LSTM-Enhanced TD3 and Behavior Cloning for UAV Trajectory Tracking Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Inspired by references [22,23,24], an LSTM network is introduced to enhance the trajectory tracking capability of drones in dynamic environments. By mimicking the memory and temporal processing capabilities of biological neural systems, the LSTM layer extracts time-dependent features from the sequential observations of the UAV. These features are processed by the policy network to generate continuous control actions, which significantly improves the adaptability and control stability of the algorithm in partially observable environments.
- (2)
- Based on the advantages of the BC method, this paper innovatively combines expert demonstration data with reinforcement learning by using the principle of biomimetics. By pre-training the policy network to imitate the expert behavior, it not only greatly shortens the exploration time in the early stage of training but also avoids the generation of dangerous control actions.
- (3)
- A TD3-LSTM-BC algorithm that integrates TD3, LSTM, and BC is proposed for drone trajectory tracking control. The algorithm captures the time-series dependency through LSTM and uses BC to provide expert prior knowledge, achieving the coordinated optimization of control accuracy, learning efficiency, and robustness under the TD3 framework.
2. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle System Modeling
3. Preliminaries
3.1. Reinforcement Learning
- –
- is the state space,
- –
- is the action space,
- –
- is the transition probability,
- –
- is the reward function,
- –
- is the discount factor.
- –
- the actor outputs continuous actions,
- –
- the critic estimates the action-value function:
3.2. TD3 Algorithm
- Clipped Double Q-learning: maintain two critics and , and use the smaller Q-value in the target:where adds noise for target smoothing.
- Delayed Policy Update: to reduce the discrepancy, the actor network is updated less frequently than the critic network.
- Target Policy Smoothing: adds noise to the target action for smoother Q-function estimation.
