Effect of Surfactant on Bubble Formation on Superhydrophobic Surface in Quasi-Static Regime
Abstract
1. Introduction
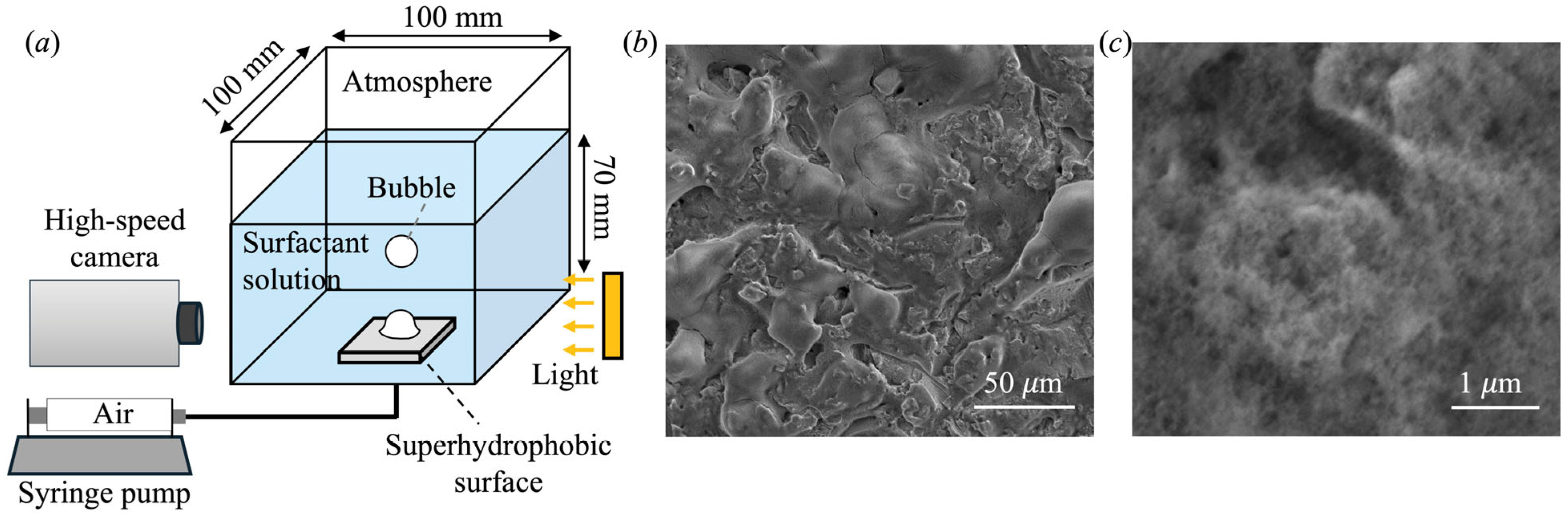
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- As the surfactant concentration increased, all bubble geometrical parameters, including the bubble detached size, decreased.
