Recent Advancements in Humanoid Robot Heads: Mechanics, Perception, and Computational Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
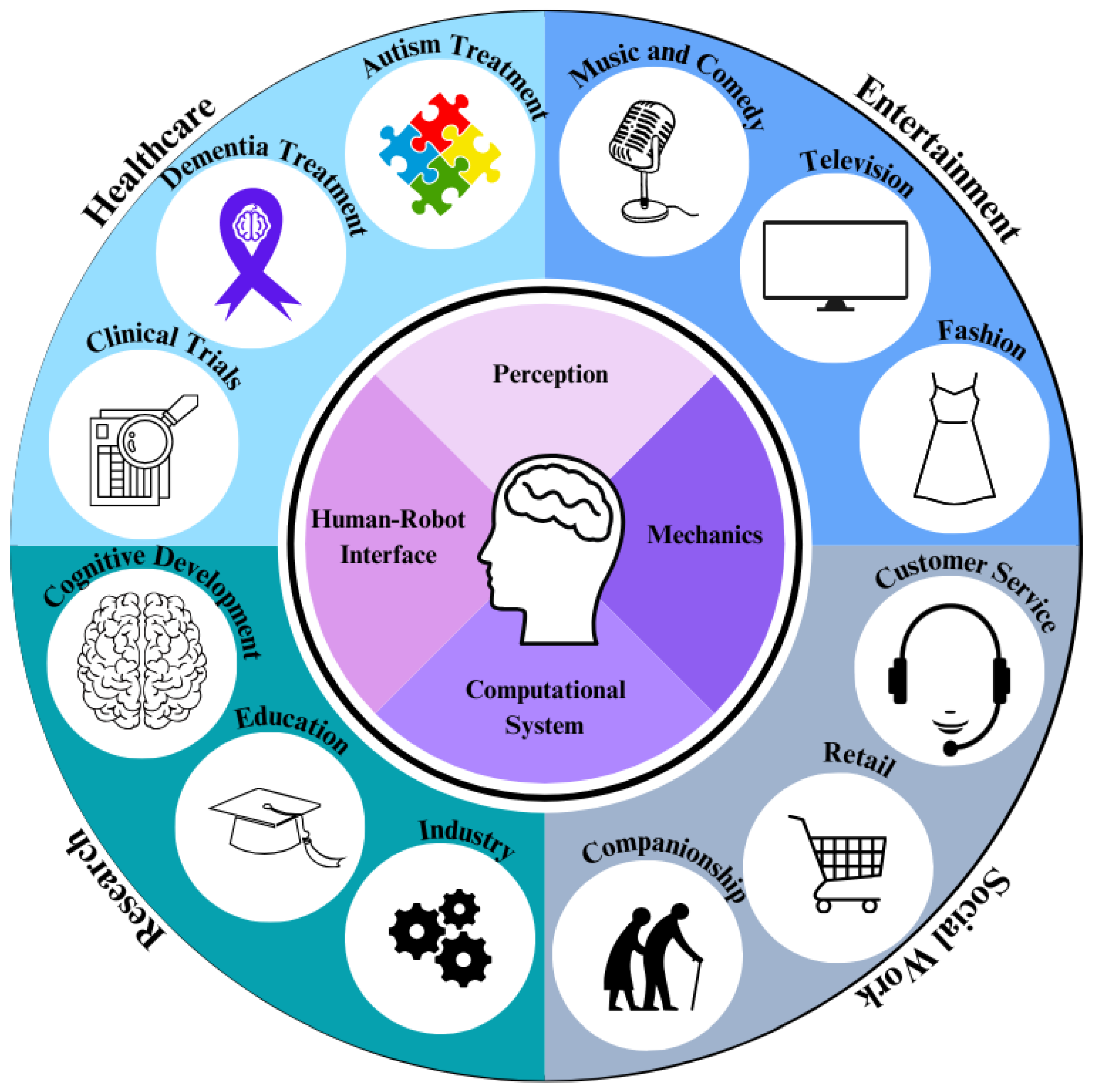
3. Application and Marketplace
3.1. Healthcare and Communication
3.2. Research Platforms
3.3. Entertainment
3.4. Other Applications
3.5. Commercial Study
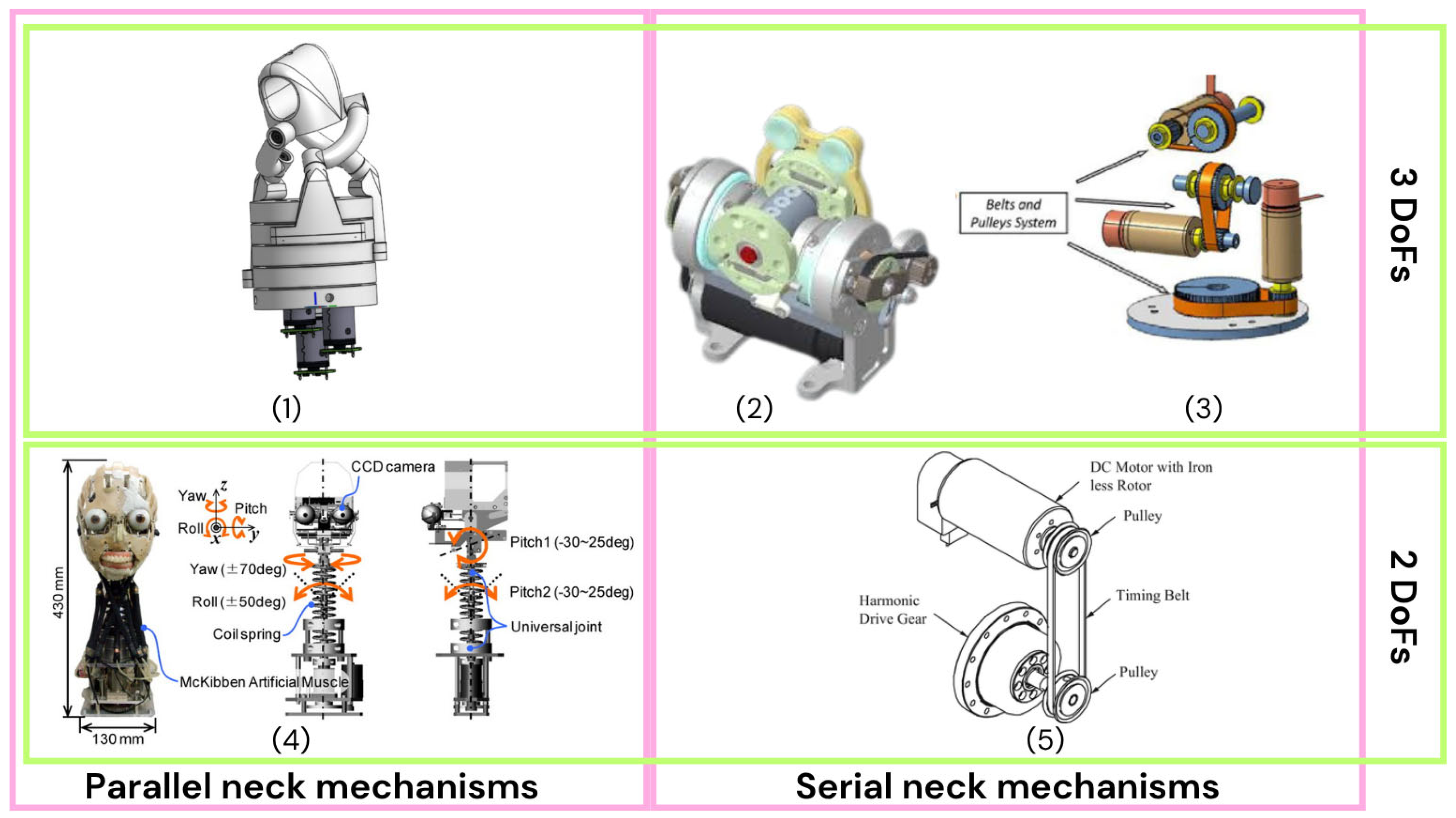
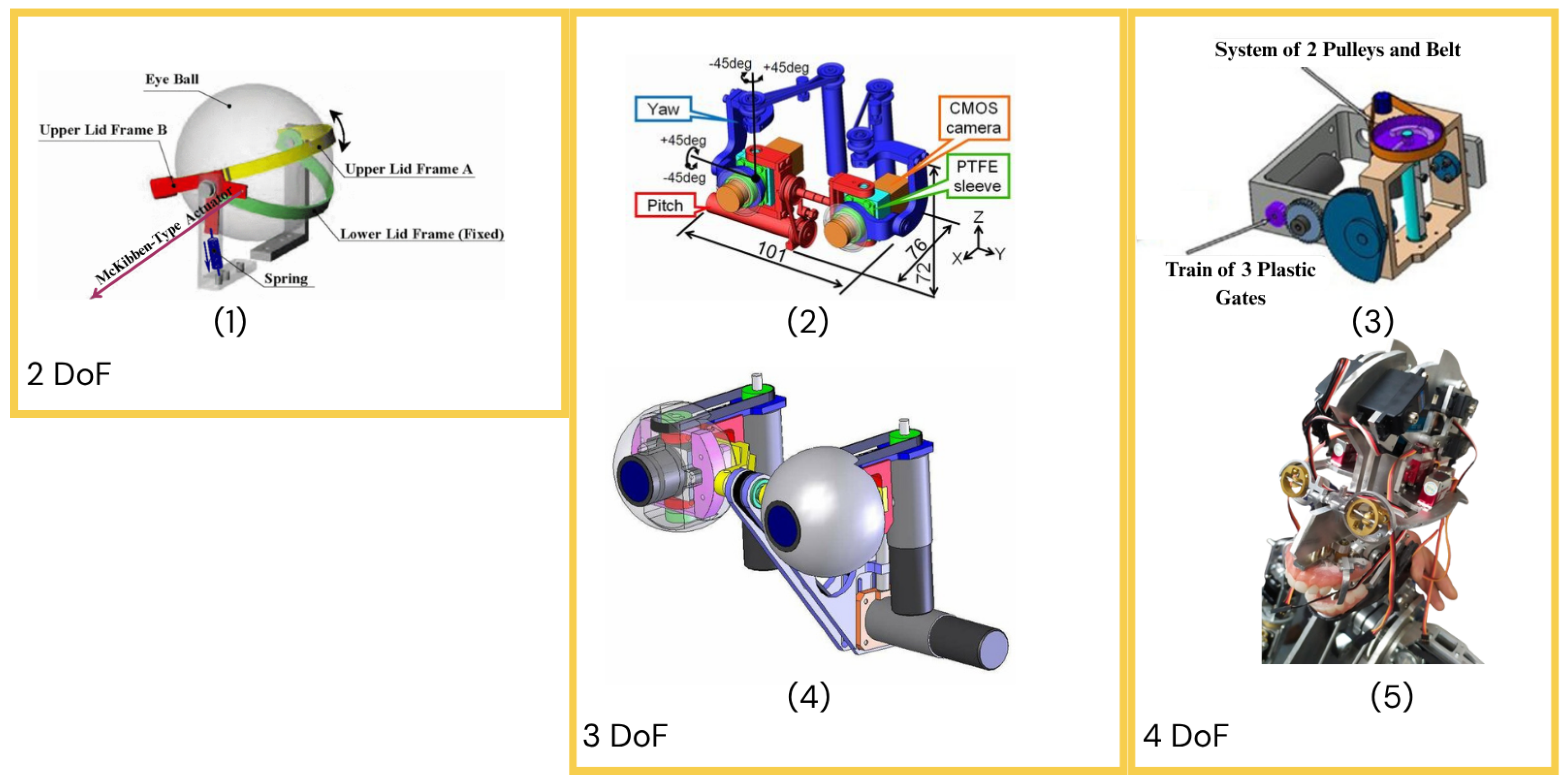
4. Mechanical Structure
4.1. Artificial Facial Skin and Structural Materials
4.2. Neck Mechanism Mechanical Design
4.3. Eye Mechanism Mechanical Design
4.4. Emotional Expressive Capabilities
4.5. Synthesis and Open Problems
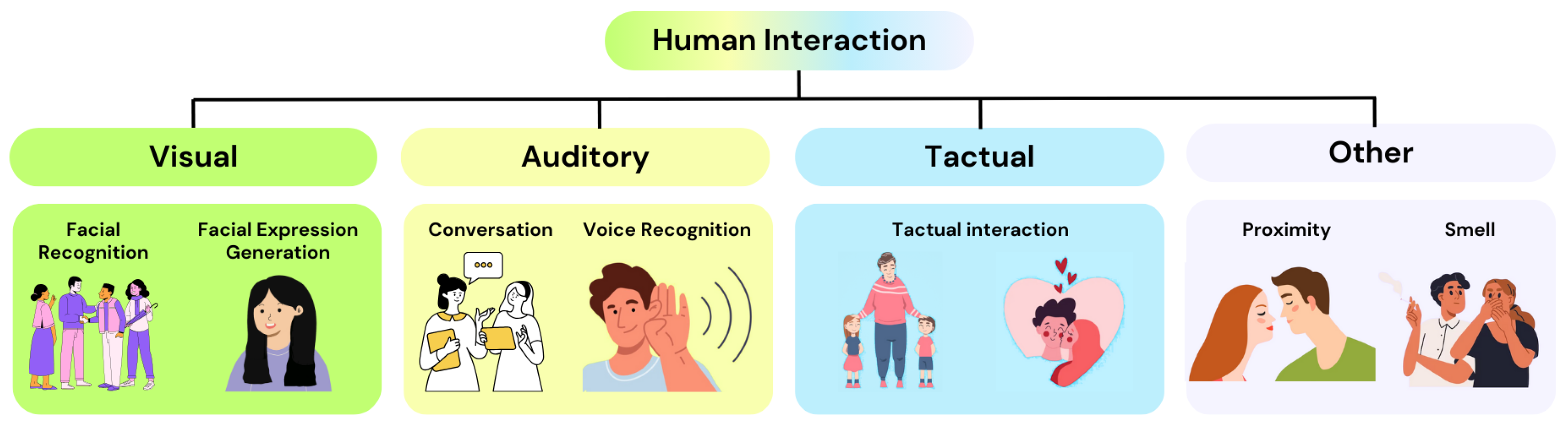
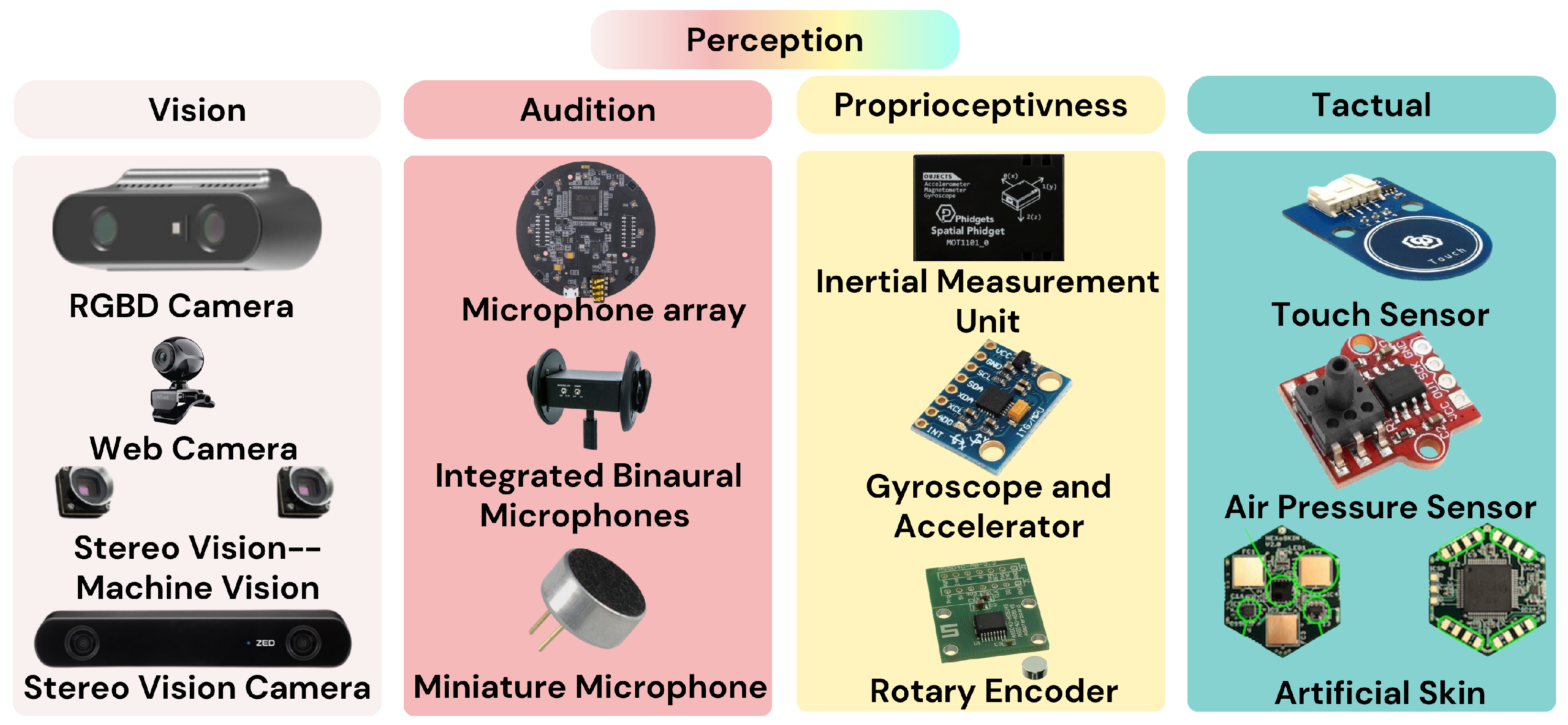
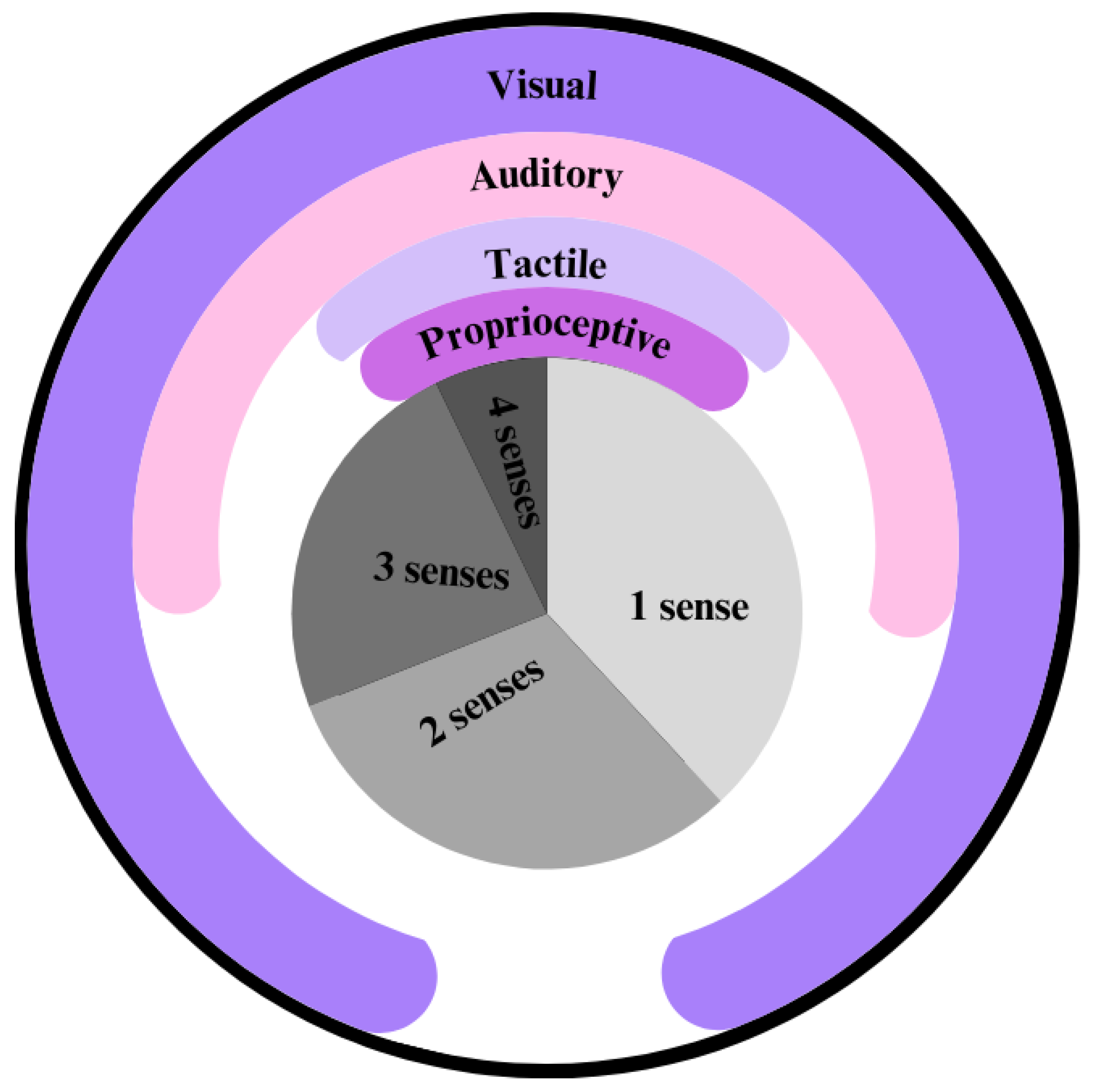
5. Perception
5.1. Visual Perception
5.2. Auditory Perception
5.3. Proprioceptive Perception
5.4. Tactile Perception
5.5. Perceptual Challenges
5.6. Synthesis and Open Problems
6. Computational Systems
6.1. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
6.2. Operating System
6.3. Hardware Abstraction Layer
6.4. Custom Applications
6.5. Communication Protocols
6.6. Power Sources
6.7. Synthesis and Open Problems
7. Role of AI in Humanoid Robotics
7.1. Advanced Navigation Systems
7.2. Speech Generation and Voice Recognition
7.3. Large Language Models
7.4. Emotional Intelligence
7.5. Synthesis and Open Problems
8. Ethical, Sociological, and Economic Implications
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henschel, A. New Approaches to the Emerging Social Neuroscience of Human-Robot Interaction. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, H.; Ishiguro, H.; Friedman, B.; Kanda, T.; Freier, N.; Severson, R.; Wolk, J. What Is a Human? Toward Psychological Benchmarks in the Field of Human-Robot Interaction. Interact. Stud. 2007, 8, 363–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wykowska, A.; Chaminade, T.; Cheng, G. Embodied artificial agents for understanding human social cognition. Philos. Trans. Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, M.C.; Gonzalez, C.A.; Wiese, E. Seeing Minds in Others – Can Agents with Robotic Appearance Have Human-Like Preferences? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, M.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Hashimoto, M. Humanoid robot heads for human-robot interaction: A review. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2024, 67, 357–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Quintero, J.A.; Rodríguez-Liñán, M.C. A literature review of sensor heads for humanoid robots. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2021, 143, 103834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
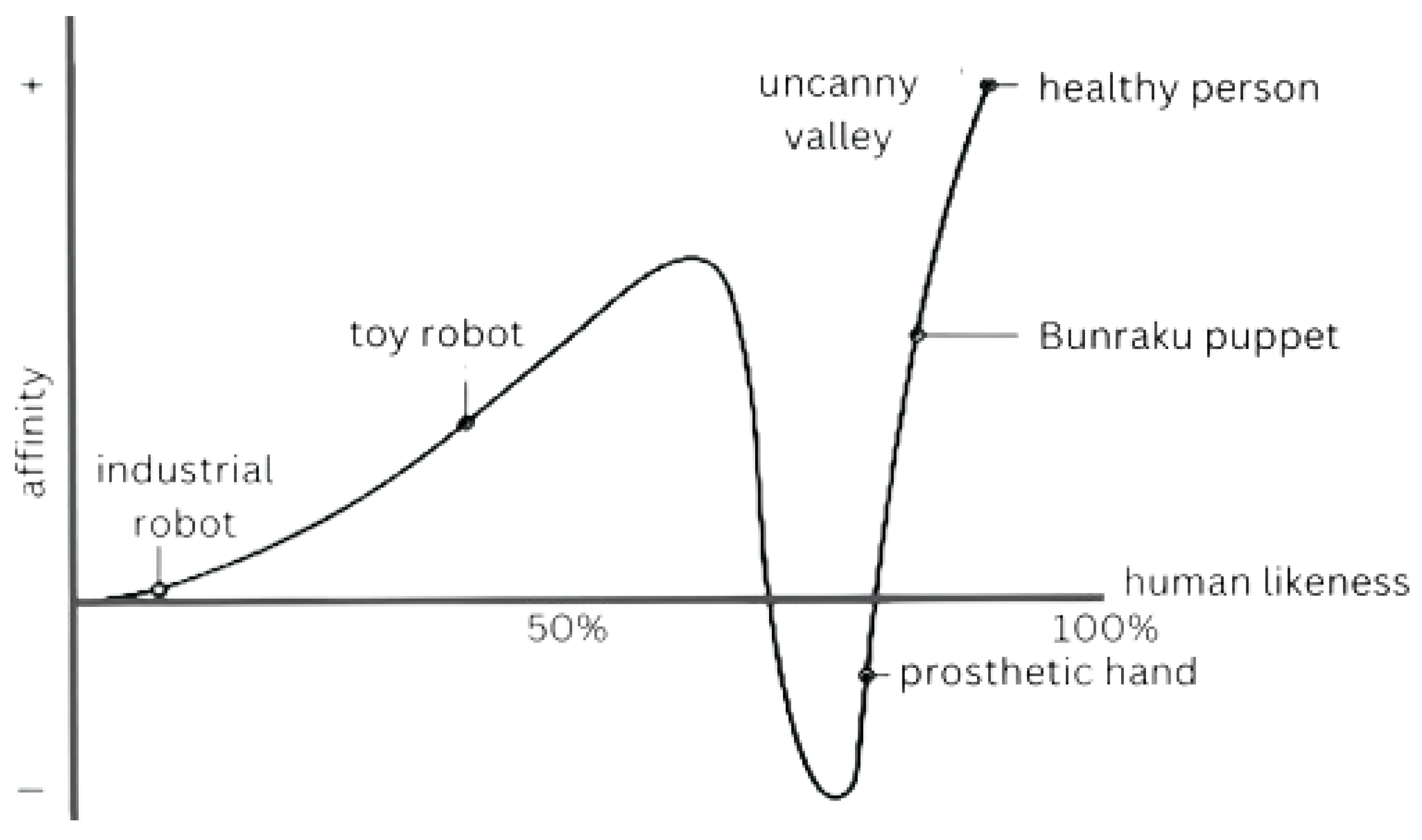
- Mori, M.; MacDorman, K.F.; Kageki, N. The Uncanny Valley [From the Field]. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2012, 19, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Y. Humanoid Robot Head Design Based on Uncanny Valley and FACS. J. Robot. 2014, 2014, 208924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. ROBOTS: Your Guide to the World of Robotics. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Robots. Available online: https://sites.utexas.edu/hcrl/robots/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Feingold Polak, R.; Elishay, A.; Shachar, Y.; Stein, M.; Edan, Y.; Levy Tzedek, S. Differences between Young and Old Users when Interacting with a Humanoid Robot: A Qualitative Usability Study. In Proceedings of the Companion of the 2018 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, Chicago, IL, USA, 5–8 March 2018; pp. 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitachi Ltd. EMIEW3 and Robotics IT Platform: Robotics: Research & Development: Hitachi. Available online: https://www.hitachi.com/rd/research/mechanical/robotics/emiew3_01/index.html (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Emiew 3. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/emiew (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Hon Hai’s Success with Pepper Humanoid a Matter of Molding. Available online: https://asia.nikkei.com/Business/Hon-Hai-s-success-with-Pepper-humanoid-a-matter-of-molding2 (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Flobi. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/flobi (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Lütkebohle, I.; Hegel, F.; Schulz, S.; Hackel, M.; Wrede, B.; Wachsmuth, S.; Sagerer, G. The Bielefeld Anthropomorphic Robot Head “Flobi”. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; Volume 3, pp. 3384–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. M1. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/m1 (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Ferland, F.; Tapus, A. Functional and Non-functional Expressive Dimensions: Classification of the Expressiveness of Humanoid Robots. In Social Robotics; Agah, A., Cabibihan, J.J., Howard, A.M., Salichs, M.A., He, H., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9979, pp. 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, S.; Ishiguro, H.; Hagita, N. Geminoid: Teleoperated Android of an Existing Person. In Humanoid Robots: New Developments; I-Tech: Vienna, Austria, 2007; ISBN 978-3-902613-00-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro Lab. Ishiguro Lab.—Robots. Available online: https://eng.irl.sys.es.osaka-u.ac.jp/robot (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Geminoid DK. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/geminoiddk (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Minh Trieu, N.; Truong Thinh, N. A Comprehensive Review: Interaction of Appearance and Behavior, Artificial Skin, and Humanoid Robot. J. Robot. 2023, 2023, e5589845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. EVE. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/eve (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Nadine. Available online: https://nadineforgood.ch/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Ramanathan, M.; Mishra, N.; Thalmann, N.M. Nadine Humanoid Social Robotics Platform. In Advances in Computer Graphics; Gavrilova, M., Chang, J., Thalmann, N.M., Hitzer, E., Ishikawa, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadine Social Robot—MIRALab. Available online: https://www.miralab.ch/index.php/nadine-social-robot/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Nadine Robot: Social Robot. Available online: https://robot.cfp.co.ir/en/newsdetail/37 (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- IEEE Spectrum. Singapore Researchers Unveil Social Robot Olivia—IEEE Spectrum. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/social-robot-olivia (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Niculescu, A.; van Dijk, B.; Nijholt, A.; Limbu, D.K.; See, S.L.; Wong, A.H.Y. Socializing with Olivia, the Youngest Robot Receptionist Outside the Lab. In Social Robotics; Ge, S.S., Li, H., Cabibihan, J.J., Tan, Y.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, L.; Nori, F.; Metta, G.; Fumagalli, M.; Ivaldi, S.; Pattacini, U.; Randazzo, M.; Schmitz, A.; Sandini, G. The iCub Platform: A Tool for Studying Intrinsically Motivated Learning. In Intrinsically Motivated Learning in Natural and Artificial Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Kalyanasundaram Balasubramanian, K.; Torazza, D.; Rea, F.; Jirak, D.; Sandini, G.; Yanagi, T.; Takamatsu, A.; Bouet, S.; Yamamura, T. A Novel Wire-driven 3D Eyebrow Design for Communication with Humanoid Robot iCub. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. iCub. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/icub (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Telenoid. Available online: http://www.geminoid.jp/projects/kibans/Telenoid-overview.html (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Hiroshi Ishiguro Laboratories. Available online: http://www.geminoid.jp/en/robots.html (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Diego-san. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/diegosan (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Robot|Diego-San|Description|Robotics Today. Available online: https://www.roboticstoday.com/robots/diego-san-description (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Minato, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Noda, T.; Ikemoto, S.; Ishiguro, H.; Asada, M. CB2: A child robot with biomimetic body for cognitive developmental robotics. In Proceedings of the 2007 7th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 29 November–1 December 2007; pp. 