3.3. Long Short-Term Memory
- –
- denotes the sigmoid activation,
- –
- ⊙ denotes element-wise multiplication,
- –
- and are weight matrices and bias vectors.
3.4. Behavior Cloning
- –
- is the observed state,
- –
- is the expert’s action.
- –
- is a weighting coefficient balancing between imitation and value maximization,
- –
- is the critic network.
4. Control Design
4.1. Input and Output
4.2. TD3-LSTM Design
4.3. TD3-LSTM-BC Design
| Algorithm 1 TD3 with LSTM-Actor and BC for UAV Trajectory Tracking |
|
5. Simulation
5.1. Training Performance
5.2. Tracking Control Performance
5.3. Anti-Disturbance Performance
5.4. Generalization Performance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; He, W.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, R.; He, X.; Liu, J. Scale optimization using evolutionary reinforcement learning for object detection on drone imagery. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 410–418. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Sanchez, I.; Moreno-Valenzuela, J. PID control of quadrotor UAVs: A survey. Annu. Rev. Control 2023, 56, 100900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvaritakis, B.; Cannon, M. Model Predictive Control; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 38, p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Ma, A.; Zhao, S. Autonomous Tracked Vehicle Trajectory Tracking Control Based on Disturbance Observation and Sliding Mode Control. Actuators 2025, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M. Application of PID Control Technology in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2024, 96, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwek, M.; Baranowski, L.; Ładyżyńska-Kozdraś, E. The Application and Optimisation of a Neural Network PID Controller for Trajectory Tracking Using UAVs. Sensors 2024, 24, 8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boubakir, A.; Souanef, T.; Labiod, S.; Whidborne, J.F. A robust adaptive PID-like controller for quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle systems. Aerospace 