Adaptive Gait Acquisition through Learning Dynamic Stimulus Instinct of Bipedal Robot
Abstract
1. Introduction
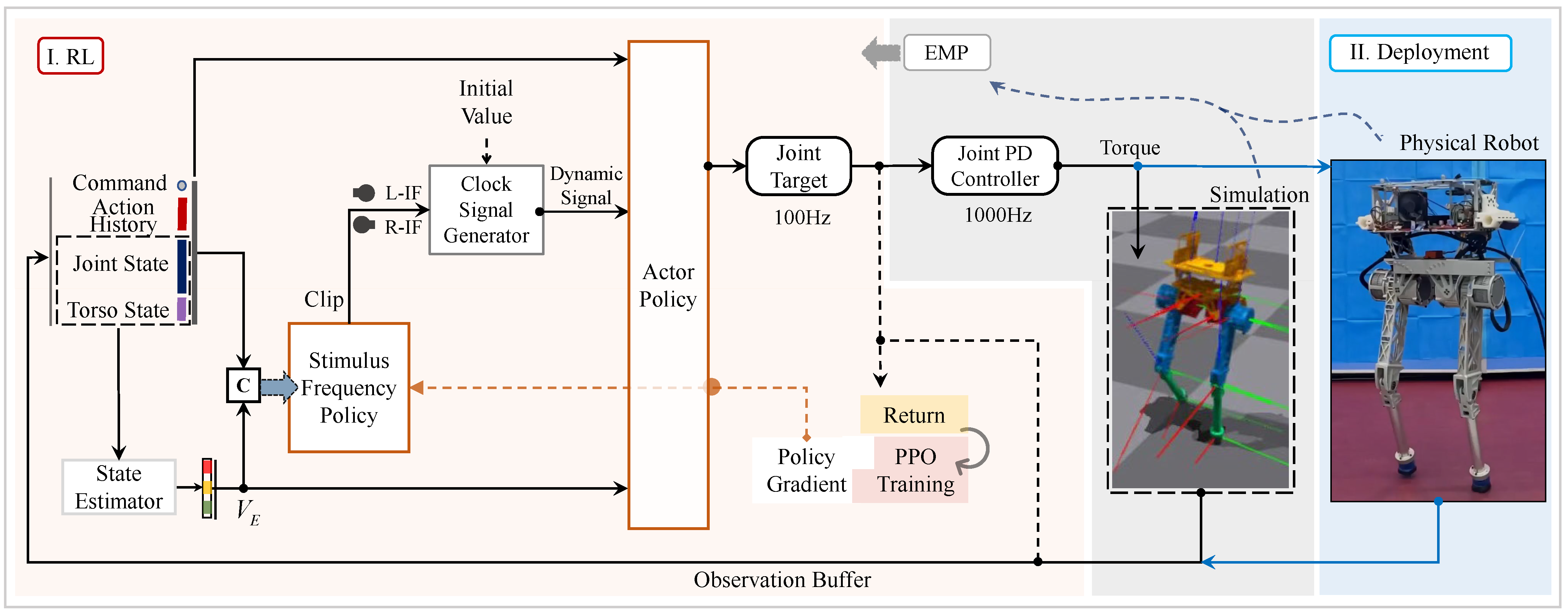
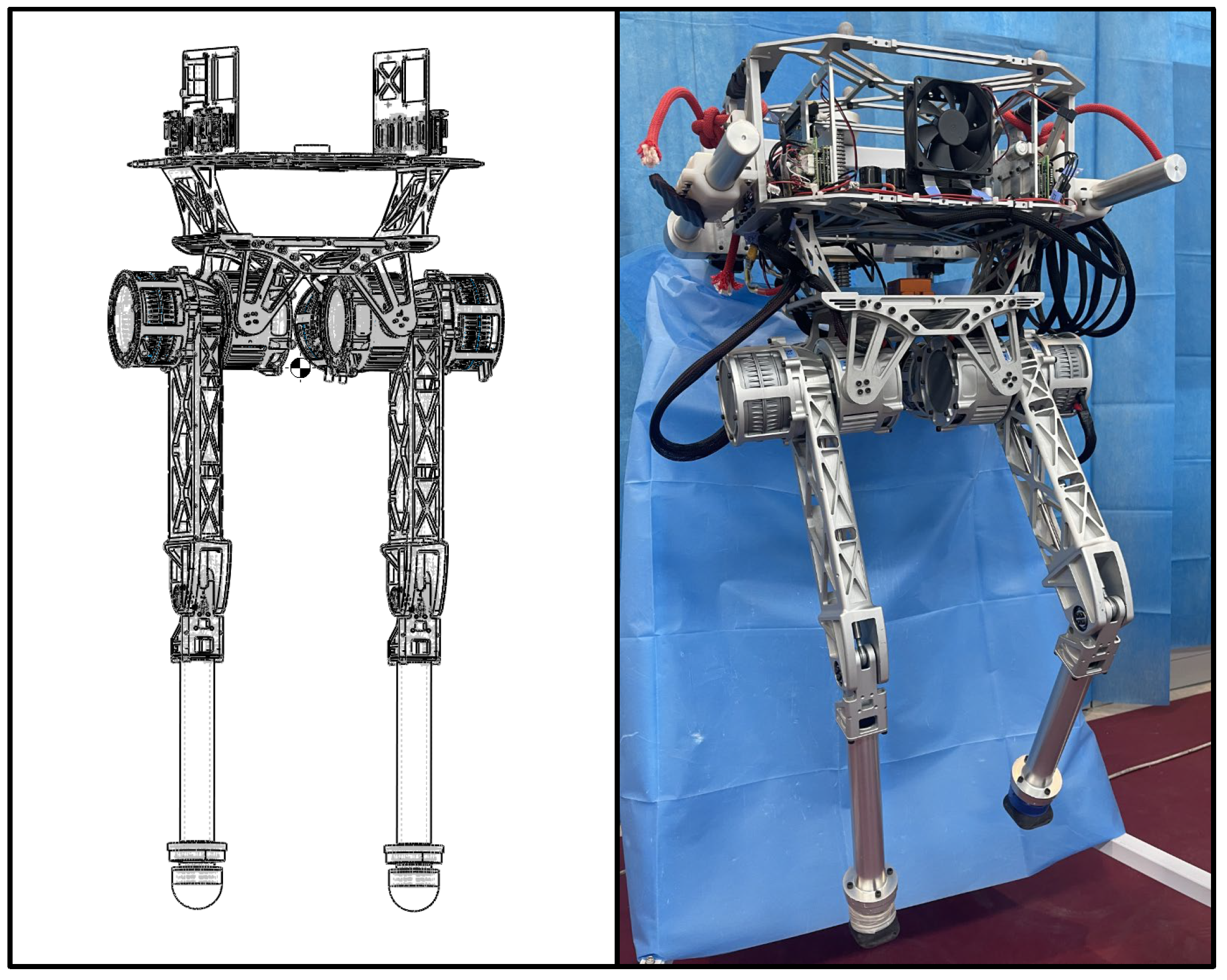
2. Reinforcement Learning Framework and Hardware Platform
2.1. Reinforcement Learning Formulation
2.2. Observation, Action, and Network Architecture
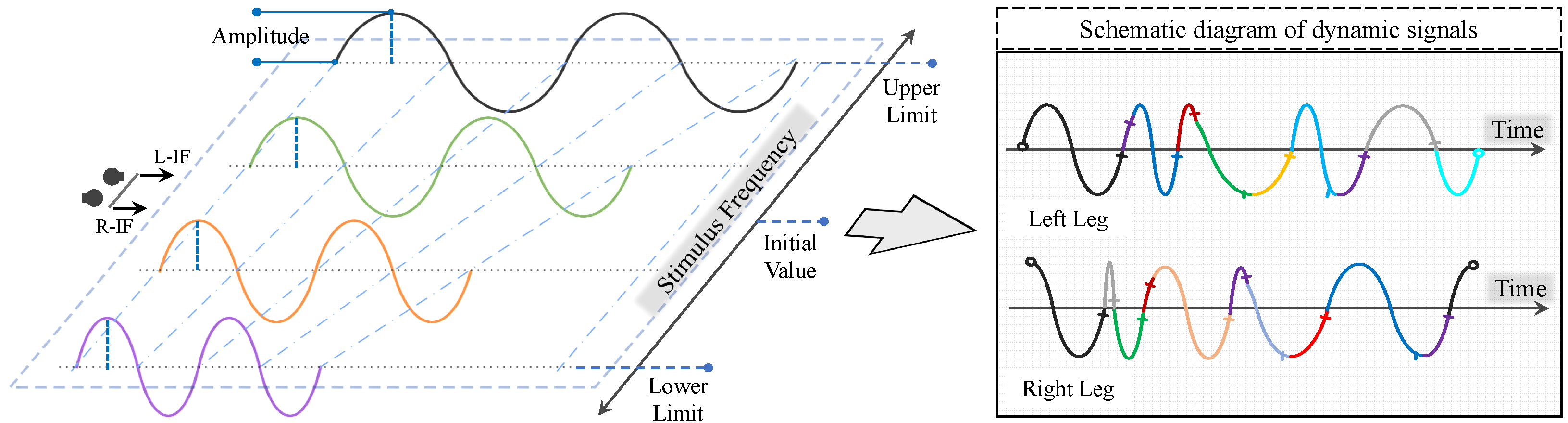
2.3. Clock Signal Generator
2.4. Rewards and Training Process
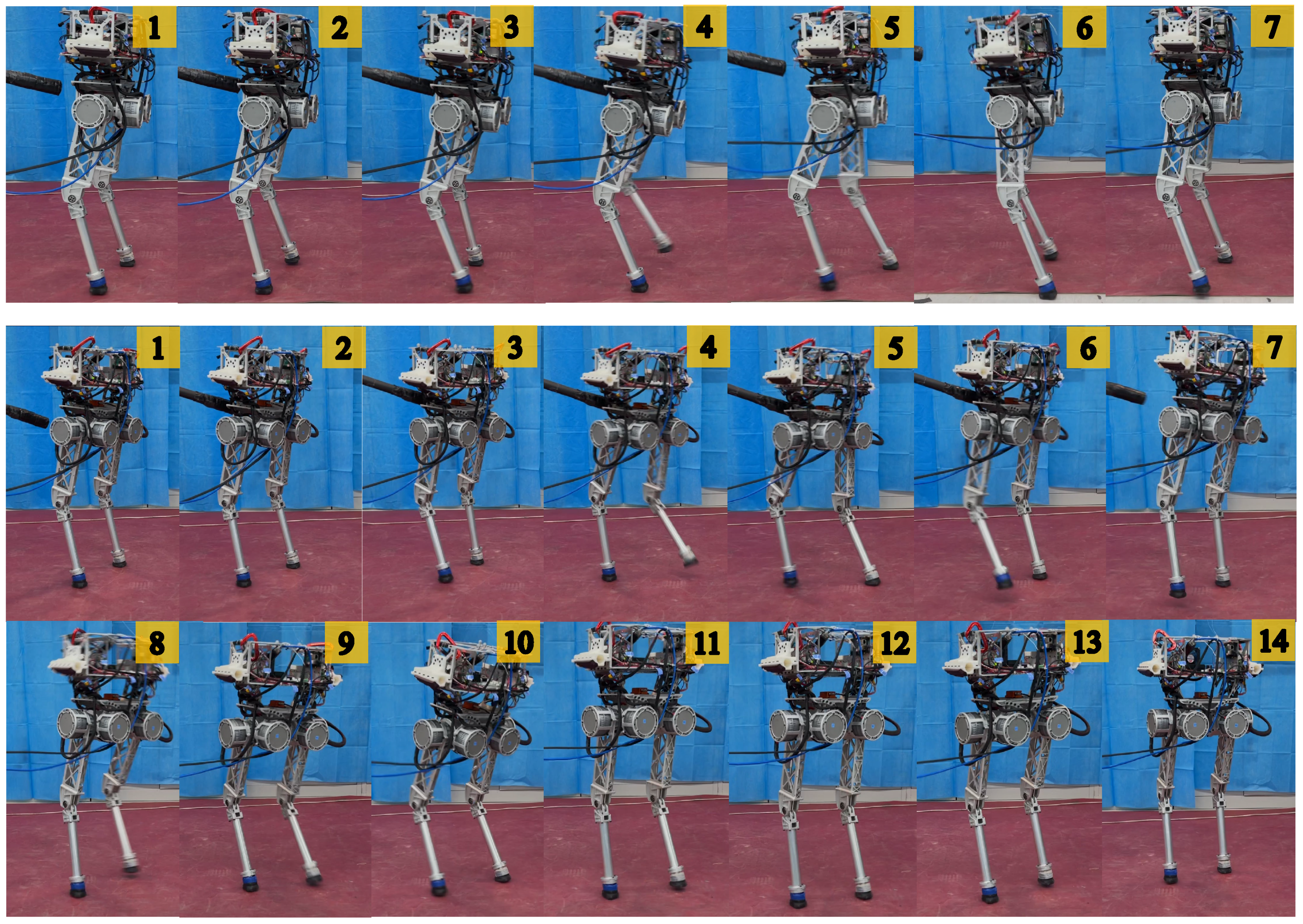
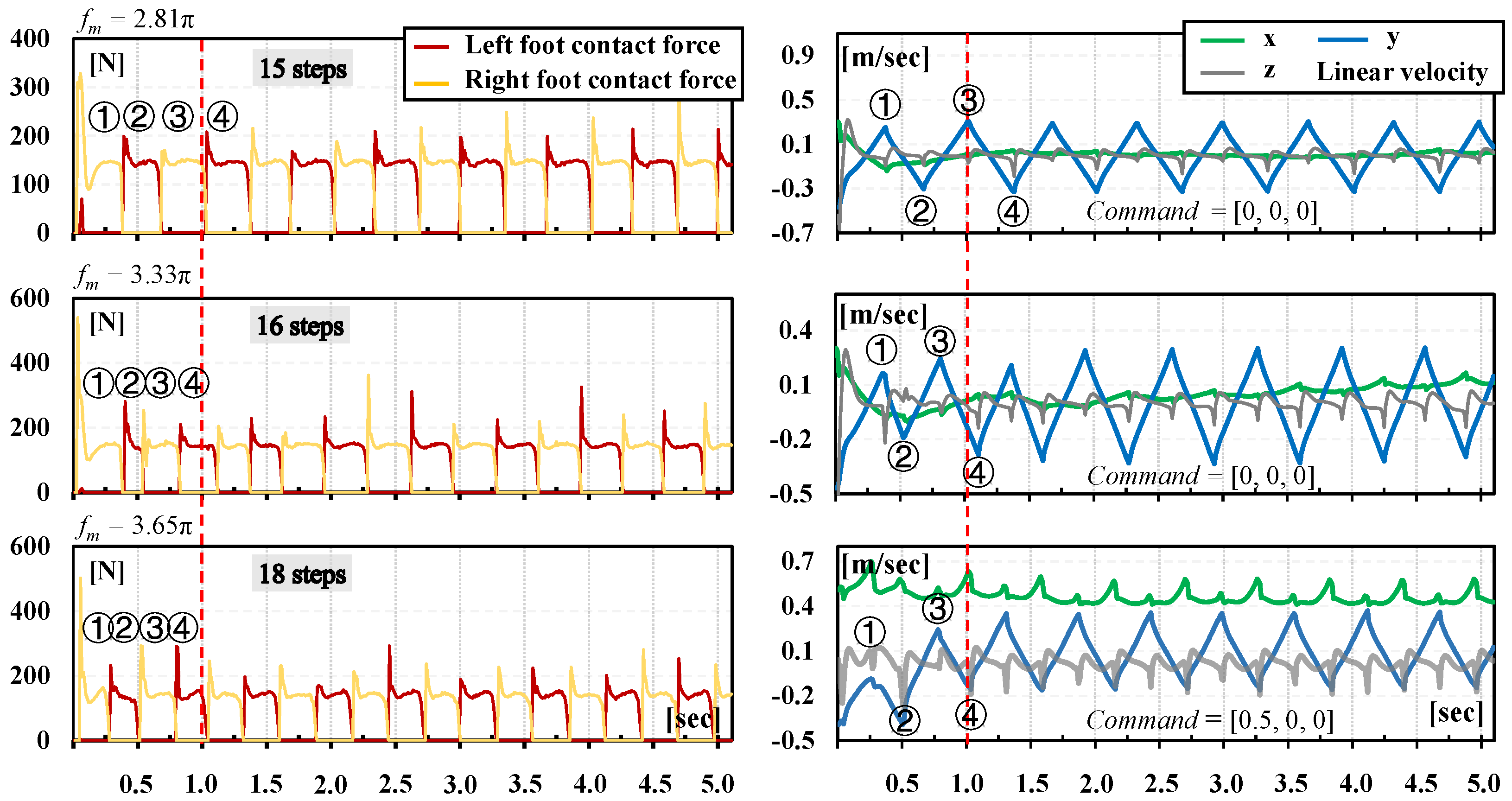
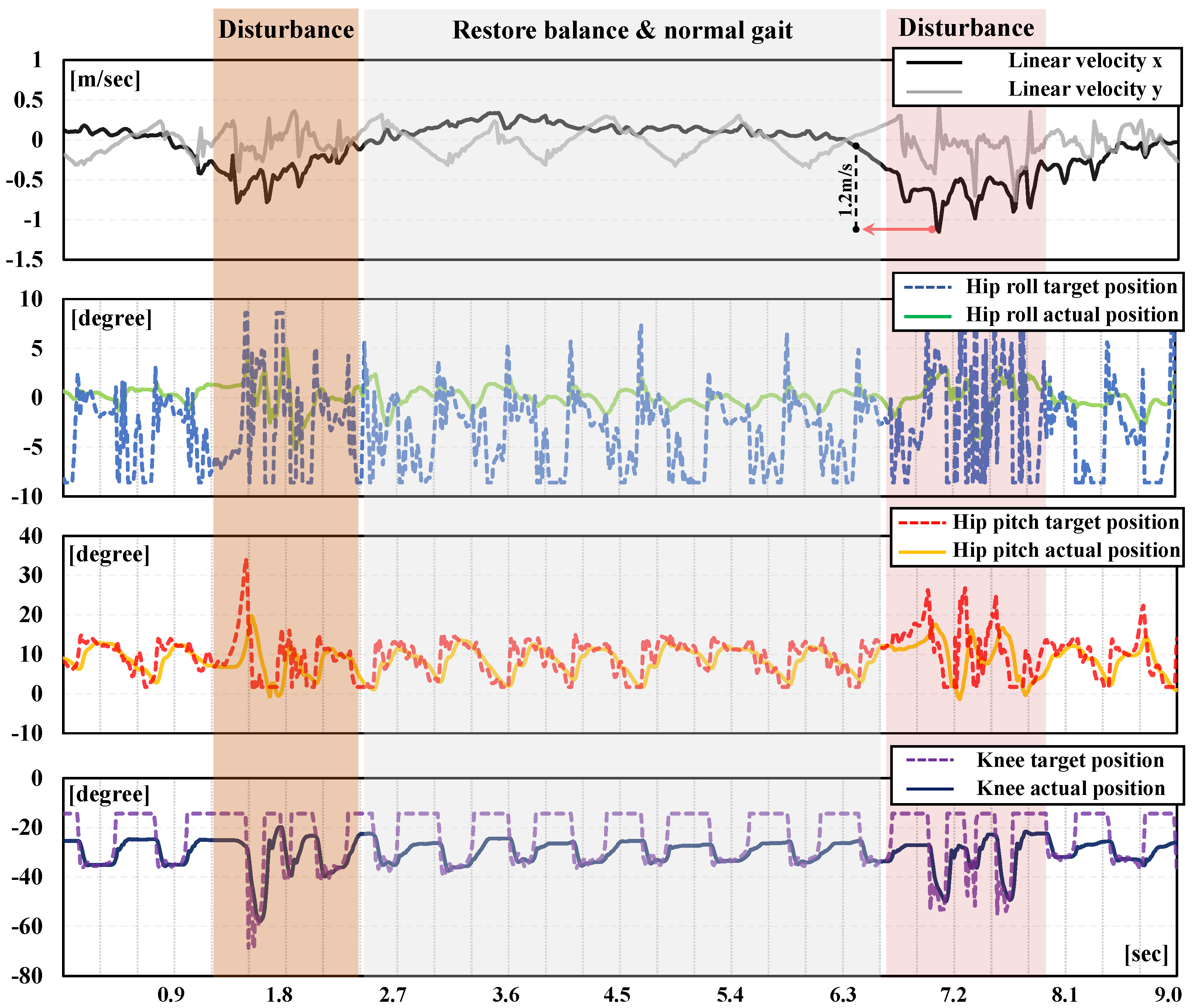
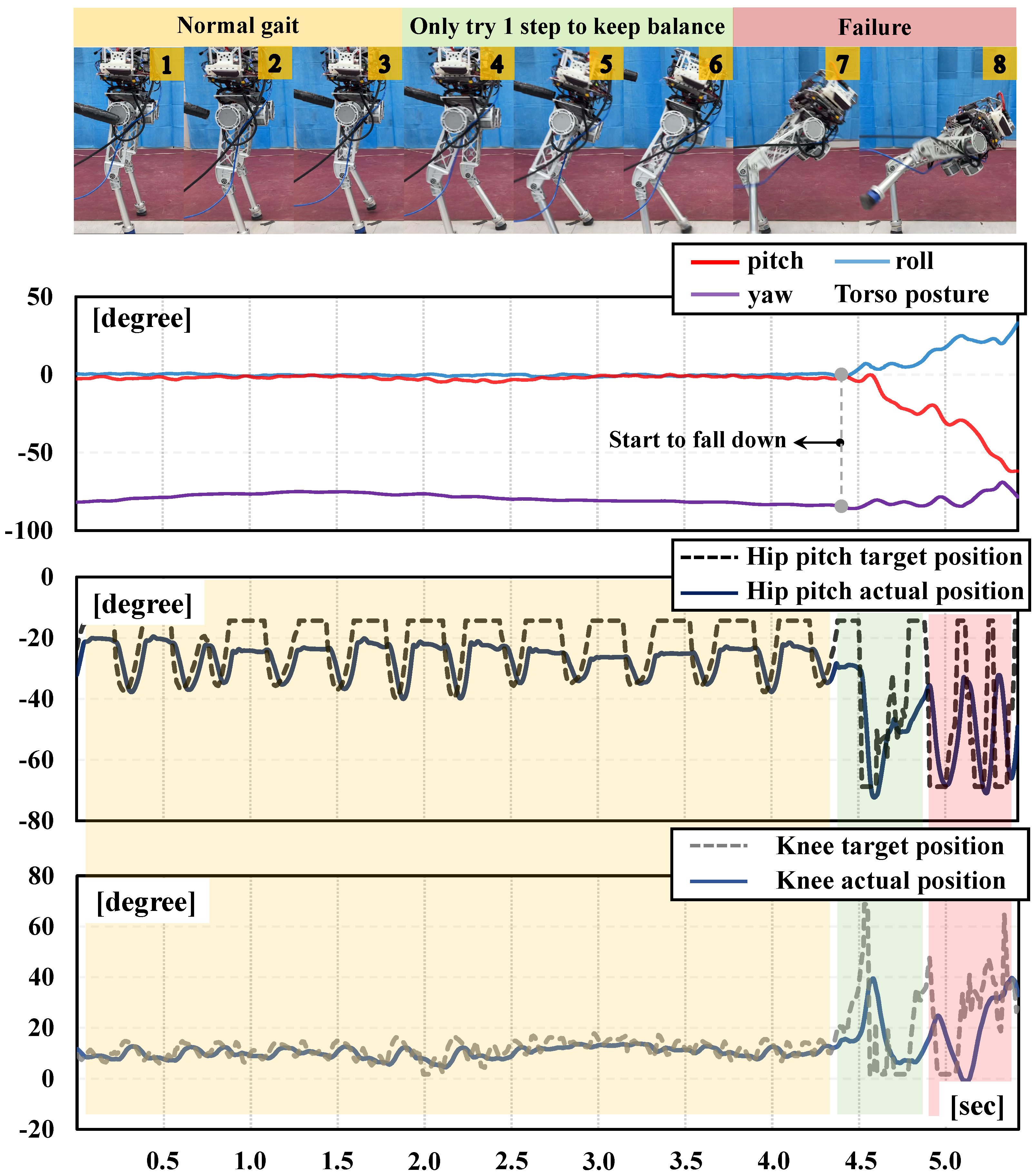
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| q | Joint position | Target joint position | |
| Joint acceleration | Joint torque | ||
| Angular velocity | Target angular velocity | ||
| Height | Target height | ||
| Linear velocity | Target linear velocity | ||
| Poses | Last linear velocity | ||
| Inductive frequency | Mean frequency of legs |
Appendix A
Definition
References
- Han, L.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Hashimoto, K.; Huang, Q. Trajectory-free dynamic locomotion using key trend states for biped robots with point feet. Inf. Sci. 2023, 66, 189201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Liu, H.; Meng, F.; Huang, Q. Swift Running Robot Leg: Mechanism Design and Motion-Guided Optimization. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemi, S. ASIMO and Humanoid Robot Research at Honda. In Humanoid Robotics: A Reference; Goswami, A., Vadakkepat, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1998, 9, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Hartley, R.; Da, X.; Hereid, A.; Harib, O.; Huang, J.K.; Grizzle, J. Feedback control of a cassie bipedal robot: Walking, standing, and riding a segway. In Proceedings of the 2019 American Control Conference (ACC), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 10–12 July 2019; pp. 4559–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, J.; Green, K.; Duan, H.; Fern, A.; Hurst, J. Sim-to-real learning for bipedal locomotion under unsensed dynamic loads. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 10449–10455. [Google Scholar]
- Batke, R.; Yu, F.; Dao, J.; Hurst, J.; Hatton, R.L.; Fern, A.; Green, K. Optimizing bipedal maneuvers of single rigid-body models for reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE-RAS 21st International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Ginowan, Japan, 28–30 November 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 714–721. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Malik, A.; Dao, J.; Saxena, A.; Green, K.; Siekmann, J.; Hurst, J. Sim-to-real learning of footstep-constrained bipedal dynamic walking. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 10428–10434. [Google Scholar]
- Siekmann, J.; Green, K.; Warila, J.; Fern, A.; Hurst, J. Blind bipedal stair traversal via sim-to-real reinforcement learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.08328. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Peng, X.B.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S.; Berseth, G.; Sreenath, K. Robust and versatile bipedal jumping control through multi-task reinforcement learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.09450. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Dao, J.; Green, K.; Apgar, T.; Fern, A.; Hurst, J. Learning task space actions for bipedal locomotion. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1276–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Siekmann, J.; Valluri, S.; Dao, J.; Bermillo, L.; Duan, H.; Fern, A.; Hurst, J. Learning memory-based control for human-scale bipedal locomotion. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.02402. [Google Scholar]