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. CB2. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/cb2 (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- CB2 Baby Humanoid Robot~Pink Tentacle. Available online: https://pinktentacle.com/2007/06/cb2-baby-humanoid-robot/#google_vignette (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Zeno R25 Expressive Humanoid Robot; With Quick-Start Guide in Polythene Sleeve; And Charger|Science Museum Group Collection. Available online: https://collection.sciencemuseumgroup.org.uk/objects/co8558820/zeno-r25-expressive-humanoid-robot-with-quick-start-guide-in-polythene-sleeve-and-charger (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Hanson Robotics Unveils Latest Version of Its Zeno Humanoid Robot. 2012. Section: Robotics. Available online: https://newatlas.com/zeno-production/23547/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Liao, Y.J.; Jao, Y.L.; Boltz, M.; Adekeye, O.T.; Berish, D.; Yuan, F.; Zhao, X. Use of a Humanoid Robot in Supporting Dementia Care: A Qualitative Analysis. SAGE Open Nurs. 2023, 9, 23779608231179528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robot ’Teacher’ to Help Children with Autism Developed by Scientists|Imperial News|Imperial College London. 2017. Section: Health. Available online: https://www.imperial.ac.uk/news/177318/robot-teacher-help-children-with-autism/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Reachy. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/reachy (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Discover Reachy, a Robotic Platform Based on AI—Reachy by Pollen Robotics, an Open Source Programmable Humanoid Robot. Available online: https://www.pollen-robotics.com/reachy/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Crampette, A. Orbita Is Turning Heads… Literally. 2020. Available online: https://medium.com/pollen-robotics/orbita-is-turning-heads-literally-d10d378550e2 (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- NAO Interactive Humanoid Robot (6th Generation) Softbank Robotics, Therapeutic, Entertainment, Reception and Telecommunications Robot + Turnkey Partner Software Solution—Leobotics. 2021. Available online: https://en.leobotics.com/comparateur-robot/robot-humanoide-interactif-nao-6eme-generation-softbank-robotics-robot-therapeutique-de-divertissement-d-accueil-et-telecommunication-%2B-solution-logicielle-partenaire-cle-en-main?category%3Drobot-telecommunication-pro (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- NAO: The Educational Robot. Available online: https://us.softbankrobotics.com/nao (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Shamsuddin, S.; Ismail, L.I.; Yussof, H.; Ismarrubie Zahari, N.; Bahari, S.; Hashim, H.; Jaffar, A. Humanoid robot NAO: Review of control and motion exploration. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering, Penang, Malaysia, 25–27 November 2011; pp. 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Programmable Humanoïd Robot NAO V6. Available online: https://www.generationrobots.com/en/403100-programmable-humanoid-robot-nao-v6.html (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Robins, B.; Dautenhahn, K. Kaspar, the social robot and ways it may help children with autism—An overview. Enfance 2018, 1, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Kaspar. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/kaspar (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Kaspar the Friendly Robot Helps Autistic Kids. Available online: https://www.cnet.com/culture/kaspar-the-friendly-robot-helps-autistic-kids/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Puglisi, A.; Caprì, T.; Pignolo, L.; Gismondo, S.; Chilà, P.; Minutoli, R.; Marino, F.; Failla, C.; Arnao, A.A.; Tartarisco, G.; et al. Social Humanoid Robots for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Review of Modalities, Indications, and Pitfalls. Children 2022, 9, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cominelli, L.; Hoegen, G.; De Rossi, D. Abel: Integrating Humanoid Body, Emotions, and Time Perception to Investigate Social Interaction and Human Cognition. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, a New Generation Hyper Realistic Humanoid Robot|ForeLab. Available online: https://forelab.unipi.it/technologies/abel-new-generation-hyper-realistic-humanoid-robot (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Kismet. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/kismet (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Sociable Machines—Overview. Available online: http://www.ai.mit.edu/projects/sociable/overview.html (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Surena 4. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/surena (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Chao, C.; Lee, J.; Begum, M.; Thomaz, A.L. Simon plays Simon says: The timing of turn-taking in an imitation game. In Proceedings of the 2011 RO-MAN, Atlanta, GA, USA, 31 July–3 August 2011; pp. 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, C.; Thomaz, A.L. The shape of Simon: Creative design of a humanoid robot shell. In Proceedings of the CHI ’11 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–12 May 2011; pp. 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Erica. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/erica (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Shah, D. Saya: A $50,000 Robot Teacher for the Future Classrooms of Japan. 2009. Available online: https://luxurylaunches.com/gadgets/saya_a_50000_robot_teacher_for_the_future_classrooms_of_japan.php (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Robot|Saya|Description|Robotics Today. Available online: https://www.roboticstoday.com/robots/saya-description (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Hashimoto, T.; Kato, N.; Kobayashi, H. Development of Educational System with the Android Robot SAYA and Evaluation. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2011, 8, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Hitramatsu, S.; Tsuji, T.; Kobayashi, H. Development of the Face Robot SAYA for Rich Facial Expressions. In Proceedings of the 2006 SICE-ICASE International Joint Conference, Busan, Republic of Korea, 18–21 October 2006; pp. 5423–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. FLASH. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/flash (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Kędzierski, J.; Kaczmarek, P.; Frontkiewicz, M.; Zagdańska, M.; Dziergwa, M. Study of a Social Robot’s Appearance Using Interviews and a Mobile Eye-Tracking Device. In Social Robotics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 8239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Roboy. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/roboy (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Alfayad, S.; El Asswad, M.; Abdellatif Hamed IBRAHIM, A.; Ouezdou, F.; Blanchard, A.; Beaussé, N.; Gaussier, P. HYDROïD Humanoid Robot Head with Perception and Emotion Capabilities: Modeling, Design, and Experimental Results. Front. Robot. AI 2016, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaussé, N. Apprentissage Visuo-Moteur, Implication pour le Développement Sensorimoteur et l’Émergence d’Interactions Sociales. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Cergy Pontoise, Cergy, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Geminoid, D.K. 2013. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20130223072819/http://geminoid.dk/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Kojiro. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/kojiro (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Mizuuchi, I.; Nakanishi, Y.; Sodeyama, Y.; Namiki, Y.; Nishino, T.; Muramatsu, N.; Urata, J.; Hongo, K.; Yoshikai, T.; Inaba, M. An advanced musculoskeletal humanoid Kojiro. In Proceedings of the 2007 7th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 29 November–1 December 2007; pp. 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Dreamer. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/dreamer (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Robot|Dreamer|Description|Robotics Today. Available online: https://www.roboticstoday.com/robots/dreamer-description (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Ameca Desktop. Available online: https://www.engineeredarts.co.uk/robot/ameca-desktop/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Na’vi Shaman. