High-Value Patents Recognition with Random Forest and Enhanced Fire Hawk Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fire Hawk Optimization Algorithm
- (1)
- Compute the fitness value for all solution candidates. The best solution candidate in the global searching space is presumed to be the main fire, with the better n solution candidates considered as the Fire Hawks, and the remaining solutions referred to as prey.
- (2)
- Calculate the length between the prey and the Fire Hawks, and assign each prey to the nearest Fire Hawk based on the distance, thus establishing a territory for each Fire Hawk. The determination of distance relies on the following equation:where represents the length between the ith Fire Hawk and the jth prey, m represents the number of prey, n represents the number of Fire Hawks, represents the coordinate of the Fire Hawk, represents the coordinate of the prey.
- (3)
- From the main fire, the Fire Hawks gather burning sticks and set fire in their specific territory to force the prey to hastily flee, then move to a new location. Meanwhile, some Fire Hawks are excited to use the sticks that are burning in other Fire Hawks’ territories. The equation of location updating procedures is as follows:where represents the updated location vector of the ith Fire Hawk (), represents the globally optimal location in the searching space that is regarded as the main fire, represents another Fire Hawk in the searching space, and are evenly distributed random integers between 0 and 1 that determine how Fire Hawks will migrate toward the main fire or other occupied territories.
- (4)
- The prey in the Fire Hawk’s territory start to run away once it sets fire; they may run away, hide, or mistakenly run in the direction of the Fire Hawk. During the location update process, these actions can be expressed by the following equation:where represents the updated location vector of the qth prey, which is denoted as that the lth Fire Hawk, which is denoted as is encircling, represents a safe location in the territory of , and are evenly distributed random integers between 0 and 1 that are used to determine how prey will move toward the safe location and the Fire Hawks. The mathematical presentation of is formulated as follows:where the is the qth prey that is encircling.
- (5)
- Additionally, the prey may run out of the current Fire Hawk’s territory, potentially to another Fire Hawk’s territory, or to a safer location. The position update equation takes these actions into consideration.In this equation, represents the updated location vector of the qth prey which is denoted as that the lth Fire Hawk which is denoted as is encircling, represents another Fire Hawk in the searching space, represents a safe location beyond the territory of , and are evenly distributed random integers between 0 and 1 that are used to determine how prey will approach the safe location beyond the territory or the other Fire Hawks. The equation of is as follows:where the is the jth prey in the search space.
- (6)
- Return to step 1, loop until certain conditions are met to obtain the global best solution, and the algorithm ends.
3. Enhanced Fire Hawk Optimization Algorithm
3.1. Adaptive Tent Chaos Mapping Strategy
3.2. Hunting Prey
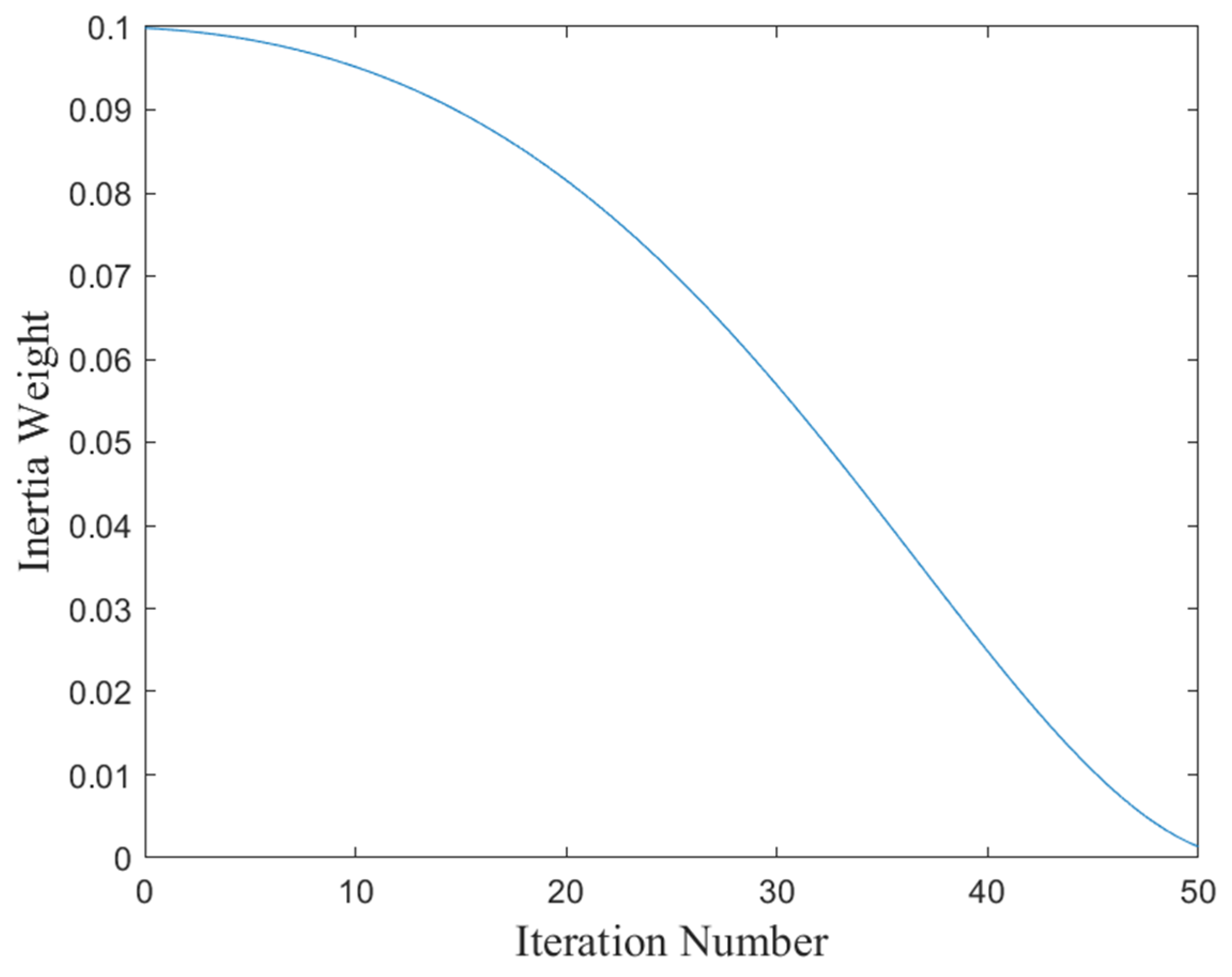