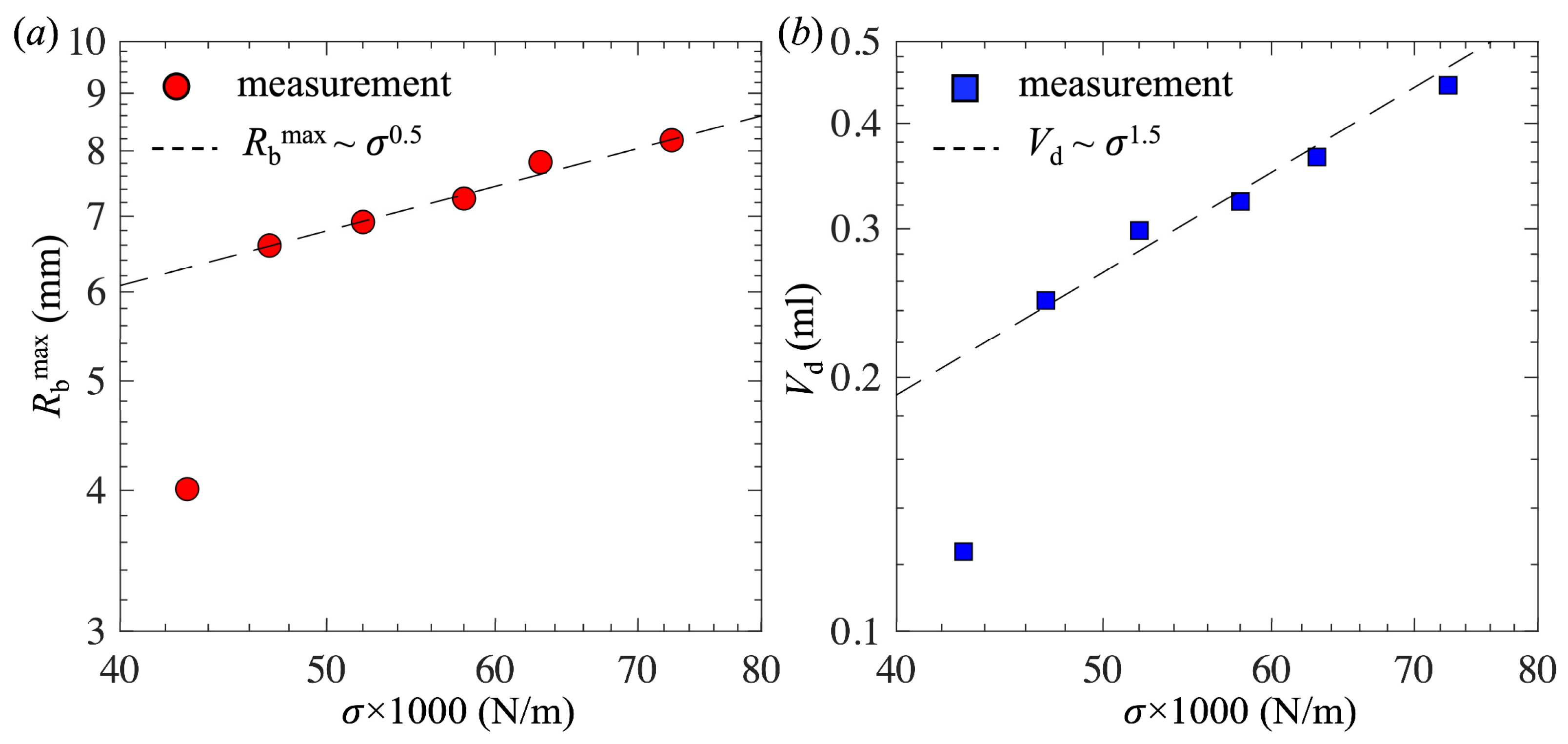
- For low surfactant concentrations, θ0 remained nearly constant, bubble shapes at different concentrations were self-similar, and Rdmax and Vd decreased following the scaling laws Rdmax~σ1/2 and Vd~σ3/2, respectively.
- For high surfactant concentrations, θ0 was greatly reduced, and Rdmax and Vd decreased due to the combined effects of reduced surface tension and a lower static contact angle.