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/navishaman (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Robots, I.S. Kibo. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/kibo (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Kim, C.G.; Choi, M.T.; Noh, H.J.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Cho, C.; Kim, M. The Development of Humanoid Robot for Human Robot Interaction. In Proceedings of the RO-MAN 2007—The 16th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 26–29 August 2007; pp. 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesmer Brochure. Available online: https://www.aparobot.com/robots/mesmer (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Motion Test for the Mesmer Robot Head Ardan. Available online: https://mecharithm.com/news/article/motion-test-for-the-mesmer-robot-head-ardan-53 (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Oh, J.H.; Hanson, D.; Kim, W.S.; Han, Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, I.W. Design of Android type Humanoid Robot Albert HUBO. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Beijing, China, 9–15 October 2006; pp. 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Albert Hubo. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/alberthubo (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- RoboThespian—Engineered Arts Wiki. Available online: https://wiki.engineeredarts.co.uk/RoboThespian (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Solis, J.; Taniguchi, K.; Ninomiya, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Takanishi, A. The waseda flutist robot No. 4 refined IV: Enhancing the sound clarity and the articulation between notes by improving the design of the lips and tonguing mechanisms. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 October–2 November 2007; pp. 2041–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Waseda Flutist. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/flutist (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Solis, J.; Sugita, Y.; Petersen, K.; Takanishi, A. Development of an anthropomorphic musical performance robot capable of playing the flute and saxophone: Embedding pressure sensors into the artificial lips as well as the re-designing of the artificial lips and lung mechanisms. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 86, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, N.; Endo, K.; Zecca, M.; Takanishi, A. Modular Design of Emotion Expression Humanoid Robot KOBIAN. In ROMANSY 18 Robot Design, Dynamics and Control; Parenti Castelli, V., Schiehlen, W., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2010; pp. 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum. Humanoid Robot KOBIAN Learning to Be a Comedian—IEEE Spectrum. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/waseda-humanoid-robot-kobian-comedy (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Zecca, M.; Endo, N.; Momoki, S.; Itoh, K.; Takanishi, A. Design of the humanoid robot KOBIAN-preliminary analysis of facial and whole body emotion expression capabilities. In Proceedings of the Humanoids 2008—8th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 1–3 December 2008; pp. 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajita, S. Mechanism Design of Human-Like HRP-4C. In Humanoid Robotics: A Reference; Goswami, A., Vadakkepat, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 597–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. HRP-4C. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/hrp4c (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Robots, I.S. Sophia. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/sophia (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Goertzel, B.; Mossbridge, J.; Monroe, E.; Hanson, D.; Yu, G. Humanoid Robots as Agents of Human Consciousness Expansion. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.07791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. CyberOne. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/cyberone (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Heater, B. Meet CyberOne, Xiaomi’s New Humanoid Robot. 2022. Available online: https://techcrunch.com/2022/08/11/meet-xiaomis-new-humanoid-robot-cyberone/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. HRP-5P. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/hrp5p (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Construction Worker Humanoid Robots. Available online: https://www.trendhunter.com/trends/hrp5p (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Martinson, E.; Lawson, W.; Trafton, J.G. Identifying people with soft-biometrics at Fleet Week. In Proceedings of the 2013 8th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), Tokyo, Japan, 3–6 March 2013; pp. 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Spectrum Robots. Octavia. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/octavia (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Robot: Geminoid F. Available online: https://robotsguide.com/robots/geminoidf (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Nagua, L.; Muñoz, J.; Monje, C.A.; Balaguer, C. A first approach to a proposal of a soft robotic link acting as a neck. In Proceedings of the Actas de las XXXIX Jornadas de Automática, Badajoz, Spain, 5–7 September 2018; pp. 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medical Device and Diagnostic Industry. Meet Dreamer: One of the Best Humanoid Robots Yet. 2025. Available online: https://www.mddionline.com/automation/meet-dreamer-one-of-the-best-humanoid-robots-yet (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Su, H.; Qi, W.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Sandoval, J.; Laribi, M.A. Recent advancements in multimodal human–robot interaction. Front. Neurorobot. 2023, 17, 1084000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.I.; Kanade, T.; Cohn, J. Recognizing action units for facial expression analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasse, O.; Flayols, T. An Overview of Humanoid Robots Technologies. In Biomechanics of Anthropomorphic Systems; Venture, G., Laumond, J.P., Watier, B., Eds.; Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 124, pp. 281–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.K.; Nicolescu, M.; Nicolescu, M. Enhancing Human–Robot Collaboration through a Multi-Module Interaction Framework with Sensor Fusion: Object Recognition, Verbal Communication, User of Interest Detection, Gesture and Gaze Recognition. Sensors 2023, 23, 5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanishi, A.; Sato, K.; Segawa, K.; Takanobu, H.; Miwa, H. An anthropomorphic head-eye robot expressing emotions based on equations of emotion. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 2000 ICRA. Millennium Conference. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37065), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; Volume 3, pp. 2243–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertzel, B.; Hanson, D.; Yu, G. A Software Architecture for Generally Intelligent Humanoid Robotics. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 41, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- agROBOfood. Robot Software Platforms—agROBOfood Case Studies Documentation. 2024. Available online: https://agrobofood.github.io/agrobofood-case-studies/case_studies/Robot-Software-Platforms.html (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- USB 2.0 Vs. Bluetooth. Available online: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/usb-20-vs-bluetooth-47408.html (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- What is the EtherCAT Communication Protocol—Acontis Technologies. Available online: https://www.acontis.com/en/what-is-ethercat-communication-protocol.html (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Matthews, D.; Spielberg, A.; Rus, D.; Kriegman, S.; Bongard, J. Efficient automatic design of robots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2305180120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vegavid. The Power of AI in Image Processing: A Comprehensive Guide. 2025. Available online: https://vegavid.com/blog/power-of-ai-in-image-processing (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Majumder, S.; Pratihar, D.K. Multi-sensors data fusion through fuzzy clustering and predictive tools. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 107, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratihar, D.K. AI-Assisted Intelligent Humanoid Robot. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2024, 9, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakoor, M.; Kosari, A.; Jafarzadeh, M. Humanoid robot path planning with fuzzy Markov decision processes. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2016, 14, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, A.K.; Parhi, D.R.; Muni, M.K.; Pandey, K.K. A hybrid technique for path planning of humanoid robot NAO in static and dynamic terrains. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 96, 106581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian. Dynamic Window Algorithm Motion Planning. 2012. Available online: https://adrianboeing.blogspot.com/2012/05/dynamic-window-algorithm-motion.html (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Navigation—ROS Wiki. Available online: https://wiki.ros.org/navigation (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- dwa_local_planner—ROS Wiki. Available online: https://wiki.ros.org/dwa_local_planner?distro=noetic (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Teaching Learning Based Optimization (TLBO). 2021. Section: Machine Learning. Available online: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/machine-learning/teaching-learning-based-optimization-tlbo/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Mao, Z. Large language models for human–robot interaction: A review. Biomim. Intell. Robot. 2023, 3, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birhane, A.; Kasirzadeh, A.; Leslie, D.; Wachter, S. Science in the age of large language models. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2023, 5, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Gan, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Yu, P.S. Large Language Models for Robotics: A Survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.07226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, E.; Mossbridge, J. Team Hanson-Lia-SingularityNet: Deep-Learning Assessment of Emotional Dynamics Predicts Self-Transcendent Feelings During Constrained Brief Interactions with Emotionally Responsive AI Embedded in Android Technology. 2018; Unpublished XPrize Submission. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/44435808/Team_Hanson_Lia_SingularityNet_Deep_learning_Assessment_of_Emotional_Dynamics_Predicts_Self_Transcendent_Feelings_During_Constrained_Brief_Interactions_with_Emotionally_Responsive_AI_Embedded_in_Android_Technology (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Cai, Z.; Goertzel, B.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Yu, G. Dynamics of a computational affective model inspired by Dörner’s PSI theory. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2012, 17–18, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, M. Component Process Model (CPM; Scherer, 2001). In Psychology of Human Emotion: An Open Access Textbook; Affordable Course Transformation; Pennsylvania State University: University Park, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Stamboliev, E. Challenging Robot Morality: An Ethical Debate on Humanoid Companions, Dataveillance, and Algorithms. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Plymouth, Plymouth, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Databases | IEEE Xplore; ACM Digital Library; Scopus; Web of Science Core Collection; ScienceDirect; SpringerLink; PubMed; arXiv (screened) |
| Conferences | ICRA; IROS; Humanoids; HRI; RO-MAN (proceedings screened) |
| Time window/last search | January 1998–December 2022; final search on 31 December 2022 |
| Representative terms | “humanoid head”, “android head”, “robot head”, “robotic face”; mechanics, “neck mechanism”, “eye mechanism”, FACS, actuator*, “artificial skin”; vision, stereo, RGB-D, LiDAR, catadioptric, microphone*, IMU, tactile; ROS/ROS2, middleware, YARP, “real-time”, EtherCAT; HRI, “uncanny valley” |
