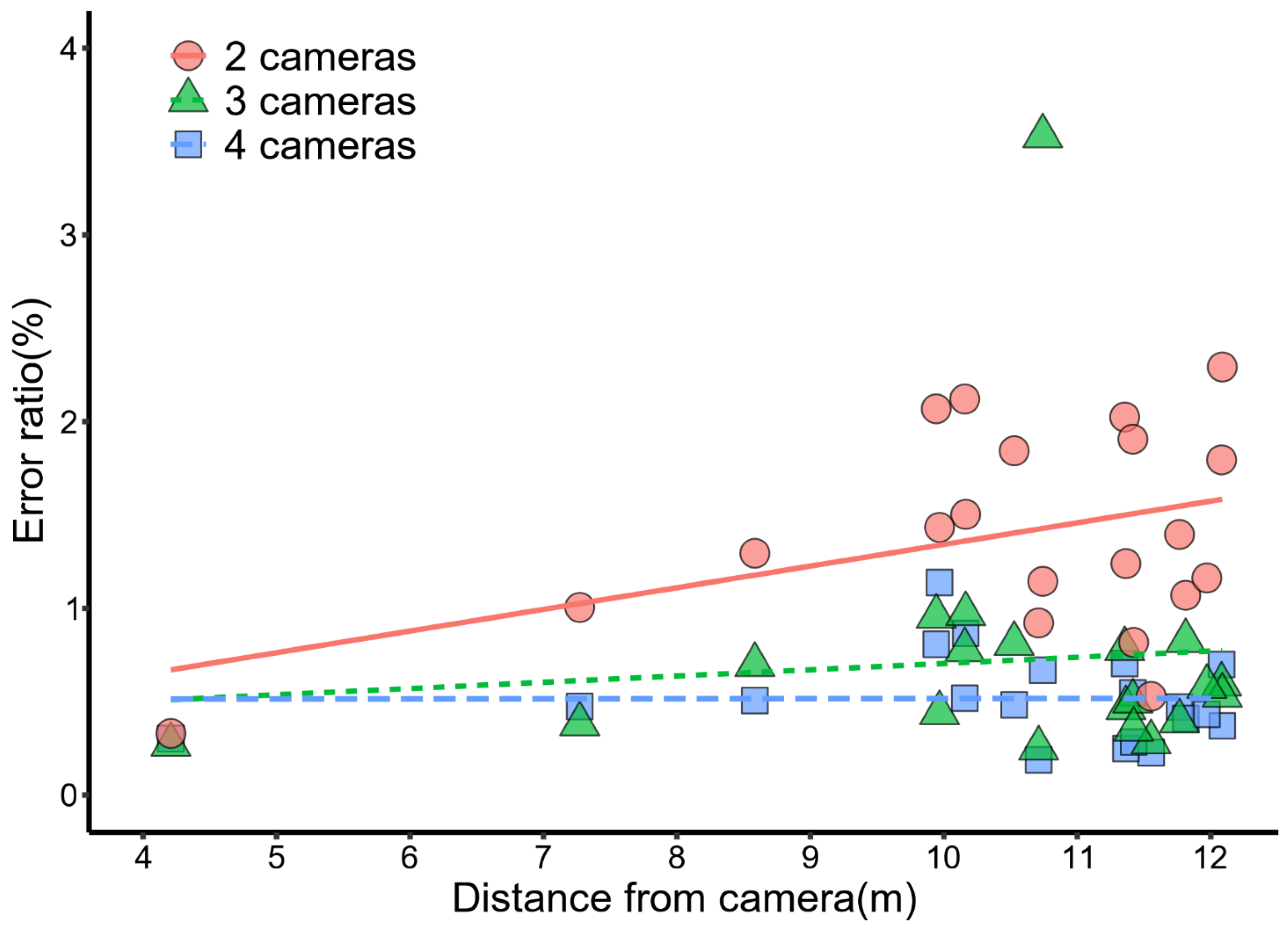
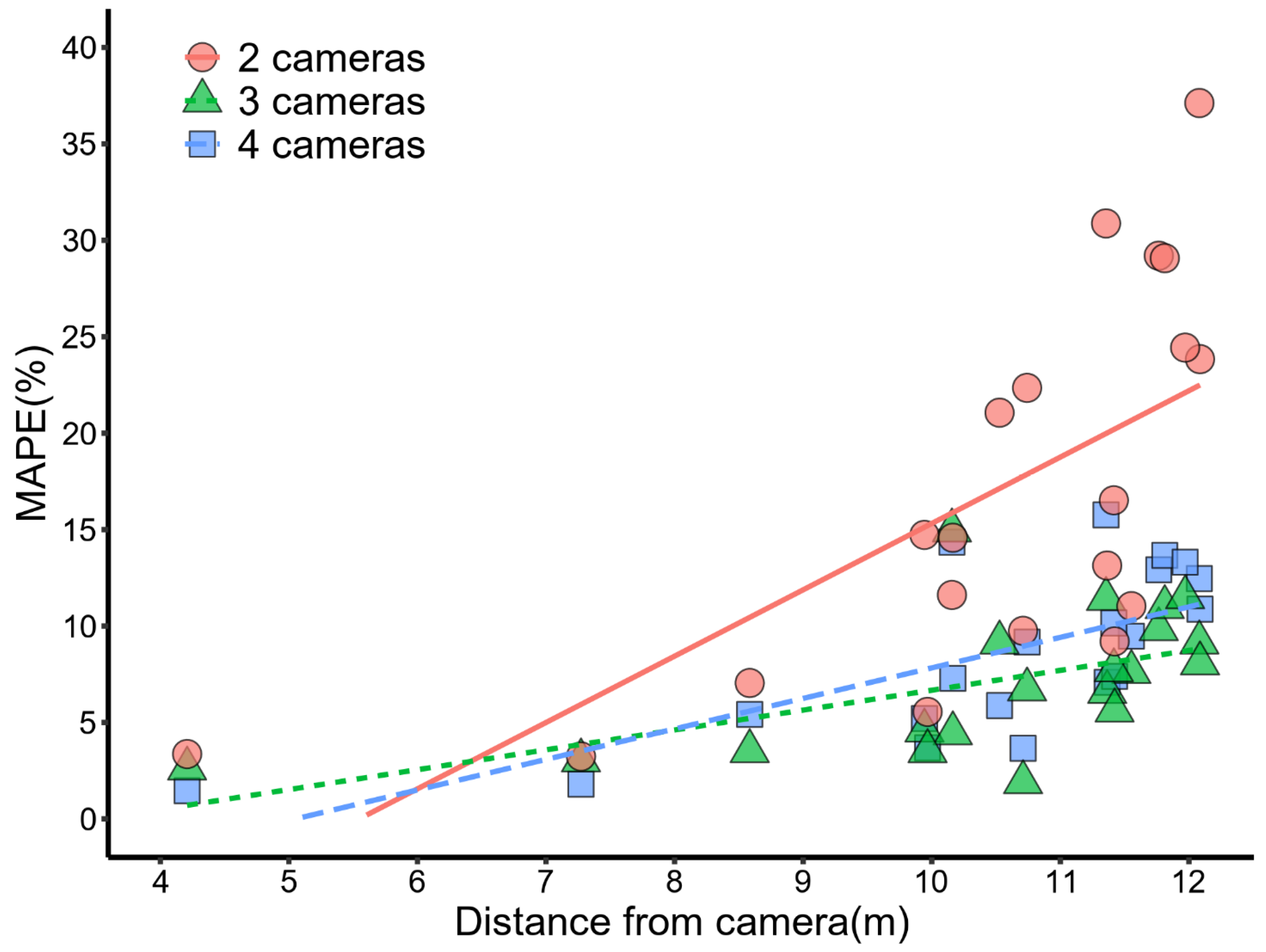
| Error Ratio | MAPE | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t Value | df | p Value | r | Regression Line | t Value | df | p Value | r | Regression Line | |
| 2 cameras | 1.900 | 18 | 0.076 | 0.410 | y = 0.12x + 0.18 | 3.8 | 18 | 0.0013 | 0.67 | y = 3.4x − 19 |
| 3 cameras | 0.390 | 18 | 0.700 | 0.092 | y = 0.034x + 0.37 | 2.8 | 18 | 0.0110 | 0.56 | y = 1.0x − 3.6 |
| 4 cameras | 0.017 | 18 | 0.990 | 0.004 | y = 0.00050x + 0.51 | 4.2 | 18 | 0.0006 | 0.70 | y = 1.6x − 8.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamamoto, H.; Sasaki, A.; Kanna, T.; Mitsunaga, Y.; Torisawa, S. Estimating Whale Shark, Rhincodon typus, Length Using Multi-Stereo-Image Measurement. Fishes 2025, 10, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10100513
Yamamoto H, Sasaki A, Kanna T, Mitsunaga Y, Torisawa S. Estimating Whale Shark, Rhincodon typus, Length Using Multi-Stereo-Image Measurement. Fishes. 2025; 10(10):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10100513
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamamoto, Hiroto, Akira Sasaki, Tomoki Kanna, Yasushi Mitsunaga, and Shinsuke Torisawa. 2025. "Estimating Whale Shark, Rhincodon typus, Length Using Multi-Stereo-Image Measurement" Fishes 10, no. 10: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10100513
APA StyleYamamoto, H., Sasaki, A., Kanna, T., Mitsunaga, Y., & Torisawa, S. (2025). Estimating Whale Shark, Rhincodon typus, Length Using Multi-Stereo-Image Measurement. Fishes, 10(10), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10100513