2024, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Yin, Z.; Jin, X.; Fan, Z.; Wang, H. MPC-Based Dynamic Trajectory Spoofing for UAVs. Drones 2024, 8, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, X.; She, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, Q. Trajectory Planning for UAV Swarm Tracking Moving Target Based on an Improved Model Predictive Control Fusion Algorithm. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 19354–19369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Li, B.; Shi, M. Nonlinear Model Predictive Control for UAV Trajectory Optimization. In Guidance, Navigation and Control; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Hu, Z.; Yang, X.; Rodriguez-Andina, J.J. Time-delay sliding mode control for trajectory tracking of robot manipulators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 13083–13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Ma, T.; Su, X. Adaptive fuzzy sliding-mode fixed-time control for quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicles with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 32, 4109–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D. Event-triggered H ∞ control for unknown constrained nonlinear systems with application to robot arm. Appl. Math. Model. 2025, 144, 116089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Meng, L.; Yan, J.; Qin, C. Adaptive critic design for safety-optimal FTC of unknown nonlinear systems with asymmetric constrained-input. ISA Trans. 2024, 155, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Su, Q.; Guo, Y. Autonomous UAV navigation with adaptive control based on deep reinforcement learning. Electronics 2024, 13, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xie, N.; Li, K.; Liang, Y.; Shen, X. Trajectory tracking control for fixed-wing UAV based on DDPG. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2024, 37, 04024012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yin, C. Collaborative reinforcement learning based unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) trajectory design for 3D UAV tracking. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 10787–10802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, P.; Wu, E.; Guo, Z.; Hou, Z. TD3 Agent-Based Nonlinear Dynamic Inverse Control for Fixed-Wing UAV Attitudes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, K. Research on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Intelligent Maneuvering Method Based on Hierarchical Proximal Policy Optimization. Processes 2025, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahran, Y.; Gamal, Z.; El-Badawy, A. Reinforcement Learning Position Control of a Quadrotor Using Soft Actor-Critic (SAC). In Proceedings of the 2024 6th Novel Intelligent and Leading Emerging Sciences Conference (NILES), Giza, Egypt, 19–21 October 2024; pp. 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A.; Graves, A. Long short-term memory. In Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Alcayaga, J.M.; Menéndez, O.A.; Torres-Torriti, M.A.; Vásconez, J.P.; Arévalo-Ramirez, T.; Romo, A.J.P. LSTM-Enhanced Deep Reinforcement Learning for Robust Trajectory Tracking Control of Skid-Steer Mobile Robots Under Terra-Mechanical Constraints. Robotics 2025, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wang, X.; Han, F.; Zhou, Z.; Cai, J.; Zeng, L.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X. Research on LSTM-PPO Obstacle Avoidance Algorithm and Training Environment for Unmanned Surface Vehicles. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Qin, Y.; Guo, F.; Jiang, M. Trajectory Tracking Control for Robotic Manipulator Based on Soft Actor–Critic and Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiao, B.; Xun, Y. Multi-UAV adaptive cooperative formation trajectory planning based on an improved MATD3 algorithm of deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 12484–12499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Qian, C.; Zhao, M.; Wang, R. Cross coordination of behavior clone and reinforcement learning for autonomous within-visual-range air combat. Neurocomputing 2024, 584, 127591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Mahmoudian, N. Synergistic Reinforcement and Imitation Learning for Vision-driven Autonomous Flight of UAV Along River. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 14–18 October 2024; pp. 9976–9982. [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood, O.; Si, M. A review of uncertainty for deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Digital Entertainment, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2022; Volume 18, pp. 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ahangar, A.R.; Ohadi, A.; Khosravi, M.A. A novel firefighter quadrotor UAV with tilting rotors: Modeling and control. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 151, 109248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeifar, S.; Dadashi, R.; Vieillard, N.; Hussenot, L.; Bachem, O.; Pietquin, O.; Geist, M. Offline reinforcement learning as anti-exploration. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2022; Volume 36, pp. 8106–8114. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Cao, R.; Wang, R. Learning discriminative topological structure information representation for 2D shape and social network classification via persistent homology. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2025, 311, 113125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, S.; Wu, M.; Lam, S.K.; Tiwari, P.; Gao, X. Looking Clearer with Text: A Hierarchical Context Blending Network for Occluded Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2025, 20, 4296–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Ran, X.; Zhang, D. Unsupervised image stitching based on Generative Adversarial Networks and feature frequency awareness algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 183, 113466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lam, S.K.; Wu, M.; Hu, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, J. Destination intention estimation-based convolutional encoder-decoder for pedestrian trajectory multimodality forecast. Measurement 2025, 239, 115470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hu, J.; Qin, Y.; Guo, F.; Jiang, M. Trajectory Tracking