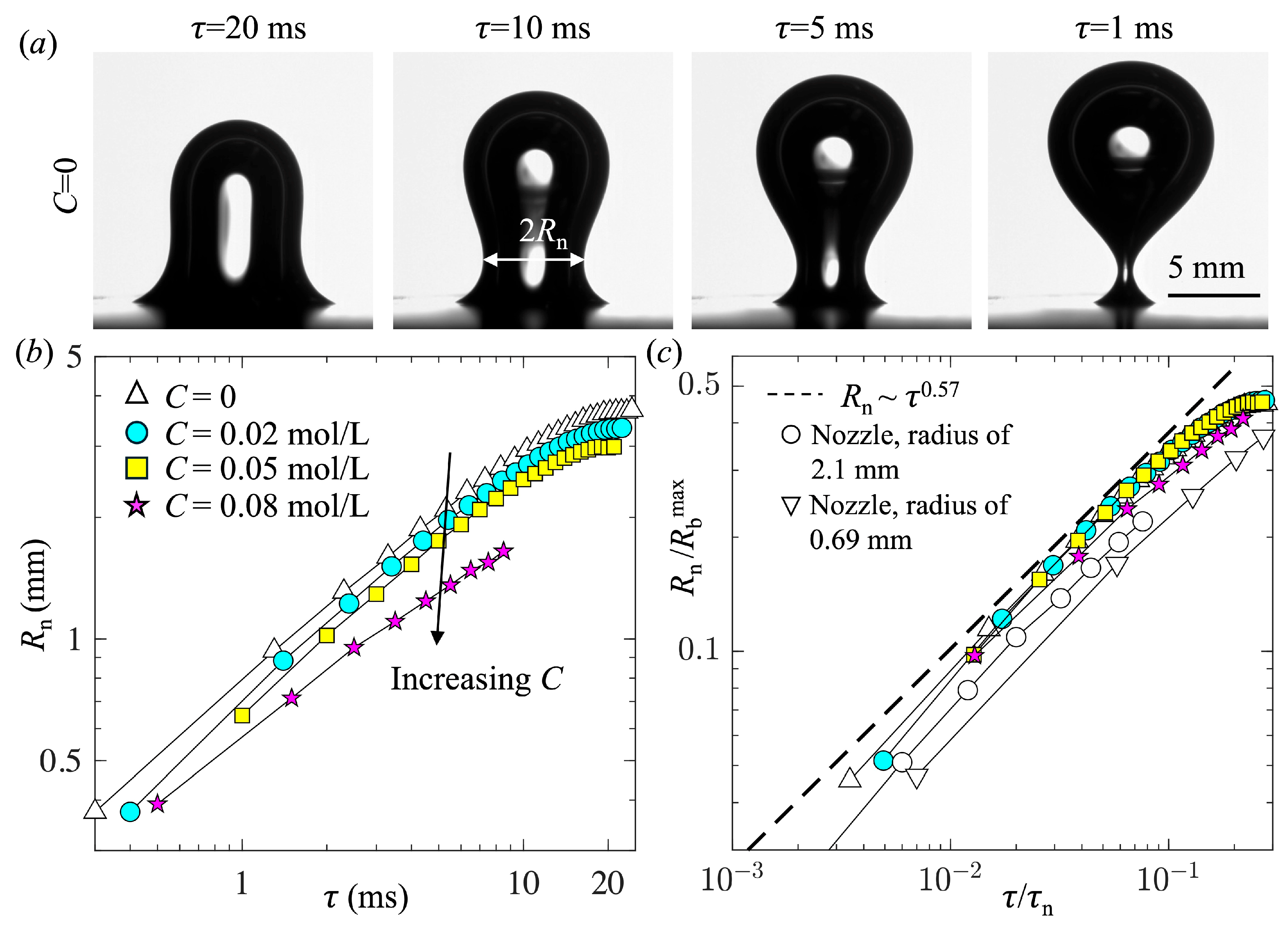
- The surfactant had little impact on the dynamics of bubble pinch-off, except for reducing the time and length scales. The minimum neck radius followed a power-law relation, Rn~τ0.57, similar to that observed for bubble pinch-off from a nozzle.
