Newborn Screening for Sickle Cell Disease: Indian Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geographic Distribution of HbS in India
3. Sickle Haplotypes in India
4. Clinical Manifestations of Sickle Cell Disease in India
5. Providing Comprehensive Care in Rural Regions
6. Benefits of Newborn Screening and Comprehensive Care
7. Newborn Screening Initiatives in India
8. Technologies Used for Newborn Screening in India
9. Follow up of Birth Cohorts of Sickle Cell Disease in India
10. Lessons Learnt from Pilot Studies on Newborn Screening for Sickle Cell Disease in India
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serjeant, G.R.; Serjeant, B.E. (Eds.) Sickle Cell Disease; Oxford Medical Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Urade, B.P. Incidence of sickle cell anemia and thalassemia in Central India. Open J. Blood Dis. 2012, 2, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colah, R.; Mukherjee, M.; Ghosh, K. Sickle cell disease in India. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2014, 21, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colah, R.B.; Mukherjee, M.B.; Martin, S.; Ghosh, K. Sickle cell disease in tribal populations in India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2015, 141, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jain, D.; Warthe, V.; Dayama, P.; Sarate, D.; Colah, R.; Mehta, P.; Serjeant, G. Sickle Cell Disease in Central India: A Potentially Severe Syndrome. Indian J. Pediatr. 2016, 83, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagnier, J.; Mears, J.G.; Dunda-Belkhodja, O.; Schaefer-Rego, K.E.; Beldjord, C.; Nagel, R.L.; Labie, D. Evidence for the multicentric origin of the sickle cell hemoglobin gene in Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 1771–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, M.B.; Surve, R.R.; Gangakhedkar, R.R.; Ghosh, K.; Colah, R.B.; Mohanty, D. β-globin gene cluster haplotypes linked to the βS gene in western India. Hemoglobin 2004, 28, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, B.C.; Satapathy, R.K.; Kulozik, A.E.; Kulozik, M.; Sirr, S.; Serjeant, B.E.; Serjeant, G.R. Sickle cell disease in Orissa State, India. Lancet 1986, 2, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M.B.; Lu, C.Y.; Ducrocq, R.; Gangakhedkar, R.R.; Colah, R.B.; Kadam, M.D.; Mohanty, D.; Nagel, R.L.; Krishnamoorthy, R. The effect of alpha thalassemia on sickle cell anemia linked to the Arab-Indian haplotype among a tribal and non-tribal population in India. Am. J. Hematol. 1997, 55, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Italia, K.; Sarathi, V.; Ghosh, K.; Colah, R. Sickle cell anemia from central India: A retrospective analysis. Indian Pediatr. 2012, 49, 911–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Italia, K.; Kangne, H.; Shanmukaiah, C.; Nadkarni, A.H.; Ghosh, K.; Colah, R.B. Variable phenotypes of sickle cell disease in India with the Arab-Indian haplotype. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 168, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Patel, B.; Gamit, M.; Serjeant, G.R. Screening for the sickle cell gene in Gujarat, India; a village based model. J. Community Genet. 2013, 4, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimgaonkar, V.; Krishnamurti, L.; Prabhakar, H.; Menon, N. Comprehensive integrated care of patients with sickle cell disease in a remote aboriginal tribal population in southern India. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, G.; Dave, K.P.; Bannerjee, S.; Barbaria, P.; Gupta, R. Initial outcomes of a comprehensive care model for sickle cell disease among a tribal population in rural western India. Int. J. Community Med. Public Health 2016, 3, 1282–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, M.H.; Verter, J.I.; Woods, G.; Pegelow, C.; Kelleher, J.; Presbury, G.; Zarkowsky, H.; Vichinsky, E.; Iyer, R.; Lobel, J.S.; et al. Prophylaxis with oral penicillin in children with sickle cell anemia: A randomized trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 314, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamkiewicz, T.V.; Sarnaik, S.; Buchanan, G.R.; Iyer, R.V.; Miller, S.T.; Pegelow, C.H.; Rogers, Z.R.; Vichinsky, E.; Elliott, J.; Facklam, R.R.; et al. Invasive pneumococcal infections in children with sickle cell disease in the era of penicillin prophylaxis, antibiotic resistance, and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccination. J. Pediatr. 2003, 143, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piel, F.B.; Hay, S.I.; Gupta, S.; Weatherall, D.J.; Williams, T.N. Global burden of sickle cell anaemia in children under five, 2010–2050: Modelling based on demographics, excess mortality, and interventions. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Italia, Y.; Krishnamurti, L.; Mehta, V.; Raicha, B.; Italia, K.; Mehta, P.; Ghosh, K.; Colah, R. Feasibility of a Newborn Screening and Follow-up Programme for Sickle Cell Disease among South Gujarat (India) Tribal Populations. J. Med. Screen. 2015, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhye, D.S.; Jain, D.L.; Trivedi, Y.L.; Nadkarni, A.H.; Ghosh, K.; Colah, R.B. Neonatal screening and the clinical outcome in children with sickle cell disease in central India. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, S.; Patra, P.K.; Khodiar, P.K. Neonatal screening of sickle cell anemia: A preliminary report. Indian J. Pediatr. 2012, 79, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, D.; Das, K.; Mishra, K. Newborn screening for sickle cell disease and congenital hypothyroidism in western Orissa. In Proceedings of the 4th International Congress on Sickle Cell Disease, Raipur, India, 22–27 November 2010; pp. 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, S.; Sahu, P.; Kar, S.K.; Negi, S. Identification of the hot spot areas for sickle cell disease using cord blood screening at a district hospital: An Indian perspective. J. Community Genet. 2015, 6, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhye, D.; Das, R.; Ray, J.; Acharjee, S.; Ghosh, K.; Colah, R.; Mukherjee, M. Newborn screening for hemoglobinopathies and red cell enzymopathies in Tripura state: A malaria endemic state in Northeast India. Hemoglobin 2018, 42, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consensus Development Summaries. Newborn Screening for Sickle Cell Disease and Other Hemoglobinophathies; Connecticut Medicine; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1987; Volume 51, pp. 459–463. [Google Scholar]
- Michlitsch, J.; Azimi, M.; Hoppe, C.; Walters, M.C.; Lubin, B.; Lorey, F.; Vichinsky, E. Newborn screening for hemoglobinopathies in California. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2009, 52, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhye, D.S.; Jain, D.; Nair, S.B.; Nadkarni, A.H.; Ghosh, K.; Colah, R.B. First case of Hb Fontainebleau with sickle haemoglobin and other non-deletional α gene variants identified in neonates during newborn screening for sickle cell disorders. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 65, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piety, N.Z.; George, A.; Serrano, A.; Lanzi, M.R.; Patel, P.R.; Note, M.P.; Kahan, S.; Nirenburg, D.; Camanda, J.F.; Airewale, G.; et al. A paper based test for screening newborns for sickle cell disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, C.T.; Paniagua, M.C.; DiNello, R.K.; Panchal, A.; Geisberg, M. A rapid inexpensive and disposable point-of-care blood test for sickle cell disease using novel, highly specific monoclonal antibodies. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 175, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serjeant, G.R. Evolving locally appropriate models of care for Indian sickle cell disease. Indian J. Med. Res. 2016, 143, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Mission Guidelines on Hemoglobinopathies in India; Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2016.
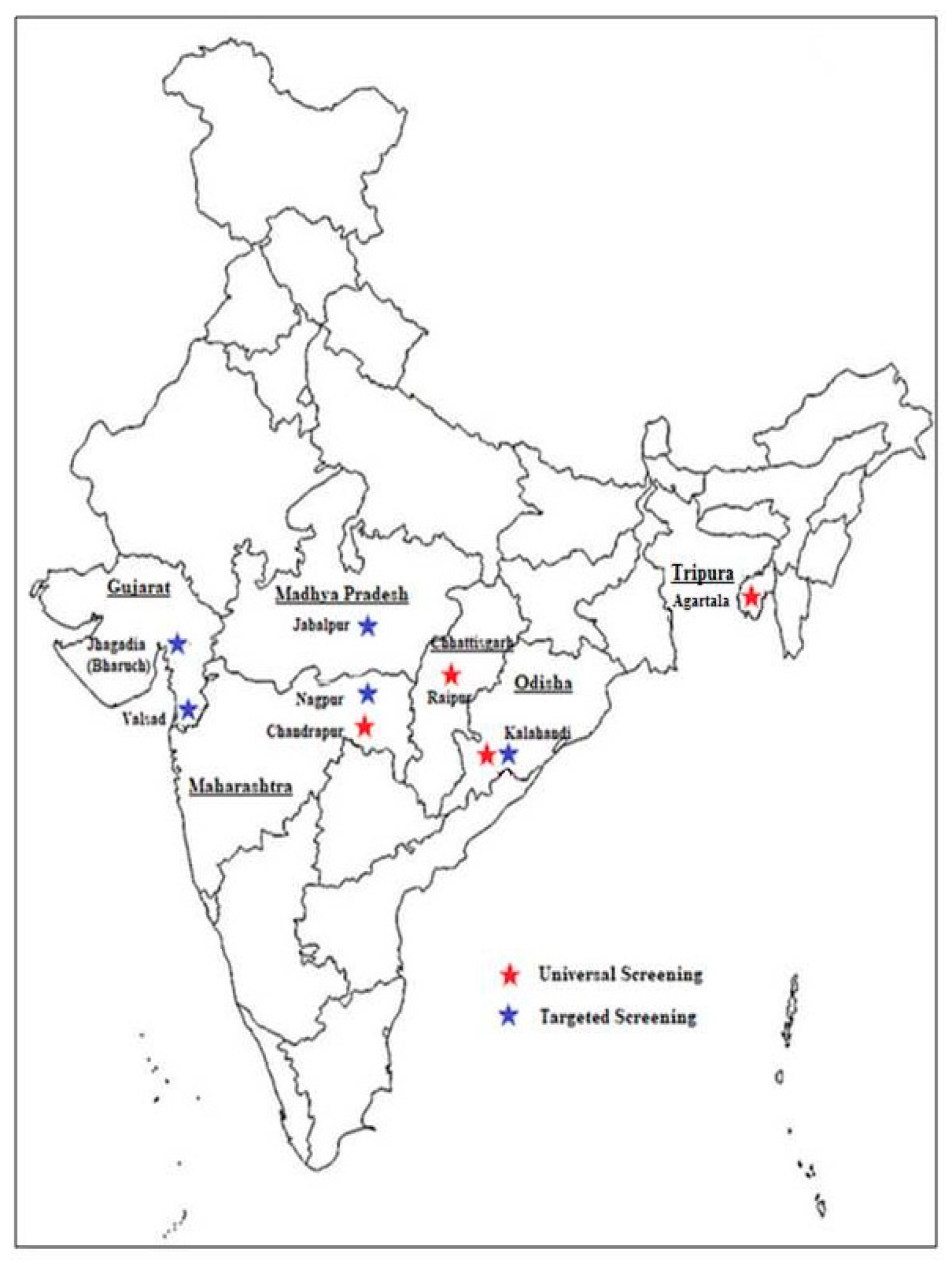
| State | District | Target Population | Sample | Technology for Screening | No. Screened | No(%)AS | No(%)SCD | Follow Up | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Gujarat Phase 1 | Valsad | All Tribal babies | Heel prick-Dried blood spot | HPLC-Variant NBS machine | 5467 | 687 (12.5%) | 46 (0.8%) | 5–6 years | Italia et al., 2015 [18] |
| South Gujarat Phase 2 | Valsad, Bharuch | All Tribal babies | Heel prick-Dried blood spot | HPLC-Variant NBS machine | 2944 | 649 (22.0%) | 76 (2.6%) | 2 years | Unpublished |
| Maharashtra | Nagpur | Largely non-tribal, babies of AS mothers | Cord blood, heel prick | HPLC-Variant Hb Testing System | 2134 | 978 (45.8%) | 113 (5.3%) | 4-5 years | Upadhye et al., 2016 [19] |
| Madhya Pradesh | Jabalpur | Tribal, babies of AS mothers | Cord blood, heel prick | HPLC-Variant Hb Testing System | 461 | 36 (7.8%) | 6 (1.3%) | 1 year | Unpublished |
| Chhattisgarh | Raipur | Tribal and non-tribal babies | Heel prick-Dried blood spot | HPLC-Variant NBS machine | 1158 | 61 (5.3%) | 6 (0.5%) | No follow up reported | Panigrahi et al., 2012 [20] |
| Odisha | Kalahandi | Tribal and non-tribal babies | Heel prick-Dried blood spot | HPLC-Variant Hb Testing System | 1668 | 293 (17.6%) | 34 (2.0%) | No follow up reported | Mohanty et al., 2010 [21] |
| Odisha | Kalahandi | Tribal babies | Cord blood | HPLC-Variant Hb Testing System | 761 | 112 (14.7%) | 13 (1.7%) | No follow up reported | Dixit et al., 2015 [22] |
| Tripura | Agartala | Tribal & non tribal babies | Cord blood | HPLC-Variant Hb Testing System | 2400 | 15 (0.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | Not done | Upadhye et al., 2018 [23] |
| Maharashtra | Chandrapur | Tribal and non-tribal babies | Cord blood, heel prick | HPLC-Variant Hb Testing System | 1010 | 85 (8.4%) | 4 (0.4%) | Not done | Unpublished |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colah, R.B.; Mehta, P.; Mukherjee, M.B. Newborn Screening for Sickle Cell Disease: Indian Experience. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2018, 4, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns4040031
Colah RB, Mehta P, Mukherjee MB. Newborn Screening for Sickle Cell Disease: Indian Experience. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2018; 4(4):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns4040031
Chicago/Turabian StyleColah, Roshan B., Pallavi Mehta, and Malay B. Mukherjee. 2018. "Newborn Screening for Sickle Cell Disease: Indian Experience" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 4, no. 4: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns4040031
APA StyleColah, R. B., Mehta, P., & Mukherjee, M. B. (2018). Newborn Screening for Sickle Cell Disease: Indian Experience. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 4(4), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns4040031