3.3. Adding the Inertia Weight
3.4. Enhanced Flee Strategy
4. Simulation Experiment
4.1. Experiment Setup
4.2. Performance Comparison
4.3. EFHO’s Scalability Test for Large-Scale Problems
5. High-Value Patents Recognition with Random Forest
5.1. Dataset
5.2. Data Preprocessing
5.3. Experiments and Results
- Experiment Setup
- 2.
- Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| EFHO vs. FHO (p) | EFHO vs. PSO (p) | EFHO vs. GWO (p) | EFHO vs. WOA (p) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 |
| F2 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 |
| F3 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 |
| F4 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 |
| F5 | 2.7455 × 10−3 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 |
| F6 | 2.4836 × 10−6 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 1.2377 × 10−6 | 9.1269 × 10−7 |
| F7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 1.0106 × 10−6 |
| F8 | 6.4886 × 10−6 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 2.7389 × 10−6 |
| F9 | 1.0000 × 100 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 8.9229 × 10−7 | 5.0000 × 10−1 |
| F10 | 1.0000 × 100 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 8.6624 × 10−7 | 3.8176 × 10−6 |
| F11 | 1.0000 × 100 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.7656 × 10−4 | 5.0000 × 10−1 |
| F12 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0621 × 10−2 | 7.1267 × 10−6 | 9.9493 × 10−1 |
| F13 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 | 9.1269 × 10−7 |
| F14 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0000 × 100 | 9.9550 × 10−1 | 1.0000 × 100 |
| F15 | 8.2267 × 10−1 | 8.7948 × 10−1 | 6.5960 × 10−1 | 9.8112 × 10−1 |
| F16 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0000 × 100 |
| F17 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0000 × 100 |
| F18 | 9.9996 × 10−1 | 1.0000 × 100 | 9.9999 × 10−1 | 1.0000 × 100 |
| F19 | 9.9837 × 10−1 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0000 × 100 |
| F20 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0000 × 100 |
| F21 | 9.4338 × 10−1 | 3.0623 × 10−2 | 8.1727 × 10−1 | 7.2097 × 10−2 |
| F23 | 9.5215 × 10−1 | 8.1727 × 10−1 | 1.0000 × 100 | 1.0621 × 10−2 |
References
- Hu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Lin, A. Evaluation and identification of potential high-value patents in the field of integrated circuits using a multidimensional patent indicators pre-screening strategy and machine learning approaches. J. Informetr. 2023, 17, 101406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Shi, F.; Tan, R. Evaluation and cultivation method of high-tech value patents for mechanical products. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, 0298144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artz, K.W.; Norman, P.M.; Hatfield, D.E.; Cardinal, L.B. A longitudinal study of the impact of r&d, patents, and product innovation on firm performance. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2010, 27, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Zhang, J. Hmfm: A method for identifying high-value patents by fusing multiple features. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 82, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, T. Configuration paths to high-value patents: Evidence from patents winning the china patent awards. Scientometrics 2024, 129, 2633–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, U.; Sterzi, V. Original but of low value: The paradox of science-industry collaborative patents. Rev. D’economie Ind. 2023, 183, 113–142. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.-j.; Cao, C.; Song, M. China’s agricultural patents: How has their value changed amid recent patent boom? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2014, 88, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.G.-L.; Huang, C.; Shen, H.; Mao, H. Assessing the value of china’s patented inventions. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 170, 120868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Tong, Y.; Wang, H. Analysis of key features of high-value patent based on lasso-logit. Financ. Eng. Risk Manag. 2023, 6, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Miric, M.; Jia, N.; Huang, K.G. Using supervised machine learning for large-scale classification in management research: The case for identifying artificial intelligence patents. Strateg. Manag. J. 2023, 44, 491–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, F.; Liu, Y.; Ran, L. A deep learning framework to early identify emerging technologies in large-scale outlier patents: An empirical study of cnc machine tool. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 969–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, S.; Shi, A. Research on transferable patent recognition based on machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Data Science and Information Technology, Shanghai, China, 23–25 July 2021; pp. 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Hido, S.; Suzuki, S.; Nishiyama, R.; Imamichi, T.; Takahashi, R.; Nasukawa, T.; Id´e, T.; Kanehira, Y.; Yohda, R.; Ueno, T.; et al. Modeling patent quality: A system for large-scale patentability analysis using text mining. Inf. Media Technol. 2012, 7, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-L.; Chang, P.-C.; Tsao, C.-C.; Fan, C.-Y. A patent quality analysis and classification system using self-organizing maps with support vector machine. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 41, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kwon, O.; Kim, M.; Kwon, D. Early identification of emerging technologies: A machine learning approach using multiple patent indicators. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2018, 127, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappey, A.J.; Trappey, C.V.; Govindarajan, U.H.; Sun, J.J. Patent value analysis using deep learning models—The case of iot technology mining for the manufacturing industry. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2019, 68, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, U.; Geum, Y. Identification of promising inventions considering the quality of knowledge accumulation: A machine learning approach. Scientometrics 2020, 125, 1877–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, S.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y. Multi-task learning based high-value patent and standard-essential patent identification model. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Jeong, B.; Yoon, J.; Coh, B.