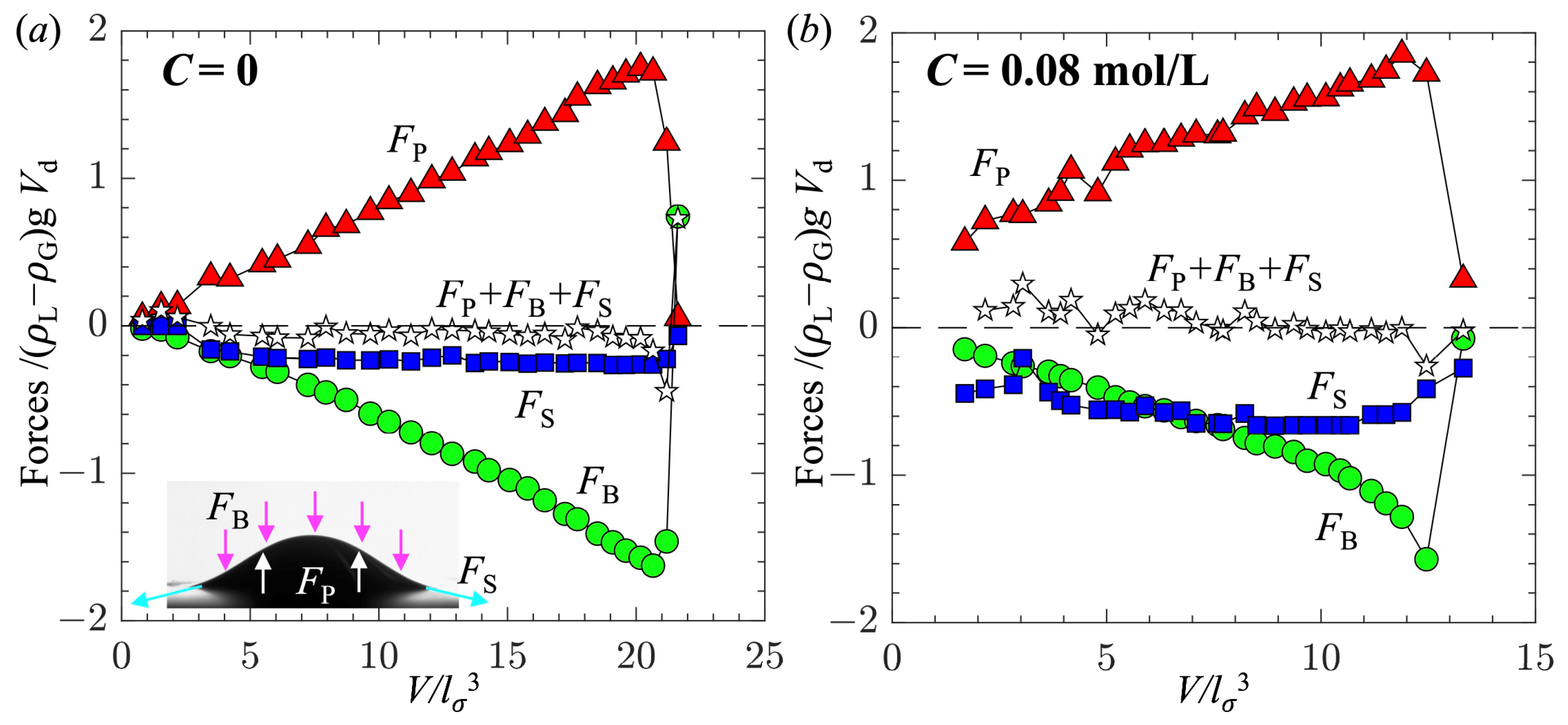
- The surfactant had negligible impact on the forces acting on the bubble, except for reducing their magnitudes. The growth of the bubble was governed by a balance between surface tension and hydrostatic pressure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Searle, M.; Emerson, P.; Crockett, J.; Maynes, D. Influence of microstructure geometry on pool boiling at superhydrophobic surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 127, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, A.R.; Jenkins, J.; Kim, C.-J.; Attinger, D. Boiling heat transfer on superhydrophilic, superhydrophobic, and superbiphilic surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 57, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.S.; Di Sia, G.; Hung, Y.M. Extraordinry enhancement of nucleate pool boiling on intrinsically biphilic graphene nanostructured surfaces. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 218, 119354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, S.H.; Zahidi, A.A.A.; Muradoglu, M.; Cheong, B.H.P.; Ng, T.W. Plastron-Mediated Growth of Captive Bubbles on Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6695–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, Z.; Shi, L.A.; Jiao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Chu, J.; Wu, D.; Jiang, L. Remote Photothermal Actuation of Underwater Bubble toward Arbitrary Direction on Planar Slippery Fe3O4-Doped Surfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, S.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Wu, D.; Chu, J. Switchable Underwater Bubble Wettability on Laser-Induced Titanium Multiscale Micro-/Nanostructures by Vertically Crossed Scanning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16867–16873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadshahi, S.; Breveleri, J.; Ling, H. Fabrication and characterization of super-hydrophobic surfaces based on sandpapers and nano-particle coatings. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 666, 131358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadshahi, S.; O’Coin, D.; Ling, H. Impact of sandpaper grit size on drag reduction and plastron stability of super-hydrophobic surface in turbulent flows. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 025139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, N. Experimental investigation on the modified coherent structures in the turbulent boundary layer by superhydrophobic surface. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 035195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Srinivasan, S.; Golovin, K.; McKinley, G.H.; Tuteja, A.; Katz, J. High-resolution velocity measurement in the inner part of turbulent boundary layers over super-hydrophobic surfaces. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 801, 670–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Ji, J.; Tao, T.; Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Jiao, Y.; Liu, K. Underwater Drag Reduction and Buoyancy Enhancement on Biomimetic Antiabrasive Superhydrophobic Coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48270–48280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elius, M.; Richard, S.; Boyle, K.; Chang, W.S.; Moisander, P.H.; Ling, H. Impact of gas bubbles on bacterial adhesion on super-hydrophobic aluminum surfaces. Res. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 15, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Pei, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Han, X.; Guo, Z. Hierarchical dandelion-like superhydrophobic surfaces with excellent stability and photothermal performance for efficient anti-/deicing. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 510, 161582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wu, R.; Gu, X.K.; Zhao, C.Y. Pool boiling inside micro-nano composite pores: Thermofluids behaviors and heat transfer enhancement. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2024, 124, 093508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, C.; Wang, Q.; Smith, W.; Liu, W.; Walmsley, A.D. Cleaning effects due to shape oscillation of bubbles over a rigid boundary. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 123335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.B.; Lu, Y.W. Applications of textured surfaces on bubble trapping and degassing for microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2014, 17, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Lu, J.; Tryggvason, G. A numerical study of the capture of hydrophobic particles by a buoyant bubble. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 013343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roovers, S.; Segers, T.; Lajoinie, G.; Deprez, J.; Versluis, M.; De Smedt, S.C.; Lentacker, I. The Role of Ultrasound-Driven Microbubble Dynamics in Drug Delivery: From Microbubble Fundamentals to Clinical Translation. Langmuir 2019, 35, 10173–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.A.; Joshi, J.B. Bubble Formation and Bubble Rise Velocity in Gas−Liquid Systems: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 5873–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, A.; Huang, Q.; Yang, C. Theoretical model for predicting bubble formation from submerged orifices. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaka, K.; Tsuge, H. Bubble formation at a single orifice in non-Newtonian liquids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1991, 46, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, S.; Wen, D. Spreading of triple line and dynamics of bubble growth inside nanoparticle dispersions on top of a substrate plate. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 362, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vafaei, S.; Wen, D. Effect of Gold Nanoparticles on the Dynamics of Gas Bubbles. Langmuir 2010, 26, 6902–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, B.; Yang, Z.; Feng, J. Oil-coated bubble formation from submerged coaxial orifices. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2021, 6, 33602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ji, B.; Zhao, C.; Bo, H. Bubble formation from a submerged orifice in a thin liquid layer: Detachment and bursting. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 013305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Pang, M. Influence of wettability and surface tension on bubble formation from a needle. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2025, 20, e3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Mo, D.; Moon, S.; Janowitz, J.; Ringle, D.; Mays, D.; Diddle, A.; Rexroat, J.; Lee, E.; Luo, T. Bubble nucleation and growth on microstructured surfaces under microgravity. Npj Microgravity 2024, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarian, A.; Sun, B.; Soria, J. Effects of nozzle size and surface hydrophobicity on microbubble generation. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsandi, H.; Smit, W.J.; Kong, G.; Baltussen, M.W.; Peters, E.A.J.F.; Kuipers, J.A.M. Influence of wetting conditions on bubble formation from a submerged orifice. Exp. Fluids 2020, 61, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corchero, G.; Medina, A.; Higuera, F.J. Effect of wetting conditions and flow rate on bubble formation at orifices submerged in water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 290, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhu, X.; Liao, Q.; Wang, H.; Ding, Y.-D. Dynamics of bubble formation and detachment from an immersed micro-orifice on a plate. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 3205–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, E.; Jose Kalayathine, J.; Reinecke, S.F.; Hampel, U. Dynamics of bubble formation at micro-orifices under constant gas flow conditions. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2020, 132, 103407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafizadeh, P.; Sattari, A.; Hosseini-Doost, S.E.; Nouri, A.G.; Ashjaee, M. Effect of orifice shape on bubble formation mechanism. Meccanica 2018, 53, 2461–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J. Experimental study of bubbling regimes on submerged micro-orifices. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 111, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Qu, C.; Zhang, Y. Experimental study and numerical simulation of periodic bubble formation at submerged micron-sized nozzles with constant gas flow rate. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 168, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, H.N.; Prosperetti, A. Dynamics of bubble growth and detachment from a needle. J. Fluid Mech. 1993, 257, 111–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, P.; Song, Y.; Chai, L.; Zhou, C.Q. A viewpoint on the dynamics of bubble formation from a submerged nozzle. Eur. J. Mech.-B/Fluids 2019, 78, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, D.; Biswas, G.; Durst, F.; Kolobaric, V. Quasi-static bubble formation on submerged orifices. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 48, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, K.J.; Velagala, S.; Easo, D.A.; Saleem, M.A.; Krause, U. Influence of Wettability on Bubble Formation from Submerged Orifices. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 4071–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnyloskurenko, S.; Byakova, A.; Nakamura, T.; Raychenko, O. Influence of wettability on bubble formation in liquid. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 2437–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Rubio, M.; Bolaños-Jiménez, R.; Martínez-Bazán, C.; Muñoz-Hervás, J.C.; Sevilla, A. Superhydrophobic substrates allow the generation of giant quasi-static bubbles. J. Fluid Mech. 2021, 912, A25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.; Cautela, R.; Moita, A.; Moreira, A. Effect of the Size of the Superhydrophobic Regions of Biphilic Surfaces on the Bubble Dynamics. Symmetry 2023, 15, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Cai, C.; Chen, W.; Pan, C.; Liu, Y. Control of the shape of bubble growth on underwater substrates with different sizes of superhydrophobic circles. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 067110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Coin, D.; Ling, H. Dynamics of bubble formation on superhydrophobic surface under a constant gas flow rate at quasi-static regime. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 083303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breveleri, J.; Mohammadshahi, S.; Dunigan, T.; Ling, H. Plastron restoration for underwater superhydrophobic surface by porous material and gas injection. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 676, 132319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Coin, D.; Ling, H. Effect of gas flow rate on bubble formation on superhydrophobic surface. Droplet 2025, 4, e148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Nakajima, M.; Ichikawa, S.; Nakamura, N.; Roy, P.; Okadome, H.; Shiina, T. Effects of surfactant and electrolyte concentrations on bubble formation and stabilization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 332, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loubière, K.; Hébrard, G. Influence of liquid surface tension (surfactants) on bubble formation at rigid and flexible orifices. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2004, 43, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukizaki, M.; Baba, Y. Effect of surfactant type on microbubble formation behavior using Shirasu porous glass (SPG) membranes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 326, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Uddin, M.d.H.; Yang, H.; Toikka, G.; Ducker, W.; Maeda, N. Effects of Surfactants on the Formation and the Stability of Interfacial Nanobubbles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 10471–10477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-H.; Lee, W.-H.; Yang, Y.-M.; Chang, C.-H.; Maa, J.-R. Bubble Formation at an Orifice in Surfactant Solutions under Constant-Flow Conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, R.; Das, M.K. Effects of surface-active agents on bubble growth and detachment from submerged orifice. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 179, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-M.; Yeh, S.-J.; Hsiung, C.-K.; Chien, C.-L.; Chang, C.-H.; Maa, J.-R. Bubble Formation in Catanionic Surfactant Solutions under Constant-Flow Conditions. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2001, 34, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurimoto, R.; Yasuda, T.; Minagawa, H. Effects of surfactant on quasi-static bubble growth from an orifice. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2016, 104, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.; Sadhal, S.S. Effect of surfactants on the growth and departure of bubbles from solid surfaces. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 50, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R.; Wassink, J.; Amirfazli, A. Effect of Surfactants on Wetting of Super-Hydrophobic Surfaces. Langmuir 2004, 20, 9657–9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.-M.; Sheng, Y.-J.; Chen, H.; Tsao, H.-K. From superhydrophobic to superhydrophilic surfaces tuned by surfactant solutions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 094108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainerman, V.B. Dynamic Surface Tension and kinetics of Adsorption in Solutions of Normal Alcohls. Kolloid. Z. 1982, 44, 598–603. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, S.; Uda, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Matsumoto, Y. Behavior of a Rising Bubble in Water with Surfactant Dissolution: 1st Report, Steady Behavior. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. Ser. B 2003, 69, 2192–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Daerr, A.; Mogne, A. Pendent_Drop: An ImageJ Plugin to Measure the Surface Tension from an Image of a Pendent Drop. J. Open Res. Softw. 2016, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, M.J.; Kippax, P.G. Surface tensions of mixed aqueous solutions of tert-butanol and n-pentanol. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 262, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagawa, Y.; Takagi, S.; Matsumoto, Y. Surfactant effect on path instability of a rising bubble. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 738, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.-L.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Wang, M.-J.; Lin, S.-Y. A simple method for measuring the superhydrophobic contact angle with high accuracy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2010, 81, 065105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tate, T. On the magnitude of a drop of liquid formed under different circumstances. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1864, 27, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoroddsen, S.T.; Etoh, T.G.; Takehara, K. Experiments on bubble pinch-off. Phys. Fluids 2007, 19, 042101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, J.C.; Waldrep, R.; Taborek, P. Scaling and Instabilities in Bubble Pinch-Off. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 184502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, N.C.; Møller, P.; Zhang, W.W.; Nagel, S.R. Breakup of Air Bubbles in Water: Memory and Breakdown of Cylindrical Symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 144503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.; Hua, J. Numerical studies of bubble necking in viscous liquids. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 77, 66303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


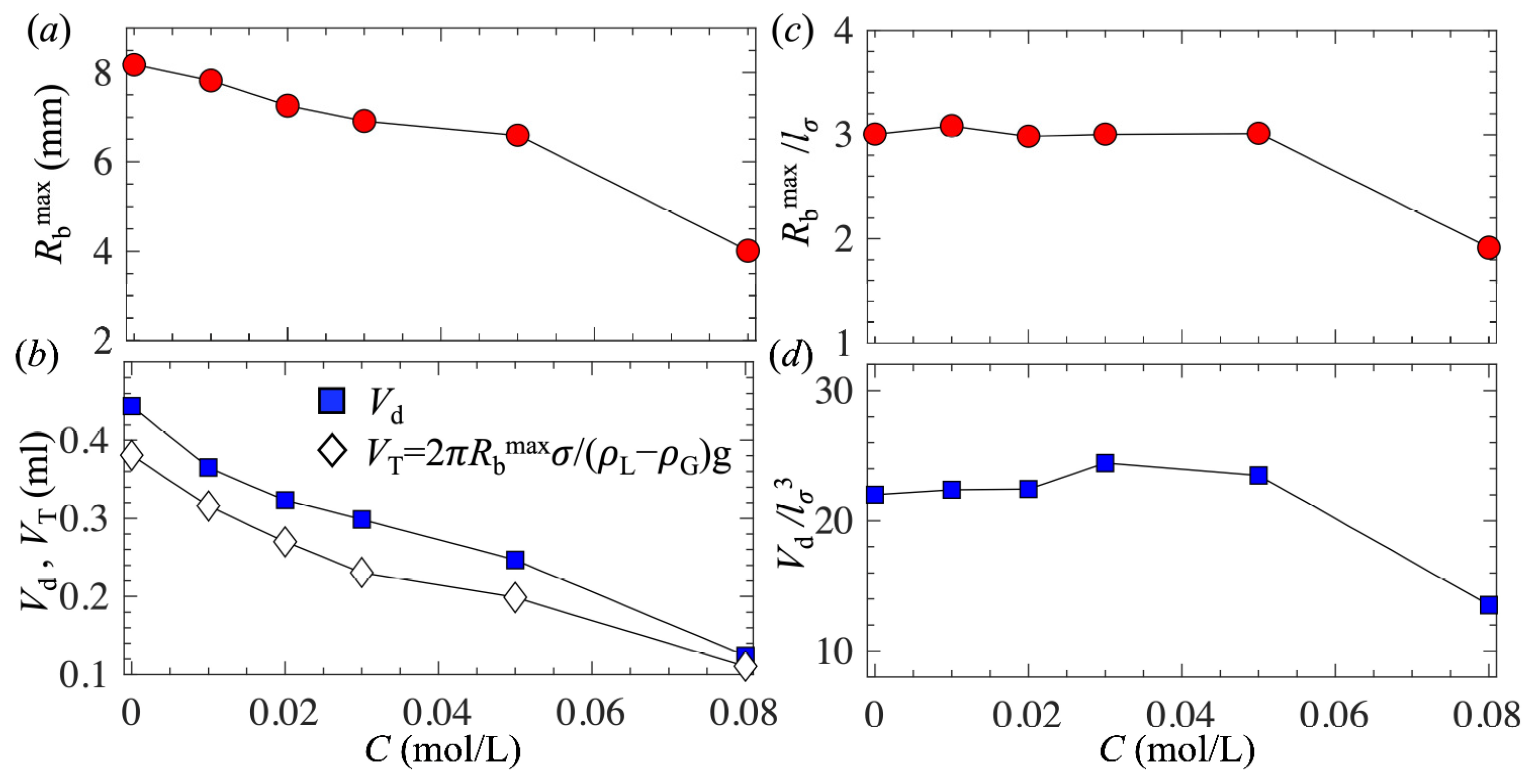


| C (mol/L) | σ (mN/m) | θ0 (°) | Rbmax (mm) | Vd (mL) | lσ (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 72 | 159 | 8.2 | 0.44 | 2.7 |
| 0.01 | 63 | 159 | 7.8 | 0.37 | 2.5 |
| 0.02 | 58 | 158 | 7.3 | 0.32 | 2.4 |
| 0.03 | 52 | 156 | 6.9 | 0.30 | 2.3 |
| 0.05 | 47 | 155 | 6.6 | 0.25 | 2.2 |
| 0.08 | 43 | 131 | 4.0 | 0.12 | 2.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ling, H.; Ready, J.; O’Coin, D. Effect of Surfactant on Bubble Formation on Superhydrophobic Surface in Quasi-Static Regime. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060382
Ling H, Ready J, O’Coin D. Effect of Surfactant on Bubble Formation on Superhydrophobic Surface in Quasi-Static Regime. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(6):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060382
Chicago/Turabian StyleLing, Hangjian, John Ready, and Daniel O’Coin. 2025. "Effect of Surfactant on Bubble Formation on Superhydrophobic Surface in Quasi-Static Regime" Biomimetics 10, no. 6: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060382
APA StyleLing, H., Ready, J., & O’Coin, D. (2025). Effect of Surfactant on Bubble Formation on Superhydrophobic Surface in Quasi-Static Regime. Biomimetics, 10(6), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10060382





