A Five-Year Review of Newborn Screening for Spinal Muscular Atrophy in the State of Utah: Lessons Learned
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
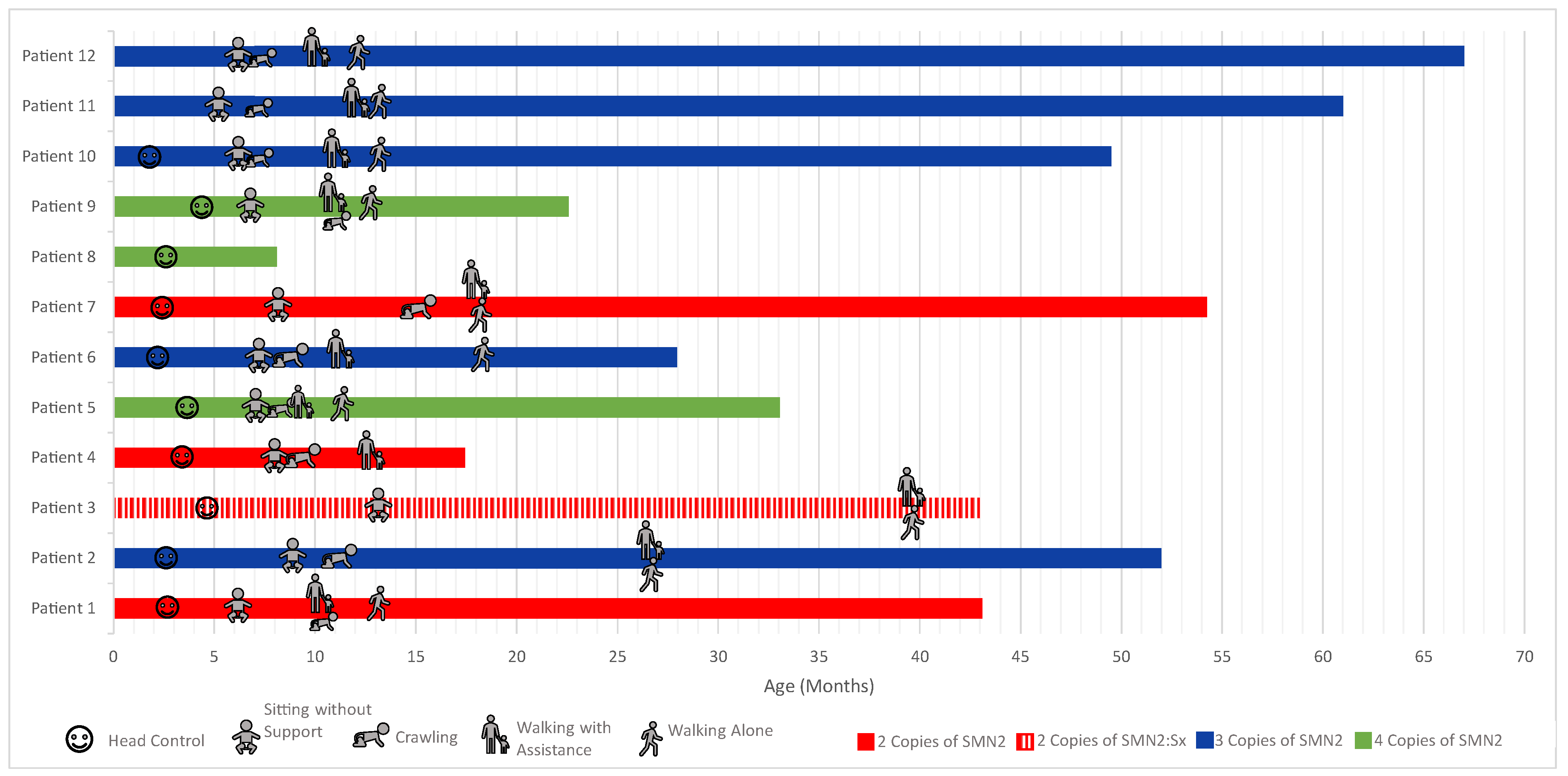
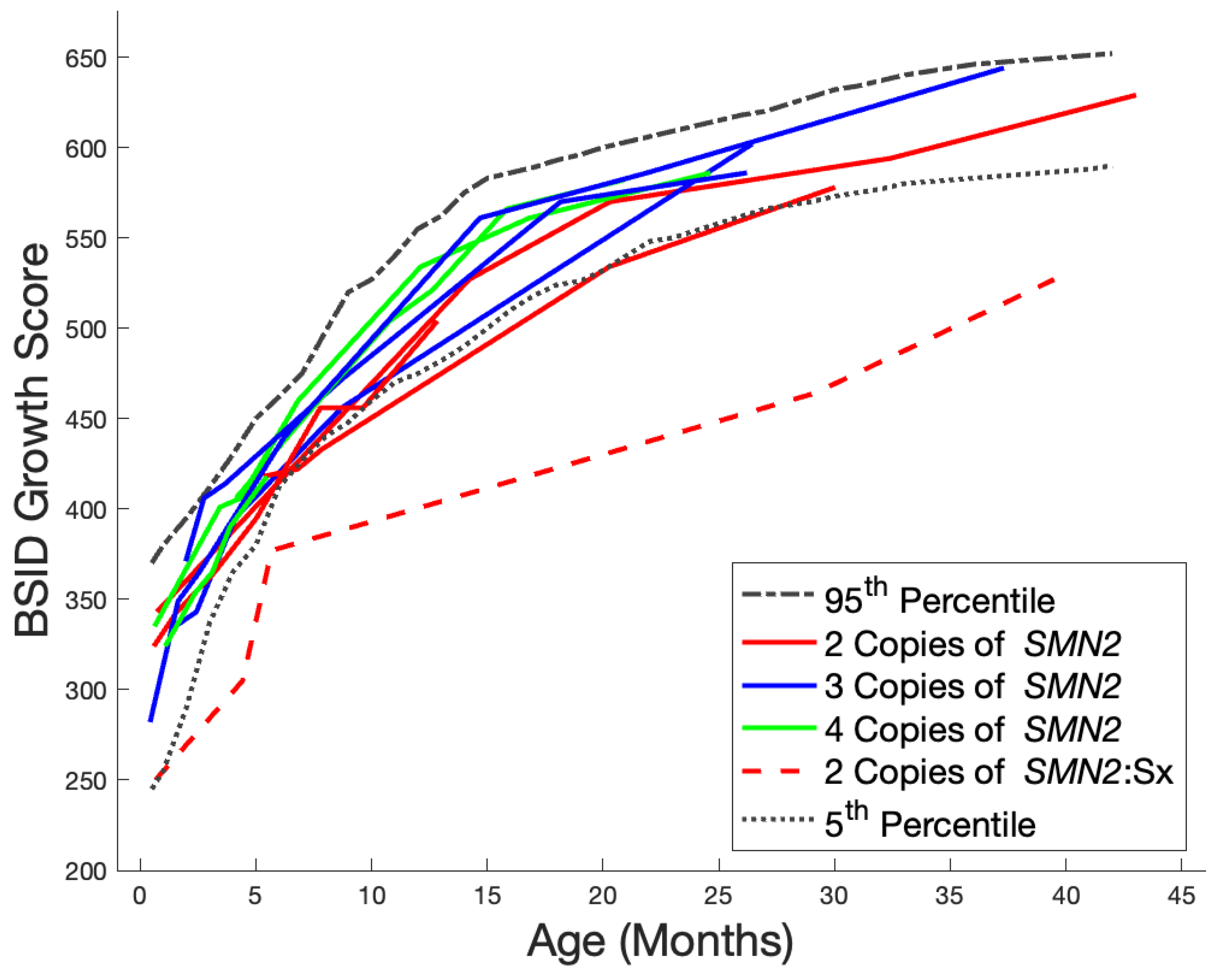
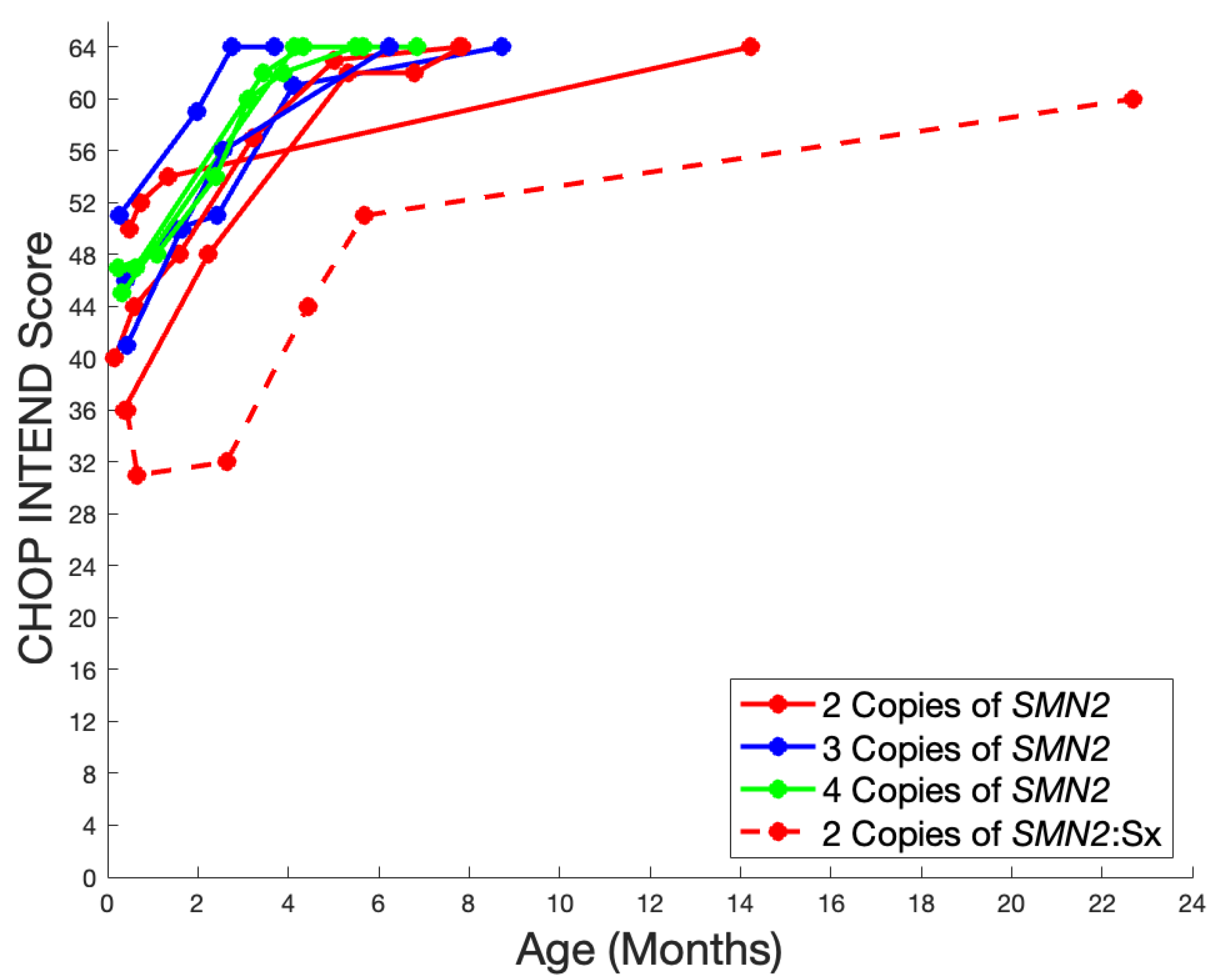
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prior, T.W.; Leach, M.E.; Finanger, E. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. [2000 February 24 Updated 2020 December 3]. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1352/ (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Nicolau, S.; Waldrop, M.A.; Connolly, A.M.; Mendell, J.R. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. In Seminars in Pediatric Neurology; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; Volume 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nance, J.R. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Continuum Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2020, 26, 1348–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calucho, M.; Bernal, S.; Alías, L.; March, F.; Venceslá, A.; Rodríguez-Álvarez, F.J.; Aller, E.; Fernández, R.M.; Borrego, S.; Millán, J.M.; et al. Correlation between SMA type and SMN2 copy number revisited: An analysis of 625 unrelated Spanish patients and a compilation of 2834 reported cases. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2018, 28, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaart, I.E.; Robertson, A.; Wilson, I.J.; Aartsma-Rus, A.; Cameron, S.; Jones, C.C.; Cook, S.F.; Lochmüller, H. Prevalence, incidence and carrier frequency of 5q-linked spinal muscular atrophy—A literature review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, K.A.; Farrar, M.A.; Muntoni, F.; Saito, K.; Mendell, J.R.; Servais, L.; McMillan, H.J.; Finkel, R.S.; Swoboda, K.J.; Kwon, J.M.; et al. Onasemnogene abeparvovec for presymptomatic infants with three copies of SMN2 at risk for spinal muscular atrophy: The Phase III SPR1NT trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, K.A.; Farrar, M.A.; Muntoni, F.; Saito, K.; Mendell, J.R.; Servais, L.; McMillan, H.J.; Finkel, R.S.; Swoboda, K.J.; Kwon, J.M.; et al. Onasemnogene abeparvovec for presymptomatic infants with two copies of SMN2 at risk for spinal muscular atrophy type 1: The Phase III SPR1NT trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darryl, C.; Bertini, E.; Swoboda, K.J.; Hwu, W.L.; Crawford, T.O.; Finkel, R.S.; Kirschner, J.; Kuntz, N.L.; Parsons, J.A.; Ryan, M.M.; et al. Nusinersen initiated in infants during the presymptomatic stage of spinal muscular atrophy: Interim efficacy and safety results from the Phase 2 NURTURE study. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2019, 29, 842–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, T.O.; Swoboda, K.J.; De Vivo, D.C.; Bertini, E.; Hwu, W.L.; Finkel, R.S.; Kirschner, J.; Kuntz, N.L.; Nazario, A.N.; Parsons, J.A.; et al. Continued benefit of nusinersen initiated in the presymptomatic stage of spinal muscular atrophy: 5-year update of the NURTURE study. Muscle Nerve 2023, 68, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendell, J.R.; Al-Zaidy, S.; Shell, R.; Arnold, W.D.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R.; Prior, T.W.; Lowes, L.; Alfano, L.; Berry, K.; Church, K.; et al. Single-Dose Gene-Replacement Therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiriboga, C.A.; Swoboda, K.J.; Darras, B.T.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Montes, J.; De Vivo, D.C.; Norris, D.A.; Bennett, C.F.; Bishop, K.M. Results from a phase 1 study of nusinersen (ISIS-SMN Rx) in children with spinal muscular atrophy. Neurology 2016, 86, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, F.; Gigure, Y.; Berthier, M.-T.; Gurette, D.; Girard, J.-G.; Dry, M. Newborn Screening by Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Impacts, Implications and Perspectives. In Tandem Mass Spectrometry—Applications and Principles; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.S.; Mann, M.Y.; Lloyd-Puryear, M.A.; Rinaldo, P.; Howell, R.R. Newborn screening: Toward a uniform screening panel and system. Genet. Med. 2006, 8 (Suppl. 