-Y.; Lee, J.-M. A novel approach to evaluating the business potential of intellectual properties: A machine learning-based predictive analysis of patent lifetime. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 145, 106544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ranjan, P.; Koley, A.; Danish, S. A new hybrid machine learning model for predicting the renewal life of patents. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, 0306186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, N.; Shreya, K.; Chinmay, A. Optimization of the random forest algorithm. In Advances in Data Science and Management: Proceedings of ICDSM 2019, Hunan, China, 22–23 February 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Shami, A. On hyperparameter optimization of machine learning algorithms: Theory and practice. Neurocomputing 2020, 415, 295–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G. A review of automatic selection methods for machine learning algorithms and hyper-parameter values. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinform. 2016, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolrasol, M.G.; Hussain, S.S.; Ustun, T.S.; Sarker, M.R.; Hannan, M.A.; Mohamed, R.; Ali, J.A.; Mekhilef, S.; Milad, A. Artificial neural networks based optimization techniques: A review. Electronics 2021, 10, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, D.K. A survey on the latest development of machine learning in genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization. In Optimization in Machine Learning and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 91–112. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Elaziz, M.; Dahou, A.; Abualigah, L.; Yu, L.; Alshinwan, M.; Khasawneh, A.M.; Lu, S. Advanced metaheuristic optimization techniques in applications of deep neural networks: A review. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 14079–14099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Talatahari, S.; Gandomi, A.H. Fire hawk optimizer: A novel metaheuristic algorithm. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 287–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishehgarkhaneh, M.B.; Azizi, M.; Basiri, M.; Moehler, R.C. Bim-based resource tradeoff in project scheduling using fire hawk optimizer (FHO). Buildings 2022, 12, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Yoo, J.; Ali, S.; Lansky, J.; Mildeova, S.; Yousefpoor, M.S.; Ahmed, O.H.; Rahmani, A.M.; Tightiz, L. A cluster-based trusted routing method using fire hawk optimizer (FHO) in wireless sensor networks (WSNs). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Anwaar, A.; Haider Bangyal, W.; Shakir, R.; Ur Rehman, N.; Qingjie, Z. An improved fire hawks optimizer for function optimization. In Advances in Swarm Intelligence, Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Swarm Intelligence 2023, Shenzhen, China, 14–18 July 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Baweja, D.; Jain, A.; Bhandari, A.; Bohat, V.K. Levy flight based fire hawk optimizer. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP), New Delhi, India, 27–29 September 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alonazi, M.; Alnfiai, M.M. Fire Hawk Optimizer with Deep Learning Enabled Human Activity Recognition. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 45, 3135–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.; Ismaeel, A.A.; El-Rifaie, A.M.; Hashim, F.A.; Bouaouda, A.; Hassan, A.Y.; Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Houssein, E.H. Evaluation of modified fire hawk optimizer for new modification in double diode solar cell model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajuria, R.; Bukya, M.; Lamba, R.; Kumar, R. Optimal parameter identification of solid oxide fuel cell using modified fire hawk algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hao, Z.; Sun, W. Enhancing sparrow search algorithm via multi-strategies for continuous optimization problems. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 102854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Deep, K.; Pant, M. Novel inertia weight strategies for particle swarm optimization. Memetic Comput. 2013, 5, 229–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherkhani, M.; Safabakhsh, R. A novel stability-based adaptive inertia weight for particle swarm optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 38, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Lu, H.; Xiang, L.; Shen, W. Adaptive simplified chicken swarm optimization based on inverted s-shaped inertia weight. Chin. J. Electron. 2022, 31, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; An, Q.; Lei, H.; Deng, Q.; Wang, G.-G. Survey of Lévy flight-based metaheuristics for optimization. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wu, H.; Peng, J. Improvement of electric fish optimization algorithm for standstill label combined with Levy flight strategy. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Liang, W.; Liang, X.; Yao, J. Intelligent quantification of natural gas pipeline defects using improved sparrow search algorithm and deep extreme learning machine. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 183, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, F.; Galea, M.; Henr´ıquez, C.; Arellano-Valle, R. Addressing non-normality in multivariate analysis using the t-distribution. AStA Adv. Stat. Anal. 2023, 107, 785–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganthan, P.N.; Hansen, N.; Liang, J.J.; Deb, K.; Chen, Y.-P.; Auger, A.; Tiwari, S. Problem definitions and evaluation criteria for the cec 2005 special session on real-parameter optimization. KanGAL Rep. 2005, 2005005, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Lin, A.; Holford, M.; Enerson, B.E.; Lu, B.; Lawton, M.P.; Floyd, E.; Zhao, H. Pathway analysis using random forests classification and regression. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2028–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, H.A.; Kalakech, A.; Steiti, A. Random forest algorithm overview. Babylon. J. Mach. Learn. 2024, 2024, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, S.A.; Ahmadi, K.; Daneshi, A. Application of support vector machine, random forest, and genetic algorithm optimized random forest models in groundwater potential mapping. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 2761–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, P.; Wright, M.N.; Boulesteix, A.-L. Hyperparameters and tuning strategies for random forest. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2019, 9, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumbado-Corrales, M.; Esquivel-Rodríguez, J. Evoseg: Automated electron microscopy segmentation through random forests and evolutionary optimization. Biomimetics 2021, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, S.; Qiu, Y. Optimization of random forest through the use of MVO, GWO and MFO in evaluating the stability of underground entry-type excavations. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 124, 104494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, G.; Wang, S. Hybrid random forest models optimized by sparrow search algorithm (SSA) and harris hawk optimization algorithm (HHO) for slope stability prediction. Transp. Geotech. 2024, 48, 101305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, M.; Cricelli, L. Indexes of patent value: A systematic literature review and classification. Knowl. Manag. Res. Pract. 2020, 18, 214–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Results | PSO | FHO | GWO | WOA | EFHO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Best | 5.86 × 10−1 | 1.4875 × 10−83 | 6.5908 × 10−29 | 1.0343 × 10−84 | 0 |
| Mean | 2.17 × 100 | 1.3582 × 10−69 | 1.1309 × 10−27 | 7.9071 × 10−73 | 0 | |
| Std | 8.76 × 10−1 | 7.0382 × 10−69 | 1.5143 × 10−27 | 4.1528 × 10−72 | 0 | |
| F2 | Best | 2.69 × 100 | 3.0352 × 10−21 | 1.5109 × 10−17 | 5.31 × 10−58 | 0 |
| Mean | 4.52 × 100 | 2.4074 × 10−19 | 8.9556 × 10−17 | 1.0498 × 10−50 | 0 | |
| Std | 1.24 × 100 | 3.3718 × 10−19 | 5.7898 × 10−17 | 4.4941 × 10−50 | 0 | |
| F3 | Best | 6.92 × 101 | 5.4193 × 10−82 | 9.7792 × 10−9 | 1.59 × 104 | 0 |
| Mean | 1.83 × 102 | 1.6619 × 10−69 | 4.6808 × 10−6 | 4.38 × 104 | 0 | |
| Std | 5.94 × 101 | 5.1581 × 10−69 | 7.6958 × 10−5 | 1.40 × 104 | 0 | |
| F4 | Best | 1.48 × 100 | 3.2607 × 10−35 | 1.2102 × 10−7 | 1.78 × 100 | 0 |
| Mean | 2.06 × 100 | 1.0124 × 10−30 | 7.4167 × 10−7 | 5.33 × 101 | 0 | |
| Std | 2.71 × 10−1 | 3.5189 × 10−30 | 6.7046 × 10−7 | 2.79 × 101 | 0 | |
| F5 | Best | 2.79 × 102 | 3.52 × 10−2 | 2.61 × 101 | 2.71 × 101 | 2.11 × 10−3 |
| Mean | 1.10 × 103 | 2.80 × 10−1 | 2.71 × 101 | 2.80 × 101 | 9.58 × 10−2 | |
| Std | 7.26 × 102 | 2.09 × 10−1 | 7.51 × 10−1 | 4.92 × 10−1 | 9.21 × 10−2 | |
| F6 | Best | 9.05 × 10−1 | 7.85 × 10−3 | 2.50 × 10−1 | 6.70 × 10−2 | 5.21 × 10−3 |
| Mean | 2.26 × 100 | 8.94 × 10−1 | 8.35 × 10−1 | 3.75 × 10−1 | 1.48 × 10−2 | |
| Std | 8.27 × 10−1 | 1.66 × 100 | 3.20 × 10−1 | 2.09 × 10−1 | 8.00 × 10−3 | |
| F7 | Best | 2.83 × 100 | 2.30 × 10−4 | 2.43 × 10−4 | 6.7084 × 10−5 | 5.5551 × 10−7 |
| Mean | 1.67 × 101 | 9.06 × 10−4 | 1.70 × 10−3 | 2.14 × 10−3 | 3.6111 × 10−5 | |
| Std | 1.37 × 101 | 4.29 × 10−4 | 9.03 × 10−4 | 1.99 × 10−3 | 3.6888 × 10−5 | |
| F8 | Best | 4.31 × 103 | 3.61 × 100 | 4.89 × 103 | 6.76 × 10−1 | 1.34 × 10−2 |
| Mean | 6.40 × 103 | 3.93 × 102 | 6.54 × 103 | 2.32 × 103 | 2.61 × 101 | |
| Std | 1.46 × 103 | 7.02 × 102 | 6.88 × 102 | 1.73 × 103 | 3.40 × 101 | |
| F9 | Best | 9.46 × 101 | 0 | 5.6843 × 10−14 | 0 | 0 |
| Mean | 1.60 × 102 | 0 | 1.93 × 100 | 0 | 0 | |
| Std | 3.98 × 101 | 0 | 3.31 × 100 | 0 | 0 | |
| F10 | Best | 2.06 × 100 | 4.4409 × 10−16 | 7.1498 × 10−14 | 4.4409 × 10−16 | 4.4409 × 10−16 |
| Mean | 2.78 × 100 | 4.4409 × 10−16 | 9.6959 × 10−14 | 3.4047 × 10−15 | 4.4409 × 10−16 | |
