Running-Time Analysis of Brain Storm Optimization Based on Average Gain Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model for Running-Time Analysis of BSO
2.1. Brain Storm Optimization
2.2. Stochastic Process Model of BSO
2.3. Running-Time Analysis of BSO Based on Average Gain Model
3. Running-Time Analysis of BSO Instances for Equal Coefficient Linear Functions
3.1. Case Study of BSO without Disrupting Operator
| Algorithm 1 Brain Storm Optimization (BSO) |
|
3.1.1. When
| Algorithm 2 BSO-I |
|
- (1)
- If ,
- (2)
- If ,
- (1)
- If , according to the definition of where , it has .
- (2)
- If , the probability density function of is symmetric in the y axis, so .
- (3)
- If , .
3.1.2. When
- (1)
- If .
- (2)
- If , where , and are independent of each other. According to the Lindeberg–Levy center limit theorem, obeys .
- (1)
- If , .
- (2)
- If , .
- (3)
- If , .
3.1.3. When
- (1)
- If .
- (2)
- If .
- (1)
- If , .
- (2)
- If , .
- (3)
- If , .
3.2. Case Study of BSO with Disrupting Operator
| Algorithm 3 BSO-II |
|
3.2.1. When
- (1)
- If , it is the same as the result of the case with no disrupting operation in Section 3.1, and the average gain is
- (2)
- If and the mutation operator obeys , the distribution function of is represented by Lemma 4.
- (1)
- If .
- (2)
- If ,
- (1)
- If , .
- (2)
- If , .
- (3)
- If , .
3.2.2. When
- (1)
- If , the result is the same as the case in Section 3.1 with no disrupting operation. The average gain is
- (2)
- If and the mutation operator obeys , the distribution function of is represented by Lemma 5.
- (1)
- If .
- (2)
- If
- (1)
- If , .
- (2)
- If , .
- (3)
- If , .
3.2.3. When
- (1)
- If , the result is the same as the case in Section 3.1 with no disrupting operation. The average gain is
- (2)
- If , and the mutation operator obeys , the distribution function of is represented by Lemma 6.
- (1)
- If .
- (2)
- If
- (1)
- If , .
- (2)
- If , .
- (3)
- If , .
3.3. Summary
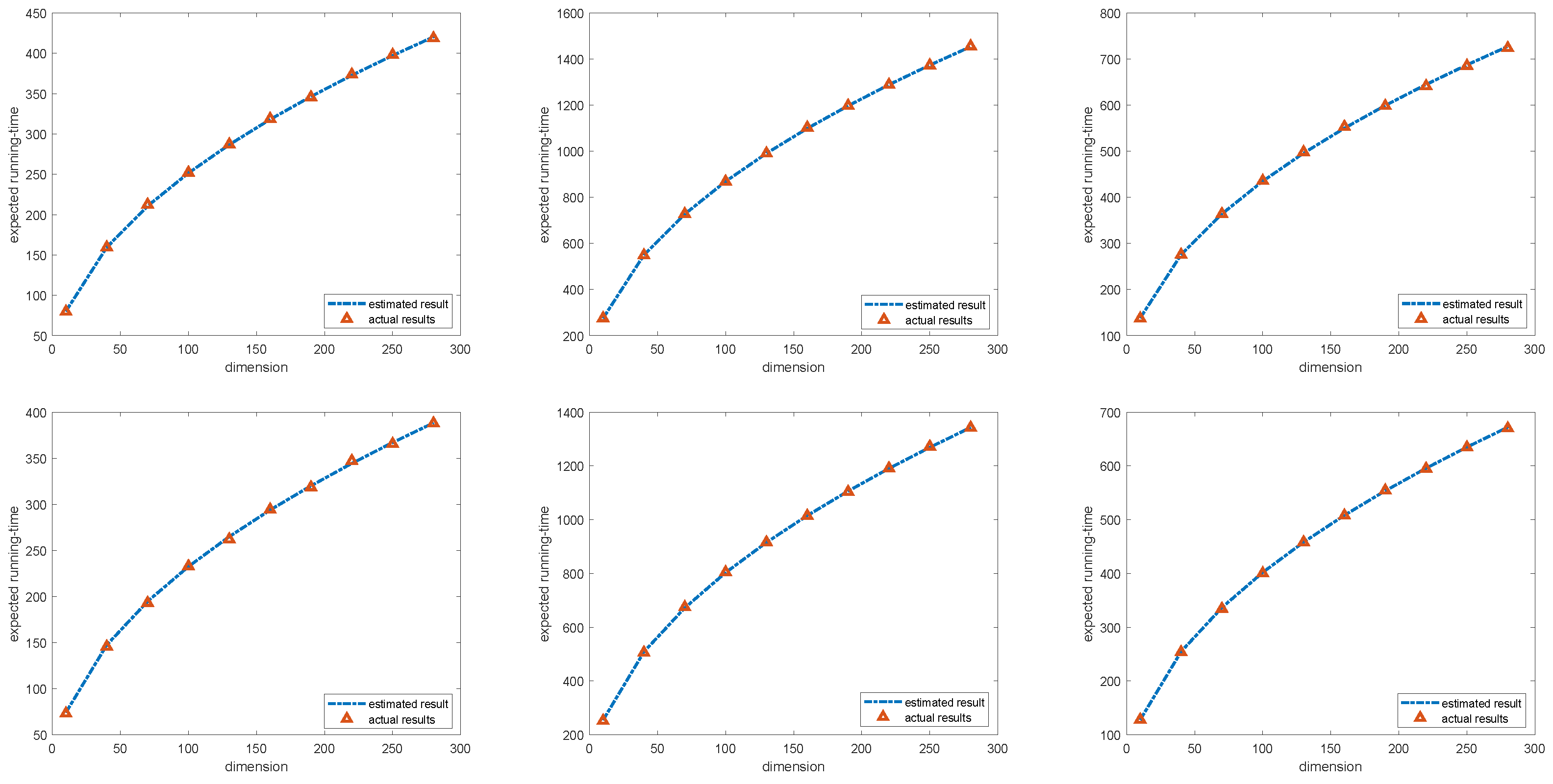
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michaloglou, A.; Tsitsas, N.L. A Brain Storm and Chaotic Accelerated Particle Swarm Optimization Hybridization. Algorithms 2023, 16, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowik, A.; Kwasnicka, H. Nature inspired methods and their industry applications-swarm intelligence algorithms. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 14, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, B.; Ma, T. A self-adaptive artificial bee colony algorithm based on global best for global optimization. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 2935–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhan, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kwong, S.; Zhang, J. Coevolutionary Particle Swarm Optimization With Bottleneck Objective Learning Strategy for Many-Objective Optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2019, 23, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, C. Two-Stage Multi-Swarm Particle Swarm Optimizer for Unconstrained and Constrained Global Optimization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 124905–124927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, W.; Gu, T.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. ACO-A*: Ant Colony Optimization Plus A* for 3-D Traveling in Environments with Dense Obstacles. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2019, 23, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Duan, D.; Lin, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Tilting Path Optimization of Tilt Quad Rotor in Conversion Process Based on Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 140777–140791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chipecane, M.T.; Yao, J. Cooperative Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm with Multiple Populations for Interval Multiobjective Optimization Problems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 27, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Mishra, K. Co-variance guided artificial bee colony. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 70, 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Qin, Q.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y. Brain storm optimization algorithm: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2016, 46, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Qin, Q.; Chu, X.; Lei, X.; Shi, Y. A comprehensive survey of brain storm optimization algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), San Sebastián, Spain, 5–8 June 2017; pp. 1637–1644. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Lei, X.; Hui, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y. Generalized pigeon-inspired optimization algorithms. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2019, 62, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Shi, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. A binary coded brain storm optimization for fault section diagnosis of power systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 163, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, J.; Xu, Y.; Crossley, P.; Zhang, D. Multi-objective optimisation method of power grid partitioning for wide-area backup protection. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2018, 12, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, S.; Mori, H. A Hierarchical Scheme for Voltage and Reactive Power Control with Predator-Prey Brain Storm Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th International Conference on Intelligent System Application to Power Systems (ISAP), New Delhi, India, 10–14 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Fukuyama, Y. Voltage and Reactive Power Control by Parallel Modified Brain Storm Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Fukuoka, Japan, 19–21 February 2020; pp. 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyinka, O.K.; Duan, H. Optimal Impulsive Thrust Trajectories for Satellite Formation via Improved Brainstorm Optimization. In Proceedings of the Advances in Swarm Intelligence; Tan, Y., Shi, Y., Niu, B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 491–499. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Duan, H. Simplified brain storm optimization approach to control parameter optimization in F/A-18 automatic carrier landing system. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2015, 42, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Shi, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, C.; Duan, H. Binocular Pose Estimation for UAV Autonomous Aerial Refueling via Brain Storm Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Wellington, New Zealand, 10–13 June 2019; pp. 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuba, E.; Strumberger, I.; Zivkovic, D.; Bacanin, N.; Tuba, M. Mobile Robot Path Planning by Improved Brain Storm Optimization Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, D.; Shi, Y. An Unknown Environment Exploration Strategy for Swarm Robotics Based on Brain Storm Optimization Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Wellington, New Zealand, 10–13 June 2019; pp. 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhafeeri, A.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Brain Storm Optimization for Electromagnetic Applications: Continuous and Discrete. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 2710–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. A Hybrid Approach by Integrating Brain Storm Optimization Algorithm with Grey Neural Network for Stock Index Forecasting. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014, 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xiong, G.; Shi, D. Hybrid biogeography-based optimization with brain storm optimization for non-convex dynamic economic dispatch with valve-point effects. Energy 2018, 157, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Y. Multi-objective Differential-Based Brain Storm Optimization for Environmental Economic Dispatch Problem. In Proceedings of the Brain Storm Optimization Algorithms: Concepts, Principles and Applications; Cheng, S., Shi, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 79–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Jin, Y.; Dong, Q. A generalized dynamic fuzzy neural network based on singular spectrum analysis optimized by brain storm optimization for short-term wind speed forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 54, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.J.; Wang, P.; Yue, C.T.; Yu, K.; Li, Z.H.; Qu, B. Multi-objective Brainstorm Optimization Algorithm for Sparse Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Tian, G.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Ahmadi, A.; Zhang, C. Stochastic multi-objective modelling and optimization of an energy-conscious distributed permutation flow shop scheduling problem with the total tardiness constraint. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourpanah, F.; Shi, Y.; Lim, C.P.; Hao, Q.; Tan, C.J. Feature selection based on brain storm optimization for data classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 80, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wang, H.; Yu, Q. Multi-Clusters Adaptive Brain Storm Optimization Algorithm for QoS-Aware Service Composition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 48822–48835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Duan, H.; Shi, Y. Convergence analysis of brain storm optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 3747–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Gao, Y. The Global Convergence Analysis of Brain Storm Optimization. NeuroQuantology 2018, 16, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Hongyue, W.; Hao, Z. Theoretical analysis of the convergence property of a basic pigeon-inspired optimizer in a continuous search space. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2019, 62, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudholt, D. A New Method for Lower Bounds on the Running Time of Evolutionary Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2013, 17, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yao, X. Average Drift Analysis and Population Scalability. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2017, 21, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Qian, C.; Zhou, Z.H. Switch Analysis for Running Time Analysis of Evolutionary Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2015, 19, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Ji, D. Wave models and dynamical analysis of evolutionary algorithms. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2019, 62, 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lehre, P.K.; Witt, C. Concentrated Hitting Times of Randomized Search Heuristics with Variable Drift. In Proceedings of the Algorithms and Computation; Ahn, H.K., Shin, C.S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 686–697. [Google Scholar]
- Witt, C. Fitness levels with tail bounds for the analysis of randomized search heuristics. Inf. Process. Lett. 2014, 114, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Qian, C. Running time analysis: Convergence-based analysis reduces to switch analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Sendai, Japan, 25–28 May 2015; pp. 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Hao, Z. Runtime analysis for continuous (1 + 1) evolutionary algorithm based on average gain model. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2014, 44, 811–824. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Z. An Experimental Method to Estimate Running Time of Evolutionary Algorithms for Continuous Optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2020, 24, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Hao, Z.; Hu, G. First hitting time analysis of continuous evolutionary algorithms based on average gain. Clust. Comput. 2016, 19, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, Z.H. A new approach to estimating the expected first hitting time of evolutionary algorithms. Artif. Intell. 2006, 172, 1809–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Application of data mining based on swarm intelligence algorithm in financial support of livestock and poultry breeding insurance. Soft Comput. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Liu, H. A modified brain storm optimization. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 10–15 June 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- El-Abd, M. Brain storm optimization algorithm with re-initialized ideas and adaptive step size. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 2682–2686. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y. Brain Storm Optimization Algorithm. In Proceedings of the Advances in Swarm Intelligence; Tan, Y., Shi, Y., Chai, Y., Wang, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y. An Optimization Algorithm Based on Brainstorming Process. Int. J. Swarm Intell. Res. 2011, 2, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Xu, Y. Recent advances in evolutionary computation. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2006, 21, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapie, A.; Agapie, M.; Zbaganu, G. Evolutionary algorithms for continuous-space optimisation. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2013, 44, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yao, X. Drift analysis and average time complexity of evolutionary algorithms. Artif. Intell. 2001, 127, 57–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, U. Riemann Integrals. In Proceedings of the Stochastic Processes and Calculus: An Elementary Introduction with Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Jägersküpper, J. Combining Markov-chain analysis and drift analysis: The (1 + 1) evolutionary algorithm on linear functions reloaded. Algorithmica 2011, 59, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, C. Tight Bounds on the Optimization Time of a Randomized Search Heuristic on Linear Functions. Comb. Probab. Comput. 2013, 22, 294–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Tu, K. A Time Complexity Analysis of ACO for Linear Functions. In Proceedings of the Simulated Evolution and Learning, 6th International Conference, SEAL 2006, Hefei, China, 15–18 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jgersküpper, J. Algorithmic analysis of a basic evolutionary algorithm for continuous optimization. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2007, 379, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, W. An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Z.H.; Chen, W.N.; Lin, Y.; Gong, Y.J.; Li, Y.L.; Zhang, J. Parameter investigation in brain storm optimization. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Symposium on Swarm Intelligence (SIS), Singapore, 16–19 April 2013; pp. 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Algorithm | Mutation Operator | Display Expression for | Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| BSO-I | |||
| BSO-II | |||
| Algorithm | n | 10 | 40 | 70 | 100 | 130 | 160 | 190 | 220 | 250 | 280 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSO-I | 80.27 | 159.53 | 210.72 | 251.66 | 286.80 | 318.07 | 346.51 | 372.79 | 397.33 | 420.44 | ||
| 79.65 | 159.57 | 212.51 | 252.09 | 287.14 | 316.84 | 345.61 | 373.66 | 398.08 | 418.75 | |||
| 275.59 | 550.17 | 727.49 | 869.32 | 991.04 | 1099.35 | 1197.90 | 1288.93 | 1373.94 | 1453.98 | |||
| 275.81 | 548.63 | 727.97 | 868.67 | 990.57 | 1102.96 | 1198.00 | 1288.83 | 1373.06 | 1455.95 | |||