1), 1S–252S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, B.H.; Deng, S.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Kay, D.M.; Irumudomon, O.; Laureta, E.; Delfiner, L.; Treidler, S.O.; Anziska, Y.; Sakonju, A.; et al. Newborn Screening for Spinal Muscular Atrophy in New York State: Clinical Outcomes From the First 3 Years. Neurology 2022, 99, E1527–E1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glascock, J.; Sampson, J.; Haidet-Phillips, A.; Connolly, A.; Darras, B.; Day, J.; Finkel, R.; Howell, R.R.; Klinger, K.; Kuntz, N.; et al. Treatment Algorithm for Infants Diagnosed with Spinal Muscular Atrophy through Newborn Screening. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2018, 5, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glascock, J.; Sampson, J.; Connolly, A.M.; Darras, B.T.; Day, J.W.; Finkel, R.; Howell, R.R.; Klinger, K.W.; Kuntz, N.; Prior, T.; et al. Revised Recommendations for the Treatment of Infants Diagnosed with Spinal Muscular Atrophy Via Newborn Screening Who Have 4 Copies of SMN2. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2020, 7, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CureSMA. 100% of States Now Screening Newborns for SMA. Available online: https://www.curesma.org/100-of-states-now-screening-newborns-for-sma/ (accessed on 28 January 2024).