| Std | 3.75 × 10−1 | 0 × 100 | 1.4564 × 10−14 | 2.2625 × 10−15 | 0 | |
| F11 | Best | 3.07 × 10−2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mean | 1.48 × 10−1 | 0 | 5.12 × 10−3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Std | 4.71 × 10−2 | 0 | 8.16 × 10−3 | 0 | 0 | |
| F12 | Best | 5.78 × 10−3 | 4.95 × 10−4 | 6.43 × 10−3 | 5.25 × 10−3 | 3.53 × 10−3 |
| Mean | 3.31 × 10−2 | 1.47 × 10−3 | 4.08 × 10−2 | 2.31 × 10−2 | 2.35 × 10−2 | |
| Std | 2.57 × 10−2 | 6.48 × 10−4 | 2.23 × 10−2 | 1.13 × 10−2 | 6.51 × 10−3 | |
| F13 | Best | 2.26 × 10−1 | 3.96 × 10−3 | 4.08 × 10−1 | 1.19 × 10−1 | 7.9238 × 10−9 |
| Mean | 5.11 × 10−1 | 1.08 × 10−2 | 6.87 × 10−1 | 5.22 × 10−1 | 5.9291 × 10−7 | |
| Std | 2.13 × 10−1 | 4.94 × 10−3 | 2.38 × 10−1 | 2.44 × 10−1 | 6.9933 × 10−7 | |
| F14 | Best | 0 × 100 | 1.7555 × 10−8 | 1.8985 × 10−11 | 1.0154 × 10−11 | 1.98 × 100 |
| Mean | 2.00 × 100 | 5.71 × 10−1 | 3.46 × 100 | 1.83 × 100 | 6.12 × 100 | |
| Std | 2.70 × 100 | 6.20 × 10−1 | 4.35 × 100 | 2.96 × 100 | 1.31 × 100 | |
| F15 | Best | 1.34 × 10−4 | 1.3838 × 10−5 | 6.009 × 10−10 | 1.667 × 10−6 | 1.06 × 10−4 |
| Mean | 5.91 × 10−4 | 9.51 × 10−4 | 2.71 × 10−3 | 3.87 × 10−4 | 9.25 × 10−4 | |
| Std | 1.48 × 10−4 | 1.94 × 10−3 | 6.80 × 10−3 | 3.76 × 10−4 | 6.42 × 10−4 | |
| F16 | Best | 2.2204 × 10−15 | 2.1008 × 10−7 | 3.8243 × 10−10 | 6.9722 × 10−14 | 7.1983 × 10−6 |
| Mean | 2.4351 × 10−15 | 9.9372 × 10−6 | 2.3649 × 10−8 | 1.1901 × 10−9 | 3.53 × 10−3 | |
| Std | 3.9858 × 10−17 | 1.0288 × 10−5 | 2.6884 × 10−8 | 4.2983 × 10−9 | 3.65 × 10−3 | |
| F17 | Best | 1.6653 × 10−16 | 2.4405 × 10−5 | 7.4074 × 10−8 | 1.7071 × 10−11 | 4.7274 × 10−5 |
| Mean | 1.6653 × 10−16 | 3.77 × 10−4 | 2.1562 × 10−6 | 5.8586 × 10−6 | 6.94 × 10−3 | |
| Std | 0 × 100 | 3.50 × 10−4 | 2.0217 × 10−6 | 1.1906 × 10−5 | 7.36 × 10−3 | |
| F18 | Best | 2.2204 × 10−15 | 1.2711 × 10−5 | 1.4177 × 10−7 | 7.6656 × 10−8 | 3.0105 × 10−6 |
| Mean | 1.0214 × 10−14 | 1.23 × 10−3 | 3.0221 × 10−5 | 5.6182 × 10−5 | 1.03 × 10−1 | |
| Std | 4.704 × 10−15 | 1.08 × 10−3 | 4.3207 × 10−5 | 1.01 × 10−4 | 3.54 × 10−1 | |
| F19 | Best | 3.9968 × 10−15 | 2.34 × 10−4 | 1.9841 × 10−6 | 3.8805 × 10−7 | 6.17 × 10−3 |
| Mean | 5.1514 × 10−15 | 1.59 × 10−2 | 1.09 × 10−3 | 5.90 × 10−3 | 1.23 × 10−1 | |
| Std | 1.907 × 10−15 | 5.06 × 10−2 | 2.22 × 10−3 | 7.07 × 10−3 | 1.32 × 10−1 | |
| F20 | Best | 7.0895 × 10−10 | 1.96 × 10−2 | 1.582 × 10−6 | 5.8291 × 10−5 | 3.13 × 10−1 |
| Mean | 3.96 × 10−2 | 1.25 × 10−1 | 7.13 × 10−2 | 8.22 × 10−2 | 7.69 × 10−1 | |
| Std | 5.60 × 10−2 | 1.11 × 10−1 | 8.25 × 10−2 | 9.90 × 10−2 | 3.33 × 10−1 | |
| F21 | Best | 1.7764 × 10−15 | 1.07 × 10−1 | 4.06 × 10−4 | 4.41 × 10−4 | 1.77 × 10−4 |
| Mean | 3.34 × 100 | 3.78 × 10−1 | 1.10 × 100 | 2.30 × 100 | 8.31 × 10−1 | |
| Std | 3.44 × 100 | 1.93 × 10−1 | 2.22 × 100 | 2.86 × 100 | 7.97 × 10−1 | |
| F22 | Best | 0 × 100 | 7.39 × 10−2 | 4.29 × 10−4 | 3.47 × 10−4 | 1.98 × 10−2 |
| Mean | 7.87 × 10−1 | 4.85 × 10−1 | 1.73 × 10−3 | 2.09 × 100 | 8.65 × 10−1 | |
| Std | 2.03 × 100 | 2.23 × 10−1 | 7.32 × 10−4 | 2.74 × 100 | 7.89 × 10−1 | |
| F23 | Best | 8.3489 × 10−14 | 1.13 × 10−1 | 9.8691 × 10−5 | 1.20 × 10−3 | 1.08 × 10−2 |
| Mean | 1.24 × 100 | 5.42 × 10−1 | 1.82 × 10−1 | 2.81 × 100 | 1.12 × 100 | |