Control Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning for a Robotic Manipulator with an Input Deadzone. Symmetry 2025, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumiea, E.H.; Abdulkadir, S.J.; Alhussian, H.S.; Al-Selwi, S.M.; Alqushaibi, A.; Ragab, M.G.; Fati, S.M. Deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm: A systematic review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
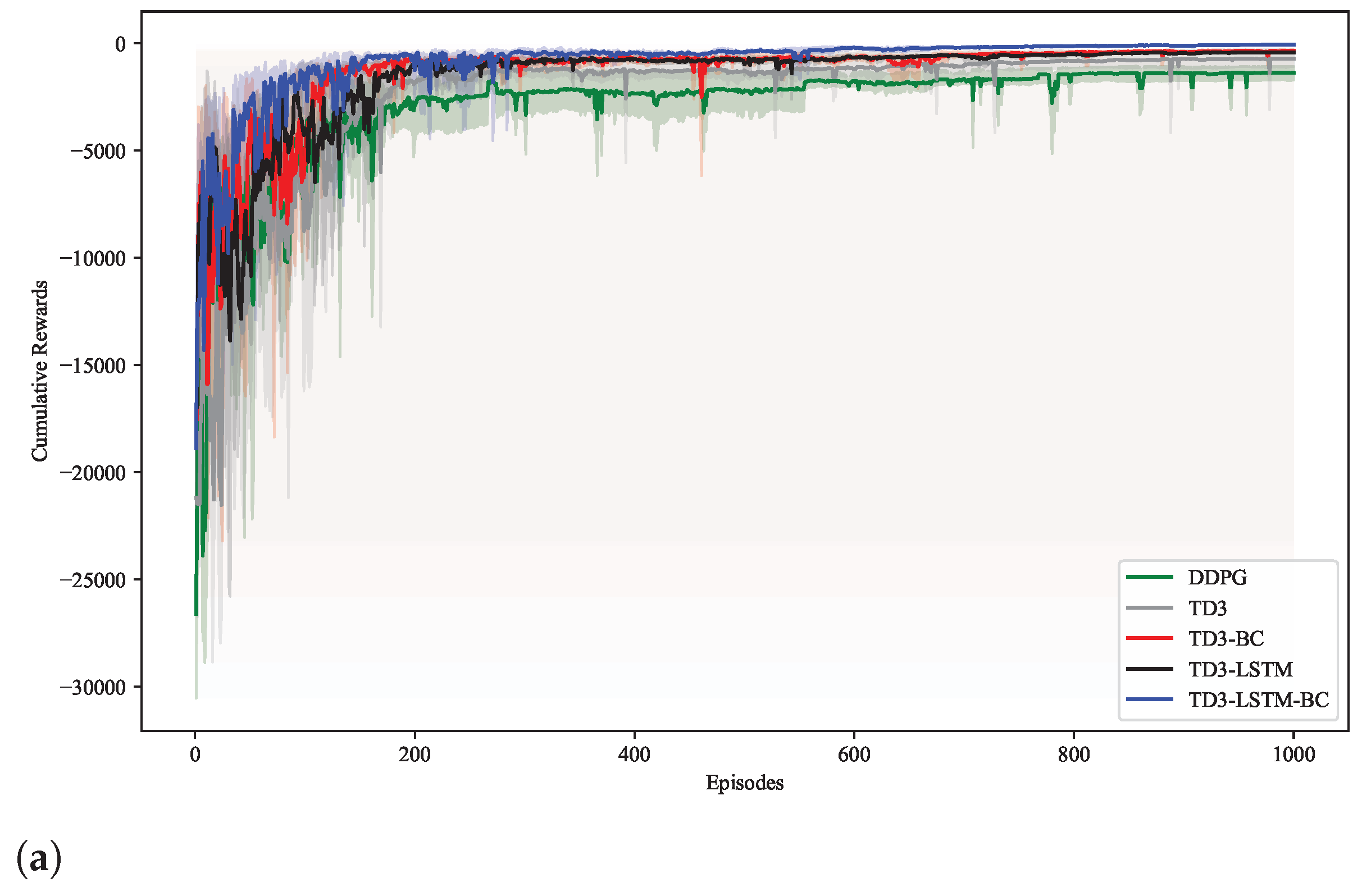

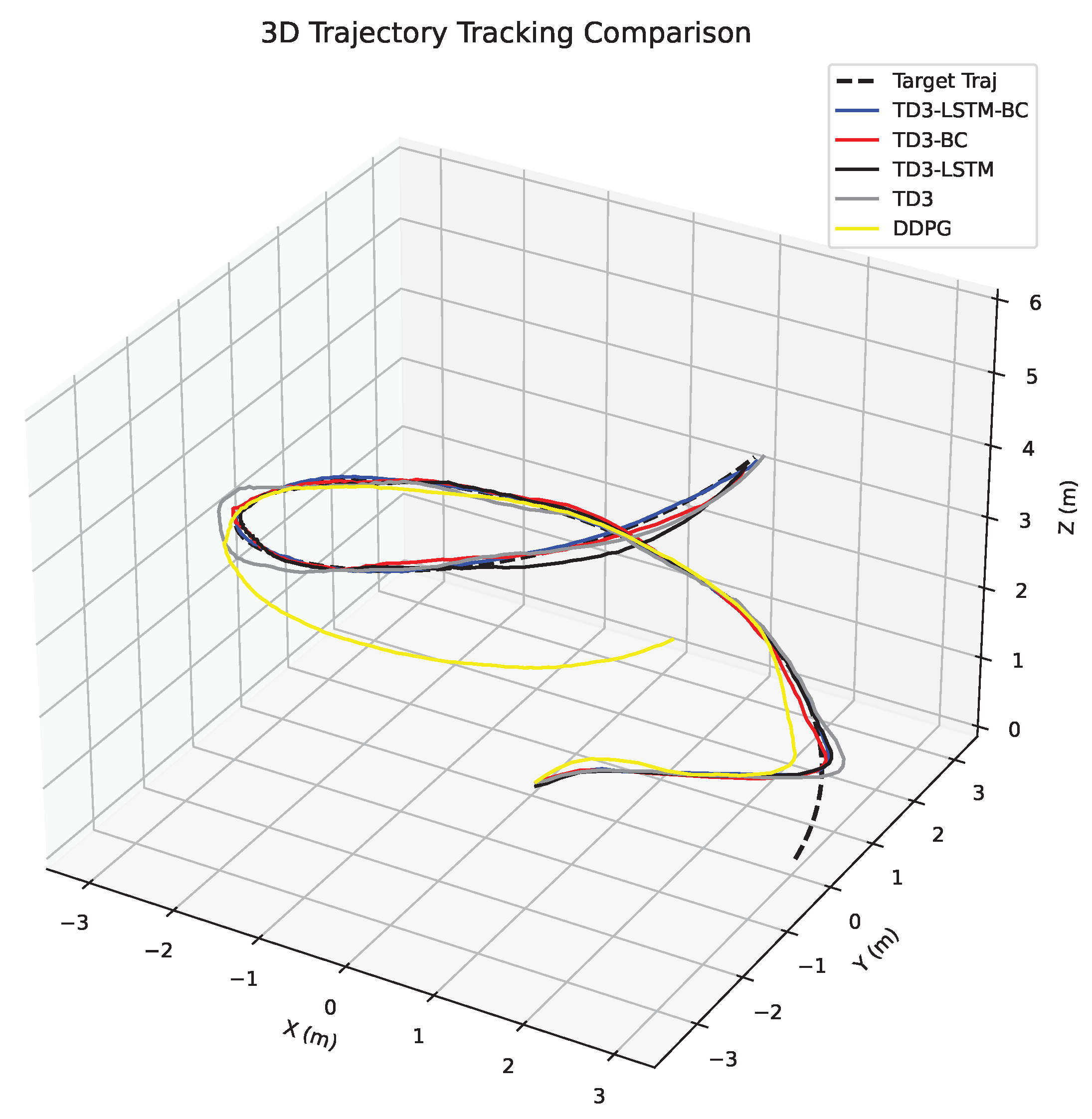

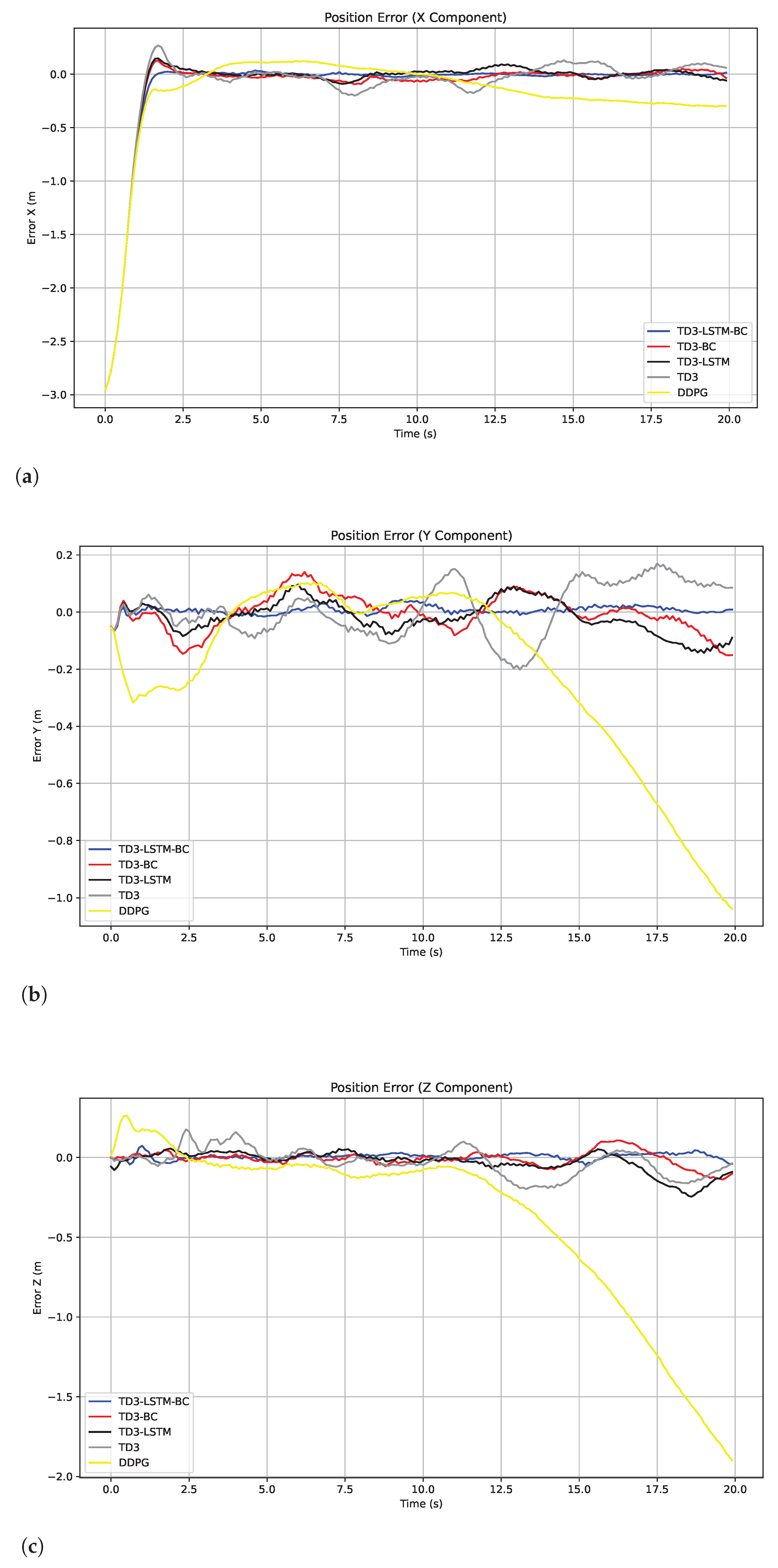

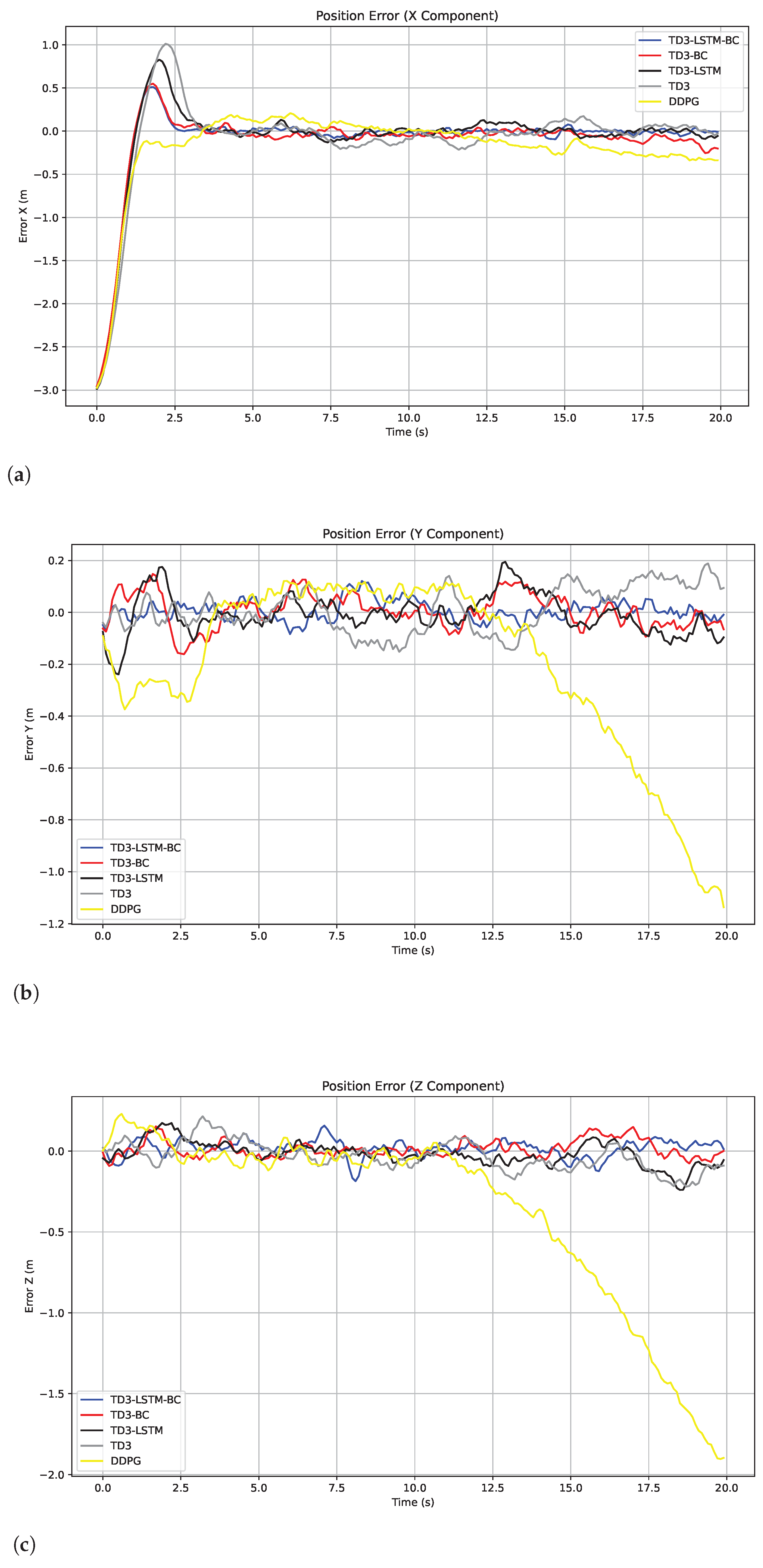
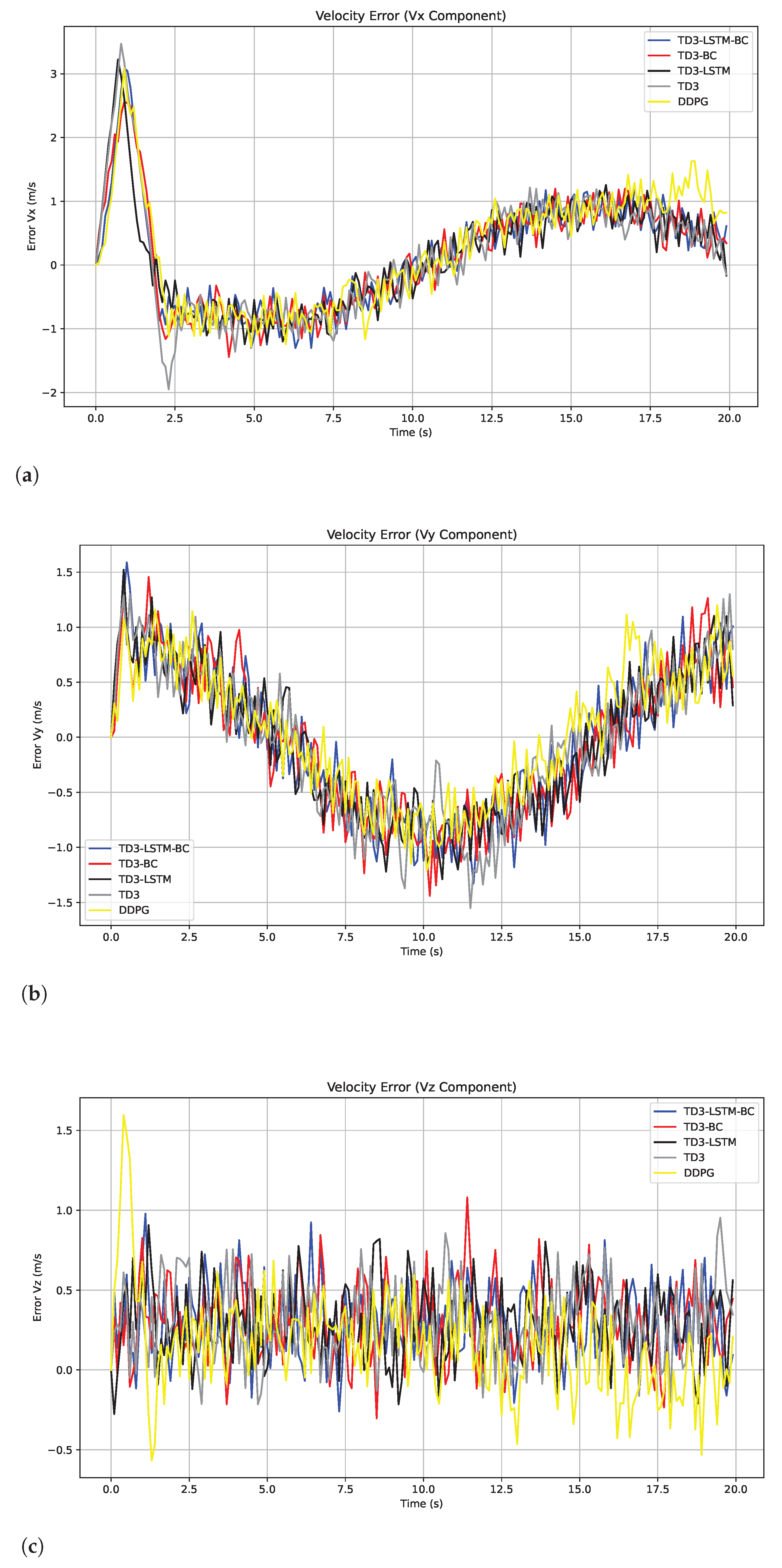
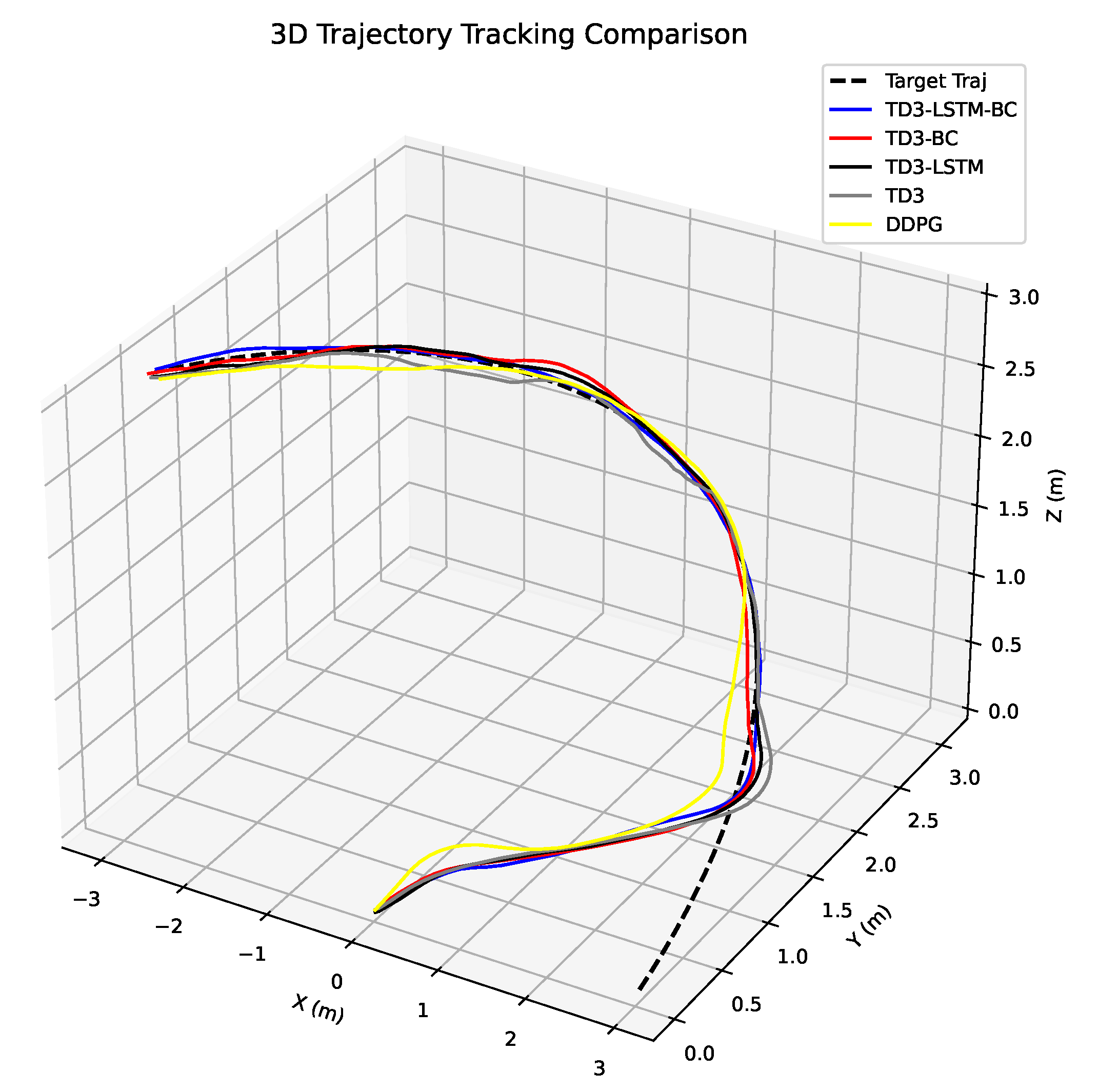
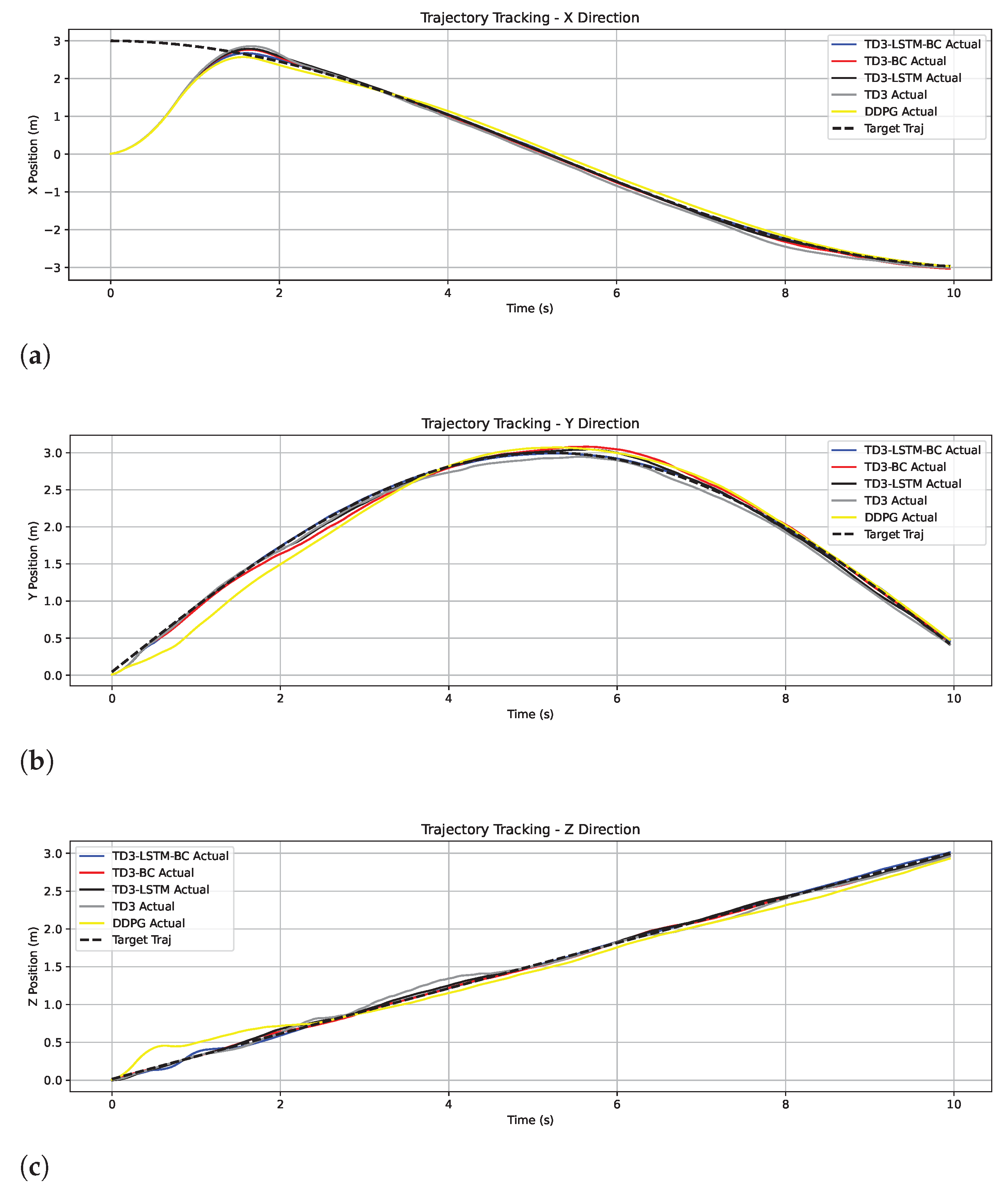
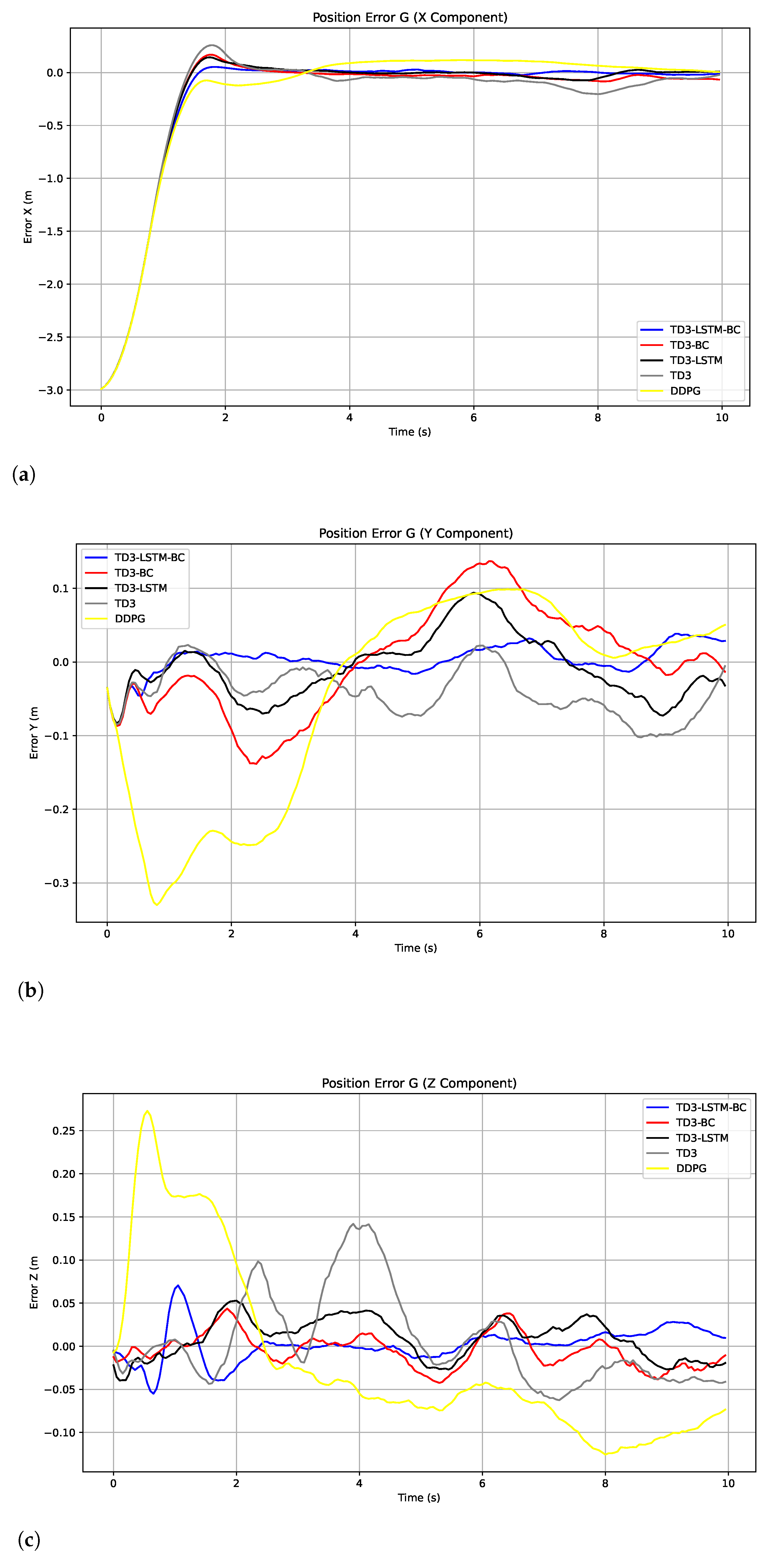

| Category | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Properties | Mass (m) | 1.0 kg |
| Linear Acceleration Bound | ± 5.0 m/ | |
| Angular Acceleration Bound | ± 5.0 rad/ | |
| Euler Angle Constraints | Roll/Pitch: | |
| Yaw: | ||
| State Space | Position (x,y,z) | (unbounded) |
| Velocity (vx,vy,vz) | ||
| Attitude (roll,pitch,yaw) | ||
| Angular Velocity | ||
| Action Space | Linear + Angular Acc. | 6D: |
| Simulation | Time Step () | 0.1 s |
| Max Episode Steps | 200 |
| Algorithms | TD3-LSTM-BC | TD3-BC | TD3-LSTM | TD3 | DDPG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis | ||||||
| X | MAE | 0.1249 | 0.1415 | 0.1394 | 0.1877 | 0.5088 |
| RMSE | 0.5033 | 0.5057 | 0.5039 | 0.5115 | 0.7492 | |
| Y | MAE | 0.0113 | 0.0526 | 0.0477 | 0.0771 | 0.6744 |
| RMSE | 0.0157 | 0.0675 | 0.0600 | 0.0894 | 1.0208 | |
| Z | MAE | 0.0148 | 0.0327 | 0.0461 | 0.0630 | 0.7880 |
| RMSE | 0.0183 | 0.0471 | 0.0690 | 0.0800 | 1.1669 | |
| Overall | MAE | 0.0503 | 0.0756 | 0.0777 | 0.1093 | 0.6571 |
| RMSE | 0.1791 | 0.2068 | 0.2110 | 0.2270 | 0.9789 |
| Algorithms | TD3-LSTM-BC | TD3-BC | TD3-LSTM | TD3 | DDPG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis | ||||||
| X | MAE | 0.7169 | 0.7235 | 0.7158 | 0.7416 | 0.7370 |
| RMSE | 0.8493 | 0.8570 | 0.8534 | 0.8902 | 0.8492 | |
| Y | MAE | 0.5519 | 0.5578 | 0.5595 | 0.5477 | 0.5239 |