- Glanzman, A.M.; Mazzone, E.; Main, M.; Pelliccioni, M.; Wood, J.; Swoboda, K.J.; Scott, C.; Pane, M.; Messina, S.; Bertini, E.; et al. The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Infant Test of Neuromuscular Disorders (CHOP INTEND): Test development and reliability. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2010, 20, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanzman, A.M.; McDermott, M.P.; Montes, J.; Martens, W.B.; Flickinger, J.; Riley, S.; Quigley, J.; Dunaway, S.; O’Hagen, J.; Deng, L.; et al. Validation of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Infant Test of Neuromuscular Disorders (CHOP INTEND). Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2011, 23, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayley, N. Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, 3rd ed.; (Bayley–III®); APA PsycTests: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman, E.A.; Nagan, N.; Zhu, H.; Akmaev, V.R.; Zhou, Z.; Rohlfs, E.M.; Flynn, K.; Hendrickson, B.C.; Scholl, T.; Sirko-Osadsa, D.A.; et al. Pan-ethnic carrier screening and prenatal diagnosis for spinal muscular atrophy: Clinical laboratory analysis of >72,400 specimens. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 20, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, S.; Biggio, J.R.; Saller, D.N.; Giardine, R. Committee Opinion Number 432. 2023. Available online: https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/committee-opinion/articles/2017/03/carrier-screening-for-genetic-conditions (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- Vill, K.; Schwartz, O.; Blaschek, A.; Gläser, D.; Nennstiel, U.; Wirth, B.; Burggraf, S.; Röschinger, W.; Becker, M.; Czibere, L.; et al. Newborn screening for spinal muscular atrophy in Germany: Clinical results after 2 years. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, O.; Kölbel, H.; Blaschek, A.; Gläser, D.; Burggraf, S.; Röschinger, W.; Schara, U.; Müller-Felber, W.; Vill, K. Spinal Muscular Atrophy—Is Newborn Screening Too Late for Children with Two SMN2 Copies? J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2022, 9, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, R.S.; Benatar, M. Pre-symptomatic spinal muscular atrophy: A proposed nosology. Brain 2022, 145, 2247–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, C.J.; Crawford, T.O. Two breakthrough gene-targeted treatments for spinal muscular atrophy: Challenges remain. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3219–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.A.; Trujillo-Priego, I.A.; Lane, C.J.; Finley, J.M.; Horak, F.B. Daily quantity of infant leg movement: Wearable sensor algorithm and relationship to walking onset. Sensors 2015, 15, 19006–19020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Vanderbilt, D.L.; Smith, B.A. Differences in spontaneous leg movement patterns between infants with typical development and infants at risk for developmental delay: Cross-sectional observation prior to sitting onset. J. Mot. Learn. Dev. 2018, 6, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrishami, M.S.; Nocera, L.; Mert, M.; Trujillo-Priego, I.A.; Purushotham, S.; Shahabi, C.; Smith, B.A. Identification of developmental delay in infants using wearable sensors: Full-day leg movement statistical feature analysis. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2019, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, M.; Dunn, L.; David, J.; Devine, C.; Smith, B.A. Daily Quantity and Kinematic Characteristics of Leg Movement in a Child with SMA (2 Copies SMN2). Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2023, 35, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Number of Screens | Number of Positive Screens |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 48,218 | 3 |
| 2019 | 46,832 | 3 |
| 2020 | 46,862 | 3 |
| 2021 | 47,503 | 3 |
| 2022 | 46,754 | 2 |
| To 27 January 2023 | 3675 | 0 |
| Total | 239,844 | 14 |
| SMN2 Copy # | # of Cases | Treatment | Median Time to Treatment from Initial Clinic Visit in Days (Range) | Median Age at Treatment in Days (Range) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palliative | NU + OA | OA | ||||
| 1 | 1 (8%) | 1 | - | - | ||
| 2 | 4 (31%) | 2 | 2 | 13.5 (7–16) | 19 (15–23) | |
| 3 | 5 (38%) | 5 | 39 (15–201) | 47 (23–210) | ||
| 4 | 3 (23%) | 3 | 89 (87–182) | 106 (96–187) | ||
| Patient SMN2 Copy Number | Anti-AAV9 Antibody Technical Result (Normal < 1:25) | Time to Normal Anti-AAV9 Antibody Result from Initial Abnormal (Months) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ≥1:200 | N/A |
| 2 | ≥1:200 | 4 |
| 2 | 1:50 | 3.3 |
| 4 | ≥1:200 | 2.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wong, K.N.; McIntyre, M.; Cook, S.; Hart, K.; Wilson, A.; Moldt, S.; Rohrwasser, A.; Butterfield, R.J. A Five-Year Review of Newborn Screening for Spinal Muscular Atrophy in the State of Utah: Lessons Learned. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2024, 10, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns10030054
Wong KN, McIntyre M, Cook S, Hart K, Wilson A, Moldt S, Rohrwasser A, Butterfield RJ. A Five-Year Review of Newborn Screening for Spinal Muscular Atrophy in the State of Utah: Lessons Learned. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2024; 10(3):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns10030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleWong, Kristen N., Melissa McIntyre, Sabina Cook, Kim Hart, Amelia Wilson, Sarah Moldt, Andreas Rohrwasser, and Russell J. Butterfield. 2024. "A Five-Year Review of Newborn Screening for Spinal Muscular Atrophy in the State of Utah: Lessons Learned" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 10, no. 3: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns10030054
APA StyleWong, K. N., McIntyre, M., Cook, S., Hart, K., Wilson, A., Moldt, S., Rohrwasser, A., & Butterfield, R. J. (2024). A Five-Year Review of Newborn Screening for Spinal Muscular Atrophy in the State of Utah: Lessons Learned. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 10(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns10030054