| Std | 2.51 × 100 | 2.95 × 10−1 | 9.70 × 10−1 | 3.25 × 100 | 9.19 × 10−1 |
| Comparison | Functions with p < 0.05 (n/23) | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| EFHO vs. FHO | 9/23 | 39.13 |
| EFHO vs. PSO | 14/23 | 60.87 |
| EFHO vs. GWO | 13/23 | 56.52 |
| EFHO vs. WOA | 12/23 | 52.17 |
| EFHO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 Dimensions | 1000 Dimensions | |||
| Mean | Std | Mean | Std | |
| F1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| F2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| F3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| F4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| F5 | 7.76 × 100 | 4.09 × 101 | 9.48 × 10−2 | 1.28 × 10−1 |
| F6 | 6.61 × 10−3 | 6.66 × 10−3 | 1.72 × 10−2 | 9.96 × 10−3 |
| F7 | 3.3296 × 10−5 | 4.4944 × 10−5 | 2.9348 × 10−5 | 2.603 × 10−5 |
| F8 | 1.65 × 101 | 1.18 × 101 | 2.55 × 101 | 3.47 × 101 |
| F9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| F10 | 4.4409 × 10−16 | 0 | 4.4409 × 10−16 | 0 |
| F11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| F12 | 1.62 × 10−2 | 4.78 × 10−3 | 2.64 × 10−2 | 5.58 × 10−3 |
| F13 | 5.5754 × 10−6 | 1.2471 × 10−5 | 2.8439 × 10−7 | 4.072 × 10−7 |
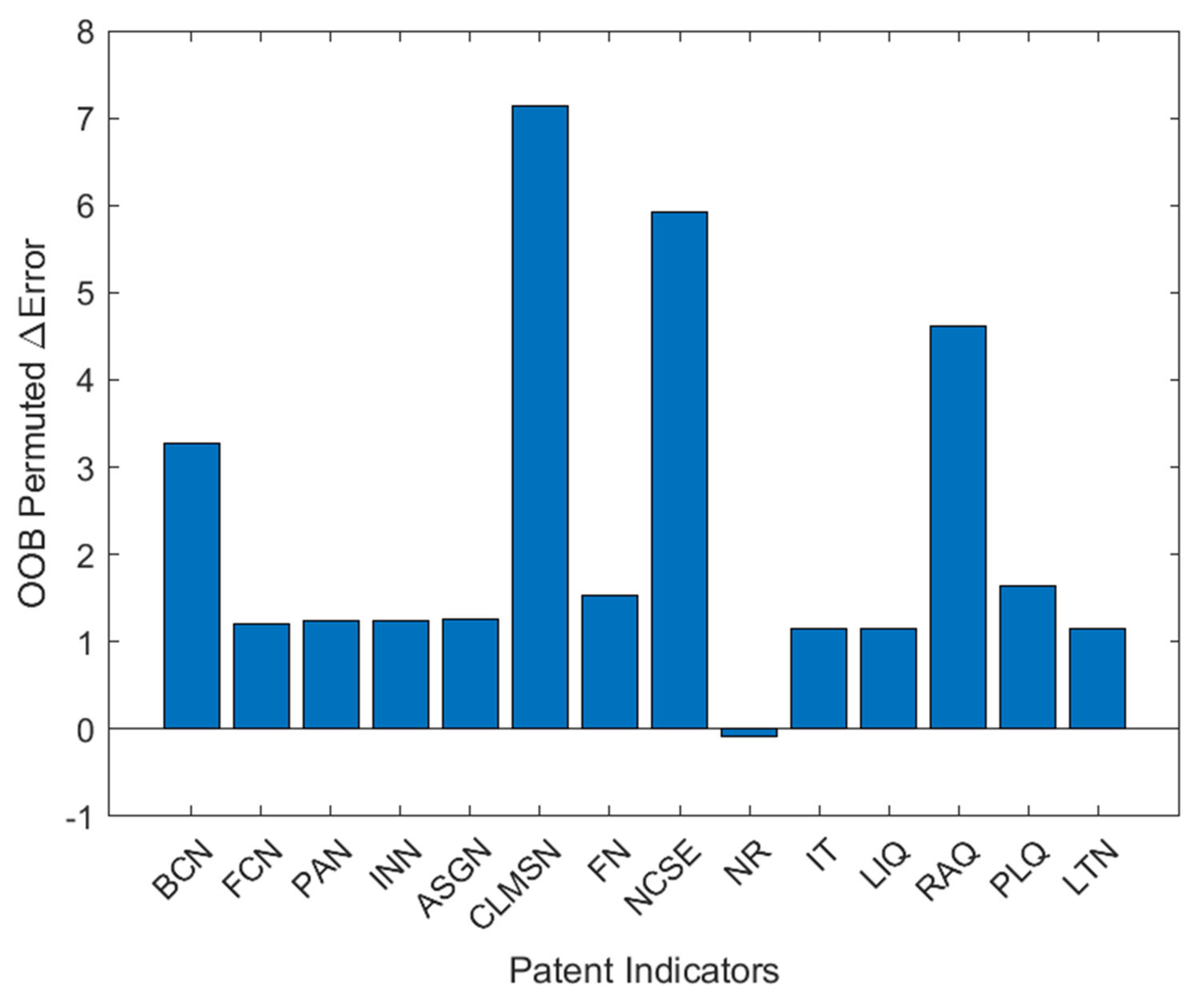
| No. | Abbr. | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | BCN | The backward citation number |
| 2 | FCN | The forward citation number |
| 3 | PAN | The applicants number |
| 4 | INN | The inventors number |
| 5 | ASGN | The patent holders number |
| 6 | CLMSN | The claims number |
| 7 | FN | The patent family number |
| 8 | NCSE | The country’s number belongs to the same family |
| 9 | NR | The reexaminations number |
| 10 | IT | The invalidation times |
| 11 | LIQ | The licensing frequency |
| 12 | RAQ | The assignments number |
| 13 | PLQ | The pledging frequency |
| 14 | LTN | The lawsuits number |
| Algorithm | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | F1 Measure | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | 0.918 | 0.910 | 0.874 | 0.891 | 0.950 |
| LR | 0.950 | 0.898 | 0.953 | 0.925 | 0.966 |
| RF | 0.958 | 0.918 | 0.967 | 0.942 | 0.988 |
| SVM | 0.943 | 0.880 | 0.964 | 0.920 | 0.977 |
| BP | 0.947 | 0.883 | 0.971 | 0.925 | 0.966 |
| EFHO-BP | 0.959 | 0.950 | 0.963 | 0.960 | 0.985 |
| EFHO-RF | 0.966 | 0.958 | 0.970 | 0.963 | 0.990 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, X.; Li, H.; Wang, S. High-Value Patents Recognition with Random Forest and Enhanced Fire Hawk Optimization Algorithm. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090561
Yao X, Li H, Wang S. High-Value Patents Recognition with Random Forest and Enhanced Fire Hawk Optimization Algorithm. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(9):561. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090561
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Xiaona, Huijia Li, and Sili Wang. 2025. "High-Value Patents Recognition with Random Forest and Enhanced Fire Hawk Optimization Algorithm" Biomimetics 10, no. 9: 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090561
APA StyleYao, X., Li, H., & Wang, S. (2025). High-Value Patents Recognition with Random Forest and Enhanced Fire Hawk Optimization Algorithm. Biomimetics, 10(9), 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090561