| Boolean pattern (example) | (“humanoid head” OR “android head” OR “robot head” OR “robotic face”) AND (mechanics OR “neck mechanism” OR “eye mechanism” OR FACS OR actuator OR “artificial skin”) AND (vision OR stereo OR RGB-D OR LiDAR OR catadioptric OR microphone OR IMU OR tactile) AND (ROS OR ROS2 OR middleware OR YARP OR “real-time” OR EtherCAT) AND (HRI OR “human-robot interaction” OR “uncanny valley”) |
| Inclusion criteria | (i) humanoid/android head or humanoid platform with a documented head module; (ii) human-like appearance; (iii) at least one head-mounted perceptual modality and/or a head-specific mechanical design relevant to HRI; (iv) technical details on mechanics, sensing, computation, or control/HMI; English source preferred when duplicates existed |
| Exclusion criteria | Headless platforms; purely artistic installations without reproducible technical description; non-human-like shells with no HRI relevance; no head-mounted perception; duplicates |
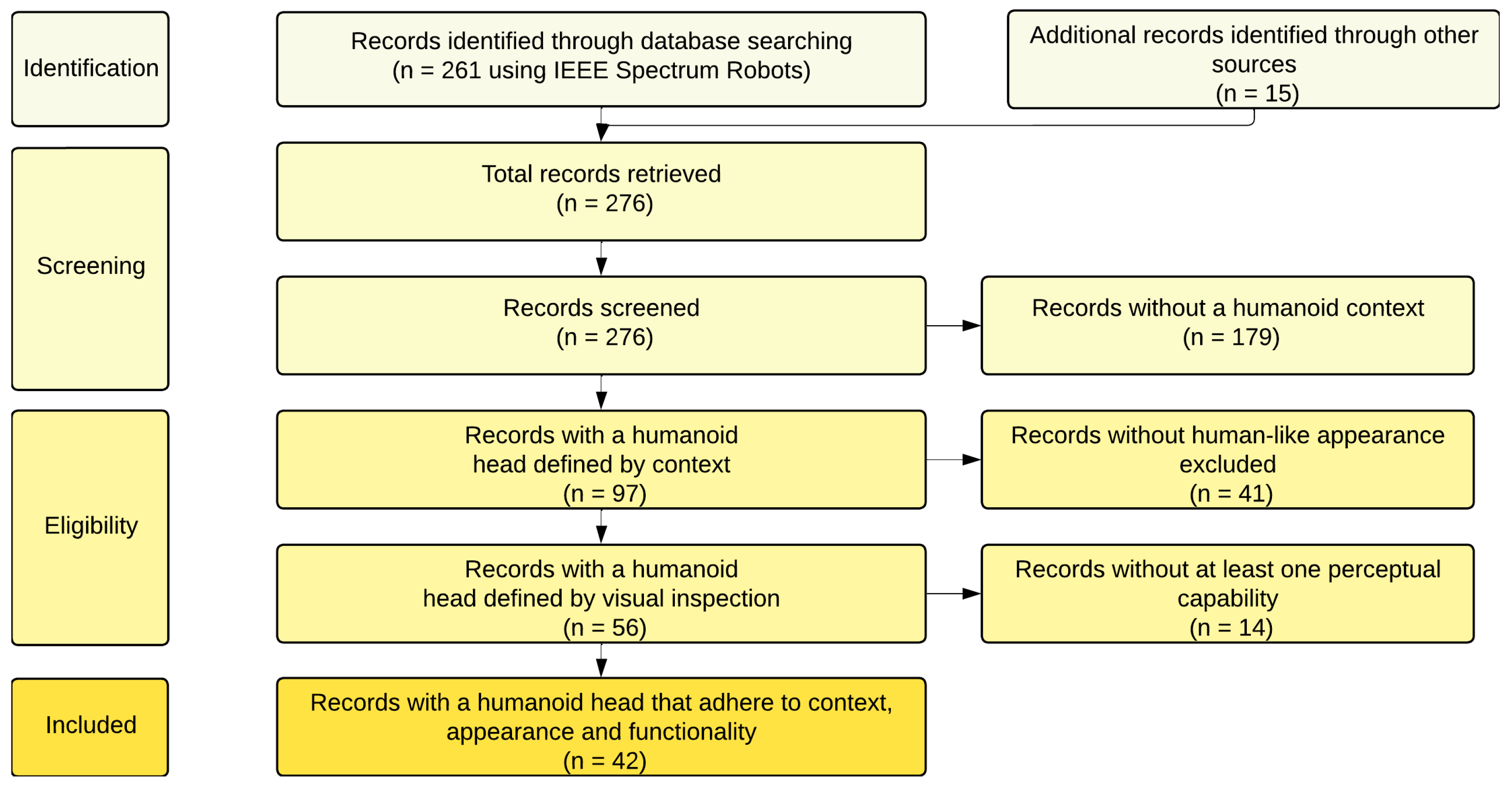
| PRISMA counts | Retrieved: ; after contextual screening: ; after appearance filter: (excluded 41); after functionality filter ( sense): (excluded 14); see Figure 4. |
| Robot | Vision | Audition | Proprioceptive | Tactile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CyberOne | Intel RealSense D455 RGB-D camera | – | – | – |
| Ameca | Binocular eye-mounted cameras; chest camera | Embedded microphones | – | Current sensing on all servos |
| Abel | Integrated camera | Integrated binaural microphones | – | – |
| Surena 4 | RealSense D435 camera | – | – | – |
| HRP-5P | Stereo vision; LiDAR; 3D sensors | – | – | – |
| Na’Vi Shaman | – | – | Rotary encoders for absolute positioning | – |
| Mesmer | Cameras; depth sensors; LiDAR | Microphones | – | – |
| Sophia | Intel RealSense camera | External USB microphone; audio localization array | IMU | – |
| Emiew 3 | CCD camera | Microphone array | – | – |
| Tino | Two cameras | – | – | – |
| Erica | Two CMOS cameras | Two microphones | – | – |
| Pepper | Two HD 5-MP cameras (mouth/forehead); 3D sensor (behind eyes) | Four microphones | – | 3 touch sensors |
| KOBIAN-RII | CMOS camera | Capacitor microphone | IMU | – |
| Roboy | Two cameras | One microphone | – | – |
| Telenoid R4 | – | Two microphones | – | – |
| Nadine | Microsoft Kinect V2 RGB-D camera; web cameras | Microphone | – | – |
| Dreamer | Stereo cameras on eyes | Microphones | – | – |
| Flash | Microsoft Kinect; Logitech QuickCam Sphere camera | – | Analog Devices inertial system | – |
| Diego-San | Two Point Grey Dragonfly2 cameras | Two microphones | Two IMUs | 38 potentiometers; 88 pressure sensors |
| Geminoid F | External webcam | – | – | – |
| HRP-4C | CCD camera | – | – | – |
| Simon | Point Grey FireflyMV CMOS cameras | – | – | – |
| Saya | CCD camera | Microphones | – | – |
| Zeno | Two 720p, 30 fps HD cameras | Microphones | Three-axis gyroscope; three-axis accelerometer; compass | – |
| iCub | Stereo cameras | Microphones | Gyroscopes; accelerometers | – |
| Kismet | Four CCD cameras | Two microphones + one for person speaking | – | 21 encoders |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Josic, K.; Ghandour, M.; Sleiman, M.; Qi, W.; Su, H.; AitOufroukh-Mammar, N.; Alfayad, S. Recent Advancements in Humanoid Robot Heads: Mechanics, Perception, and Computational Systems. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110716
Josic K, Ghandour M, Sleiman M, Qi W, Su H, AitOufroukh-Mammar N, Alfayad S. Recent Advancements in Humanoid Robot Heads: Mechanics, Perception, and Computational Systems. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(11):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110716
Chicago/Turabian StyleJosic, Katarina, Maysoon Ghandour, Maya Sleiman, Wen Qi, Hang Su, Naima AitOufroukh-Mammar, and Samer Alfayad. 2025. "Recent Advancements in Humanoid Robot Heads: Mechanics, Perception, and Computational Systems" Biomimetics 10, no. 11: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110716
APA StyleJosic, K., Ghandour, M., Sleiman, M., Qi, W., Su, H., AitOufroukh-Mammar, N., & Alfayad, S. (2025). Recent Advancements in Humanoid Robot Heads: Mechanics, Perception, and Computational Systems. Biomimetics, 10(11), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110716