| RMSE | 0.6261 | 0.6237 | 0.6275 | 0.6308 | 0.5885 | |
| Z | MAE | 0.2962 | 0.2929 | 0.2936 | 0.3049 | 0.2031 |
| RMSE | 0.3124 | 0.3166 | 0.3130 | 0.3418 | 0.2897 | |
| Overall | MAE | 0.5216 | 0.5247 | 0.5230 | 0.5314 | 0.4880 |
| RMSE | 0.5959 | 0.5991 | 0.5980 | 0.6210 | 0.5758 |
| Algorithms | TD3-LSTM-BC | TD3-BC | TD3-LSTM | TD3 | DDPG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis | ||||||
| X | w/o Dist. | 0.1249 | 0.1415 | 0.1394 | 0.1877 | 0.5088 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.1291 | 0.1512 | 0.1701 | 0.2240 | 0.5009 | |
| Y | w/o Dist. | 0.0113 | 0.0526 | 0.0477 | 0.0771 | 0.6744 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.0125 | 0.0587 | 0.0486 | 0.0861 | 0.6519 | |
| Z | w/o Dist. | 0.0148 | 0.0327 | 0.0461 | 0.0630 | 0.7880 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.0162 | 0.0468 | 0.0494 | 0.0769 | 0.7821 | |
| Overall | w/o Dist. | 0.0503 | 0.0756 | 0.0777 | 0.1093 | 0.6571 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.0526 | 0.0856 | 0.0894 | 0.1290 | 0.6450 |
| Algorithms | TD3-LSTM-BC | TD3-BC | TD3-LSTM | TD3 | DDPG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis | ||||||
| X | w/o Dist. | 0.5033 | 0.5057 | 0.5039 | 0.5115 | 0.7492 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.5051 | 0.5208 | 0.5321 | 0.5559 | 0.7591 | |
| Y | w/o Dist. | 0.0157 | 0.0675 | 0.0600 | 0.0894 | 1.0208 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.0172 | 0.0750 | 0.0586 | 0.0963 | 0.9653 | |
| Z | w/o Dist. | 0.0183 | 0.0471 | 0.0690 | 0.0800 | 1.1669 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.0198 | 0.0578 | 0.0666 | 0.0931 | 1.1552 | |
| Overall | w/o Dist. | 0.1791 | 0.2068 | 0.2110 | 0.2270 | 0.9789 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.1807 | 0.2179 | 0.2191 | 0.2484 | 0.9599 |
| Algorithms | TD3-LSTM-BC | TD3-BC | TD3-LSTM | TD3 | DDPG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis | ||||||
| X | w/o Dist. | 0.7169 | 0.7235 | 0.7158 | 0.7416 | 0.7370 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.7205 | 0.7340 | 0.7668 | 0.7856 | 0.7795 | |