| 138.29 | 275.59 | 364.24 | 435.16 | 496.02 | 550.17 | 599.45 | 644.96 | 687.47 | 727.49 | |||
| 137.27 | 275.45 | 363.95 | 435.81 | 498.34 | 553.30 | 598.41 | 641.36 | 685.46 | 723.91 | |||
| BSO-II | 74.20 | 147.40 | 194.68 | 232.49 | 264.93 | 293.81 | 320.08 | 344.35 | 367.01 | 388.35 | ||
| 72.97 | 145.55 | 193.03 | 232.77 | 262.05 | 294.26 | 318.51 | 347.10 | 365.51 | 387.87 | |||
| 254.58 | 508.16 | 671.91 | 802.89 | 915.30 | 1015.32 | 1106.33 | 1190.40 | 1268.90 | 1342.82 | |||
| 251.80 | 505.49 | 674.53 | 804.58 | 915.61 | 1014.22 | 1103.21 | 1190.82 | 1271.88 | 1342.12 | |||
| 127.79 | 254.58 | 336.45 | 401.95 | 458.15 | 508.16 | 553.67 | 595.70 | 634.95 | 671.91 | |||
| 128.10 | 253.61 | 334.30 | 400.20 | 458.07 | 507.69 | 554.34 | 594.77 | 634.45 | 669.75 |
| Algorithm | n | 10 | 40 | 70 | 100 | 130 | 160 | 190 | 220 | 250 | 280 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSO-I | h | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| p | 0.80 | 0.48 | 0.06 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.81 | 0.72 | 0.31 | 0.34 | 0.83 | ||
| 78.41 | 157.86 | 210.57 | 249.84 | 284.76 | 314.52 | 343.03 | 370.82 | 395.13 | 415.87 | |||
| Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | |||
| h | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| p | 0.44 | 0.79 | 0.42 | 0.60 | 0.57 | 0.10 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.61 | 0.27 | ||
| 273.43 | 545.49 | 724.19 | 864.51 | 986.22 | 1098.22 | 1193.50 | 1283.96 | 1367.75 | 1450.62 | |||
| Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | |||
| h | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| p | 0.85 | 0.54 | 0.57 | 0.36 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.69 | 0.95 | 0.81 | 0.94 | ||
| 135.64 | 273.05 | 361.29 | 432.88 | 495.38 | 549.76 | 595.05 | 637.79 | 681.73 | 720.20 | |||
| Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | |||
| BSO-II | h | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| p | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.42 | 0.99 | 0.38 | 0.83 | 0.06 | 0.81 | 0.61 | ||
| 71.71 | 143.86 | 191.16 | 230.52 | 259.89 | 291.83 | 315.84 | 344.26 | 362.73 | 385.06 | |||
| Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | |||
| h | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| p | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 0.86 | 0.44 | 0.18 | 0.59 | ||
| 249.47 | 502.38 | 670.91 | 800.79 | 911.60 | 1009.53 | 1098.54 | 1185.87 | 1266.44 | 1337.20 | |||
| Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | |||
| h | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| p | 0.37 | 0.77 | 0.92 | 0.84 | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.37 | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.83 | ||
| 126.53 | 251.47 | 331.78 | 397.34 | 455.24 | 504.80 | 551.07 | 591.02 | 630.94 | 665.97 | |||
| Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mai, G.; Liu, F.; Hong, Y.; Liu, D.; Su, J.; Yang, X.; Huang, H. Running-Time Analysis of Brain Storm Optimization Based on Average Gain Model. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020117
Mai G, Liu F, Hong Y, Liu D, Su J, Yang X, Huang H. Running-Time Analysis of Brain Storm Optimization Based on Average Gain Model. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(2):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020117
Chicago/Turabian StyleMai, Guizhen, Fangqing Liu, Yinghan Hong, Dingrong Liu, Junpeng Su, Xiaowei Yang, and Han Huang. 2024. "Running-Time Analysis of Brain Storm Optimization Based on Average Gain Model" Biomimetics 9, no. 2: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020117
APA StyleMai, G., Liu, F., Hong, Y., Liu, D., Su, J., Yang, X., & Huang, H. (2024). Running-Time Analysis of Brain Storm Optimization Based on Average Gain Model. Biomimetics, 9(2), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020117