- Johannink, T.; Bahl, S.; Nair, A.; Luo, J.; Kumar, A.; Loskyll, M.; Ojea, J.A.; Solowjow, E.; Levine, S. Residual reinforcement learning for robot control. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 6023–6029. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Boehmer, W.; Whiteson, S. Deep residual reinforcement learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.01072. [Google Scholar]
- Alakuijala, M.; Dulac-Arnold, G.; Mairal, J.; Ponce, J.; Schmid, C. Residual reinforcement learning from demonstrations. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.08050. [Google Scholar]
- Csomay-Shanklin, N.; Tucker, M.; Dai, M.; Reher, J.; Ames, A.D. Learning controller gains on bipedal walking robots via user preferences. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 10405–10411. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, I.; Knepper, R.A.; Saxena, A. DeepMPC: Learning deep latent features for model predictive control. In Robotics: Science and Systems; 2015; Volume 10, p. 25. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:10130184 (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Peng, X.B.; Ma, Z.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S.; Kanazawa, A. Amp: Adversarial motion priors for stylized physics-based character control. ACM Trans. Graph. ToG 2021, 40, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollenweider, E.; Bjelonic, M.; Klemm, V.; Rudin, N.; Lee, J.; Hutter, M. Advanced skills through multiple adversarial motion priors in reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 5120–5126. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Cheng, X.; Peng, X.B.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S.; Berseth, G.; Sreenath, K. Reinforcement learning for robust parameterized locomotion control of bipedal robots. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 2811–2817. [Google Scholar]
- Siekmann, J.; Godse, Y.; Fern, A.; Hurst, J. Sim-to-real learning of all common bipedal gaits via periodic reward composition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 7309–7315. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Turk, G.; Liu, C.K. Learning symmetric and low-energy locomotion. ACM Trans. Graph. TOG 2018, 37, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloesch, M. State Estimation for Legged Robots-Kinematics, Inertial Sensing, and Computer Vision. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hwangbo, J.; Lee, J.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Bellicoso, D.; Tsounis, V.; Koltun, V.; Hutter, M. Learning agile and dynamic motor skills for legged robots. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaau5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Hwangbo, J.; Wellhausen, L.; Koltun, V.; Hutter, M. Learning quadrupedal locomotion over challenging terrain. Sci. Robot. 2020, 5, eabc5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, T.; Lee, J.; Hwangbo, J.; Wellhausen, L.; Koltun, V.; Hutter, M. Learning robust perceptive locomotion for quadrupedal robots in the wild. Sci. Robot. 2022, 7, eabk2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Ji, G.; Park, J.; Kim, H.; Mun, J.; Lee, J.H.; Hwangbo, J. Learning quadrupedal locomotion on deformable terrain. Sci. Robot. 2023, 8, eade2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutter, M.; Gehring, C.; Jud, D.; Lauber, A.; Bellicoso, C.D.; Tsounis, V.; Hwangbo, J.; Bodie, K.; Fankhauser, P.; Bloesch, M.; et al. Anymal-a highly mobile and dynamic quadrupedal robot. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Iscen, A.; Caluwaerts, K.; Tan, J.; Zhang, T.; Coumans, E.; Sindhwani, V.; Vanhoucke, V. Policies modulating trajectory generators. In Proceedings of the PMLR: Conference on Robot Learning, Zürich, Switzerland, 29–31 October 2018; pp. 916–926. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Meng, F.; Yu, Z.; Du, Y.; Gao, J.; Huang, Q. Learning Robust Locomotion for Bipedal Robot via Embedded Mechanics Properties. J. Bionic Eng. 2024, 21, 1278–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Clary, P.; Dao, J.; Morais, P.; Hurst, J.; Panne, M. Learning locomotion skills for cassie: Iterative design and sim-to-real. In Proceedings of the PMLR: Conference on Robot Learning, Virtual, 16–18 November 2020; pp. 317–329. [Google Scholar]
- Makoviychuk, V.; Wawrzyniak, L.; Guo, Y.; Lu, M.; Storey, K.; Macklin, M.; Hoeller, D.; Rudin, N.; Allshire, A.; Handa, A.; et al. Isaac gym: High performance gpu-based physics simulation for robot learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.10470. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, J.; Wolski, F.; Dhariwal, P.; Radford, A.; Klimov, O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.06347. [Google Scholar]
- Konda, V.; Tsitsiklis, J. Actor-critic algorithms. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1999, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5999–6009. [Google Scholar]

| Data | Dimension | Actor Policy | Stimulus Frequency Policy | State Estimator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Command | 3 | ✔ | ✔ | ✗ |
| Joint state | 12 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Torso state | 6 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Action history | 6 | ✔ | ✔ | ✗ |
| Linear velocity | 3 | ✔ | ✔ | ▸ |
| Dynamic signal | 2 | ✔ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Joint target | 6 | ▸ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Clipped frequency | 2 | ✗ | ▸ | ✗ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Meng, F.; Yu, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, J. Adaptive Gait Acquisition through Learning Dynamic Stimulus Instinct of Bipedal Robot. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9060310
Zhang Y, Chen X, Meng F, Yu Z, Du Y, Zhou Z, Gao J. Adaptive Gait Acquisition through Learning Dynamic Stimulus Instinct of Bipedal Robot. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(6):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9060310
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuanxi, Xuechao Chen, Fei Meng, Zhangguo Yu, Yidong Du, Zishun Zhou, and Junyao Gao. 2024. "Adaptive Gait Acquisition through Learning Dynamic Stimulus Instinct of Bipedal Robot" Biomimetics 9, no. 6: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9060310
APA StyleZhang, Y., Chen, X., Meng, F., Yu, Z., Du, Y., Zhou, Z., & Gao, J. (2024). Adaptive Gait Acquisition through Learning Dynamic Stimulus Instinct of Bipedal Robot. Biomimetics, 9(6), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9060310