| Y | w/o Dist. | 0.5519 | 0.5578 | 0.5595 | 0.5477 | 0.5239 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.5532 | 0.5653 | 0.5671 | 0.5680 | 0.5186 | |
| Z | w/o Dist. | 0.2962 | 0.2929 | 0.2936 | 0.3049 | 0.2031 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.2981 | 0.3094 | 0.3225 | 0.3217 | 0.2593 | |
| Overall | w/o Dist. | 0.5216 | 0.5247 | 0.5230 | 0.5314 | 0.4880 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.5239 | 0.5362 | 0.5521 | 0.5584 | 0.5192 |
| Algorithms | TD3-LSTM-BC | TD3-BC | TD3-LSTM | TD3 | DDPG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis | ||||||
| X | w/o Dist. | 0.8493 | 0.8570 | 0.8534 | 0.8902 | 0.8492 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.8510 | 0.8764 | 0.9438 | 0.9376 | 0.8951 | |
| Y | w/o Dist. | 0.6261 | 0.6237 | 0.6275 | 0.6308 | 0.5885 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.6275 | 0.6536 | 0.6540 | 0.6619 | 0.6032 | |
| Z | w/o Dist. | 0.3124 | 0.3166 | 0.3130 | 0.3418 | 0.2897 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.3142 | 0.3647 | 0.3922 | 0.3814 | 0.3568 | |
| Overall | w/o Dist. | 0.5959 | 0.5991 | 0.5980 | 0.6210 | 0.5758 |
| w/ Dist. | 0.5976 | 0.6316 | 0.6633 | 0.6603 | 0.6184 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, F.; Huang, G. LSTM-Enhanced TD3 and Behavior Cloning for UAV Trajectory Tracking Control. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090591
Qi Y, Hu J, Wang F, Huang G. LSTM-Enhanced TD3 and Behavior Cloning for UAV Trajectory Tracking Control. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(9):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090591
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Yuanhang, Jintao Hu, Fujie Wang, and Gewen Huang. 2025. "LSTM-Enhanced TD3 and Behavior Cloning for UAV Trajectory Tracking Control" Biomimetics 10, no. 9: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090591
APA StyleQi, Y., Hu, J., Wang, F., & Huang, G. (2025). LSTM-Enhanced TD3 and Behavior Cloning for UAV Trajectory Tracking Control. Biomimetics, 10(9), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090591






